Application of Low-Resolution Hall Position Sensor in Control and Position Estimation of PMSM—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Section 2 discusses the working principle of Hall-based position sensing and the potential consequences of misplacing Hall sensors.
- Section 3 presents various estimation methods for rotor position and speed using very low-resolution Hall position sensors.
- Section 4 explores the application of linear Hall signals in PMSM drives.
- Section 5 reviews fault-tolerant and fault diagnosis methods based on Hall position signals.
- Section 6 discusses future trends and recent studies, including fault-tolerant control of PMSMs using Hall position sensors.
- Finally, Section 7 provides concluding remarks for this review.
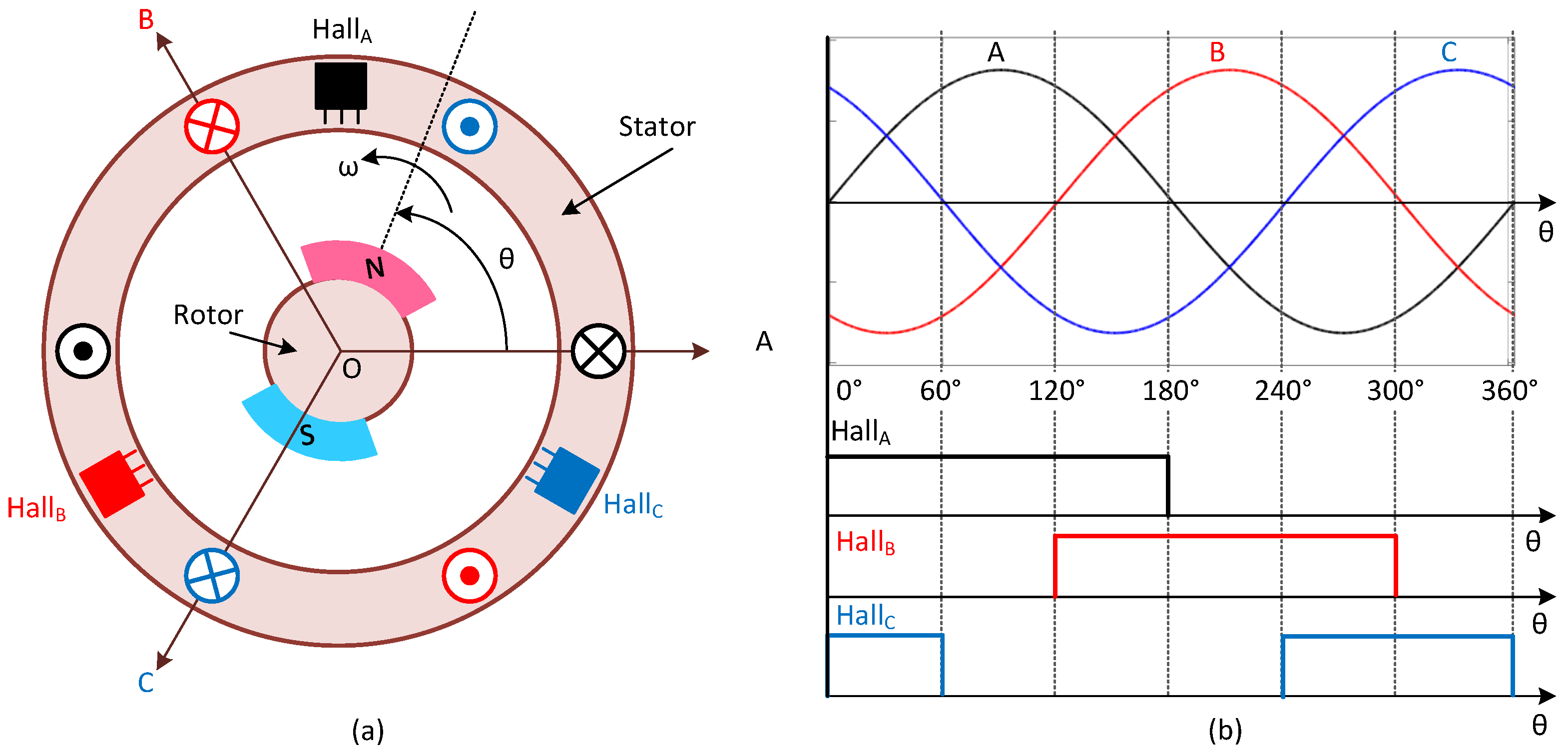
2. Analysis of Hall Position Sensor Signals
2.1. Working Principle of Hall-Based Position Sensing
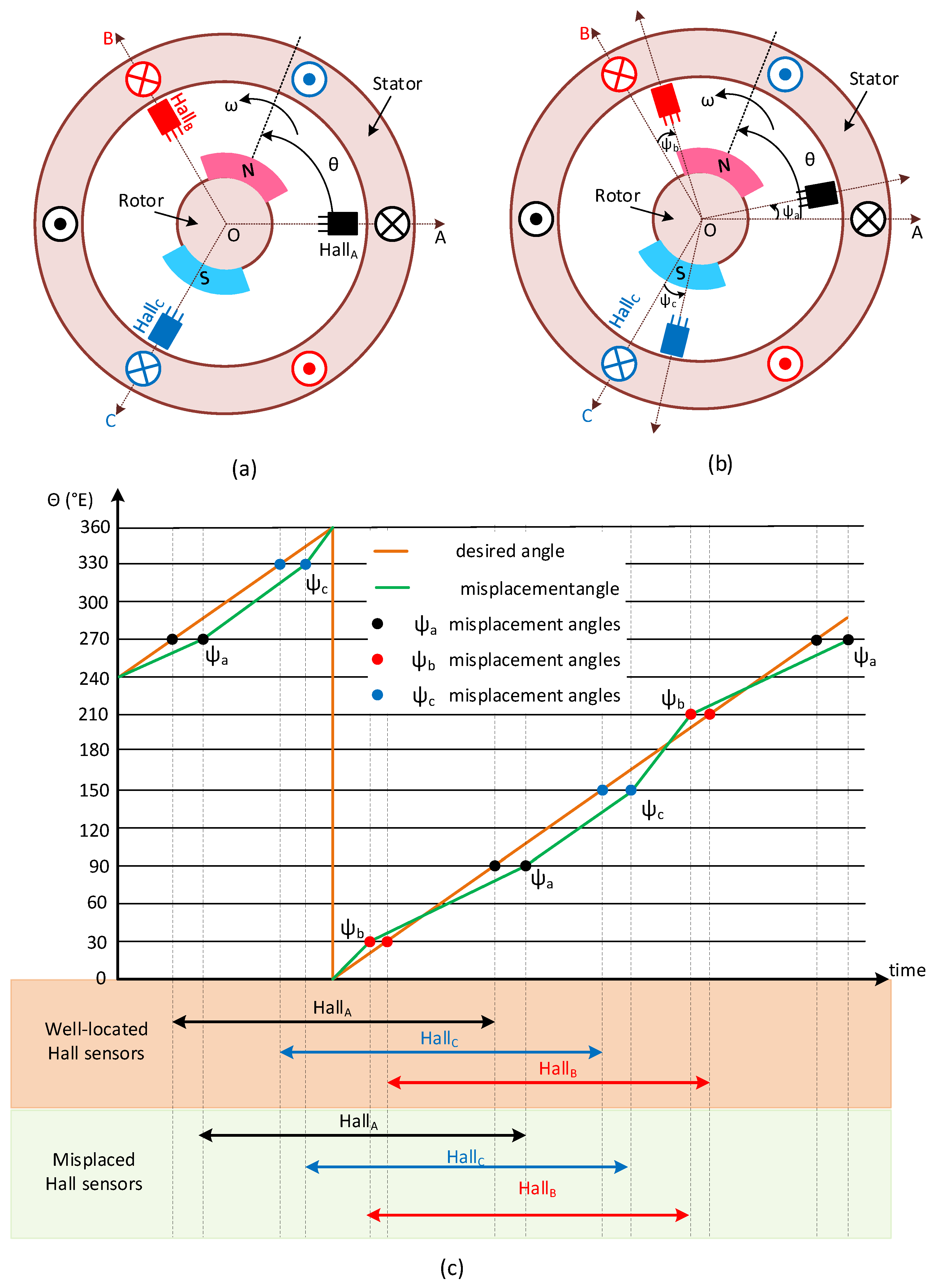
2.2. Consequences of Misplacement of Hall Sensors
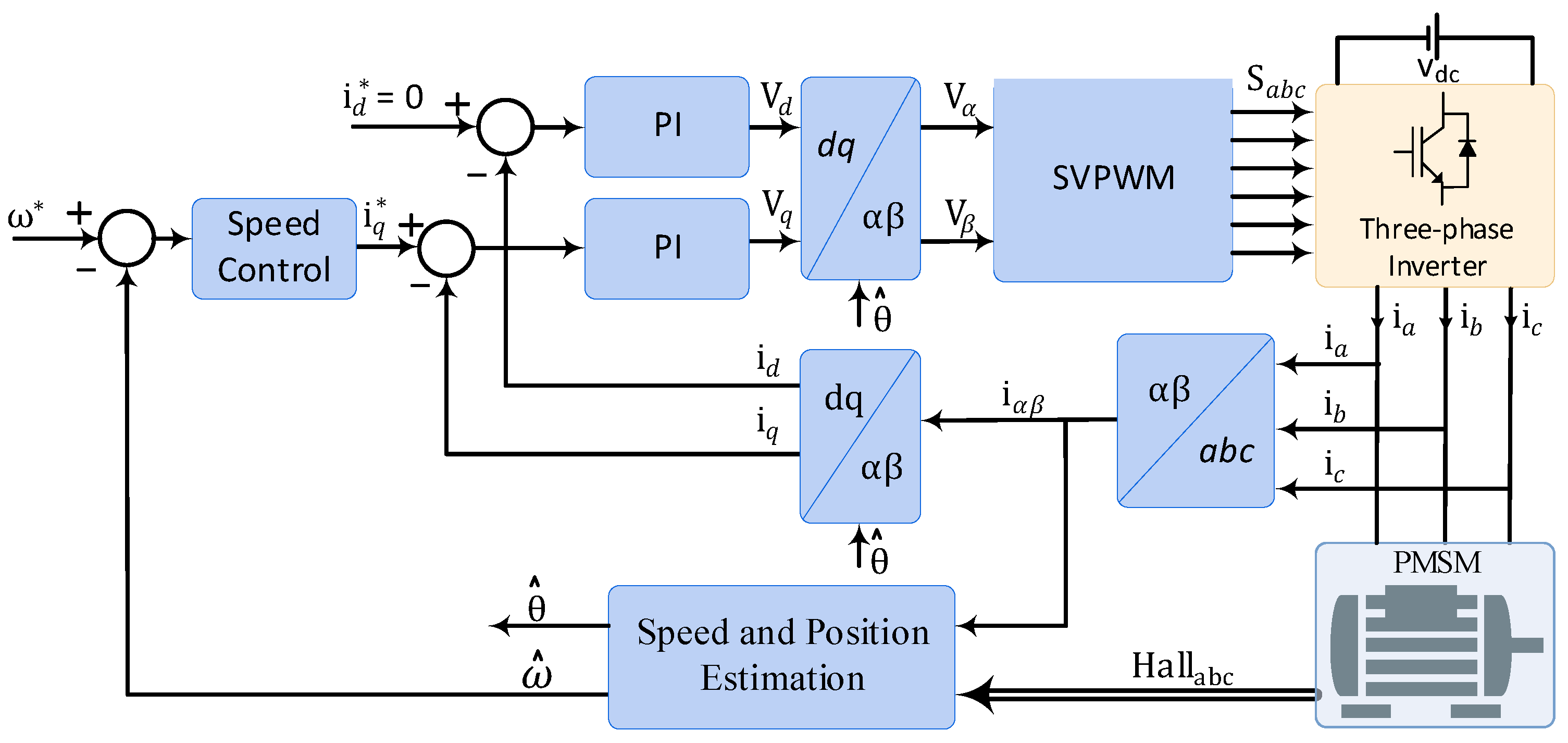
