A Power Circulating Suppression Method for Parallel Transient Inverters with Instantaneous Phase Angle Compensation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The power circulation in inverters is comprehensively analyzed by constructing a parallel mathematical model.
- Based on the absorbed energy obtained by integrating the output power, the phase angle and frequency of the inverter’s output voltage are adjusted to realize the suppression of transient power circulation and the balance of steady DC-side energy.
- System stability is evaluated through the Lyapunov function method following an examination of control process state changes.
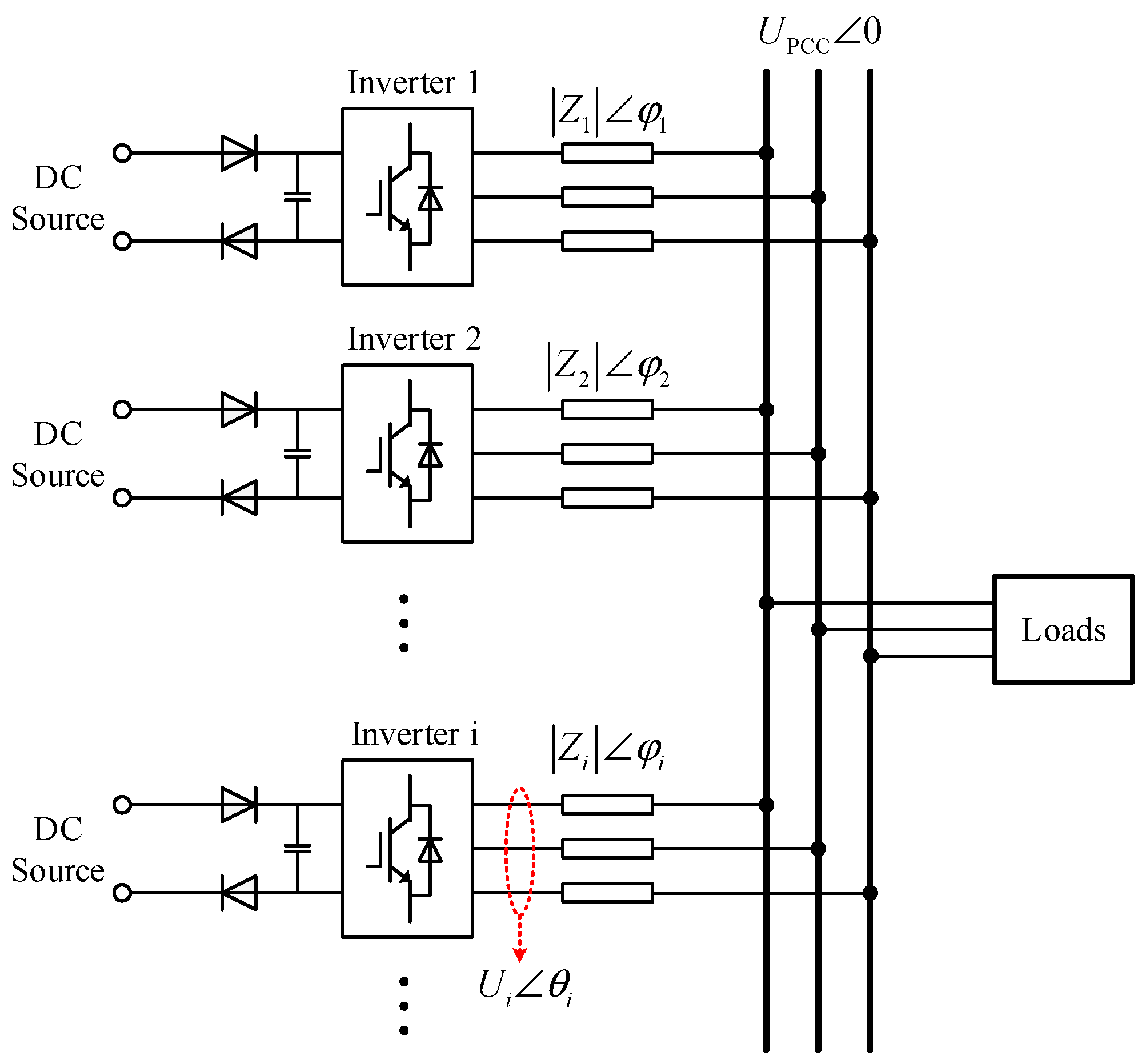
2. Analysis of the Power Circulation of Inverters in Parallel Transients
2.1. Power Circulation Analysis Based on the General Parallel Model
2.2. Analysis of Power Circulation of Parallel Inverters under Unloaded Condition
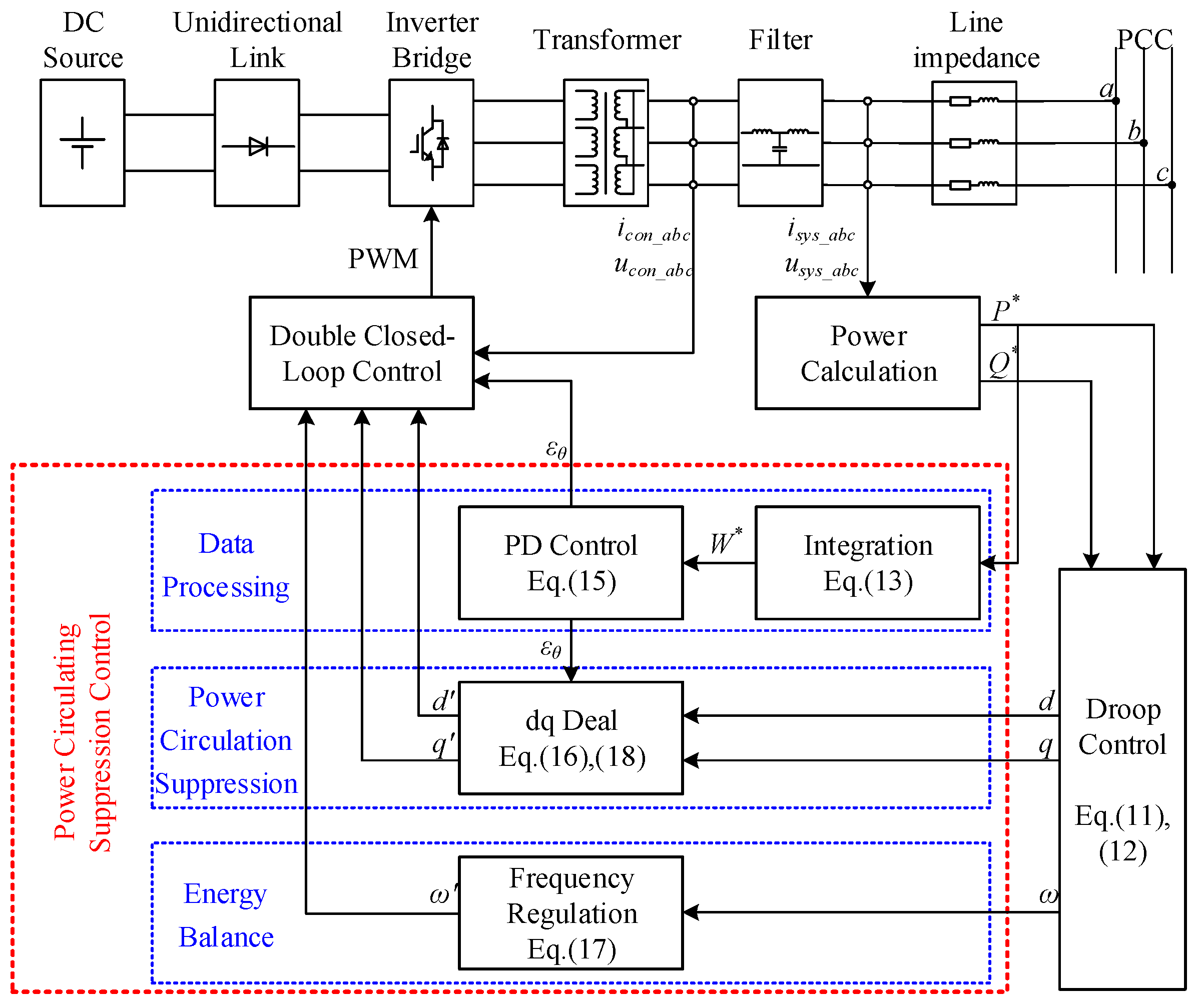
3. Control Strategy for Suppressing Power Circulation in Parallel Transients
3.1. Data Processing
3.2. Power Circulation Suppression
3.3. Energy Balance
4. Stability Assessment Based on Lyapunov Function Method
- (1)
- and ;
- (2)
- and ;
- (3)
- and ;
- (4)
- and .
