Optimising Ion Conductivity in NdBaInO4-Based Phases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Characterization of the Chemical Composition
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy Dispersive Spectrometry
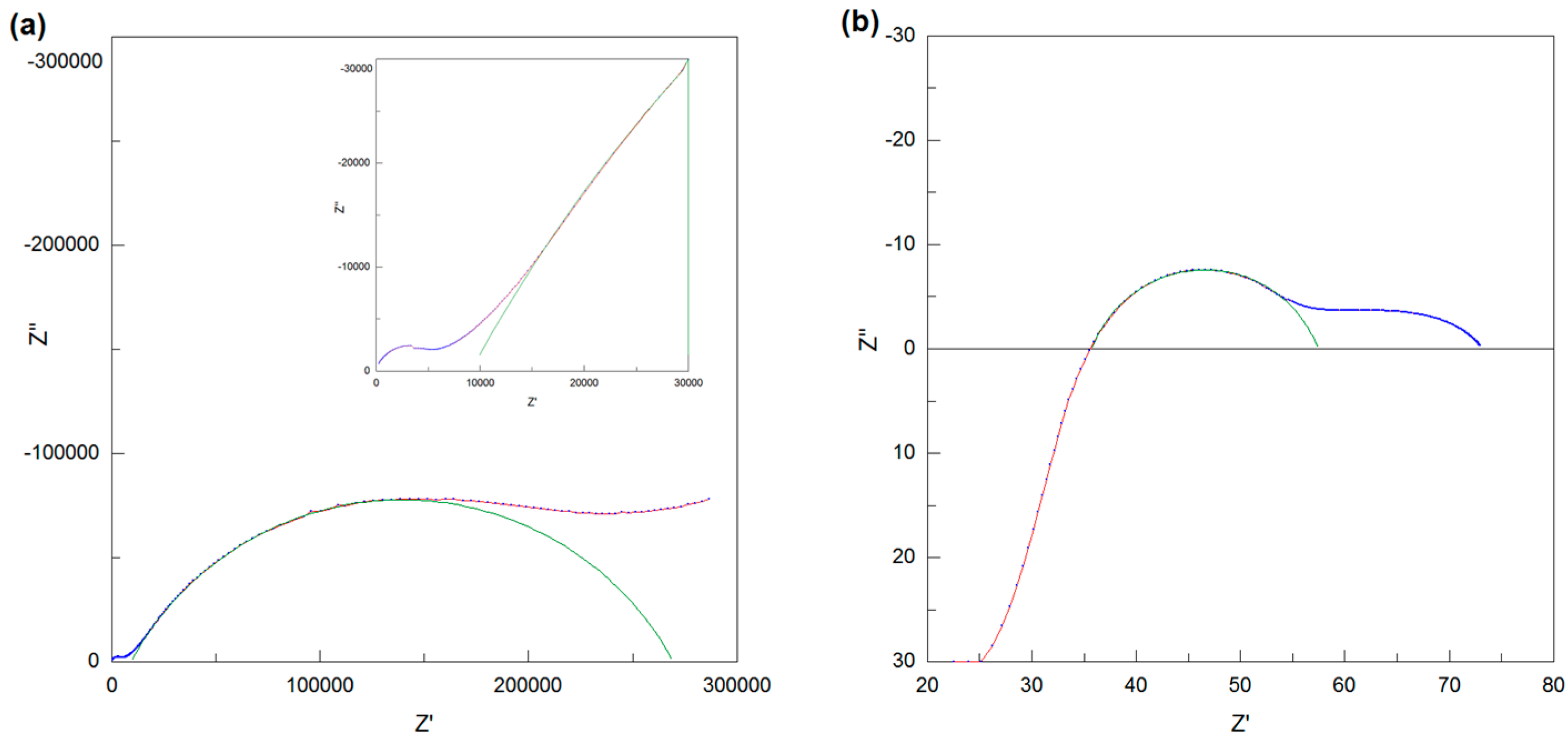
2.4. Electrical Conductivity Measurements
2.5. Oxygen Isotope Exchange
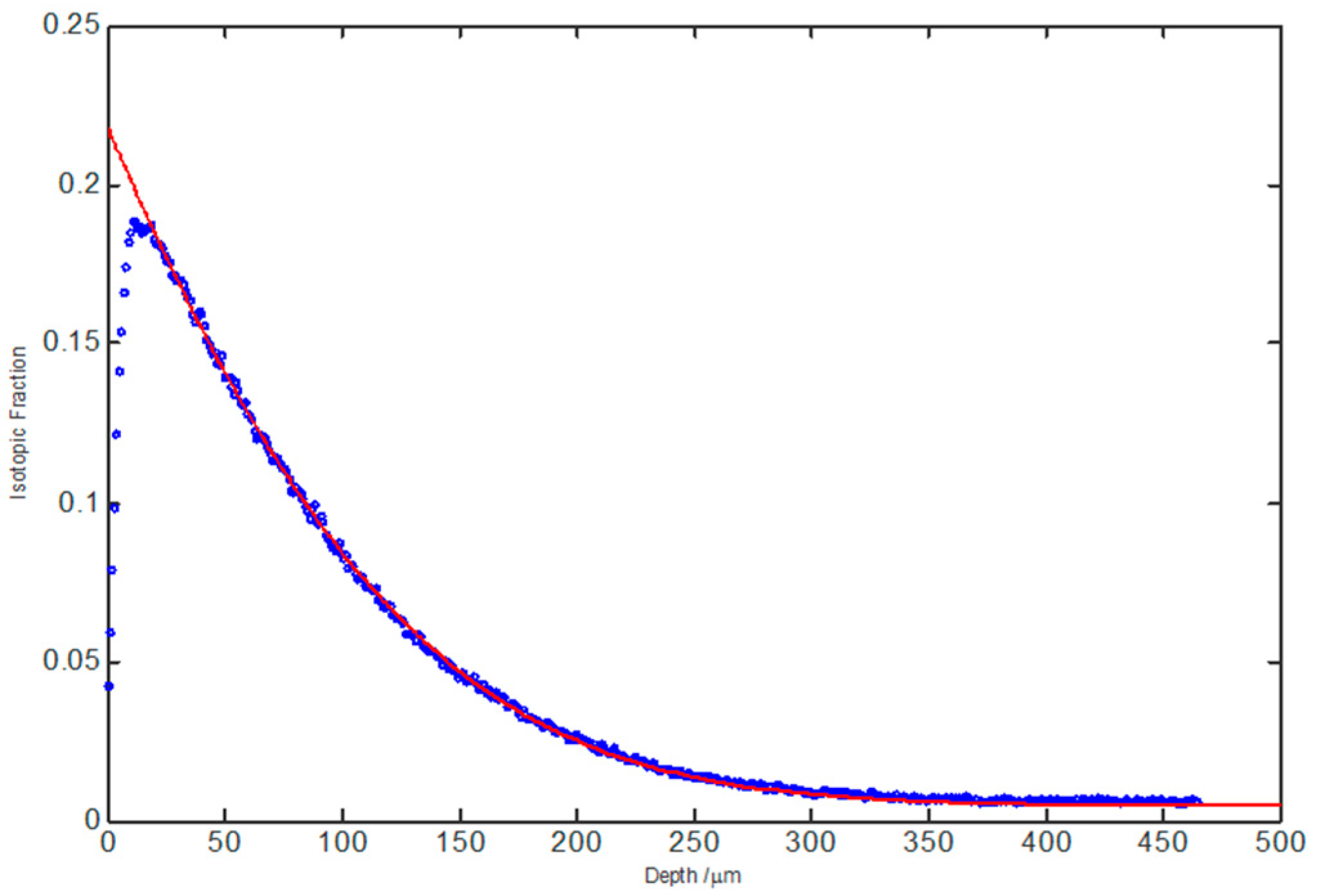
2.6. Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry
3. Results and Discussion
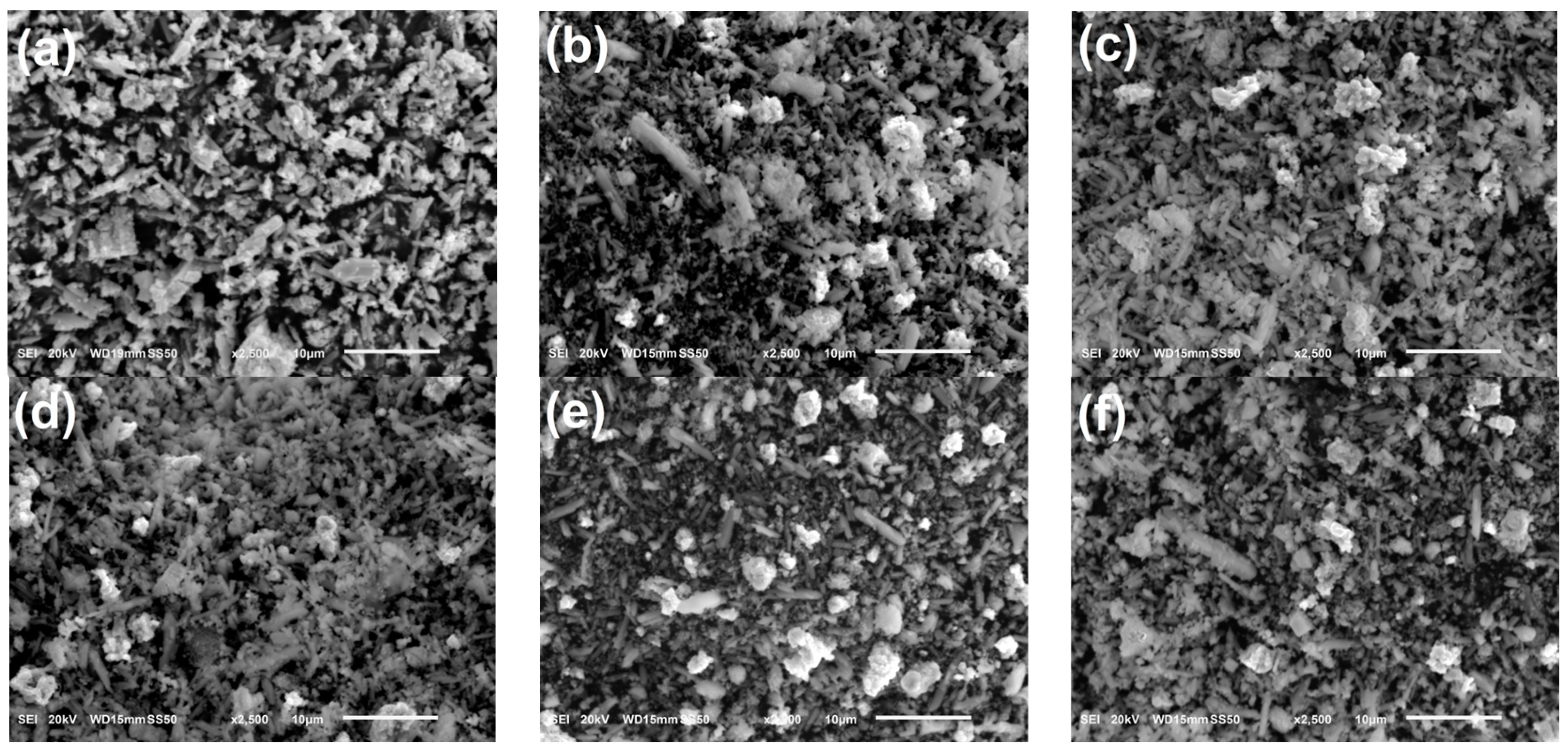
3.1. Ball Milling Time Determination
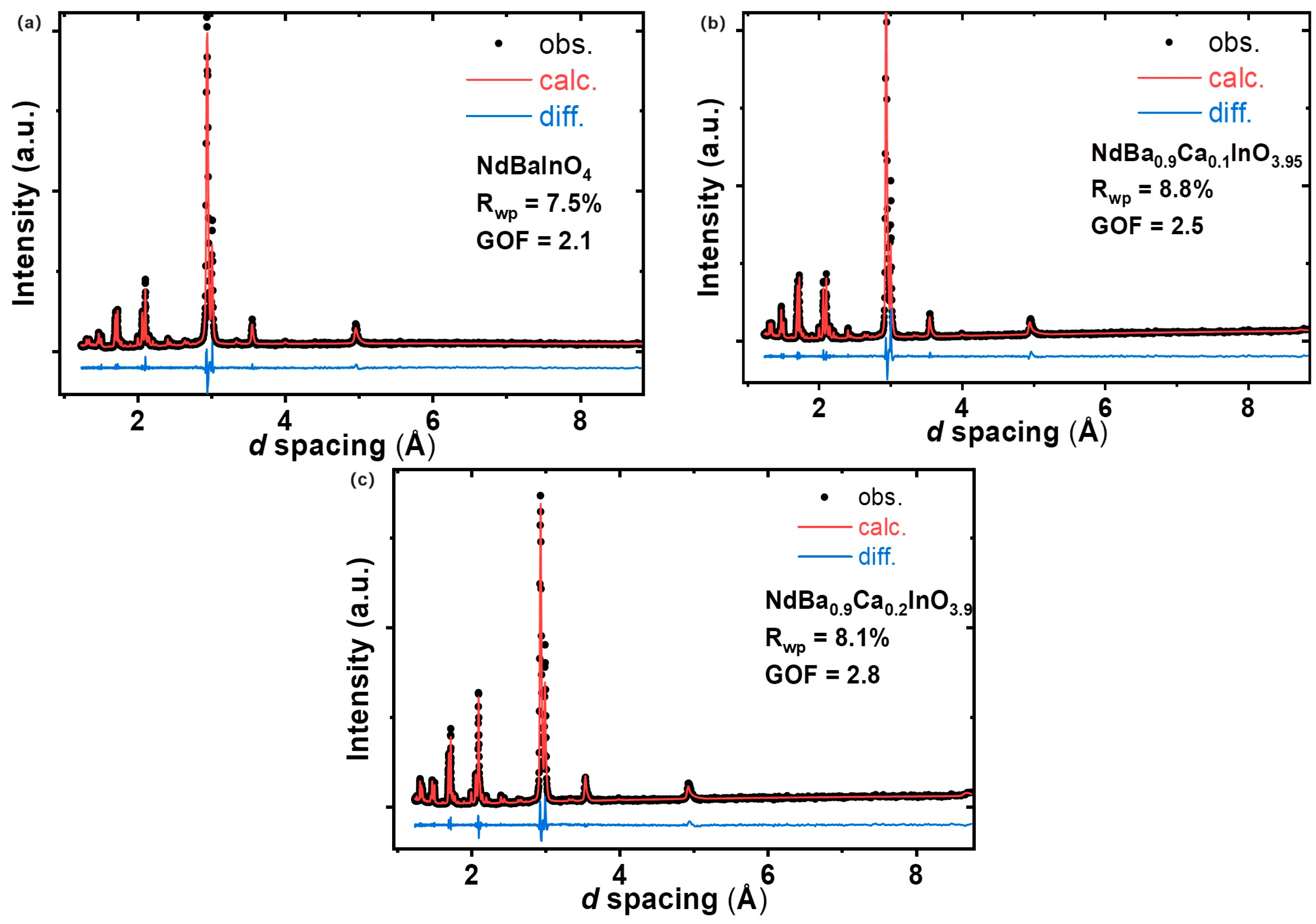
3.2. Crystal Structure of NdBaInO4 and Ca-Doped NdBaInO4 via Le Bail Refinement
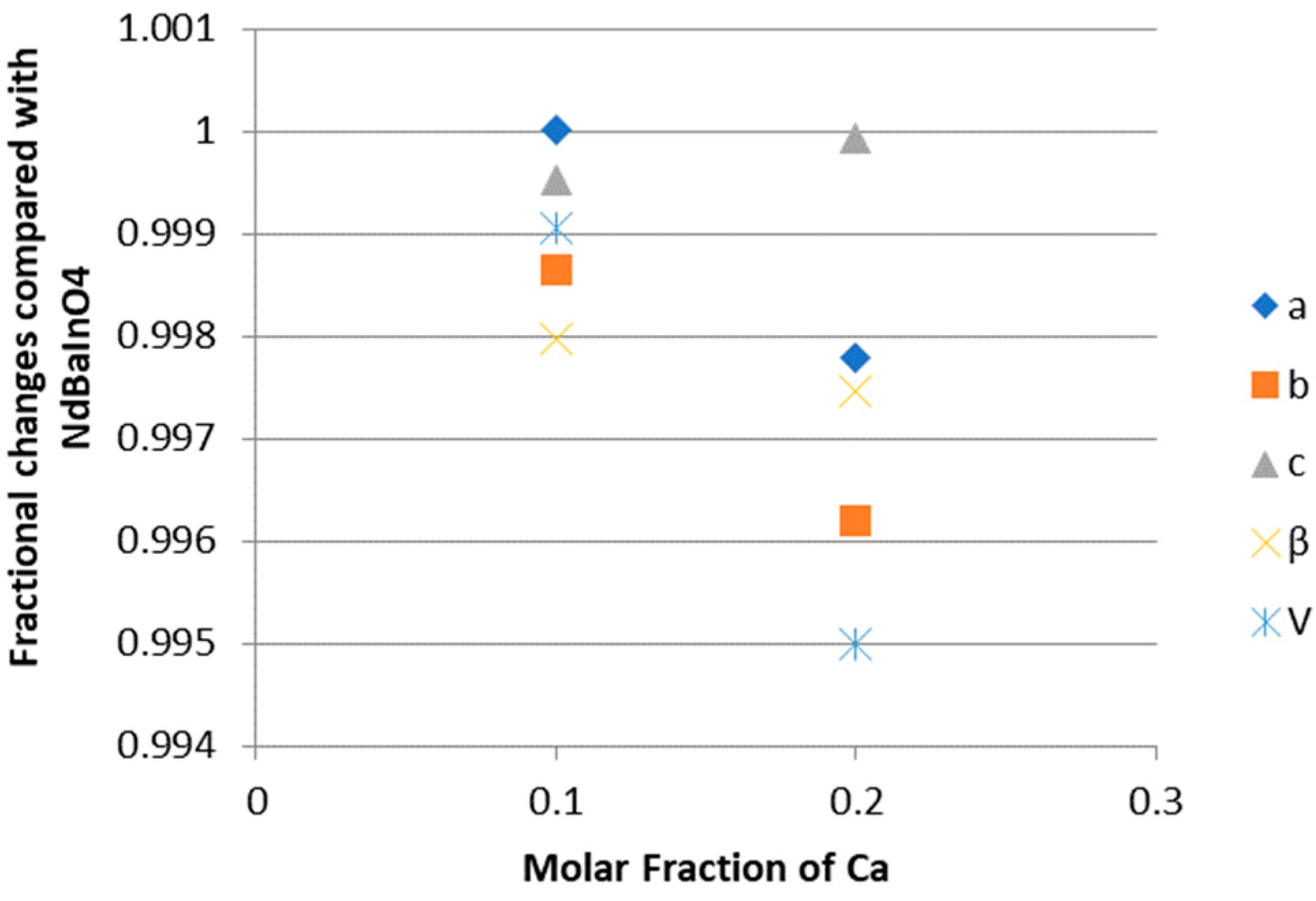
3.3. Fractional Change in Crystallographic Data
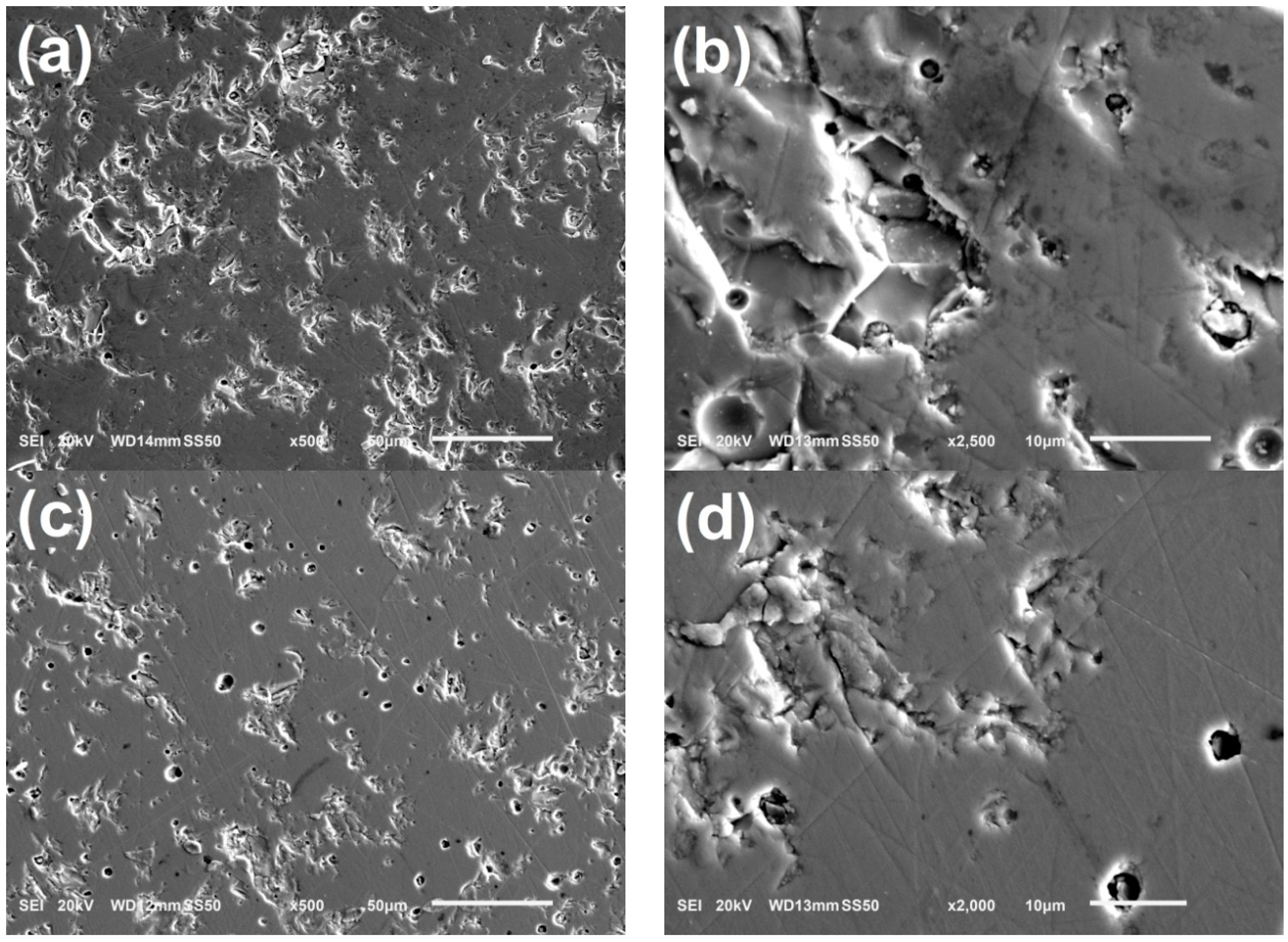
3.4. Microscope Structure of NdBaInO4 and Ca-Doped NdBaInO4
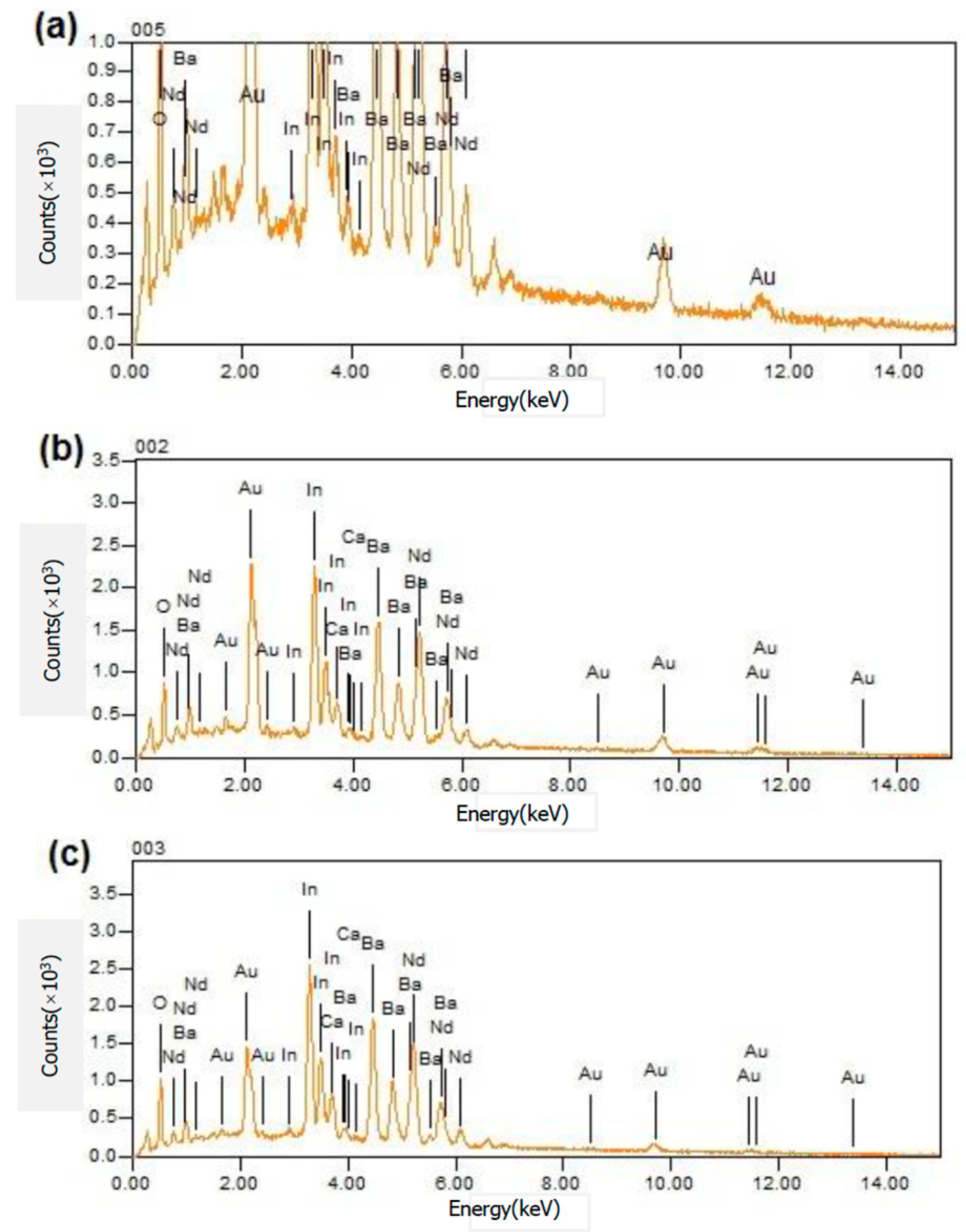
3.5. Energy Dispersive Spectrometry
3.6. Temperature Programme Modification
