Heavy Metal Control and Dry Matter Assessment in Digested Sewage Sludge for Biogas Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- Evaluate the relationship between dry matter in sewage sludge before and after digestion;
- (ii)
- Determine the heavy metal and nutrient content after the digestion process;
- (iii)
- Verify whether the addition of glycerin water to sewage sludge increases biogas production in the cogeneration system (boilers and power generation units).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Object
2.2. Stages of Sewage Sludge Processing
2.2.1. Process Control, Automation, and Real-Time Monitoring
2.2.2. Biological Treatment, Precision Aeration, and Chemical Intervention
2.2.3. Excess Wastewater and Robust Emergency Response Mechanisms
2.2.4. Precise Pumping and Advanced Biological Treatment
2.2.5. Precise Dosing, Effective Clarification, and Robust Monitoring Systems
2.2.6. Effective Resource Recovery and Sustainable Energy Use
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
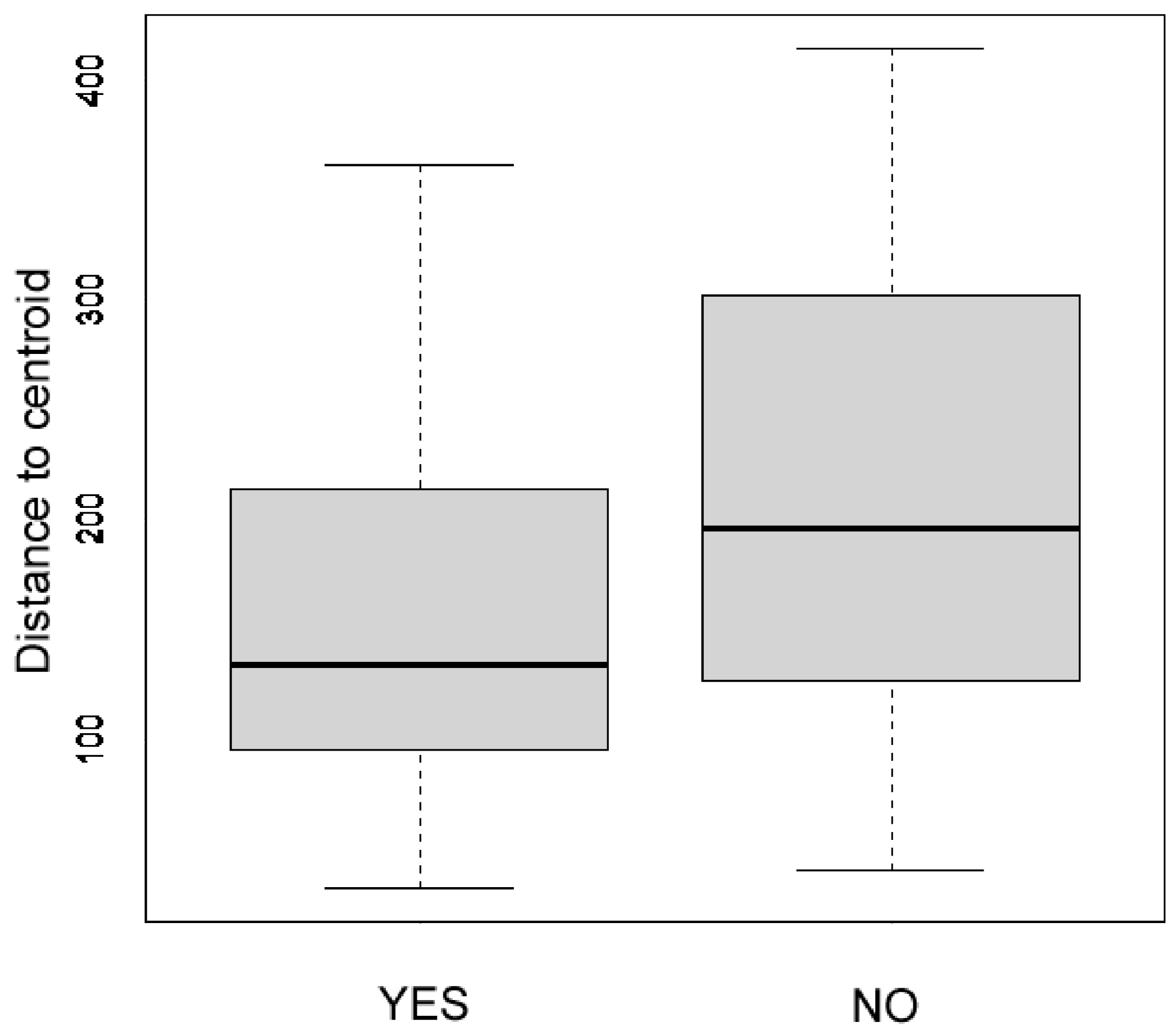
2.4. Statistical Analysis
- Di is the dispersion for group i;
- ni is the number of samples in group i;
- dij is the distance of point j from the centroid of group i.
