Electrical Transients in Industrial Facilities
Abstract
1. Introduction
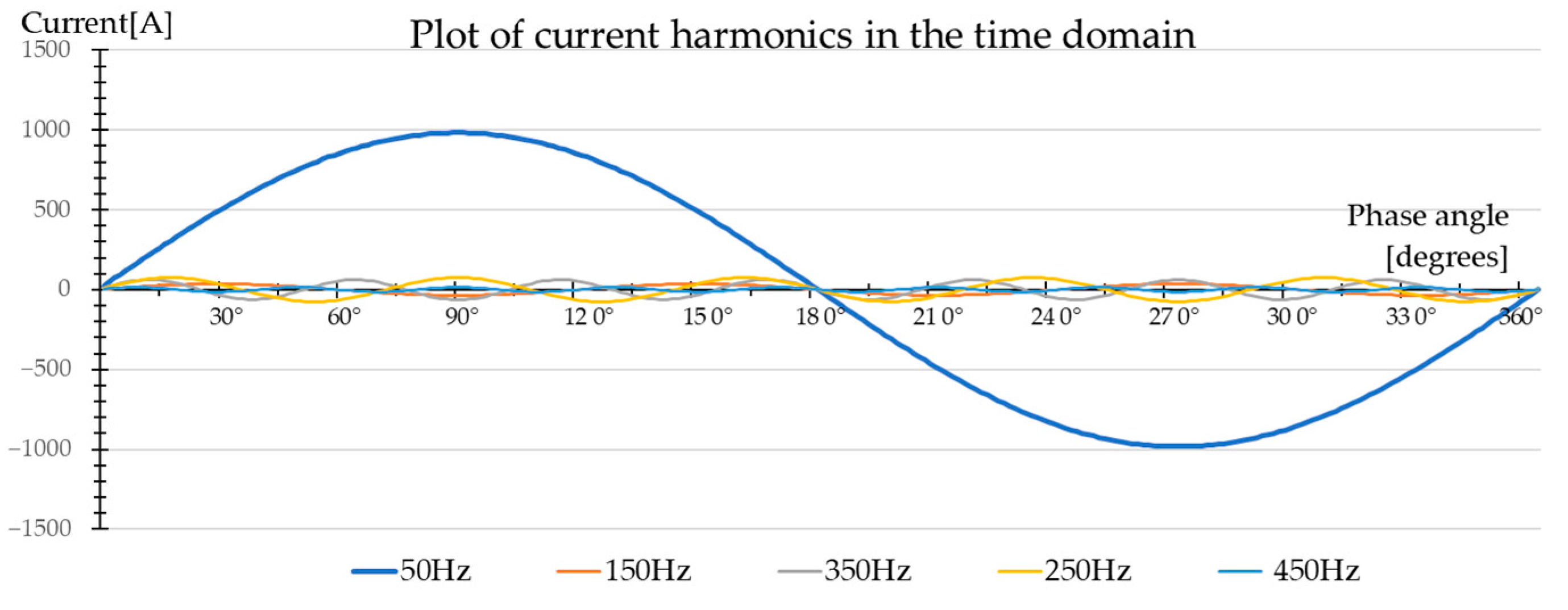
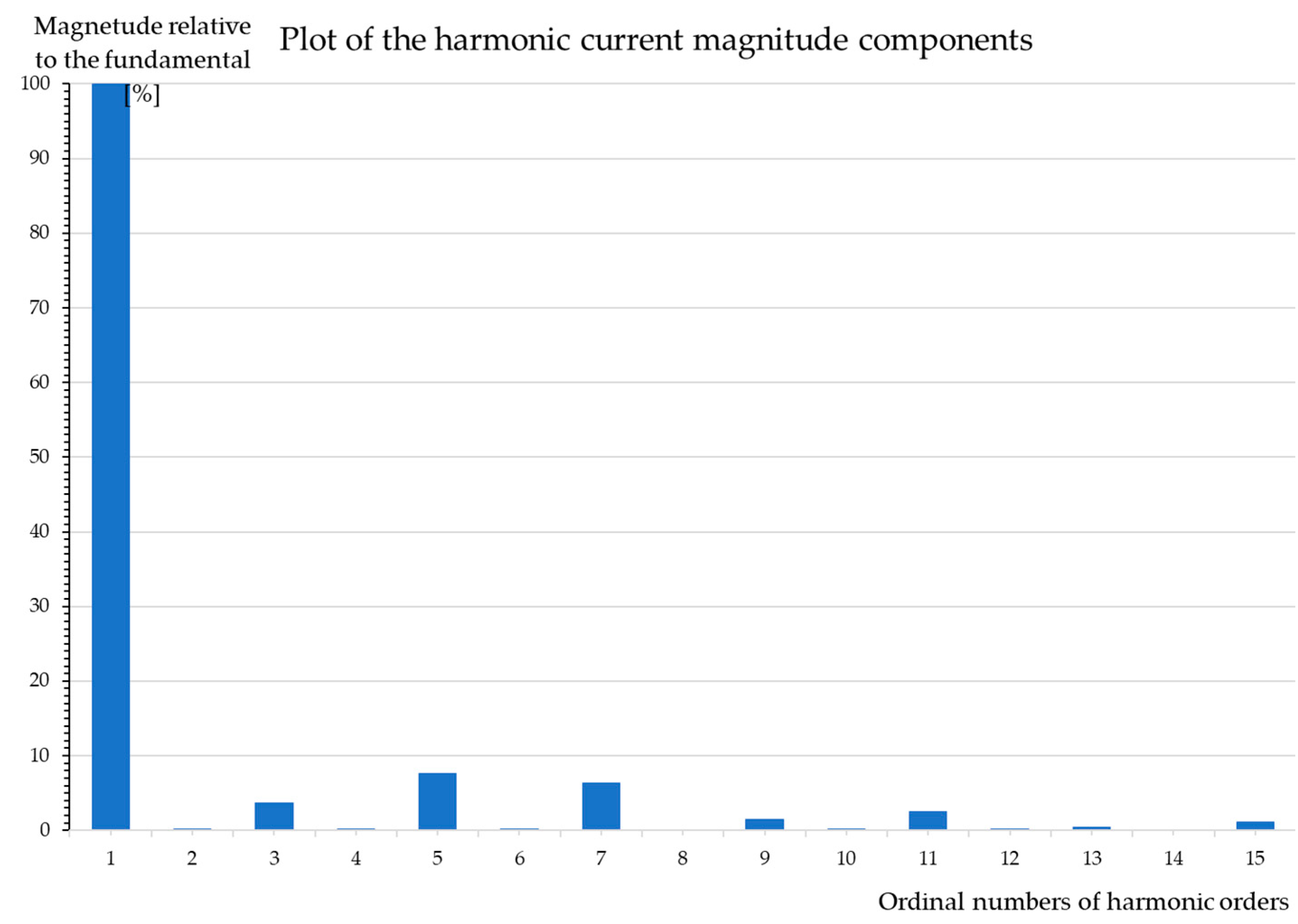
