The Operation Strategy of a Multi-Microgrid Considering the Interaction of Different Subjects’ Interests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Operational Frameworks
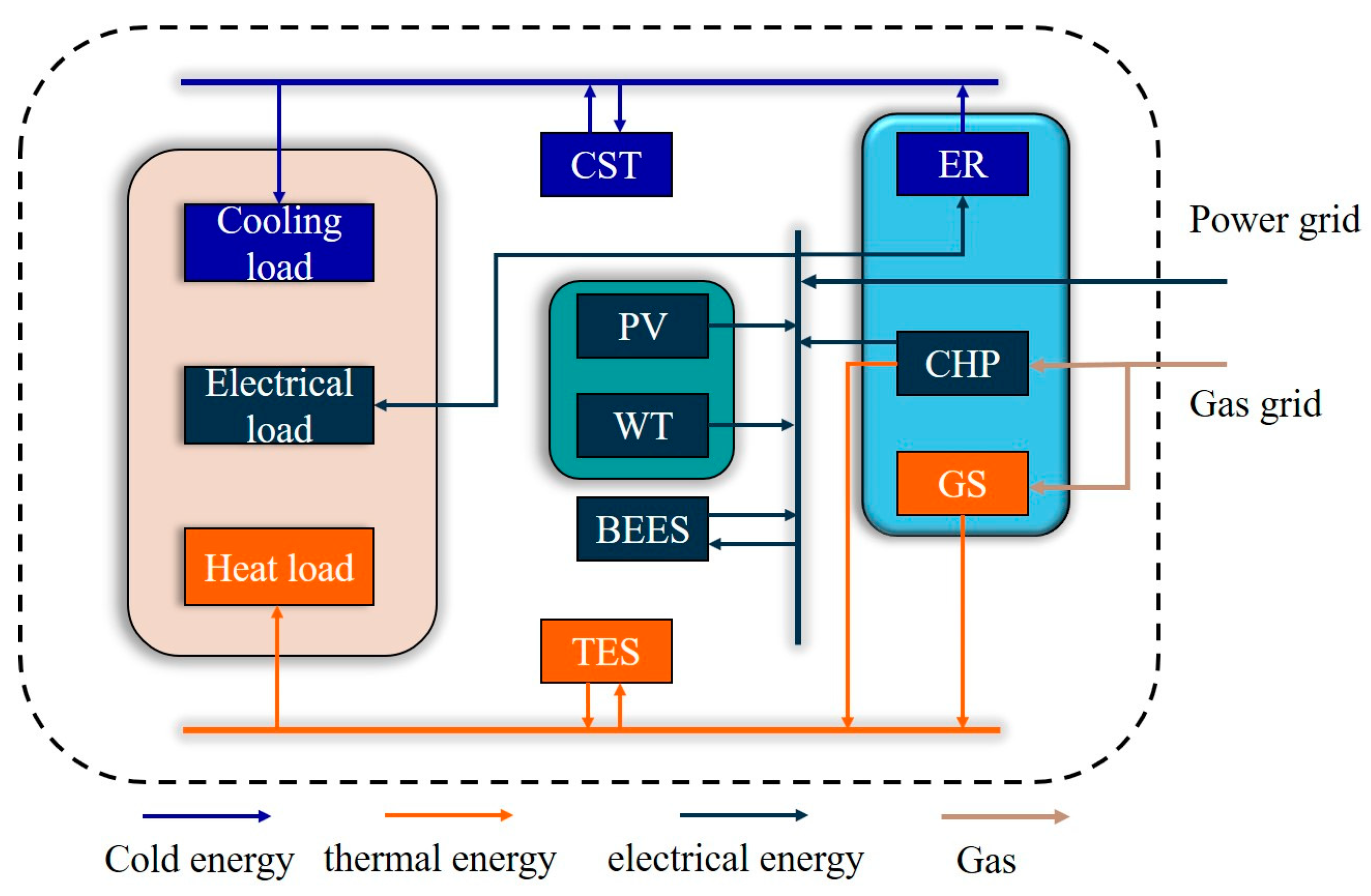
