Multi-Temperature State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Spatial Transformer Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Traditional Physics-Based SOC Estimation
2.2. Deep Learning-Based SOC Estimation
3. Proposed Method
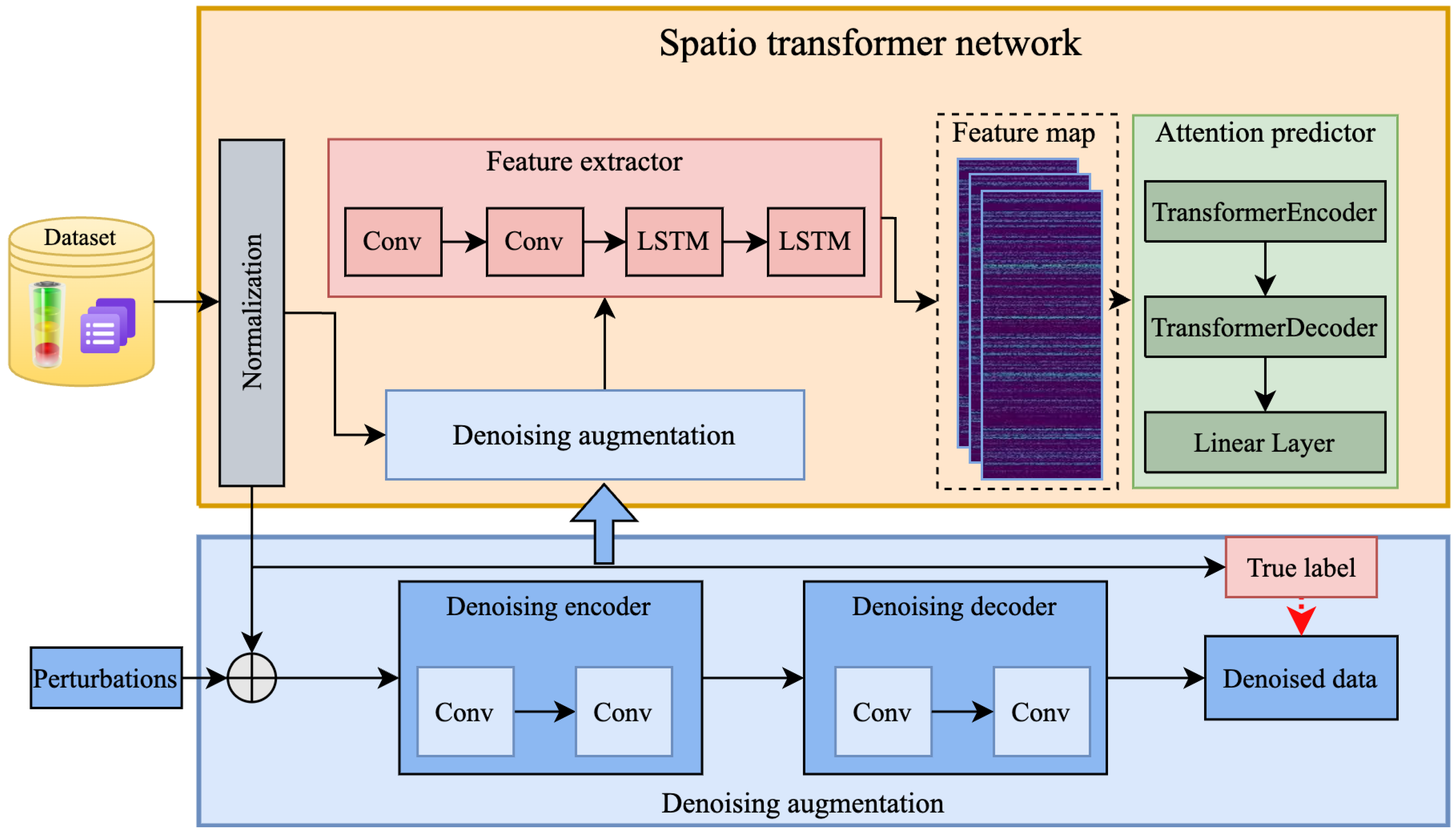
3.1. Model Architecture
3.1.1. Normalization
3.1.2. Denoising Augmentation
3.1.3. Attention Prediction
3.2. Objective Function Based on Spatial Transformer Network
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
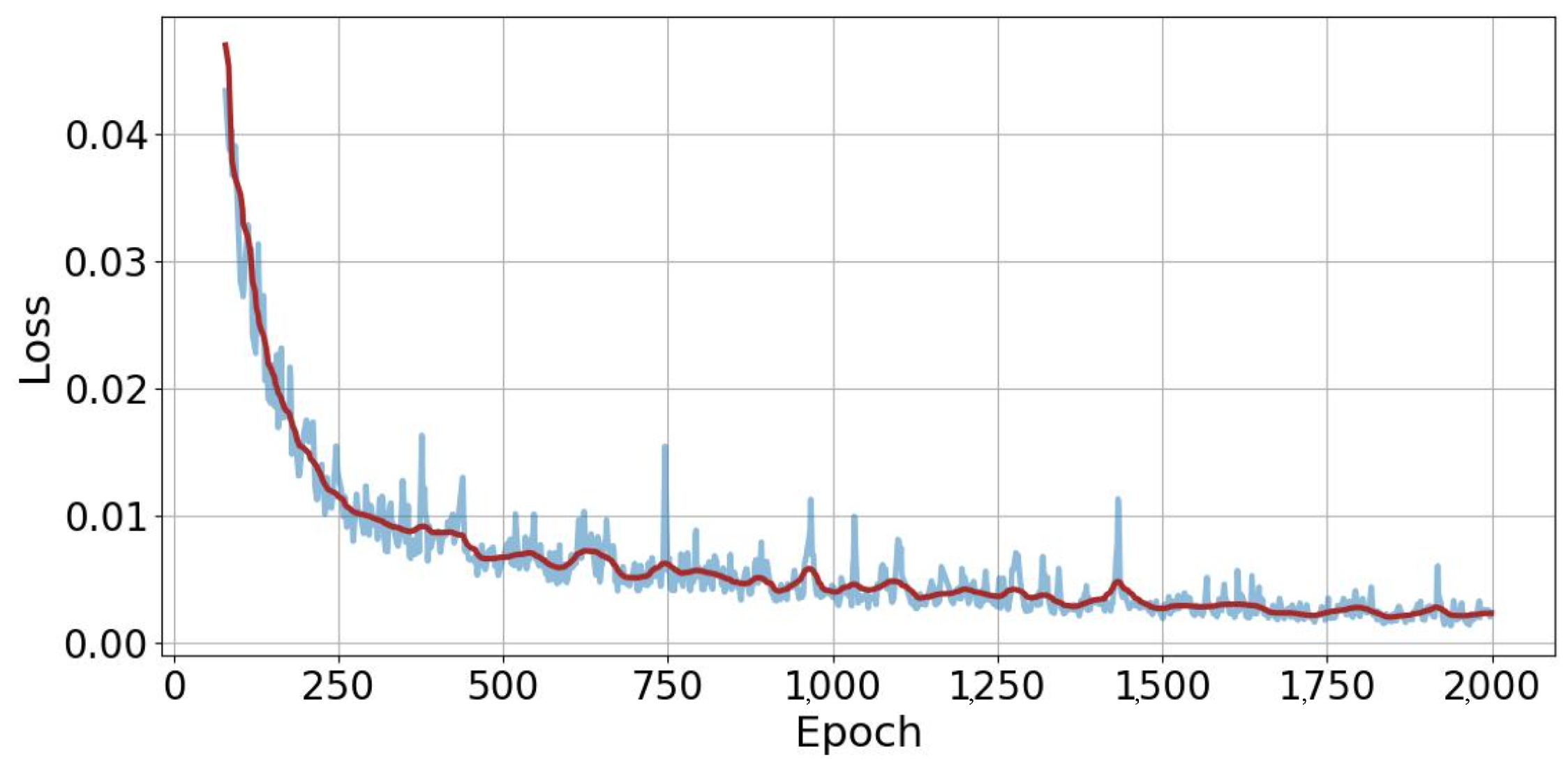
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Compared Methods
4.3.1. Overall Performance
4.3.2. Network Architecture Comparison
4.3.3. Semi-Supervised Estimation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saw, L.H.; Ye, Y.; Tay, A.A. Integration issues of lithium-ion battery into electric vehicles battery pack. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Cao, R.; Li, Q.; Gao, Z.; Fan, C.; Yang, S. A capacity fade reliability model for lithium-ion battery packs based on real-vehicle data. Energy 2024, 307, 132782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. Aging behavior and mechanisms of lithium-ion battery under multi-aging path. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, S.; Venkateswarlu, B.; Prabakaran, R.; Salman, M.; Joo, S.W.; Choi, G.S.; Kim, S.C. Thermal runaway and mitigation strategies for electric vehicle lithium-ion batteries using battery cooling approach: A review of the current status and challenges. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, M. SoC estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on machine learning techniques: A filtered approach. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, C.; Huang, L.; Jie, H.; Li, H.; Hao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; See, K.Y. State of charge estimation of lithium batteries: Review for equivalent circuit model methods. Measurement 2024, 236, 115148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Dou, X.; Zhang, X. A data-driven coulomb counting method for state of charge calibration and estimation of lithium-ion battery. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 40, 100752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Jiang, H.; Long, N.; Kang, Q.; Meng, X.; Zhou, M.; Yan, L.; Ma, T. Machine learning for full lifecycle management of lithium-ion batteries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 202, 114647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Hussain, A.; Ker, P.J.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Mansor, M.; Ayob, A.; Saad, M.H.; Dong, Z.Y. Toward Enhanced State of Charge Estimation of Lithium-ion Batteries Using Optimized Machine Learning Techniques. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Wang, D. A beetle antennae search optimized recurrent extreme learning machine for battery state of charge estimation. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 19190–19205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2019, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, T.; Dhahad, H.A.; Fadhil Jasim, K.; Sharma, K.; Zhou, J.; Fouad, H.; El-Shafai, W. Deep learning-based prediction of lithium-ion batteries state of charge for electric vehicles in standard driving cycle. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 60, 103461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Zhang, T.; Huang, J. Advanced hybrid LSTM-transformer architecture for real-time multi-task prediction in engineering systems. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ul Hassan, M.; Saha, S.; Haque, M.E.; Islam, S.; Mahmud, A.; Mendis, N. A comprehensive review of battery state of charge estimation techniques. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 54, 102801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D.V.S.R., S.; Badachi, C.; Green, R.C., II. A review on data-driven SOC estimation with Li-Ion batteries: Implementation methods and future aspirations. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Cheng, W.; Zhu, Q. SOC estimation for lithium-ion battery using the LSTM-RNN with extended input and constrained output. Energy 2023, 262, 125375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fallah, S.; Kharbach, J.; Hammouch, Z.; Rezzouk, A.; Ouazzani Jamil, M. State of charge estimation of an electric vehicle’s battery using Deep Neural Networks: Simulation and experimental results. J. Energy Storage 2023, 62, 106904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.; Lipu, M.; Hussain, A.; Mohamed, A. A review of lithium-ion battery state of charge estimation and management system in electric vehicle applications: Challenges and recommendations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 834–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J. Simplified Extended Kalman Filter Observer for SOC Estimation of Commercial Power-Oriented LFP Lithium Battery Cells (2013-01-1544). In Progress in Modeling and Simulation of Batteries; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016; Chapter 3; pp. 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Wang, L.; Lin, H.; Lv, Z. High accuracy state-of-charge online estimation of EV/HEV lithium batteries based on Adaptive Wavelet Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE ECCE Asia Downunder, Melbourne, Australia, 3–6 June 2013; pp. 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Yang, K.; Yin, X.; Geng, Y.; Wang, J. State of Charge Estimation for Lithium-Bismuth Liquid Metal Batteries. Energies 2019, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Qi, P.; Kan, Y.; Huang, J.; Huang, H.; Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y.; Xiao, R.; Zhao, S. State of charge estimation method based on the extended Kalman filter algorithm with consideration of time-varying battery parameters. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 10538–10550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, K.; Pang, H.; Jin, J. Online SOC Estimation Based on Simplified Electrochemical Model for Lithium-Ion Batteries Considering Current Bias. Energies 2021, 14, 5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, Z.; Su, H.; Zhuang, W. Electrochemical-distributed thermal coupled model-based state of charge estimation for cylindrical lithium-ion batteries. Control. Eng. Pract. 