Variable Delayed Time Control for Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Double Central Symmetry Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
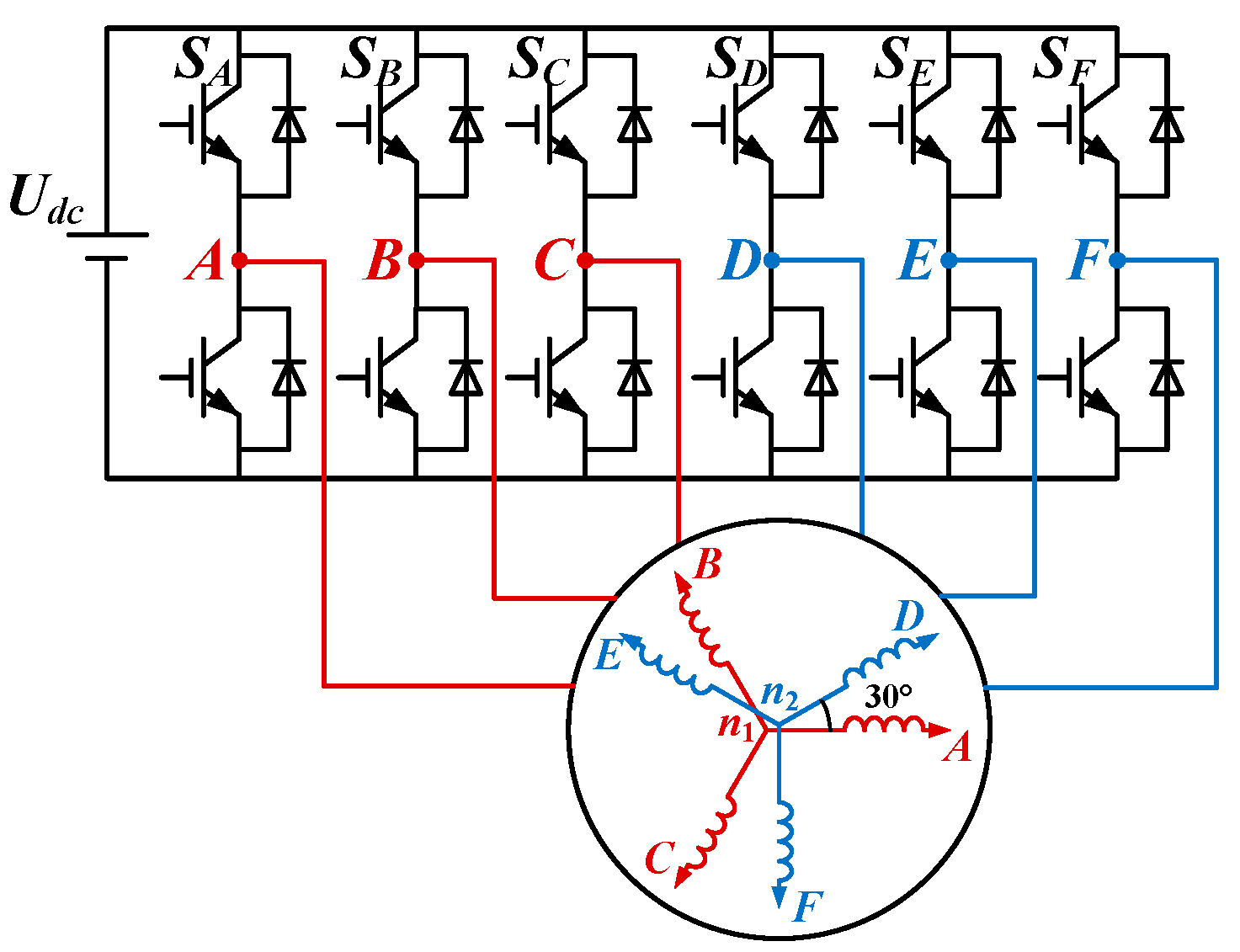
2. SVPWM for Dual-Three Phase Machine
3. Proposed Method
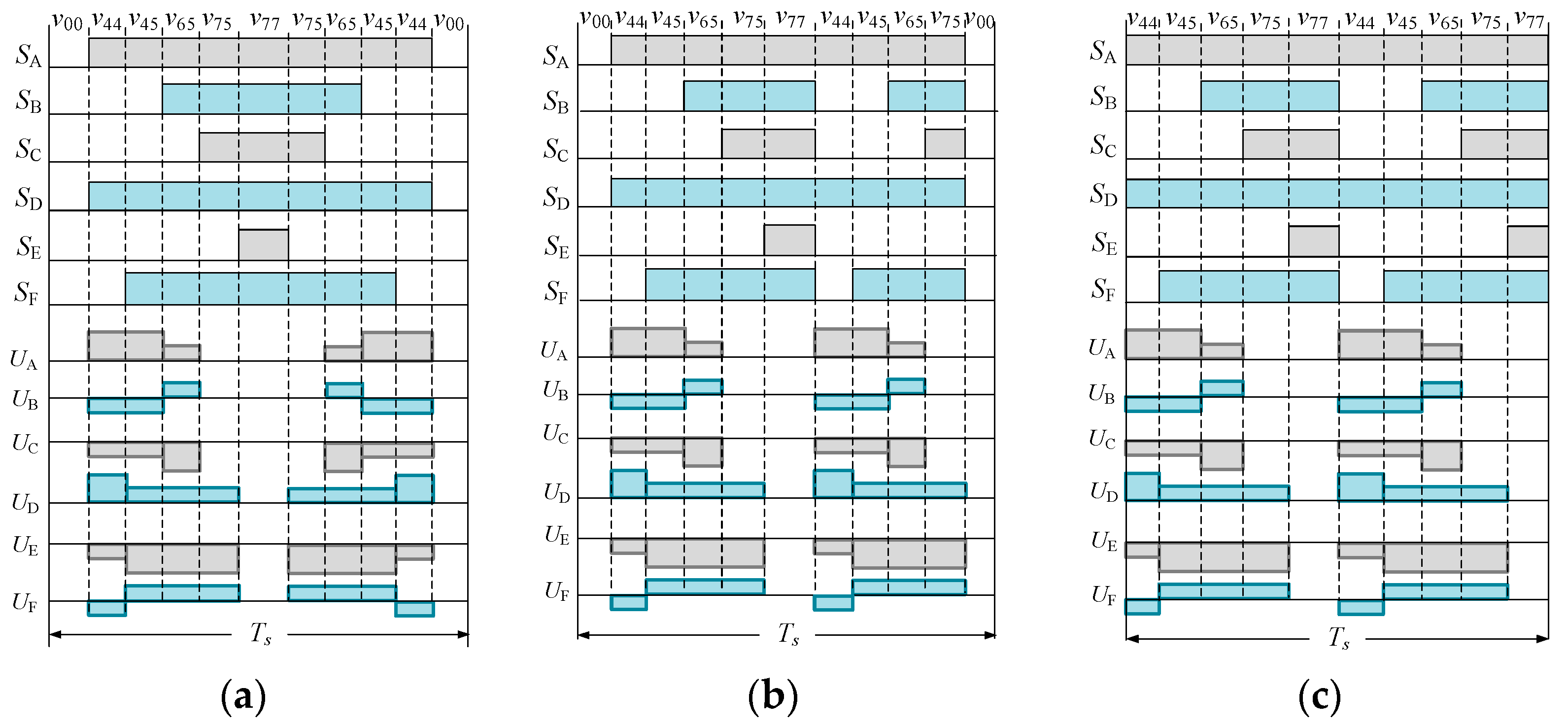
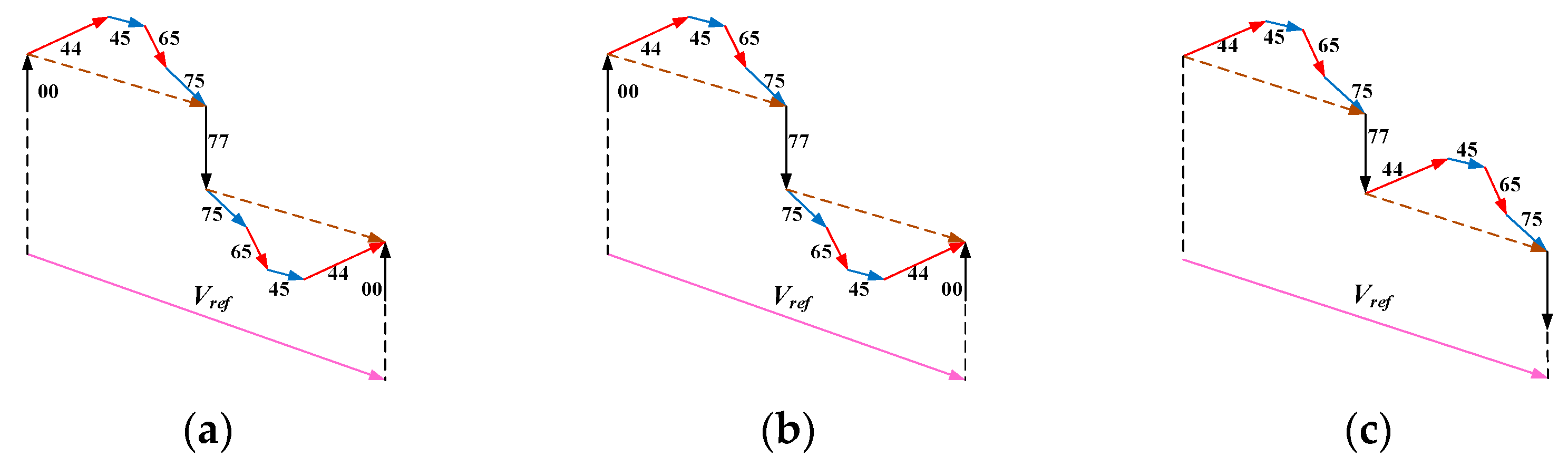
3.1. Sequence Rearrangement for Harmonic Elimination
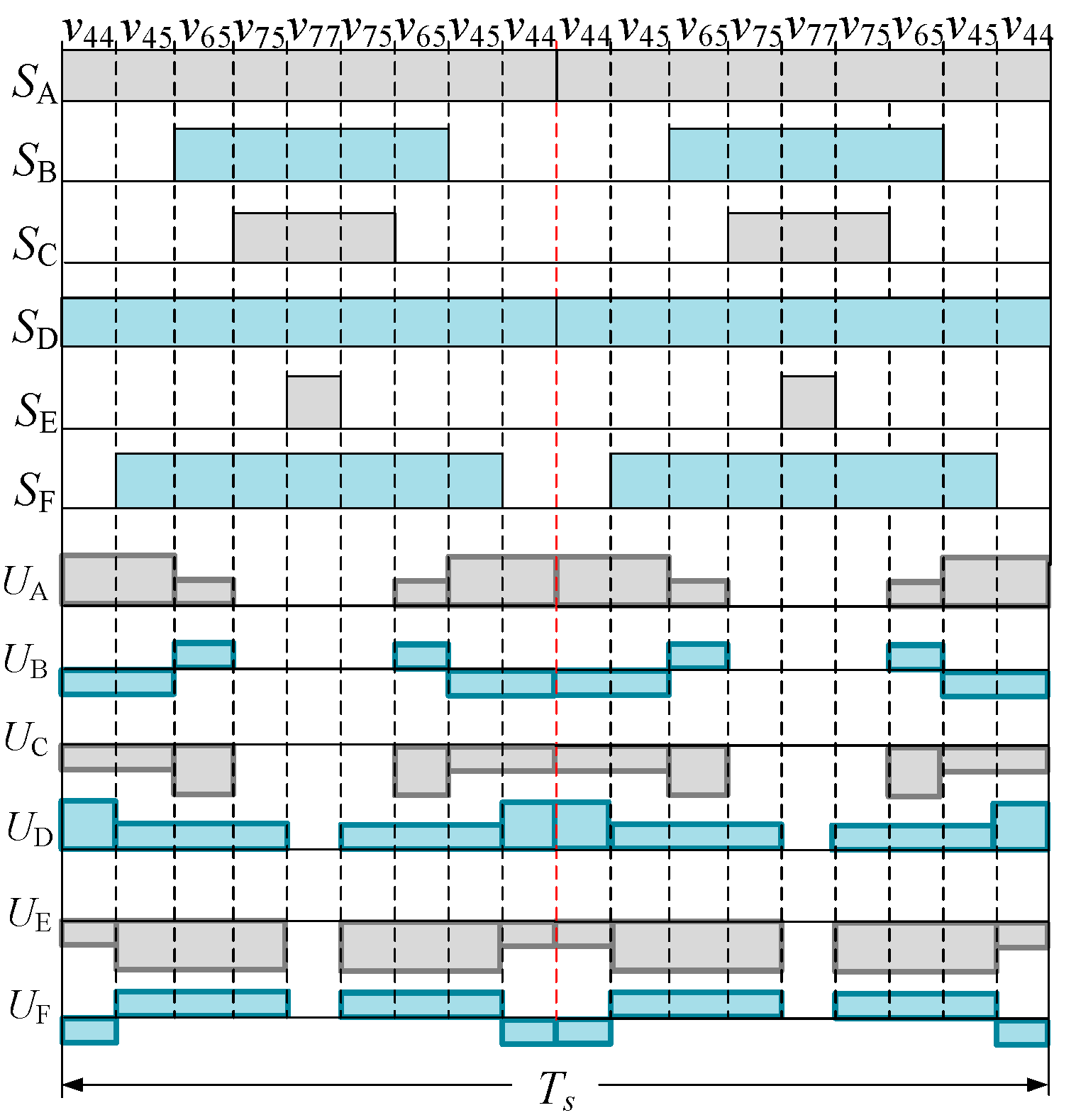
3.2. VDT-SVPWM with Double Central Symmetry
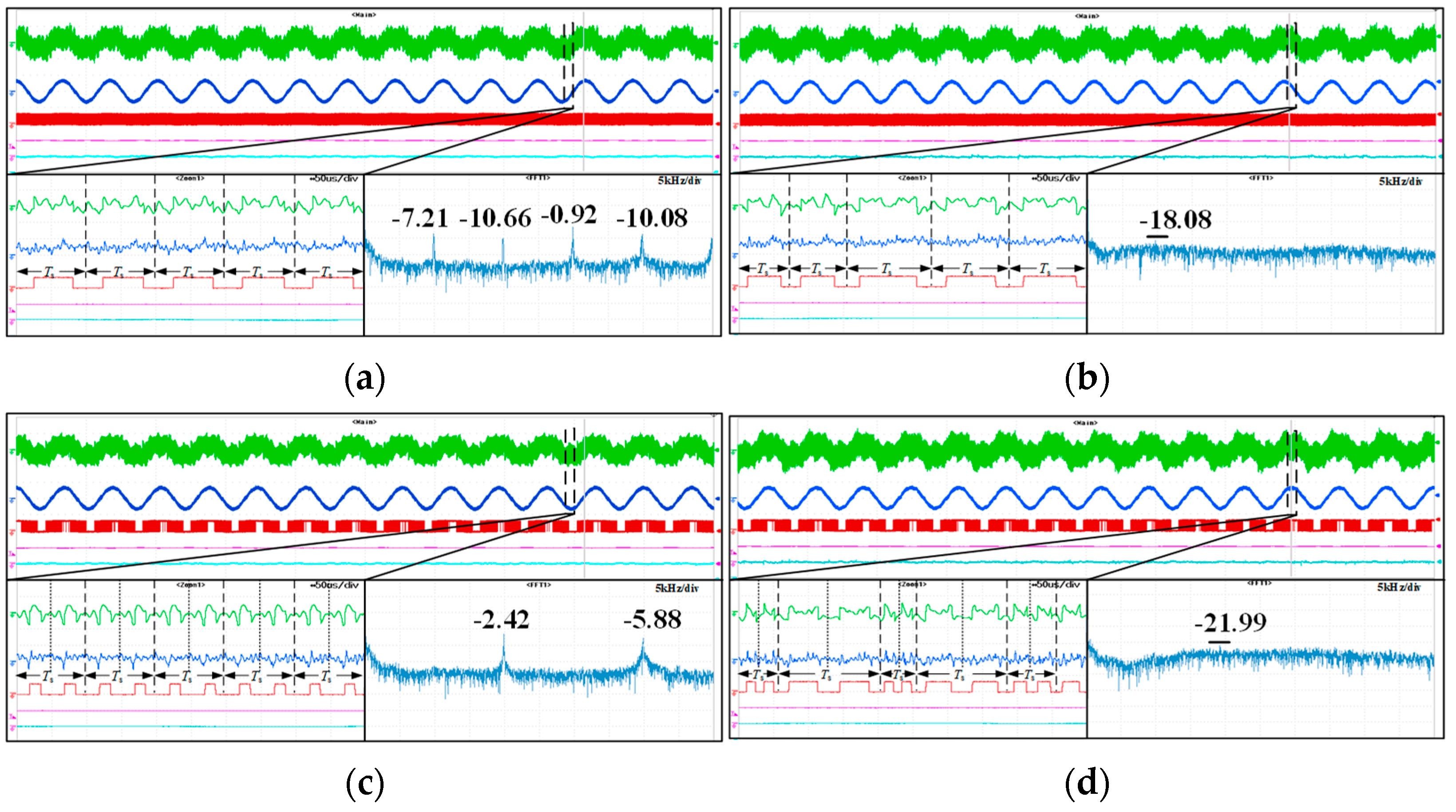
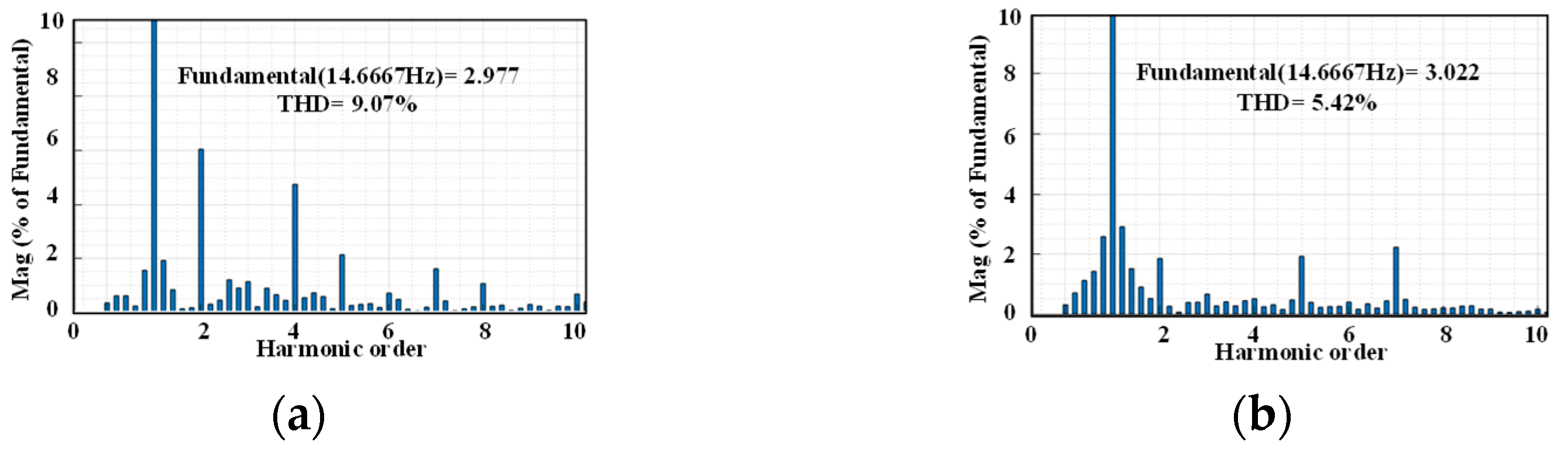
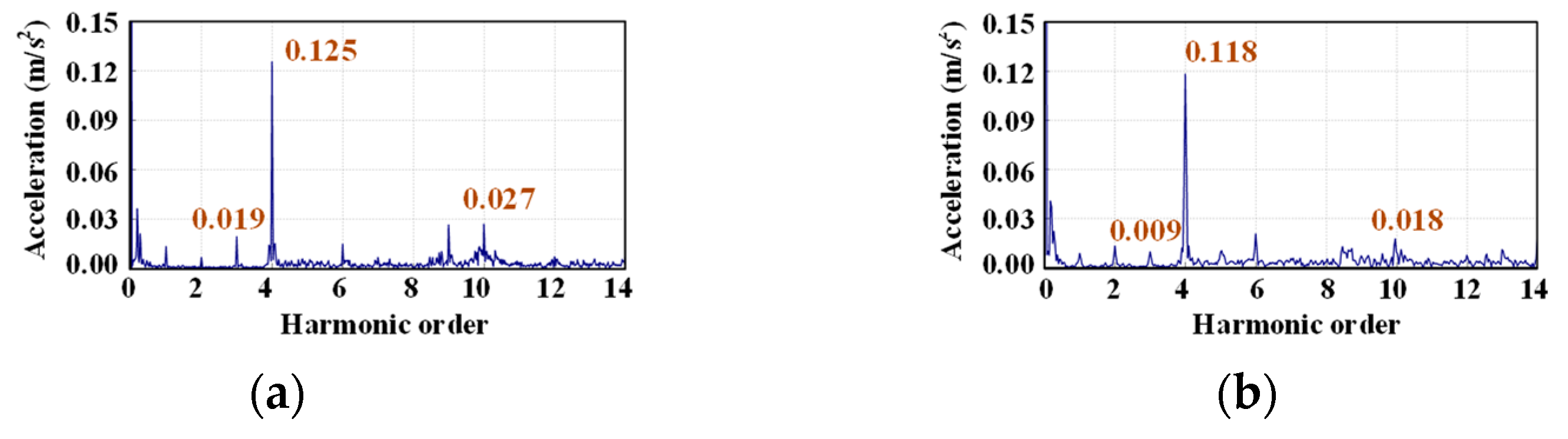
4. Experimental Verifications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, X.; Li, B.; Li, G.; Zhu, Q. An SVPWM strategy with extended linear modulation range for dual three-phase machine drives under unbalanced power sharing conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 4527–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Mao, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, P.; Lu, L.; Wang, Z. Optimization-based maximum-torque fault-tolerant control of dual three-phase PMSM drives under open-phase fault. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 4527–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Jia, Y.; Liu, C. Open-phase fault-tolerant control strategy for dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous machines without controller reconfiguration and fault detection. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Cambranis, F.; Zaragoza, J.; Berbel, N.; Capella, G.J.; Romeral, L. Constant common-mode voltage strategies using sigma–delta modulators in five-phase VSI. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yang, M.; Chen, Y.; Long, J.; Xu, D. EMI-regulated SiC-based motor drives with markov chain pseudo-random frequency space vector pulse width modulation strategy. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 2348–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Huang, J.; Qian, Z.; Qian, C.; Zhong, D. A random pulse position-based selective noise cancellation modulation method for SVPWM driven PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 2190–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Shen, G.; Yao, W.; Lu, Z. Performance characterization of random pulse width modulation algorithms in industrial and commercial adjustable-speed drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Jiang, D.; Hu, F.; Liu, Z. Research on common mode EMI and its reduction for active magnetic bearings. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 4246–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.E.; Kowalewski, D.L. Implementation of variable-delay random PWM for automotive applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2007, 56, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirlin, R.L.; Bech, M.M.; Trzynadlowski, A.M. Analysis of power and power spectral density in PWM inverters with randomized switching frequency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzynadlowski, A.M.; Kirlin, R.L.; Legowski, S.F. Space vector PWM technique with minimum switching losses and a variable pulse rate. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1997, 44, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, A.; Naudé, J.; Hofsajer, I. An argument for the relationship between spectral spreading and probability spreading for EMI-Reduction in DC–DC converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 35, 1459–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Liu, Q.; Pu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, B.; Ma, C.; Degano, M.; Gerada, C. Analysis and performance of five-phase piecewise-random-switching-frequency space vector pulse width modulation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 2339–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, S.; Li, Y. Performance and analysis of n-state random pulse position SVPWM with constant sampling frequency. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 13606–13625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Chang, Y.; Chen, B. Novel random-switching PWM technique with constant sampling frequency and constant inductor average current for digitally controlled converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech, M.M.; Blaabjerg, F.; Pedersen, J.K. Random modulation techniques with fixed switching frequency for three-phase power converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2000, 15, 753–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Pu, T.; Huang, W.; Zhu, L. Performance and evaluation of five-phase dual random SVPWM strategy with optimized probability density function. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 3323–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyghambari, A.; Dastfan, A.; Ahmadyfard, A. Selective voltage noise cancellation in three-phase inverter using random SVPWM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 4604–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Li, J.; Qu, R.; Jiang, D.; Xiao, L.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, J. Variable switching sequence PWM strategy of dual three-phase machine drive for high-frequency current harmonic suppression. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 35, 4984–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zou, J. Modified single-edge SVPWM technique to reduce the switching losses and increase PWM harmonics frequency for three-phase VSIs. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 35, 10643–10653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zou, J. Hybrid RPWM technique based on modified SVPWM to reduce the PWM acoustic noise. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 5667–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Specification | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fundamental flux | 0.88 | Wb |
| Stator resistance | 0.92 | Ω |
| d-axis inductance | 15.2 | mH |
| q-axis inductance | 15.7 | mH |
| Number of pole pairs | 11 | / |
| Number of slots | 48 | / |
| Control frequency | 10 | kHz |
| Rated voltage | 200 | V |
| Rated current | 3.2 | A |
| Modulation Method | Spread Factor | |
|---|---|---|
| Current Harmonic | Vibration | |
| Traditional SVPWM | 0.166 | 0.561 |
| Double central symmetry SVPWM | 0.145 | 0.509 |
| VDT-SVPWM | 0.115 | 0.259 |
| Proposed method | 0.103 | 0.226 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, T.; Liu, S. Variable Delayed Time Control for Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Double Central Symmetry Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation. Energies 2024, 17, 4347. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174347
Tao T, Liu S. Variable Delayed Time Control for Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Double Central Symmetry Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation. Energies. 2024; 17(17):4347. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174347
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Tao, and Sen Liu. 2024. "Variable Delayed Time Control for Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Double Central Symmetry Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation" Energies 17, no. 17: 4347. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174347
APA StyleTao, T., & Liu, S. (2024). Variable Delayed Time Control for Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Double Central Symmetry Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation. Energies, 17(17), 4347. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174347