2.1. Operation Framework Diagram of a Single Microgrid
2.2. Multi-Microgrid Centralized Cooperative Operation Framework
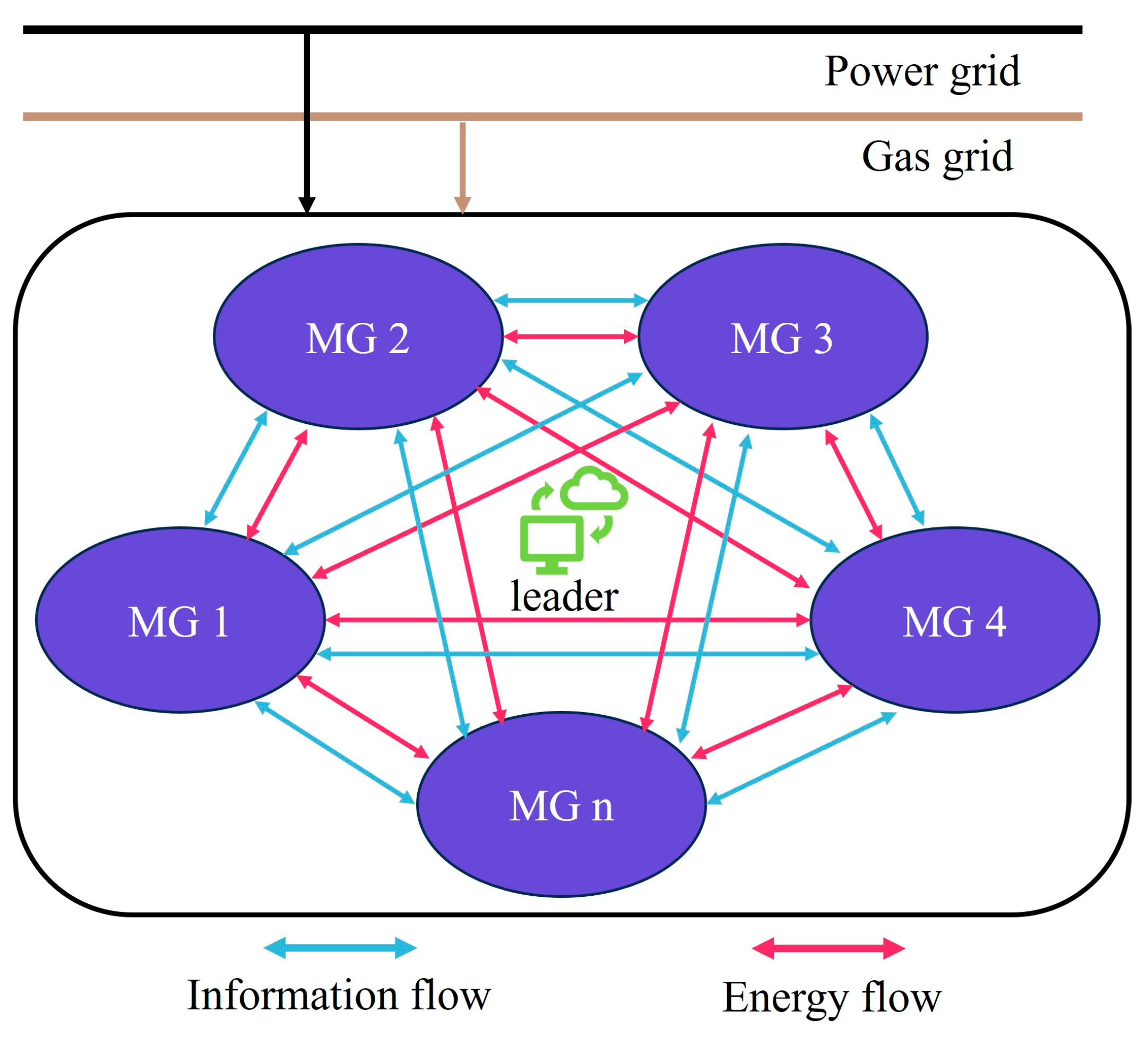
2.3. Multi-Microgrid Distributed Cooperative Operation Framework