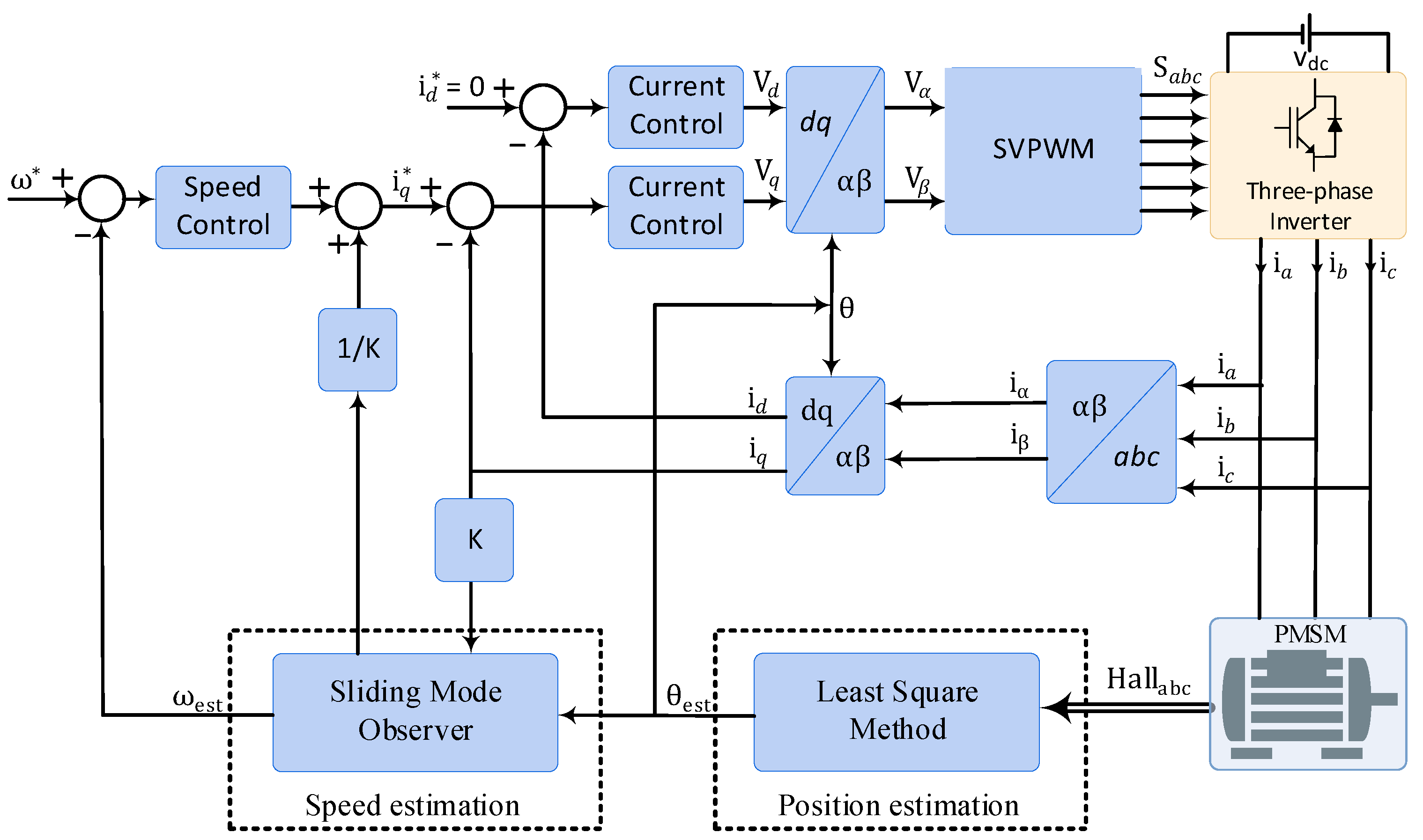
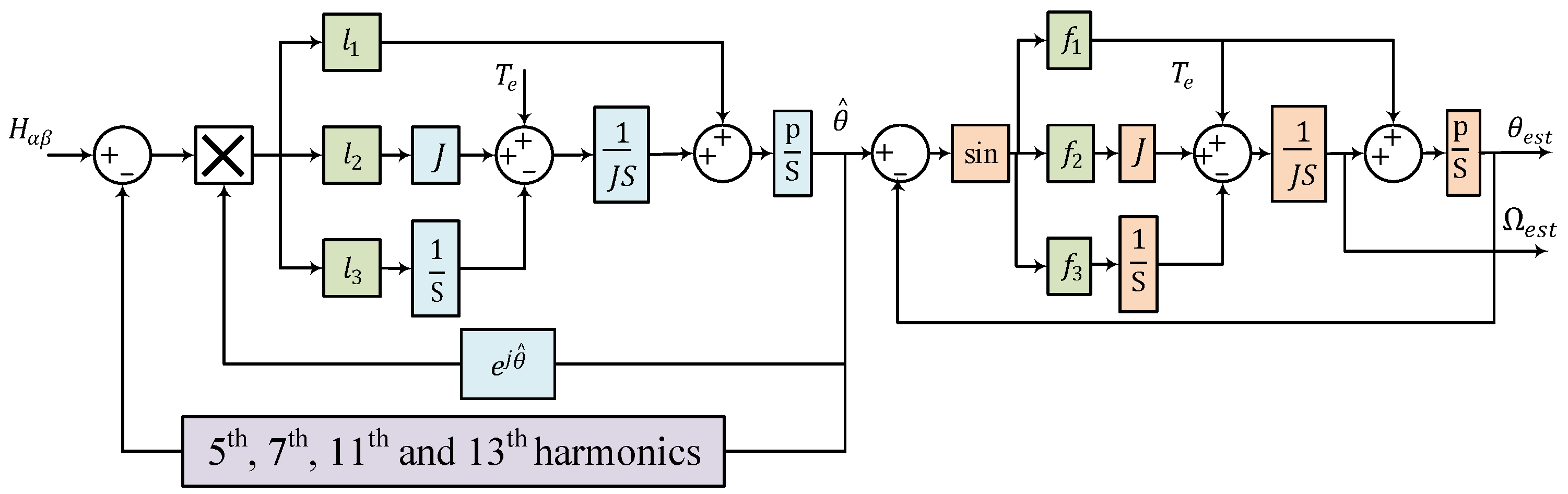
3. Estimation Methods of Motor Speed and Rotor Position
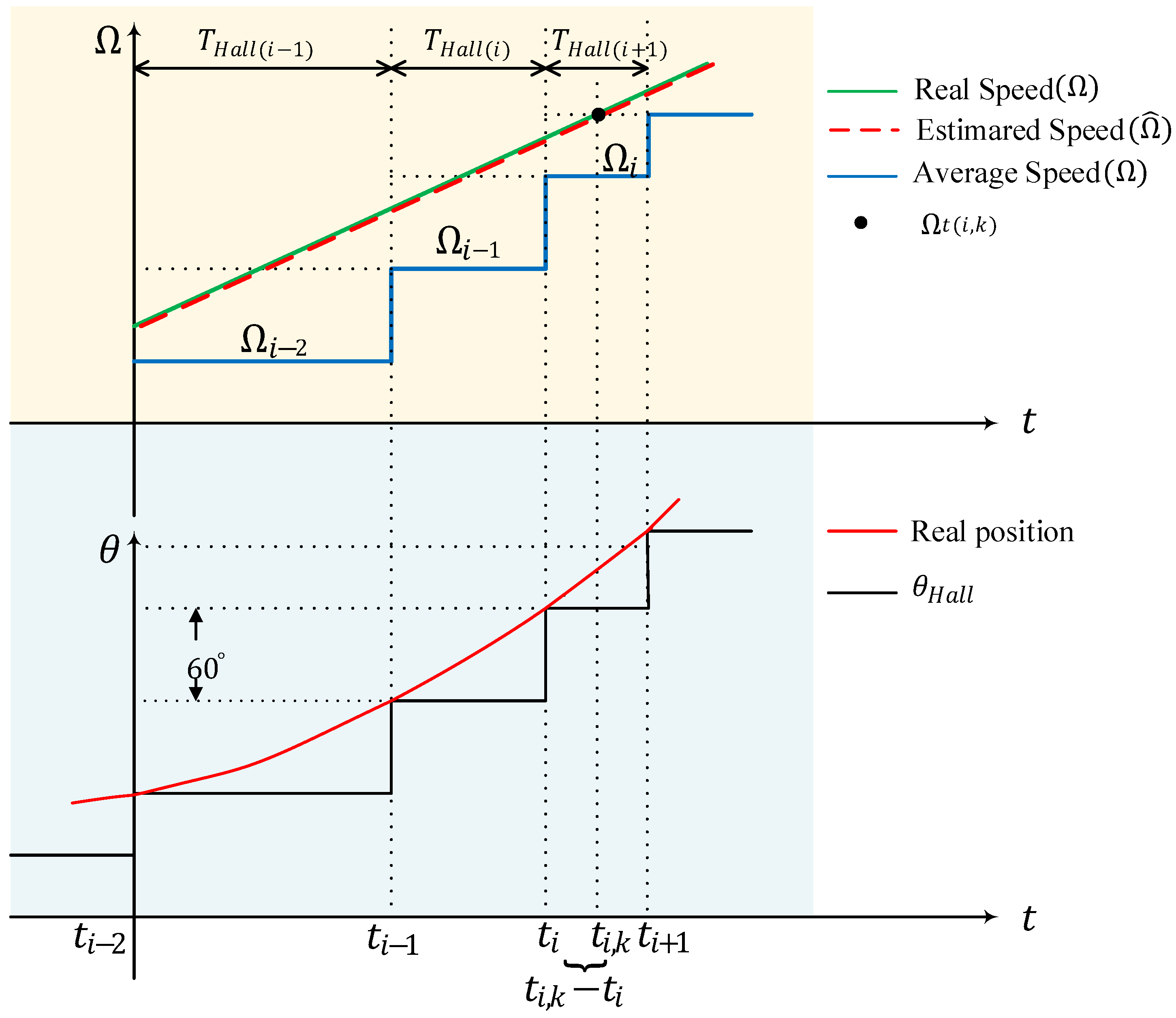
3.1. Interpolation Method
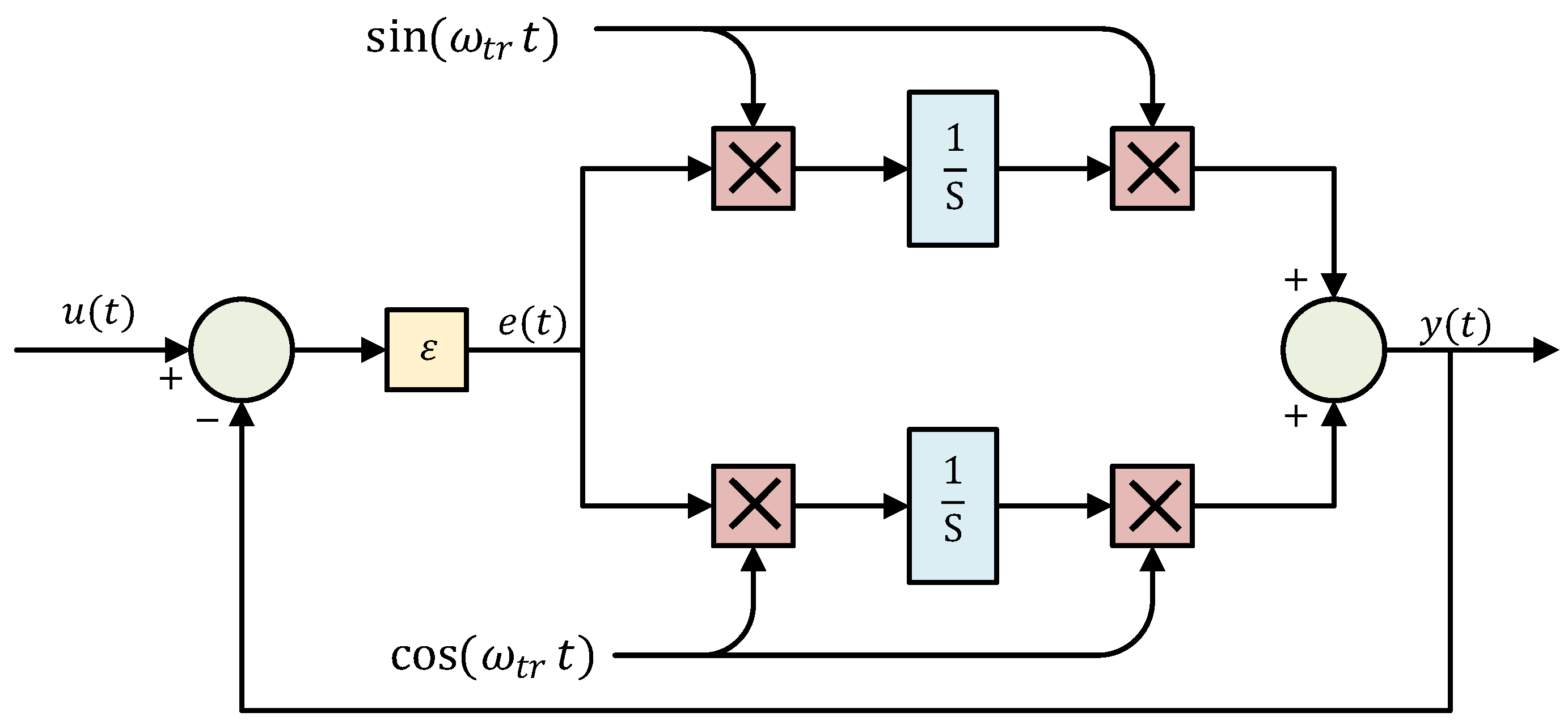
3.2. Filter Method
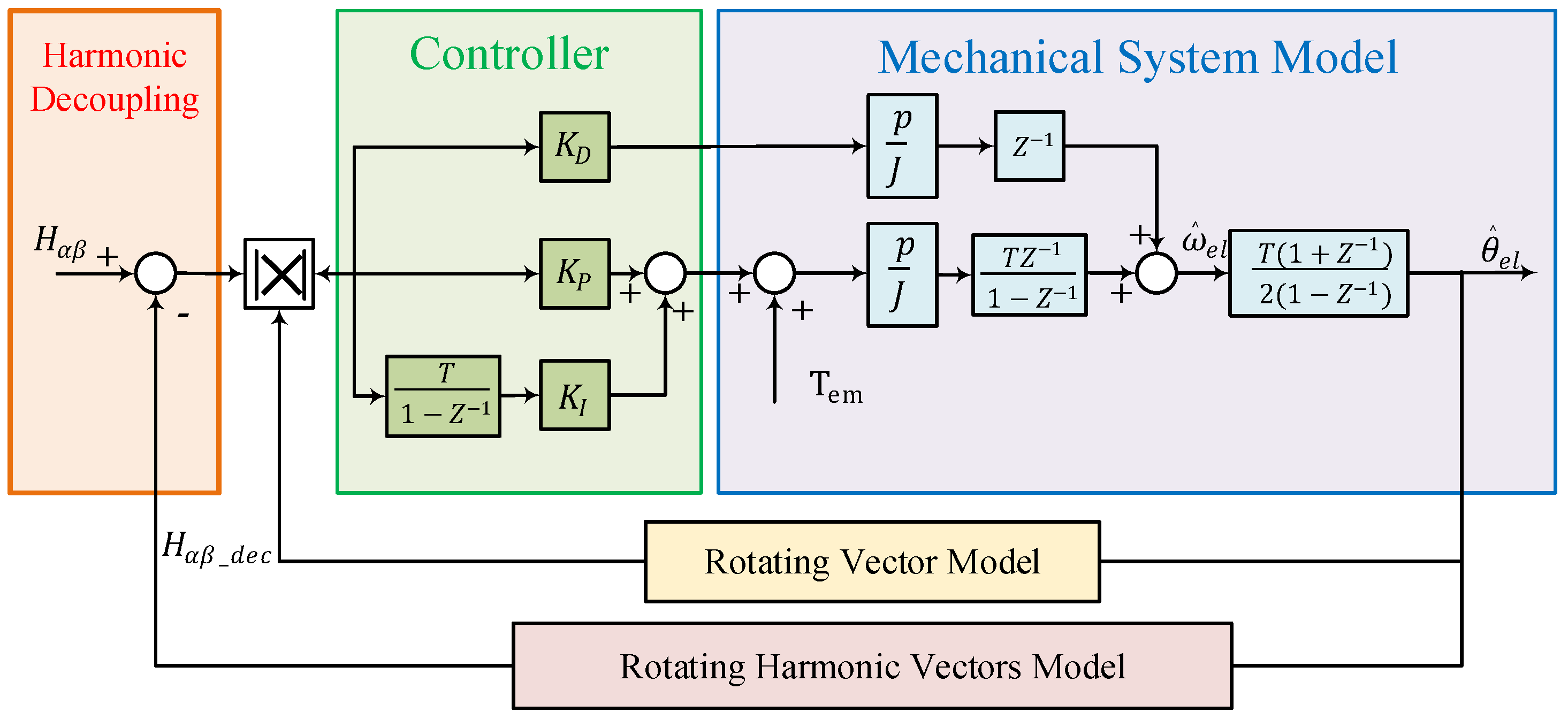
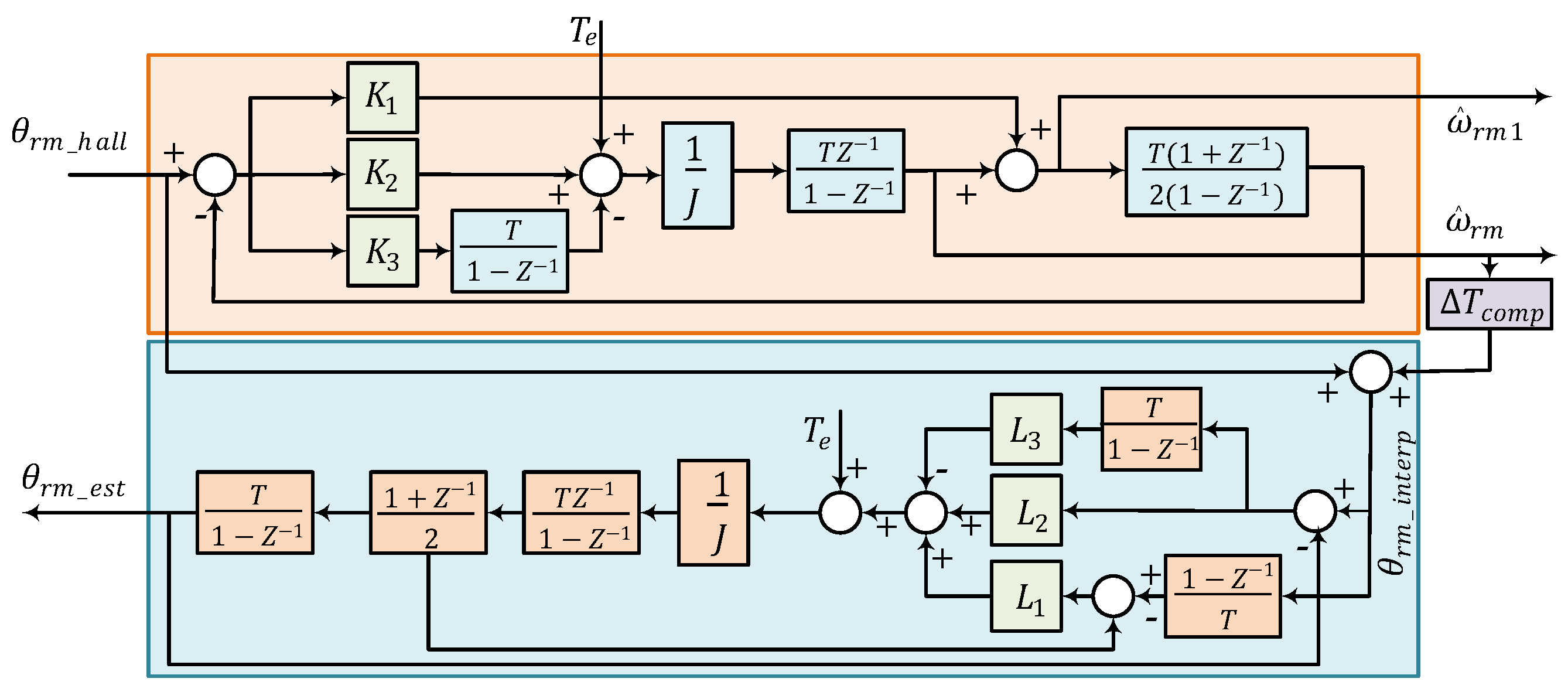
