Slow Pyrolysis of De-Oiled Rapeseed Cake: Influence of Pyrolysis Parameters on the Yield and Characteristics of the Liquid Obtained
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Feedstock
2.2. Pyrolysis System and Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of Feedstock
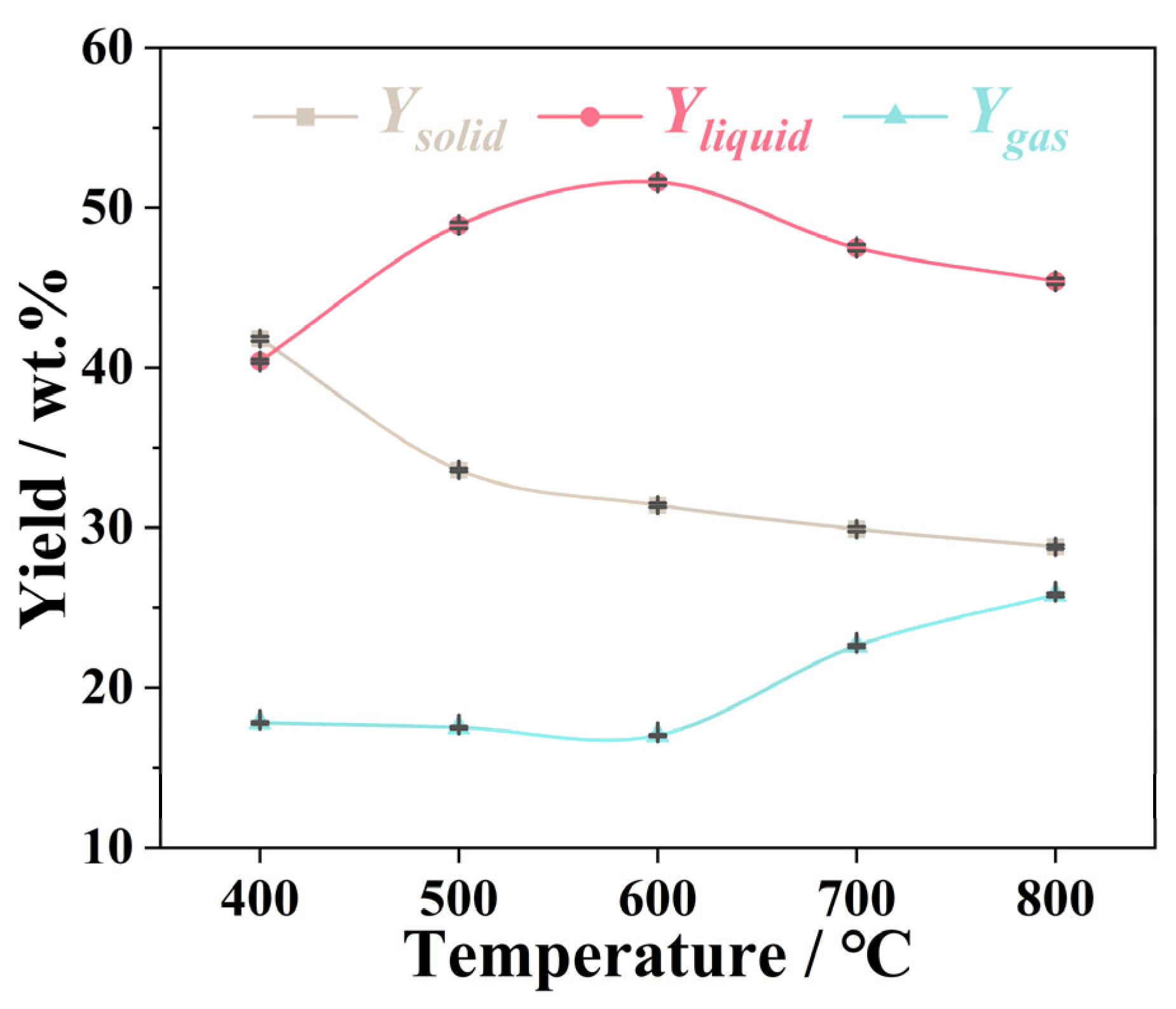
3.2. Effect of Pyrolysis Temperatures on Products Distribution
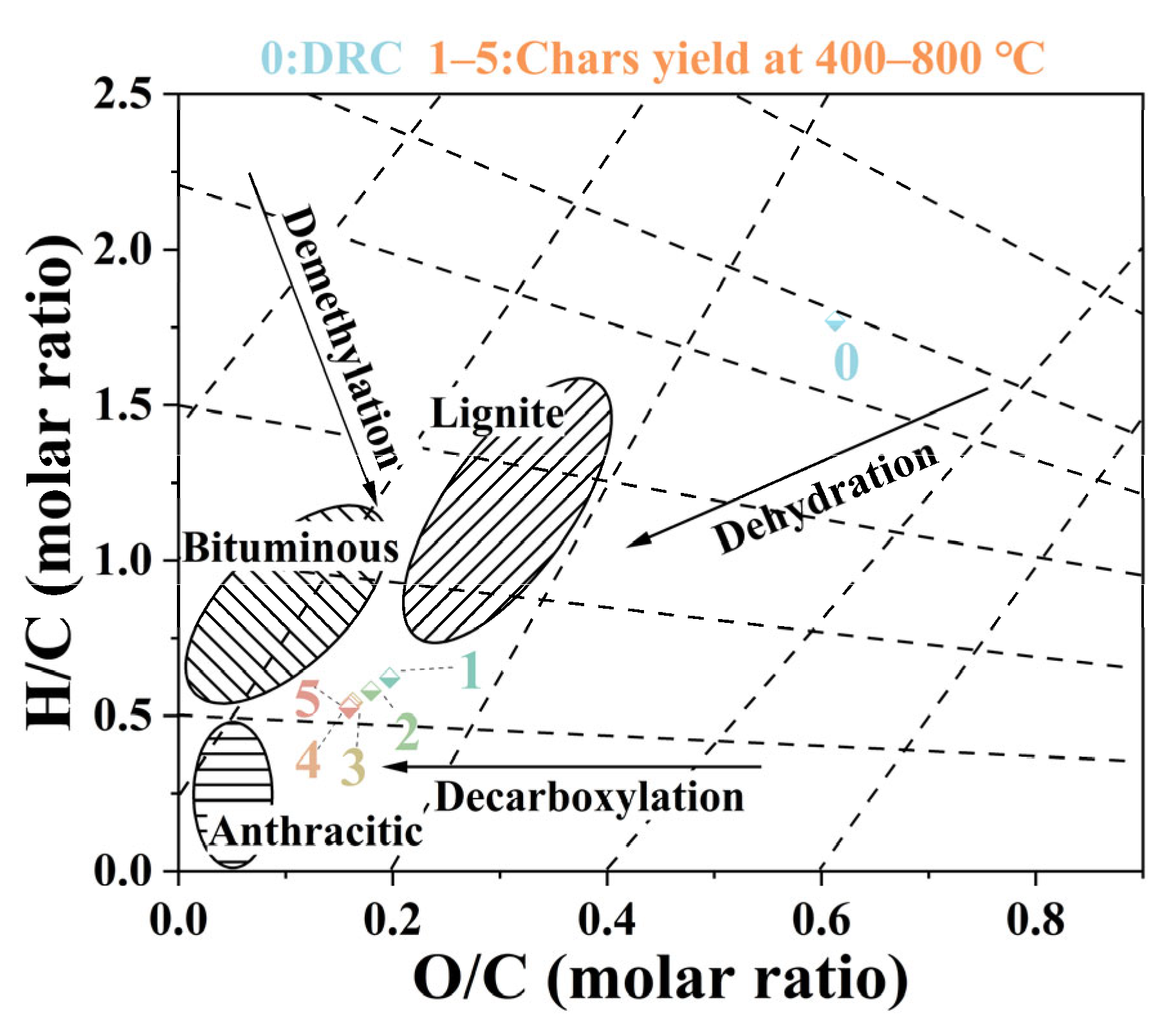
3.3. Effect of Pyrolysis Temperatures on Characteristics of Bio-Chars
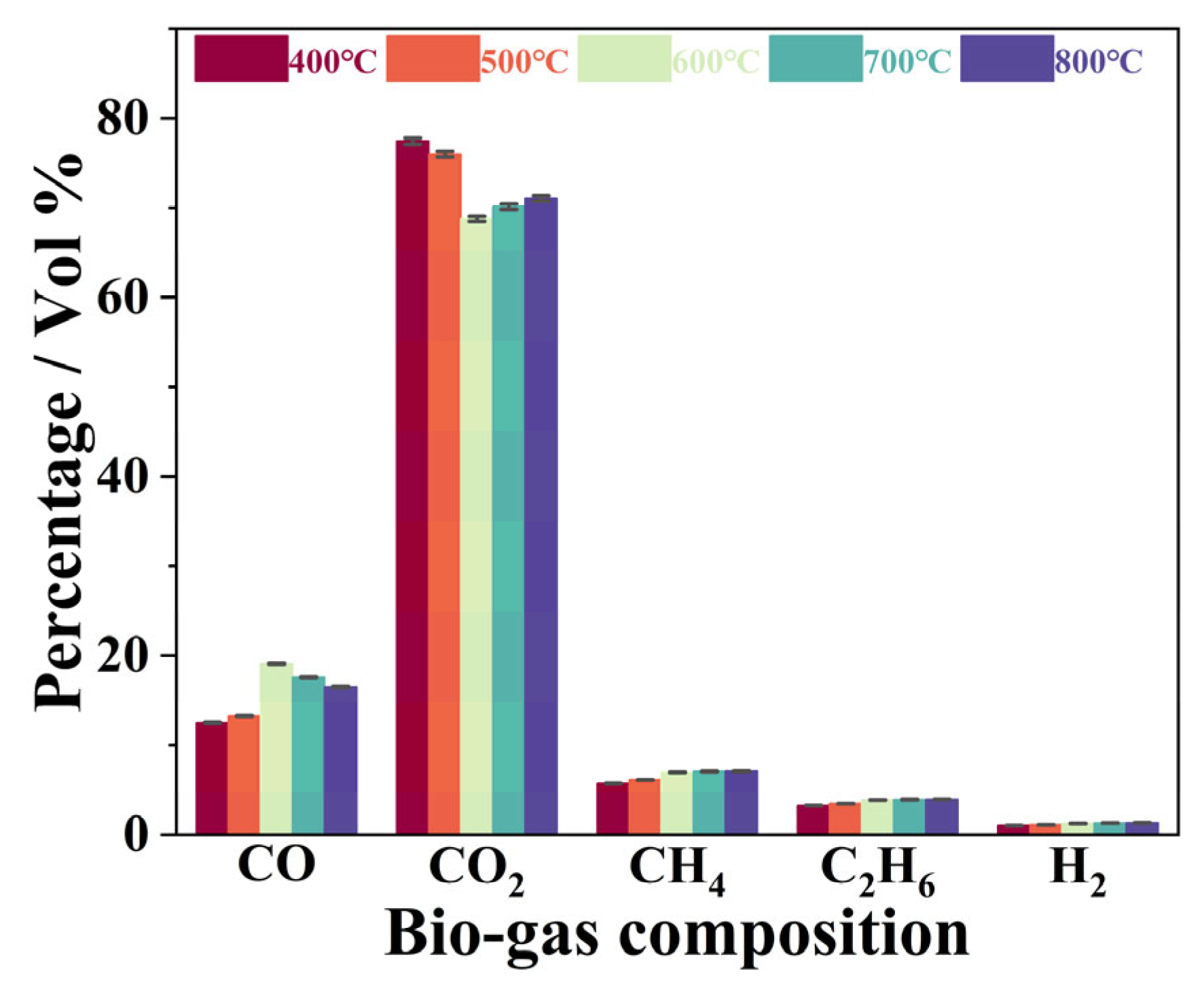
3.4. Effect of Pyrolysis Temperatures on Composition of Gaseous Products Obtained
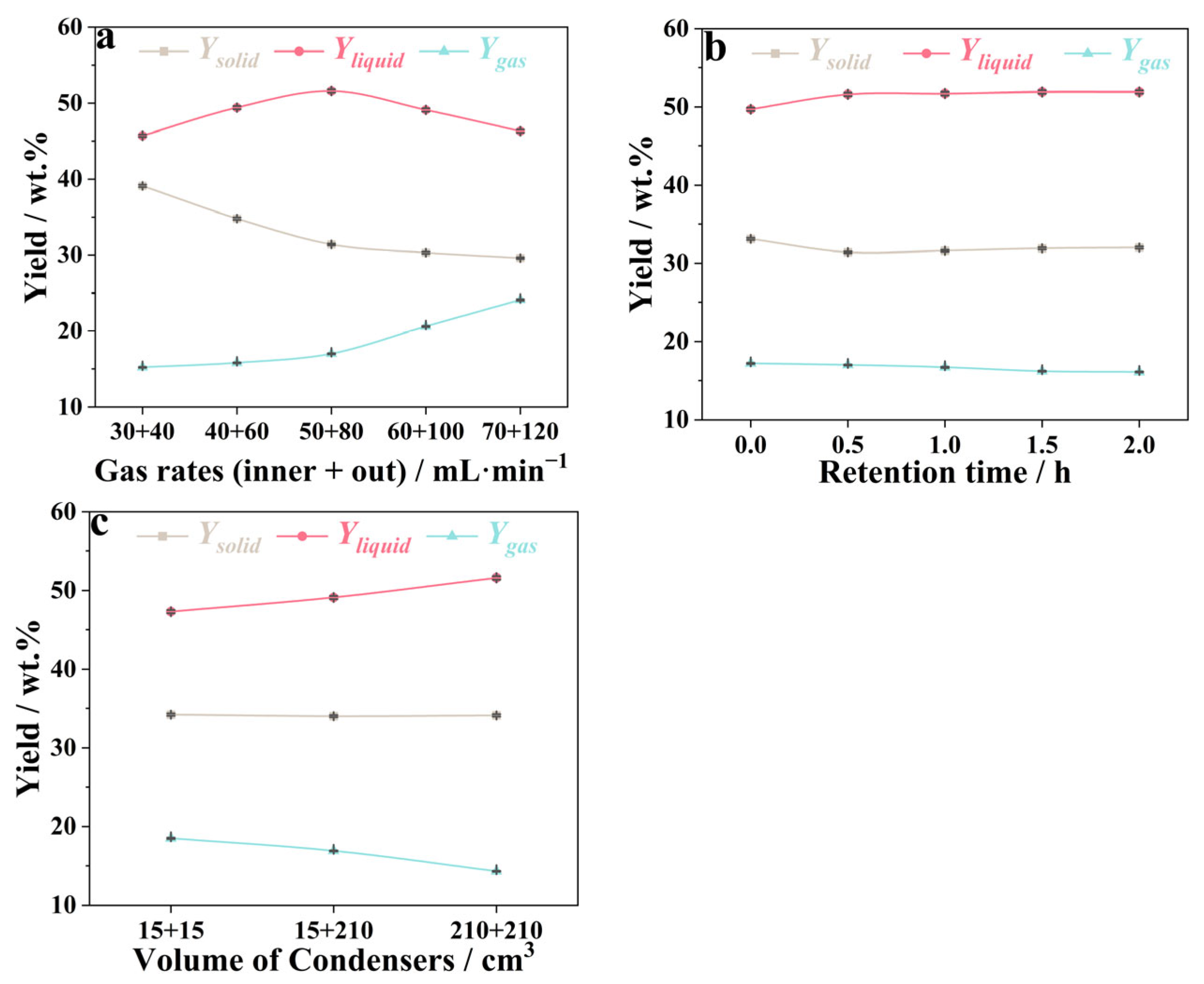
3.5. Optimization of Pyrolysis Parameters
3.6. Characteristic of Bio-Oil Obtained from DRC Pyrolysis with Optimized Parameters
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.M. Carbon neutrality: Toward a sustainable future. Innovation 2021, 2, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queneau, Y.; Han, B. Biomass: Renewable carbon resource for chemical and energy industry. Innovation 2021, 3, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Harindintwali, J.D.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Yin, Z.; Huang, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Technologies and perspectives for achieving carbon neutrality. Innovation 2021, 2, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Bartocci, P.; Fantozzi, F.; Masek, O.; Agblevor, F.A.; Wei, Z.; Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Lu, X.; et al. Prospective contributions of biomass pyrolysis to China’s 2050 carbon reduction and renewable energy goals. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obersteiner, M.; Bednar, J.; Wagner, F.; Gasser, T.; Ciais, P.; Forsell, N.; Frank, S.; Havlik, P.; Valin, H.; Janssens, I.A.; et al. How to spend a dwindling greenhouse gas budget. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.; Peters, G. The trouble with negative emissions. Science 2016, 354, 182–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-J.; Li, W.-W.; Jiang, H.; Yu, H.-Q. Fates of Chemical Elements in Biomass during Its Pyrolysis. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6367–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Karim, A.M.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y. Catalytic fast pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7594–7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, S.-F.; Huang, B.-C.; Shen, X.-C.; Chen, W.-J.; Zhou, T.-P.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Cheng, B.-H.; Wu, C.-Z.; Li, W.