Numerical Simulation Study on Different Exhaust Air Transfer Conditions and Safety of Pulverized Coal System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Object and Methodology
2.1. Research Object and Fuel Analysis
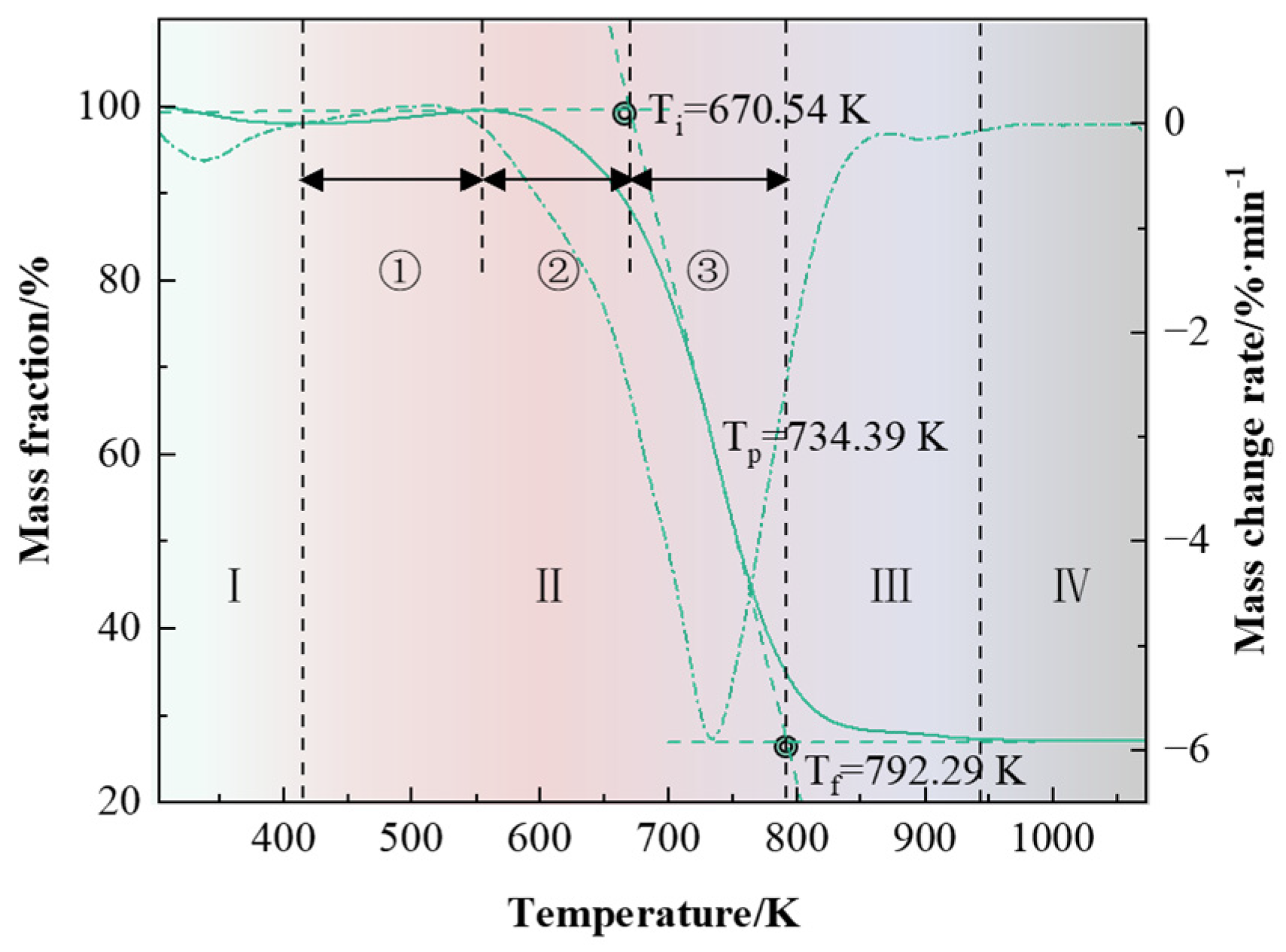
- Dehydration stage (303 K to 415 K), where moisture is removed from the coal.
- Primary combustion stage (415 K to 792 K), which is the main phase of coal combustion.
- Silicate mineral decomposition stage (792 K to 943 K), during which mineral components undergo thermal decomposition.
- Burnout stage (>943 K), where the remaining carbon content is nearly completely consumed, and further temperature increases result in minimal mass change.
2.2. Mathematical Models and Parameters
- The interactions and agglomeration between coal particles were neglected.
- Coal particles were assumed to enter the computational domain uniformly from the exhaust air inlet.
- The complex pyrolysis reactions of coal are simplified by considering only the main reactions, as listed in Table 2.
- It was assumed that the exhaust air transfer device walls are sufficiently airtight, with no leakage.
