Microstructure-Dependent Macroscopic Electro-Chemo- Mechanical Behaviors of Li-Ion Battery Composite Electrodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
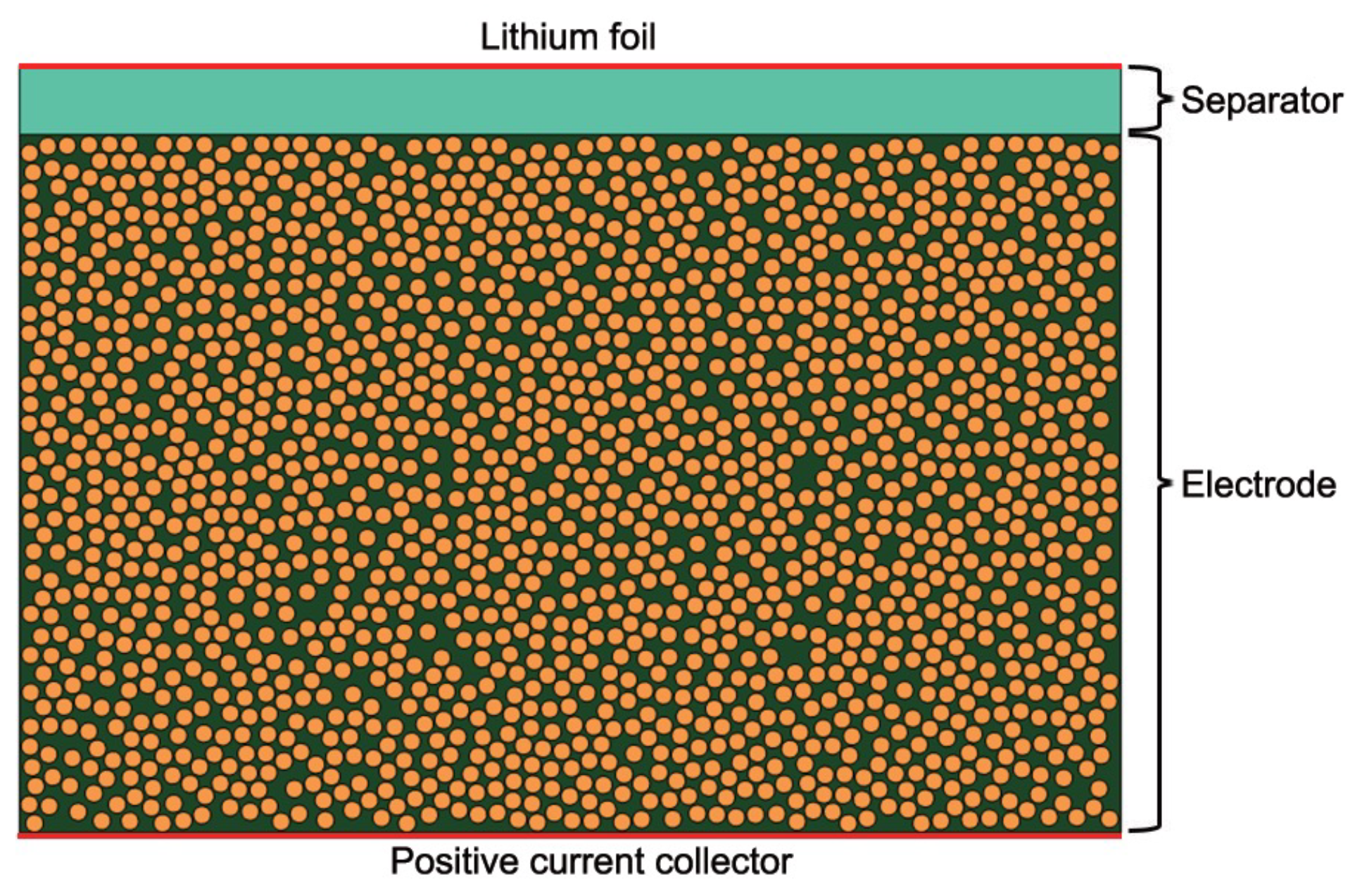
2. Mathematical Models
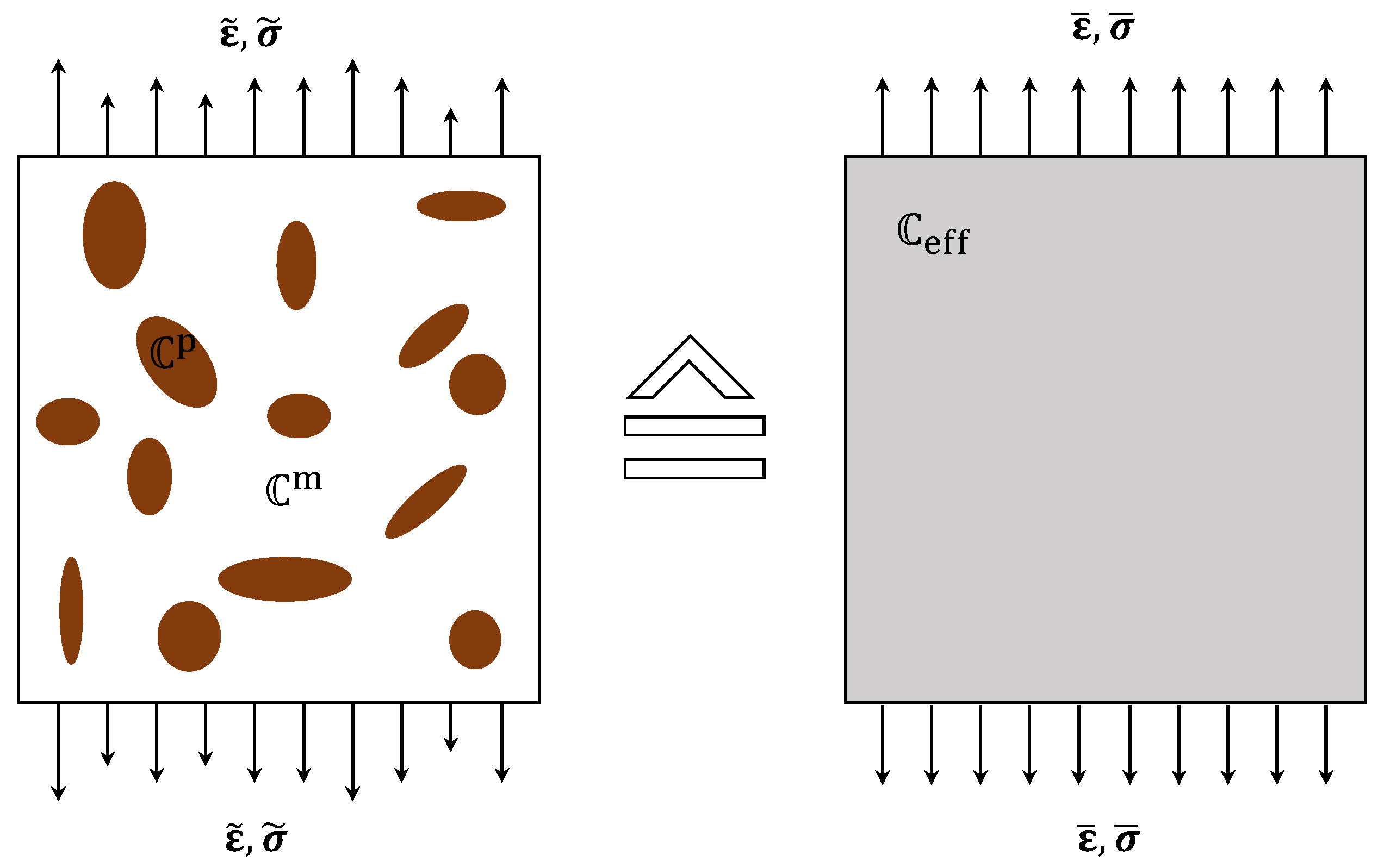
2.1. Heterogeneous Model
2.2. Homogeneous Model
3. Results and Discussion
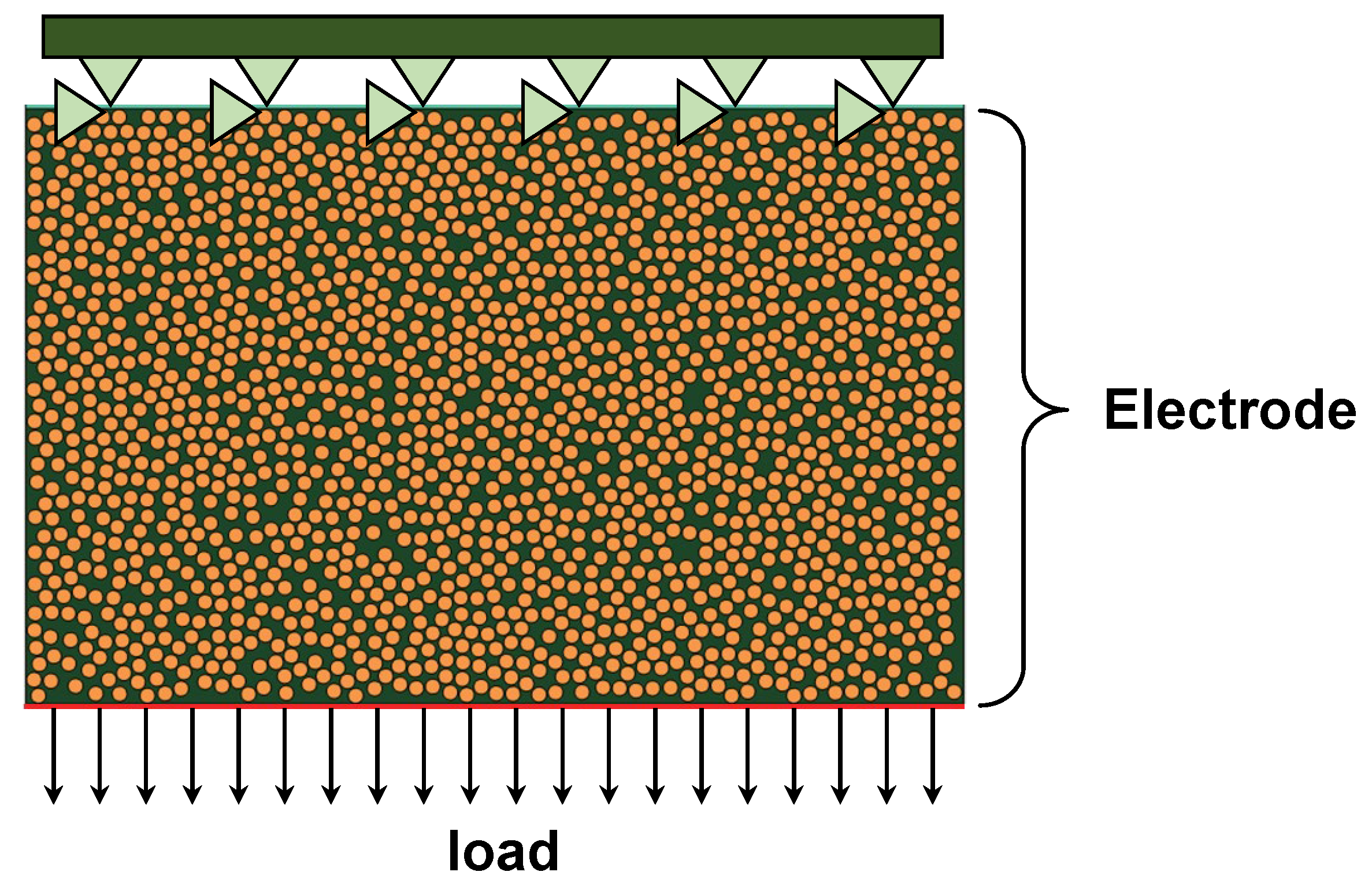
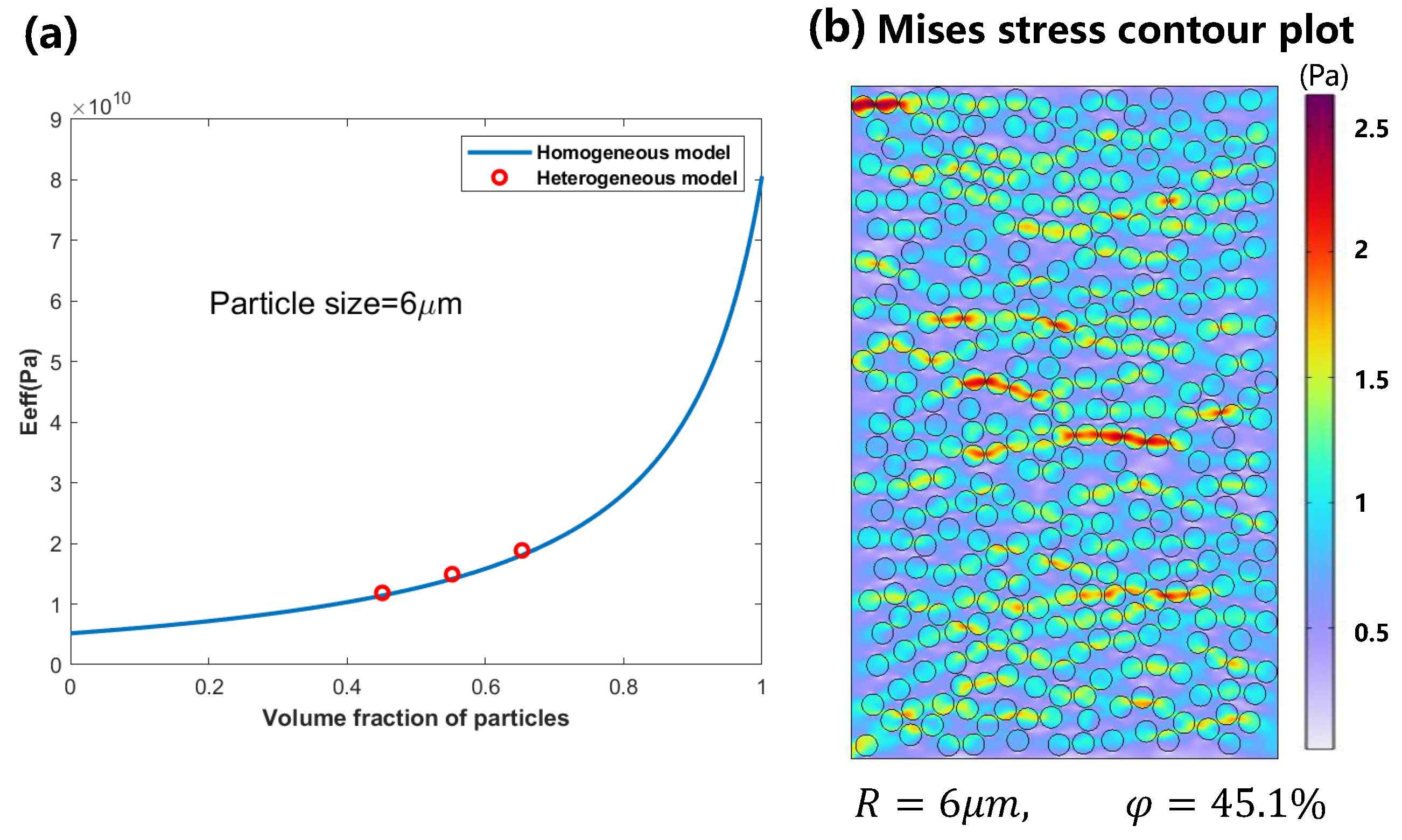
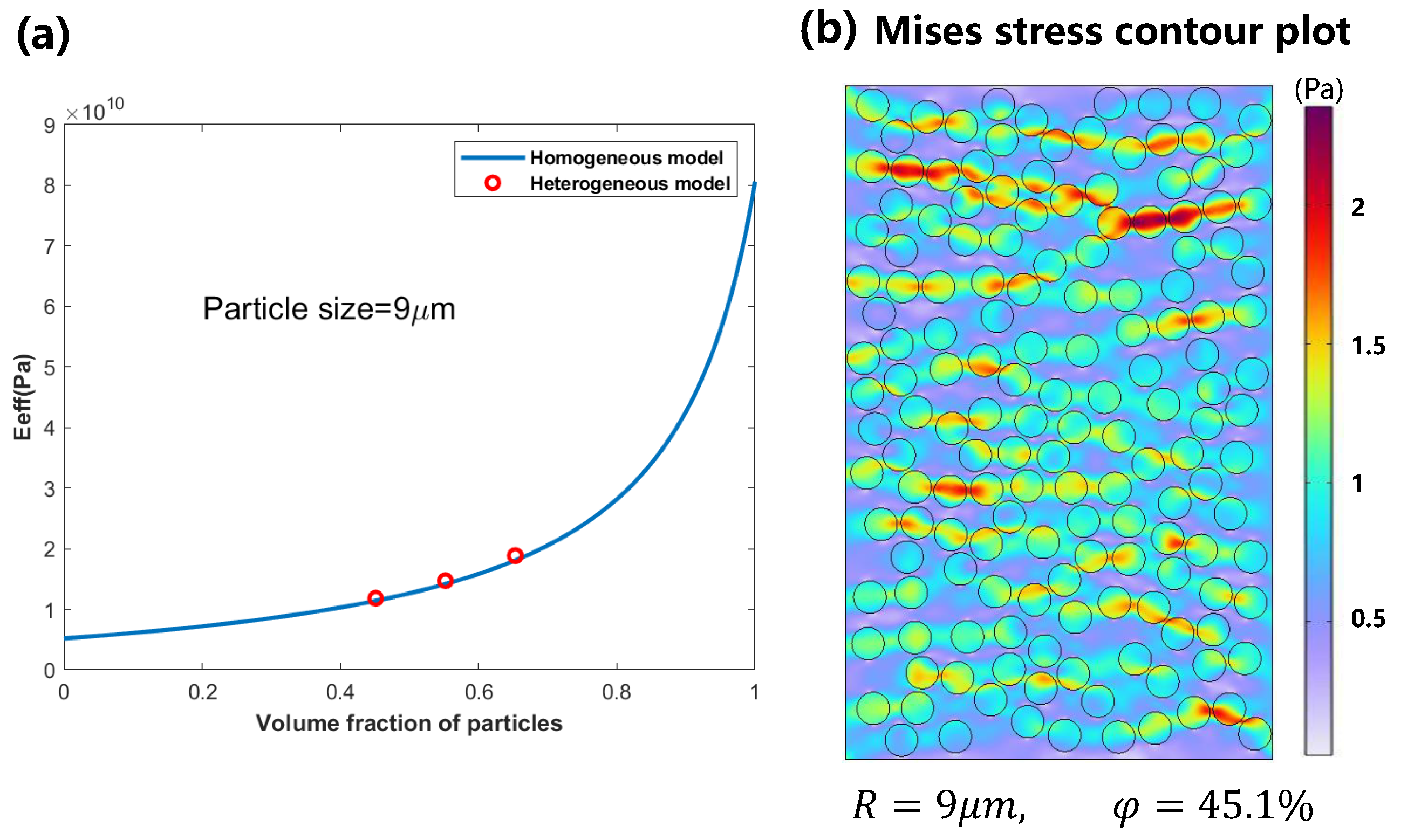
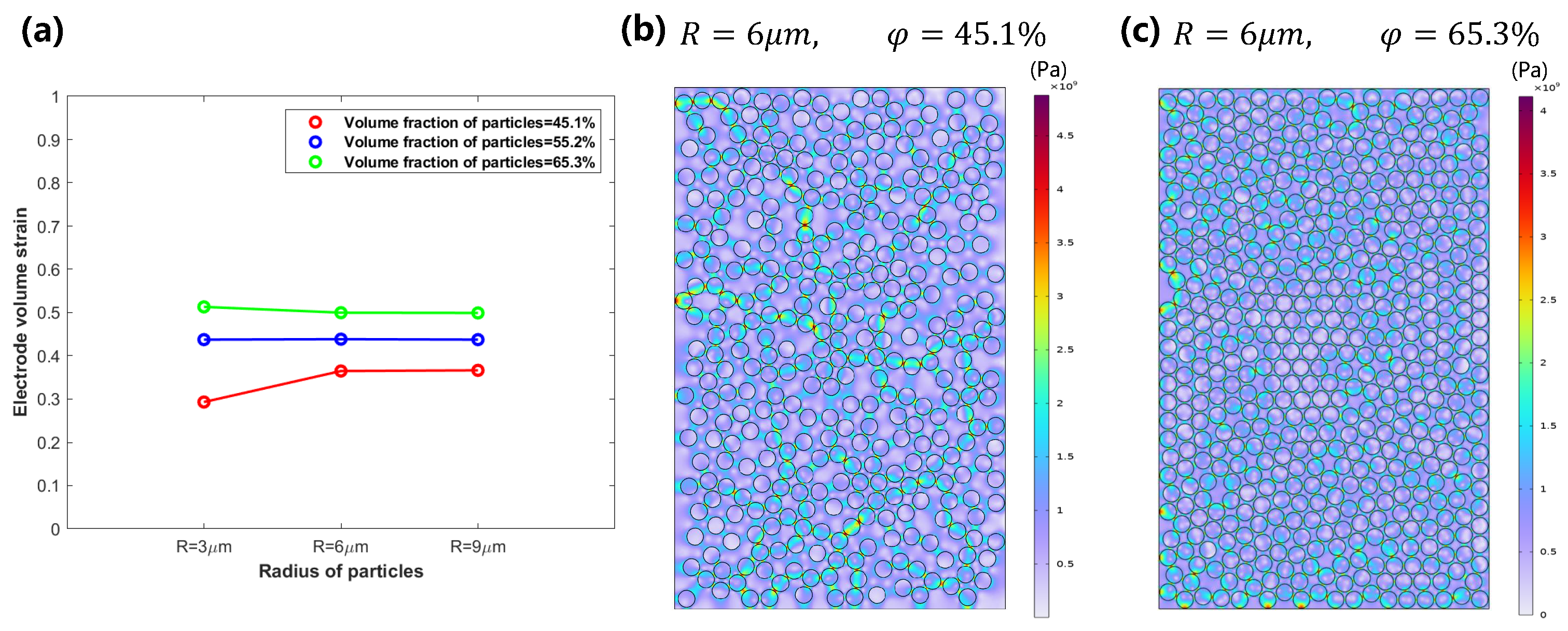
3.1. Mechanical Behavior
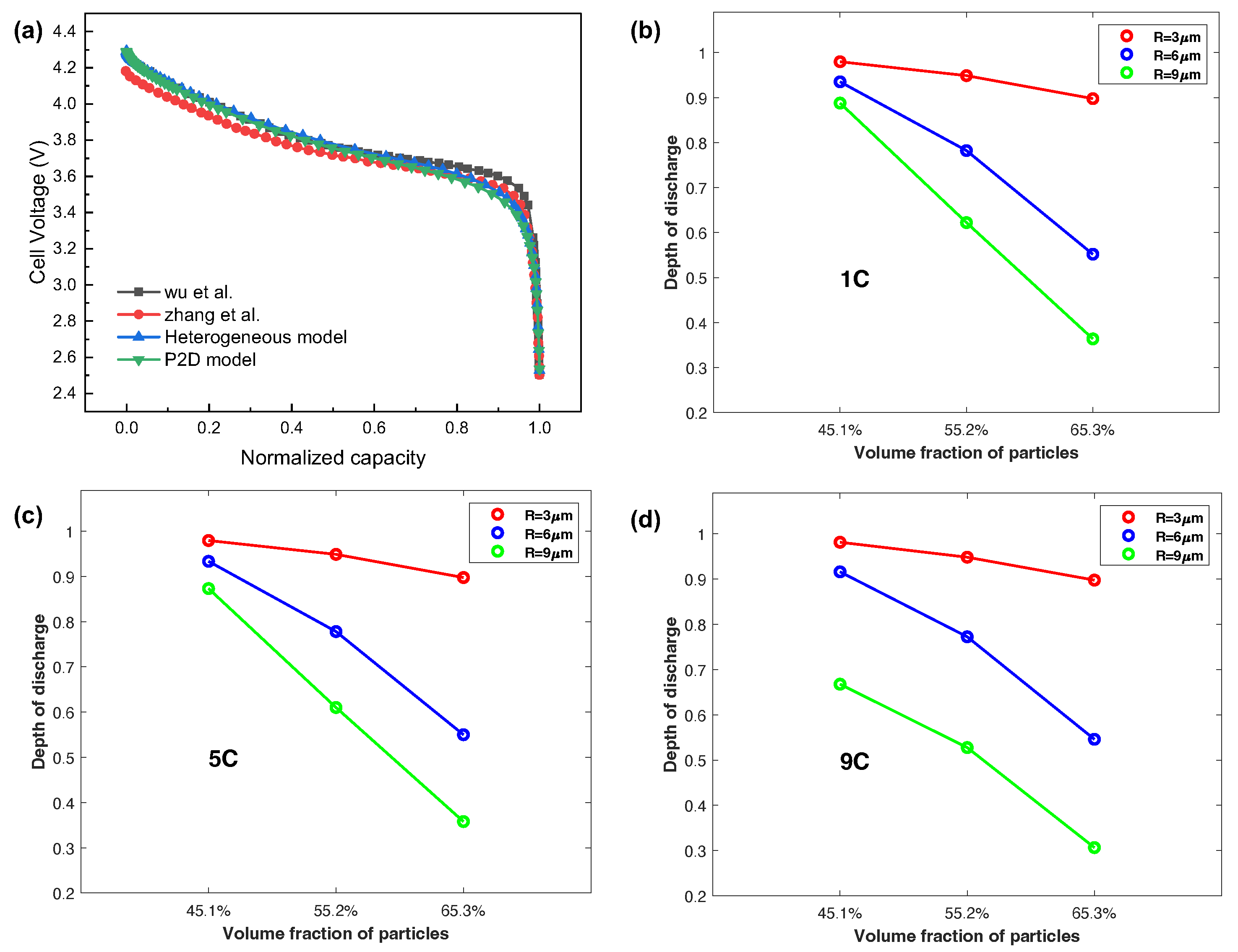
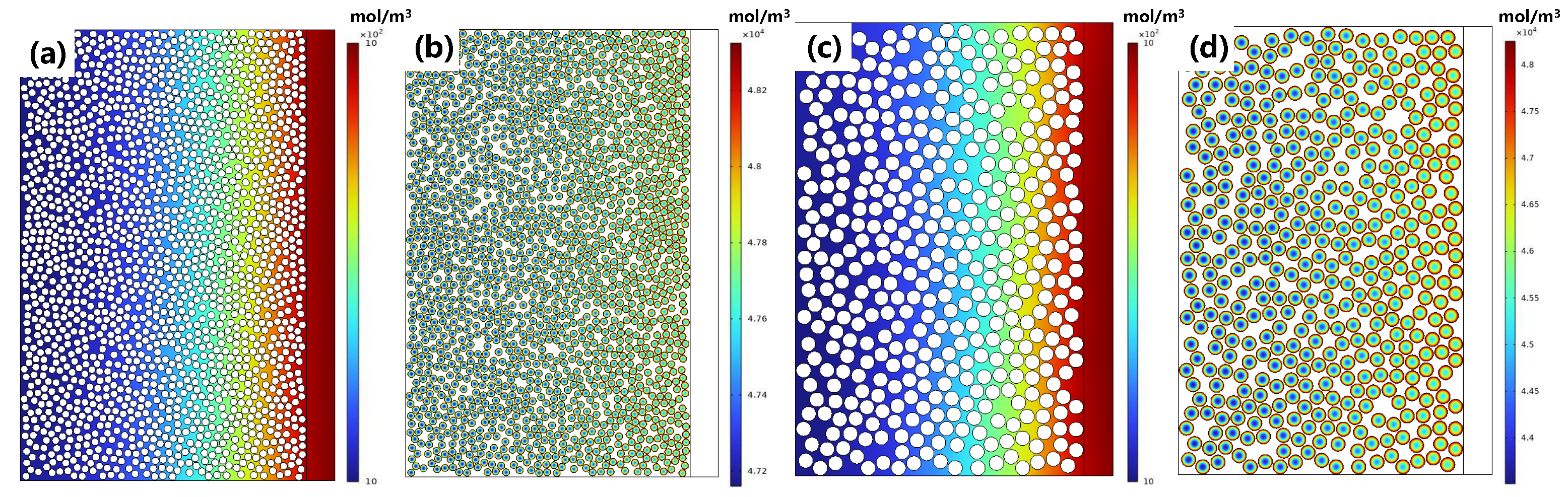
3.2. Electrochemical Behavior
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LIB | Lithium-ion battery |
| CBD | Carbon-binder domain |
| P2D | Pseudo two-dimensional |
| DOD | Depth of discharge |
References
- Zhao, Y.; Stein, P.; Bai, Y.; Al-Siraj, M.; Yang, Y.; Xu, B.X. A review on modeling of electro-chemo-mechanics in lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2019, 413, 259–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Suo, Z. Averting cracks caused by insertion reaction in lithium–ion batteries. J. Mater. Res. 2010, 25, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Zhong, L.; Huang, S.; Mao, S.X.; Zhu, T.; Huang, J.Y. Size-Dependent Fracture of Silicon Nanoparticles during Lithiation. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Schillinger, D.; Xu, B.X. Variational boundary conditions based on the Nitsche method for fitted and unfitted isogeometric discretizations of the mechanically coupled Cahn–Hilliard equation. J. Comput. Phys. 2017, 340, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, R.; Zhang, K.; Lee, S.J.; Mu, L.; Liu, P.; Waters, C.K.; Spence, S.; Xu, Z.; Wei, C.; et al. Quantification of Heterogeneous Degradation in Li-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1900674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubner, C.; Nick, A.; Seeba, J.; Reuber, S.; Junker, N.; Wolter, M.; Schneider, M.; Michaelis, A. Understanding thickness and porosity effects on the electrochemical performance of LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2-based cathodes for high energy Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2019, 419, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itou, Y.; Ukyo, Y. Performance of LiNiCoO2 materials for advanced lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2005, 146, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, G.; Swamy, T.; Chiang, Y.M.; Carter, W.C. Random Walk Analysis of the Effect of Mechanical Degradation on All-Solid-State Battery Power. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A2660–A2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, G.W.; Park, N.Y.; Park, K.J.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Yoon, C.S.; Sun, Y.K. Capacity Fading of Ni-Rich NCA Cathodes: Effect of Microcracking Extent. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 2995–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Yang, Y.; Yin, F.; Liu, P.; Cloetens, P.; Liu, Y.; Lin, F.; Zhao, K. Heterogeneous damage in Li-ion batteries: Experimental analysis and theoretical modeling. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2019, 129, 160–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bläubaum, L.; Röder, F.; Nowak, C.; Chan, H.S.; Kwade, A.; Krewer, U. Impact of Particle Size Distribution on Performance of Lithium-Ion Batteries. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 4755–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Gan, Y.; Yao, M. Numerical analysis on the aging characteristics of a LiFePO4 battery: Effect of active particle sizes in electrodes. J. Energy Storage 2023, 67, 107546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K. Effect of porous structure and morphology of cathode on the degradation of lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52, 104788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y. A quasi-physical method for random packing of spherical particles. Powder Technol. 2022, 412, 118002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y. Tortuosity estimation and microstructure optimization of non-uniform porous heterogeneous electrodes. J. Power Sources 2024, 596, 234095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.; Kim, H.; Shin, H.; Park, H.; Cho, M. Multiscale study to investigate nanoparticle agglomeration effect on electrical conductivity of nano-SiC reinforced polypropylene matrix composites. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2023, 30, 2442–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagda, V.; Kulachenko, A.; Lindström, S.B. Image-based 3D characterization and reconstruction of heterogeneous battery electrode microstructure. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2023, 223, 112139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, S.; Feinauer, J.; Westhoff, D.; Manke, I.; Schmidt, V.; Latz, A. Stochastic microstructure modeling and electrochemical simulation of lithium-ion cell anodes in 3D. J. Power Sources 2016, 336, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashkooli, A.G.; Farhad, S.; Lee, D.U.; Feng, K.; Lister, S.; Babu, S.K.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Z. Multiscale modeling of lithium-ion battery electrodes based on nano-scale X-ray computed tomography. J. Power Sources 2016, 307, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Bertei, A.; Finegan, D.P.; Tan, C.; Daemi, S.R.; Weaving, J.S.; O’Regan, K.B.; Heenan, T.M.M.; Hinds, G.; Kendrick, E.; et al. 3D microstructure design of lithium-ion battery electrodes assisted by X-ray nano-computed tomography and modelling. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, A.M.; Lu, X.; Brett, D.J.L.; Shearing, P.R. Exploring the influence of porosity and thickness on lithium-ion battery electrodes using an image-based model. J. Power Sources 2022, 542, 231779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Arcelus, O.; Lombardo, T.; Oularbi, H.; Franco, A.A. Towards