-W.; et al. Sustainable production of value-added carbon nanomaterials from biomass pyrolysis. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vispute, T.P.; Zhang, H.; Sanna, A.; Xiao, R.; Huber, G.W. Renewable Chemical Commodity Feedstocks from Integrated Catalytic Processing of Pyrolysis Oils. Science 2010, 330, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.H.; Huang, B.C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Y.L.; Jiang, S.F.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.S.; Jiang, H.; Yu, H.Q. Bio-coal: A renewable and massively producible fuel from lignocellulosic biomass. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Yang, Q.; Hao, H.; Zhu, B.; Chen, H. Torrefaction of agriculture straws and its application on biomass pyrolysis poly-generation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 156, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Che, Q.; Cui, X.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, H. Application of biomass pyrolytic polygeneration by a moving bed: Characteristics of products and energy efficiency analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 254, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, Q.; Chen, H. Application of biomass pyrolytic polygeneration technology using retort reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigljević, B.; Liu, J.J.; Lim, H. Comprehensive feasibility assessment of a poly-generation process integrating fast pyrolysis of S. japonica and the Rankine cycle. Appl. Energ. 2019, 254, 113704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wu, L. Design and optimization of poly-generation system for municipal solid waste disposal. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.; Meng, H.; Mašek, O.; Yao, Z.; Li, L.; Yu, B.; Qin, C.; Zhao, L. Comprehensive analysis of industrial-scale heating plants based on different biomass slow pyrolysis technologies: Product property, energy balance, and ecological impact. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 6, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, J.; Oasmaa, A.; Solantausta, Y.; Kytö, M.; Chiaramonti, D. Review of fuel oil quality and combustion of fast pyrolysis bio-oils from lignocellulosic biomass. Appl. Energ. 2014, 116, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stas, M.; Kubicka, D.; Chudoba, J.; Pospísil, M. Overview of Applications of Pyrolysis Bio-oil. Chem. Listy 2015, 109, 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U.; Steele, P.H. Pyrolysis of wood/biomass for bio-oil: A critical review. Energ. Fuel 2006, 20, 848–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.N.; Jensen, P.A.