2.3. Grid Division and Reliability Verification
3. Result and Discussion
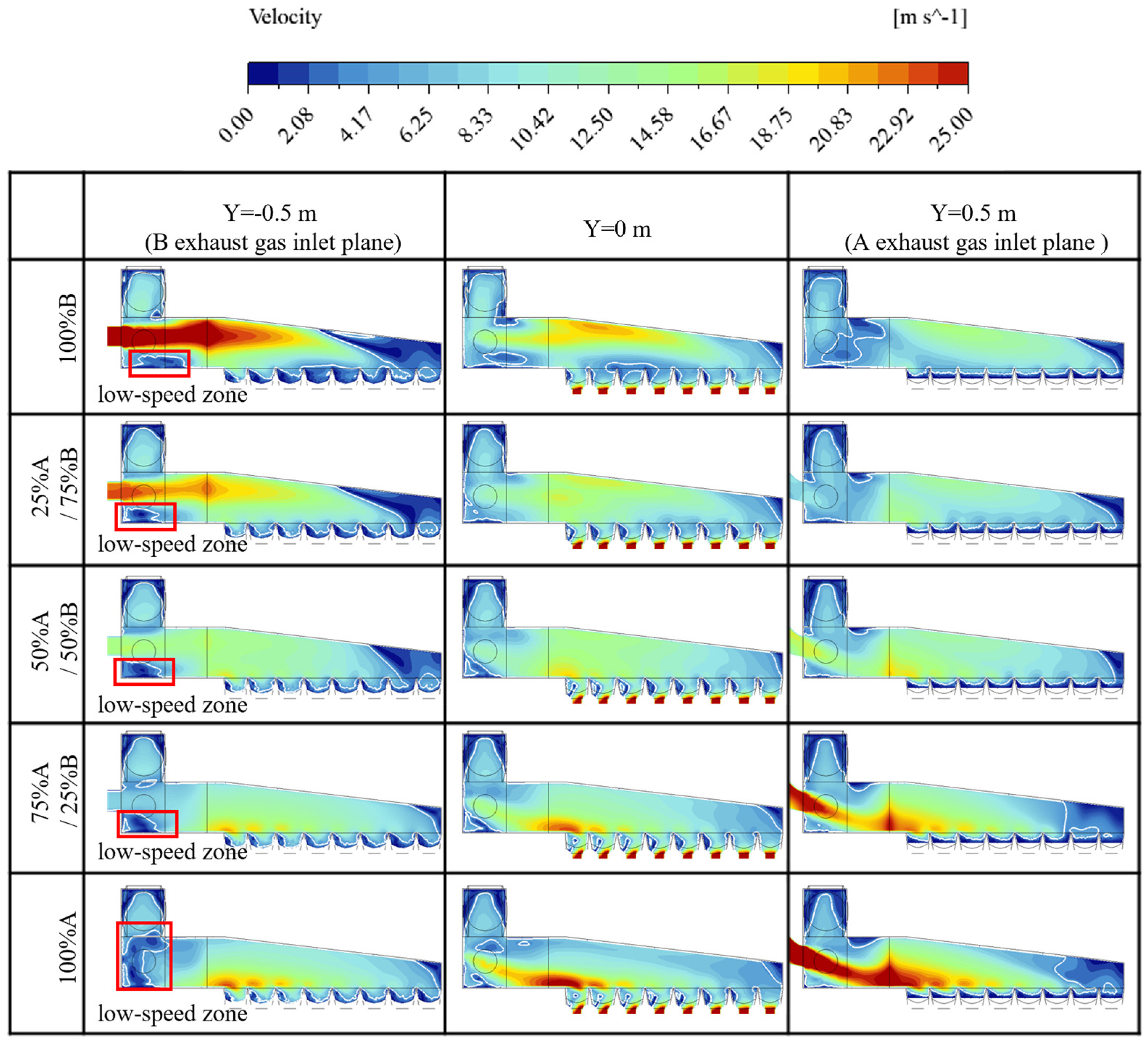
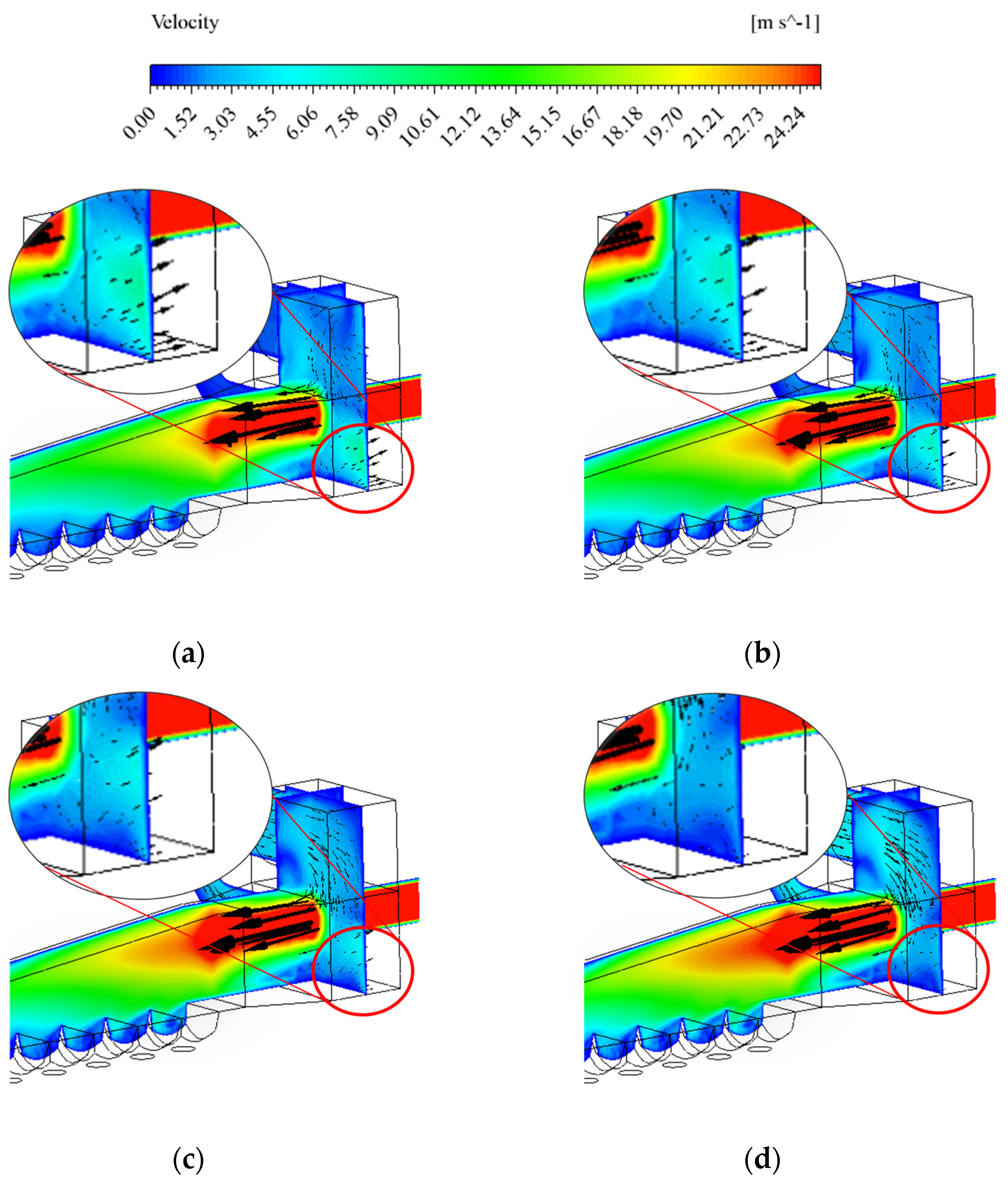
3.1. Flow Field in the Primary Air Box
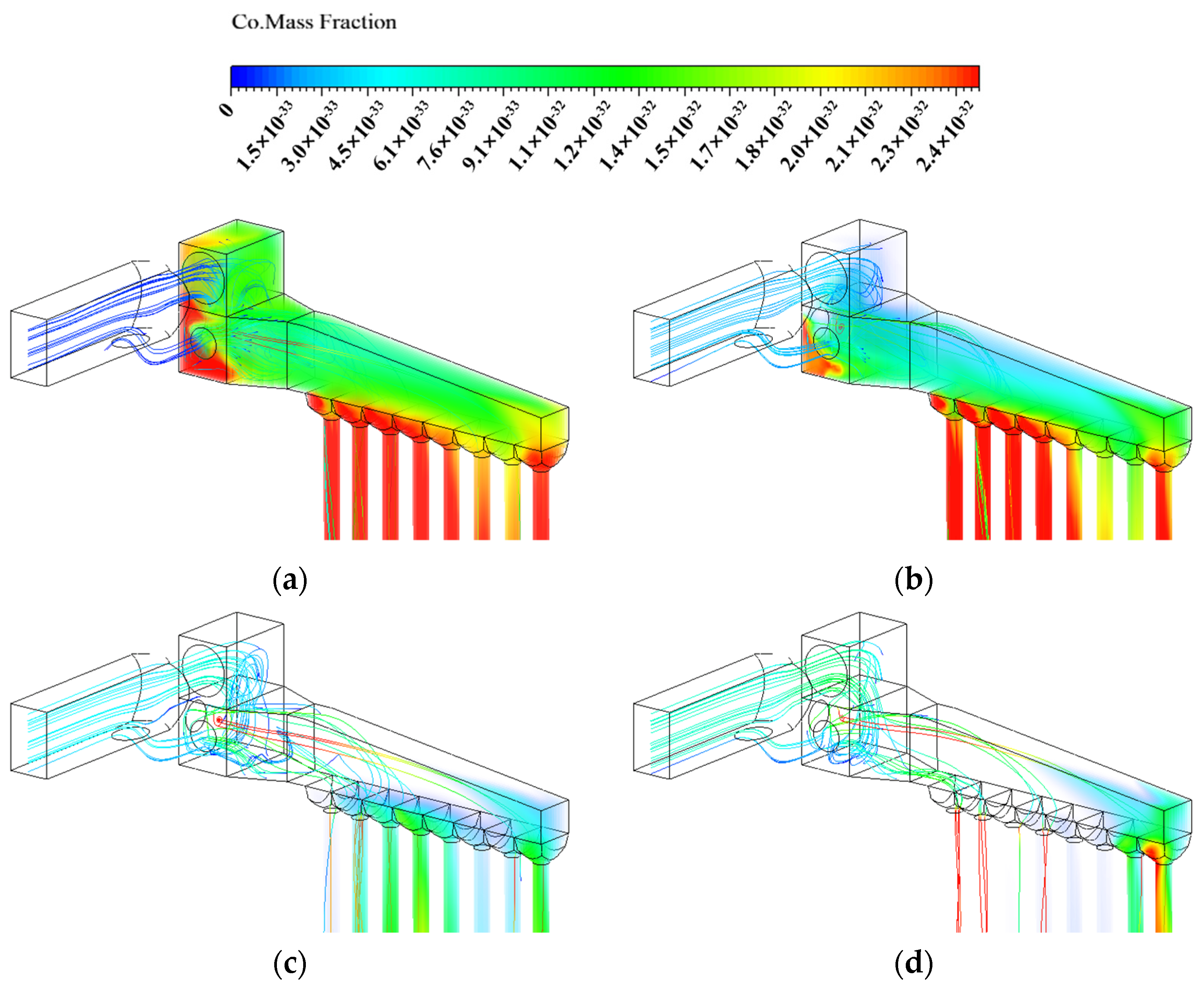
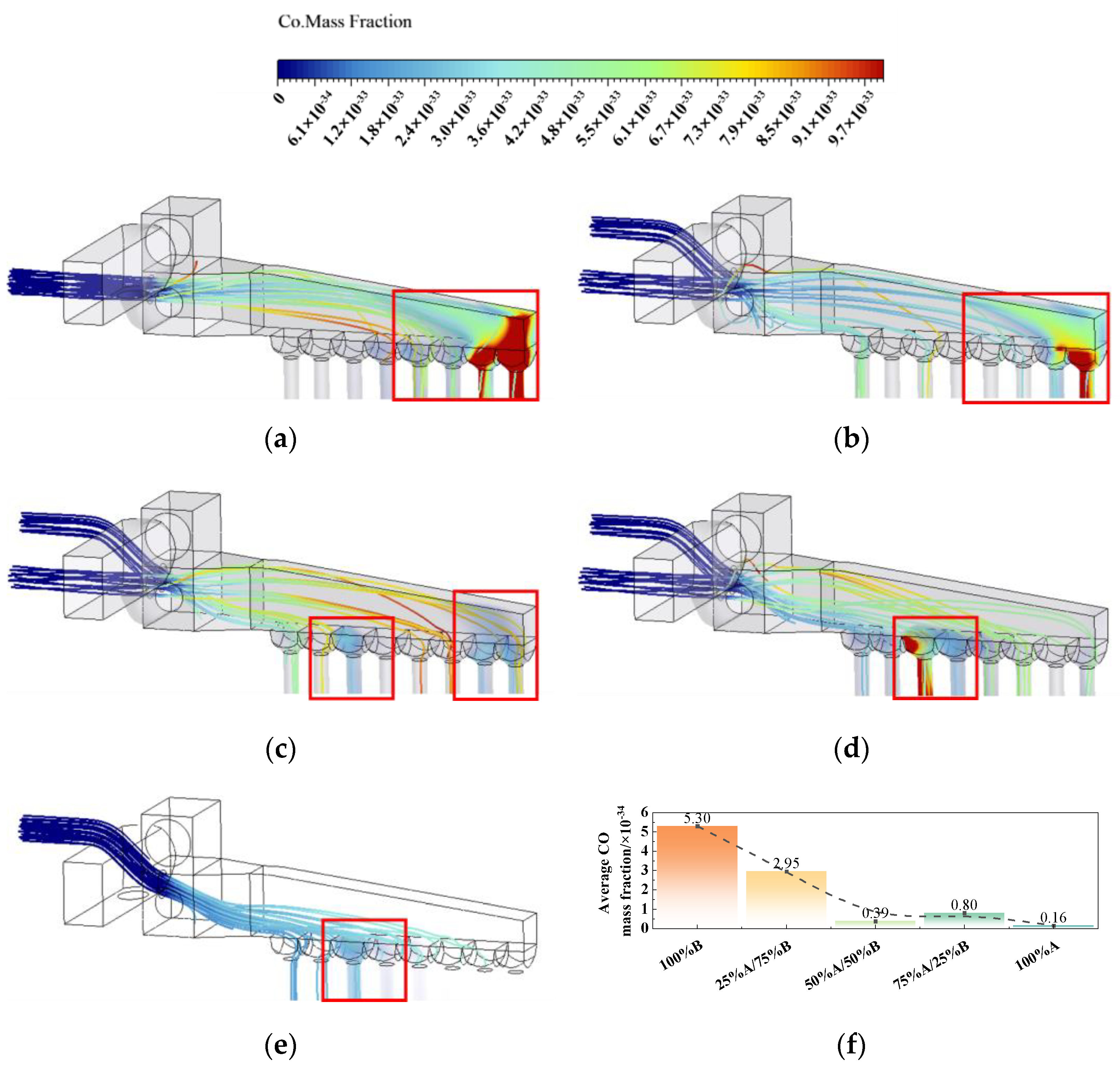
3.2. CO Distribution Inside the Primary Airbox
3.3. Adjustment of Hot Air Parameters Under the 100% B Exhaust Air Transfer Condition
3.3.1. Adjustment of Hot Air Velocity
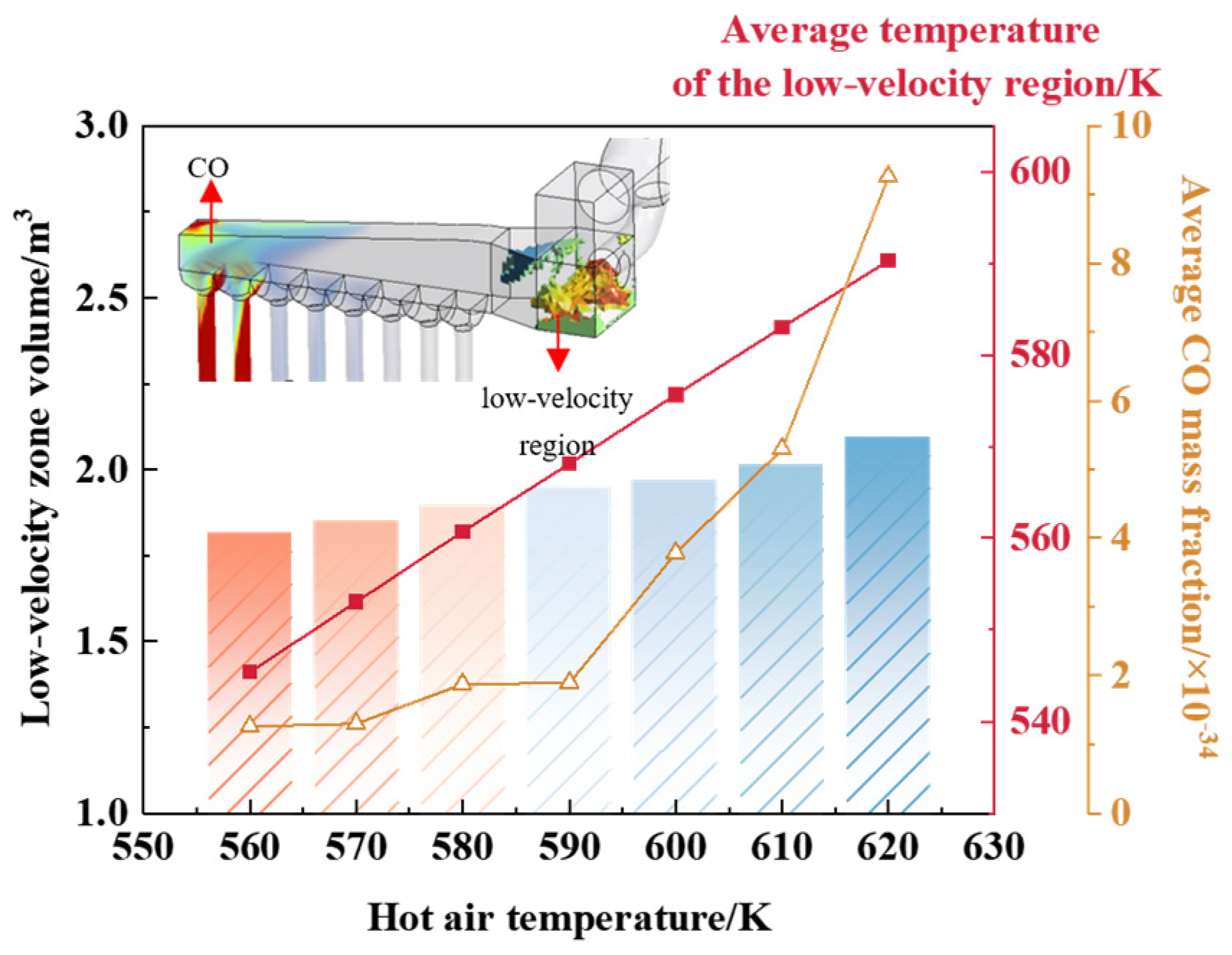
3.3.2. Adjustment of Hot Air Temperature
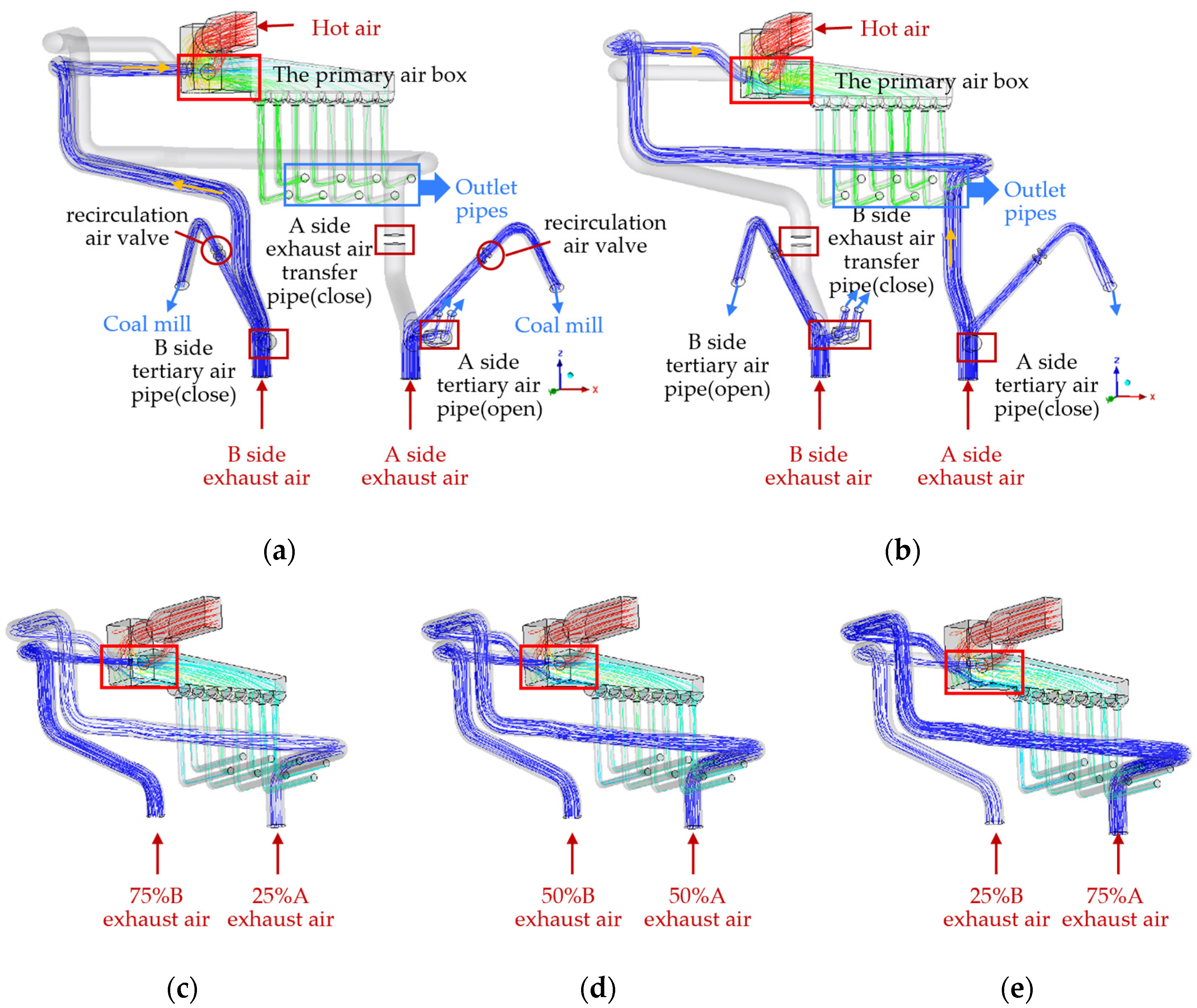
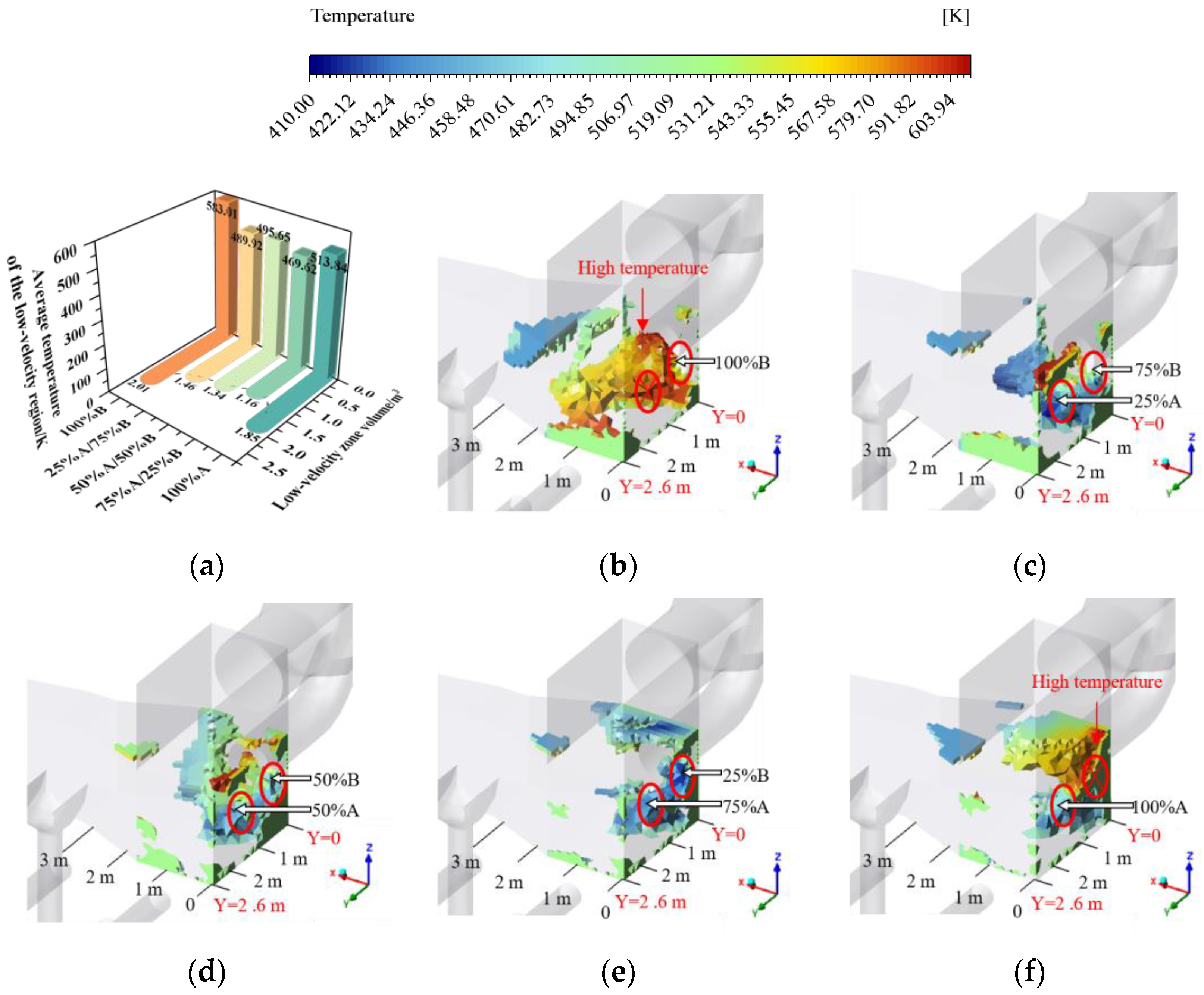
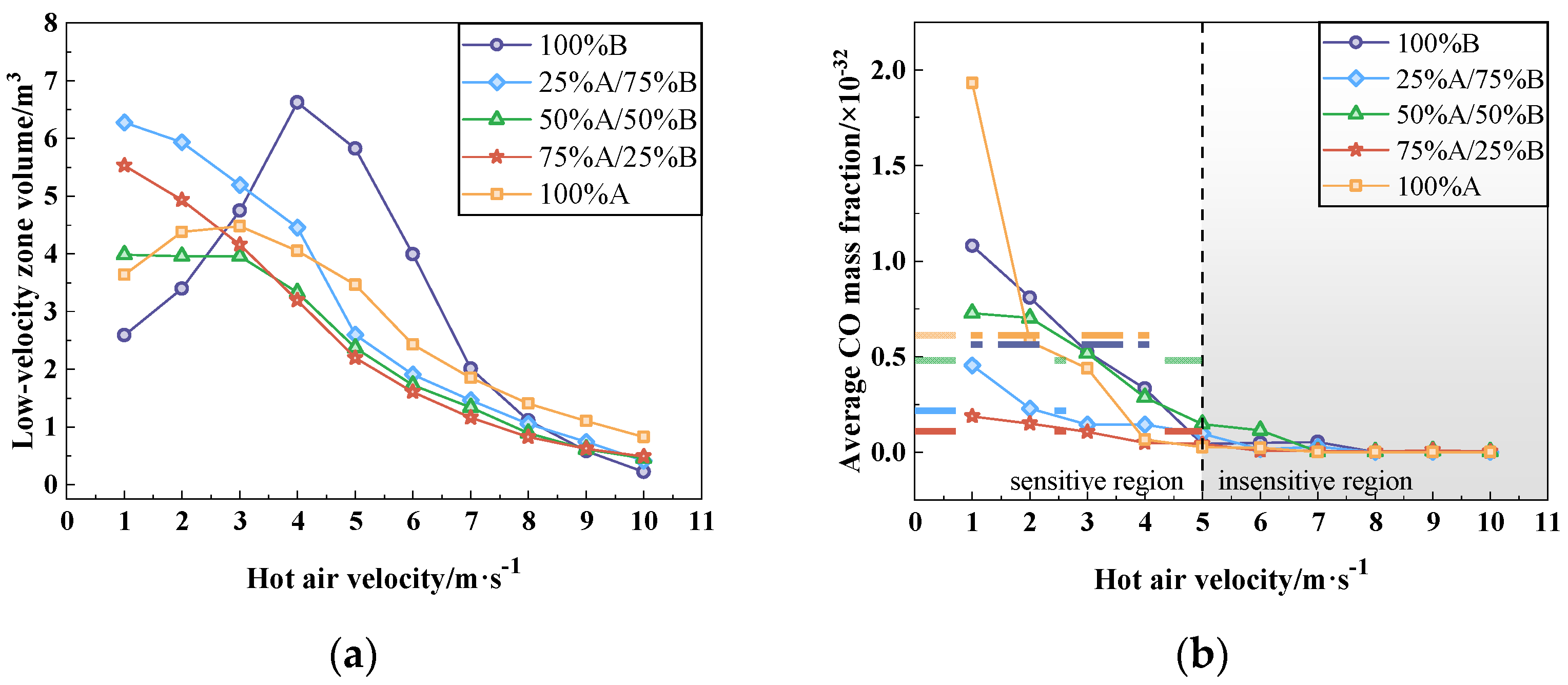
3.4. Adjustment of Hot Air Parameters in Other Exhaust Air Transfer Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Nomenclature | Subscript | ||
| A | pre-exponential factor | a | ash content in the particle |
| C | the molar concentration | b | reverse reaction rate constant |
| D | volume diffusion coefficient | C | coke |
| E | activation energy | c | chemical reaction |
| f | mass fraction | f | forward reaction rate constant |
| K | empirical constant | g | gas |
| k | reaction rate | i,j | component |
| M | molecular weight | P | product |
| m | mass | p | particle |
| N | the number of components | R | reactant |
| n | apparent reaction order | r | reaction |
| R | universal gas constant | s | particle surface |
| T | temperature | v | volatile matter |
| t | time | w | evaporating/boiling material |
| v | stoichiometric coefficient | FR | finite rate |
| Symbol | ED | eddy dissipation | |
| α | yield factor | exp1 | the first empirical constant |
| ε | turbulent dissipation rate | exp2 | the second empirical constant |
| η | rate exponent | 0 | initial state |
| ρ | density | 1 | low temperature, slow reaction |
| third-body influence coefficient | 2 | high temperature, fast reaction | |
| competing rate | |||
References
