Evaluation Method and Analysis on Performance of Diffuser in Heat Storage Tank
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Determination Method of Non-Uniformity Coefficient
2.1. Putting Forward the Non-Uniformity Coefficient
2.2. Dimensional Analysis of Non-Uniformity Coefficient
2.3. Calculation of Non-Uniformity Coefficient and Fitting of Formula
2.4. Influence of Inlet Velocity on Non-Uniformity Coefficient
2.5. Experimental Verification
2.5.1. Experimental System and Operation Process
- Set the flow rate to the desired value. Open pump 1 and valve 2. Achieve the target flow by adjusting the pump 1 frequency and the valve 2 opening. When the flow reaches, keep the valve 2 opening unchanged and turn off water pump 1.
- Close valve 2, then open the heating equipment and pump 1, and heat the water to 90 °C. Stop heating when the measured temperature difference in the longitudinal direction is lower than 0.5 °C. At this time, the constant temperature water tank has a uniform temperature field.
- Begin the experiment; valve 2 is opened, valve 1 and 3 are closed. Collect the flow rate of each hole.
2.5.2. Experimental Error and Sensitivity
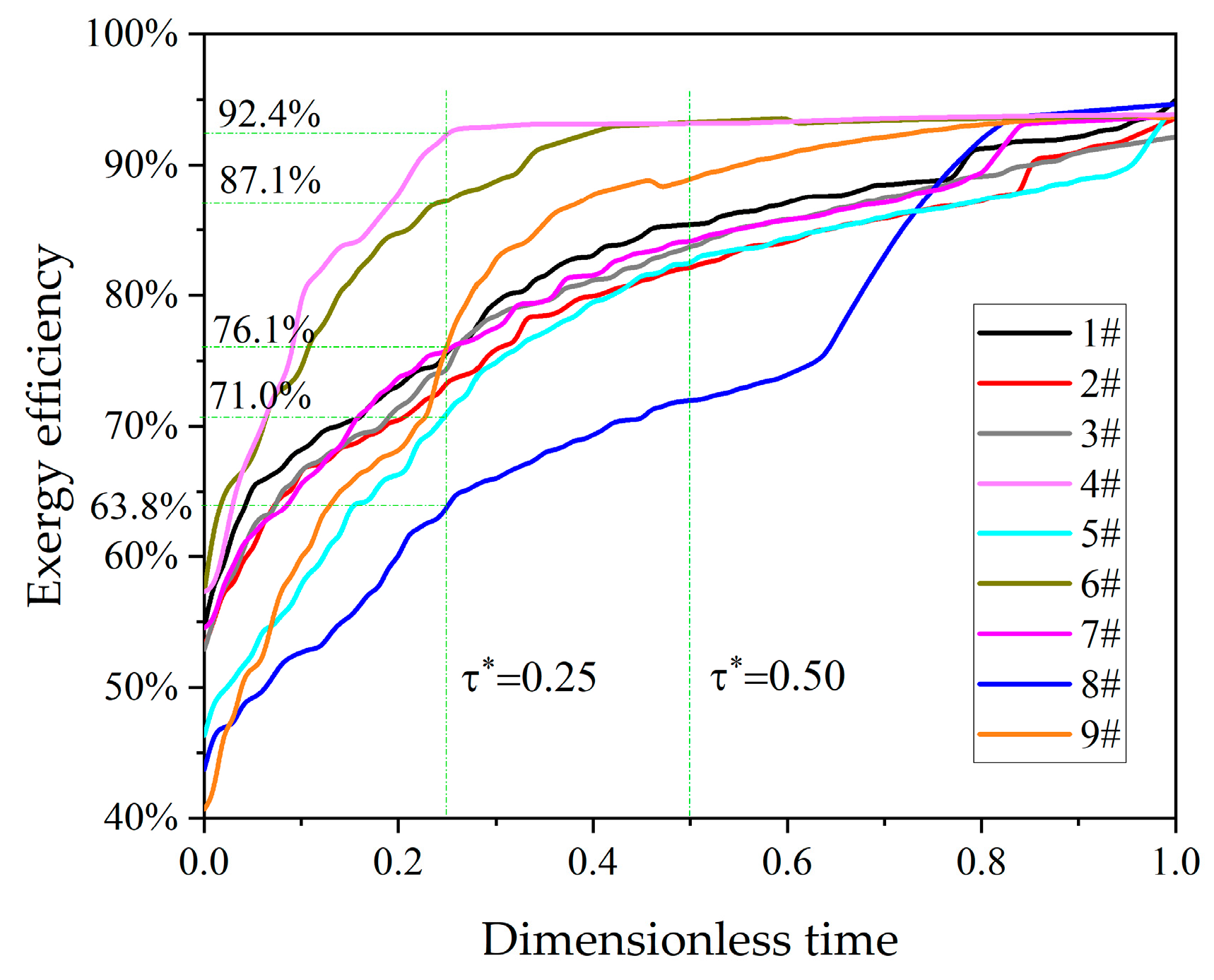
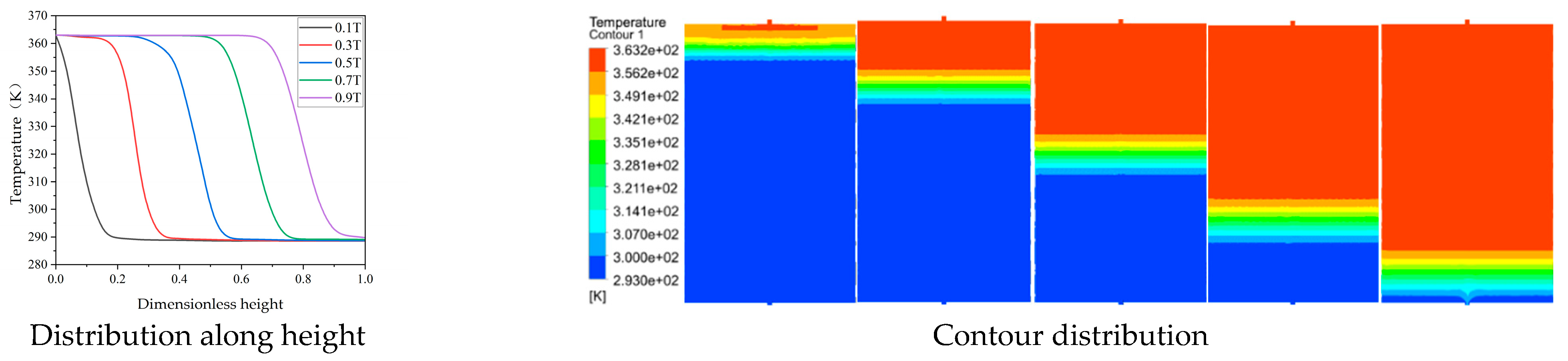
3. Relationship of Non-Uniformity Coefficient, Temperature Stratification, and Exergy Efficiency
4. Universality Verification of Evaluation Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Nomenclature Symbols | p | Pressure/MPa | |
| Non-uniformity coefficient/% | Mass flow rate/kg/s | ||
