Efficiency Testing of Pelton Turbines with Artificial Defects—Part 1: Buckets
Abstract
1. Introduction
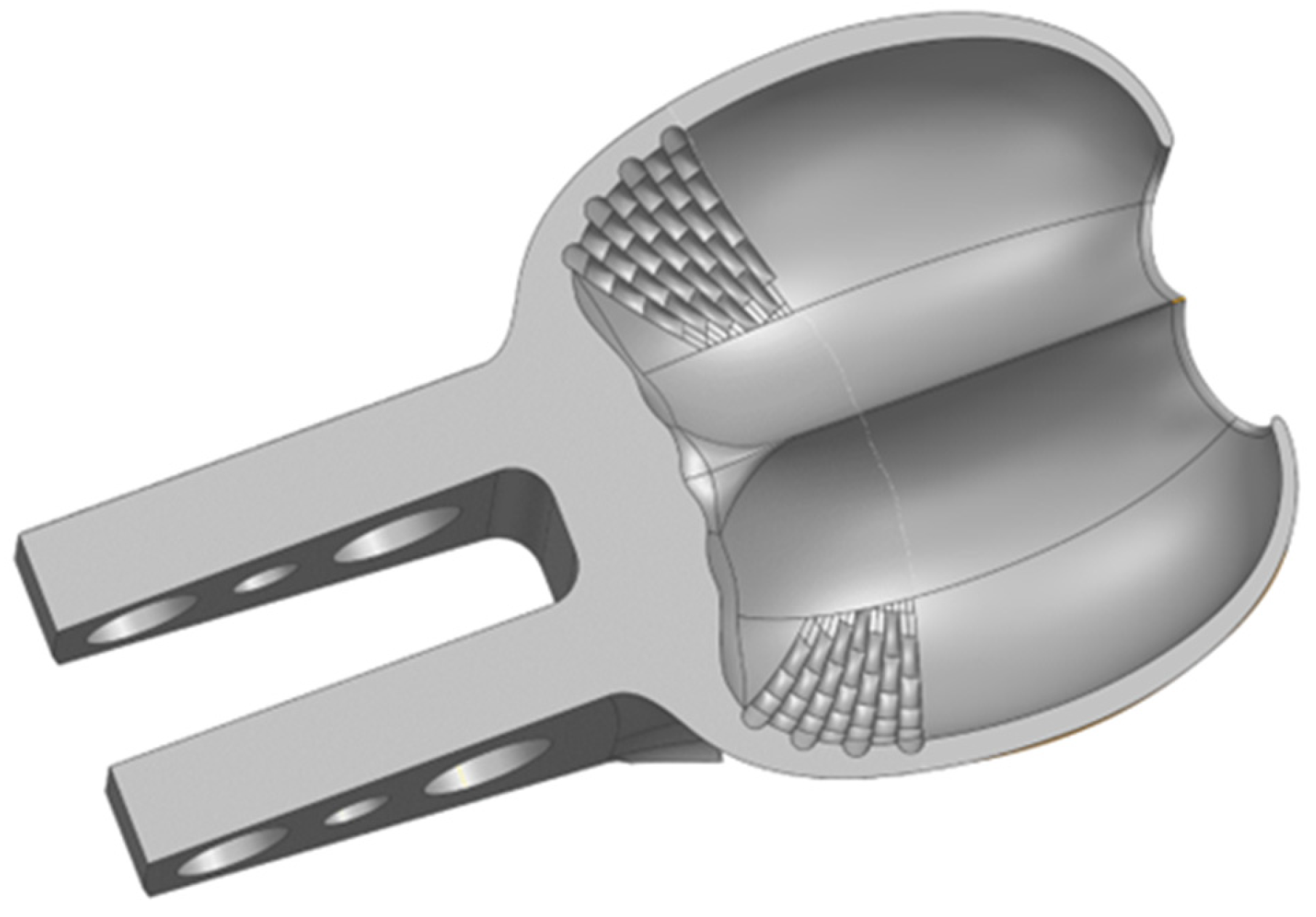
2. Test Rig and Data Acquisition
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Hydraulic Efficiency and Uncertainty Analysis
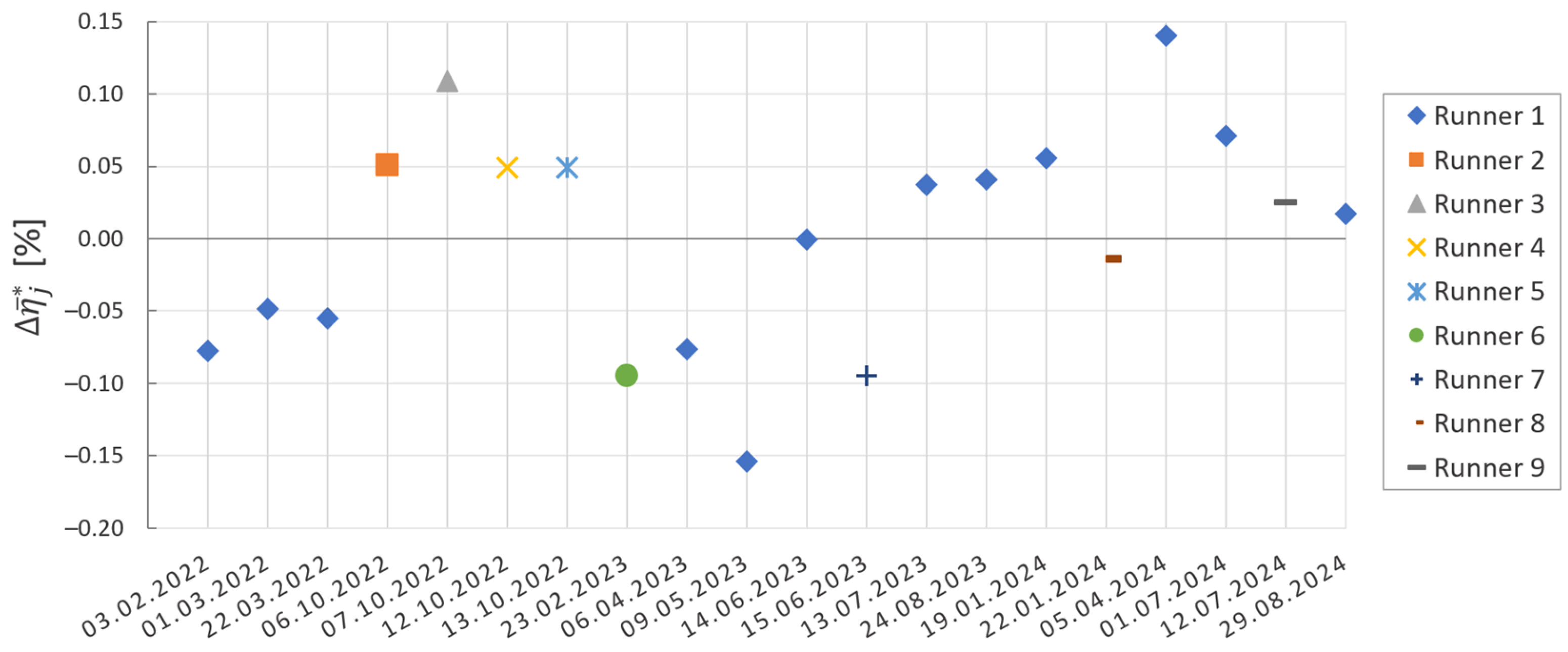
2.3. Repeatability
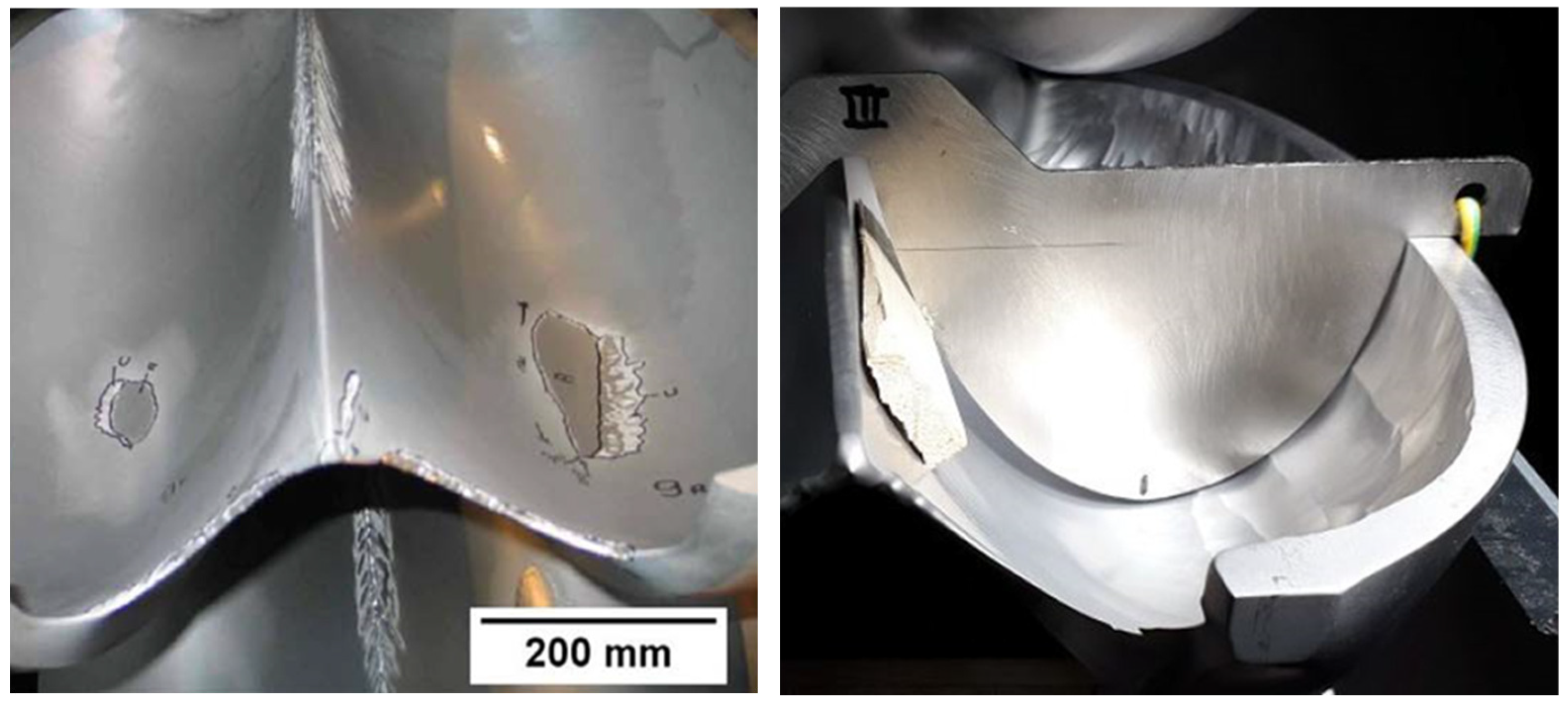
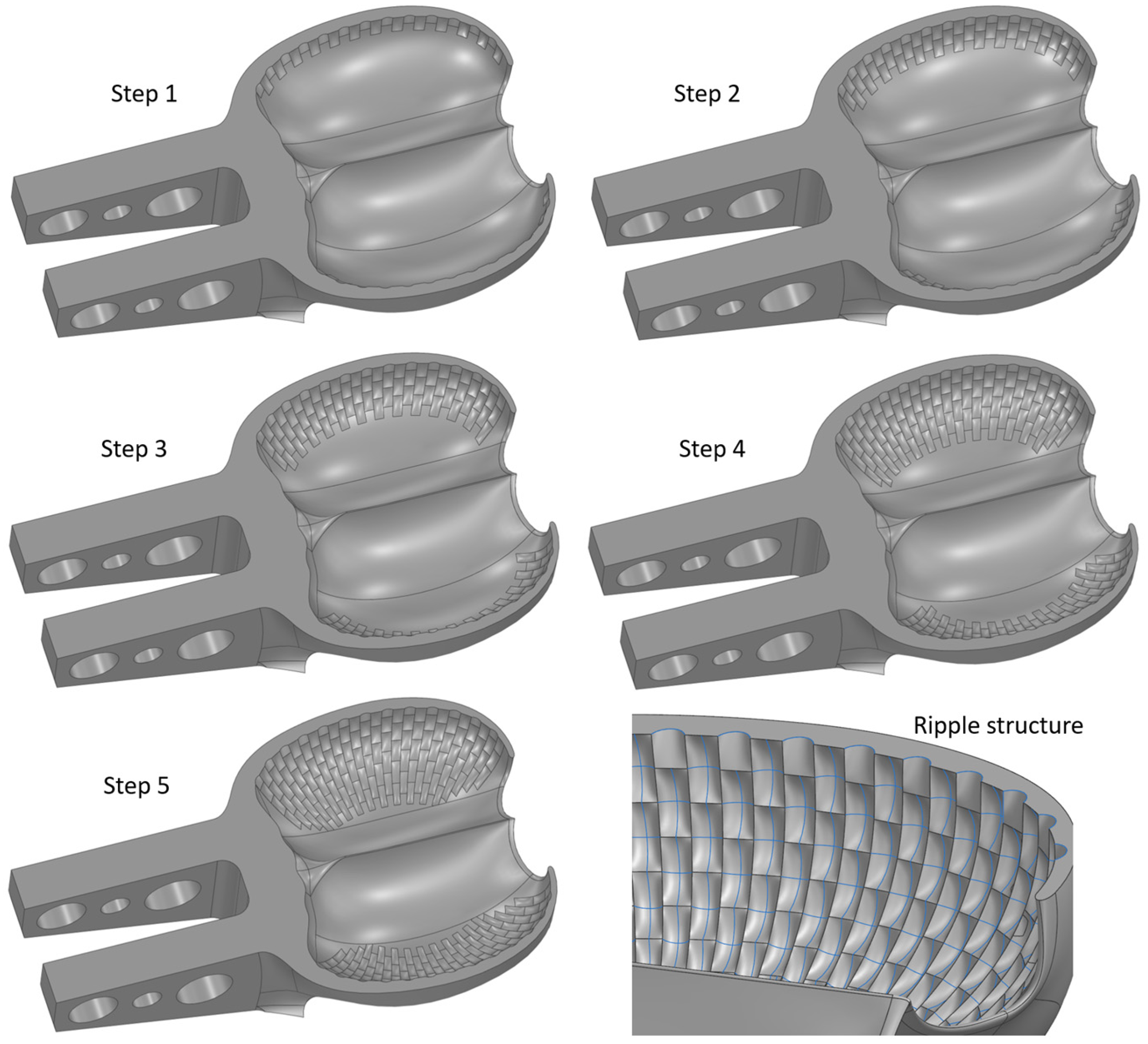
3. Processing Steps of the Buckets
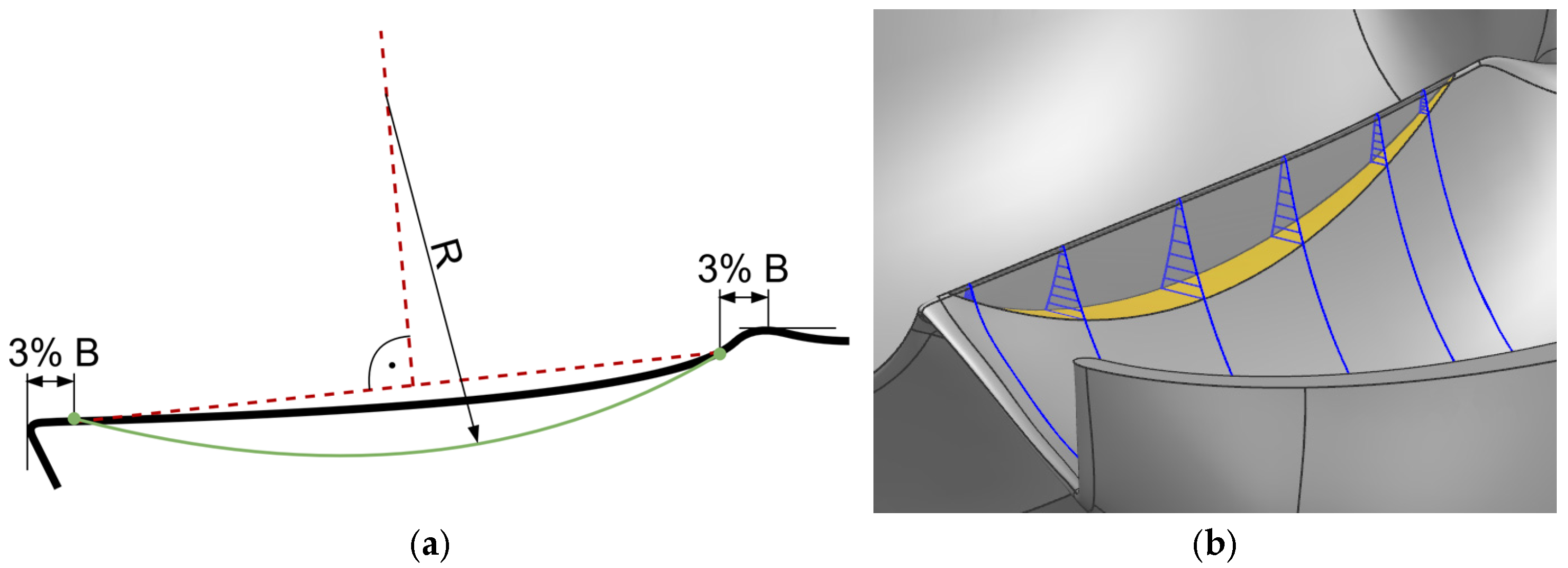
3.1. Sharp-Edged Splitter Crest
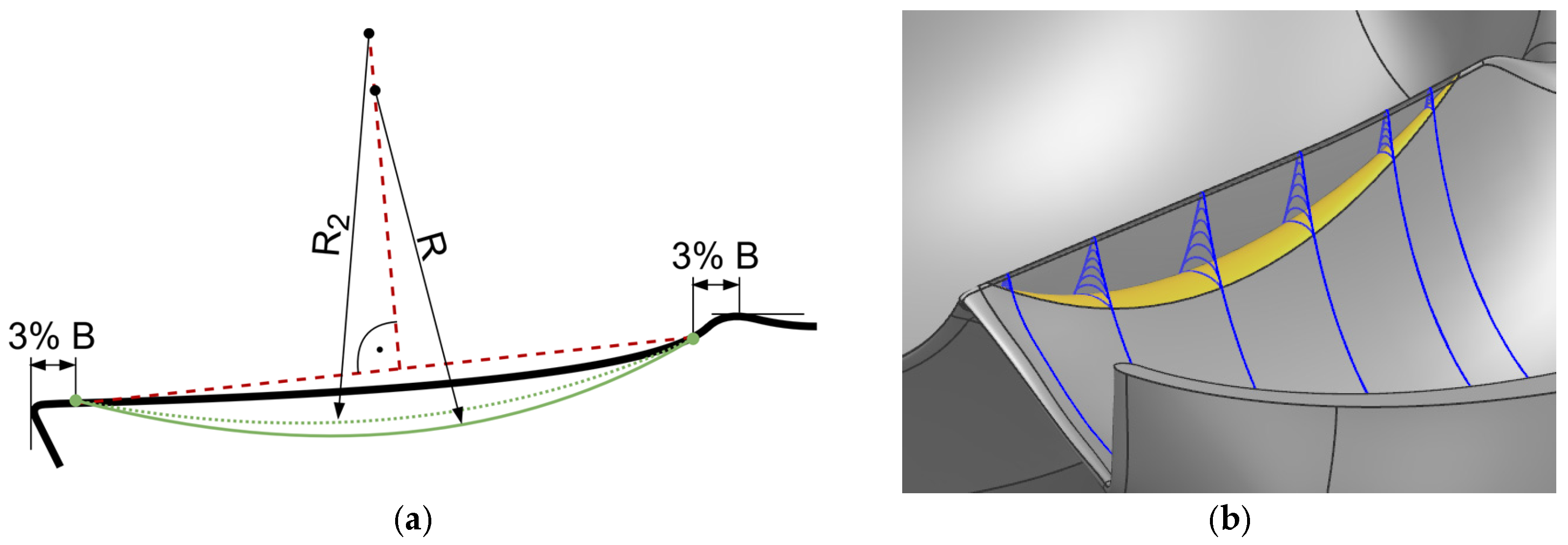
3.2. Rounded Splitter Crest
3.3. Cutout
3.4. Splitter Tip
3.5. Cutout and Splitter Tip
3.6. Bucket Base, Smooth, and Sharp-Edged
3.7. Bucket Base, Depth
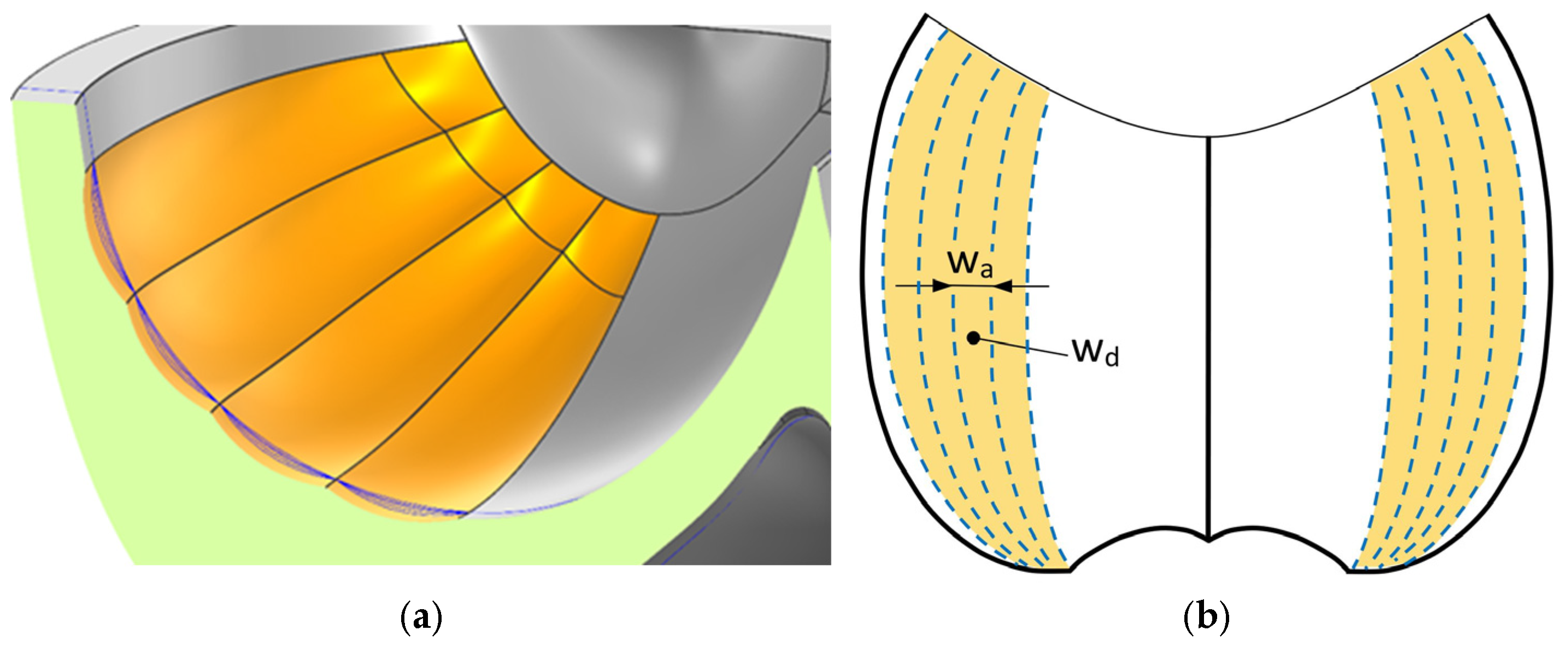
3.8. Bucket Sides, Number of Ripples
3.9. Bucket Sides, Depth of Ripples
3.10. Bucket Side in Bucket Root
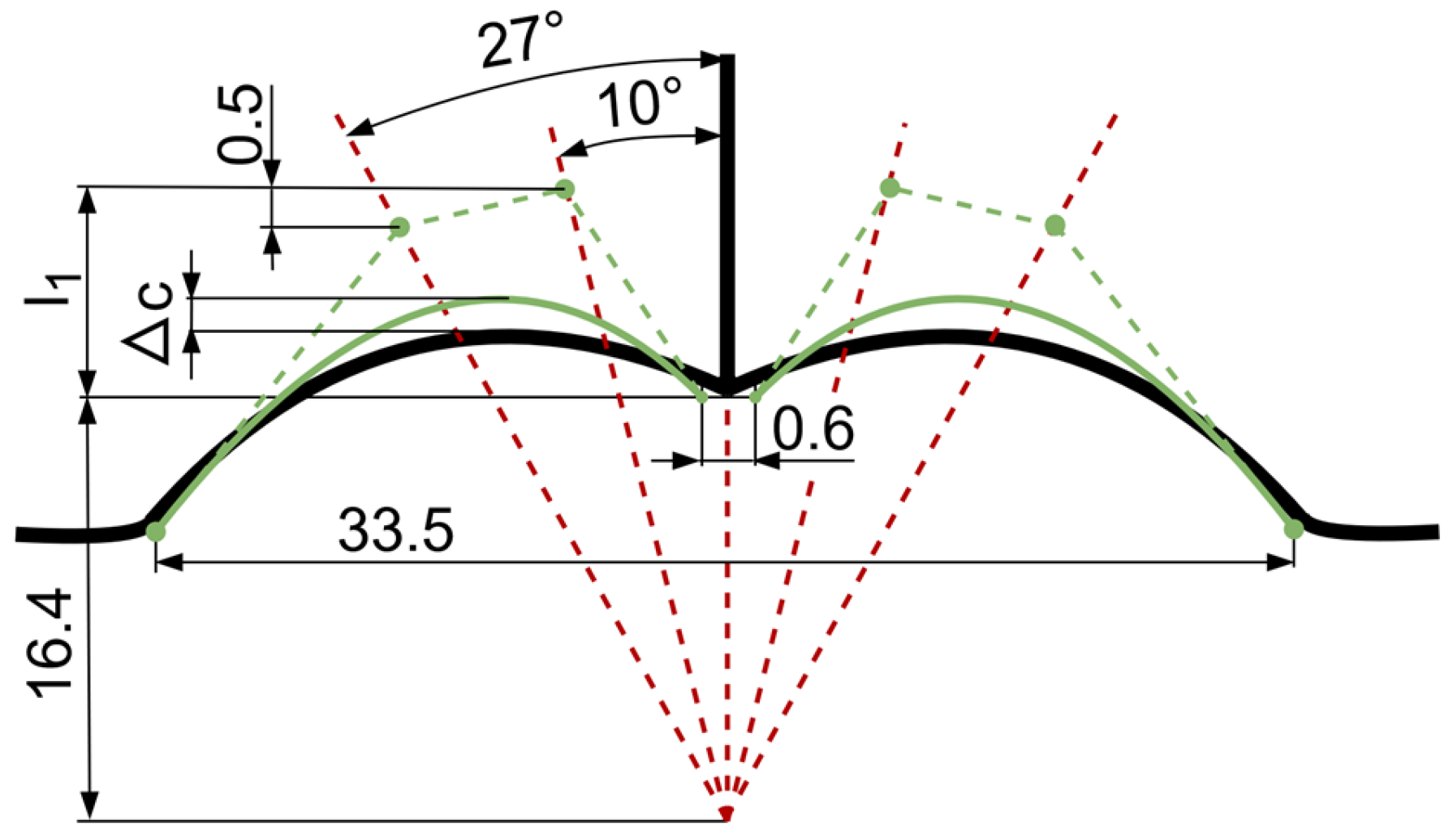
3.11. Wave-Type Defects at Bucket Wall
3.12. Superposition of Defects
4. Hill Chart Measurement
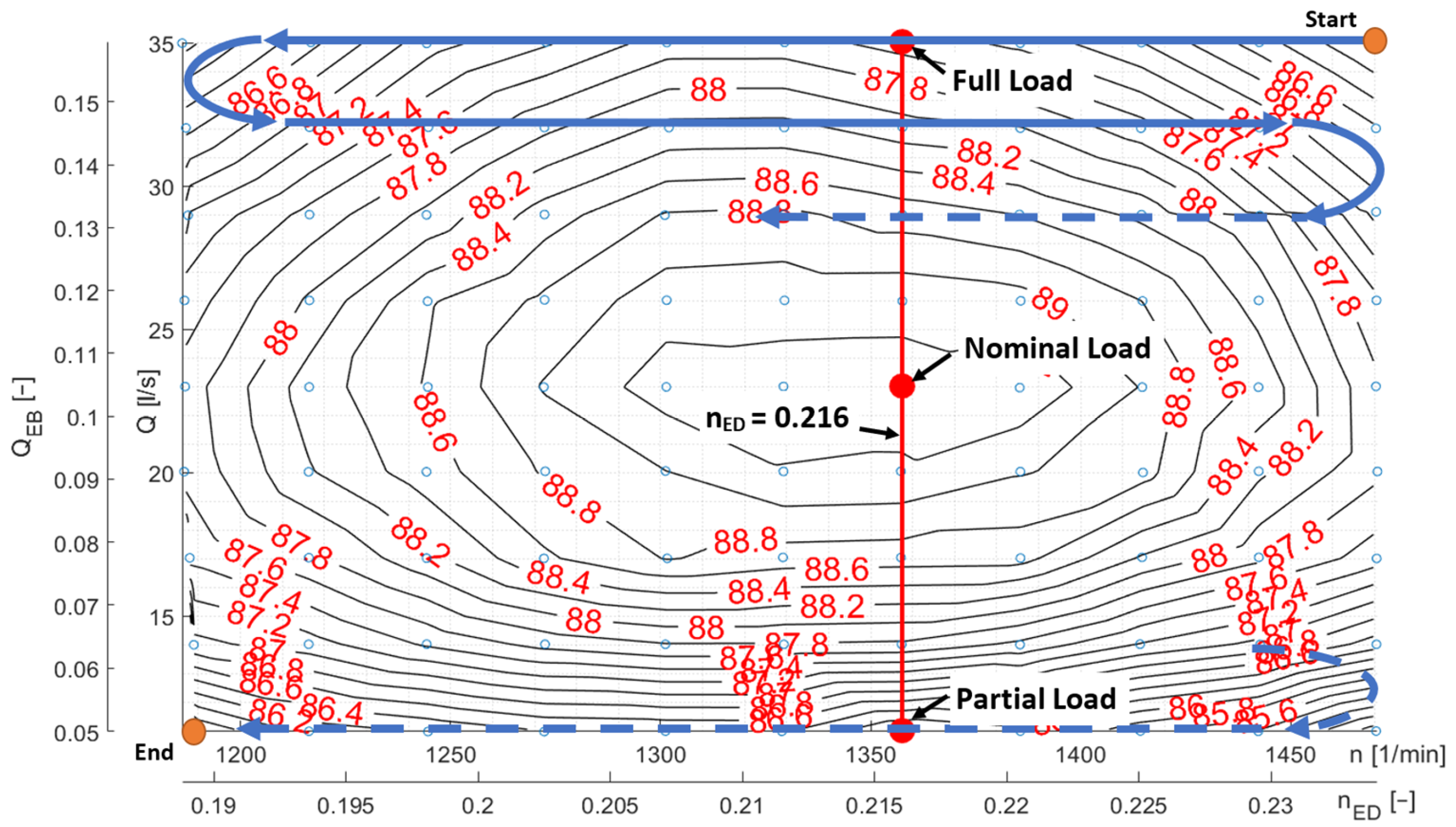
4.1. Procedure
4.2. Example of Sharp-Edged Splitter (Series A, Section 3.1)
4.3. Example of the Cutout (Series G, Section 3.3)
4.4. Examples of Waveform Defects at Bucket Walls (Series X, Section 3.11)
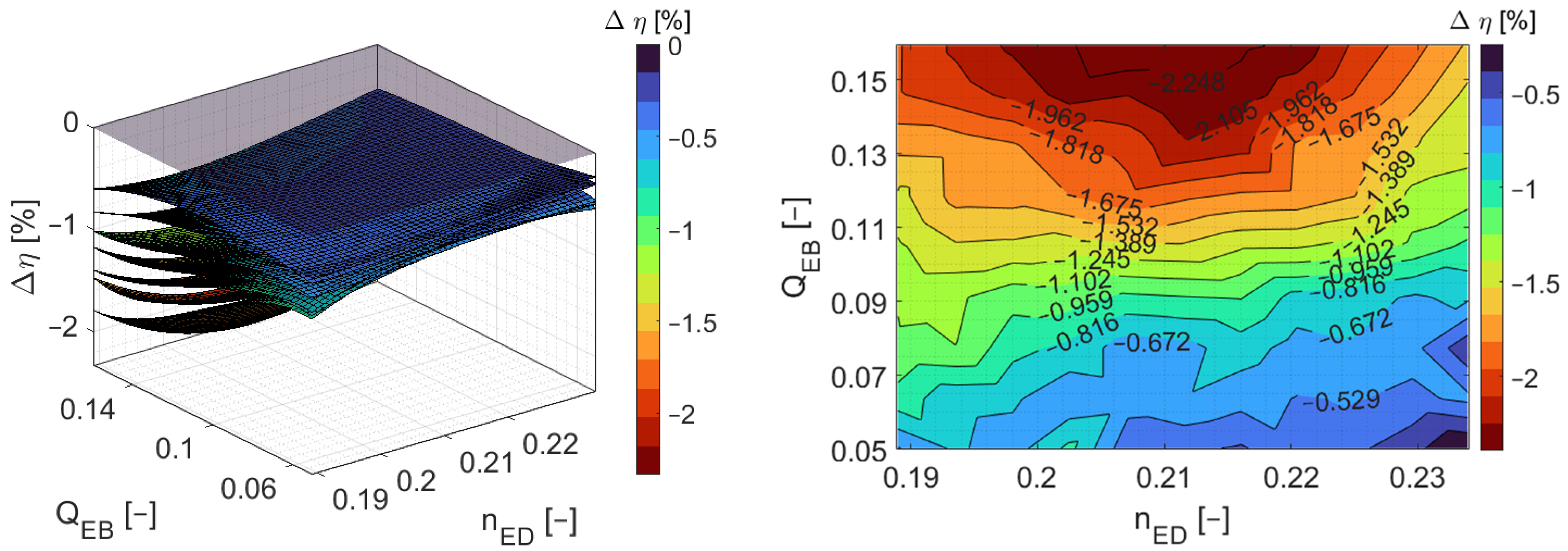
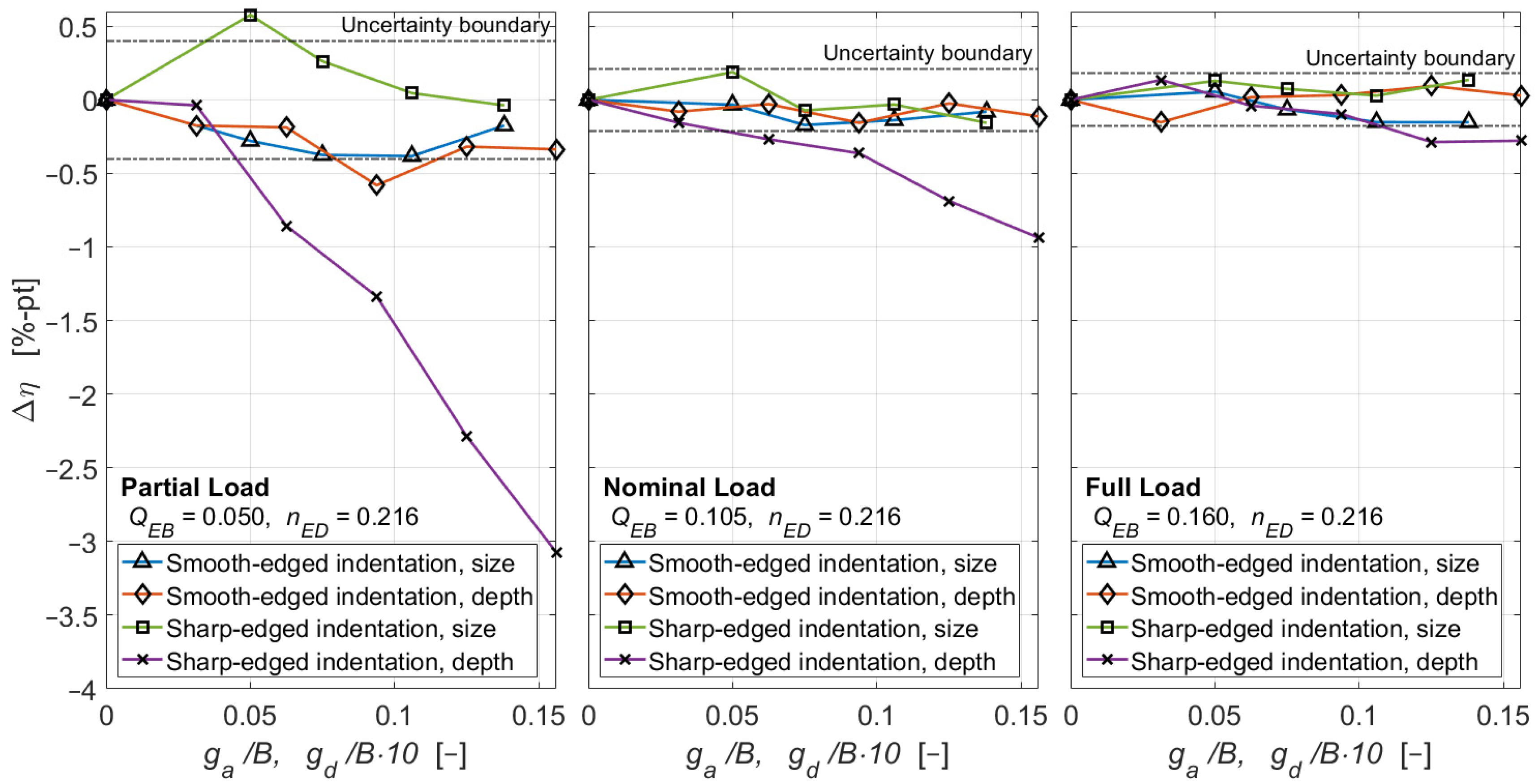
4.5. Efficiency Decay Due to Indentations in the Bucket Base (Series M, N, U, and V, Section 3.6 and Section 3.7)
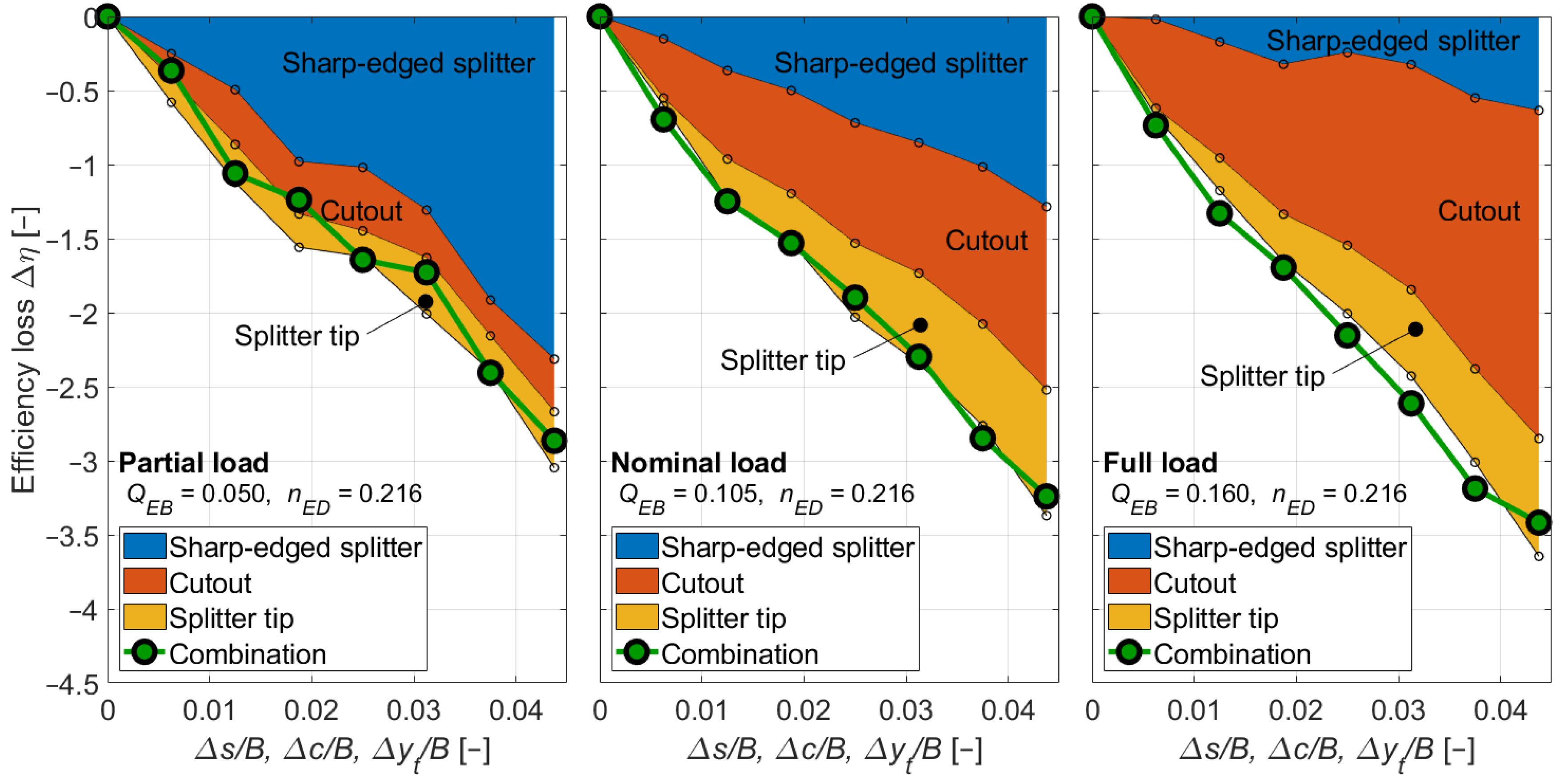
4.6. Combination of Splitter, Cutout, and Tip (Series P)
4.7. Types of Efficiency Decay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbol | Unit | Definition |
| B | m, mm | Inner bucket width |
| ba | mm | Width of ripples (axial direction) |