a 3D-resolved model of Si/Graphite composite electrodes from manufacturing simulations. J. Power Sources 2021, 512, 230486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikpour, M.; Barrett, N.; Hillman, Z.; Thompson, A.I.; Mazzeo, B.A.; Wheeler, D.R. A Model for Investigating Sources of Li-Ion Battery Electrode Heterogeneity: Part I. Electrode Drying and Calendering Processes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 060547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, C.S.; Finke, B.; Schilde, C.; Froböse, L.; Kwade, A. Numerical simulation of the behavior of lithium-ion battery electrodes during the calendaring process via the discrete element method. Powder Technol. 2019, 349, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.; Cumming, D.J.; Smith, R.M. Discrete element method (DEM) analysis of lithium ion battery electrode structures from X-ray tomography-the effect of calendering conditions. Powder Technol. 2022, 403, 117366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Ge, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. A Two-Dimensional Heterogeneous Model of Lithium-Ion Battery and Application on Designing Electrode with Non-Uniform Porosity. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 130513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Hoang, T.D.; Han, S.C.; Bang, J.A.; Kang, H.W.; Kim, J.; Park, H.; Park, J.H.; Park, J.W.; Park, G.; et al. Exploring optimal cathode composite design for high-performance all-solid-state batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2024, 71, 103607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Lu, B.; He, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J. Modulus Estimation of Composites with High Porosity, High Particle Volume Fraction, and Particle Eigenstrain: Application to the LIB Active Layer with a Bridged-Particle Mesostructure. Energies 2023, 16, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundson, P.; Larsson, P.L. An analytic model for effective mechanical properties and local contact stresses in lithium-ion porous electrodes. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2021, 42, 101067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ücel, I.B.; Gudmundson, P. A statistical RVE model for effective mechanical properties and contact forces in lithium-ion porous electrodes. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2022, 244–245, 111602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y. Assessment of Optimization Strategies for Battery Electrode-Active Particles Based on Chemomechanical Analysis. J. Electrochem. Energy Convers. Storage 2022, 19, 041001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benveniste, Y. A new approach to the application of Mori-Tanaka’s theory in composite materials. Mech. Mater. 1987, 6, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmon, S.; Maute, K.; Dunn, M.L. Numerical modeling of electrochemical–mechanical interactions in lithium polymer batteries. Comput. Struct. 