3. Operating Model
3.1. Demand-Side Response
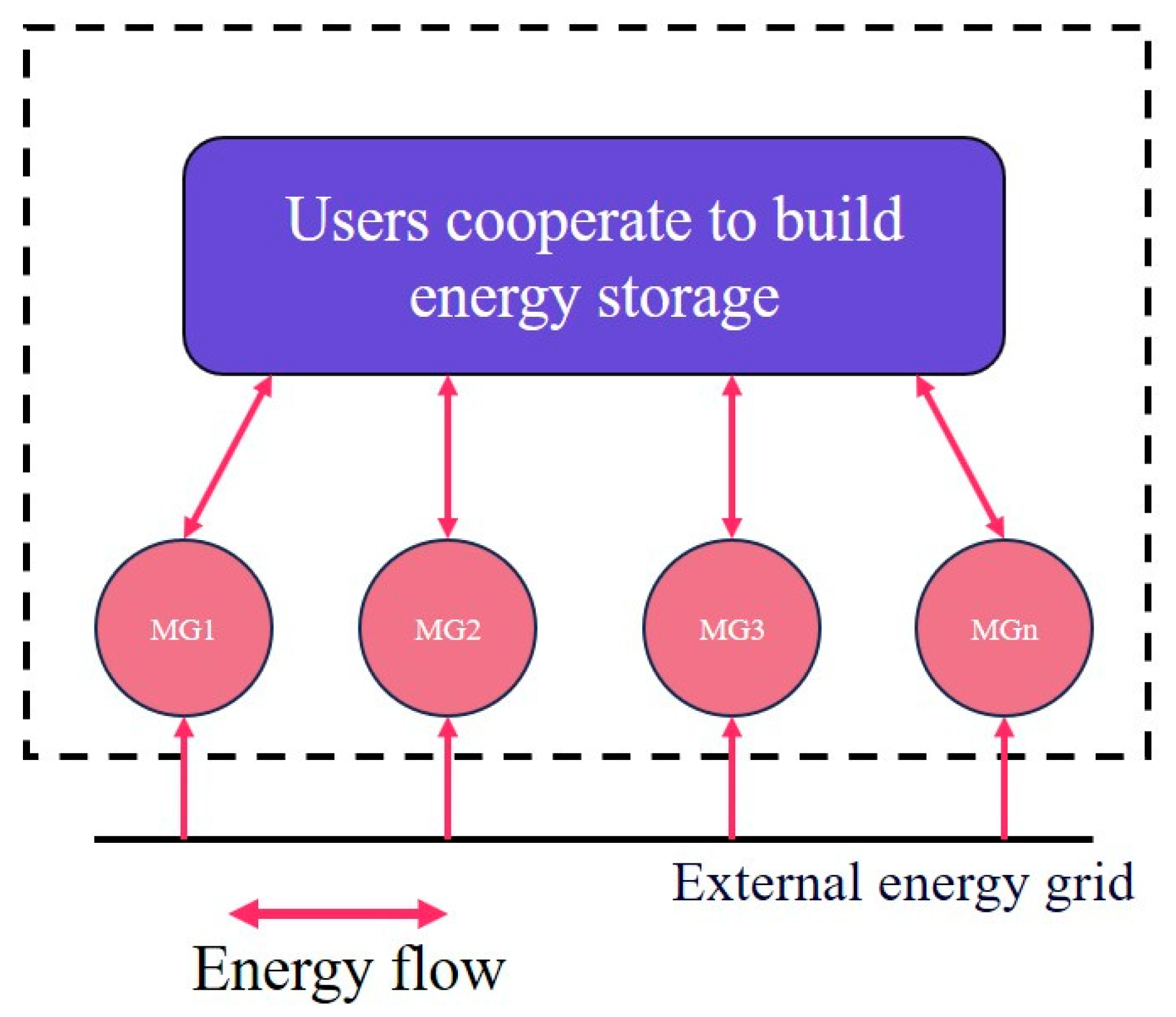
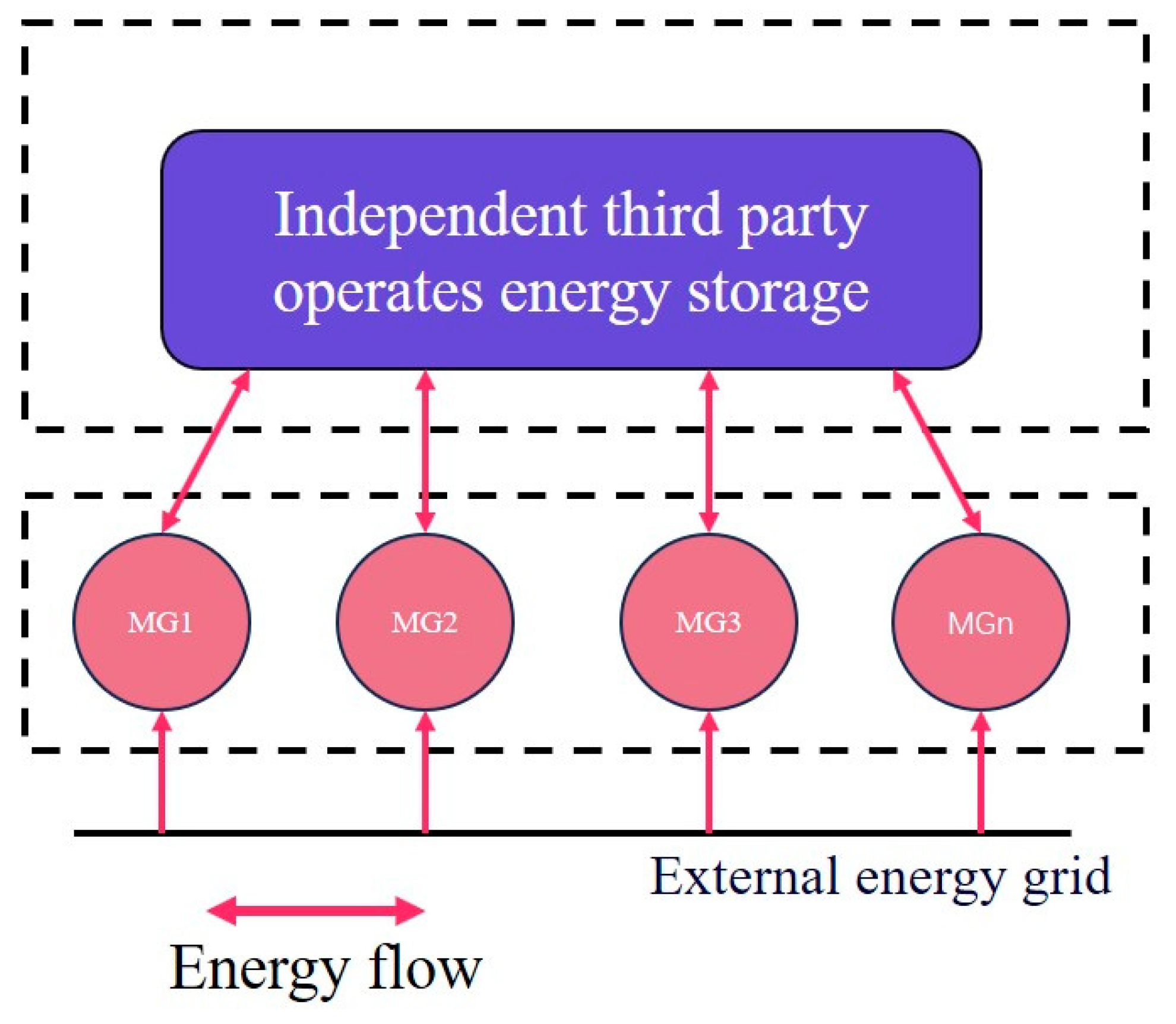
3.2. Shared Energy Storage
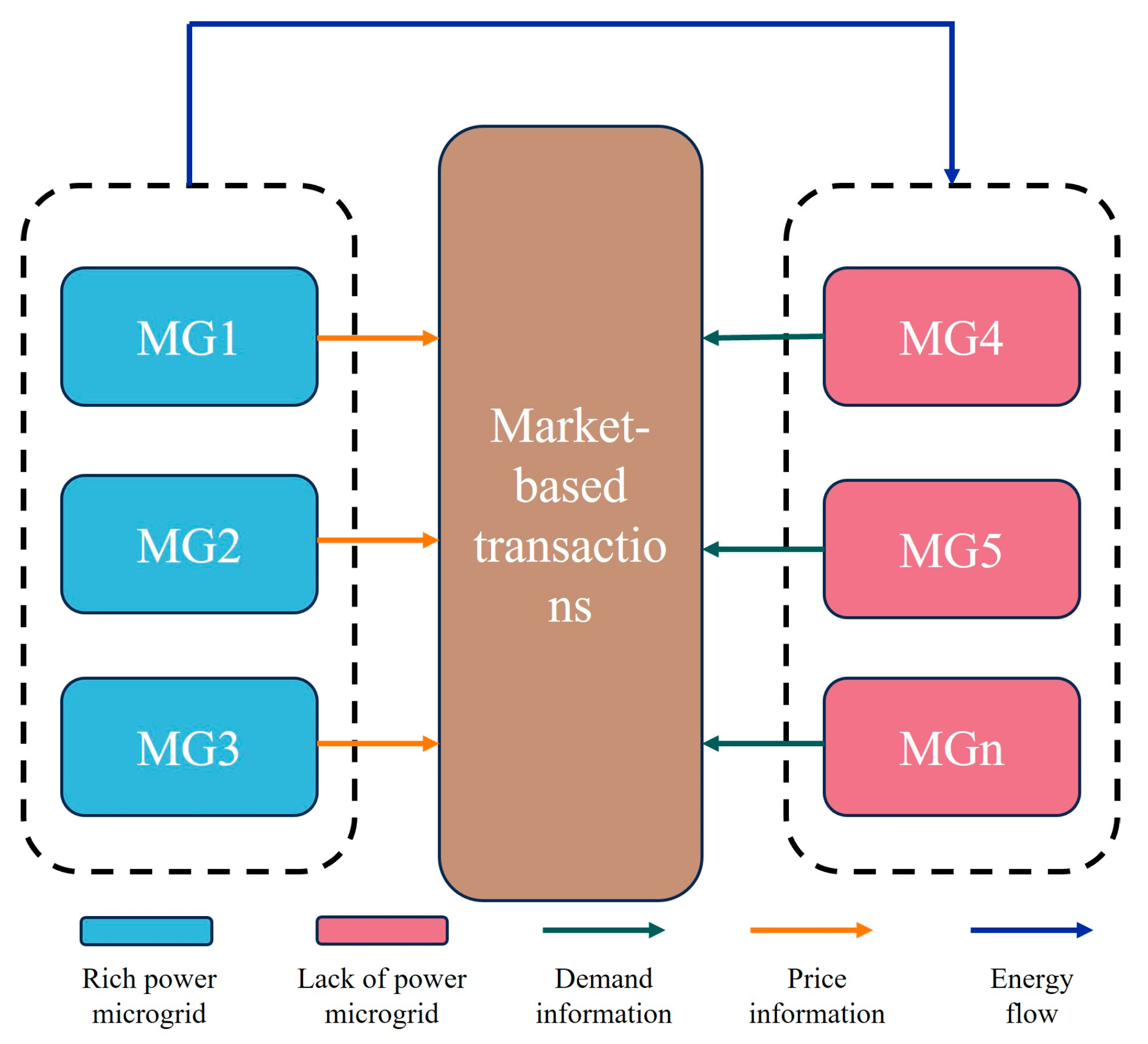
3.3. Peer-to-Peer Trading
- [1]
- Centralized Pricing P2P Transaction Model [44]: In this model, users report their needs to a central platform, which sets the prices based on the collected data. Examples include platforms like Didi and Uber.
