A Comprehensive Review of Self-Assembled Monolayers as Hole-Transport Layers in Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Structure of Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells and SAM Molecules
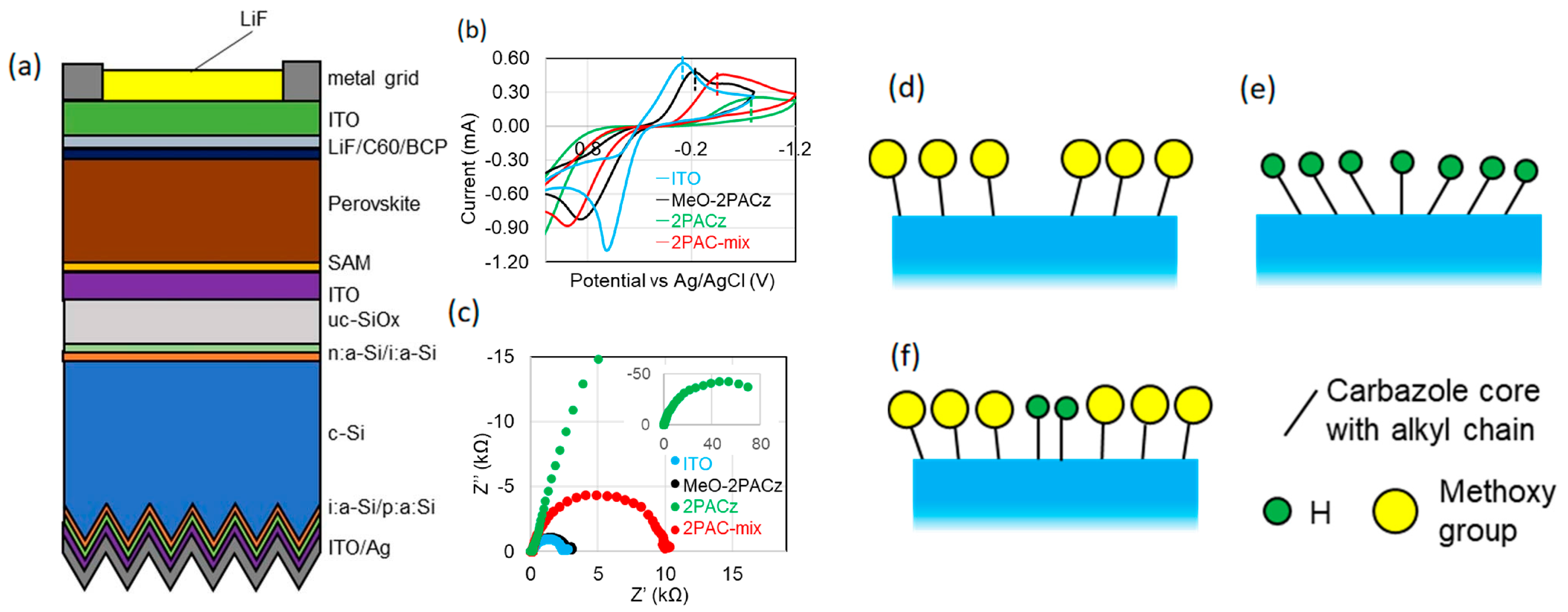
2.1. The Structure of Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells
- Anode and cathode: PSC employs a dual-electrode system for efficient charge extraction and current generation. The front electrode typically consists of TCOs, such as indium tin oxide (ITO) and fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) which are the most widely used. These TCO substrates maintain high optical transparency while providing effective electrical conductivity for charge collection. Opposing the TCO electrode, metallic contacts (commonly gold or silver) serve as the back electrode in the device architecture. This electrode configuration establishes a complete pathway for charge carriers
- HTL: In the p–i–n PSC, the HTL is initially fabricated onto the TCO substrate, serving as a fundamental component that significantly impacts overall device efficiency. This functional layer performs multiple essential roles, including facilitating hole collection, preventing electron recombination, and modulating the crystallization process and surface morphology of the perovskite active layer. To achieve optimal device performance, an effective HTL must meet several key criteria: the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) level must align properly with the valence band maximum of the perovskite material to ensure selective hole extraction and effective electron blocking; excellent charge carrier mobility is required to ensure efficient hole transport and collection; appropriate surface properties, including controlled wettability, are necessary to facilitate uniform deposition of perovskite precursors and promote high-quality crystal growth and the material should exhibit straightforward processability and maintain stable interfacial characteristics during device operation and aging.
- Perovskite absorber layer: The perovskite layer serves as the fundamental component for photovoltaic conversion, performing three essential functions: photon capture, exciton generation, and charge separation. To achieve optimal device performance, the absorber layer must satisfy multiple critical criteria: dense, pinhole-free microstructure, homogeneous surface coverage. In p–i–n structured PSCs, the absorber layer’s morphological quality assumes particular significance. The surface topography directly influences the subsequent deposition of ultrathin ETLs, where conformal coverage and interfacial contact quality are paramount for efficient charge extraction. Superior film uniformity minimizes shunt pathways while maximizing interfacial contact area between functional layers.
- ETL: The ETL serves dual critical functions in perovskite photovoltaic devices: facilitating selective electron extraction and providing inherent encapsulation that mitigates environmental degradation of the perovskite absorber. In p–i–n devices, commonly employed ETL materials include: fullerene derivatives, n-type organic semiconductors, metal oxide compounds. To achieve optimal device performance, an efficient ETL must satisfy several essential criteria: proper band offset for electron extraction, sufficient energy barrier for hole blocking, high electron mobility, high transparency (particularly critical for tandem and bifacial configurations). These multifunctional requirements highlight the importance of careful ETL material selection and engineering in high-performance perovskite optoelectronic devices.
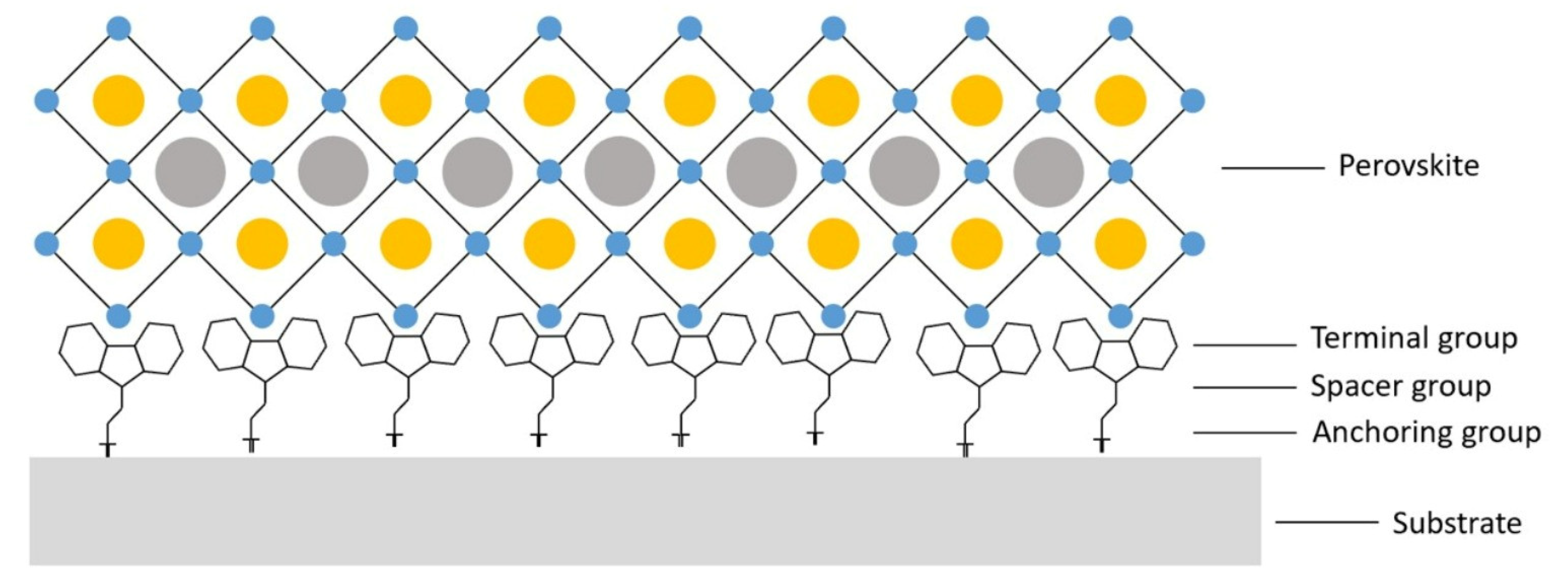
2.2. The Structure of SAM Molecules
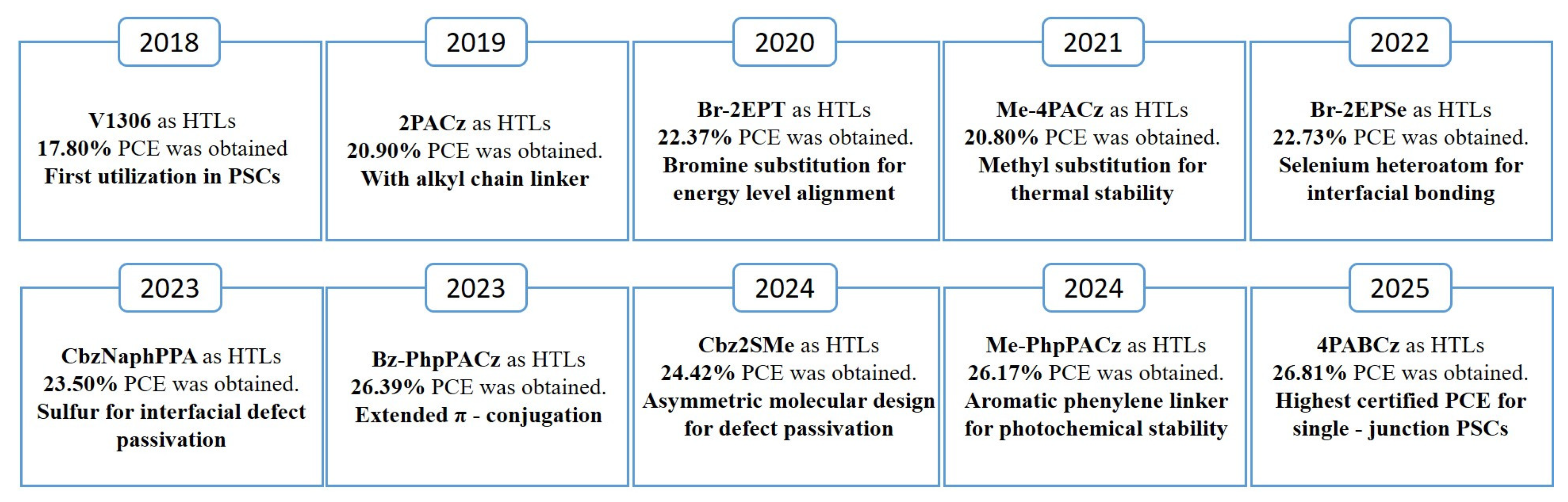
3. SAMs Adopted as Functional HTL
3.1. The Design of SAMs for Advanced Devices
3.1.1. Terminal Groups

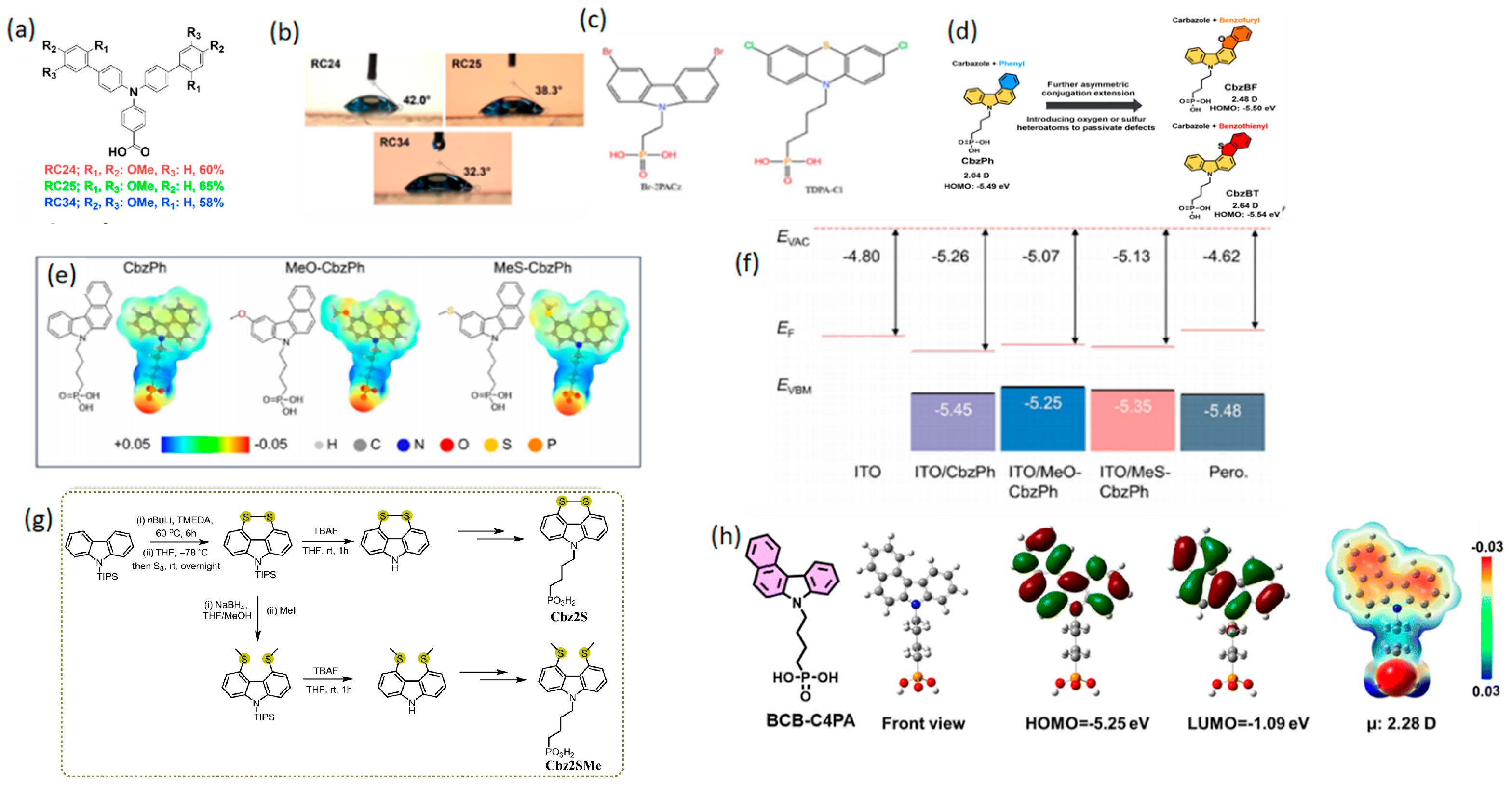
3.1.2. Spacer Groups
3.1.3. Anchoring Groups
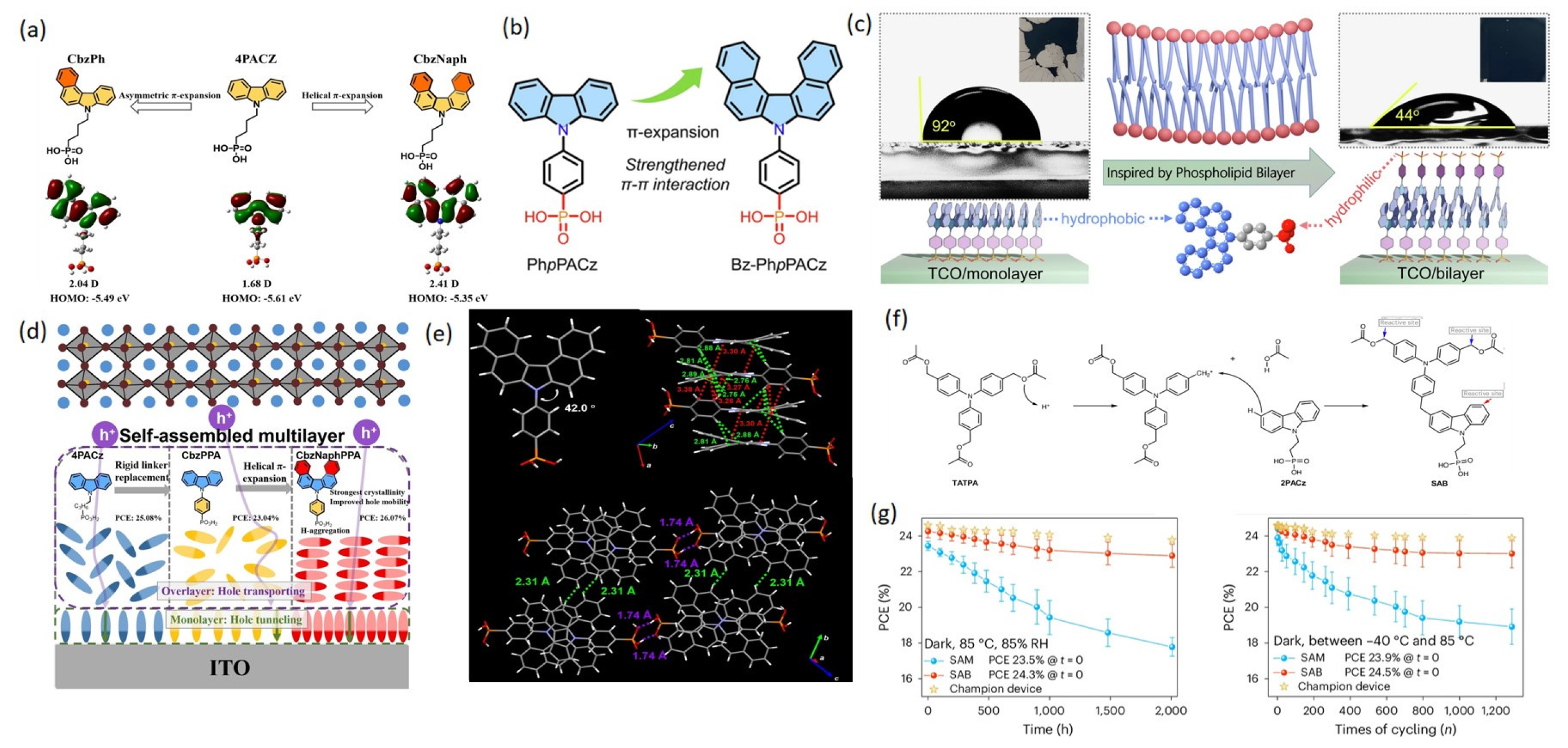
3.2. Other Strategies for Advanced Devices
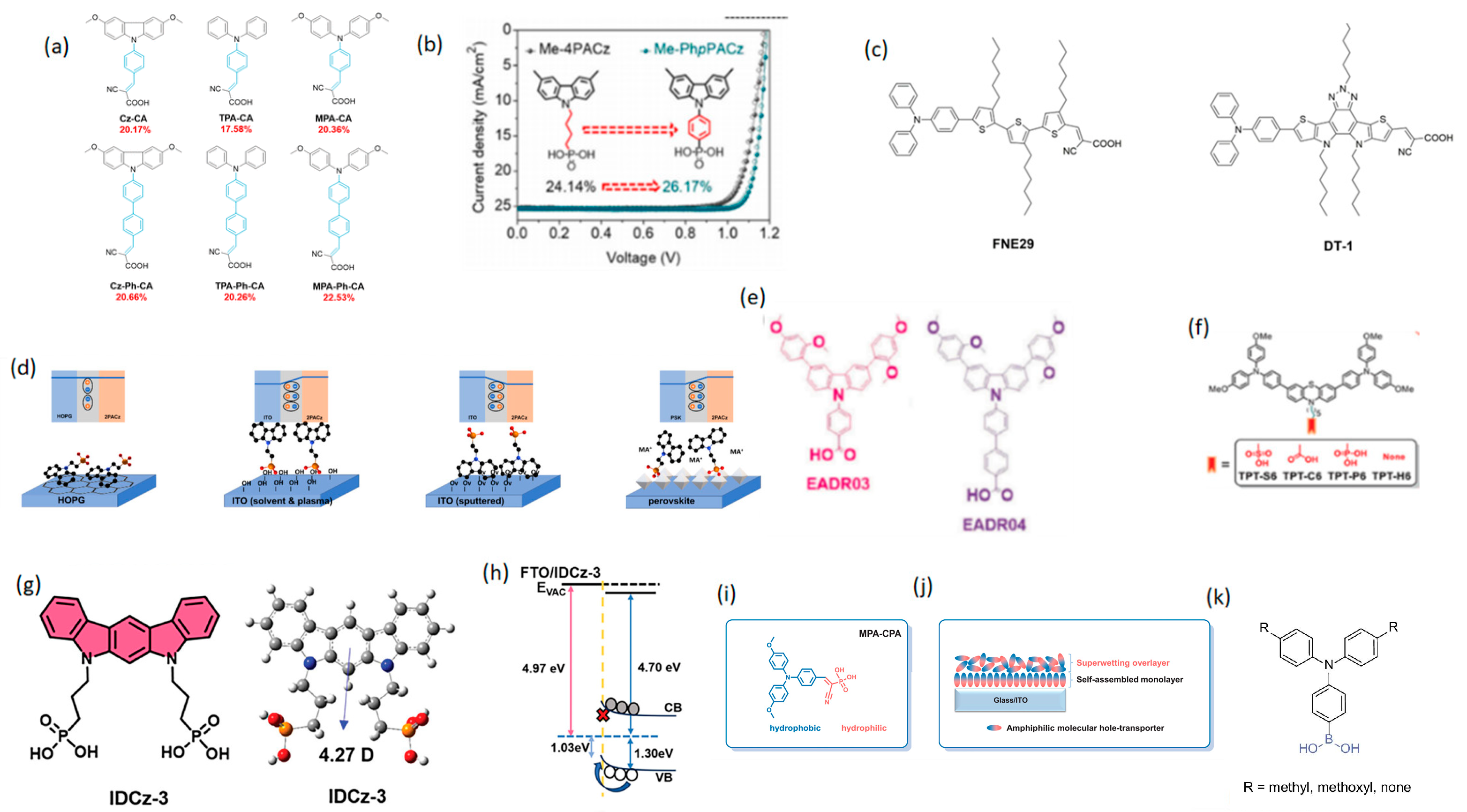
3.2.1. Additive Strategy
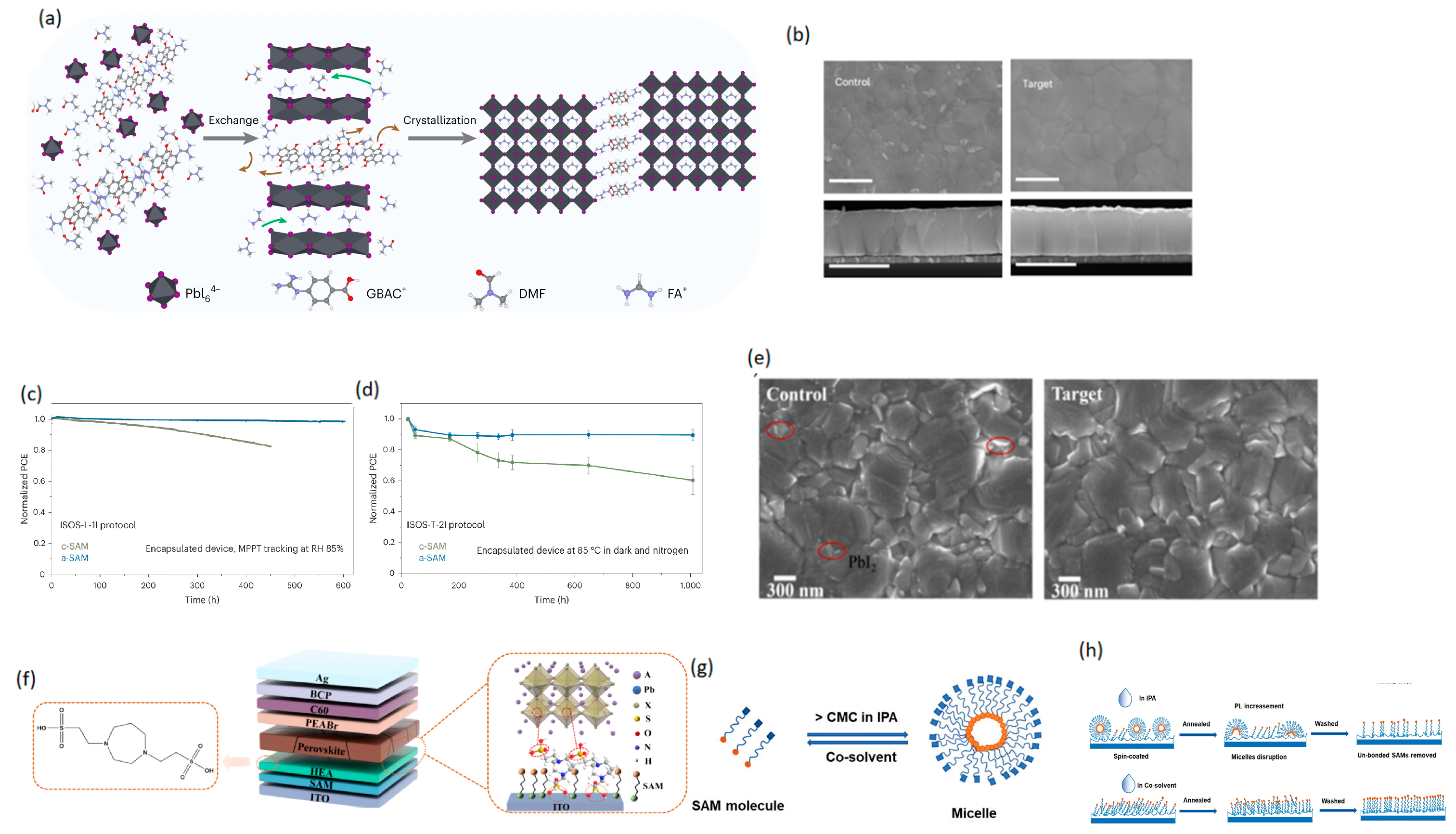
3.2.2. Co-Self-Assembly Strategy

4. SAMs Adopted to Modify HTL
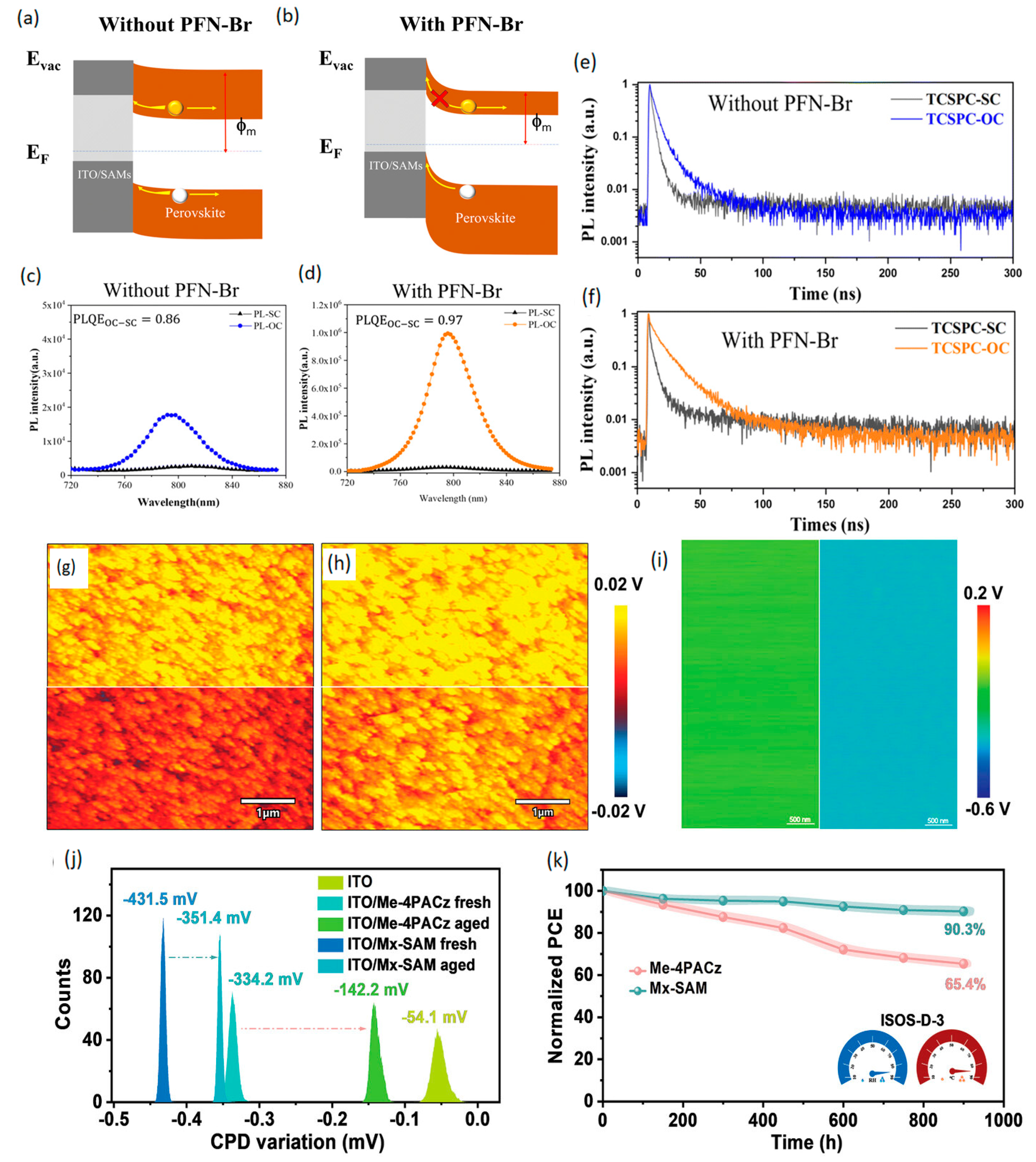
4.1. SAM Modification for Enhanced Performance of Polymer HTLs

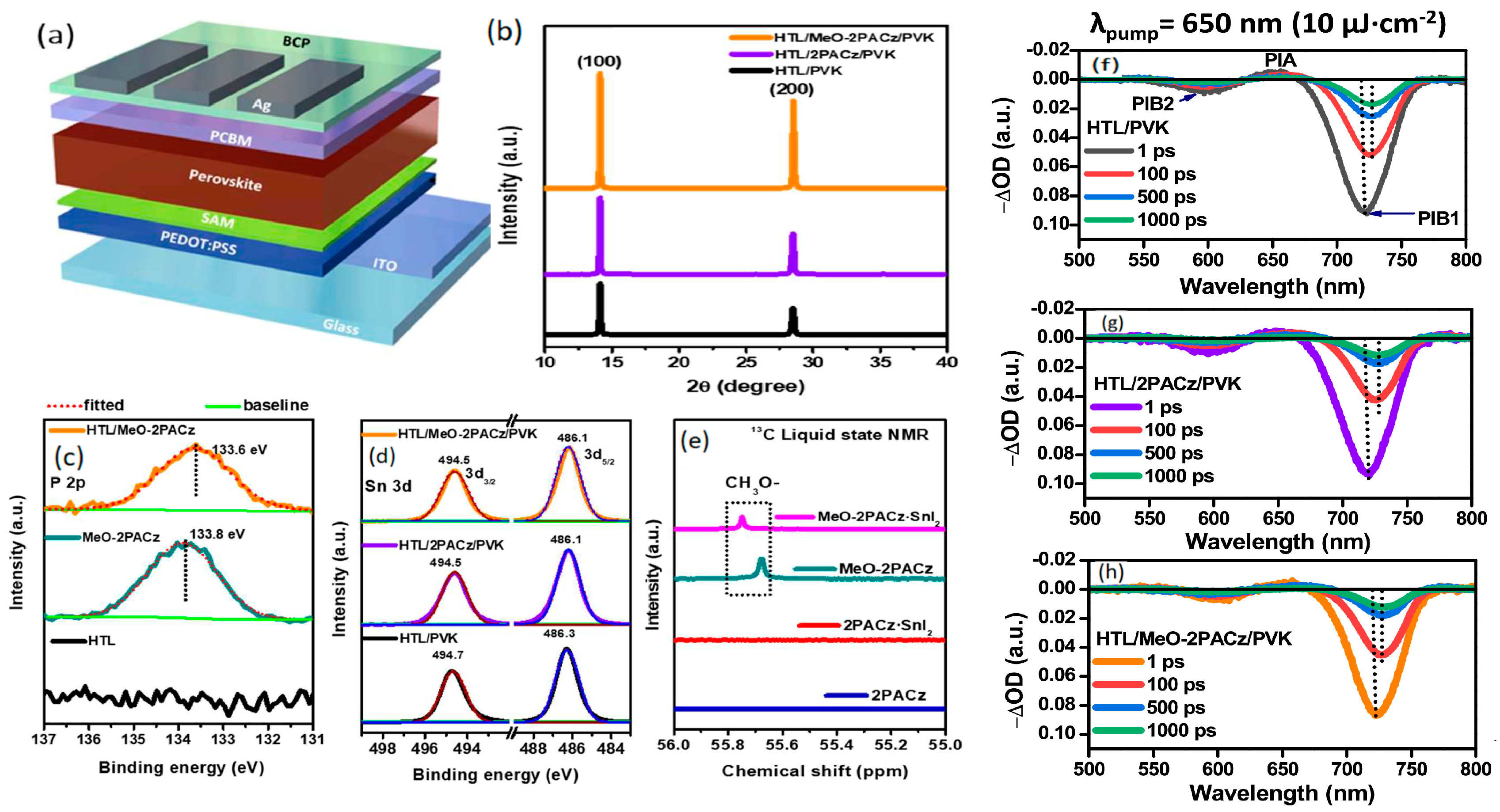
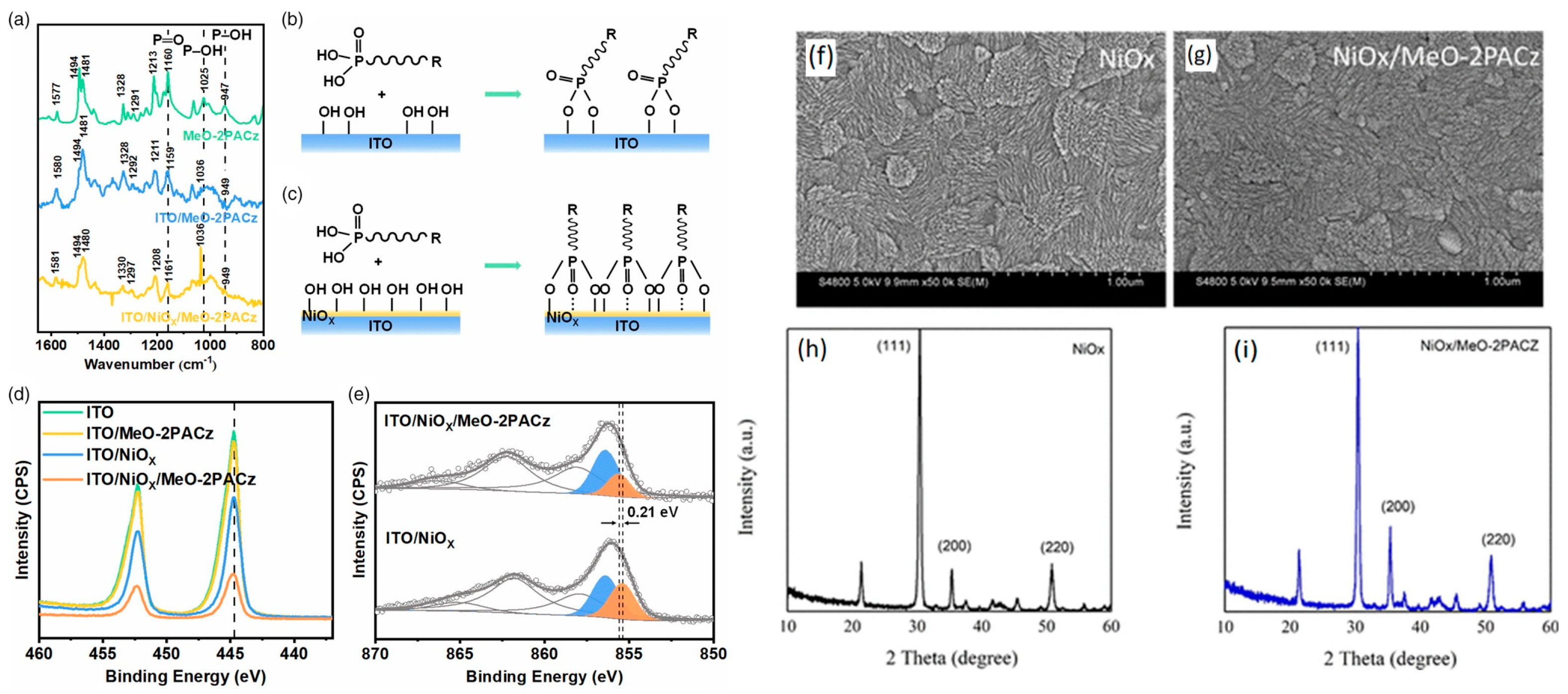
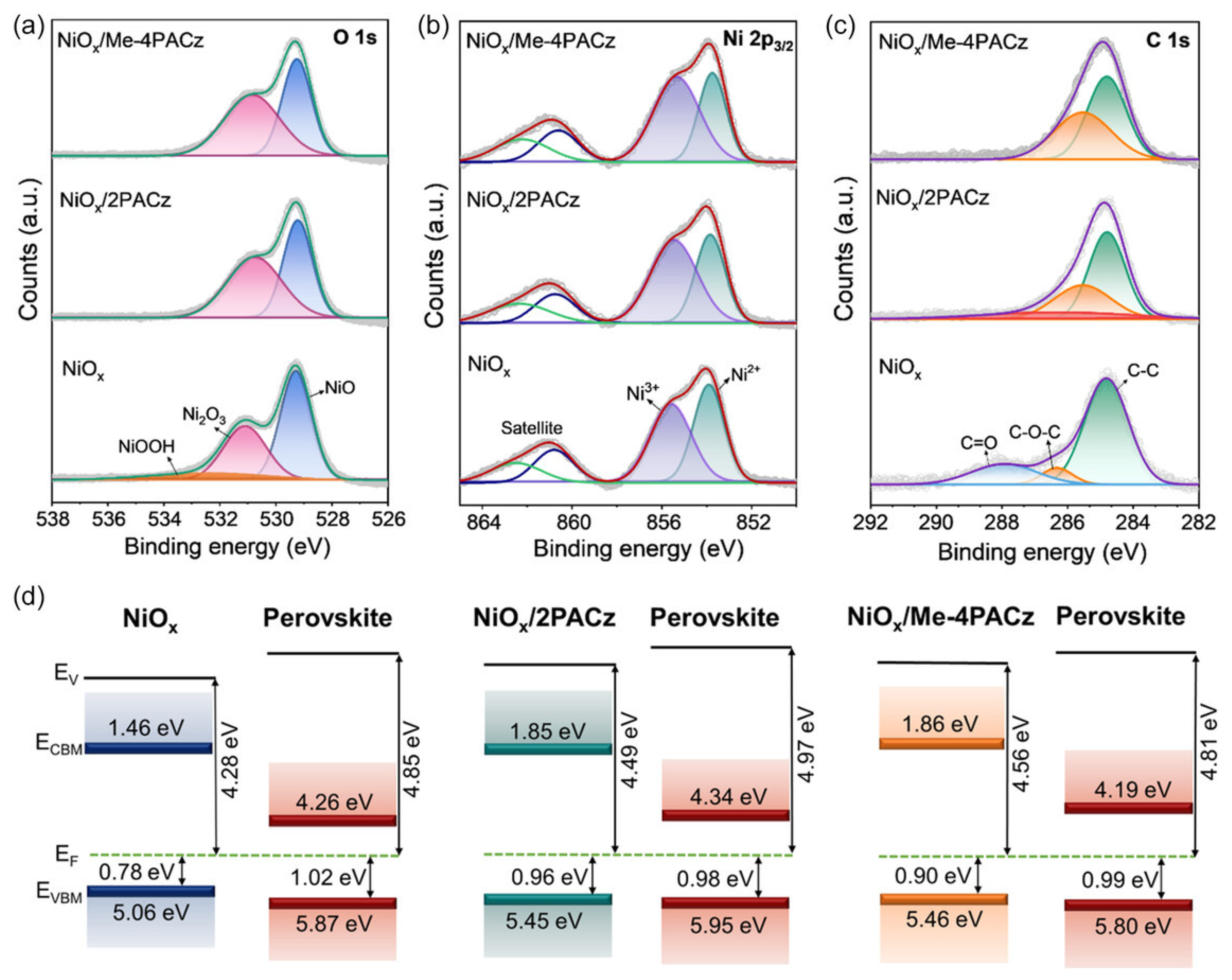
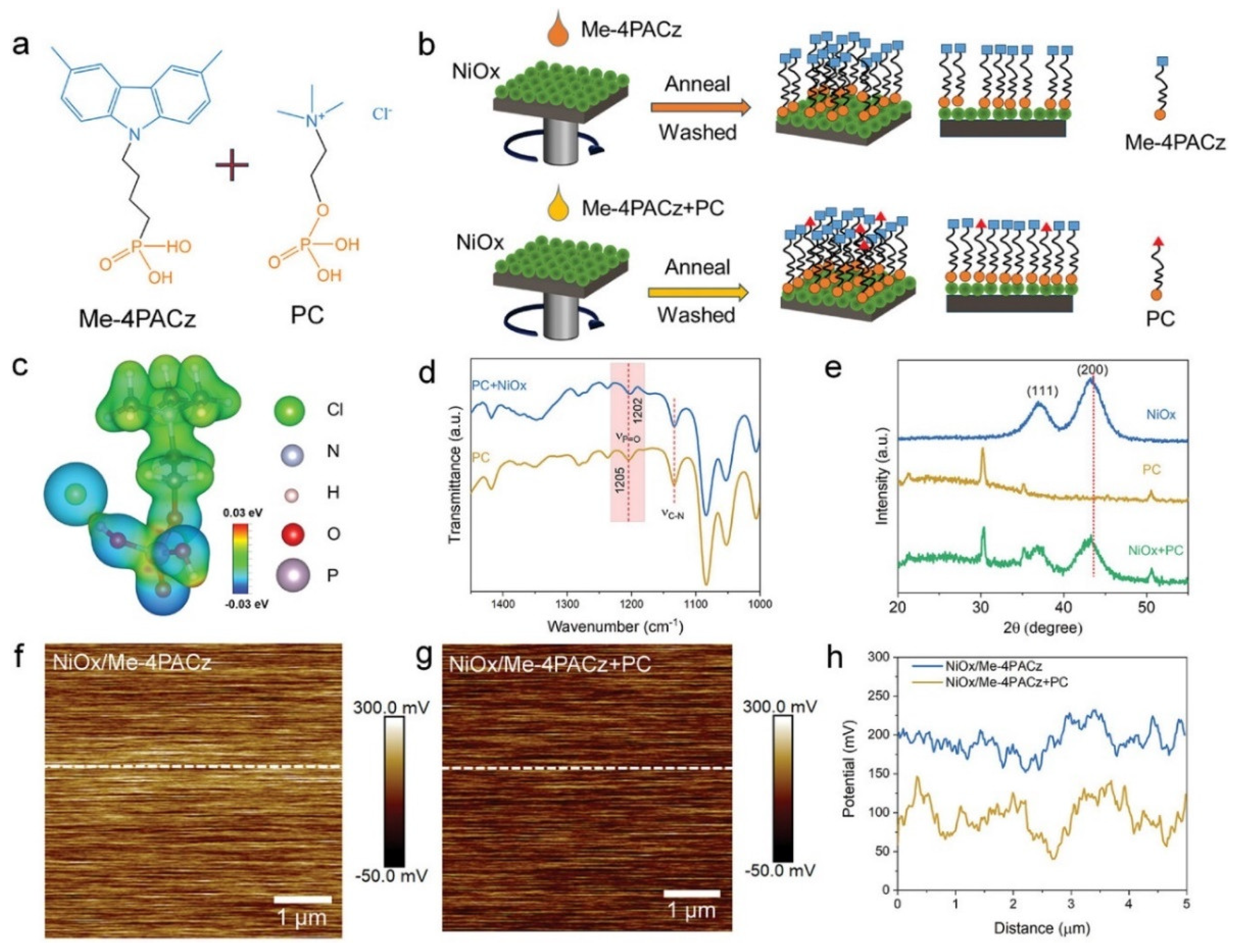
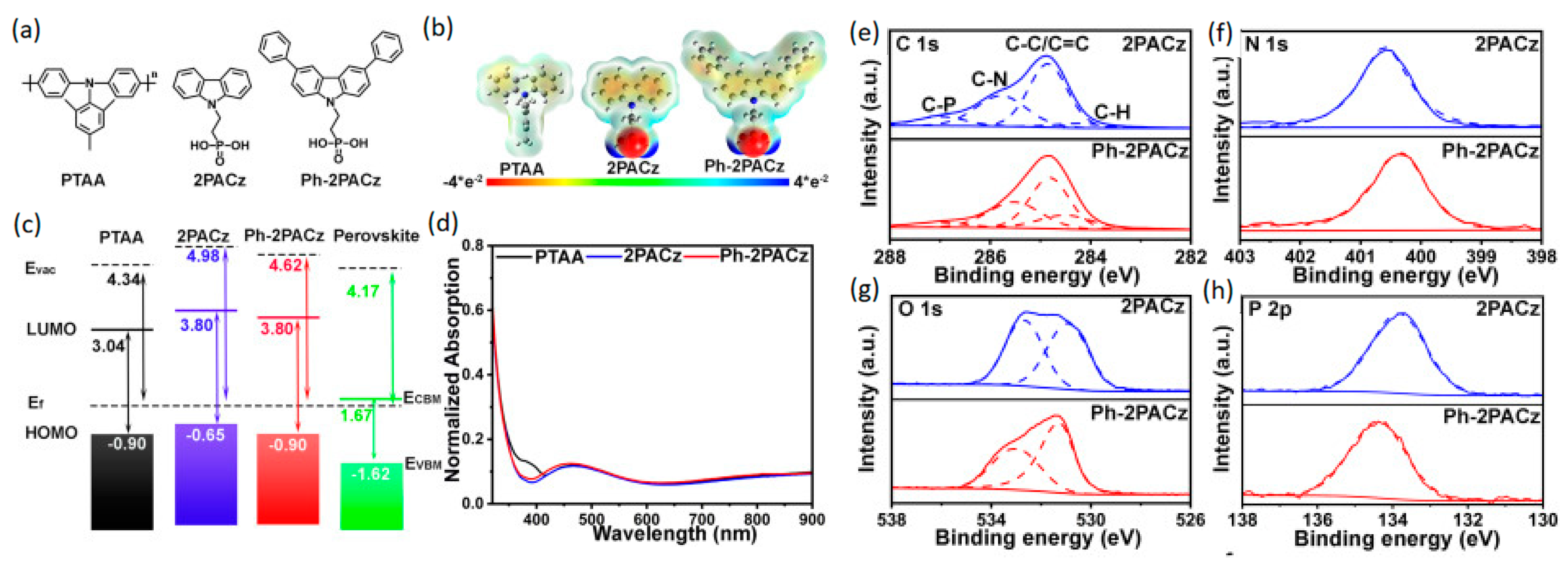
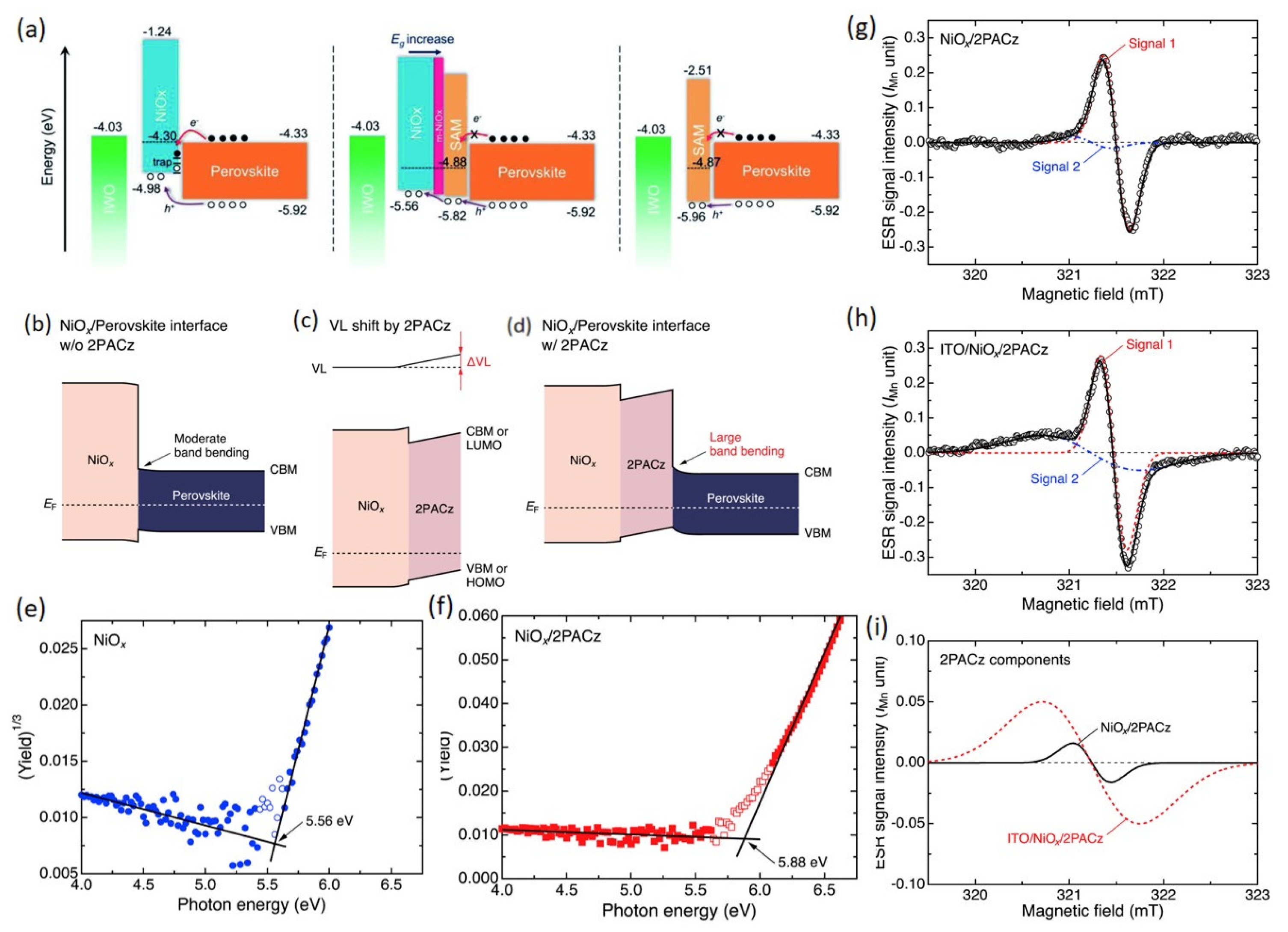
4.2. SAM Modification for Enhanced Performance of NiOx HTLs
| SAM | Device Structure | VOC/(V) | JSC/(mA·cm−2) | FF/(%) | PCE/(%) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-bromobenzoic acid | ITO/NiOx with SAM/MAPbI3/PCBM/bis-C60/Ag | 1.11 | 21.7 | 76.3 | 18.4 | [103] |
| TSPA | ITO/NiO/TSPA/perovskite/PCBM/ZnO/Ag | 1.11 | 22.8 | 80.3 | 20.21 | [105] |
| 3PAIDCz | PET/ITO/NiOx/SAMs/Perovskite/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.145 | 24.68 | 81.64 | 23.07 | [106] |
| Br-BPA | ITO/NiOx/SAM/perovskite/PC60BM/Ag | 1.059 | 19.69 | 61.28 | 12.60 | [107] |
| TBT-BA | ITO/NiOx/SAMs/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 1.14 | 24.2 | 81.9 | 22.7 | [108] |
| 2PACz | ITO/NiOx-amine//2PACz/perovskite/PEAI/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.12 | 21.39 | 74.0 | 18.04 | [109] |
| 2PACz | ITO/NiOx/SAMs/perovskite/LiF/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.14 | 22.6 | 77.9 | 20.1 | [110] |
| 2PACz | ITO/NiOx wo/w modifications/CsFAMA perovskite/PEAI/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.17 | 23.10 | 77.3 | 20.81 | [109] |
| 2PACz | FTO/NiO/interlayer/perovskite/LiF/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.05 | 22.5 | 84.0 | 22.2 | [111] |