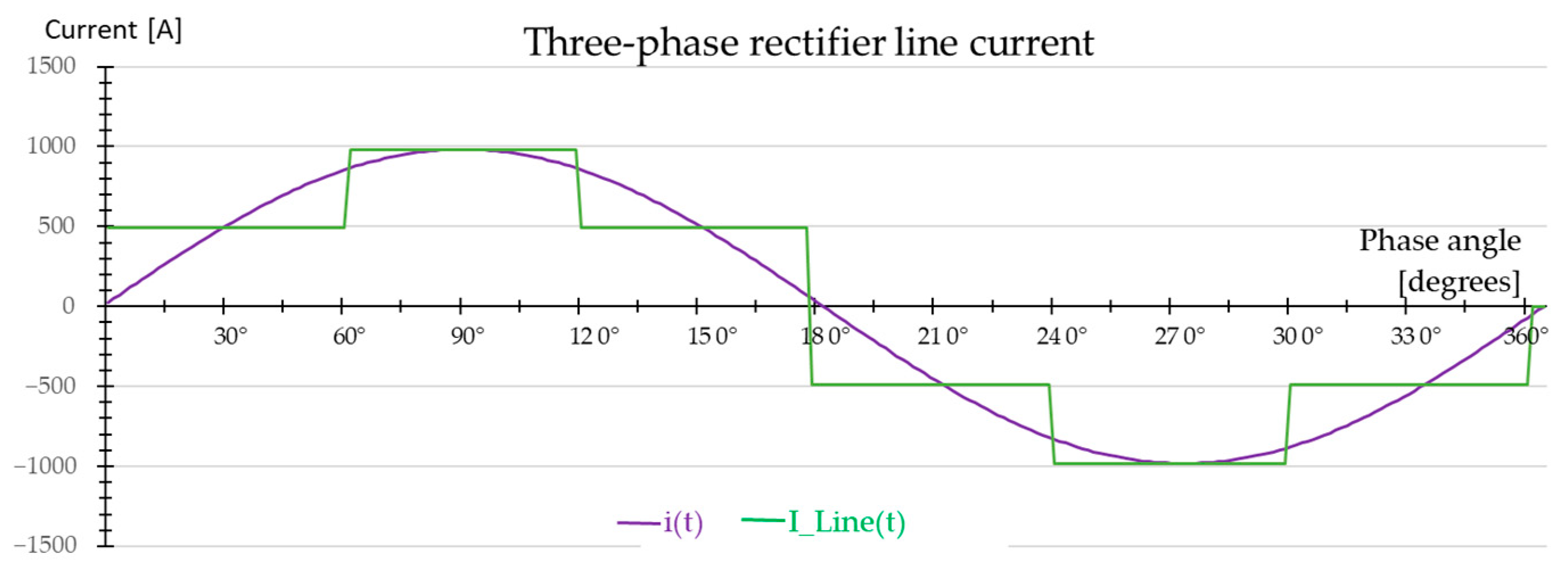
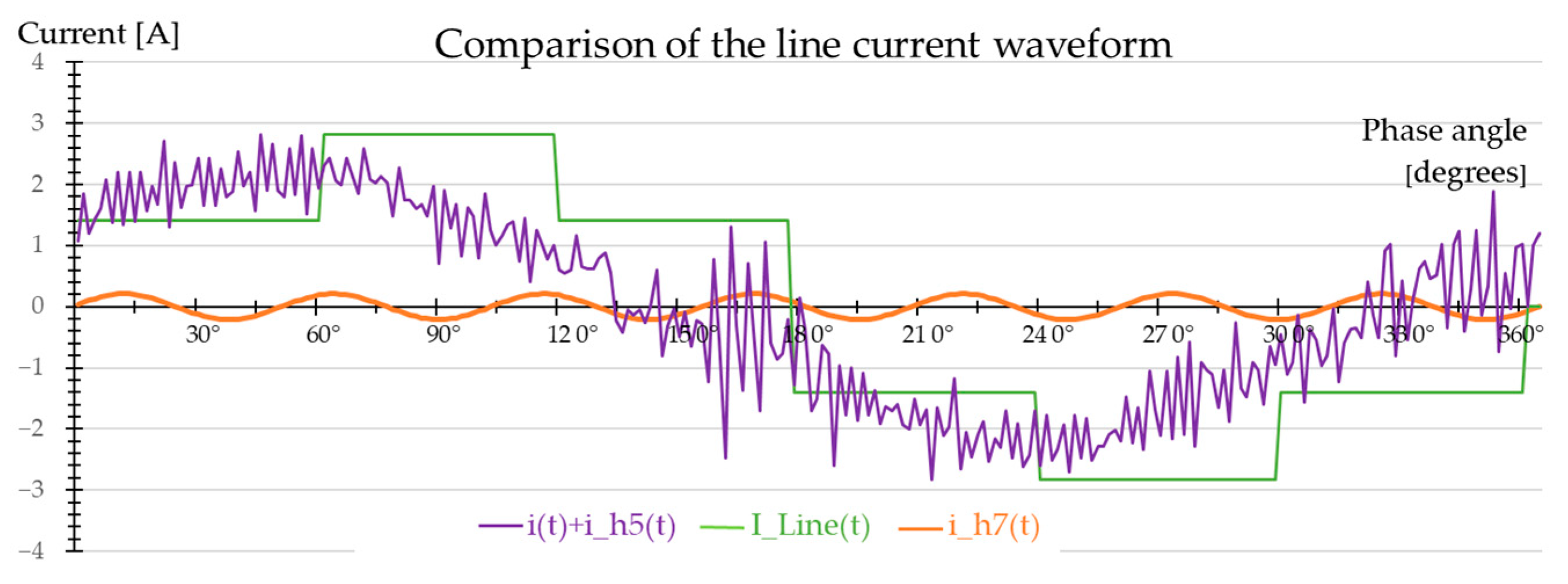
2. Harmonic Disturbance Sources
- The DC component, if applicable;
- A sinusoidal term at the fundamental frequency;
- Sinusoidal members (harmonics) with a frequency represented by a multiple of the fundamental frequency.