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Knudsen, N.O.; Sorensen, H.R.; Hvilsted, S. Comparison of Lignin, Macroalgae, Wood, and Straw Fast Pyrolysis. Energ. Fuel 2013, 27, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.L.; Wu, Q.Y.; Yang, C.Y. Fast pyrolysis of microalgae to produce renewable fuels. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2004, 71, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.F.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, Q.L.; Gholizadeh, M.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Xiang, J.; Hu, X. Pyrolysis of soybean residue: Understanding characteristics of the products. Renew. Energy 2021, 174, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpoot, L.; Tagade, A.; Deshpande, G.; Verma, K.; Geed, S.R.; Patle, D.S.; Sawarkar, A.N. An overview of pyrolysis of de-oiled cakes for the production of biochar, bio-oil, and pyro-gas: Current status, challenges, and future perspective. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 19, 101205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, S.; Ozkan, A.R. Characterization of products from the pyrolysis of rapeseed oil cake. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8771–8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcimen, D.; Karaosmanoglu, F. Production and characterization of bio-oil and biochar from rapeseed cake. Renew. Energ. 2004, 29, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, M.A.; Islam, M.R.; Parveen, M.; Haniu, H.; Takai, K. Pyrolysis decomposition of tamarind seed for alternative fuel. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 149, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensoz, S.; Angin, D. Pyrolysis of safflower (Charthamus tinctorius L.) seed press cake: Part 1. The effects of pyrolysis parameters on the product yields. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5492–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Shadangi, K.P. Liquid fuel from castor seeds by pyrolysis. Fuel 2011, 90, 2538–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wurzer, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Lv, X.; Mašek, O.; Hu, C. Enhancing the production of small molecular products from pubescens via stepwise pyrolysis process. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 168, 105708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.X.; Fu, X.; Li, J.D.; Wang, Y.; Lv, X.Y.; Hu, C.W. Effect of Heating Rate on Yields and Distribution of Oil Products from the Pyrolysis of Pubescen. Energy Technol. 