| Exergy efficiency | Average mass flow rate /kg/s | ||
| λ | Hole distance/mm | Re | Reynolds number |
| μ | Water dynamic viscosity/Pa·s | T | Temperature/K |
| dimensional coefficient of each parameter | x | Flow rate/kg/s | |
| Relative error | Subscripts | ||
| Time/min | * | Dimensionless | |
| u | Water flow velocity/m/s | actual | Actual stratification process |
| d | Hole diameter/mm | c | Calculation result |
| D | Inlet diameter of diffuser/mm | m | Measured result |
| the amount of exergy/J | i | Substitute symbol of hole number | |
| H | Height/m | ideal | Ideal stratification process |
| k | Basic coefficient of solution | Abbreviations | |
| n | Total number of holes | CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
References
- Han, Y.; Wang, R.; Dai, Y. Thermal stratification within the water tank. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Dou, B.; Huang, H.; Zhang, G. The thermal stratification characteristics affected by a novel equalizer in a dynamic hot water storage tank. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 126, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, P.; Salunkhe, N.; Kedare, S.; Bose, M. Experimental investigation of single media thermocline storage with eccentrically mounted vertical porous flow distributor. Sol. Energy 2018, 162, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilotelli, M.; Grassi, B.; Lezzi, A.; Beretta, G. Flow models of perforated manifolds and plates for the design of a large thermal storage tank for district heating with minimal maldistribution