| 2PACz | FTO/HTL/perovskite/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.12 | 24.96 | 82.89 | 23.25 | [112] |
| MeO-2PACz | ITO/sp-NiOx/MeO-2PACz/perovskite/PC61BM/AZO/Ag | 1.11 | 20.1 | 80.0 | 17.2 | [113] |
| MeO-2PACz | ITO/NiOx/Me-4PACz/perovskite/spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 1.04 | 22.61 | 73.10 | 17.3 | [114] |
| MeO-2PACz | ITO/NiOx/CH3NH3PbI3/PCBM/AZO/Ag | 0.88 | 19.13 | 72.0 | 17.35 | [115] |
| MeO-2PACz | ITO/NiOx/perovskite/LiF/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.13 | 22.7 | 79.9 | 20.5 | [110] |
| MeO-2PACz | ITO/NiOx/SAMs/perovskite/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.10 | 24.9 | 83.0 | 20.8 | [116] |
| MeO-2PACz | FTO/NiO/NR/SAM/Perovskite/C60/SnOx/Ag | 1.16 | 25.57 | 86.35 | 25.66 | [117] |
| Me-4PACz | ITO/NiOx/SAM/FAPbI3/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.04 | 22.61 | 73.10 | 17.3 | [114] |
| Me-4PACz | ITO/NiOx/SAMs/perovskite/LiF/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.15 | 23.0 | 80.0 | 21.2 | [110] |
| Me-4PACz | ITO/NiO/SAMs/FA0.95Cs0.05PbI3/PI/PC61BM/BCP/Ag | 1.135 | 25.80 | 79.53 | 23.29 | [118] |
| Me-4PACz and PC | ITO/NiOx/SAM/perovskite/PEABr/PCBM+ C60/BCP/Ag | 1.175 | 25.88 | 82.54 | 25.09 | [119] |
| Me-4PACz | FTO/NiOx/NR/MeO-4PACz/Cs0.05MA0.1FA0.85PbI3/C60/SnOx/Ag | 1.162 | 25.67 | 86.35 | 25.66 | [117] |
5. SAMs Used in Tandem Systems
5.1. Functional SAMs in Tandem Solar Cells
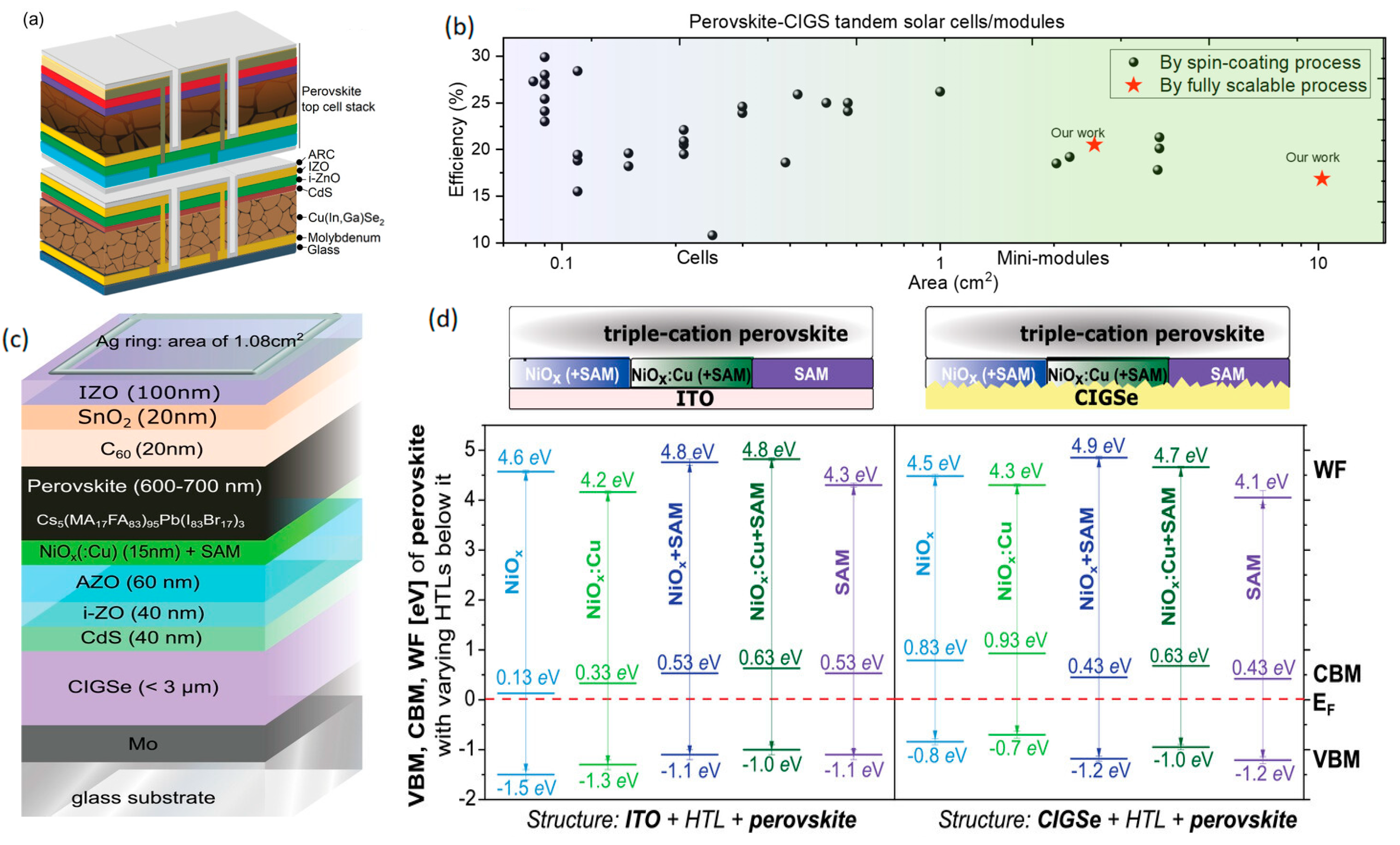
5.2. SAMs with NiOx in Tandem Solar Cells
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Green, M.A.; Dunlop, E.D.; Yoshita, M.; Kopidakis, N.; Bothe, K.; Siefer, G.; Hinken, D.; Rauer, M.; Hohl-Ebinger, J.; Hao, X. Solar cell efficiency tables (version 64). Prog. Photovolt. 2024, 32, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiano, P.; Prete, P.; Speiser, E.; Lovergine, N.; Richter, W.; Tapfer, L.; Mancini, A.M. GaAs nanowires grown by Au-catalyst-assisted MOVPE using tertiarybutylarsine as group-V precursor. J. Cryst. Growth 2007, 298, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, A.; Nabet, B.; Taurino, A.; Prete, P.; Lovergine, N.; Cola, A. Polarization anisotropy of individual core/shell GaAs/AlGaAs nanowires by photocurrent spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 153106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, R.; Di Dio, M.; Lomascolo, M.; Rinaldi, R.; Prete, P.; Vasanelli, L.; Vanzetti, L.; Bassani, F.; Bonanni, A.; Sorba, L.; et al. Photocurrent spectroscopy of Zn1−xCdxSe/ZnSe quantum wells in p-i-n heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 12179–12182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqoma, H.; Lee, S.-H.; Imran, I.F.; Hwang, J.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Jang, S.-Y. Alkyl ammonium iodide-based ligand exchange strategy for high-efficiency organic-cation perovskite quantum dot solar cells. Nat. Energy 2024, 9, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, A.; Teshima, K.; Shirai, Y.; Miyasaka, T. Organometal halide perovskites as visible-light sensitizers for photovoltaic cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6050–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Chen, J.; Ouyang, B.; Sun, A.; Tian, C.; Zhuang, R.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; et al. Face-on oriented self-assembled molecules with enhanced π–π stacking for highly efficient inverted perovskite solar cells on rough FTO substrates. Energy Environ. Sci. 2025, 18, 3196–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Wei, D.; Ji, J.; Huang, H.; Jia, E.; Dou, S.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Li, M. Planar p–n homojunction perovskite solar cells with efficiency exceeding 21.3%. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Brunetti, G.; Armenise, M.N.; Carlo, A.D.; Ciminelli, C. Modeling highly efficient homojunction perovskite solar cells with graphene-TiO2 nanocomposite as the electron transport layer. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2023, 13, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ma, T.; Ai, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, X. A theoretical investigation of transport layer-free homojunction perovskite solar cells via a detailed photoelectric simulation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2203366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, R.; Hino, M.; Kanematsu, M.; Kishimoto, K.; Ishibashi, H.; Konishi, K.; Okamoto, S.; Irie, T.; Fujimoto, T.; Yoshida, W.; et al. 28.3% efficient perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells with mixed self-assembled monolayers. Appl. Phys. Express 2022, 15, 76503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zheng, J.; Duan, W.; Yang, J.; Mahmud, M.A.; Lian, Q.; Tang, S.; Liao, C.; Bing, J.; Yi, J.; et al. Molecular engineering of hole-selective layer for high band gap perovskites for highly efficient and stable perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells. Joule 2023, 7, 2583–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Hsu, S.E.; Wu, D.T.; Sathasivam, S.; Daboczi, M.; Hsieh, H.J.; Zeng, C.S.; Hsu, T.G.; Eslava, S.; et al. Highly reproducible self-assembled monolayer based perovskite solar cells via amphiphilic polyelectrolyte. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 2856–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Y.H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, S.T.; Zhang, Z.L.; Lin, F.L.; Liang, L.S.; Gong, L.J.; Hao, H.W.; et al. Enhancing efficiency of industrially-compatible monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells with dually-mixed self-assembled monolayers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2407805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Meng, J.; Liu, H.; Yin, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; You, J. Enhanced electron extraction using SnO2 for high-efficiency planar-structure HC(NH2)2PbI3-based perovskite solar cells. Nat. Energy 2016, 2, 16177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaraki, E.H.; Kermanpur, A.; Steier, L.; Domanski, K.; Matsui, T.; Tress, W.; Saliba, M.; Abate, A.; Gratzel, M.; Hagfeldt, A.J.E.; et al. Highly efficient and stable planar perovskite solar cells by solution-processed tin oxide. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 3128–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.J.; Seo, G.; Chua, M.R.; Park, T.G.; Lu, Y.; Rotermund, F.; Kim, Y.-K.; Moon, C.S.; Jeon, N.J.; Correa-Baena, J.-P.; et al. Efficient perovskite solar cells via improved carrier management. Nature 2021, 590, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, T.; Li, J.; Zheng, F.; Chen, W.; Wen, X.; Ku, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhong, J.; Cheng, Y.B.; Huang, F.J.N.C. Universal passivation strategy to slot-die printed SnO2 for hysteresis-free efficient flexible perovskite solar module. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.; Choi, I.W.; Yim, K.; Jeong, S.; Kim, M.; Choi, S.J.; Cho, Y.; An, J.-H.; Kim, H.-B.; Jo, Y.; et al. Large-area perovskite solar cells employing spiro-Naph hole transport material. Nat. Photonics 2022, 16, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, K.; Hodgson, P.; Birbilis, N.; Weyland, M.; Fraser, H.L.; Lim, S.C.V.; Peng, H.; et al. Ultrastrong nanotwinned titanium alloys through additive manufacturing. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degani, M.; An, Q.; Albaladejo-Siguan, M.; Hofstetter, Y.J.; Cho, C.; Paulus, F.; Grancini, G.; Vaynzof, Y. 23.7% efficient inverted perovskite solar cells by dual interfacial modification. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabj7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Cui, D.; Luo, X.; Zhang, C.; Han, Q.; Wang, Y.; Han, L. Efficiency progress of inverted perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 3823–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momblona, C.; Gil-Escrig, L.; Bandiello, E.; Hutter, E.M.; Sessolo, M.; Lederer, K.; Blochwitz-Nimoth, J.; Bolink, H.J. Efficient vacuum deposited p-i-n and n-i-p perovskite solar cells employing doped charge transport layers. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 3456–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Ren, N.; Li, Y.; Yan, L.; Mazumdar, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X. Insights into the development of monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2003628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Tong, J.; Xian, Y.; Kerner, R.A.; Dunfield, S.P.; Xiao, C.; Scheidt, R.A.; Kuciauskas, D.; Wang, X.; Hautzinger, M.P.; et al. Surface reaction for efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Nature 2022, 611, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ashouri, A.; Magomedov, A.; Roß, M.; Jošt, M.; Talaikis, M.; Chistiakova, G.; Bertram, T.; Márquez, J.A.; Köhnen, E.; Kasparavičius, E.; et al. Conformal monolayer contacts with lossless interfaces for perovskite single junction and monolithic tandem solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 3356–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Teale, S.; Chen, B.; Hou, Y.; Grater, L.; Zhu, T.; Bertens, K.; Park, S.M.; Atapattu, H.R.; Gao, Y.; et al. Quantum-size-tuned heterostructures enable efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Nat. Photonics 2022, 16, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Deng, X.; Qi, F.; Li, Z.; Liu, D.; Shen, D.; Qin, M.; Wu, S.; Lin, F.; Jang, S.-H.; et al. Regulating surface termination for efficient inverted perovskite solar cells with greater than 23% efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 20134–20142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Su, R.; Zhang, W.; Gong, Q.; Zhu, R. Minimizing non-radiative recombination losses in perovskite solar cells. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Sakai, N.; Da, P.; Wu, J.; Sansom, H.C.; Ramadan, A.J.; Mahesh, S.; Liu, J.; Oliver, R.D.J.; Lim, J.; et al. A piperidinium salt stabilizes efficient metal-halide perovskite solar cells. Science 2020, 369, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Guo, X.; Lu, C.; Wei, J.; Fang, J. Constructing heterojunctions by surface sulfidation for efficient inverted perovskite solar cells. Science 2022, 375, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, A.; Bati, A.S.R.; Zhu, H.; Grater, L.; Hadke, S.S.; Huang, C.; et al. Bimolecularly passivated interface enables efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Science 2023, 382, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Tan, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Hua, R.; et al. Highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells via a multifunctional hole transporting material. Joule 2024, 8, 1691–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, C.; Hu, H.; Wang, K.; De Wolf, S. Organic hole-transport layers for efficient, stable, and scalable inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2203794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chen, K.; Cheng, L.; Wang, D.; Meng, F.; Xiang, W. Application of hole-selective self-assembled monolayers in inverted perovskite solar cells. Sol. Res. Rev. Lett. 2024, 8, 2300996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docampo, P.; Ball, J.M.; Darwich, M.; Eperon, G.E.; Snaith, H.J. Efficient organometal trihalide perovskite planar-heterojunction solar cells on flexible polymer substrates. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, K.; Wang, Z.-S. Pyridine-terminated conjugated organic molecules as an interfacial hole transfer bridge for NiOx-based perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 28960–28967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, J.; Yang, B.; Bogachuk, D.; Boschloo, G.; Hagfeldt, A. The dual use of SAM molecules for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2025, 15, 2400205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, D.; Shin, J.; Kim, D.; Jaung, J.Y.; Jung, I.H. Self-assembled monolayer-based hole-transporting materials for perovskite solar cells. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Bi, E.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Chen, H.; Han, L.; Tian, H.; Zhu, W.-H. Synergistic coassembly of highly wettable and uniform hole-extraction monolayers for scaling-up perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magomedov, A.; Al-Ashouri, A.; Kasparavičius, E.; Strazdaite, S.; Niaura, G.; Jošt, M.; Malinauskas, T.; Albrecht, S.; Getautis, V. Self-assembled hole transporting monolayer for highly efficient perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1801892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, E.; Can, M.; Rodriguez-Seco, C.; Aktas, E.; Pudi, R.; Cambarau, W.; Demic, S.; Palomares, E. Semiconductor self-assembled monolayers as selective contacts for efficient PiN perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, H.; Datta, K.; Wang, J.; van der Pol, T.P.A.; Li, J.; Wienk, M.M.; Janssen, R.A.J. Finetuning hole-extracting monolayers for efficient organic solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 16497–16504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ashouri, A.; Köhnen, E.; Li, B.; Magomedov, A.; Hempel, H.; Caprioglio, P.; Márquez, J.A.; Morales Vilches, A.B.; Kasparavicius, E.; Smith, J.A.; et al. Monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cell with >29% efficiency by enhanced hole extraction. Science 2020, 370, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisorio, R.; Roose, B.; Colella, S.; Listorti, A.; Suranna, G.P.; Abate, A. Molecular tailoring of phenothiazine-based hole-transporting materials for high-performing perovskite solar cells. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, C.; Meng, F.; Zhang, C.; Wei, G.; Gao, L.; Ma, T. Recent progress in perovskite solar cells modified by sulfur compounds. Sol. Res. Rev. Lett. 2021, 5, 2000713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-H.; Sun, T.-G.; Shao, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-D.; Hu, J.-S.; Zhong, Y.-W. A sulfur-rich small molecule as a bifunctional interfacial layer for stable perovskite solar cells with efficiencies exceeding 22%. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Park, K.H.; Lee, Y.; Park, S.; Faheem, A.B.; Nguyen, H.D.; Siddique, Y.; Lee, K.-K.; Jo, Y.; Han, C.-H.; et al. Versatile hole selective molecules containing a series of heteroatoms as self-assembled monolayers for efficient p-i-n perovskite and organic solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2208793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, K.; Shi, Y.; Feng, K.; Li, B.; Huang, J.; Gao, P.; Guo, X. Self-assembled donor-acceptor hole contacts for inverted perovskite solar cells with an efficiency approaching 22%: The impact of anchoring groups. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 68, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luo, L.; You, S.; Li, W.; et al. Tailoring multifunctional self-assembled hole transporting molecules for highly efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2211955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Liu, Q.; Yao, L.; Değer, C.; Shen, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, P.; Tian, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xu, J.; et al. Peri-fused polyaromatic molecular contacts for perovskite solar cells. Nature 2024, 632, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Q.; Li, Z.; Luo, G.; Zhang, X.; Che, B.; Chen, G.; Gao, H.; He, D.; Ma, G.; Wang, J.; et al. Inverted perovskite solar cells using dimethylacridine-based dopants. Nature 2023, 620, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Sun, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, B.; Gao, D.; Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Li, S.; Gong, J.; Luther, J.M.; et al. Stabilized hole-selective layer for high-performance inverted p-i-n perovskite solar cells. Science 2023, 382, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Bi, L.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, B.; Jen, A.K.Y. Self-assembled monolayer enabling improved buried interfaces in blade-coated perovskite solar cells for high efficiency and stability. Nano Res. Energy 2022, 1, 9120004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, E.; Pudi, R.; Phung, N.; Wenisch, R.; Gregori, L.; Meggiolaro, D.; Flatken, M.A.; De Angelis, F.; Lauermann, I.; Abate, A.; et al. Role of terminal group position in triphenylamine-based self-assembled hole-selective molecules in perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 17461–17469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canil, L.; Salunke, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, M.; Köbler, H.; Flatken, M.; Gregori, L.; Meggiolaro, D.; Ricciarelli, D.; De Angelis, F.; et al. Halogen-bonded hole-transport material suppresses charge recombination and enhances stability of perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Yadavalli, S.K.; Chen, M.; Abbaspourtamijani, A.; Qi, Y.; Padture, N.P. Interfacial toughening with self-assembled monolayers enhances perovskite solar cell reliability. Science 2021, 372, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Park, K.H.; Hieu Dinh, N.; Siddique, Y.; Shah, S.F.A.; Huyen, T.; Park, S.; Lee, S.I.; Lee, K.