| br | mm | Height of ripples (radial direction) |
| bd | mm | Depth of ripples |
| Δc | mm | Difference of cutout depth |
| D | m, mm | Pitch circle diameter |
| D0 | mm | Nozzle seat ring diameter |
| d0 | mm | Jet diameter |
| d1 | m | Inlet diameter 1 |
| E | m2/s2 | Specific hydraulic energy |
| (ex)s,r | div. | Absolute uncertainty of quantity x, systematic, random |
| (fx)s,r | % | Relative uncertainty of quantity x, systematic, random |
| g | m/s2 | Gravity |
| ga | mm | Width of bucket base modification (axial direction) |
| gr | mm | Height of bucket base modification (radial direction) |
| gd | mm | Depth of bucket base modification |
| H | m | Head |
| i | - | Measuring point |
| j | - | Machining step |
| l1, l2 | mm | Length in drawings |
| mbearing | kg | Mass measured at the bearing |
| mgen | kg | Mass measured at the generator |
| mweight | kg | Applied weights |
| n | - | Number of data points |
| n | s−1 | Rotational speed |
| p1 | Pa | Pressure at inlet (position 1) |
| pabs | Pa | Absolute pressure |
| pamb | Pa | Ambient pressure |
| Ph | W | Hydraulic power |
| Pm | W | Mechanical power |
| Q | l/s, m3/s | Flow rate |
| R, R2 | mm | Radius in drawings |
| s | mm | Needle stroke |
| s | mm | Splitter width |
| sx | - | Standard deviation of quantity x |
| rbearings | m | Lever arm for load cell bearings |
| rgen | m | Lever arm for load cell generator |
| rweight | m | Lever arm for weights |
| t | - | Student’s t factor |
| Tm | Nm | Mechanical torque |
| QEB | - | Discharge factor |
| nED | - | Speed factor |
| wa | mm | Width of bucket side waves (axial direction) |
| wd | mm | Depth of bucket side waves |
| v1, v2 | m/s | Velocity at inlet (position 1), jet velocity (position 2) |
