Performance Predictions of Solar-Assisted Heat Pumps: Methodological Approach and Comparison Between Various Artificial Intelligence Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Description
3. Methodology
3.1. Machine Learning Method
3.1.1. MLP Algorithm with Back Propagation (MLP Neural Network)
3.1.2. SVR Algorithm
3.1.3. Random Forest
3.2. Model Performance Evaluation
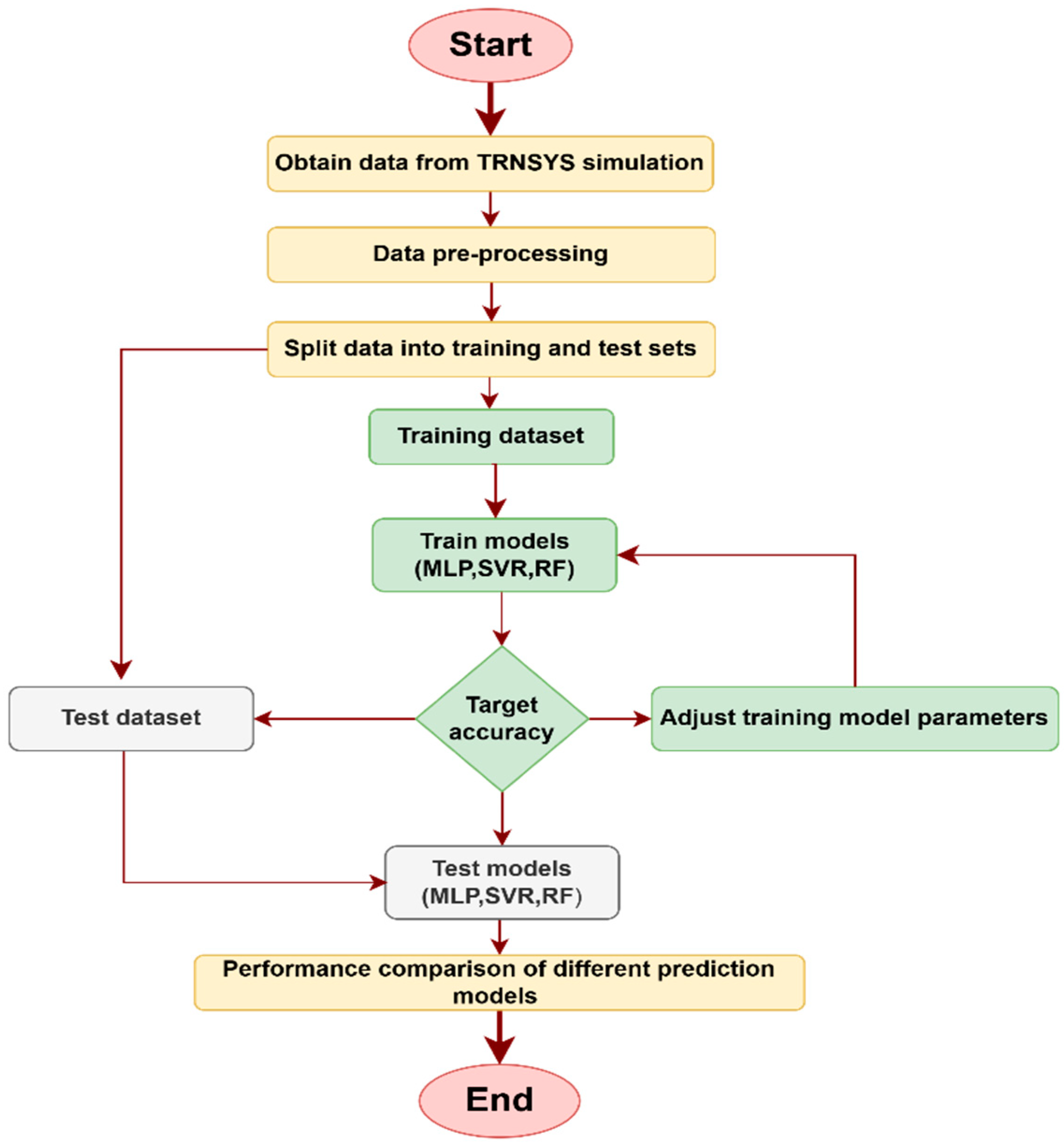
4. Machine Learning Modeling
4.1. Database and Data Preprocessing
4.1.1. Data Outliers and Detection
4.1.2. Min–Max Normalization Cop (Output)
4.2. Modeling Optimization
5. Result and Discussion
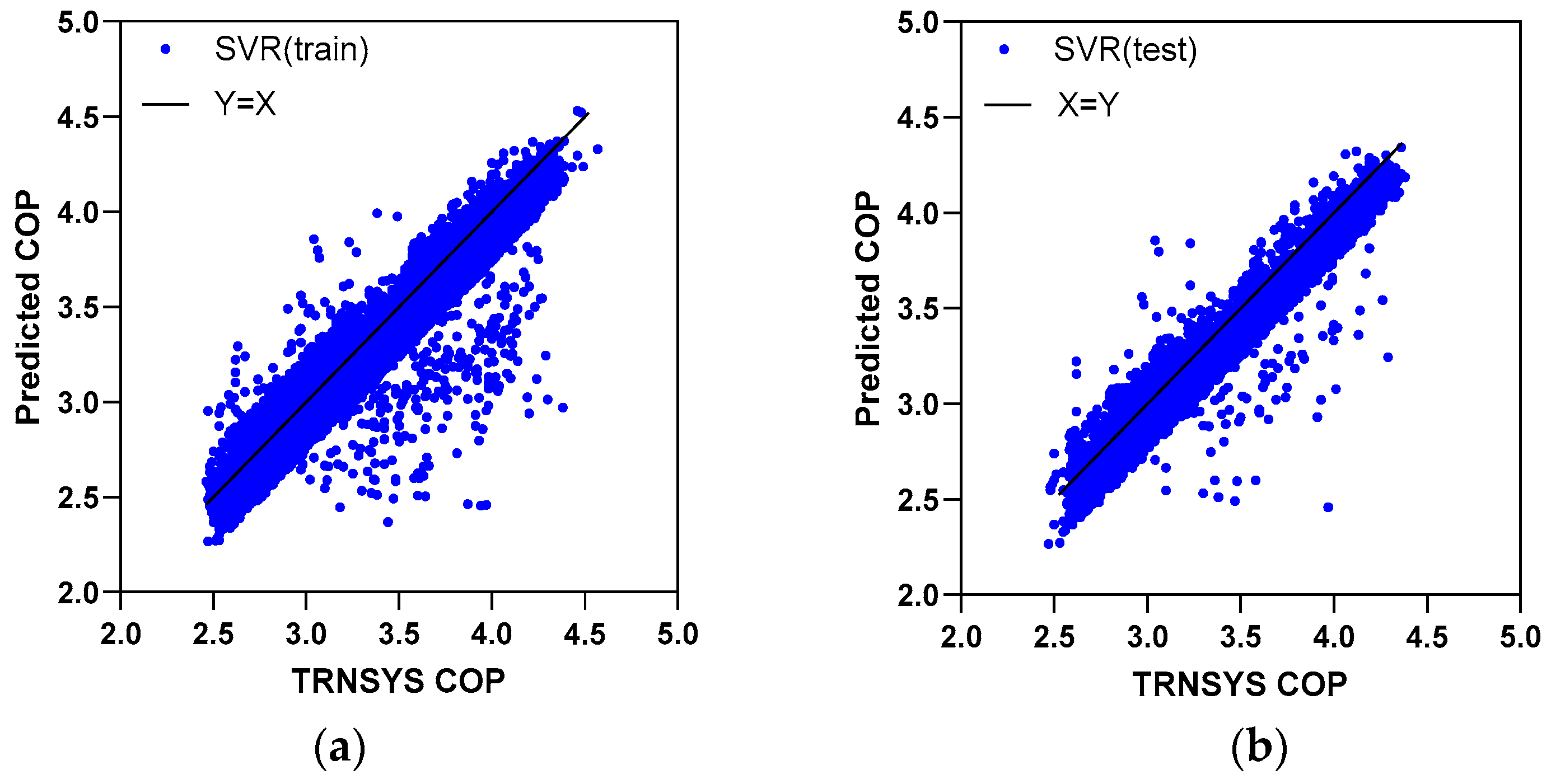
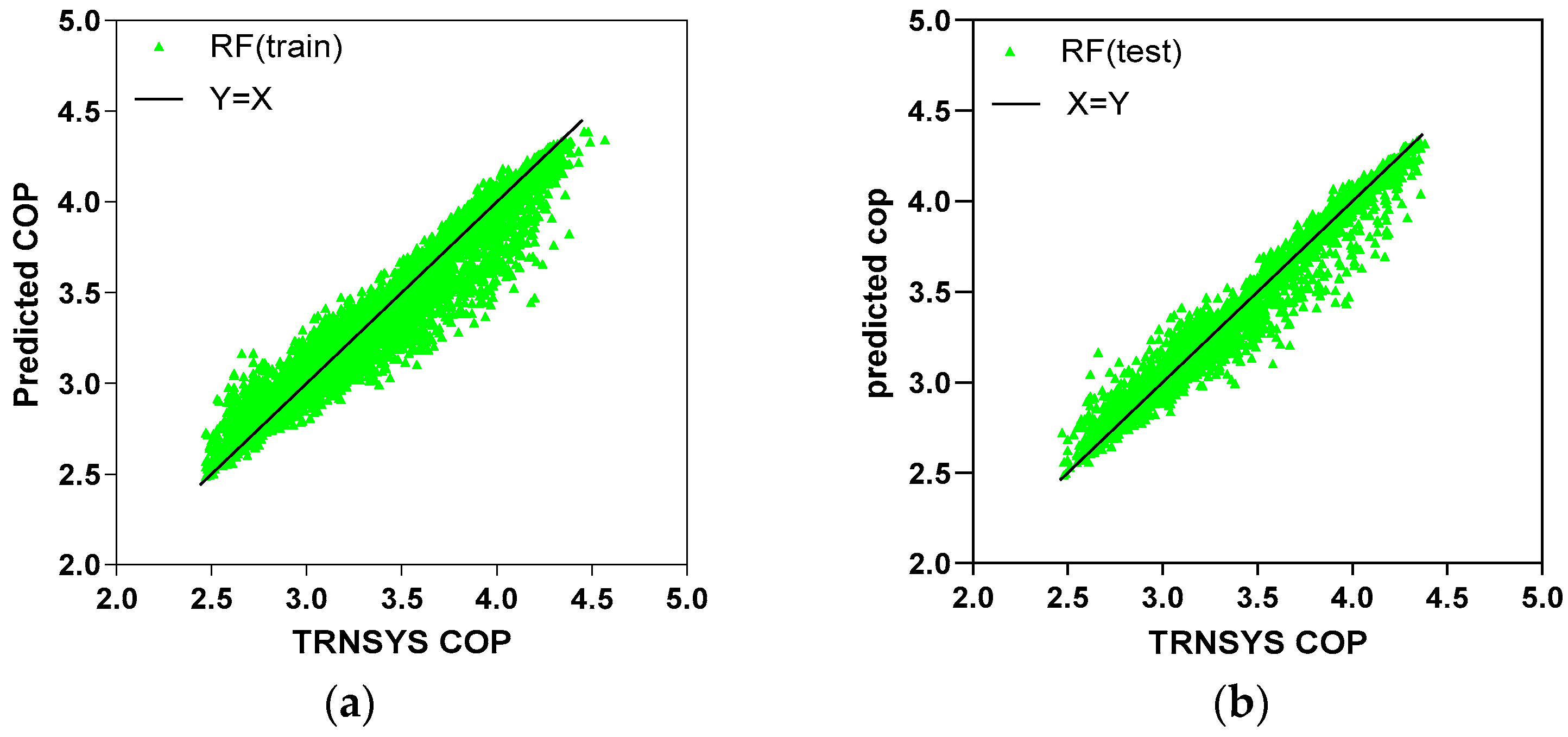
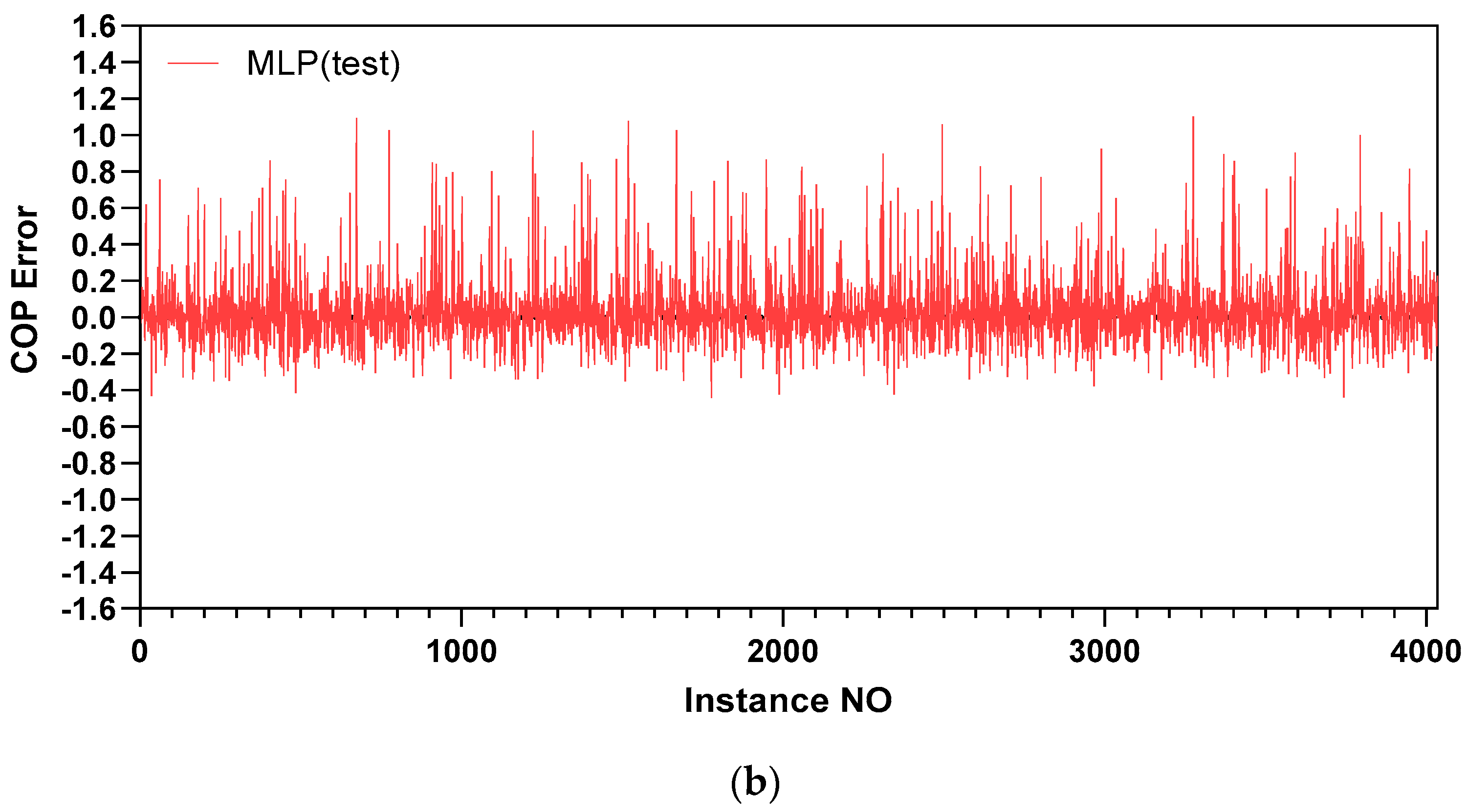
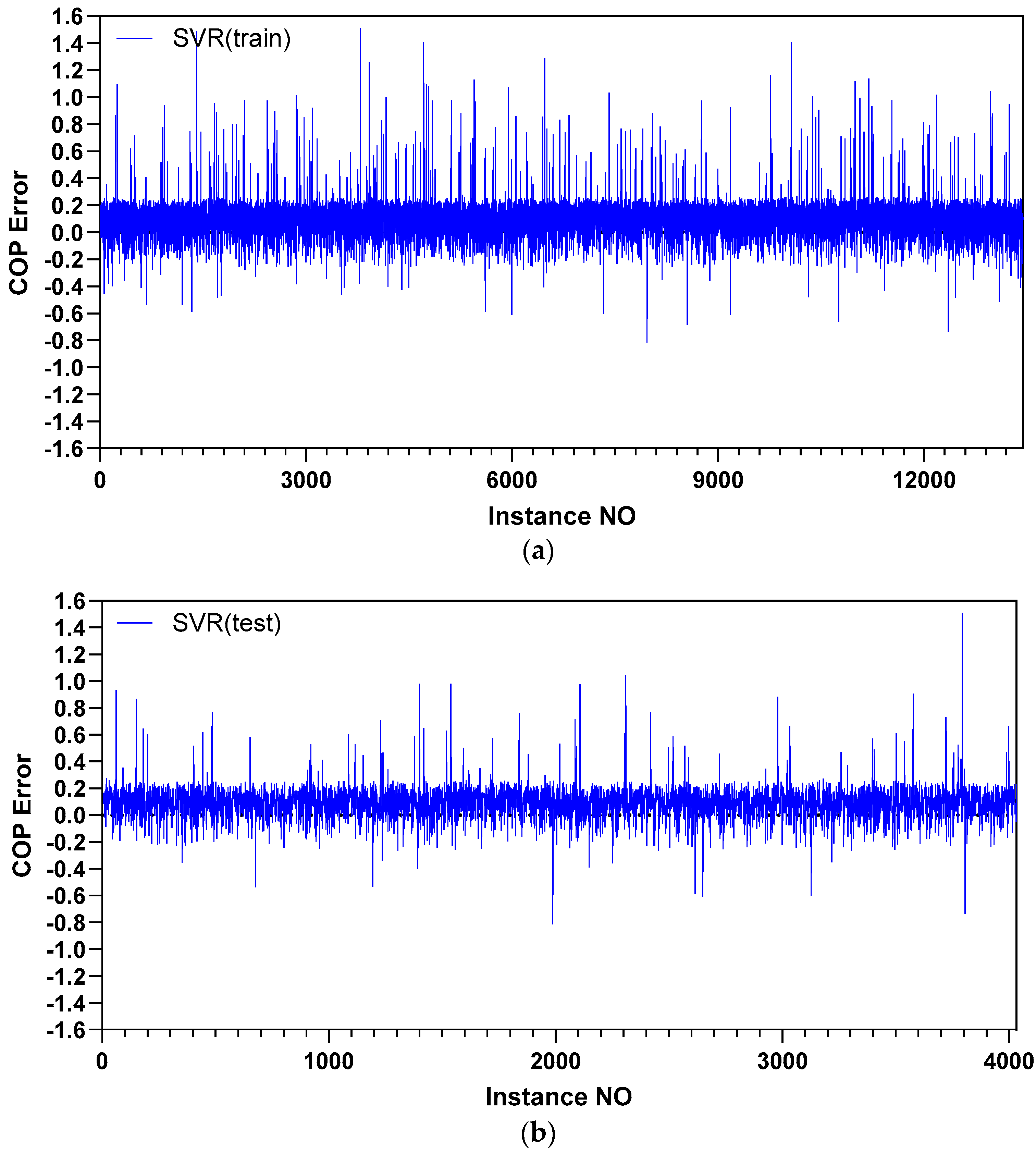
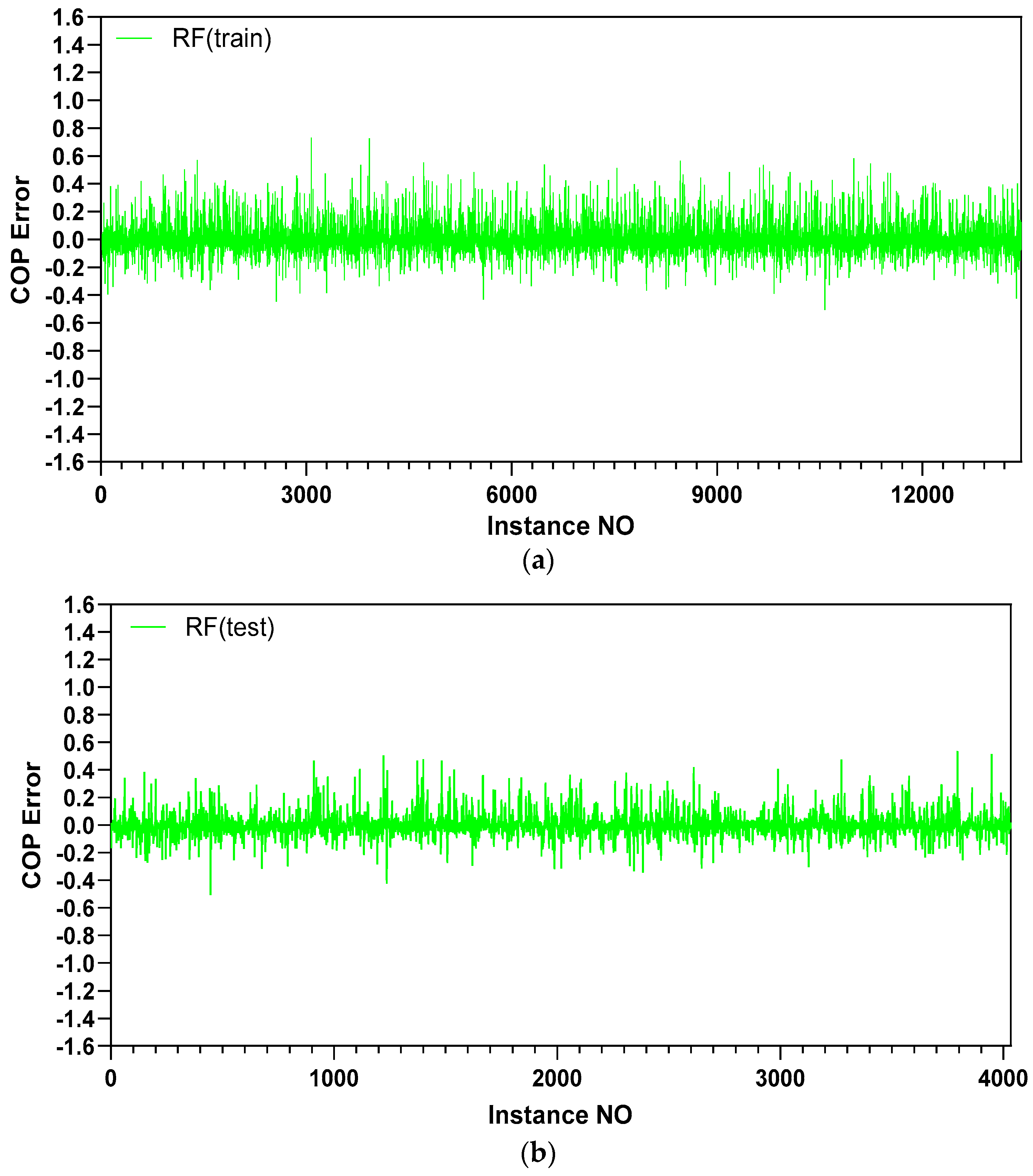
5.1. Prediction Accuracy
5.2. Training Time
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEA. World Energy Outlook. 2019. Available online: https://www.iea.org/weo2019/ (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Angelidis, O.; Ioannou, A.; Friedrich, D.; Thomson, A.; Falcone, G. District heating and cooling networks with decentralised energy substations: Opportunities and barriers for holistic energy system decarbonisation. Energy 2023, 269, 