5. Simulation and Experiment
5.1. Simulation
5.2. Experiment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hatziargyriou, N.; Asano, H.; Iravani, R.; Marnay, C. Microgrids. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2007, 5, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhizi, S.; Lotfi, H.; Khodaei, A.; Bahramirad, S. State of the art in research on microgrids: A review. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 890–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero, C.X.; Velasco, M.; Marti, P.; Camacho, A.; Miret, J.; Castilla, M. Active power sharing and frequency regulation in droop-free control for islanded microgrids under electrical and communication failures. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 6461–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandorkar, M.C.; Divan, D.M. Decentralized operation of distributed UPS systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems for Industrial Growth, New Delhi, India, 8–11 January 1996; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Katiraei, F.; Iravani, M.R. Power management strategies for a microgrid with multiple distributed generation units. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, D.E.; Ali, M.S.; Etemadi, A.H.; Canizares, C.A.; Iravani, R.; Kazerani, M.; Hajimiragha, A.H.; Gomis-Bellmunt, O.; Saeedifard, M.; Palma-Behnke, R.; et al. Trends in microgrid control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 1905–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.S.; Li, Q.K.; Wang, W.; Yao, G.Z.; Ma, H.H.; Zeng, X.J.; Guerrero, J.M. A novel droop control strategy of reactive power sharing based on adaptive virtual impedance in microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 11335–11347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Xue, Y.; Chang, X.; Su, J.; Wang, P.; Guo, Q.; Sun, H. A Stochastic Bi-level Optimal Allocation Approach of Intelligent Buildings Considering Energy Storage Sharing Services. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.W.; Sangwongwanich, A.; Yang, Y.H.; Blaabjerg, F. Distributed control of islanded series PV-battery-hybrid systems with low communication burden. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 10199–10213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.; Rueda-Escobedo, J.G.; Schiffer, J. Robust design of phase-locked loops in grid-connected power converters. Eur. J. Control 2024, 101055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Shao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Q. A new topology of the distributed power flow controller and its electromagnetic transient characteristics. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 163, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, N.M.; Lu, D.D.-C. A Bidirectional Two-Switch Flyback Converter With Cross-Coupled LCD Snubbers for Minimizing Circulating Current. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 5948–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Guerrero, J.M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guo, X. A Circulating-Current Suppression Method for Parallel-Connected Voltage-Source Inverters With Common DC and AC Buses. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 3758–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, N.; Bhattacharya, S. Adaptive Droop Control Method for Suppressing Circulating Currents in DC Microgrids. IEEE Open Access J. Power Energy 2020, 7, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero, C.X.; Gavilánez, M.; Mejía-Echeverría, C. Droop-Free Sliding-Mode Control for Active-Power Sharing and Frequency Regulation in Inverter-Based Islanded Microgrids. Energies 2023, 16, 6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Pen, H. Cooperative voltage control in distribution networks considering multiple uncertainties in communication. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2024, 39, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Esa, Y.; Hariri, M.E.; Mohamed, A. Impact of information and communication technology limitations on microgrid operation. Energies 2019, 12, 2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhong, H.; Li, Y.; Liao, J.; Chen, X.; Nan, X.; Gao, B. An event-triggered quantization communication strategy for distributed optimal resource allocation. Syst. Control Lett. 2023, 180, 105619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasis, A.; Monshizadeh, N.; Lestas, I. A distributed scheme for secondary frequency control with stability guarantees and optimal power allocation. Syst. Control Lett. 2020, 144, 104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, Z.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, X. Consensus-based secondary frequency control for parallel virtual synchronous generators. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2024, 38, 101341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-T.; Yoo, H.-J.; Kim, H.-M.; Nguyen-Duc, H. Direct Phase Angle and Voltage Amplitude Model Predictive Control of a Power Converter for Microgrid Applications. Energies 2018, 11, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, B.; Ghosh, A.; Zare, F. Load Sharing in Medium Voltage Islanded Microgrids With Advanced Angle Droop Control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 6461–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hou, S.; Li, X. Decentralized Circulating Currents Suppression for Paralleled Inverters in Microgrids Using Adaptive Virtual Inductances. Energies 2018, 11, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Wang, Y.; Lei, W.; Li, T.; Yin, S. Modeling and Enhanced Error-Free Current Control Strategy for Inverter with Virtual Resistor Damping. Energies 2018, 11, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chan, K.W.; Hu, J.; Guerrero, J.M. Adaptive Droop Control Using Adaptive Virtual Impedance for Microgrids With Variable PV Outputs and Load Demands. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 9630–9640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, P.; Coelho, E.A.A.; Guerrero, J.M. Review of active and reactive power sharing strategies in hierarchical controlled microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 2427–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| System parameter | ||
| Input DC Voltage | ||
| DC capacity | ||
| Output voltage root mean square | ||
| Output voltage radian frequency | ||
| Initial phase error | Simulation: Experiment: Actual | |
| 1.0 p.u. load | ||
| Line impedance 1 | ||
| Line impedance 2 | ||
| Control parameter | ||
| Active power–frequency coefficient | ||
| Reactive power–frequency coefficient | ||
| Active power–voltage coefficient | ||
| Reactive power–voltage coefficient | ||
| Radian frequency correction coefficient | ||
| Proportional coefficient | ||
| Differential coefficient | ||
| System efficiency | Simulation: 0.99 Experiment: 0.92 | |
| Stage | ||
| Stage 1 | Parallel connection | |
| Stage 2 | 0.5 p.u. load increasing | |
| Stage 3 | 0.5 p.u. load shedding | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, S.; Xiao, F.; Jie, G.; Gao, S.; Ye, J. A Power Circulating Suppression Method for Parallel Transient Inverters with Instantaneous Phase Angle Compensation. Energies 2024, 17, 4368. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174368
Ji S, Xiao F, Jie G, Gao S, Ye J. A Power Circulating Suppression Method for Parallel Transient Inverters with Instantaneous Phase Angle Compensation. Energies. 2024; 17(17):4368. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174368
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Shengxian, Fei Xiao, Guisheng Jie, Shan Gao, and Jiamin Ye. 2024. "A Power Circulating Suppression Method for Parallel Transient Inverters with Instantaneous Phase Angle Compensation" Energies 17, no. 17: 4368. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174368
APA StyleJi, S., Xiao, F., Jie, G., Gao, S., & Ye, J. (2024). A Power Circulating Suppression Method for Parallel Transient Inverters with Instantaneous Phase Angle Compensation. Energies, 17(17), 4368. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174368