-K.; Han, C.-H.; et al. Novel phenothiazine-based self-assembled monolayer as a hole selective contact for highly efficient and stable p-i-n perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Fu, H.; Qi, F.; Lin, F.R.; Walsh, A.; Jen, A.K.Y. A hole-selective self-assembled monolayer for both efficient perovskite and organic solar cells. Langmuir 2024, 40, 4772–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Liu, G.-W.; Chen, X.; Deger, C.; Jin, R.-J.; Wang, K.-L.; Chen, J.; Xia, Y.; Huang, L.; Yavuz, I.; et al. Methylthio substituent in SAM constructing regulatory bridge with photovoltaic perovskites. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202419375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Lin, F.R.; Jen, A.K.Y. Rational molecular design of multifunctional self-assembled monolayers for efficient hole selection and buried interface passivation in inverted perovskite solar cells. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 2778–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, F.; Lin, F.R.; Jen, A.K.Y. Hole-selective contact with molecularly tailorable reactivity for passivating high-performing inverted perovskite solar cells. Ccs Chem. 2024, 6, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wei, K.; Yang, L.; Deng, J.; Zhang, J.; Tang, W. Dynamic self-assembly of small molecules enables the spontaneous fabrication of hole conductors at perovskite/electrode interfaces for over 22% stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 2609–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Li, F.; Li, M.; Qi, F.; Lin, F.R.; Jen, A.K.-Y. π-Expanded carbazoles as hole-selective self-assembled monolayers for high-performance perovskite solar cells. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202213560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.P.; Zhang, L.T.; Qiao, Y.; Gong, S.K.; Ding, Y.J.; Tao, Y.L.; Cai, S.Y.; Chang, X.Y.; Chen, Q.; Xie, P.F.; et al. Self-assembled materials with an ordered hydrophilic bilayer for high performance inverted Perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, D.; Shang, W.; Li, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, B.; Mei, L.; Chen, X.-K.; Xu, Z.-X.; et al. Spin-coated and vacuum-processed hole-extracting self-assembled multilayers with h-aggregation for high-performance inverted perovskite solar cells. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202411730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Wei, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ran, Y.; Cui, M.; Su, Z.; Fan, Q.; et al. Self-assembled bilayer for perovskite solar cells with improved tolerance against thermal stresses. Nat. Energy 2025, 10, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, I.; Al-Ashouri, A.; Musiienko, A.; Hempel, H.; Magomedov, A.; Drevilkauskaite, A.; Getautis, V.; Menzel, D.; Hinrichs, K.; Unold, T.; et al. Charge transfer rates and electron trapping at buried interfaces of perovskite solar cells. Joule 2021, 5, 2915–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, R.; Mu, C.; Wang, Y.; Han, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, W.-H. Conjugated self-assembled monolayer as stable hole-selective contact for inverted perovskite solar cells. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 1976–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Cai, S.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, D.; Gong, S.; Khan, D.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, K.; Chen, Q.; Zhan, L.; et al. Conjugated linker-boosted self-assembled monolayer molecule for inverted perovskite solar cells. Joule 2024, 8, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Huang, Z.-S. Self-assembled organic molecules with a fused aromatic ring as hole-transport layers for inverted perovskite solar cells: The effect of linkers on performance. New J. Chem. 2024, 48, 6833–6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Li, S.W.; He, B.C.; Zheng, R.F.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, S. An energy level alignment study of 2PACz molecule on perovskite device-related interfaces by vacuum deposition. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2025, 6, 2400336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, E.; Phung, N.; Köbler, H.; González, D.A.; Méndez, M.; Kafedjiska, I.; Turren-Cruz, S.-H.; Wenisch, R.; Lauermann, I.; Abate, A.; et al. Understanding the perovskite/self-assembled selective contact interface for ultra-stable and highly efficient p–i–n perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 3976–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-M.; Mai, C.-L.; Wu, C.-C.; Chen, B.-H.; Lu, C.-H.; Chu, C.-C.; Wang, M.-C.; Yang, S.-D.; Chen, H.-C.; Yeh, C.-Y.; et al. Self-assembled monolayers of bi-functionalized porphyrins: A novel class of hole-layer-coordinating perovskites and indium tin oxide in inverted solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202309831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Liu, C.; Lin, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, M.; Cao, X.-M.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, W.-H. Bonding strength regulates anchoring-based self-assembly monolayers for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yan, P.; Yang, D.; Guan, H.; Yang, S.; Cao, X.; Liao, X.; Ding, P.; Sun, H.; Ge, Z. Bisphosphonate-anchored self-assembled molecules with larger dipole moments for efficient inverted perovskite solar cells with excellent stability. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2401537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Ye, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, L.