and thermocline growth. Appl. Energy 2022, 322, 119436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, L.J.; Furbo, S. Entrance effects in solar storage tanks. Sol. Energy 2003, 75, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Shi, Y.; Ouyang, Z. Optimization design of the octagonal water diffuser with uniform flow orifice plate. J. Energy Storage 2021, 44, 103374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M. Experimental investigation of a stratified chilled-water thermal storage system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2011, 31, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Ortega-Fernández, I.; Müller, R.; Bielsa, D.; Fluri, T. Improved thermocline initialization through optimized inlet design for single-tank thermal energy storage systems. J. Energy Storage 2021, 42, 103088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.Y.; Yan, Q.W. Study of the influence of new type water inlet structure on the characteristics of a solar power stratified water tank. J. Eng. Therm. Energy Power 2016, 31, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowska, K.; Jadwiszczak, P. The impact of inflow velocity on thermal stratification in a water storage tank. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 44, 00079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.F.; Tang, C.Q.; Chen, Z.Q. Simulation study of the velocity field of naturally stratifitied chilled water storage tank diffuser. J. Chongqing Univ. 2011, 34, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, E.M.; Padilla, A.M.; Elkins, C.J.; Eaton, J.K. Three-dimensional velocity measurements in annular diffuser segments including the effects of upstream strut wakes. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2010, 31, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-H.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.-S. Experimental study of inlet structure on the discharging performance of a solar water storage tank. Energy Build. 2014, 70, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.H.; Zhang, F.Y.; Zhang, Y.J. Simulation on performance improvement of single thermocline energy storage tank. Proc. CSEE039 2019, 3, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Seara, J.; Uhı’a, F.J.; Sieres, J. Experimental analysis of a domestic electric hot water storage tank. Part II: Dynamic mode of operation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Marí, E.; Gasque, M.; Gutiérrez-Colomer, R.P.; Ibáñez, F.; González-Altozano, P. A new inlet device that enhances thermal stratification during charging in a hot water storage tank. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 61, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Wen, C.; Zhang, X.S.; Zhou, X. Effect of inlet structure on discharging performance of solar storage tank. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2013, 34, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, A.A. Effect of inlet design on the performance of storage-type domestic electrical water heaters. Appl. Energy 2007, 84, 1338–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, W.; Xie, B.; Aubril, J.; Fan, Y.; Luo, L.; Arrivé, A. Optimized flow distributor for stabilized thermal stratification in a single-medium thermocline storage tank: A numerical and experimental study. Energy 2023, 263, 125709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczęśniak, A.; Milewski, J.; Dybiński, O.; Futyma, K.; Skibiński, J.; Martsinchyk, A.; Szabłowski, Ł. Determination of Thermocline Heat Transfer Coefficient by Using CFD Simulation. Energies 2023, 16, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, K.H.B.; Lim, E.W.C. Dimensionless numbers and correlations for characterizing heat transfer in a pulsating fluidized bed. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 153, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, C.; Teke, I. Developing a new solar radiation estimation model based on Buckingham theorem. Results Phys. 2018, 9, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misic, T.; Najdanovic-Lukic, M.; Nesic, L. Dimensional analysis in physics and the Buckingham theorem. Eur. J. Phys. 2010, 31, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciulla, G.; D’amico, A.; Brano, V.L. Evaluation of building heating loads with dimensional analysis: Application of the Buckingham π theorem. Energy Build. 2017, 154, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haftkhani, A.R.; Arabi, M. Improve regression-based models for prediction of internal-bond strength of particleboard using Buckingham’s pi-theorem. J. For. Res. 2013, 24, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Dou, B.; Huang, H.