- Ma, L.; Wei, Z.; Zou, L.; Yi, X.; He, C. Influence factors and prediction of critical parameters of spontaneous combustion of pulverized coal. Coal Sci. Technol. 2021, 49, 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ajrash, M.J.; Zanganeh, J.; Moghtaderi, B. The flame deflagration of hybrid methane coal dusts in a large-scale detonation tube (LSDT). Fuel 2017, 194, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Norman, F.; Schmidt, M.; Vanierschot, M.; Verplaetsen, F.; Berghmans, J.; Bulck, E.V.D. Numerical investigation on the self-ignition behaviour of coal dust accumulations: The roles of oxygen, diluent gas, and dust volume. Fuel 2017, 188, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Norman, F.; Vanierschot, M.; Verplaetsen, F.; Berghmans, J. Self-heating characteristics of coal dust deposits by a hot gas flow in oxy-fuel atmospheres. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 131, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glushkov, D.O.; Kuznetso, G.V.; Strizhak, P.A. Experimental and numerical study of coal dust ignition by a hot particle. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 13, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q. Experimental study on coal dust explosions in a large-scale tube. China Saf. Sci. J. 2011, 21, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.; Deng, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhai, X. Numerical simulation on formation mechanism of pulverized coal cloud and flame dynamic behaviors during the explosion process in an open vessel. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 2600–2613. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B. Analysis and summary of explosion accident of steel ball mill powder. Mod. Manuf. Technol. Equip. 2019, 10, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, J.; Yin, L. Study on coal dust explosion characteristics of coal-pulverizing system. Electr. Power Sci. Eng. 2010, 26, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Wei, H. Cause analysis for explosion in coal pulverizing system of a power plant based on numerical simulation and retrofit. Therm. Power Gener. 