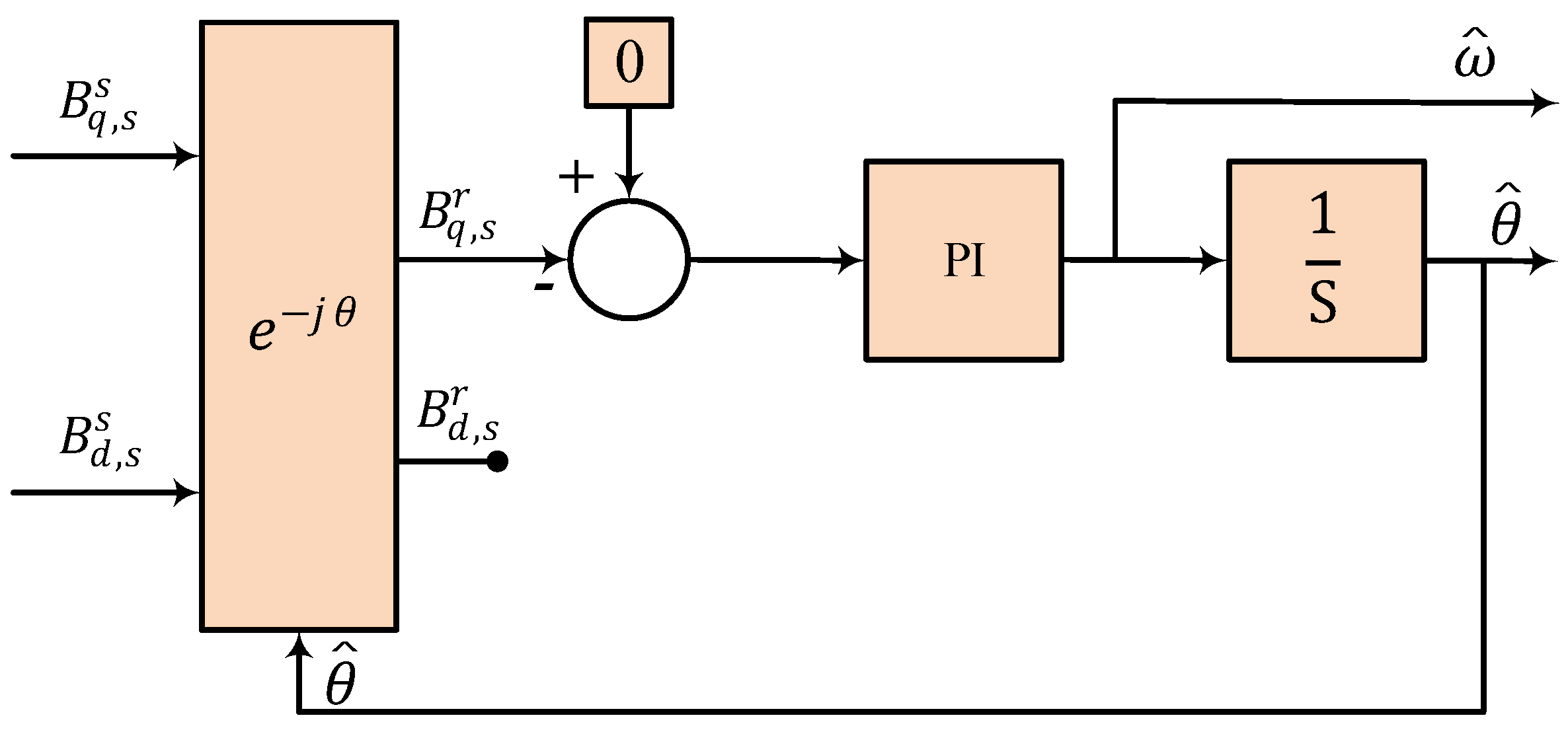
3.3. Observer Method
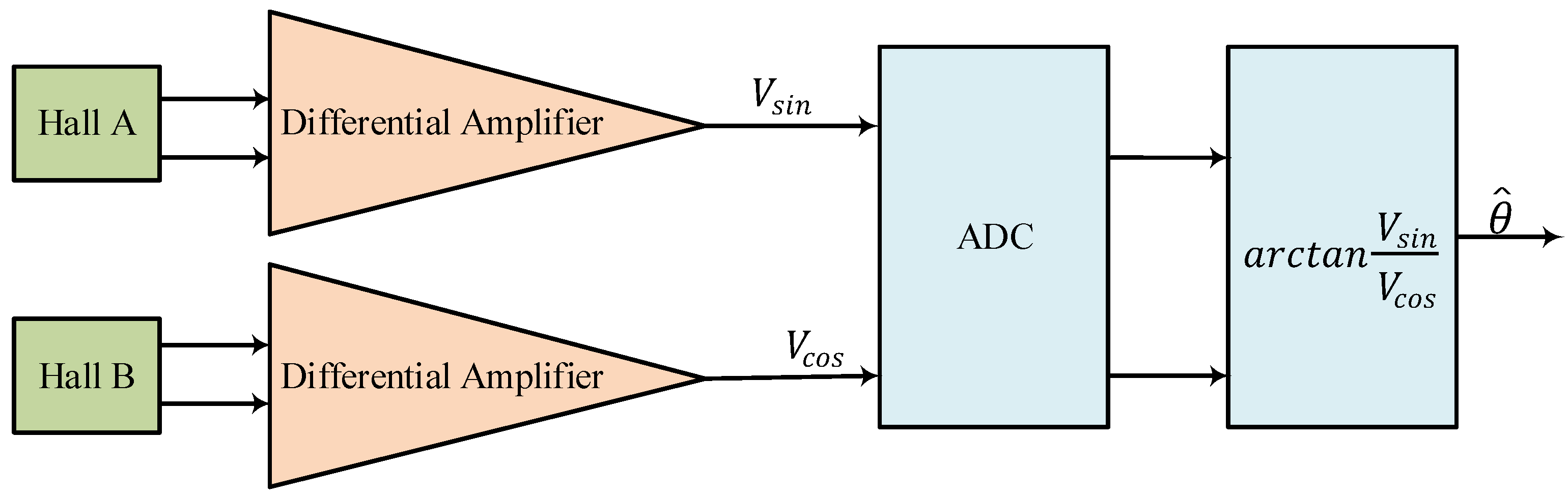
4. Drive of PMSMs Using Linear Hall-Effect Sensors
- fluctuations in the magnetization of the PMs
- uneven widths of the PMs
- variations in air gap temperature
- eccentricity of the PM ring
- harmonics within the air-gap magnetic field.