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z. Experimental and numerical research of thermal stratification with a novel inlet in a dynamic hot water storage tank. Renew. Energy 2017, 111, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaïci, W.; Ghorab, M.; Entchev, E.; Hayden, S. Three-dimensional unsteady CFD simulations of a thermal storage tank performance for optimum design. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 60, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczęśniak, A.; Milewski, J.; Dybiński, O.; Futyma, K.; Skibiński, J.; Martsinchyk, A. Dynamic simulation of a four tank 200 m3 seasonal thermal energy storage system oriented to air conditioning at a dietary supplements factory. Energy 2023, 264, 126106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.L. Research status on stratification of hot water storage tank. Chin. J. Refrig. Technol. 2016, 36, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
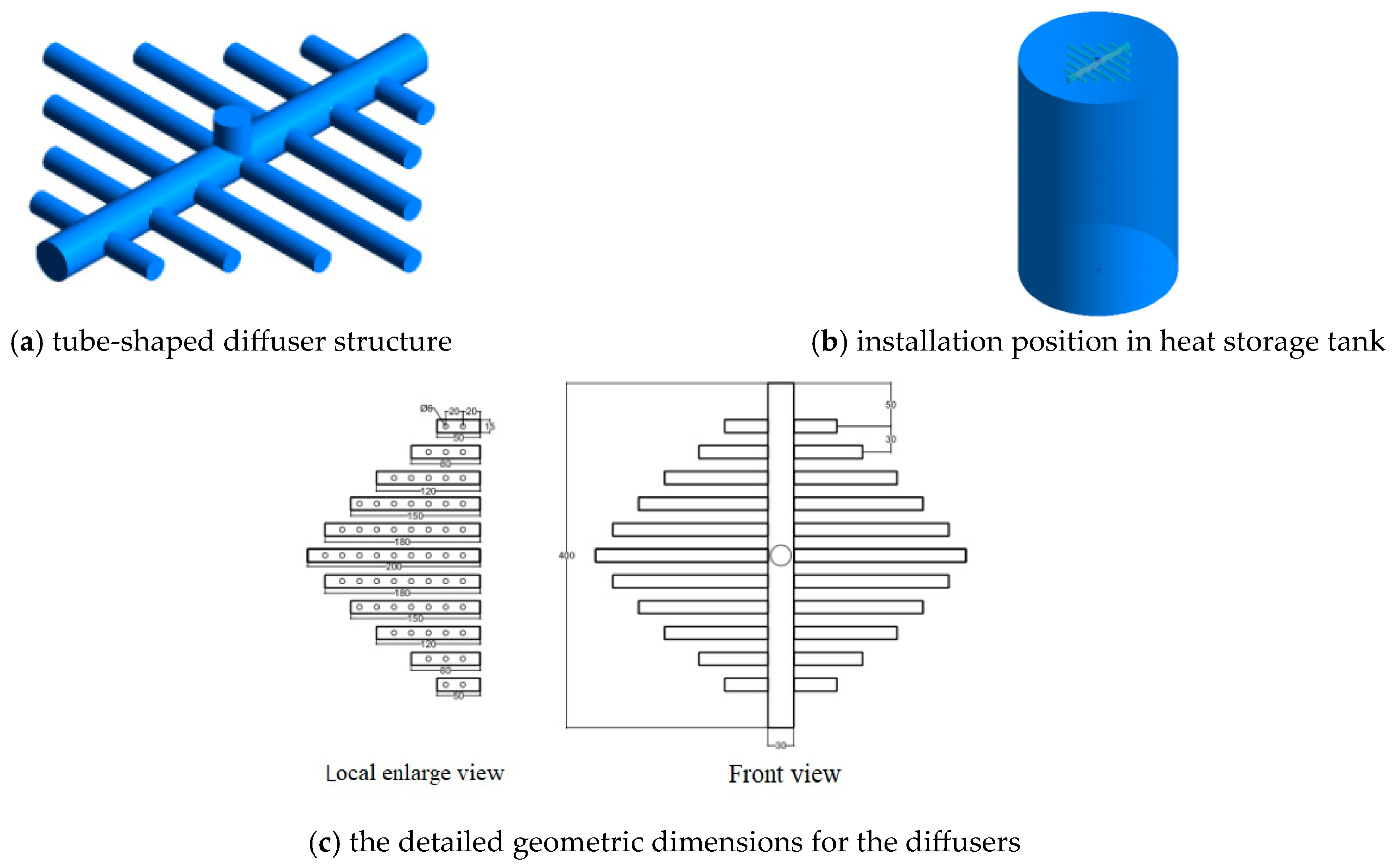
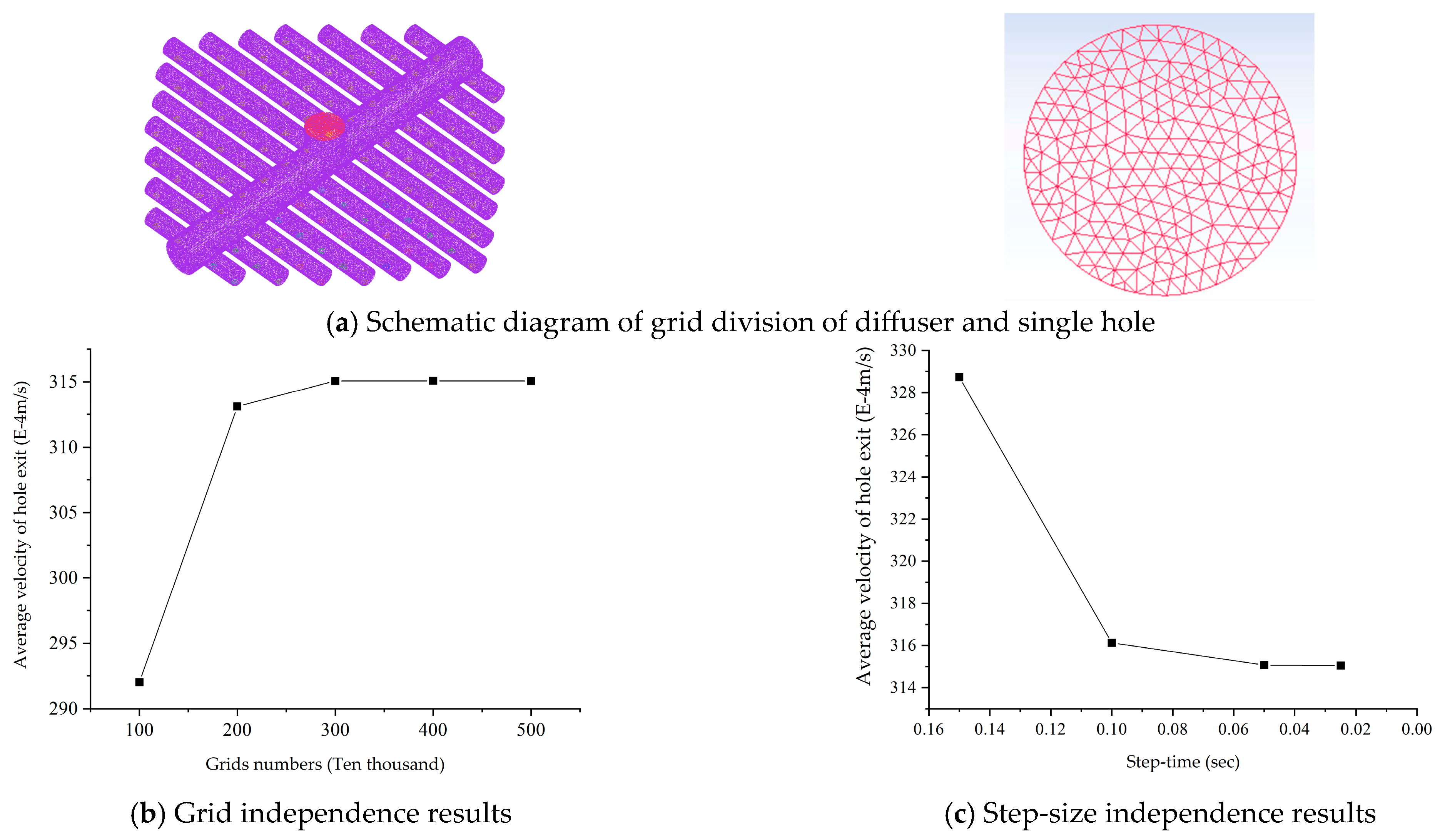

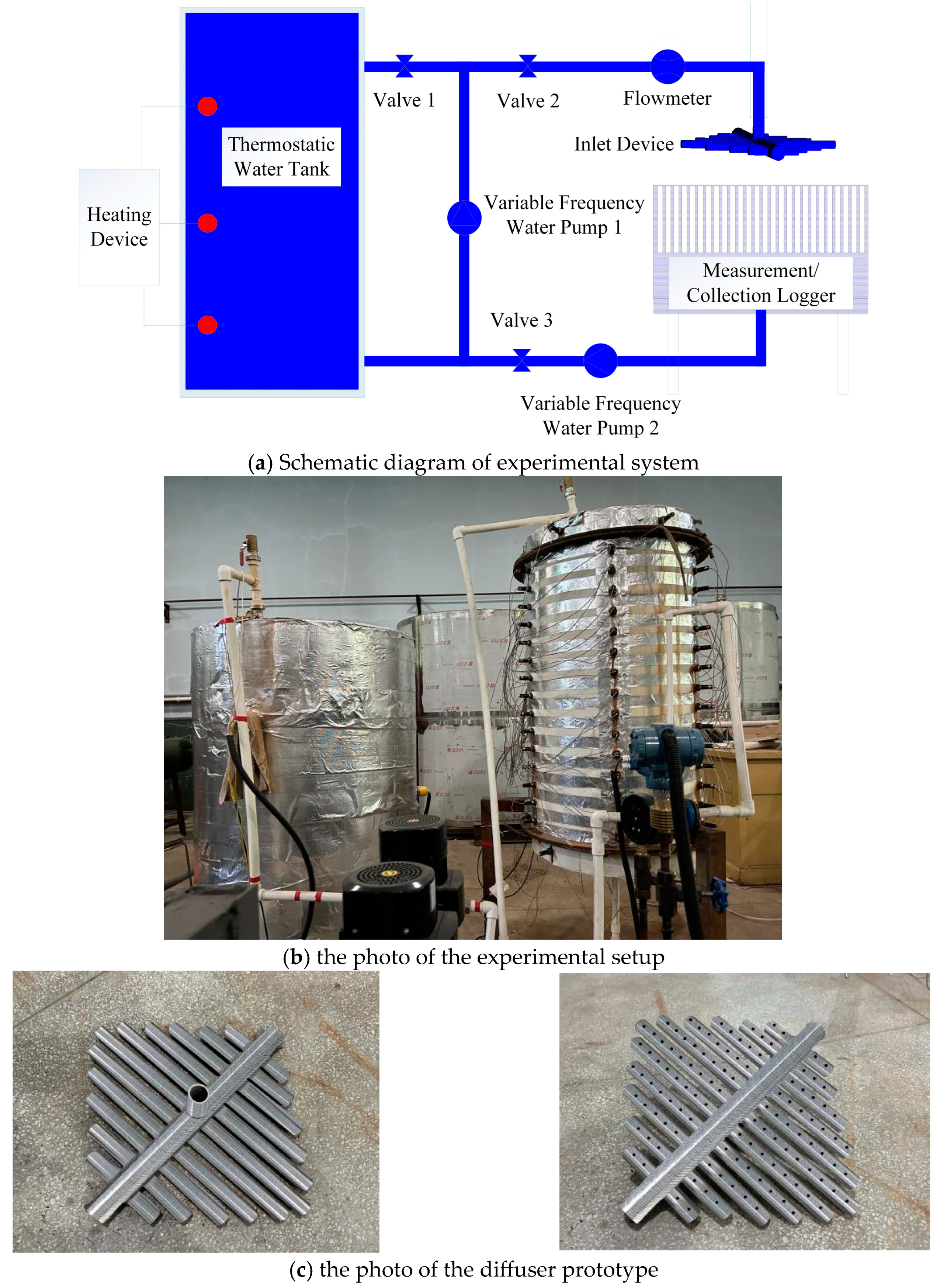
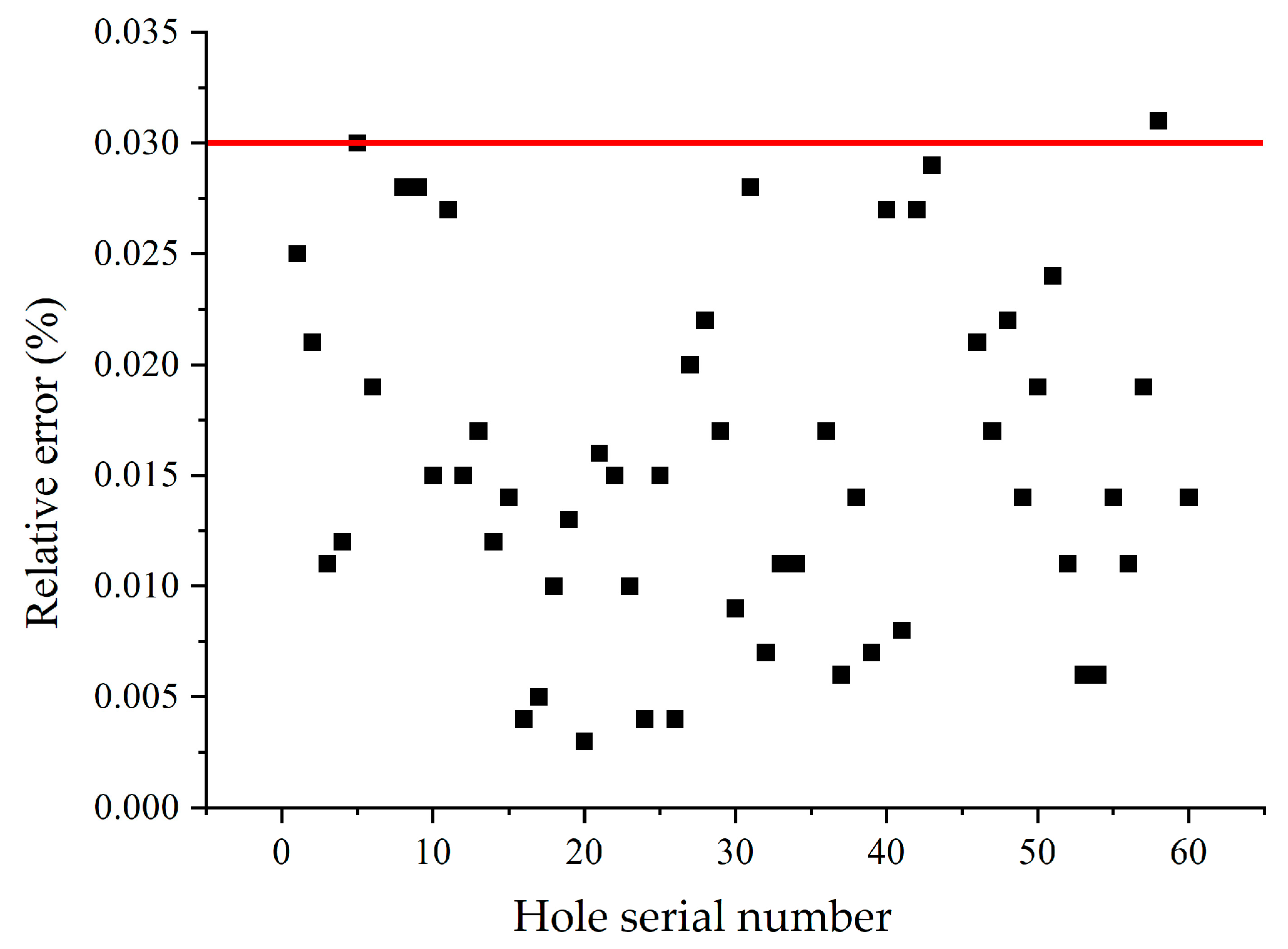





| Serial Number | Inlet Diameter (mm) | Hole Diameter (mm) | Hole Distance (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 20 | 6 | 30 |
| 2# | 20 | 8 | 40 |
| 3# | 30 | 8 | 50 |
| 4# | 40 | 6 | 50 |
| 5# | 40 | 8 | 30 |
| 6# | 30 | 6 | 40 |
| 7# | 20 | 10 | 50 |
| 8# | 30 | 10 | 30 |
| 9# | 40 | 10 | 40 |