2007, 6, 58–60+79. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, M.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Z.; Yang, H. Gas-solid two-phase numerical simulation in the gas-solid distributor of a pulverizing system. Coal Convers. 2022, 45, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ye, Y.; Tan, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D. Discrete element simulation of particle motion in ball mills based on similarity. Powder Technol. 2018, 335, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ma, G.; Li, H. Analysis of the blockage of coal powder pipeline in a power plant and the transformation scheme. Electr. Power Surv. Des. 2023, 11, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Feng, Y. Retrofitted technology and engineering practice for the coal blockage prevention in a coal fired furnace. J. Eng. Therm. Power 2017, 32, 109–112+135. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Lei, L.; Zhang, F. Optimization and application of flow field of ZGM medium speed coal mill. Eng. Therm. Energy Power 2025, 40, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, Z. Study on explosion characteristics in coal pulverizing process for pulverizer. Jilin Electr. Power 2018, 46, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Min, H.; Liang, F.; Yan, X. A Universal Pulverizing System for Bituminous and Lean Coal Using Low Temperature Furnace Smoke Drying and Using Exhaust Hot Air Compound to Send Powder. CN201010013734.5. 30 June 2010. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=0iq8nzQYh5SWmTGkU0_9s9e44ekNdJLe_NivTfVl2hUTsgXdpi0t1J6rfZoAVf0Gyc08W3Jm1HYjXobjkUDJfAClL9RxGs9nDSTg0_ZBgmH5iE0UhMlTBWt4KPkSuLvvkDF-kISGljzuEyY_vJ-SqELgEKLEf5bw4-eRDayCWt2Jk5HAQRv1161LC_s_hW8R&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Ou, M.; Gao, Z.; Peng, J.; Luo, Z.; Liang, H. Application of burning high volatile coal in a 1 069 t/h lean coal boiler. Energy Res. Manag. 