2018, 6, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Jiang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Tong, D.; Hu, C. Low-Temperature Torrefaction of Phyllostachys heterocycla cv. pubescens: Effect of Two Torrefaction Procedures on the Composition of Bio-Oil Obtained. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4869–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fan, X.; Jiang, B.; Mu, L.; Yao, P.; Yin, H.; Song, X. Pyrolysis of oil-plant wastes in a TGA and a fixed-bed reactor: Thermochemical behaviors, kinetics, and products characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moško, J.; Pohořelý, M.; Skoblia, S.; Beňo, Z.; Jeremiáš, M. Detailed Analysis of Sewage Sludge Pyrolysis Gas: Effect of Pyrolysis Temperature. Energies 2020, 13, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Ouadi, M.; Jahangiri, H.; Hornung, A. Valorisation of lignocellulosic biomass investigating different pyrolysis temperatures. J. Energy Inst. 2020, 93, 1960–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogancioglu, M.; Yel, E.; Ahmetli, G. Pyrolysis of waste high density polyethylene (HDPE) and low density polyethylene (LDPE) plastics and production of epoxy composites with their pyrolysis chars. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, R.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, L. Comparative study on characteristics of the bio-oil from microwave-assisted pyrolysis of lignocellulose and triacylglycerol. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, X.; Li, Y.; Han, L. Effect of pyrolysis temperature and correlation analysis on the yield and physicochemical properties of crop residue biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 296, 122318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, L.R.; Torres, E.; Zalazar, D.; Zhang, H.; Rodriguez, R.; Mazza, G. Influence of pyrolysis temperature and bio-waste composition on biochar characteristics. Renew. Energ. 2020, 155, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Konvalina, P.; Neugschwandtner, R.W.; Soja, G.; Bárta, J.; Chen, W.-H.; Amirahmadi, E. How do different feedstocks and pyrolysis conditions effectively change biochar modification scenarios? A critical analysis of engineered biochars under H2O2 oxidation. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2024, 300, 117924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.M.; Boddu, V.M.; Jackson, M.A.; Moser, B.; Ray, P. Pyrolysis of creosote -treated railroad ties to recover creosote and produce biochar. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 149, 104826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierski, P.; Hercel, P.; Januszewicz, K.; Kardas, D. Pre-Treatment of Furniture Waste for Smokeless Charcoal Production. Materials 2020, 13, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, M.; Rosi, L.; Giovannelli, A.; Frediani, P.; Frediani, M. Characterization of bio-oil and bio-char produced by low-temperature microwave-assisted pyrolysis of olive pruning residue using various absorbers. Waste Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Hu, Q.; Hao, W.; Ma, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, B. Products distribution and kinetic analysis on gaseous products during fast pyrolysis of two kinds of biomass pellet. Fuel 2019, 249, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Daud, W.M.A.W.; Abbas, H.F. Effects of pyrolysis parameters on hydrogen formations from biomass: A review. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 10467–10490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanavath, K.N.; Bankupalli, S.; Sugali, C.S.; Perupogu, V.; V Nandury, S.; Bhargava, S.; Parthasarathy, R. Optimization of process parameters for slow pyrolysis of neem press seed cake for liquid and char production. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Ferreira Martins, M.; Debenest, G. Pyrolysis of waste polyethylene in a semi-batch reactor to produce liquid fuel: Optimization of operating conditions. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2021, 237, 114114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pütün, E. Catalytic pyrolysis of biomass: Effects of pyrolysis temperature, sweeping gas flow rate and MgO catalyst. Energy 2010, 35, 2761–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, X. Coupling effect of condensing temperature and residence time on bio-oil component enrichment during the condensation of biomass pyrolysis vapors. Fuel 2020, 274, 117861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papari, S.; Hawboldt, K.; Fransham, P. Study of selective condensation for woody biomass pyrolysis oil vapours. Fuel 2019, 245, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.D.; Lv, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.X.; Hu, C.W. Hydrotreatment Upgrading of Bio-oil from Torrefaction of Pubescens in Alcohol over Pd/NbOPO4. Acs Omega 2018, 3, 4836–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanoglu, A.; Yumrutas, R. Rotary kiln and batch pyrolysis of waste tire to produce gasoline and diesel like fuels. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2016, 111, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nautiyal, P.; Subramanian, K.A.; Dastidar, M.G. Production and characterization of biodiesel from algae. Fuel Process Technol. 