The Development of Porosity-Enhanced Synthetic Coal Plugs for Simulating Deep Coalbed Methane Reservoirs: A Novel Laboratory Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
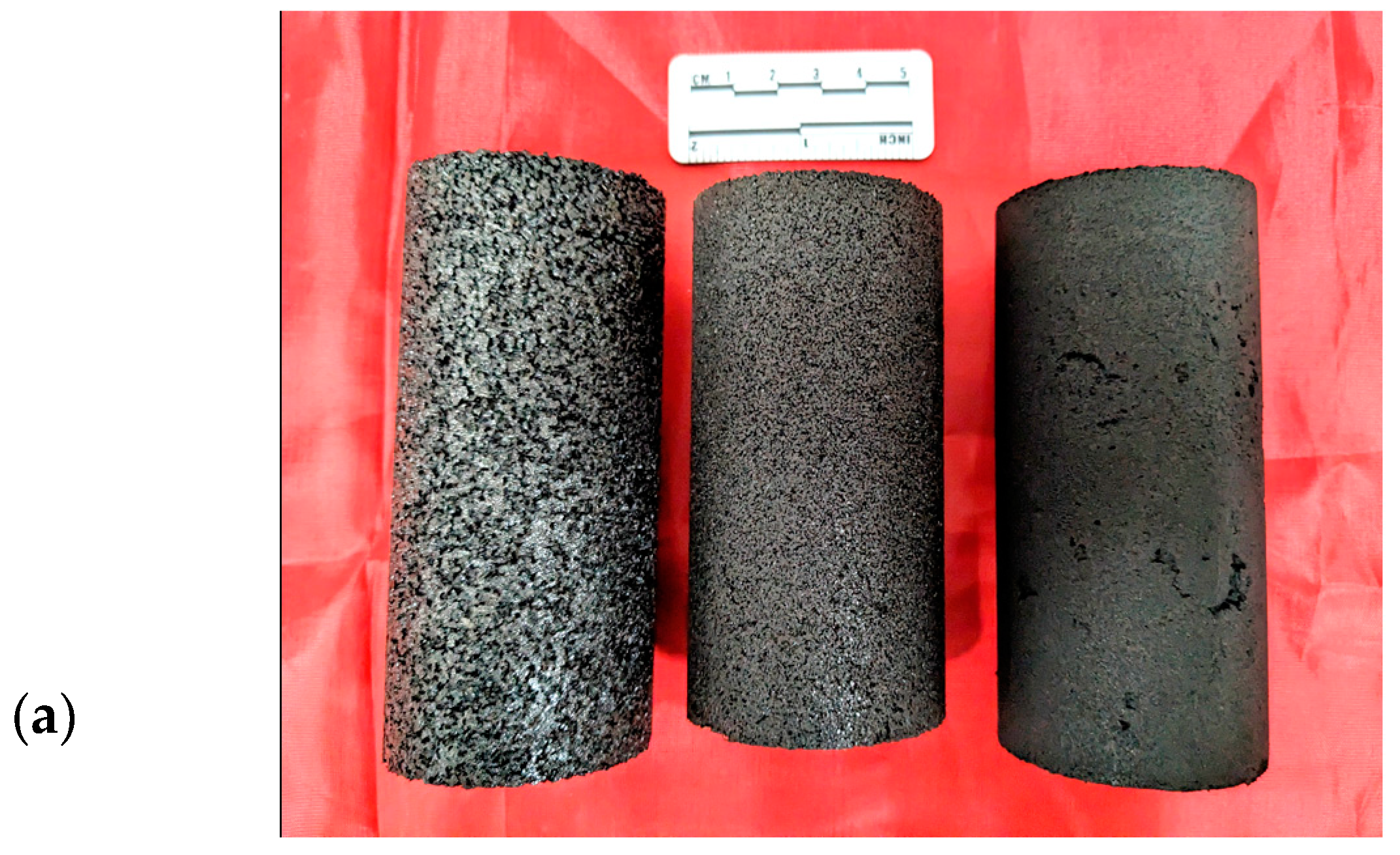
2.1. Sample Preparation
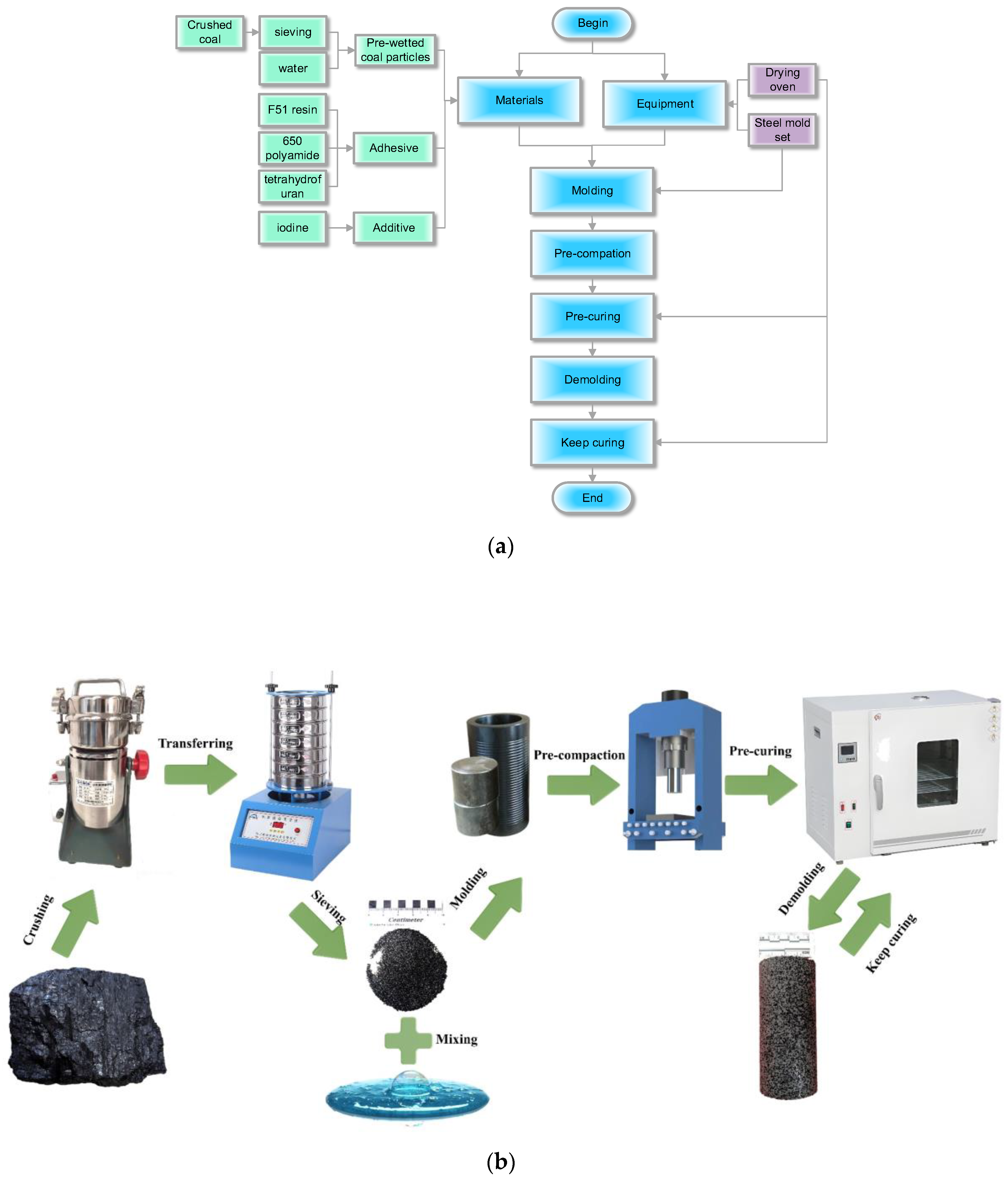
2.1.1. Preparation of Materials and Equipment
2.1.2. Procedures
2.2. Experimental Methods
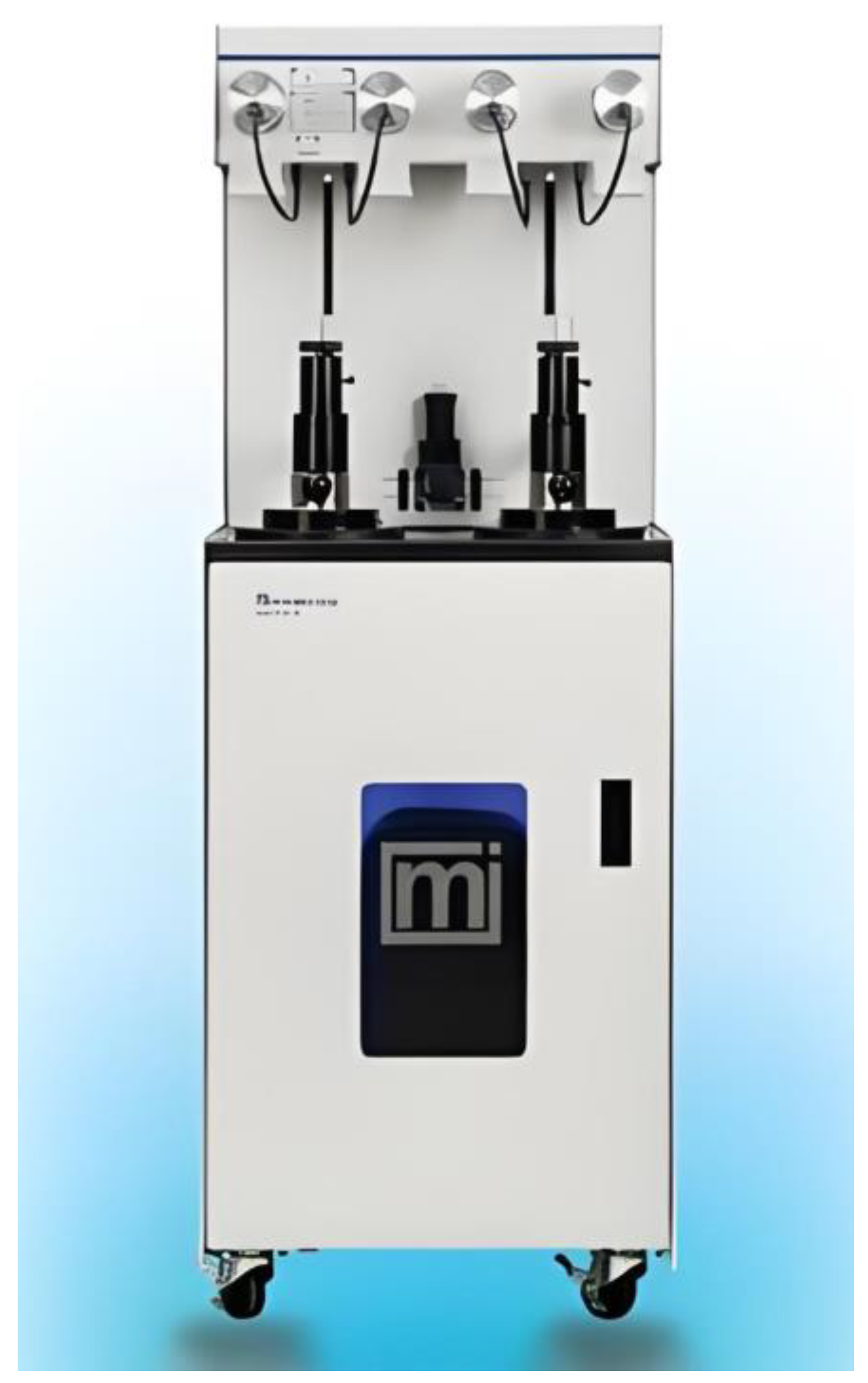
2.2.1. Helium Porosimetry
2.2.2. Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry
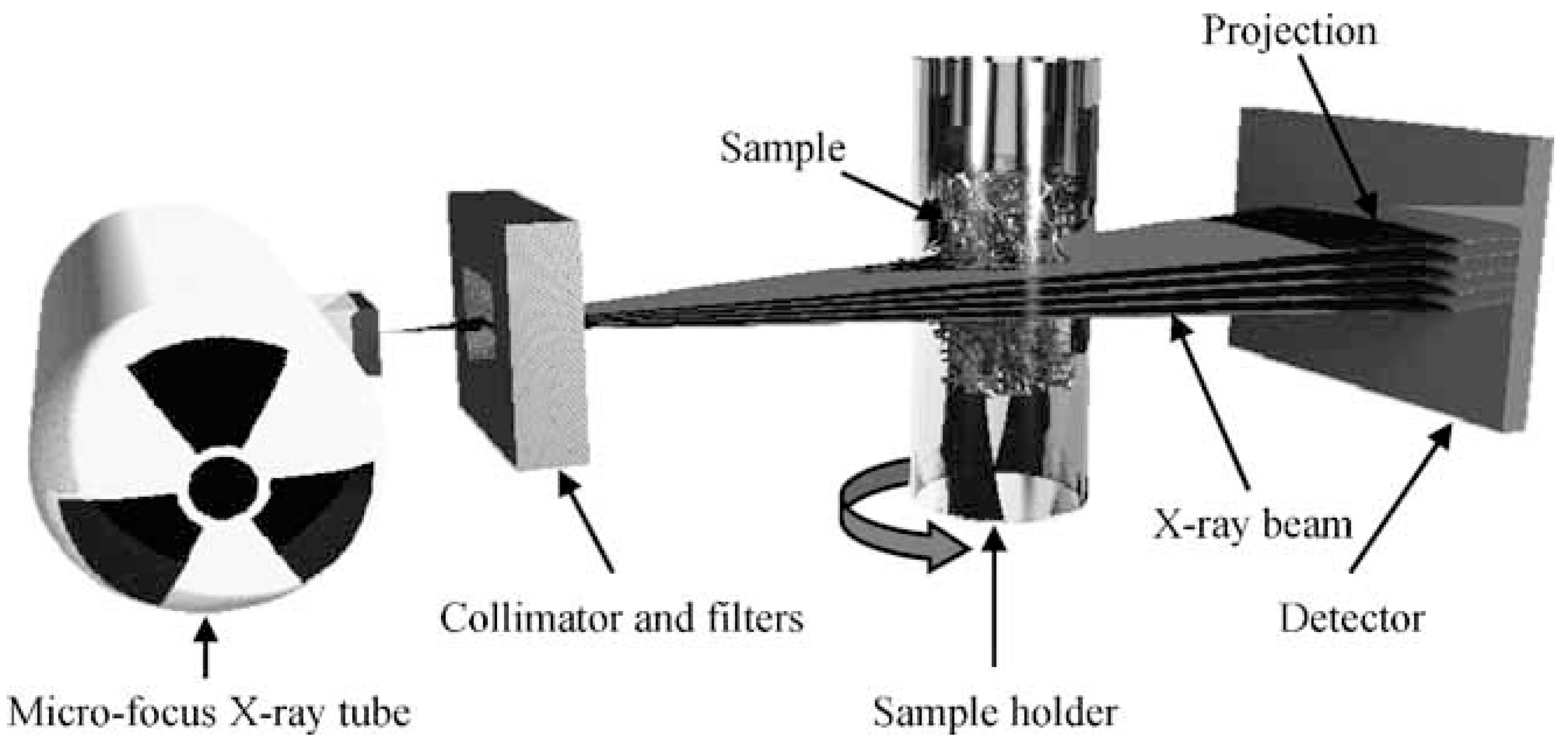
2.2.3. Micro-CT Analysis of Coal and Synthetic Coal Plugs
3. Results and Discussion
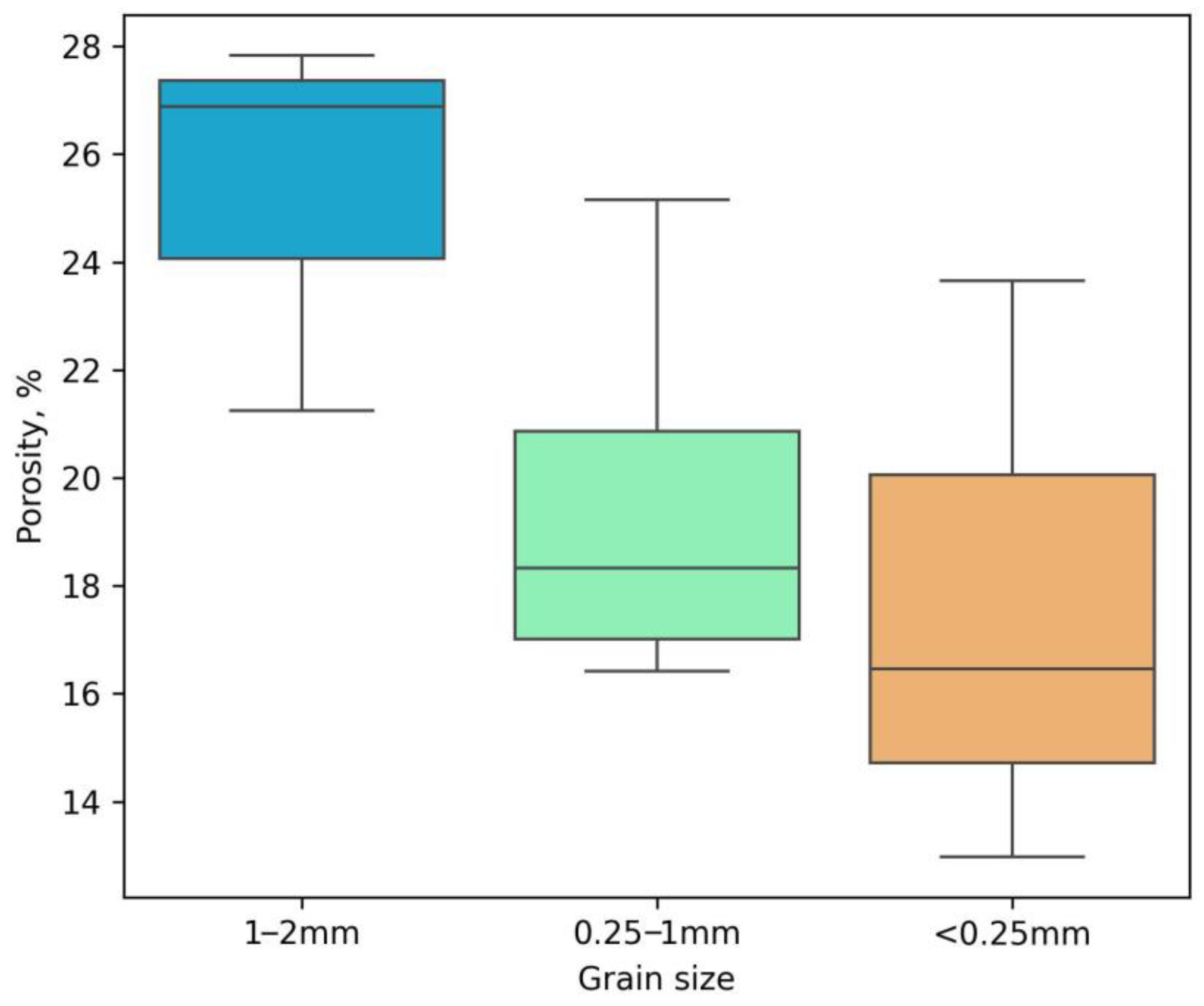
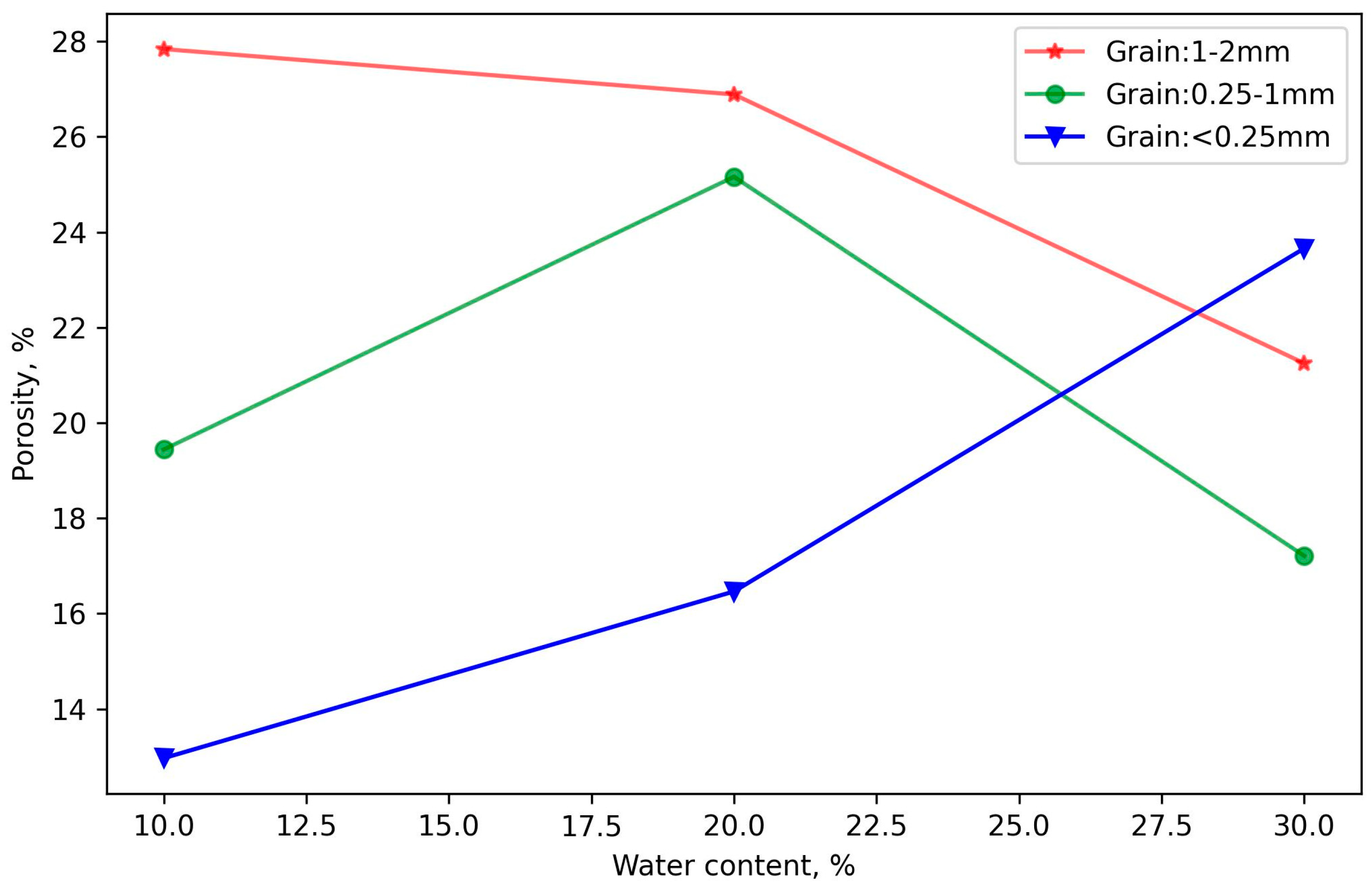
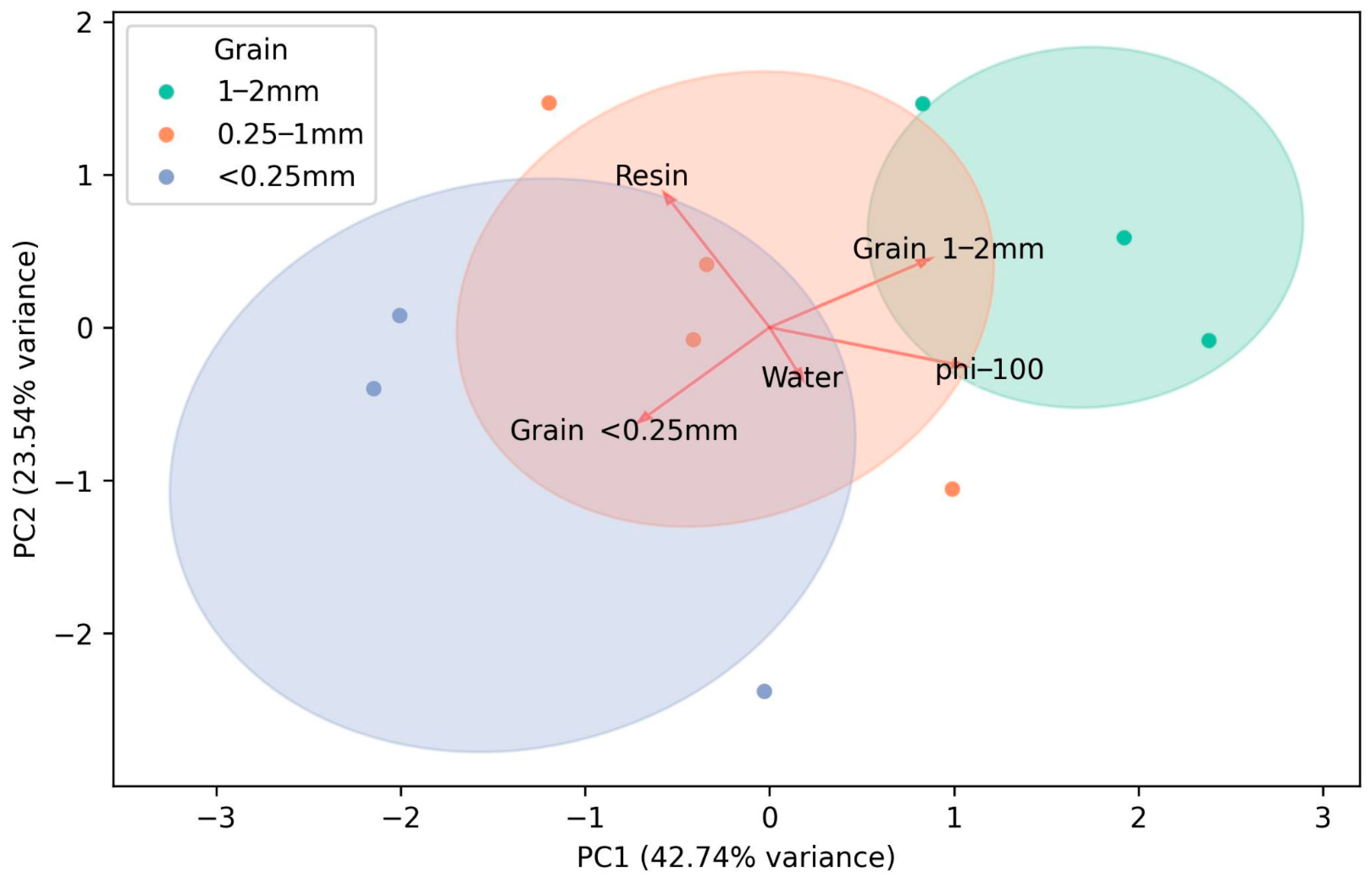
3.1. Helium Porosity of Synthetic Coal Plugs and Its Influencing Factors
3.2. Characterization of Pore Structure of Synthetic Coal Plugs
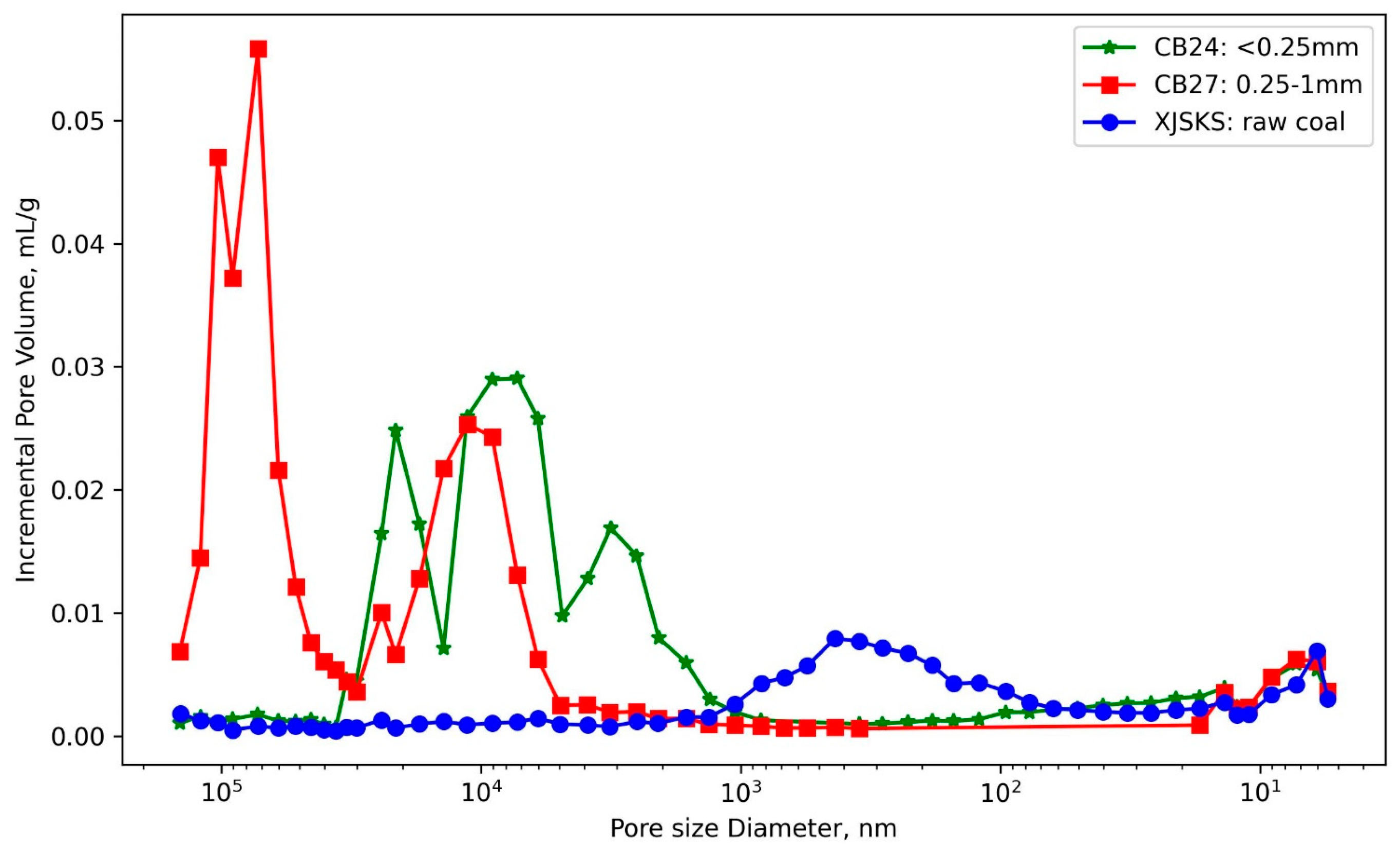
3.2.1. Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP) for Characterizing the Pore Structure of Synthetic Plugs
| Hodot [37] | Dubinin (1966) [38] | IUPAC (1985) [39,40] | Gan (1972) [41] | Qin (1995) [21] |
| <10, Micropore | <2, Micropore | <2, Micropore | 0.4~1.2, Micropore | <15, Micropore |
| 10~100, Transition pore | 2~20, Transition pore | 2~50, Transition pore | 1.2~30, Transition pore | 15~50 Transition pore |
| 100~1000, Mesopore | 50~400, Mesopore | |||
| >1000, Macropore | >20, Macropore | >50, Macropore | 30–2960, Macropore | >400, Macropore |
3.2.2. Micro-CT-Based Description of the Pore Structure of Synthetic Plugs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, F.; Yan, X.; Li, S.; Xiong, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Han, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhen, H.; et al. Theoretical and Technological Difficulties and Countermeasures of Deep CBM Exploration and Development in the Eastern Edge of Ordos Basin. Meitiandizhi Yu Kantan/Coal Geol. Explor. 