2024, 16, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Ou, M.; Gao, Z.; Sun, L. Research and engineering application of burning bituminous coals with high volatile content in a 360 MW lean coal-fired boiler. J. Eng. Therm. Energy Power 2024, 39, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, P. Optimization and application of 300 MW boiler lean to smoke transformation technology. Autom. Appl. 2024, 65, 51–53+63. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Gao, W.; Peng, Y.; Liang, J.; Pan, F.; Xu, S. Experimental and numerical study on flame propagation behaviors in coal dust explosions. Powder Technol. 2014, 266, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Zhou, H.; He, C.; Chen, X.; Shen, X. Numerical simulation on pneumatic conveying of dense phase pulverized coal in horizontal pipe at high pressure. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 2012, 46, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Dong, P. Experimental study on ignition characteristics of pulverized coal under high-temperature oxygen condition. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 40, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, B. Study on oxygen consumption characteristics of coal under different temperatures in latent period of spontaneous combustion. J. Saf. Sci. Technol. 2017, 13, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, R.; Qiu, T.; Chao, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, J.; Li, C. Thermal evolution of the oxidation characteristics of pulverized coal with different particle sizes and heating rates. Thermochim. Acta 2020, 685, 178516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheed, R.; Mohammadian, A.; Gildeh, H.K. A comparison of standard k–ε and realizable k–ε turbulence models in curved and confluent channels. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2019, 19, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Singh, R.K.