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Ji, X.; Liu, S.; et al. Minimizing buried interfacial defects for efficient inverted perovskite solar cells. Science 2023, 380, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Liu, C.; Hu, H.; Zhang, S.; Ji, X.; Cao, X.-M.; Ning, Z.; Zhu, W.-H.; Tian, H.; Wu, Y. Neglected acidity pitfall: Boric acid-anchoring hole-selective contact for perovskite solar cells. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, M.A.; Funasaki, T.; Ueberricke, L.; Nojo, W.; Murdey, R.; Yamada, T.; Hu, S.; Akatsuka, A.; Sekiguchi, N.; Hira, S.; et al. Tripodal triazatruxene derivative as a face-on oriented hole-collecting monolayer for efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 7528–7539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Ji, X.; He, J.; Guo, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, W.; Zhu, W.-H.; Wu, Y. Formamidinium lead iodide-based inverted perovskite solar cells with efficiency over 25 % enabled by an amphiphilic molecular hole-transporter. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202401260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Deng, X.; Shi, Z.; Wu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Qi, F.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; et al. Hydrogen-bond-bridged intermediate for perovskite solar cells with enhanced efficiency and stability. Nat. Photonics 2023, 17, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Guo, R.; Yin, X.; Luo, R.; Guo, D.; Ji, K.; Dai, L.; Liang, H.; Jia, X.; et al. Regulating phase homogeneity by self-assembled molecules for enhanced efficiency and stability of inverted perovskite solar cells. Nat. Photonics 2024, 18, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Yang, F.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, M. Multifunctional action site strategy of a buried interface for high-performance perovskite solar cells. Acs Photonics 2024, 11, 4916–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yu, B.; Lin, C.; Yao, R.; Yu, H.; Wang, H. Constructing stable perovskite with small molecule bridge interface passivation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2025, 2405571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Bi, L.; Jiang, W.; Zeng, Z.; Tsang, S.-W.; Lin, F.R.; Jen, A.K.Y. Compact hole-selective self-assembled monolayers enabled by disassembling micelles in solution for efficient perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2304415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Liu, X.; Nakazaki, J.; Segawa, H.; Wang, Y.; Han, L. Facile posttreatment of self-assembled monolayers for efficient inverted perovskite solar cells. Sol. RRL 2024, 8, 2300931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pininti, A.R.; Subbiah, A.S.; Deger, C.; Yavuz, I.; Prasetio, A.; Dally, P.; Hnapovskyi, V.; Said, A.A.; Torres, L.; Mannar, S.; et al. Resolving scaling issues in self-assembled monolayer-based perovskite solar modules via additive engineering. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 15, 2403530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, K.; Kulkarni, A.; Bothra, U.; Klingebiel, B.; Kirchartz, T.; Saliba, M.; Kabra, D. Resolving the hydrophobicity of the Me-4PACz hole transport layer for inverted perovskite solar cells with efficiency > 20%. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 3860–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, J.; Xiao, W.; Chen, R.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, X.; Hu, S.; Kober-Czerny, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Buried interface molecular hybrid for inverted perovskite solar cells. Nature 2024, 632, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Qi, F.; Li, F.; Wu, S.; Lin, F.R.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Lee, C.-S.; Jen, A.K.-Y. Co-assembled monolayers as hole-selective contact for high-performance inverted perovskite solar cells with optimized recombination loss and long-term stability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202203088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Tao, M.; Guo, H.; Guo, L.; Song, Z.; Wen, J.; Yang, Y.; Hou, Y.; et al. Reinforcing coverage of self-assembled monomolecular layers for inverted perovskite solar cells with efficiency of 25.70 %. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202423827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.R.; Cui, M.J.; Dong, B.T.; Zhang, Y.S.; Ran, Y.B.; Qi, G.Y.; Yang, Y.G.; Edvinsson, T.; Hagfeldt, A.; Jiang, L.; et al. Stereo-hindrance induced conformal self-assembled monolayer for high efficiency inverted perovskite solar cells. Small 2024, 20, e2407387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Kong, T.; Chen, W.; Liu, W.; Gao, P.; Bi, D. Improving buried interface contact for inverted perovskite solar cells via dual modification strategy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2417575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Liu, L.; Qi, L.; Du, J.; Du, Q.; Yu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Jiu, T.; Li, Y. Highly oriented and ordered co-assembly monolayers for inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2025, 64, e202418883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Narra, S.; Li, M.-Y.; Lin, J.-S.; Diau, E.W.-G. Interfacial engineering with a hole-selective self-assembled monolayer for tin perovskite solar cells via a two-step fabrication. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 4179–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.-J.; Li, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-T. Scalable post-treatment for improved self-assembled monolayer coverage in perovskite solar cells. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2024, 8, 5399–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, J.J.; Ciampi, S. The molecular level modification of surfaces: From self-assembled monolayers to complex molecular assemblies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2704–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zheng, L.; Feng, W.; Yang, L.; Song, P.; Luo, J.; Tian, W.; Gao, W.; Tian, C.; Xie, L.; et al. Modulation of the interfacial contact via self-assembled molecule interlayer towards highly efficient and stable poly(3-hexylthiophene)-based perovskite solar cells. Mater. Today Energy 2024, 41, 101523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Ren, G.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Bao, H.; Liu, C.; Guo, W. Recent progress of inverted perovskite solar cells with a modified PEDOT:PSS hole transport layer. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 49297–49322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Zuo, L.; Larsen-Olsen, T.T.; Ye, T.; Wu, G.; Krebs, F.C.; Chen, H. Interfacial engineering of self-assembled monolayer modified semi-roll-to-roll planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells on flexible substrates. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 24254–24260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Kapil, G.; Wang, L.; Razey Sahamir, S.; Baranwal, A.K.; Nishimura, K.; Sanehira, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Akmal Kamarudin, M.; Shen, Q.; et al. High performance wide bandgap Lead-free perovskite solar cells by monolayer engineering. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 436, 135196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Pandey, P.; Yoon, S.; Ryu, J.; Lee, D.-G.; Shen, Q.; Hayase, S.; Song, H.; Choi, H.; Ahn, H.; et al. Anchoring self-assembled monolayer at perovskite/hole collector interface for wide bandgap Sn-based solar cells with a record efficiency over 12%. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 42, 103478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chueh, C.-C.; Zhao, T.; Cheng, J.; Eslamian, M.; Choy, W.C.H.; Jen, A.K.-Y. Effects of self-assembled monolayer modification of nickel oxide nanoparticles layer on the performance and application of inverted perovskite solar cells. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 3794–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Feng, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Du, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhu, W.; Xi, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; et al. Buried interface bilayer engineering toward high efficiency and stable perovskite modules. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2025, 46, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.S.; Patil, P.; Kwon, S.-N.; Na, S.-I. Enhanced performance of p-i-n perovskite solar cell via defect passivation of nickel oxide/perovskite interface with self-assembled monolayer. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 560, 149973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.L.; Chen, W.F.; Gang, Y.; Xiong, Q.; Li, X. Engineering a thermally robust hole-selective layer for stable flexible perovskite solar cells. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 503, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalam, J.; Rath, T.; Weber, S.; Kunert, B.; Dimopoulos, T.; Fian, A.; Trimmel, G. Modification of NiOx hole transport layers with 4-bromobenzylphosphonic acid and its influence on the performance of lead halide perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 9602–9611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, W.; Chen, H. Interfacial modification of NiOx for highly efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2400616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Khaleed, A.; Syed, A.A.; He, Y.; Chan, C.C.S.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, G.; Wong, K.S.; et al. Dual surface modifications of NiOx/perovskite interface for enhancement of device stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 24437–24447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutundzic, M.; Zhang, X.; Lammar, S.; Singh, S.; Marchezi, P.; Merckx, T.; Aguirre, A.; Moons, E.; Aernouts, T.; Kuang, Y.; et al. Toward efficient and fully scalable sputtered NiOX-based inverted perovskite solar modules via co-ordinated modification strategies. Sol. Res. Rev. Lett. 2024, 8, 2300862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Lau, C.F.J.; Mo, K.; Cheng, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, C.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; et al. Inverted planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells with high ultraviolet stability. Nano Energy 2022, 103, 107849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Khan, D.; Zhou, W.; Sui, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yu, G.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Yan, H.; et al. Ion-dipole interaction for self-assembled monolayers: A new strategy for buried interface in inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2316202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.R.M.; Yanagida, M.; Shirai, Y.; Andersson, G.G.; Miyano, K. Surface passivation of sputtered NiOx using a SAM interface layer to enhance the performance of perovskite solar cells. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 12147–12157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Tong, Y.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, T.; Kang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, K. Modification of nickel oxide via self-assembled monolayer for enhanced performance of air-processed fapbl3 perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida, M.