2023, 51, 115–130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Nie, Z.; Sun, W.; Xiong, X.; Xu, B.; Zhang, L.; Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Theoretical and Technological System for Highly Efficient Development of Deep Coalbed Methane in Daning-Jixian Block. J. China Coal Soc. 2024, 49, 528–544. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y. Progress on Geological Research of Deep Coalbed Methane in China. ACTA Pet. Sin. 2023, 44, 1791–1811. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Qin, Y.; Tang, D.; Shen, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, S. A Comprehensive Review of Deep Coalbed Methane and Recent Developments in China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2023, 279, 104369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Kang, J.; Chen, Y.; Duan, C.; Lu, J.; Zhang, B. Analysis on Terminologies Related to Coalbed Methane. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2025, 54, 26–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Chen, Z.; He, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y. “Effective Support” Concept and Innovative Practice of Deep CBM in South Yanchuan Gas Field of the Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2022, 42, 97–106. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. China’s CBM Exploration and Production and Associated Technological Advancements: A Review and Reflections. Coal Geol. Explor. 2025, 53, 114–127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, S.; He, H.; He, X.; Zhao, Z.; Niu, X.; Xiong, X.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, X.; Hou, Y.; et al. Coal-Rock Gas:Concept, Connotation and Classification Criteria. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 783–795. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Ding, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Cai, B.; Yang, Z.; He, C.; et al. Concept, Technology and Practice of “Man-Made Reservoirs”Development. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2017, 44, 144–154. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warpinski, N.R.; Lorenz, J.C.; Branagan, P.T.; Myal, F.R.; Gall, B.L. Examination of a Cored Hydraulic Fracture in a Deep Gas Well. SPE Prod. Facil. 1993, 8, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornet, F.H.; Valette, B. In Situ Stress Determination from Hydraulic Injection Test Data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1984, 89, 11527–11537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warpinski, N.R.; Laboratories, S.N.; Teufel, L.W.; Laboratories, S.N. Influence of Geologic Discontinuities on Hydraulic Fracture Propagation. J. Pet. Technol. 1987, 39, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raterman, K.T.; Farrell, H.E.; Mora, O.S.; Janssen, A.L.; Gomez, G.A.; Busetti, S.; McEwen, J.; Friehauf, K.; Rutherford, J.; Reid, R.; et al. Sampling a Stimulated Rock Volume: An Eagle Ford Example. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2018, 21, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Li, W.; Han, X.; Liu, C.; Su, H. 3D Visualization of Tectonic Coal Microstructure and Quantitative Characterization on Topological Connectivity of Pore-Fracture Networks by Micro-CT. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liang, W.; Hou, S.; Zhu, X.; Huang, W. Experimental Study of Effect of Temperature and Stress on Permeability Characteristics of Raw Coal and Shaped Coal. Chinese J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2012, 31, 1222–1229. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Liu, C. Analysis of Moulded Coal Porosity Base on Surface Characteristics. Procedia Eng. 2011, 26, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulepov, M.I.; Sassykova, L.R.; Kerimkulova, A.R.; Tureshova, G.O.; Tolep, D.M.; Zhapekova, A.O.; Spanova, G.A.; Abdrakova, F.Y.; Mansurov, Z.A. Preparation of Coal Briquettes and Determination of Their Physical and Chemical Properties. Orient. J. Chem. 2019, 35, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L. Research on the Influences of Particle Gradation and Added Moisture on the Compactibility of Jincheng Anthracite. China Coal 2023, 49, 117–121. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Deng, J.; Tian, D.; Yu, B.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, Z. Research on Uniaxial Mechanical Properties of Synthetic Sandstones Cemented with Epoxy Resin Adhesives. Pet. Sci. Bull. 2023, 8, 600–613. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Q. Preparation and Evaluation on Artificial Core of Extra High Permeability Unconsolidated Sandstone. Oil Drill. Prod. Technol. 2017, 39, 477–483. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J. Natural Classification of the High-Rank Coal Pore Structure and Its Application. J. China Coal Soc. 1995, 20, 266–271. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Li, Z.; Tao, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, K. A Comprehensive Study of Multiscale Pore Structural Characteristics in Deep-Buried Coals of Different Ranks. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Jia, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Tang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lin, P. Study on Full-Scale Pores Characterization and Heterogeneity of Coal Based on Low-Temperature Nitrogen Adsorption and Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Experiments. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.-M.; Yue, W.-Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, M.-Y. Advances on the Calculation Methods of Tortuosity in Porous Media. Prog. Geophys. 2023, 38, 1293–1304. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zdravkov, B.D.; Čermák, J.J.; Šefara, M.; Janků, J. Pore Classification in the Characterization of Porous Materials: A Perspective. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2007, 5, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wei, W.; Liu, X.; Wu, J. Study on Seepage Characteristics and Visualization of Coal and Rock under Coupled Stress-Strain-Seepage Conditions. Min. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 49, 59–63. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Ren, T.; Li, X.; Qiao, M.; Yang, X.; Tan, L.; Nie, B. Multi-Scale Pore Fractal Characteristics of Differently Ranked Coal and Its Impact on Gas Adsorption. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 33, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouxsein, M.L.; Boyd, S.K.; Christiansen, B.A.; Guldberg, R.E.; Jepsen, K.J.; Müller, R. Guidelines for Assessment of Bone Microstructure in Rodents Using Micro-Computed Tomography. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 1468–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 29172-2012; Practices for Core Analysis. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 34533-2017; Measurement of Helium Porosity and Pulse Decay Permeability of Shale. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Washburn, E.W. The Dynamics of Capillary Flow. Phys. Rev. 1921, 17, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Pan, Z. Classification Methods of Pore Structures in Coal: A Review and New Insight. Gas Sci. Eng. 2023, 110, 204876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 21650.1-2008/ISO 15901-1:2005; Pore Size Distribution and Porosity of Solid Materials by Mercury Porosimetry and Gas Adsorption—Part 1: Mercury Porosimetry. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of China & China National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Wang, Y.; Rahman, S.S. Numerical Modelling of Reservoir at Pore Scale: A Comprehensive Review. J. Comput. Phys. 2023, 472, 111680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Qi, Q.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, B. Review of Research on Test, Simulation and Prediction of Coal Reservoir Permeability. J. China Coal Soc. 2022, 47, 2369–2385. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Carman, P.C. Flow of Gases Through Porous Media, 1st ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Hodot, B.B.; Song, S.; Wang, Y. Coal and Gas Outburst, 1st ed.; China Building Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1966. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dubinin, M.M. Modern State of the Theory of Gas and Vapour Adsorption by Microporous Adsorbents. Pure Appl. Chem. 1965, 10, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Nandi, S.P.; Walker, P.L. Nature of the Porosity in American Coals. Fuel 1972, 51, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Excess Pore Pressure Behavior and Evolution in Deep Coalbed Methane Reservoirs. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2024, 34, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Sample ID | Particle Size, mm | F51 Resin Content, g | Weight of Particles, g | Water Content in Weight, % | Diameter, cm | Height, cm | Pore Volume, cm3 | Helium Porosity, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orth01 | 1~2 | 9.00 | 150.00 | 10.00 | 4.98 | 9.33 | 50.66 | 27.84 |
| Orth02 | 1~2 | 15.00 | 150.00 | 20.00 | 4.99 | 10.13 | 53.26 | 26.89 |
| Orth03 | 1~2 | 21.00 | 150.00 | 30.00 | 4.98 | 9.07 | 37.48 | 21.25 |
| Orth04 | 0.25~1 | 9.00 | 150.00 | 20.00 | 4.97 | 9.56 | 46.61 | 25.16 |
| Orth05 | 0.25~1 | 15.00 | 150.00 | 10.00 | 4.98 | 9.18 | 34.79 | 19.44 |
| Orth06 | 0.25~1 | 21.00 | 150.00 | 10.00 | 4.98 | 8.89 | 28.42 | 16.41 |
| Orth07 | <0.25 | 9.00 | 150.00 | 30.00 | 4.99 | 9.17 | 42.43 | 23.66 |
| Orth08 | <0.25 | 15.00 | 150.00 | 10.00 | 5.00 | 9.40 | 23.94 | 12.97 |
| Orth09 | <0.25 | 21.00 | 150.00 | 20.00 | 5.00 | 9.30 | 30.07 | 16.47 |
| Orth10 | 0.25~1 | 15.00 | 150.00 | 30.00 | 4.99 | 9.15 | 30.80 | 17.21 |
| Grain Size/Type | Total Pore Area, m2/g | Median Pore Diameter, nm | Porosity, % | Threshold Pressure, kPa | Estimated Permeability, mD | Tortuosity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw coal | 14.26 | 287.80 | 14.52 | 24.13 | 42.35 | 12.83 |
| Grain: <0.25 mm | 15.55 | 7625.10 | 28.56 | 57.78 | 172.45 | 6.57 |
| Grain: 0.25–1 mm | 13.82 | 52315.20 | 32.19 | 12.00 | 4778.10 | 4.26 |
| Sample ID | CT Porosity, % | Label Volume, ×1019 | Mask Volume, ×1020 | Label Voxel Count, ×107 | Mask Voxel Count, ×107 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB10 | 31.00 | 8.86 | 2.86 | 12.20 | 39.20 | synthetic coal with iodine; Grain diameter: 1–2 mm; |