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, A.; Dwivedi, Y.D.; Rana, S.C.; Roy, M.; Singh, P.; Ansu, A.K.; Goya, A.; et al. Comparative study using renormalized group k-ɛ, realizable k-ɛ, and standard k-ɛ models for flow through S-shaped diffuser. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2024, 18, 3397–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Xu, G.; Zhou, F.; Mullins, B.; Abishek, S. Comparison of underground mine DPM simulation using discrete phase and continuous phase models. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 127, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Shang, B.; Guo, X.; Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L. Study on Combustion Characteristics and NOx Formation in 600 MW Coal-Fired Boiler Based on Numerical Simulation. Energies 2023, 16, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Jin, Y.; Li, L.; Lv, W. Numerical investigation on the impact of exergy analysis and structural improvement in power plant boiler through co-simulation. Energies 2022, 15, 8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.R.; Smith, P.J. Three-dimensional discrete ordinates modelling of radiative transfer in a geometrically complex furnace. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1993, 88, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mao, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, C. Numerical simulation of MILD combustion on coal-water slurry. Clean Coal Technol. 2017, 23, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ansys Inc. Ansys Fluent Theory Guide, Release 2024 R1; Ansys Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2024; pp. 475–476. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, H.; Howard, J.B.; Sarofim, A.F. Coal Devolatilization at High Temperatures. In Proceedings of the 16th Symposium (International) on Combustion, The Combustion Institute, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 15–20 August 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X. Study on the adaptability of EDM, PDF and FR/ED models to pulverized coal combustion process simulation. Clean Coal Technol. 