2014, 120, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagu, R.M.; Sundaram, E.G. Preparation and characterization of pyrolytic oil through pyrolysis of neem seed and study of performance, combustion and emission characteristics in CI engine. J. Energy Inst. 2018, 91, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knothe, G.; Razon, L.F. Biodiesel fuels. Prog. Energ. Combust. 2017, 58, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, C.; Mourant, D.; He, M.; Gunawan, R.; Li, X.; Li, C.Z. An FT-IR spectroscopic study of carbonyl functionalities in bio-oils. Fuel 2011, 90, 3417–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, D.C.P.; Ramirez, C.X.; Chaparro, J.A.S.; Thomas, M.J.; Gavard, R.; Jones, H.E.; Hernandez, R.C.; Mejia-Ospino, E.; Barrow, M.P. Characterization of bio-crude components derived from pyrolysis of soft wood and its esterified product by ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry and spectroscopic techniques. Fuel 2020, 259, 116085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, B.B.; Apaydin-Varol, E.; Ates, F.; Ozbay, N.; Putun, A.E. Synthetic fuel production from tea waste: Characterisation of bio-oil and bio-char. Fuel 2010, 89, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.Y.; Yang, H.M.; Wu, H.; Wang, M.; Cheng, D.Q. Catalytic pyrolysis of rice husk by mixing with zinc oxide: Characterization of bio-oil and its rheological behavior. Fuel Process Technol. 2013, 106, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, R.; Ramesh, K.; Shameer, P.M.; Purnachandran, R. Experimental investigation on improvement of storage stability of bio-oil derived from intermediate pyrolysis of Calophyllum inophyllum seed cake. J. Energy Inst. 2019, 92, 768–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.D.; Li, J.M.; Jiang, Z.C.; Hu, C.W. Performances of Several Solvents on the Cleavage of Inter- and Intramolecular Linkages of Lignin in Corncob Residue. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 1494–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, E.; Kopac, J. Pyrolysis of rapeseed oil cake in a fixed bed reactor to produce bio-oil. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 134, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Tong, D.; Hu, C. Microwave-enhanced pyrolysis of natural algae from water blooms. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 212, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.Z.; Lei, X.M.; Zhou, L.Y.; Peng, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, H.R.; Li, D.; Hu, C.W.; Garcia, H. Bimetallic Ni and Mo Nitride as an Efficient Catalyst for Hydrodeoxygenation of Palmitic Acid. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 4333–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Guo, K.; Li, D.; Yang, H.Q.; Hu, C.W. Production of high-grade diesel from palmitic acid over activated carbon-supported nickel phosphide catalysts. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2016, 187, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, C.W.M.; Noor, M.M.; Mamat, R. Biodiesel as alternative fuel for marine diesel engine applications: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2018, 94, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbers, M.M.E.; Zhang, W.Y.; Tonin, F.; Hollmann, F. Light-Driven Enzymatic Decarboxylation of Fatty Acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 13648–13651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.T.; Wu, Y.Q.; Sutor, A.; Burek, B.O.; Hollmann, F.; Bloh, J.Z. Intensification of Photobiocatalytic Decarboxylation of Fatty Acids for the Production of Biodiesel. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.T.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, L.Y.; Li, Z.M. Catalytic upgrading of Jatropha oil biodiesel by partial hydrogenation using Raney-Ni as catalyst under microwave heating. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2018, 163, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Zeng, Y.Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, L.; Duan, P.G.; Luque, R.; Ge, R.; Zhang, W.Y. Advances in catalytic decarboxylation of bioderived fatty acids to diesel-range alkanes. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2022, 158, 112178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Fang, Y.; Li, K.X.; Chen, Z.Q.; Xia, M.W.; Gong, M.; Chen, Y.Q.; Yang, H.P.; Tu, X.; Chen, H.P. Bamboo wastes catalytic pyrolysis with N-doped biochar catalyst for phenols products. Appl. Energ. 2020, 260, 114242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, I. Methods in Agricultural Chemical Analysis, A Practical Handbook, by N. T. FAITHFULL. xxii+266 pp. Wallingford: CABI Publishing. £60.00 (hardback). ISBN 0 85199 608 6; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; Volume 140, p. 249. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, W.Y.; Hu, C.W.; Li, G.Y.; Guo, L.H.; Yang, Y.; Luo, J.; Miao, X.; Du, Y. Catalytic pyrolysis of several kinds of bamboos over zeolite NaY. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, A.; Padouvas, E.; Rotter, H.; Varmuza, K. Prediction of heating values of biomass fuel from elemental composition. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 544, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