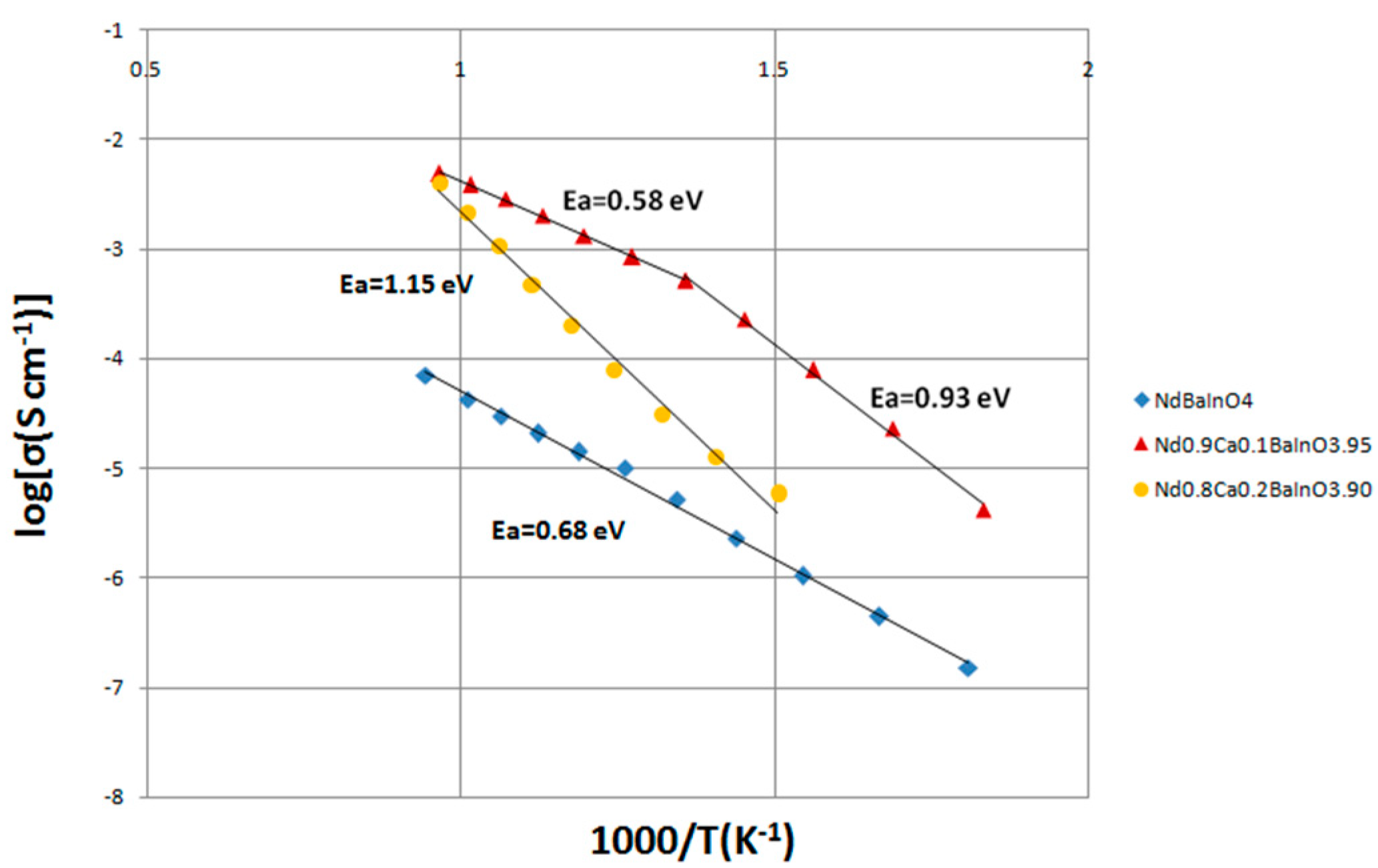
3.7. Electrical Conductivity of NdBaInO4 and Ca-Doped NdBaInO4 in Dry Air
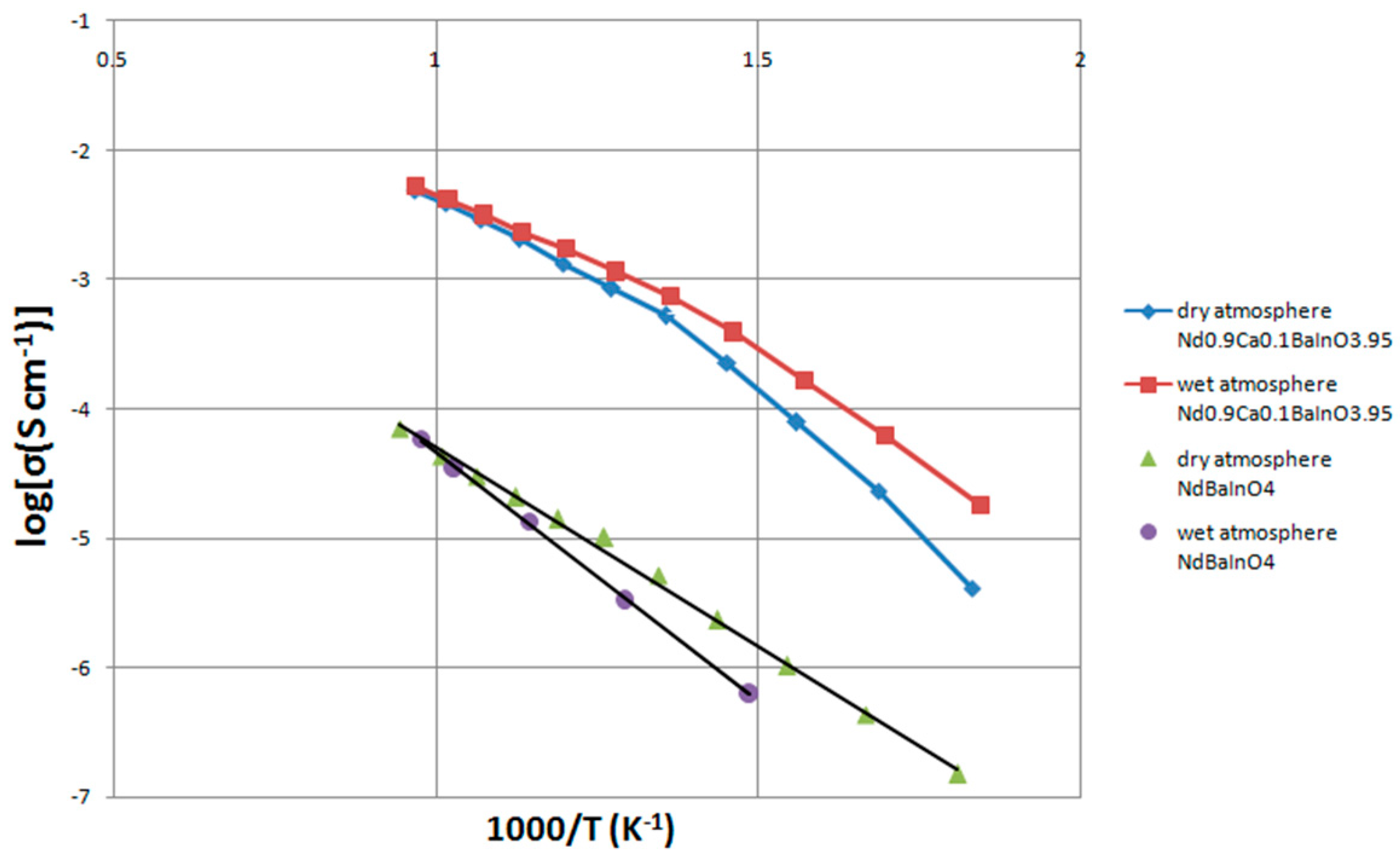
3.8. The Effects of the Humidified Atmosphere on the Conductivity of NdBaInO4 and Nd0.9Ca0.1BaInO3.95
3.9. IEDP of Ca-Doped NdBaInO4
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Goodenough, J.B.; Ruiz-Diaz, J.E.; Zhen, Y.S. Oxide-ion conduction in Ba2In2O5 and Ba3In2MO8 (M = Ce, Hf, or Zr). Solid State Ion. 1990, 44, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, T.; Matsuda, H.; Takita, Y. Doped LaGaO3 perovskite type oxide as a new oxide ionic conductor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 3801–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, J.B. Oxide-ion conductors by design. Nature 2000, 404, 821–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Reina, L.; Losilla, E.R.; Martínez-Lara, M.; Martín-Sedeño, M.C.; Bruque, S.; Núñez, P.; Sheptyakov, D.V.; Aranda, M.A.G. High oxide ion conductivity in Al-doped germanium oxyapatite. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Pietrowski, M.J.; De Souza, R.A.; Zhang, H.; Reaney, I.M.; Cook, S.N.; Kilner, J.A.; Sinclair, D.C. A family of oxide ion conductors based on the ferroelectric perovskite Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Sengodan, S.; Kim, S.; Kwon, O.; Bud, Y.; Kim, G. Proton conducting oxides: A review of materials and applications for renewable energy conversion and storage. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 109, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fujii, K.; Niwa, E.; Hagihala, M.; Kamiyama, T.; Yashima, M. Oxide-ion conduction in the Dion−Jacobson phase CsBi2Ti2NbO10-δ. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvonareva, I.; Fu, X.-Z.; Medvedev, D.; Shao, Z. Electrochemistry and energy conversion features of protonic ceramic cells with mixed ionic-electronic electrolytes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 15, 439–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Fu, M.; Hu, W.; Tong, H.; Tao, Z. A comprehensive review of recent progresses in cathode materials for Proton-conducting SOFCs. Energy Rev. 2023, 2, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, N. Proton-Conducting Polymers: Key to Next-Generation Fuel Cells, Electrolyzers, Batteries, Actuators, and Sensors. ChemElectroChem 2024, 2024, e202300846. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, K.; Esaki, Y.; Omoto, K.; Yashima, M.; Hoshikawa, A.; Ishigaki, T.; Hester, J.R. New Perovskite-Related Structure Family of Oxide-Ion Conducting Materials NdBaInO4. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2488–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Shiraiwa, M.; Esaki, Y.; Yashima, M.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, S. Improved oxide-ion conductivity of NdBaInO4 by Sr doping. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 11985–11990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, T.; Yan, Y.; Sakai, T.; Ida, S. Oxide ion conductivity in doped NdBaInO4. Solid State Ion. 2016, 288, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, D.; Chater, R. Oxygen exchange and diffusion measurements: The importance of extracting the correct initial and boundary conditions. Solid State Ion. 2005, 176, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Kilner; Steele, B.; Ilkov, L. Oxygen self-diffusion studies using negative-ion secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS). Solid State Ion. 1984, 12, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.T. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Cryst. Phys. Diffr. Theor. Gen. Crystallogr. 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, S.R. The origin and status of the Arrhenius equation. J. Chem. Educ. 1982, 59, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugsrud, R.; Norby, T. Proton conduction in rare-earth ortho-niobates and ortho-tantalates. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Chemical Formula | NdBaInO4 Ref [11] | NdBaInO4 Exp. | Nd0.9Ca0.1BaInO3.95 | Nd0.8Ca0.2BaInO3.90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula weight | 460.39 | 460.39 | 449.17 | 437.96 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Monoclinic | Monoclinic | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P21/c | P21/c | P21/c | P21/c |
| a/Å | 9.09538(3) | 9.1079(16) | 9.0926(10) | 9.0822(17) |
| b/Å | 6.04934(2) | 6.0522(11) | 6.0322(9) | 6.0195(12) |
| c/Å | 8.25620(2) | 8.2815(14) | 8.2636(10) | 8.2613(14) |
| β/° | 103.4041(3) | 103.486(13) | 103.392 (9) | 103.337(19) |
| Unit-cell volume/Å3 | 441.89(2) | 443.92(14) | 440.92(10) | 439.47(15) |
| Calculated density/Mg m−3 | 6.92 | 6.78 | 6.63 | |
| Measured density/Mg m−3 | 6.68 | 6.55 | 6.45 | |
| Relative density | 96.53% | 96.61% | 97.29% |