3. Results
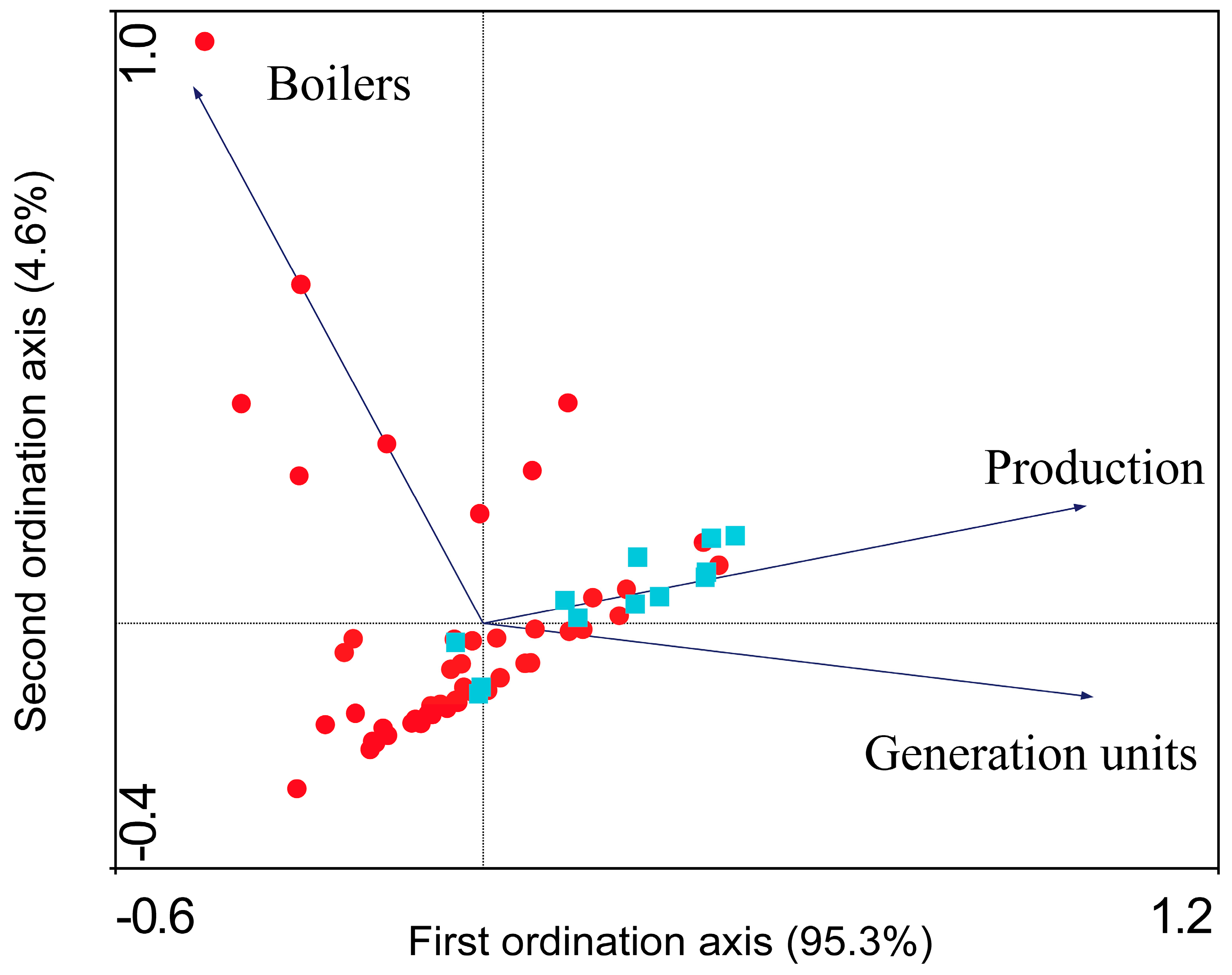
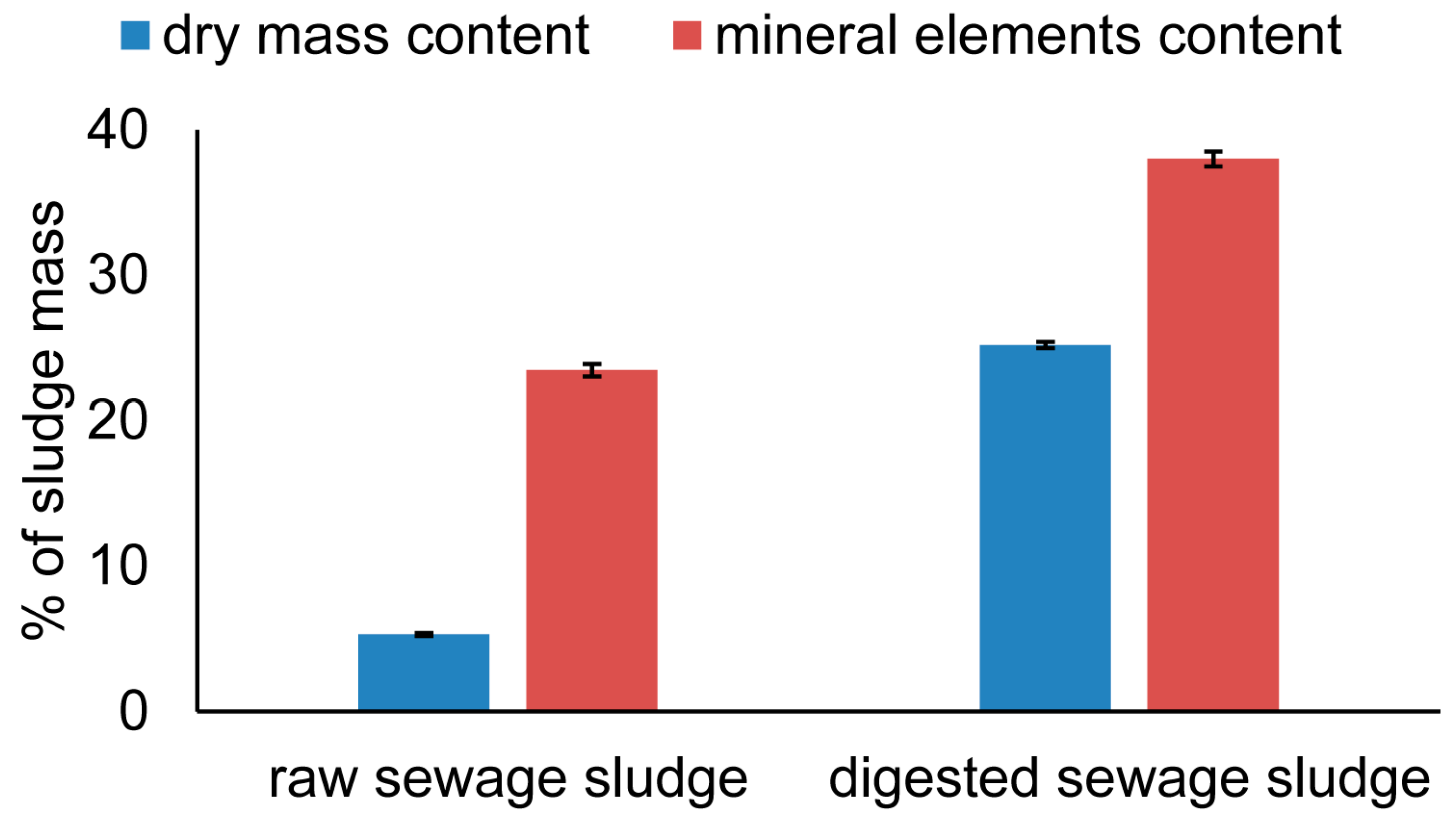
3.1. Heavy Metal and Nutrient Contents
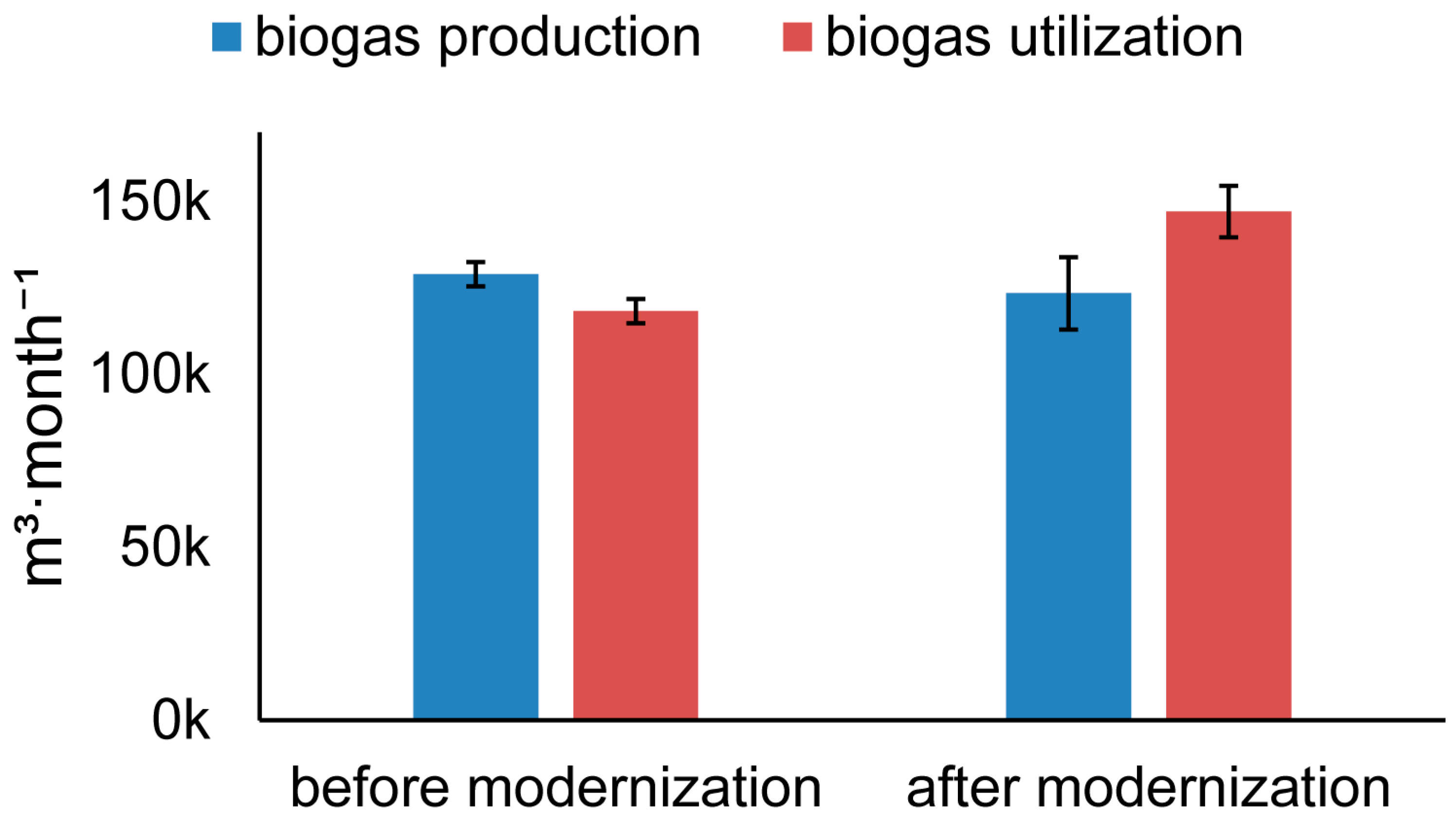
3.2. Biogas Production
4. Discussion
4.1. Managing Sewage Sludge in a Circular Economy: Challenges, Digestion Treatment Effects, and Resource Utilization Benefits
4.2. Contribution of Sewage Sludge Treatment to Renewable Energy Production
4.3. Future Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sariatli, F. Linear economy versus circular economy: A comparative and analyzer study for optimization of economy for sustainability. Visegr. J. Bioecon. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 6, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiguobarueghian, I.; Adanma, U.M.; Ogunbiyi, E.O.; Solomon, N.O. Waste management and circular economy: A review of sustainable practices and economic benefits. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 22, 1708–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuttke, J. The Circular Economy Package of the European Union. In Factor X: Challenges, Implementation Strategies and Examples for a Sustainable Use of Natural Resources; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 251–262. [Google Scholar]
- Michalski, K.; Kośka-Wolny, M.; Chmielowski, K.; Bedla, D.; Petryk, A.; Guzdek, P.; Dąbek, K.A.; Gąsiorek, M.; Grübel, K.; Halecki, W. Examining the Potential of Biogas: A Pathway from Post-Fermented Waste into Energy in a Wastewater Treatment Plant. Energies 2024, 17, 5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płonka, I.; Kudlek, E.; Pieczykolan, B. Municipal Sewage Sludge Disposal in the Republic of Poland. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.B.; Shima, K. Composting of sewage sludge with a simple aeration method and its utilization as a soil fertilizer. Environ. Manag. 