| X | - | Measured quantity |
| αD | deg. | Nozzle seat ring angle |
| αN | deg. | Needle angle |
| ηh | % | Hydraulic efficiency |
| r | kg/m3 | Density |
References
- Ge, X.; Sun, J.; Chu, D.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Binama, M.; Zheng, Y. Sediment erosion on Pelton turbines: A review. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2023, 36, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, N.; Rai, A.K. Hydro-abrasive erosion in Pelton turbines: Comprehensive review and future outlook. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 207, 114957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.K. Hydro-Abrasive Erosion of Pelton Turbine. Ph.D. Thesis, IIT Roorkee, Roorkee, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Abgottspon, A.; Staubli, T.; Bieri, E.; Felix, D. Economic optimization of maintenance measures based on continuous efficiency monitoring. In Proceedings of the Vienna Hydro 2022, Vienna, Austria, 9–11 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Staubli, T. Financial analysis for optimization of hydropower plants regarding hydro-abrasive erosion: A study from Indian Himalaya. In Proceedings of the 29th Symposium of Hydraulic Machinery and Systems, Kyoto, Japan, 17–21 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Monseco, F.J. Analysis of maintenance optimization in a hydroelectric power plant. J. Appl. Res. Technol. Eng. 2020, 1, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank. Operation and Maintenance Strategies for Hydropower, Handbook for Practitioners and Decision Makers; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Felix, D. Experimental Investigation on Suspended Sediment, Hydro-Abrasive Erosion and Efficiency Reductions of Coated Pelton Turbines. Ph.D. Thesis, ETHZ, Zürich, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thapa, B. Sand Erosion in Hydraulic Machinery. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Engineering & Technology, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bajracharya, T.R.; Acharya, B.; Joshi, C.B.; Saini, R.P.; Dahlhaug, O.G. Sand erosion of Pelton turbine nozzles and buckets: A case study of Chilime Hydropower Plant. Wear 2008, 26, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhy, M.K.; Saini, R.P. Study of silt erosion on performance of a Pelton turbine. Energy 2011, 36, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhy, M.K.; Saini, R.P. Effect of size and concentration of silt particles on erosion of Pelton turbine buckets. Energy 2009, 34, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, D.; Kastinger, M.; Cracknell, N.; Boes, R. Umgang mit Feinsedimenten am Kleinwasserkraftwerk Susasca; Fachtagung Kleinwasserkraft: Flums, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Abgottspon, A.; Staubli, T.; Felix, D. Erosion of Pelton buckets and changes in turbine efficiency measured in the HPP Fieschertal. In Proceedings of the 28th IAHR Symposium on Hydraulic Machinery and Systems, Grenoble, France, 4–8 July 2016; Volume 48, p. 122008. [Google Scholar]
- Felix, D.; Kastinger, M.; Cracknell, N.; Davidis, S.; Marschall, Y.; Albayrak, I.; Boes, R. OptiSed—Optimierung von Hochdruck-Kleinwasser-Kraftanlagen an feinsedimentreichen Flüssen. In Fallstudie zu Entsandung und Turbinenabrasion am Kleinwasserkraftwerk Susasca; SI/501760; Swiss Federal Office of Energy (SFOE) Bundesamt für Energie: Bern, Switzerland, 2023. Available