| Boundary Conditions | p1 = 101,500 Pa T = 363 K | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Serial Number | u = 0.01 m/s | u = 0.1 m/s | u = 0.5 m/s | u = 0.9 m/s | u = 2.0 m/s | |
| 1# | 46.66% | 53.37% | 53.77% | 49.98% | 58.08% | |
| 2# | 45.54% | 39.49% | 48.76% | 56.9% | 70.37% | |
| 3# | 15.50% | 15.89% | 19.96% | 15.71% | 13.32% | |
| 4# | 4.24% | 8.64% | 3.39% | 6.85% | 6.36% | |
| 5# | 37.76% | 40.81% | 35.98% | 38.54% | 42.45% | |
| 6# | 17.54% | 21.87% | 13.31% | 12.36% | 13.38% | |
| 7# | 50.08% | 47.07% | 58.86% | 55.79% | 45.12% | |
| 8# | 77.15% | 72.71% | 75.17% | 78.02% | 80.02% | |
| 9# | 36.47% | 44.05% | 36.21% | 40.49% | 34.46% | |
| Serial Number | Experimental Measurement (ml/s) | Numerical Simulation Result (ml/s) | Serial Number | Experimental Measurement (ml/s) | Numerical Simulation Result (ml/s) | Serial Number | Experimental Measurement (ml/s) | Numerical Simulation Result (ml/s) | Serial Number | Experimental Measurement (ml/s) | Numerical Simulation Result (ml/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 36.0 | 35.1 | 16 | 20.7 | 20.8 | 31 | 36.0 | 35.0 | 46 | 26.1 | 25.6 |
| 2 | 34.2 | 34.9 | 17 | 18.9 | 19.0 | 32 | 37.8 | 37.5 | 47 | 26.1 | 26.6 |
| 3 | 24.3 | 24.6 | 18 | 27.0 | 26.7 | 33 | 32.4 | 32.0 | 48 | 36.9 | 37.7 |
| 4 | 30.6 | 30.2 | 19 | 28.8 | 28.4 | 34 | 24.3 | 24.6 | 49 | 31.5 | 31.1 |
| 5 | 27.0 | 26.2 | 20 | 35.1 | 35.0 | 35 | 17.1 | 18.9 | 50 | 28.8 | 28.3 |
| 6 | 23.4 | 23.0 | 21 | 36.9 | 36.3 | 36 | 25.2 | 24.8 | 51 | 22.5 | 23.0 |
| 7 | 36.9 | 35.1 | 22 | 38.7 | 38.1 | 37 | 27.9 | 28.1 | 52 | 25.2 | 24.9 |