2019, 63, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D. Novel design concept for a commercial-scale plant for supercritical water oxidation of industrial and sewage sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghimire, U.; Sarpong, G.; Gude, V.G. Transitioning wastewater treatment plants toward circular economy and energy sustainability. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 11794–11803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhote, J.; Ingole, S.; Chavhan, A. Review on wastewater treatment technologies. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2012, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrentino, R.; Langone, M.; Fiori, L.; Andreottola, G. Full-scale sewage sludge reduction technologies: A review with a focus on energy consumption. Water 2023, 15, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, P.; Anggraeni, K.; Weber, U. The relevance of circular economy practices to the sustainable development goals. J. Ind. Ecol. 2019, 23, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilnáček, V.; Innemanová, P.; Šereš, M.; Michalíková, K.; Stránská, Š.; Wimmerová, L.; Cajthaml, T. Micropollutant biodegradation and the hygienization potential of biodrying as a pretreatment method prior to the application of sewage sludge in agriculture. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Liu, X. Emerging electrochemical processes for materials recovery from wastewater: Mechanisms and prospects. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Lee, D.J.; Chang, Y.; Lee, Y.J. Sludge treatment: Current research trends. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morello, R.; Di Capua, F.; Cesaro, A.; Esposito, G.; Pirozzi, F.; Fratino, U.; Spasiano, D. Solutions for solid minimization in the sludge streamline of municipal wastewater treatment plants: Current state and recent developments. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 64, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaddel, S.; Bakhtiary-Davijany, H.; Kabbe, C.; Dadgar, F.; Østerhus, S.W. Sustainable sewage sludge management: From current practices to emerging nutrient recovery technologies. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halecki, W.; Gąsiorek, M.; Gambuś, F.; Abram, R. The potential of hydrated and dehydrated sewage sludge discharges from soil reclamation appliances. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2016, 25, 1935–1941. [Google Scholar]
- Adeoye, J.B.; Tan, Y.H.; Lau, S.Y.; Tan, Y.Y.; Chiong, T.; Mubarak, N.M.; Khalid, M. Advanced oxidation and biological integrated processes for pharmaceutical wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marguti, A.L.; Ferreira Filho, S.S.; Piveli, R.P. Full-scale effects of addition of sludge from water treatment stations into processes of sewage treatment by conventional activated sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 215, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Zhang, R.; Ngo, H.H.; He, X.; Ma, J.; Nan, J.; Li, G. Life cycle assessment of sewage sludge treatment and disposal based on nutrient and energy recovery: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.H.; Tan, H.K.; Lau, S.Y.; Yap, P.S.; Danquah, M.K. Potential and challenges of enzyme incorporated nanotechnology in dye wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Walia, S.; Kazemian, H. Advancements in combined electrocoagulation processes for sustainable wastewater treatment: A comprehensive review of mechanisms, performance, and emerging applications. Water Res. 2024, 230, 121248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halecki, W.; Sionkowski, T.; Chmielowski, K.; Kowalczyk, A.; Kalarus, K. Municipal wastewater quality control: Heavy metal comparative analysis—Case study. Environ. Prot. Nat. Resour. 