2020, 26, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, P.; Li, X.; Sun, R.; Sun, S. Numerical study of the emission from co-combustion of large-proportion semi-coke and pulverized coal. Huadian Technol. 2020, 42, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, F. Study on reaction kinetics of steam-coal chars gasification with TGA. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2004, 29, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F. Study on the gasification reaction dynamic of coal coke and CO2. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2003, 9, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, I.W. The combustion rates of coal chars: A review. Symp. Int. Combust. 1982, 19, 1045–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhao, S.; Wei, G.; Zhuo, J.; Yao, Q.; Li, S. Combustion characteristics of non-premixed hydrogen/natural gas flue gas based on flue gas internal recirculation. J. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2025, 31, 212–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Yang, C.; Zhou, H.; Niu, B.; Li, J.; Luo, T. Numerical simulation study on flow characteristics of hydrogen blending in T-shaped natural gas pipeline. J. Yan’an Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2023, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Material | Proximate Analysis (As Received, wt%) | Ultimate Analysis (Dry Ash Free, wt%) | Qnet,d/ MJ·kg−1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | Ash | Volatile | Fixed Carbon | C | H | O | N | ||
| Pulverized coal | 14.5 | 22.02 | 23.81 | 39.67 | 78.32 | 4.93 | 14.54 | 1.43 | 22.16 |
| Reaction | A/s−1 | E/kJ·mol−1 |
|---|---|---|
| mv_vol + 1.706 O2 → CO2 + 1.543 H2O | 2.1 × 1011 | 2.01 × 108 |
| C(s) + O2 → CO2 | 3.0 × 102 | 1.30 × 108 |
| C(s) + CO2 → 2 CO | 2.2 × 103 | 2.20 × 108 |
| C(s) + H2O → CO + H2 | 1.1 × 103 | 1.82 × 108 |
| CO + 1/2 O2 → CO2 | 3.2 × 1012 | 1.67 × 108 |