| CB24 | 16.32 | 4.39 | 2.69 | 1.60 | 9.80 | synthetic coal with iodine; Grain diameter <0.25 mm |
| CB27 | 25.51 | 6.41 | 2.51 | 12.50 | 49.10 | synthetic coal with iodine; Grain diameter: 0.25–1 mm |
| CB28 | 38.45 | 11.70 | 3.03 | 22.80 | 59.30 | synthetic coal; porosity is overestimated due to the absence of iodine addition |
| XJSKS05-01 | 8.62 | 3.65 | 4.23 | 7.12 | 82.70 | Lignite |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhou, G.; Liang, Y.; Gu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, B.; Feng, S.; et al. The Development of Porosity-Enhanced Synthetic Coal Plugs for Simulating Deep Coalbed Methane Reservoirs: A Novel Laboratory Approach. Energies 2025, 18, 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102407
Liu C, Yang Z, Chen H, Zhou G, Liang Y, Gu J, Wang Y, Li C, Lu B, Feng S, et al. The Development of Porosity-Enhanced Synthetic Coal Plugs for Simulating Deep Coalbed Methane Reservoirs: A Novel Laboratory Approach. Energies. 2025; 18(10):2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102407
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Changqing, Zhaobiao Yang, Heqing Chen, Guoxiao Zhou, Yuhui Liang, Junyu Gu, Yuqiang Wang, Cunlei Li, Benju Lu, Shuailong Feng, and et al. 2025. "The Development of Porosity-Enhanced Synthetic Coal Plugs for Simulating Deep Coalbed Methane Reservoirs: A Novel Laboratory Approach" Energies 18, no. 10: 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102407
APA StyleLiu, C., Yang, Z., Chen, H., Zhou, G., Liang, Y., Gu, J., Wang, Y., Li, C., Lu, B., Feng, S., & Wang, J. (2025). The Development of Porosity-Enhanced Synthetic Coal Plugs for Simulating Deep Coalbed Methane Reservoirs: A Novel Laboratory Approach. Energies, 18(10), 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102407