2023, 34, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, M.; Batstone, D.; Mbamba, C.K.; Keymer, P.; French, T.; Ward, A.; Cardell-Oliver, R. Deep learning in wastewater treatment: A critical review. Water Res. 2023, 232, 120518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyashanu, P.N.; Shafodino, F.S.; Mwapagha, L.M. Determining the potential human health risks posed by heavy metals present in municipal sewage sludge from a wastewater treatment plant. Sci. Afr. 2023, 20, e01735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN ISO 5667-13:2011; Jakość Wody—Pobieranie Próbek—Część 13: Wytyczne Dotyczące Pobierania Próbek Osadów (Water Quality—Sampling—Part 13: Guidance on Sampling of Sludges). The Polish Committee for Standardization (Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny—PKN): Warszawa, Poland, 2011.
- PN-EN 13346:2002; Charakterystyka Osadów Ściekowych—Oznaczanie Pierwiastków Śladowych i Fosforu—Metody Ekstrakcji Wodą Królewską (Characterization of Sewage Sludge—Determination of Trace Elements and Phosphorus—Aqua Regia Extraction Methods). The Polish Committee for Standardization (Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny—PKN): Warszawa, Poland, 2002.
- PN-EN 12880:2004; Charakterystyka Osadów Ściekowych—Oznaczanie Suchej Pozostałości i Zawartości Wody (Characterization of Sludges—Determination of Dry Residue and Water Content). The Polish Committee for Standardization (Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny—PKN): Warszawa, Poland, 2004.
- PN-EN ISO 11885:2009; Jakość Wody—Oznaczanie Wybranych Pierwiastków Metodą Optycznej Spektrometrii Emisyjnej z Plazmą Wzbudzoną Indukcyjnie (ICP-OES) (Water Quality—Determination of Selected Elements by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)). The Polish Committee for Standardization (Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny—PKN): Warszawa, Poland, 2009.