| H2 + 1/2 O2 → H2O | 2.5 × 1016 | 1.67 × 108 |
| Case | A Exhaust Air Velocity/m·s−1 | B Exhaust Air Velocity/m·s−1 | Hot Air Velocity/m·s−1 | Hot Air Temperature/K |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100%B (case 1~16) | 25 | 25 | 1~10 | 560~620 |
| 25%A/75%B (case 17~32) | 4.26 | 12.79 | 1~10 | 560~620 |
| 50%A/50%B (case 33~48) | 8.53 | 8.53 | 1~10 | 560~620 |
| 75%A/25%B (case 49~64) | 12.79 | 4.26 | 1~10 | 560~620 |
| 100%A (case 65~80) | 25 | 25 | 1~10 | 560~620 |
| Load | Hot Air Velocity/m·s−1 | Hot Air Temperature/K |
|---|---|---|
| 100% BMCR | 7.0 | 610 |
| 80% BMCR | 9.8 | 580 |
| 50% BMCR | 2.3 | 565 |
| Items | Simulation Value | Measured Value | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| average velocity at the primary air box outlet/m·s−1 | 29.19 | 31.45 | 7 |
| average temperature at the primary air box outlet/K | 447.25 | 418.36 | 7 |
| temperature near the upper wall inside the primary air box/K | 424.65 | 408.89 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Sun, G.; Guo, W.; Zhao, L. Numerical Simulation Study on Different Exhaust Air Transfer Conditions and Safety of Pulverized Coal System. Energies 2025, 18, 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102408
Zhang Y, Sun G, Guo W, Zhao L. Numerical Simulation Study on Different Exhaust Air Transfer Conditions and Safety of Pulverized Coal System. Energies. 2025; 18(10):2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102408
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yunqin, Guowei Sun, Weiwei Guo, and Lingling Zhao. 2025. "Numerical Simulation Study on Different Exhaust Air Transfer Conditions and Safety of Pulverized Coal System" Energies 18, no. 10: 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102408
APA StyleZhang, Y., Sun, G., Guo, W., & Zhao, L. (2025). Numerical Simulation Study on Different Exhaust Air Transfer Conditions and Safety of Pulverized Coal System. Energies, 18(10), 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102408