5. Fault-Tolerant Control of PMSMs Using Hall Sensors
5.1. State-Sensitive Fault Diagnosis Method
5.2. Transition-Sensitive Fault Diagnosis Method
5.3. Direction-Sensitive Fault Diagnosis Method
5.4. Binary Fault Diagnosis Method
6. Future Trends
7. Conclusions
- Cost-Effectiveness: Hall position sensors are significantly cheaper than high-resolution encoders or resolvers which makes them popular for low-cost applications.
- Simplicity and Ease of Integration: These sensors are simpler to integrate into certain applications due to the straightforward design and operation.
- Robustness: Hall position sensors are more robust against environmental factors such as dust, vibration to improve the performance in harsh industrial environments.
- Adequate Performance: Even though these sensors are not as precise as high-resolution sensors, they can provide sufficient accuracy for many industrial applications as a trade-off between cost and performance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| BLDC | Brushless DC |
| EKF | Extended Kalman Filter |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| FOC | Field-Oriented Control |
| FTC | Fault-Tolerant Control |
| HFSI | High-Frequency Signal Injection |
| LPF | Low-Pass Filter |
| PLL | Phase-Locked Loop |
| PM | Permanent magnet |
| PMSM | Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors |
| SFE | Synchronous Frequency Extractor |
| SFTF | Synchronous Frequency Tracking Filter |
| SVPWM | Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation |
| VTO | Vector Tracking Observer |
| Three-phase Leakage Flux Density Vectors | |
| CW | Clockwise |
| CCW | Counterclockwise |
| Three-phase Hall signals | |
| Hall vector in -frame | |
| J | Moment of Inertia |
| Current in dq-frame (in Amperes) | |
| Current in -frame (in Amperes) | |
| Ts | Sampling Period |
| Voltage in dq-frame (in Volts) | |
| Voltage in -frame (in Volts) | |
| Rotor position (in degrees or radians) | |
| Measured Absolute Position in The Current Hall Sector | |
| Angular velocity (in rad/s) | |
| Three-phase Unequal Misplacement Angles |
References
- Akrami, M.; Jamshidpour, E.; Frick, V. Application of Hall Position Sensor in Control and Position Estimation of PMSM—A Review. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2023 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC/I&CPS Europe), Madrid, Spain, 6–9 June 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muley, N.; Saxena, A.; Chaudhary, P. Comparative Evaluation of Methods for Continuous Rotor Position Estimation using Low Resolution Hall Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2021 National Power Electronics Conference (NPEC), Bhubaneswar, India, 15 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Deng, L.; He, Y.; Zhao, J. Control of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Linear Hall Device. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 5th International Electrical and Energy Conference (CIEEC), Nangjing, China, 27–29 May 2022; pp. 1252–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrami, M.; Jamshidpour, E.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B.; Pierfederici, S.; Frick, V. Sensorless Control Methods for BLDC Motor Drives: A Review. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Refaie, A.M. Fractional-Slot Concentrated-Windings Synchronous Permanent Magnet Machines: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, C.J.V.; Xiao, D.; Vieira, R.P.; Emadi, A. Observers for High-Speed Sensorless PMSM Drives: Design Methods, Tuning Challenges and Future Trends. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 56397–56415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Valla, M.; Solsona, J. Position Sensorless Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Drives—A Review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 5830–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognani, S.; Tubiana, L.; Zigliotto, M. Extended Kalman filter tuning in sensorless PMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M.; Takeda, Y. Sinusoidal current drive system of permanent magnet synchronous motor with low resolution position sensor. In Proceedings of the IAS ’96. Conference Record of the 1996 IEEE Industry Applications Conference Thirty-First IAS Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 October 1996; Volume 1, pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidozzi, A.; Solero, L.; Crescimbini, F.; Di Napoli, A. SVM PMSM Drive with Low Resolution Hall-Effect Sensors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Lee, B.; Nam, K. PMSM control based on edge field measurements by Hall sensors. In Proceedings of the 2010 Twenty-Fifth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Palm Springs, CA, USA, 21–25 February 2010; pp. 2002–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaim, S.; Martin, J.P.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B.; Meibody-Tabar, F. High performance low cost control of a permanent magnet wheel motor using a hall effect position sensor. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 6–9 September 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, S.B.; Kivanc, O.C.; Atila, B.; Rehman, S.U.; Akin, B.; Toliyat, H.A. A simple least squares approach for low speed performance analysis of indirect FOC induction motor drive using low-resolution position sensor. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference (IEMDC), Miami, FL, USA, 21–24 May 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Xiong, D. Review of Rotor Position and Speed Estimation Method of PMSM with Hall Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 16th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Chengdu, China, 1–4 August 2021; pp. 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Chen, C.; Zhao, M.; Ma, T.; Ge, K. Research on Rotor Position Estimation of PMSM Based on Hall Position Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 16th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Chengdu, China, 1–4 August 2021; pp. 2088–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.F.; Kang, Y.; Fernandez Laborda, D.; Gomez, M.M.; Reigosa, D.D.; Briz, F. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Torque Estimation Using Low Cost Hall-Effect Sensors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 3735–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigosa, D.; Fernandez, D.; González, C.; Lee, S.B.; Briz, F. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Drive Control Using Analog Hall-Effect Sensors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 2358–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Espinar, C.; Heredero-Peris, D.; Igor-Gross, G.; Llonch-Masachs, M.; Montesinos-Miracle, D. Accurate Angle Representation from Misplaced Hall-Effect Switch Sensors for Low-Cost Electric Vehicle Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 5227–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortajarena, J.; García, S.; Cortajarena, J.; Barambones, O.; Alkorta, P. Influence of the rotor angle precision in control of IPMSM drives and improvement method using sensorless estimator with Hall sensors. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, X.; Li, Z. An Improved Rotor Position Estimation Method for PMSM Using Low-Resolution Hall-Effect Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo, Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Haining, China, 28–31 October 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, B.H.; Sul, S.K.; Kwon, J.H.; Byeon, J.S. Implementation of sensorless vector control for super-high-speed PMSM of turbo-compressor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, A.; Sul, S.K.; Lee, D.C.; Jun, C.S. Novel Speed and Rotor Position Estimation Strategy Using a Dual Observer for Low-Resolution Position Sensors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 2897–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, W.; Yang, J.; Bu, F.; Liu, S. A PMSM rotor position estimation with low-cost Hall-effect sensors using improved PLL. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo, Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Busan, Republic of Korea, 1–4 June 2016; pp. 804–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Tiecai, L.; Yongping, L.; Bingyi, G. Position-measuring error analysis and solution of hall sensor in pseudo-sensorless PMSM driving system. In Proceedings of the IECON’03. 29th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37468), Roanoke, VA, USA, 2–6 November 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1337–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Yang, M.; Odhano, S.A.; Tang, M.; Zanchetta, P.; Liu, X.; Xu, D. A New Position and Speed Estimation Scheme for Position Control of PMSM Drives Using Low-Resolution Position Sensors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 3747–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, A.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Won, I.K.; Kim, Y.R.; Won, C.Y. Interpolation error compensation method for look-up table based IPMSM drive. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference and Expo Transportation Electrification Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Beijing, China, 31 August–3 September 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulii Capponi, F.; De Donato, G.; Del Ferraro, L.; Honorati, O.; Harke, M.; Lorenz, R. AC brushless drive with low-resolution Hall-effect sensors for surface-mounted PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 42, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baris Ozturk, S.; Akin, B.; Toliyat, H.; Ashrafzadeh, F. Low-cost direct torque control of permanent magnet synchronous motor using Hall-effect sensors. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC ’06), Dallas, TX, USA, 19–23 March 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreindler, L.; Iacob, I.; Casaru, G.; Sarca, A.; Olteanu, R.; Matianu, D. PMSM drive using digital hall position sensors for light EV applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 9th International Symposium on Advanced Topics in Electrical Engineering (ATEE), Bucharest, Romania, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Harke, M.; Lorenz, R. Sensorless control of interior permanent magnet machine drives with zero-phase-lag position estimation. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2002 IEEE Industry Applications Conference. 37th IAS Annual Meeting (Cat. No.02CH37344), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 13–18 October 2002; Volume 3, pp. 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Schneider, S.; Mulligan, M. Analysis of algorithms for velocity estimation from discrete position versus time data. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1992, 39, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. An improved rotor position estimation in PMSM with low-resolution hall-effect sensors. In Proceedings of the 2014 17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Hangzhou, China, 22–25 October 2014; pp. 2722–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, H.; Zeng, S.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Su, M. An Improved Position and Speed Estimation Scheme for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Low-Cost Hall Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 5th International Electrical and Energy Conference (CIEEC), Nangjing, China, 27–29 May 2022; pp. 1831–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovudhikulrungsri, L.; Koseki, T. Precise Speed Estimation from a Low-Resolution Encoder by Dual-Sampling-Rate Observer. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2006, 11, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.Z.; Wang, J.J.; Zhao, H.J. Rotor Position Estimation Using Harmonic-Decomposition Complex-Coefficient Filter-Based PLL for PMSM with Switch Hall-Effect Sensors. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 12, 2249–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Chen, B.; Song, X. High-Precision Speed and Position Estimation Based on Hall Vector Frequency Tracking for PMSM with Bipolar Hall-Effect Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H. Pseudo Sensorless Deadbeat Predictive Current Control for PMSM Drives with Hall-Effect Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Hartford, CT, USA, 17–20 May 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scelba, G.; De Donato, G.; Scarcella, G.; Giulii Capponi, F.; Bonaccorso, F. Fault-Tolerant Rotor Position and Velocity Estimation Using Binary Hall-Effect Sensors for Low-Cost Vector Control Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3403–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Donato, G.; Scelba, G.; Pulvirenti, M.; Scarcella, G.; Giulii Capponi, F. Low-Cost, High-Resolution, Fault-Robust Position and Speed Estimation for PMSM Drives Operating in Safety-Critical Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Wang, Z.; Xia, C. Speed Measurement Error Suppression for PMSM Control System Using Self-Adaption Kalman Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 2753–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzel, T.; Lee, K. Commutation torque ripple minimization for permanent magnet synchronous machines with Hall effect position feedback. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1998, 13, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xia, M.; Luo, H. Model Reference Adaptive Control-Based Speed Control of Brushless DC Motors with Low-Resolution Hall-Effect Sensors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Choi, C.; Lee, K.; Lee, W. An Improved Rotor Position Estimation with Vector-Tracking Observer in PMSM Drives with Low-Resolution Hall-Effect Sensors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 4078–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harke, M.C.; Donato, G.D.; Capponi, F.G.; Tesch, T.; Lorenz, R. Implementation Issues and Performance Evaluation of Surface-Mounted PM Machine Drives with Hall-Effect Position Sensors and a Vector-Tracking Observer. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2006 IEEE Industry Applications Conference Forty-First IAS Annual Meeting, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 October 2006; Volume 4, pp. 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harke, M.C.; De Donato, G.; Giulii Capponi, F.; Tesch, T.R.; Lorenz, R.D. Implementation Issues and Performance Evaluation of Sinusoidal, Surface-Mounted PM Machine Drives with Hall-Effect Position Sensors and a Vector-Tracking Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2008, 44, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scelba, G.; De Donato, G.; Pulvirenti, M.; Giulii Capponi, F.; Scarcella, G. Hall-Effect Sensor Fault Detection, Identification, and Compensation in Brushless DC Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comanescu, M. Speed, rotor position and load torque estimation of the PMSM using an extended dynamic model and cascaded sliding mode observers. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM), Capri, Italy, 22–24 June 2016; pp. 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, A.; Sul, S.K.; Lee, D.C.; Seung, C. Novel speed and rotor position estimation strategy using a dual observer for low resolution position sensors. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Rhodes, Greece, 15–19 June 2008; pp. 