2009, 87, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, M.; Fuller, T.F.; Newman, J. Modeling of Galvanostatic Charge and Discharge of the Lithium/Polymer/Insertion Cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Deshpande, V.S.; Fleck, N.A. A compliant and low-expansion 2-phase micro-architectured material, with potential application to solid-state Li-ion batteries. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2022, 158, 104683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, B.X. Two-level modeling of lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2019, 422, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Luo, J.; Huang, Y. Comprehensive aging model coupling chemical and mechanical degradation mechanisms for NCM/C6-Si lithium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2024, 71, 103620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.L.; Zhang, W.; Song, X.; Shukla, A.K.; Liu, G.; Battaglia, V.; Srinivasan, V. High Rate Capability of Li(Ni1/3Mn1/3Co1/3)O2 Electrode for Li-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mauger, A.; Jiang, W.; Groult, H.; Julien, C.M. Diffusion of Li+ Ions in LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2. ECS Trans. 2011, 35, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Definition of Parameters | Symbol (Unit) | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Electrode thickness | L () | 237 |
| Maximum concentration of Li+ of active material | () | 49,500 |
| Li+ diffusion coefficient in matrix | () | Equation (37) |
| Li+ conductivity in matrix | () | Equation (38) |
| Li+ diffusion coefficient in NMC111 particles | () | 3 × 10−14 |
| Initial concentration of Li+ in electrolyte | () | 1000 |
| Transference number of Li | 0.363 | |
| Transfer coefficients | 0.5 | |
| Temperature | T () | 298 |
| Young’s modulus of NMC particles | () | 78 |
| Poisson’s ratio of NMC particles | 0.25 | |
| Young’s modulus of matrix * | 5 | |
| Poisson’s ratio of matrix * | 0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Ge, Z.; Chen, Z. Microstructure-Dependent Macroscopic Electro-Chemo- Mechanical Behaviors of Li-Ion Battery Composite Electrodes. Energies 2024, 17, 4607. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17184607
Zhao Y, Ge Z, Chen Z. Microstructure-Dependent Macroscopic Electro-Chemo- Mechanical Behaviors of Li-Ion Battery Composite Electrodes. Energies. 2024; 17(18):4607. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17184607
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Ying, Zhongli Ge, and Zongli Chen. 2024. "Microstructure-Dependent Macroscopic Electro-Chemo- Mechanical Behaviors of Li-Ion Battery Composite Electrodes" Energies 17, no. 18: 4607. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17184607
APA StyleZhao, Y., Ge, Z., & Chen, Z. (2024). Microstructure-Dependent Macroscopic Electro-Chemo- Mechanical Behaviors of Li-Ion Battery Composite Electrodes. Energies, 17(18), 4607. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17184607