| NdBaInO4 | Nd0.9Ca0.1BaInO3.95 | Nd0.8Ca0.2BaInO3.90 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elements | |||
| In, atom% | 14.21 | 15.81 | 14.68 |
| Ba, atom% | 12.53 | 16.28 | 15.34 |
| Nd, atom% | 15.20 | 14.93 | 12.91 |
| Ca, atom% | 1.54 | 2.29 |
| NdBaInO4 | Nd0.9Ca0.1BaInO3.95 | Nd0.8Ca0.2BaInO3.90 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R at low temperature (Ω) | 9.9 × 105 (at 280 °C) | 39,585 (at 270 °C) | 33,450 (at 390 °C) |
| R at high temperature (Ω) | 3480 (at 720 °C) | 33.4 (at 760 °C) | 47.2 (at 760 °C) |
| σ (S cm−1) | 6.36 × 10−5 (at 760 °C) | 4.91 × 10−3 (at 760 °C) | 4.14 × 10−3 (at 760 °C) |
| Ea (eV) | 0.68 | 0.93 (below 464 °C) 0.58 (above 464 °C) | 1.15 |
| Nd0.9Ca0.1BaInO3.95 | Nd0.8Ca0.2BaInO3.90 | |
|---|---|---|
| D* (cm2/s) | 1.82 × 10−8 | 9.30 × 10−9 |
| 1.80 × 10−8 | 6.60 × 10−9 | |
| Average D* (cm2/s) | 1.81 × 10−8 | 7.95 × 10−9 |
| cm.s−1 | 6.60 × 10−7 | 7.00 × 10−7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Li, C.; Zhu, K.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Kong, W.; Ban, Z.; Shen, C. Optimising Ion Conductivity in NdBaInO4-Based Phases. Energies 2024, 17, 2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092029
Chen M, Li C, Zhu K, Wang J, Liu S, Kong W, Ban Z, Shen C. Optimising Ion Conductivity in NdBaInO4-Based Phases. Energies. 2024; 17(9):2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092029
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Manyu, Cheng Li, Kai Zhu, Jieyu Wang, Sida Liu, Weina Kong, Zifa Ban, and Chao Shen. 2024. "Optimising Ion Conductivity in NdBaInO4-Based Phases" Energies 17, no. 9: 2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092029
APA StyleChen, M., Li, C., Zhu, K., Wang, J., Liu, S., Kong, W., Ban, Z., & Shen, C. (2024). Optimising Ion Conductivity in NdBaInO4-Based Phases. Energies, 17(9), 2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092029