- [2]
- Fully Market-Based P2P Trading Model [45]: In this model, the P2P trading center merely provides a platform to facilitate transactions and does not participate in setting transaction prices. Energy prices are negotiated directly among users, similar to platforms like eBay and TaoBao.

3.4. Carbon Trade
4. Research Methodology
4.1. Equilibrium Distribution of Benefits Problem—Game Theory
- [1]
- Individual Rationality Condition: The payoff allocated to each individual after joining the coalition must not be less than the payoff the individual would have received by acting alone. This can be expressed as follows:
- [2]
- Collective Rationality Condition: The total revenue of the cooperative alliance should not be less than the sum of the revenues of each individual operating independently, expressed as follows:
4.2. Personal Information Protection Issues—Blockchain Technology
- [1]
- Security: Blockchain ensures transaction security by recording each energy transaction on the blockchain and encrypting it with cryptographic methods, making the data resistant to tampering or forgery.
- [2]
- Immediate Settlement: Blockchain facilitates immediate transaction settlement and clearing. As transaction records are updated and shared in near real time, energy transactions between microgrids can be settled swiftly, reducing time and management costs.
- [3]
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain’s smart contract functionality offers enhanced transaction flexibility and automation. These pre-programmed contracts automatically execute based on predefined conditions, such as dynamically adjusting energy trading strategies based on market prices or allocating energy resources according to environmental conditions.
4.3. Uncertainty Risk Problem—Robust Optimization
5. Future Outlook
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, F.; Ding, J.; Zhou, C.; Yong, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J. Key Technologies of Large-scale Grid-con nected Operation of Distributed Photovoltaic Under New-type Power System. Dianwang Jishu/Power Syst. Technol. 2024, 48, 184–196. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Xu, Z.; Yang, L. Recent advancements on the development of microgrids. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2014, 2, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhizi, S.; Lotfi, H.; Khodaei, A.; Bahramirad, S. State of the art in research on microgrids: A review. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 890–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Fang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X. The Design of the Simulation System for the Integrated Energy System. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Power System Technology (POWERCON), Guangzhou, China, 6–8 November 2018; pp. 410–416. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, P. The hierarchical modeling approach for centralized control microgrid cyber physical system. Proc. CSEE 2022, 42, 7088–7100. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Ai, Q. Demand-side response strategy of multi-microgrids based on an improved co-evolution algorithm. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 7, 903–910. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Zheng, W.; Yu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zeng, M. Optimizing Grid-Connected Multi-Microgrid Systems With Shared Energy Storage for Enhanced Local Energy Consumption. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 13663–13677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Wang, X.; Kuang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Lyu, J. Hybrid energy sharing mechanism for integrated energy systems based on the Stackelberg game. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 7, 911–921. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ge, Z. Distributed low-carbon optimal operation strategy of multi-microgrids integrated energy system based on Nash bargaining. Power Syst. Technol. 2022, 46, 1464–1482. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, K.; Zhang, C.; Ma, X. Distributed coordinative optimal operation of community integrated energy system based on Stackelberg game. Proc. CSEE 2020, 40, 5435–5445. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Zhao, B.; Gu, W.; Bo, R. Bi-level two-stage robust optimal scheduling for AC/DC hybrid multi-microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 5455–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, E.; Alizadeh, M.; Asgarimoghaddam, M.; Wang, X.; Simões, M.G. A review on application of artificial intelligence techniques in microgrids. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2022, 3, 878–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Mao, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Cheng, L. A survey of energy management in interconnected multi-microgrids. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 72158–72169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Wei, B.; Guerrero, J.M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Gui, Y. An overview of the operation architectures and energy management system for multiple microgrid clusters. iEnergy 2022, 1, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. State of art of the key technologies of multiple microgrids system. Power Syst. Technol. 2020, 44, 3804–3820. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Zou, J.; Chung, C.Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, N.; Voropai, N.; Xu, D. Multi-microgrid energy management systems: Architecture, communication, and scheduling strategies. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2021, 9, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Yang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Cao, Y. A Model of Integrated Energy System Basic Unit Based on Statistical Clustering. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; Fu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Sun, H. Universal standardized information model of integrated energy system for multiple scenarios and its application. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2022, 46, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, H.; Han, F.; Yuan, K.; Song, Y.; Fang, S. Review on district-level integrated energy system planning considering interconnection and interaction. Proc. CSEE 2021, 41, 4001–4021. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Lu, S.; Lu, H.; Luo, E.; Gu, W.; Zhuang, W. Flexibility of integrated energy system: Basic connotation, mathematical model and research framework. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2022, 46, 16–43. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, H.; Coelho, E.A.A.; Guerrero, J.M. MAS-based distributed coordinated control and optimization in microgrid and microgrid clusters: A comprehensive overview. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 6488–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yang, K.; Yang, J.; Mao, R.; Xue, N.; Zhuo, Z. A multiagent-based hierarchical energy management strategy for maximization of renewable energy consumption in interconnected multi-microgrids. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 169931–169945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, B.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, R. Energy management system research of multi-microgrid: A review. Proc. CSEE 2020, 40, 3077–3093. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiee, Q.; Dragičević, T.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M. Hierarchical control for multiple DC-microgrids clusters. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2014, 29, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhong, H.; Ma, Z.; Xia, Q.; Kang, C. Review and prospect of integrated demand response in the multi-energy system. Appl. Energy 2017, 202, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Wei, Y.; He, G.; Li, Z. Discussion on demand response mechanism for new power systems. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2022, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yunwei, S.; Yang, L.; Ciwei, G.; Lei, Z. Application of demand response in ancillary service market. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2017, 41, 151–161. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, R.; Lu, X.; Zhou, H.; Lai, J. A novel category-specific pricing strategy for demand response in microgrids. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2021, 13, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lee, W.-J. Integrated demand response for microgrids with incentive compatible bidding mechanism. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 59, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Han, X.; Li, T.; Wei, B.; Li, Y. Master-slave game optimal scheduling strategy for multi-agent integrated energy system based on demand response and power interaction. Power Syst. Technol. 2022, 46, 3333–3344. [Google Scholar]
- Bie, Z.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y. Review and prospect of planning of energy internet. Proc. CSEE 2017, 37, 6445–6462. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaverh, F.; Denai, M.; Sun, Y. A dynamic peer-to-peer electricity market model for a community microgrid with price-based demand response. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 3976–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, T.; Deng, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Blaabjerg, F. Microgrid energy management with energy storage systems: A review. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 9, 483–504. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, R.; Esmaeilbeigi, R.; Charkhgard, H. The utilization of shared energy storage in energy systems: A comprehensive review. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 3163–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Lin, G.; Meng, J.; Gao, C.; Chen, T.; Xia, S.; Ban, M. Key Technologies and Applications of Shared Energy Storage. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 2024, 58, 585. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Z.Y. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Explainable Pricing Policy for Virtual Storage Rental Service. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 4373–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Chen, Y. Review on business mode and pricing mechanism for shared energy storage. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2022, 46, 178–191. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xie, S.; Fang, Z.; Li, F.; Cheng, S. Optimal configuration of shared energy storage for multi-microgrid and its cost allocation. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2021, 41, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, C.; Ma, L.; Chen, T.; Wei, Y.; Lin, Z.; Srinivasan, D. Multi-step clustering and generalized Nash Bargaining-based planning strategy of community-shared energy storage for large-scale prosumers. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2023, 15, 1013–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, S.; Gu, W.; Zhu, C.; Chen, X. Optimal operation of micro-energy grids considering shared energy storage systems and balanced profit allocations. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 9, 254–271. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, S.; Qiu, J.; Tao, Y. Individualized pricing of energy storage sharing based on discount sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 4642–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Wang, Y.-W.; Liu, X.-K.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.-W. Economic storage sharing framework: Asymmetric bargaining-based energy cooperation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 7489–7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Qiu, J.; Tao, Y. Credit-based pricing and planning strategies for hydrogen and electricity energy storage sharing. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2021, 13, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morstyn, T.; McCulloch, M.D. Multiclass energy management for peer-to-peer energy trading driven by prosumer preferences. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 34, 4005–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Gao, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J. Design of P2P trading framework for multiple prosumers in local energy market. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2022, 42, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J. Design of P2P transaction mechanism considering differentiation characteristics of multiple prosumers in community microgrid system. Proc. CSEE 2022, 42, 1455–1470. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Gao, H.; Wang, C.; He, S.; Cai, W.; Yang, J. Multi-party co-governance decision-making method for coordinated transactions among multiple microgrids. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2022, 64, 30–42. [Google Scholar]
- An, D.; Yang, Q.; Li, D.; Wu, Z. Distributed online incentive scheme for energy trading in multi-microgrid systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2023, 21, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, X. Operation mechanism and strategies for transactive electricity market with multi-microgrid in grid-connected mode. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 79594–79603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yu, D.; Zhang, X. Prosumer Alliance in P2P Transaction of Electricity Considering Social Welfare. Proc. CSEE 2024, 44, 960–971. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, B.; Han, D.; Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Yan, Z. Pricing mechanism for community prosumers in decentralized electricity market. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2021. Early Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Gao, S.; Wei, X.; Shi, J.; Huang, T.; Hatziargyriou, N.D.; Chung, C. A shareholding-based resource sharing mechanism for promoting energy equity in peer-to-peer energy trading. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2022, 38, 5113–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Xiang, Y.; Hu, S.; Wu, G.; Liu, J. Optimal prosumers’ peer-to-peer energy trading and scheduling in distribution networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 58, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Yang, K.; Mi, Z. Quantitative models in emission trading system research: A literature review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 132, 110052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Li, C. Research on the allocation scheme of carbon emission allowances for China’s provincial power grids. Energy 2024, 299, 131551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Wang, A.-D.; Da, Y.-B. Regional allocation of carbon emission quotas in China: Evidence from the Shapley value method. Energy Policy 2014, 74, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, W.; Cui, Z.; Yuan, M.; Shan, E. Cooperation for trans-regional electricity trading from the perspective of carbon quota: A cooperative game approach. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 156, 109773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, J. Collaborative Optimization Scheduling of Multi-Microgrids Incorporating Hydrogen-Doped Natural Gas and P2G–CCS Coupling under Carbon Trading and Carbon Emission Constraints. Energies 2024, 17, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, W.; Cao, X.; Du, J.; Bai, C.; Liu, W.; Tang, M.; Zhan, W.; Chen, Z. Low-carbon economic dispatch strategy for interconnected multi-energy microgrids considering carbon emission accounting and profit allocation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 99, 104987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Xiao, D.; Bai, X.; Chen, H. AUQ–ADMM algorithm-based peer-to-peer trading strategy in large-scale interconnected microgrid systems considering carbon trading. IEEE Syst. J. 2023, 17, 6248–6259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Ding, T.; Zhu, S.; Han, O.; Du, P.; Li, F.; Siano, P. A decentralized market model for a microgrid with carbon emission rights. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 14, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Ren, H.; Li, Q.; Zhou, W. Optimal operation of multi-microgrid systems considering multi-level energy-certificate-carbon coupling trading. Renew. Energy 2024, 227, 120505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Gong, Y.; Jiang, C. A review on promoting share of renewable energy by green-trading mechanisms in power system. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ren, Z.; Trivedi, A.; Verma, P.P.; Srinivasan, D.; Li, W. A noncooperative game-based approach for microgrid planning considering existing interconnected and clustered microgrids on an island. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2022, 13, 2064–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, X. Multi-park low carbon optimal scheduling under energy sharing mode based on cooperative game. High Volt. Eng. 2023, 49, 1380–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Cai, W.; He, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, J. Stackelberg game based energy sharing for zero-carbon community considering reward and punishment of carbon emission. Energy 2023, 277, 127629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Wei, W.; Liu, F. On engineering game theory with its application in power systems. Control. Theory Technol. 2017, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Morstyn, T.; McCulloch, M. Incentivizing prosumer coalitions with energy management using cooperative game theory. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 34, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Mi, Y. Energy management for hybrid AC/DC distribution system with microgrid clusters using non-cooperative game theory and robust optimization. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 11, 1510–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.M.; Patne, N.R.; Guerrero, J.M. A novel approach to neighborhood fair energy trading in a distribution network of multiple microgrid clusters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 1520–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.; Bae, S.; Hwang, G.; Choi, J.K. Contribution-based energy-trading mechanism in microgrids for future smart grid: A game theoretic approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4255–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanoni, C.; De Grève, Z.; Vallée, F.; Deblecker, O. Long-term planning of connected industrial microgrids: A game theoretical approach including daily peer-to-microgrid exchanges. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 10, 2245–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Guo, J.; Lai, C.S.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, K.; Lai, L.L. Distributed model predictive control strategy for islands multimicrogrids based on noncooperative game. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 3803–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, E. Resilient cooperative microgrid networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Yoon, S.-G. Profit-sharing rule for networked microgrids based on Myerson value in cooperative game. IEEE Access 2020, 9, 5585–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, T.; He, S. Coordination and optimization of CCHP microgrid group game based on the interaction of electric and thermal energy considering conditional value at risk. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 88664–88673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Gao, F. Coordinated optimization scheduling of data center and electricity retailer based on cooperative game theory. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2022, 7, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoh, K.; Maharjan, S.; Ikpehai, A.; Zhang, Y.; Adebisi, B. Energy peer-to-peer trading in virtual microgrids in smart grids: A game-theoretic approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 11, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgana, A.; Rimal, B.P.; Maier, M. Open energy market strategies in microgrids: A Stackelberg game approach based on a hybrid multiobjective evolutionary algorithm. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 6, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Fan, F.; Tai, N.; Hu, Y.; Li, R. Coordinated Energy Dispatch and Flexibility Support for Microgrid Cluster Using Rule-based Stackelberg Gaming Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 1564–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Li, X.; Cheng, S. Energy management optimization of microgrid cluster based on multi-agent-system and hierarchical Stackelberg game theory. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 206183–206197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Xiao, H.; Pei, W.; Chiu, W.-Y.; Jiang, J.; Sun, H.; Matthews, P. Transactive energy and flexibility provision in multi-microgrids using Stackelberg game. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 9, 505–515. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Guo, J.; Choi, J.K.; Zukerman, M. Distributed energy trading in microgrids: A game-theoretic model and its equilibrium analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3524–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.; Zamir, T.; Liang, H. Blockchain for cybersecurity in smart grid: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Dong, Z.; Hu, J.; Huang, Q.; Wang, F. P2P smart power trading contract based on blockchain technology. Power Syst. Technol. 