- Ministry of Climate and Environment. Regulation of the Minister of Climate and Environment of December 31, 2021 amending the Regulation on Municipal Sewage Sludge. In Journal of Laws of The Republic of Poland; Ministry of Climate and Environment: Warsaw, Poland, 2022; item 89. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Šmilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination; Version 4.5; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Aust. Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Walsh, D.C.I. PERMANOVA, ANOSIM, and the Mantel test in the face of heterogeneous dispersions: What null hypothesis are you testing? Ecol. Monogr. 2013, 83, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA). In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; Balakrishnan, N., Colton, T., Everitt, B., Piegorsch, W., Ruggeri, F., Teugels, J.L., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analysis of changes in community structure. Aust. J. Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. Distance-based tests for homogeneity of multivariate dispersions. Biometrics 2006, 62, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Ellingsen, K.E.; McArdle, B.H. Multivariate dispersion as a measure of beta diversity. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindt, R.; Coe, R. Tree Diversity Analysis: A Manual and Software for Common Statistical Methods for Ecological and Biodiversity Studies; World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF): Nairobi, Kenya, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Multimodel Inference; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- TIBCO. Available online: https://www.tibco.com/ (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.L.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Szoecs, E.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package, R package version 2.6-6; The R Project for Statistical Computing: Durham, NC, USA, 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Bartoń, K. MuMIn: Multi-Model Inference, R Package Version 1.47.1; The R Project for Statistical Computing: Durham, NC, USA, 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MuMIn (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Rocha, F.; Ratola, N.; Homem, V. Heavy metal(loid)s and nutrients in sewage sludge in Portugal—Suitability for use in agricultural soils and assessment of potential risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 964, 178595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil-Ayuk, N.; Jrade, A. An Integrated Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Circular Economy (CE) Model for the Management of Construction and Deconstruction Waste Based on Construction Methods. Open J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 14, 168–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, I.; Syrou, N.; Adamopoulou, J. Greece’s current water and wastewater regulations and the risks they pose to environmental hygiene and public health, as recommended by the European Union Commission. Eur. J. Sustain. Dev. Res. 2024, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianico, A.; Bertanza, G.; Braguglia, C.M.; Canato, M.; Laera, G.; Heimersson, S.; Svanström, M.; Mininni, G. Upgrading a wastewater treatment plant with thermophilic digestion of thermally pre-treated secondary sludge: Techno-economic and environmental assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 102, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Hong, C.; Ling, W.; Hu, J.; Feng, W.; Xing, Y.; Feng, L. Research progress in improving sludge dewaterability: Sludge characteristics, chemical conditioning and influencing factors. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, N.A.; Aziz, H.A.; Pueh, L.L.L.; Othman, I.B.; Adam, J.H.; Hung, Y.T. Stabilization and Solidification of Sludges. In Industrial Waste Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 87–133. [Google Scholar]
- Sikder, S.; Toha, M.; Rahman, M.M. Municipal Solid Waste Incineration: An Incredible Method for Reducing Pressures on Landfills. In Technical Landfills and Waste Management: Volume 2: Municipal Solid Waste Management; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 169–188. [Google Scholar]
- Emmanouil, C.; Giannakis, I.; Kyzas, G.Z. Terrestrial bioassays for assessing the biochemical and toxicological impact of biosolids application derived from wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutroubas, S.D.; Antoniadis, V.; Damalas, C.A.; Fotiadis, S. Municipal sewage sludge effects on maize yield, nitrogen use efficiency, and soil properties. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherghel, A.; Teodosiu, C.; De Gisi, S. A review on wastewater sludge valorisation and its challenges in the context of circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertanza, G.; Canato, M.; Laera, G. Towards energy self-sufficiency and integral material recovery in wastewater treatment plants: Assessment of upgrading options. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Carnevale Miino, M.; Torretta, V. What advanced treatments can be used to minimize the production of sewage sludge in WWTPs? Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.I.; Rameez, H.; Farooqi, I.H.; Basheer, F. Recent advancement in commercial and other sustainable techniques for energy and material recovery from sewage sludge. Water 2023, 15, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltola, P.; Ruottu, L.; Larkimo, M.; Laasonen, A.; Myöhänen, K. A novel dual circulating fluidized bed technology for thermal treatment of municipal sewage sludge with recovery of nutrients and energy. Waste Manag. 2023, 155, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, D.; Barbiero, C.; Briens, C.; Berruti, F. Pyrolysis as an economical and ecological treatment option for municipal sewage sludge. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 122, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, L.; Wu, D.; Lyu, S. How to move from conflict to opportunity in the not-in-my-backyard dilemma: A case study of the Asuwei waste incineration plant in Beijing. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 104, 107326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jama-Rodzeńska, A.; Sowiński, J.; Koziel, J.A.; Białowiec, A. Phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge ash based on cradle-to-cradle approach—Mini-review. Minerals 2021, 11, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, E.; Fernandes, E.; Gomes, J.; Martins, R.C. Advanced oxidation processes perspective regarding swine wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masindi, V.; Foteinis, S.; Renforth, P.; Ndiritu, J.; Maree, J.P.; Tekere, M.; Chatzisymeon, E. Challenges and avenues for acid mine drainage treatment, beneficiation, and valorisation in circular economy: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 183, 106740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derco, J.; Žgajnar Gotvajn, A.; Guľašová, P.; Kassai, A.; Šoltýsová, N. Nutrient Removal and Recovery from Municipal Wastewater. Processes 2024, 12, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młyńska, A.; Halecki, W.; Chmielowski, K. Efficient Biological Treatment: Achieving Exceptional Reductions in Pollutants and Ensuring Environmental Compliance. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignogna, D.; Ceci, P.; Cafaro, C.; Corazzi, G.; Avino, P. Production of Biogas and Biomethane as Renewable Energy Sources: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.; Akram, S.; Liaqat, Z.; Mushtaq, M. Thermal/Photocatalytic Conversion of Sewage Sludge and Biomass to Energy. In Sewage and Biomass from Wastewater to Energy; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, E.C.; Martín, M.; Vega, P. Achieving energy self-sufficiency in wastewater treatment plants by integrating municipal solid waste treatment: A process design study in Spain. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, H.; Ersahin, M.E.; Ozgun, H.; Ozturk, I.; Koyuncu, I. Energy and material refineries of future: Wastewater treatment plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giwa, A.S.; Maurice, N.J.; Luoyan, A.; Liu, X.; Yunlong, Y.; Hong, Z. Advances in sewage sludge application and treatment: Process integration of plasma pyrolysis and anaerobic digestion with resource recovery. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Bai, Z.; Li, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, S. Potential of applying the thermochemical recuperation in combined cooling, heating and power generation: Optimized recuperation regulation with syngas storage. Appl. Energy 2024, 353, 122128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamda, A.S.; Mensur, D.; Berhane, B.; Sunaina; Temesgen, T. Carbon Emissions, Energy Reduction, and Energy Recovery from Wastewater Treatment Plants. In Sewage and Biomass from Wastewater to Energy; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 93–112. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Dutta, S.; You, S.; Luo, G.; Zhang, S.; Show, P.L.; Tsang, D.C. A critical review on biochar for enhancing biogas production from anaerobic digestion of food waste and sludge. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 305, 127143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.D.; Astals, S.; Lu, Y.; Devadas, M.; Batstone, D.J. Anaerobic codigestion of sewage sludge and glycerol, focusing on process kinetics, microbial dynamics and sludge dewaterability. Water Res. 2014, 67, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, S.; Rivero, M.; Solera, R.; Perez, M. Mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge with glycerine: Effect of solids retention time. Fuel 2018, 215, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobade, V.; Baudez, J.C.; Evans, G.; Eshtiaghi, N. Impact of gas injection on the apparent viscosity and viscoelastic property of waste activated sewage sludge. Water Res. 2017, 114, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, A.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Yang, C.; Lv, H.; Yao, Y.Q. Microbial mechanisms for higher hydrogen production in anaerobic digestion at constant temperature versus gradient heating. Microbiome 2024, 12, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yan, R.; Yang, C.; Zhang, H.; Lyu, H.; Li, S.; Liu, T.; Li, R.; Yao, Y.; Li, W. Soil accelerates the humification involved in co-composting of wheat straw and cattle manure by promoting humus formation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, K.O.; Ahmed, N.A.; Ogunkunle, O. Optimization of biogas yield from lignocellulosic materials with different pretreatment methods: A review. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Wu, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, C.; Lyu, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Liu, T.; Li, R.; Yao, Y. Soil decreases N2O emission and increases TN content during combined composting of wheat straw and cow manure by inhibiting denitrification. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 477, 147306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowski, T.; Halecki, W.; Jasiński, P.; Chmielowski, K. Achieving High-Efficiency Wastewater Treatment with Sequencing Batch Reactor Grundfos Technology. Processes 2025, 13, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | N | Mean | Confidence − | Confidence + | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry matter of sewage sludge before digestion (%) | 60 | 5.30 | 5.123 | 5.474 | 3.26 | 6.44 |
| Mineral substances in sewage sludge before digestion (%) | 60 | 23.46 | 22.589 | 24.336 | 18.6 | 33.77 |
| Dry matter in sludge after digestion (%) | 60 | 25.18 | 24.755 | 25.607 | 20.82 | 28.36 |
| Mineral substances in sewage sludge after digestion (%) | 60 | 37.99 | 36.997 | 39 | 30.78 | 47.03 |
| Content after digestion | ||||||
| Cd (mg·kg−1 DM *) | 60 | 2.56 | 2.323 | 2.788 | 1.21 | 5.42 |
| Ni (mg·kg−1 DM) | 60 | 65.25 | 57.7 | 72.792 | 35.3 | 196 |
| Pb (mg·kg−1 DM) | 60 | 108.08 | 80.102 | 136.062 | 13.9 | 617 |
| Cu (mg·kg−1 DM) | 60 | 305.89 | 294.26 | 317.52 | 147 | 388 |
| Zn (mg·kg−1 DM) | 60 | 1308.56 | 1236.54 | 1380.587 | 582 | 2480 |
| Cr (mg·kg−1 DM) | 60 | 103.99 | 96.578 | 111.398 | 43.8 | 242 |
| Hg (mg·kg−1 DM) | 60 | 0.73 | 0.609 | 0.854 | 0.00 | 2.56 |
| Ammonium N (% DM) | 60 | 0.85 | 0.801 | 0.889 | 0.56 | 1.24 |
| N (% DM) | 60 | 5.38 | 5.236 | 5.53 | 4.11 | 6.47 |
| P (% DM) | 60 | 2.88 | 2.767 | 2.997 | 2.18 | 5.38 |
| Ca (% DM) | 60 | 1.98 | 1.887 | 2.08 | 0.48 | 2.57 |
| Mg (% DM) | 60 | 0.71 | 0.677 | 0.734 | 0.21 | 0.94 |
| Biogas production (m3·month−1) | |||
| df | F | p | |
| Intercept | 1 | 16.363 | <0.001 |
| Dry mass | 1 | 1.924 | 0.171 |
| Waste approved | 1 | 8.766 | 0.004 |
| Modernization | 1 | 0.189 | 0.666 |
| Error | 56 | ||
| Utilization of biogas in power generation units (m3·month−1) | |||
| df | F | p | |
| Intercept | 1 | 18.765 | <0.001 |
| Dry mass | 1 | 2.904 | 0.094 |
| Modernization | 1 | 11.608 | 0.001 |
| Error | 57 | ||
| Dry mass content % | |||
| df | F | p | |
| Intercept | 1 | 16,789.542 | <0.001 |
| Repeat measure | 1 | 7803.729 | <0.001 |
| Error | 59 | ||
| Mineral elements content % | |||
| Intercept | 1 | 5173.307 | <0.001 |
| Repeat measure | 1 | 1389.108 | <0.001 |
| Error | 59 | ||
| Addition of glycerin water | |||
| YES (mean amount) | NO (mean amount) | p | |
| N | 5.036 | 5.730 | 0.001 |
| Ca | 1.755 | 2.211 | 0.001 |
| P | 2.915 | 2.850 | 0.669 |
| Ammonium N | 0.754 | 0.936 | 0.001 |
| Mg | 0.697 | 0.714 | 0.278 |
| Modernization process | |||
| BEFORE (mean amount) | AFTER (mean amount) | p | |
| N | 5.240 | 5.956 | 0.001 |
| Ca | 1.938 | 2.163 | 0.005 |
| P | 2.897 | 2.823 | 0.990 |
| Ammonium N | 0.816 | 0.961 | 0.017 |
| Mg | 0.707 | 0.700 | 0.041 |
| Mineral elements % | ||||
| Estimate | Adjusted SE | z value | p | |
| Intercept | 32.454 | 3.204 | 10.13 | <0.001 |
| Zn | 0.005 | 0.002 | 3.295 | <0.001 |
| Addition of glycerin water (YES) | 2.440 | 1.097 | 2.223 | 0.026 |
| Cu | −0.021 | 0.010 | 2.153 | 0.032 |
| Modernization (BEFORE) | 4.193 | 1.194 | 3.513 | <0.001 |
| Cd | 1.002 | 0.638 | 1.572 | 0.116 |
| Pb | 0.005 | 0.004 | 1.183 | 0.237 |
| Cr | −0.016 | 0.014 | 1.148 | 0.251 |
| Dry mass % | ||||
| Estimate | Adjusted SE | z value | p | |
| Intercept | 34.021 | 2.0586 | 16.527 | <0.001 |
| N | −1.838 | 0.3495 | 5.258 | <0.001 |
| Ca | 0.687 | 0.4837 | 1.420 | 0.155 |
| Modernization (BEFORE) | 0.638 | 0.4885 | 1.307 | 0.191 |
| P | 0.351 | 0.3842 | 0.913 | 0.361 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michalski, K.; Kóska-Wolny, M.; Chmielowski, K.; Gąsiorek, M.; Grübel, K.; Kalarus, K.; Halecki, W. Heavy Metal Control and Dry Matter Assessment in Digested Sewage Sludge for Biogas Production. Energies 2025, 18, 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102644
Michalski K, Kóska-Wolny M, Chmielowski K, Gąsiorek M, Grübel K, Kalarus K, Halecki W. Heavy Metal Control and Dry Matter Assessment in Digested Sewage Sludge for Biogas Production. Energies. 2025; 18(10):2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102644
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichalski, Krzysztof, Magdalena Kóska-Wolny, Krzysztof Chmielowski, Michał Gąsiorek, Klaudiusz Grübel, Konrad Kalarus, and Wiktor Halecki. 2025. "Heavy Metal Control and Dry Matter Assessment in Digested Sewage Sludge for Biogas Production" Energies 18, no. 10: 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102644
APA StyleMichalski, K., Kóska-Wolny, M., Chmielowski, K., Gąsiorek, M., Grübel, K., Kalarus, K., & Halecki, W. (2025). Heavy Metal Control and Dry Matter Assessment in Digested Sewage Sludge for Biogas Production. Energies, 18(10), 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102644