online: https://www.aramis.admin.ch/Texte/?ProjectID=41589 (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Khan, R.; Ullah, S.; Qahtani, F.; Pao, W.; Talha, T. Experimental and numerical investigation of hydro-abrasive erosion in the Pelton turbine buckets for multiphase flow. Renew. Energy 2024, 222, 119829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Staubli, T. Hydro-abrasive erosion in Pelton buckets: Classification and field study. Wear 2017, 392–393, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abgottspon, A.; von Burg, M.; Staubli, T.; Felix, D. Analysis of hydro-abrasive erosion and efficiency changes measured on the coated Pelton turbines of HPP Fieschertal. In Proceedings of the 30th IAHR Symposium on Hydraulic Machinery and Systems, Lausanne, Switzerland, 5–10 July 2021; Volume 774, p. 012030. [Google Scholar]
- Brekke, H.; Wu, Y.L.; Cai, B.Y. Design of Hydraulic Machinery Working in Sand Laden Water. In Abrasive Erosion & Corrosion of Hydraulic Machinery; Duan, C.G., Karelin, V.Y., Eds.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2002; pp. 155–233. [Google Scholar]
- Bozic, H.; Hassler, P.; Schnablegger, W. Prüfung und Bewertung von Peltonlaufrädern—Unter besonderer Bedachtnahme auf den Trend zu geschmiedeten Laufrädern. In Proceedings of the Jahrestagung der Deutschen, Österreichischen und Schweizerischen Gesellschaft für Zerstörungsfreie Prüfung, Salzburg, Austria, 17–19 May 2004; DGZfP: Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Maldet, R. Pelton runner with high erosion caused by glacier sediment: Assessment and measures. In Proceedings of the 15th International Seminar on Hydropower, Vienna, Austria, 26–28 November 2008; pp. 639–646. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. Pelton Turbines; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Chang, X.; Qin, B.; Pang, J.; Lai, Z.; Jiang, D.; Qin, M.; Yao, B.; Zeng, Y. Research on the mechanism of sediment erosion in the bucket of a large-scale Pelton turbine at a hydropower station. Powder Technol. 2025, 455, 120805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Xiao, Y.X.; Rai, A.K.; Liang, Q.W.; Liu, J. Analysis of the airwater-sediment flow behavior in Pelton buckets using a Eulerian-Lagrangian approach. Energy 2021, 218, 119522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Xiao, Y.X.; Rai, A.K.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Q.W. Sediment-laden flow and erosion modeling in a Pelton turbine injector. Renew. Energy 2020, 162, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, N.; Rai, A.K. Numerical analysis of hydro-abrasive erosion in a five-jet Pelton turbine distributor. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2025, 103, 102855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4185:1980; Measurement of Liquid Flow in Closed Conduits, Weighing Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1980.
- IEC 63461:2024; Pelton Hydraulic Turbines—Model Acceptance Tests. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.












| Turbine Part | Subject | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic parameters | Head, H | 120 m |
| Flow rate, Q | 11–35 L/s | |
| Nozzle seat ring diameter, D0 | 36.6 mm | |
| Injector | Nozzle seat ring angle, αD | 90° |
| Needle angle, αN | 50° | |
| Needle stroke, s | 29 mm (0 to 35 L/s) | |
| Runner | Jet pitch circle diameter, D | 327.7 mm |
| Inner bucket width, B | 80 mm | |