2021, 45, 3830–3839. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Xue, K.; Xu, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y. Blockchain based secure data aggregation and distributed power dispatching for microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 5268–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y. Blockchain-enabled cyber-resilience enhancement framework of microgrid distributed secondary control against false data injection attacks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2024, 15, 2226–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Paudel, A.; Gooi, H.B. Compensation for power loss by a proof-of-stake consortium blockchain microgrid. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 3253–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hui, H.; Zhang, H. Decentralized energy management of microgrid based on blockchain-empowered consensus algorithm with collusion prevention. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2023, 14, 2260–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Miao, W.; Li, Z.; Tian, J.; Wang, C.; Min, G. Enabling energy trading in cooperative microgrids: A scalable blockchain-based approach with redundant data exchange. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 7077–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Van Mieghem, J.A. Robust dual sourcing inventory management: Optimality of capped dual index policies and smoothing. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2019, 21, 912–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Ruan, H.; Gao, H.; Liu, J. Overview on theory analysis and application of distributionally robust optimization method in power system. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2020, 44, 179–191. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, W. Regret in the newsvendor model with demand and yield randomness. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2021, 30, 4176–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Lim, A.E. Robust multiarmed bandit problems. Manag. Sci. 2016, 62, 264–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, L. A robust data-driven approach for the newsvendor problem with nonparametric information. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2022, 24, 504–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.E.; Sadeghi, D.; Marzband, M.; Abusorrah, A.; Sedraoui, K. Decentralized bi-level stochastic optimization approach for multi-agent multi-energy networked micro-grids with multi-energy storage technologies. Energy 2022, 245, 123223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Mu, Y.; Jia, H.; Yu, X.; Hou, K.; Wang, H. A Multi-Objective Stochastic optimization approach for planning a multi-energy microgrid considering unscheduled islanded operation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2023, 15, 1300–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Cheng, M.; Yu, X.; Zhong, J.; Lei, J. Energy-sharing provider for PV prosumer clusters: A hybrid approach using stochastic programming and stackelberg game. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 6740–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, E.G.; Cañizares, C.A.; Pirnia, M.; Guedes, T.P.; Trujillo, J.D.M. Two-stage stochastic optimization model for multi-microgrid planning. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 14, 1723–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C. A risk-averse adaptive stochastic optimization method for transactive energy management of a multi-energy microgrid. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2023, 14, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Gu, W.; Xu, X.; Pan, G.; Liu, P.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L. A historical-correlation-driven robust optimization approach for microgrid dispatch. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 12, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Gu, W.; You, F. Bilayer distributed optimization for robust microgrid dispatch with coupled individual-collective profits. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2021, 12, 1525–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatloo, A.M.; Mirzaei, M.A.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B. A robust decentralized peer-to-peer energy trading in community of flexible microgrids. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 17, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Yang, G.; Dong, Z.Y. Transactive energy sharing in a microgrid via an enhanced distributed adaptive robust optimization approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 2279–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Feng, W. Robust optimization for energy transactions in multi-microgrids under uncertainty. Appl. Energy 2018, 217, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Khodaei, A.; Zhang, H.; Han, Z. Optimal energy management for multi-microgrid under a transactive energy framework with distributionally robust optimization. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 13, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Khodayar, M.E.; Wang, J.; Zhou, B. Data-driven distributionally robust co-optimization of P2P energy trading and network operation for interconnected microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 5172–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, R.; Huang, S. Optimal design and operation of islanded multi-microgrid system with distributionally robust optimization. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 221, 109437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Guo, J.; Luo, X.; Lai, C.S.; Yang, P.; Lai, L.L.; Li, P.; Guerrero, J.M.; Shahidehpour, M. Distributed robust model predictive control-based energy management strategy for islanded multi-microgrids considering uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 2107–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Gong, C.; Shang, Y.; Wang, Z. The Operation Strategy of a Multi-Microgrid Considering the Interaction of Different Subjects’ Interests. Energies 2024, 17, 4883. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194883
Wang S, Chen H, Gong C, Shang Y, Wang Z. The Operation Strategy of a Multi-Microgrid Considering the Interaction of Different Subjects’ Interests. Energies. 2024; 17(19):4883. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194883
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Siwen, Hui Chen, Chunyang Gong, Yanfei Shang, and Zhixin Wang. 2024. "The Operation Strategy of a Multi-Microgrid Considering the Interaction of Different Subjects’ Interests" Energies 17, no. 19: 4883. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194883
APA StyleWang, S., Chen, H., Gong, C., Shang, Y., & Wang, Z. (2024). The Operation Strategy of a Multi-Microgrid Considering the Interaction of Different Subjects’ Interests. Energies, 17(19), 4883. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194883