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed-Ali, T.; Cherrier, E.; M’Saad, M. Cascade high gain observers for nonlinear systems with delayed output measurement. In Proceedings of the 48h IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) held jointly with 2009 28th Chinese Control Conference, Shanghai, China, 15–18 December 2009; pp. 8226–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Yang, M.; Dong, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, D. State Estimation Error Suppression for PMSM Speed Observer Based on Hall Position Sensor. Diangong Jishu Xuebao/Transactions China Electrotech. Soc. 2017, 32, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; An, Q.; Chen, C.; Cao, F.; Li, S. Observer Based Improved Position Estimation in Field-Oriented Controlled PMSM with Misplaced Hall-Effect Sensors. Energies 2022, 15, 5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.H.; Cho, K.; Choi, S. Dual sampling rate observer for motor position estimation using linear hall sensors and iterative algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2016 19th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Chiba, Japan, 13–16 November 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Qin, M.; Chen, X.; Meng, L.; Huang, Q.; Fu, C. Computationally Efficient Coordinate Transformation for Field-Oriented Control Using Phase Shift of Linear Hall-Effect Sensor Signals. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 3442–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Ye, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H. An improved position detection method for permanent magnet linear motor using linear hall sensors. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 11–14 August 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, D.; Fernandez, D.; Martinez, M.; Reigosa, D.; Diez, A.B.; Briz, F. Resolver Emulation for PMSMs Using Low Cost Hall-Effect Sensors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 4977–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, P.T.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Chung, S.U.; Kwon, S.M. Magnetic Sensor Design for a Permanent Magnet Linear Motor Considering Edge-Effect. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 5768–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricchi, F.; Capponi, F.; Crescimbini, F.; Solero, L. Sinusoidal brushless drive with low-cost linear Hall effect position sensors. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE 32nd Annual Power Electronics Specialists Conference (IEEE Cat. No.01CH37230), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–21 June 2001; Volume 2, pp. 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, D.; Reigosa, D.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.; Briz, F. Hall-Effect Sensors as Multipurpose Devices to Control, Monitor and Diagnose AC Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–14 October 2021; pp. 4967–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zou, J.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Fu, Y. An Improved PMSM Rotor Position Sensor Based on Linear Hall Sensors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3591–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Fang, J.; Han, B. High-Precision Rotor Position Detection for High-Speed Surface PMSM Drive Based on Linear Hall-Effect Sensors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 4720–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.Y.; Nam, K. PMSM Control Based on Edge-Field Hall Sensor Signals Through ANF-PLL Processing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 5121–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Choi, S.; Cho, K.; Nam, K. Position Estimation Using Linear Hall Sensors for Permanent Magnet Linear Motor Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7644–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zou, J.; Lu, Y. Optimum design of magnet shape in permanent-magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2003, 39, 3523–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, B.; Ye, P.; Zhang, H. Analog-Hall-Sensor-Based Position Detection Method with Temperature Compensation for Permanent-Magnet Linear Motor. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Jatskevich, J.; Huang, Y.; Chapariha, M.; Liu, J. Fault Diagnosis and Signal Reconstruction of Hall Sensors in Brushless Permanent Magnet Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, W.; Yang, J. Fault diagnosis of low-cost hall-effect sensors used in controlling permanent magnet synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the 2016 19th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Chiba, Japan, 13–16 November 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mousmi, A.; Abbou, A.; El Houm, Y. Binary Diagnosis of Hall Effect Sensors in Brushless DC Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 3859–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.S.; Sul, S.K.; Schulz, S.; Patel, N. Fault detection and fault-tolerant control of interior permanent-magnet motor drive system for electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakori, A.; Ektesabi, M. A simple fault tolerant control system for Hall Effect sensors failure of BLDC motor. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 8th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 19–21 June 2013; pp. 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scelba, G.; De Donato, G.; Pulvirenti, M.; Capponi, F.G.; Scarcella, G. Hall-effect sensor fault detection, identification an compensation in brushless DC drives. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 September 2015; pp. 3987–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzine, K.; Sudhoff, S. A hybrid observer for high performance brushless DC motor drives. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1996, 11, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Y. Fault Tolerance Method of Low-Resolution Hall Sensor in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 119162–119169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.; Lu, M. The Hall Sensors Fault-Tolerant for PMSM Based on Switching Sensorless Control with PI Parameters Optimization. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 114048–114059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Huang, Y.; Jatskevich, J.; Liu, J. Improved Fault-Tolerant Control for Brushless Permanent Magnet Motor Drives with Defective Hall Sensors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Feng, M. Fast Fault Diagnosis Method for Hall Sensors in Brushless DC Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


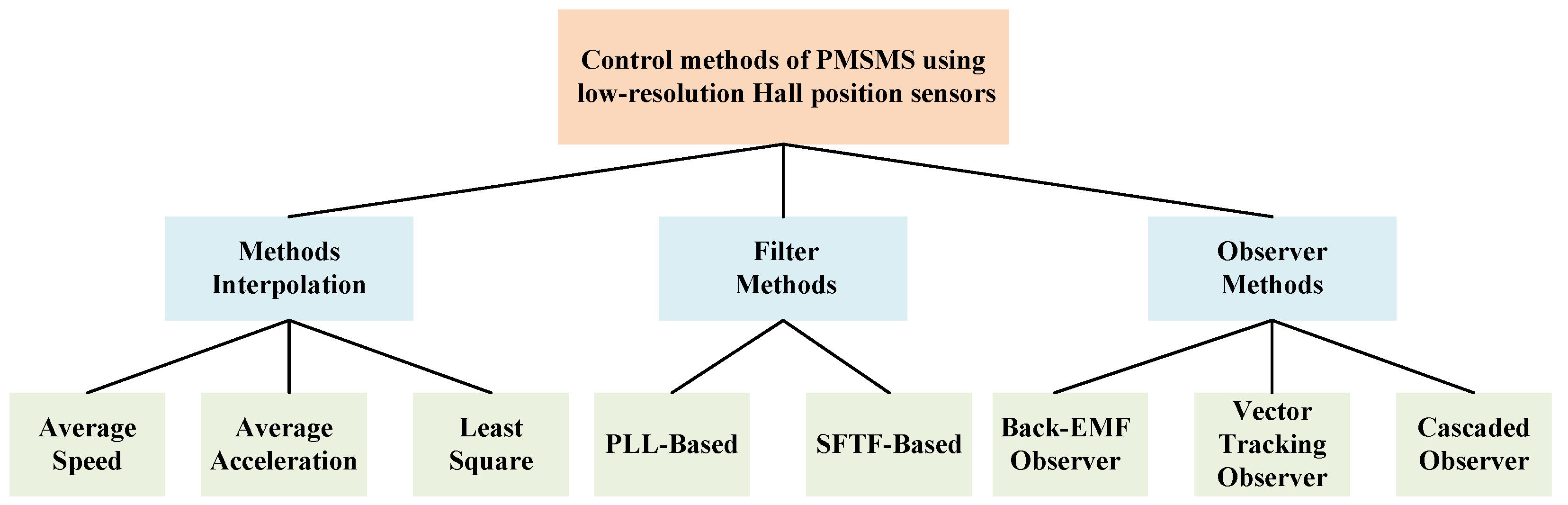
| Method | Technique | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interpolation method [20,27,28,29,31,32,33] | Average speed method |
|
|
| Average acceleration method |
|
| |
| Least Square method |
|
| |
| Filter method [23,34,35,36,37] | PLL-based methods |
|
|
| SFTF-based methods |
|
| |
| Observer method [22,27,34,38,39,40,41,43,44,45,48] | Back-EMFobserver |
|
|
| Vector Tracking observer |
|
| |
| Cascaded observer |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akrami, M.; Jamshidpour, E.; Baghli, L.; Frick, V. Application of Low-Resolution Hall Position Sensor in Control and Position Estimation of PMSM—A Review. Energies 2024, 17, 4216. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174216
Akrami M, Jamshidpour E, Baghli L, Frick V. Application of Low-Resolution Hall Position Sensor in Control and Position Estimation of PMSM—A Review. Energies. 2024; 17(17):4216. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174216
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkrami, Milad, Ehsan Jamshidpour, Lotfi Baghli, and Vincent Frick. 2024. "Application of Low-Resolution Hall Position Sensor in Control and Position Estimation of PMSM—A Review" Energies 17, no. 17: 4216. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174216
APA StyleAkrami, M., Jamshidpour, E., Baghli, L., & Frick, V. (2024). Application of Low-Resolution Hall Position Sensor in Control and Position Estimation of PMSM—A Review. Energies, 17(17), 4216. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174216