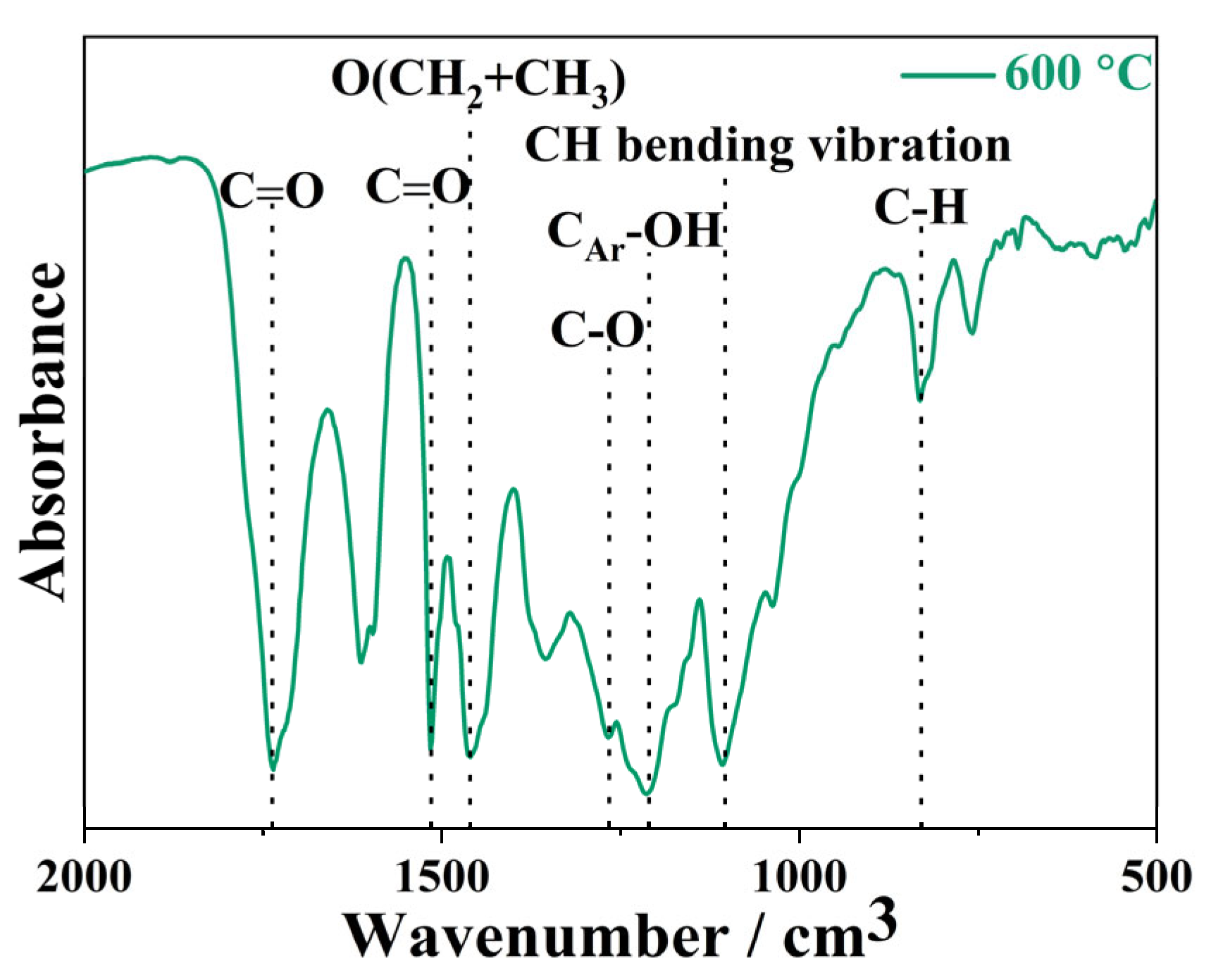
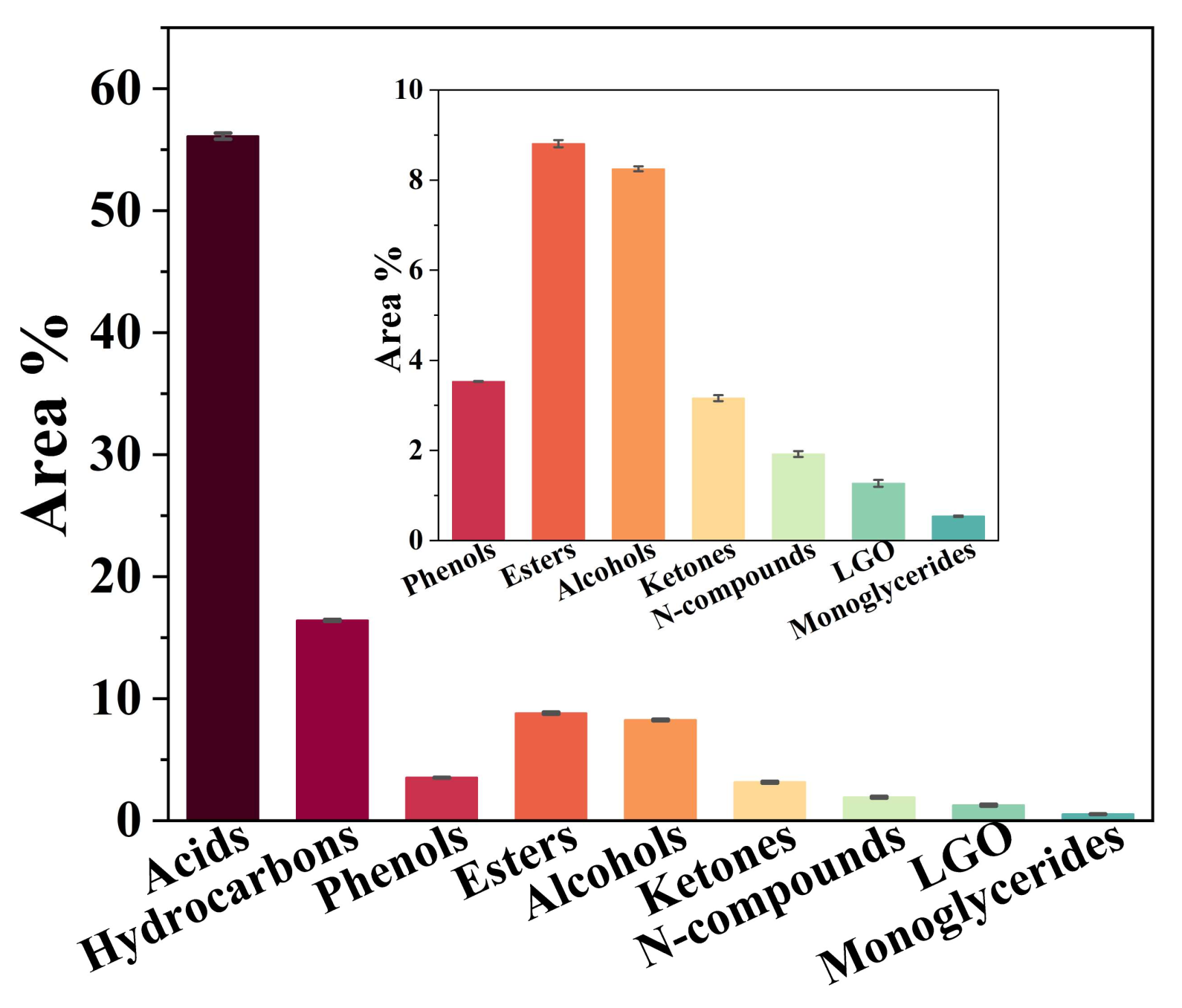
| Proximate Analysis (wt.%) | Ultimate Analysis (wt.%) | Composition Analysis (wt.%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VM a | 71.87 | C | 46.96 | Cellulose | 9.89 |
| FC b | 20.98 | H | 6.98 | Hemicellulose | 18.07 |
| Ash | 5.69 | N | 6.67 | Lignin | 14.32 |
| Moisture | 1.46 | O c | 38.36 | Protein | 34.48 |
| S | 1.03 | Extractives | 15.13 | ||
| H/C | 1.77 | ||||
| O/C | 0.61 | ||||
| HHV d, MJ·kg−1 | 19.62 | ||||
| Ultimate Analysis/wt.% | Category | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis Bio-Oil of DRC | Pyrolysis Bio-Oil of Lignocellulosic Biomass [37,51] | Bio-Diesel [52,53,54,55] | Petroleum Diesel [52,53] | |
| C | 67.41 | 53.56–61.19 | 59.94–78.10 | 86.58 |
| H | 8.64 | 4.91–7.98 | 11.00–12.40 | 13.29 |
| N | 8.99 | 0.53–2.48 | 0.07–0.50 | 0.01 |
| S | 0.55 | - | 0.06–0.31 | <0.11 |
| O a | 14.41 | 25.39–36.39 | 9.23–23.87 | 0.01 |
| H/C atomic ratio | 1.53 | 0.96–1.77 | 1.89–2.18 | 1.83 |
| O/C atomic ratio | 0.16 | 0.36–0.50 | 0.09–0.30 | <0.001 |
| Moisture/wt.% | 4.87 | >10 | <0.05 | <0.03 |
| Viscosity (40 °C, mm2·s−1) | 413.22 | - | 5.66–5.82 | 2–4.5 |
| TAN (mg KOH/g) | 44.51 | - | <0.5 | <0.5 |
| Density (g/mL) | 1.21 | - | >0.86 | 0.86–0.90 |
| Surface tension (25 °C mN·m−1) | 24.10 | - | - | - |
| HHV (MJ·kg−1) | 32.82 | 21.37–26.96 | 20.80–41 | >43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, C. Slow Pyrolysis of De-Oiled Rapeseed Cake: Influence of Pyrolysis Parameters on the Yield and Characteristics of the Liquid Obtained. Energies 2024, 17, 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030612
Wang Y, Zhao Y, Hu C. Slow Pyrolysis of De-Oiled Rapeseed Cake: Influence of Pyrolysis Parameters on the Yield and Characteristics of the Liquid Obtained. Energies. 2024; 17(3):612. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030612
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yue, Yuanjiang Zhao, and Changwei Hu. 2024. "Slow Pyrolysis of De-Oiled Rapeseed Cake: Influence of Pyrolysis Parameters on the Yield and Characteristics of the Liquid Obtained" Energies 17, no. 3: 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030612
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhao, Y., & Hu, C. (2024). Slow Pyrolysis of De-Oiled Rapeseed Cake: Influence of Pyrolysis Parameters on the Yield and Characteristics of the Liquid Obtained. Energies, 17(3), 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030612