| Lever arm for weights, rweight | 1 m | |
| Torque measurement | Lever arm for load cell generator, rgen | 1 m |
| Lever arm for load cell bearing, rbearing | 0.25 m |
| Uncertainty Type | Symbol | Error | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Instrument uncertainties | |||
| Flow rate | ±0.106 | % | |
| Pressure | ±900 | Pa | |
| Rotational speed | ±0.05 | % | |
| Pipe diameter | ±0.20 | mm | |
| Length lever arm for weights | ±0.19 | mm | |
| Length of generator lever arm | ±0.305 | mm | |
| Length of bearing lever arm | ±0.20 | mm | |
| Weights at generator | ±0.015 | kg | |
| Load cell at generator | ±0.010 | kg | |
| Load cell at bearing | ±0.014 | kg | |
| Uncertainties of physical quantities | |||
| Gravity | 0.000025 | m/s2 | |
| Density | 0.01 | % | |
| Resulting uncertainty during tests (range) | |||
| Flow rate | ±(0.118–0.172) | % | |
| Torque | ±(0.089–0.341) | % | |
| Hydraulic power | 0.14–0.22 | % | |
| Mechanical power | 0.1–0.35 | % | |
| Random uncertainty of efficiency | ±0.1 | % | |
| Systematic uncertainty of efficiency | 0.1–0.4 | % | |
| Hydraulic efficiency | 0.17–0.4 | % |
| Runner No. | Modifications | Section | Series Name | Machining Steps | Number of Measured Hill Charts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Unmodified runner for reference measurements | R | 1–7 | 11 | |
| 2 | Sharp-edged splitter | Section 3.1 | A | 1–7 | 8 |
| +Cutout | Section 3.3 | B | 8–14 | 7 | |
| +Splitter tip | Section 3.4 | C | 15–21 | 7 | |
| +Bucket base indentation, sharp | Section 3.6 | U | 22–25 | 4 | |
| +Bucket base indentation depth, sharp | Section 3.7 | V | 26–29 | 4 | |
| 3 | Rounded splitter | Section 3.2 | D | 1–7 | 8 |
| +Cutout | Section 3.3 | E | 8–14 | 7 | |