126740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiei, A.; Akhlaghi, Y.G.; Zhao, X.; Shittu, S.; Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Fan, Y.; Li, G. A chronological review of advances in solar assisted heat pump technology in 21st century. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 132, 110132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.H.; Ahmadi, R.; Zahedi, A. Modeling, simulation and dynamic control of solar assisted ground source heat pump to provide heating load and DHW. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 129, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranghi, F.; Gosselin, L.; Raymond, J.; Bourbonnais, M. Modeling of solar-assisted ground-coupled heat pumps with or without batteries in remote high north communities. Renew. Energy 2023, 207, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballerini, V.; Rossi di Schio, E.; Valdiserri, P.; Naldi, C.; Dongellini, M. A Long-Term Dynamic Analysis of Heat Pumps Coupled to Ground Heated by Solar Collectors. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballerini, V.; Lubowicka, B.; Valdiserri, P.; Krawczyk, D.A.; Sadowska, B.; Kłopotowski, M.; di Schio, E.R. The Energy Retrofit Impact in Public Buildings: A Numerical Cross-Check Supported by Real Consumption Data. Energies 2023, 16, 7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Miserocchi, L.; Testi, D. HVAC energy saving strategies for public buildings based on heat pumps and demand controlled ventilation. Energies 2021, 14, 5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelekan, D.S.; Ohunakin, O.S.; Paul, B.S. Artificial intelligence models for refrigeration, air conditioning and heat pump systems. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 8451–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, J.; Chen, J. Performance evaluation and prediction for electric vehicle heat pump using machine learning method. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 159, 113901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afram, A.; Janabi-Sharifi, F.; Fung, A.S.; Raahemifar, K. Artificial neural network (ANN) based model predictive control (MPC) and optimization of HVAC systems: A state of the art review and case study of a residential HVAC system. Energy Build. 2017, 141, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Assadi, M.; Ahmed, A.A.; Banihabib, R. Optimal design, operational controls, and data-driven machine learning in sustainable borehole heat exchanger coupled heat pumps: Key implementation challenges and advancement opportunities. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2023, 74, 231–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, H.; Inalli, M.; Sengur, A.; Esen, M. Modeling a ground-coupled heat pump system by a support vector machine. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Bao, J. Performance evaluation of ground source heat pump using linear and nonlinear regressions and artificial neural networks. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 180, 115914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, Y.H.; Chung, Y.; Park, M.; Hong, S.B.; Kim, M.S. Deep learning-based prediction method on performance change of air source heat pump system under frosting conditions. Energy 2021, 228, 120542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Cho, Y.H. Machine-learning-based coefficient of performance prediction model for heat pump systems. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesser, M.; Lyons, P.; O’Reilly, P.; Carroll, P. Air source heat pump in-situ performance. Energy Build. 2021, 251, 111365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpaydin, E. Introduction to Machine Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, T.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, D.; Tariq, R.; Bassam, A.; Ullah, F.; AlGhamdi, A.S.; Alshamrani, S.S. Energetics Systems and artificial intelligence: Applications of industry 4.0. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 334–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Hu, P.; Li, C.; Yao, Y.; Xing, L.; Lei, F.; Zhu, N. The performance prediction of ground source heat pump system based on monitoring data and data mining technology. Energy Build. 2016, 127, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M.; Nasrabadi, N.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.L.; Shah, A.A.; Leung, P.K.; Zhu, X.; Liao, Q. A comprehensive review of the applications of machine learning for HVAC. DeCarbon 2023, 2, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiodun, O.I.; Jantan, A.; Omolara, A.E.; Dada, K.V.; Mohamed, N.A.; Arshad, H. State-of-the-art in artificial neural network applications: A survey. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation; Prentice Hall PTR: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Xu, C.; Huang, R.; Huang, Y. Machine learning-based thermal response time ahead energy demand prediction for building heating systems. Appl. Energy 2018, 221, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, E.; Liu, L.; Qi, C. Machine learning-based performance prediction for ground source heat pump systems. Geothermics 2022, 105, 102509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V. Statistical Learning Theory; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; Volume 2, pp. 831–842. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Li, Q.; Bai, L.; Wang, R. Performance predictions of ground source heat pump system based on random forest and back propagation neural network models. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 197, 111864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Optimized Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| The number of layers | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 |
| The number of nodes at each layer | 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 |
| Activation function | Sigmoid |
| Momentum | 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 0.99 |
| Learning rate | 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5 |
| Number of epochs | 500, 800 |
| Batch size | 100, 1000 |
| Output | Number of Layers | Accuracy [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | MSE | RMSE | ||
| (Train) | (Train) | (Test) | (Test) | ||
| Coefficient of performance | 1 | 6.54 | 9.12 | 6.33 | 8.67 |
| 2 | 6.11 | 9.13 | 5.84 | 8.64 | |
| 3 | 5.82 | 8.84 | 5.56 | 8.34 | |
| 4 | 5.57 | 8.85 | 5.47 | 8.33 | |
| 5 | 22.83 | 27.36 | 22.8 | 27.26 |
| Output | Number of Nodes | Accuracy [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | MSE | RMSE | ||
| (Train) | (Train) | (Test) | (Test) | ||
| Coefficient of performance | 4 | 5.57 | 8.85 | 5.47 | 8.33 |
| 5 | 5.84 | 8.87 | 5.61 | 8.29 | |
| 6 | 5.77 | 9.02 | 5.51 | 8.51 | |
| 7 | 5.73 | 8.83 | 5.47 | 8.31 | |
| 8 | 5.52 | 8.68 | 5.27 | 8.18 | |
| 9 | 5.5 | 8.74 | 5.24 | 8.21 | |
| 10 | 5.58 | 8.78 | 5.33 | 8.25 | |
| 11 | 5.68 | 8.82 | 5.42 | 8.3 | |
| 12 | 5.53 | 8.75 | 5.28 | 8.22 |
| Optimized Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Kernel function | PUK, RBF, Poly |
| C | 1, 2, 5, 8, 10 |
| ε (Epsilon) | 10−1, 10−2, 10−3, 10−4 |
| σ (Sigma) | 0.1, 0.5, 1,2 |
| ω (Omega) | 1, 1.5, 2, 3 |
| Output | Kernel Function | Accuracy [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | MSE | RMSE | ||
| (Train) | (Train) | (Test) | (Test) | ||
| Coefficient of performance | PUK | 5.91 | 7.71 | 5.89 | 7.75 |
| RBF | 6.97 | 9.8 | 6.79 | 9.39 | |
| Poly | 21.49 | 25.53 | 21.58 | 25.59 |
| Optimized Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Max depth | 10, 20, 30, 35, 40, 60 |
| Max-feature | 1, 2, 3 |
| The number of trees | 100, 300, 500 |
| Output | Prediction Model | Accuracy [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | MSE | RMSE | ||
| (Train) | (Train) | (Test) | (Test) | ||
| Coefficient of performance | MLP | 5.5 | 8.74 | 5.24 | 8.21 |
| SVR | 5.91 | 7.71 | 5.89 | 7.75 | |
| RF | 2.42 | 4.01 | 2.35 | 3.84 |
| Prediction Model | Values [s] |
|---|---|
| MLP | 33.01 |
| SVR | 67.67 |
| RF | 6.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, M.; Pektezel, O.; Ballerini, V.; Valdiserri, P.; Rossi di Schio, E. Performance Predictions of Solar-Assisted Heat Pumps: Methodological Approach and Comparison Between Various Artificial Intelligence Methods. Energies 2024, 17, 5607. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225607
Ma M, Pektezel O, Ballerini V, Valdiserri P, Rossi di Schio E. Performance Predictions of Solar-Assisted Heat Pumps: Methodological Approach and Comparison Between Various Artificial Intelligence Methods. Energies. 2024; 17(22):5607. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225607
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Minghui, Oguzhan Pektezel, Vincenzo Ballerini, Paolo Valdiserri, and Eugenia Rossi di Schio. 2024. "Performance Predictions of Solar-Assisted Heat Pumps: Methodological Approach and Comparison Between Various Artificial Intelligence Methods" Energies 17, no. 22: 5607. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225607
APA StyleMa, M., Pektezel, O., Ballerini, V., Valdiserri, P., & Rossi di Schio, E. (2024). Performance Predictions of Solar-Assisted Heat Pumps: Methodological Approach and Comparison Between Various Artificial Intelligence Methods. Energies, 17(22), 5607. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225607