| 8 | 28.8 | 28.0 | 23 | 30.6 | 30.3 | 38 | 31.5 | 31.1 | 53 | 27.9 | 27.7 |
| 9 | 25.2 | 24.5 | 24 | 24.3 | 24.2 | 39 | 38.7 | 38.4 | 54 | 28.8 | 29.0 |
| 10 | 23.4 | 23.0 | 25 | 23.4 | 23.0 | 40 | 33.3 | 32.4 | 55 | 25.2 | 24.8 |
| 11 | 27.0 | 26.3 | 26 | 21.6 | 21.5 | 41 | 34.2 | 33.9 | 56 | 29.7 | 30.0 |
| 12 | 31.5 | 31.0 | 27 | 22.5 | 22.1 | 42 | 27.0 | 26.3 | 57 | 27.9 | 27.4 |
| 13 | 35.1 | 34.5 | 28 | 28.8 | 28.2 | 43 | 27.9 | 28.7 | 58 | 26.1 | 25.3 |
| 14 | 28.8 | 28.5 | 29 | 36.0 | 36.6 | 44 | 25.2 | 23.4 | 59 | 27.9 | 35.1 |
| 15 | 63.0 | 62.1 | 30 | 38.7 | 38.3 | 45 | 10.8 | 18.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, L.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z. Evaluation Method and Analysis on Performance of Diffuser in Heat Storage Tank. Energies 2024, 17, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030618
Cao L, Yu J, Liu X, Wang Z. Evaluation Method and Analysis on Performance of Diffuser in Heat Storage Tank. Energies. 2024; 17(3):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030618
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Lihua, Jingwen Yu, Xifeng Liu, and Zhanzhou Wang. 2024. "Evaluation Method and Analysis on Performance of Diffuser in Heat Storage Tank" Energies 17, no. 3: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030618
APA StyleCao, L., Yu, J., Liu, X., & Wang, Z. (2024). Evaluation Method and Analysis on Performance of Diffuser in Heat Storage Tank. Energies, 17(3), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030618