| +Splitter tip | Section 3.4 | F | 15–21 | 7 | |
| 4 | Cutout | Section 3.3 | G | 1–7 | 8 |
| +Splitter tip | Section 3.4 | H | 8–14 | 7 | |
| +Sharp-edged splitter | Section 3.1 | S | 15–21 | 7 | |
| 5 | Cutout + Splitter tip | Section 3.5 | J | 1–7 | 8 |
| +Bucket base indentation, smooth | Section 3.6 | M | 8–11 | 4 | |
| +Bucket base indentation depth, smooth | Section 3.7 | N | 12–15 | 4 | |
| +Rounded splitter | Section 3.2 | T | 16–22 | 7 | |
| 6 | Bucket side | Section 3.8 | K | 1–5 | 6 |
| +Bucket side depth | Section 3.9 | L | 6–7 | 2 | |
| 7 | Sharp-edged splitter + Cutout + Splitter tip | Section 3.1, Section 3.3, Section 3.4 | P | 1–7 | 8 |
| 8 | Bucket side in bucket root | Section 3.10 | Q | 1–3 | 4 |
| 9 | Waveform defects at bucket walls | Section 3.11 | X | 1–5 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fahrni, F.; Staubli, T.; Casartelli, E. Efficiency Testing of Pelton Turbines with Artificial Defects—Part 1: Buckets. Energies 2025, 18, 2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18112716
Fahrni F, Staubli T, Casartelli E. Efficiency Testing of Pelton Turbines with Artificial Defects—Part 1: Buckets. Energies. 2025; 18(11):2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18112716
Chicago/Turabian StyleFahrni, Florian, Thomas Staubli, and Ernesto Casartelli. 2025. "Efficiency Testing of Pelton Turbines with Artificial Defects—Part 1: Buckets" Energies 18, no. 11: 2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18112716
APA StyleFahrni, F., Staubli, T., & Casartelli, E. (2025). Efficiency Testing of Pelton Turbines with Artificial Defects—Part 1: Buckets. Energies, 18(11), 2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18112716