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshida, T.; Khadka, D.B.; Shirai, Y.; Miyano, K. Surface modification of sputtered NiOx hole transport layer for CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite solar cells. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2023, 62, SK1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, X.; Ren, H.; Hou, G.; Ding, Y.; et al. Performance amelioration of spray-coated perovskite solar cells utilizing a self-assembled monolayer. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 3540–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.Y.; Lee, M.; Tian, R.M.; Patterson, R.; Wang, Y.; Qian, C.; Sun, K.W.; Liu, Z.H.; Yun, J.S.; Xu, M.L.; et al. Doped-NiOx seed layer on textured substrates for low-loss contacts in perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 15, 2405016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhu, R.; Luo, D. Buried interface molecular hybrid enables efficient perovskite solar cells. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2024, 41, 098501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Wang, T.Y.; Pu, X.Y.; He, X.L.; Xiao, M.C.; Chen, H.; Zhuang, L.C.; Wei, Q.; Loi, H.L.; Guo, P.; et al. Co-self-assembled monolayers modified NiO for stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2311970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.J.; Shou, C.H.; Sun, J.S.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, Z.H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.R.; Yang, W.C.; Long, H.L.; Ying, Z.Q.; et al. NiO-seeded self-assembled monolayers as highly hole-selective passivating contacts for efficient inverted perovskite solar cells. Sol. Rrl 2021, 5, 2100663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Sato, A.; Ajiro, K.; Shiokawa, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Maeda, T.; Sugiyama, M.; Gotanda, T.; Marumoto, K. Performance improvement mechanisms of perovskite solar cells by modification of NiOx hole-selective contacts with self-assembled-monolayers. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2023, 258, 112428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, H.; Wu, Y. Advantages and challenges of self-assembled monolayer as a hole-selective contact for perovskite solar cells. Mater. Futures 2023, 2, 012105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.K.; Xuan, Y.M.; Wang, J.L.; Bao, S.J.; Liu, X.L.; Zhang, K. Inverted perovskite/silicon V-shaped tandem solar cells with 27.6% efficiency via self-assembled monolayer-modified nickel oxide layer. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 7251–7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothandaraman, R.K.; Siegrist, S.; Dussouillez, M.; Krause, M.; Lai, H.; Pious, J.K.; Nishiwaki, S.; Gilshtein, E.; Müller, A.; Cabas Vidani, A.; et al. Sputtered NiO interlayer for improved self-assembled monolayer coverage and pin-hole free perovskite coating for scalable near-infrared-transparent perovskite and 4-terminal all-thin-film tandem modules. Sol. Res. Rev. Lett. 2024, 8, 2400176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, M.; Dong, C.; Ye, W.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Hu, L.; Li, X.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Role of NiO in wide-bandgap perovskite solar cells based on self-assembled monolayers. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 494, 153253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafedjiska, I.; Farias-Basulto, G.A.; Reyes-Figueroa, P.; Bertram, T.; Al-Ashouri, A.; Kaufmann, C.A.; Wenisch, R.; Albrecht, S.; Schlatmann, R.; Lauermann, I. Integration of rough RPT absorbers into CIGS-perovskite monolithic tandems by NiOx(:Cu) + SAM hole-transporting bi-layers. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2023, 254, 112248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Gao, H.; Xiao, K.; Yeddu, V.; Wang, B.; Lin, R.; Sun, H.; Wu, P.; Ahmed, Y.; Bui, A.D.; et al. Scalable fabrication of wide-bandgap perovskites using green solvents for tandem solar cells. Nat. Energy 2025, 10, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Su, S.; Chen, Y.; Ren, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Miao, Y.; Ouyang, C.; Zhao, Y. Impurity-healing interface engineering for efficient perovskite submodules. Nature 2024, 634, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Li, H.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Fan, B.; Hao, X. A Comprehensive Review of Self-Assembled Monolayers as Hole-Transport Layers in Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells. Energies 2025, 18, 2577. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102577
Yuan Y, Li H, Luo H, Zhang Y, Li X, Jiang T, Yang Y, Liu L, Fan B, Hao X. A Comprehensive Review of Self-Assembled Monolayers as Hole-Transport Layers in Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells. Energies. 2025; 18(10):2577. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102577
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yuchen, Houlin Li, Haiqiang Luo, Yang Zhang, Xiaoli Li, Ting Jiang, Yajie Yang, Lei Liu, Baoyan Fan, and Xia Hao. 2025. "A Comprehensive Review of Self-Assembled Monolayers as Hole-Transport Layers in Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells" Energies 18, no. 10: 2577. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102577
APA StyleYuan, Y., Li, H., Luo, H., Zhang, Y., Li, X., Jiang, T., Yang, Y., Liu, L., Fan, B., & Hao, X. (2025). A Comprehensive Review of Self-Assembled Monolayers as Hole-Transport Layers in Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells. Energies, 18(10), 2577. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102577