2021, 109, 104734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, C.; Xu, Z.; Deng, Y. Research on Dynamic Equivalent SOC Estimation of Hybrid Energy Storage System Based on Sliding Mode Observer. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 711716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; How, D.N.T.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Ker, P.J.; Dong, Z.Y.; Mansur, M.; Blaabjerg, F. SOC Estimation of Li-ion Batteries with Learning Rate-Optimized Deep Fully Convolutional Network. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 7349–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.; He, H.; Yang, S.; Huang, T. State-of-charge sequence estimation of lithium-ion battery based on bidirectional long short-term memory encoder-decoder architecture. J. Power Sources 2020, 449, 227558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.; How, D.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Mansor, M.; Ker, P.; Dong, Z.; Sahari, K.; Tiong, S.; Muttaqi, K.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; et al. Towards Accurate State of Charge Estimation for Lithium-Ion Batteries using Self-supervised Transformer Model: A Deep Learning Approach. Sci. Rep. 2021. under review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.; Yang, S.; Miao, Q. Cross-Domain State-of-Charge Estimation of Li-Ion Batteries Based on Deep Transfer Neural Network with Multiscale Distribution Adaptation. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, T. Deep learning-based battery state of charge estimation: Enhancing estimation performance with unlabelled training samples. J. Energy Chem. 2023, 80, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ka, A.; Kosuru, V.S.R. Hybrid Deep Learning Mechanism for Charging Control and Management of Electric Vehicles. Eur. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2023, 7, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Farrell, J.; Du, J.; Barth, M. Battery State-of-Charge Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2001 American Control Conference (Cat. No.01CH37148), Arlington, VA, USA, 25–27 June 2001; Volume 2, pp. 1644–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y.; Yao, L.; Alain, G.; Vincent, P. Generalized Denoising Auto-Encoders as Generative Models. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 December 2019; Burges, C., Bottou, L., Welling, M., Ghahramani, Z., Weinberger, K., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Liang, S.; Liang, M. A generic shared attention mechanism for various backbone neural networks. Neurocomputing 2024, 128697, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.u.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. SGDR:Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kollmeyer, P. Panasonic 18650PF Li-ion Battery Data; University of Wisconsin Madison: Madison, WI, USA; McMaster University: Hamilton, ON, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Adams, S.; Yuen, C. Transfer Learning-Based State of Charge Estimation for Lithium-Ion Battery at Varying Ambient Temperatures. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 7304–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, L.; Shen, H.T. Temperature Adaptive Transfer Network for Cross-Domain State-of-Charge Estimation of Li-Ion Batteries. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 3857–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Metrics | 25 °C | 10 °C | 0 °C | −10 °C | −20 °C | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE (%) | 0.48 | 0.31 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.71 | 0.55 |
| RMSE (%) | 0.57 | 0.40 | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.92 | 0.71 |
| Architecture | Metrics | Ambient Temperature | Average | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 °C | 10 °C | 0 °C | −10 °C | −20 °C | |||
| LSTM | MAE (%) | 1.09 | 1.74 | 0.63 | 1.11 | 2.39 | 1.62 |
| RMSE (%) | 3.08 | 3.93 | 1.61 | 1.96 | 3.49 | 3.04 | |
| GRU | MAE (%) | 1.09 | 1.38 | 0.64 | 1.12 | 1.70 | 1.19 |
| RMSE (%) | 3.07 | 3.30 | 1.60 | 1.94 | 2.55 | 2.49 | |
| Qin et al. [38] | MAE (%) | 2.74 | 0.58 | 1.91 | 2.89 | 4.94 | 2.61 |
| RMSE (%) | 2.27 | 0.45 | 1.70 | 2.17 | 3.95 | 2.11 | |
| Shen et al. [39] | MAE (%) | 0.76 | 1.37 | 0.53 | 1.11 | 1.69 | 1.09 |
| RMSE (%) | 1.07 | 1.81 | 0.68 | 1.46 | 2.18 | 1.44 | |
| Proposed method | MAE (%) | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.64 | 0.86 | 0.64 |
| RMSE (%) | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.74 | 0.78 | 1.10 | 0.82 | |
| Architecture | Metrics | Ambient Temperature | Average | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 °C | 10 °C | 0 °C | −10 °C | −20 °C | |||
| Qin et al. [38] | MAE (%) | 2.88 | 1.60 | 2.10 | 2.96 | 4.99 | 2.90 |
| RMSE (%) | 2.95 | 1.72 | 2.32 | 3.11 | 5.04 | 3.02 | |
| Shen et al. [39] | MAE (%) | 0.88 | 1.40 | 0.73 | 1.23 | 1.88 | 1.22 |
| RMSE (%) | 1.27 | 1.91 | 0.98 | 1.63 | 2.48 | 1.65 | |
| Proposed method | MAE (%) | 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.94 | 1.26 | 0.93 |
| RMSE (%) | 0.91 | 1.06 | 1.04 | 0.78 | 1.33 | 1.02 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Wen, X.; Liang, H. Multi-Temperature State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Spatial Transformer Network. Energies 2024, 17, 5029. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17205029
Cao Y, Wen X, Liang H. Multi-Temperature State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Spatial Transformer Network. Energies. 2024; 17(20):5029. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17205029
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yu, Xin Wen, and Hongyu Liang. 2024. "Multi-Temperature State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Spatial Transformer Network" Energies 17, no. 20: 5029. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17205029
APA StyleCao, Y., Wen, X., & Liang, H. (2024). Multi-Temperature State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Spatial Transformer Network. Energies, 17(20), 5029. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17205029