3. Switching Power Supplies
4. Possible Consequences of the Presence of Harmonics
5. Filtering Harmonics
6. The IEEE 519-2022 Standard Recommends
7. Network Analysis
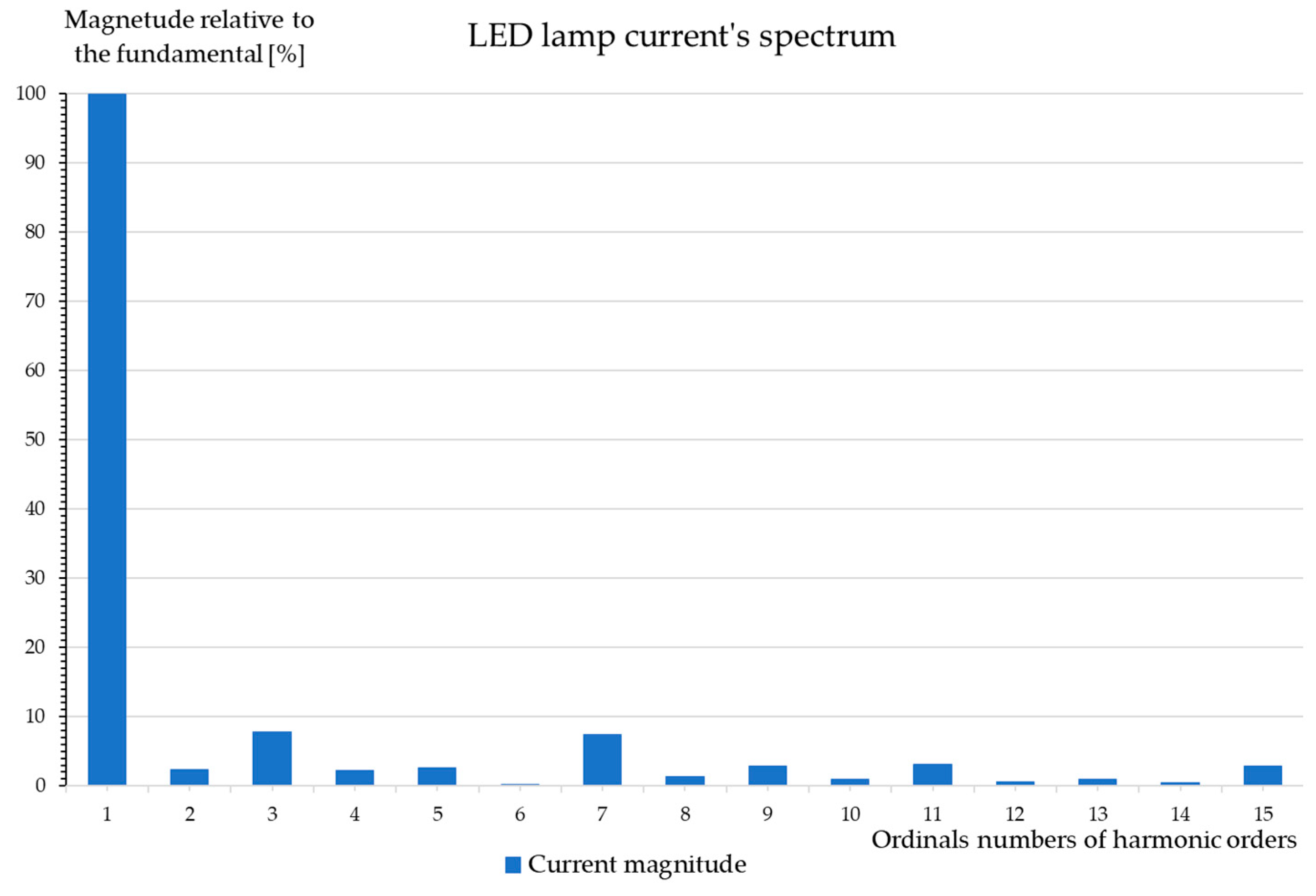
7.1. LED Lamp Built-In Passive Harmonic Filter Validation
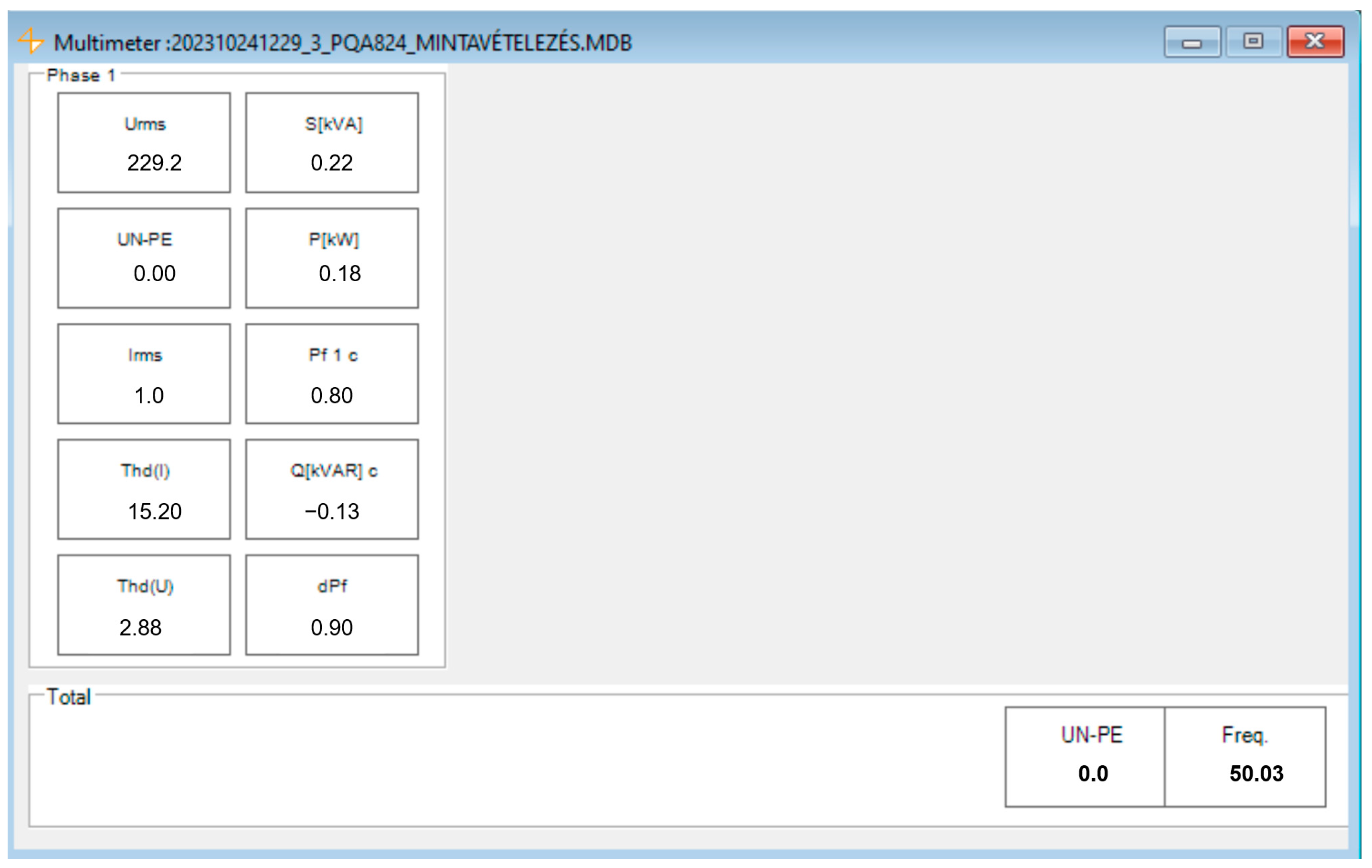
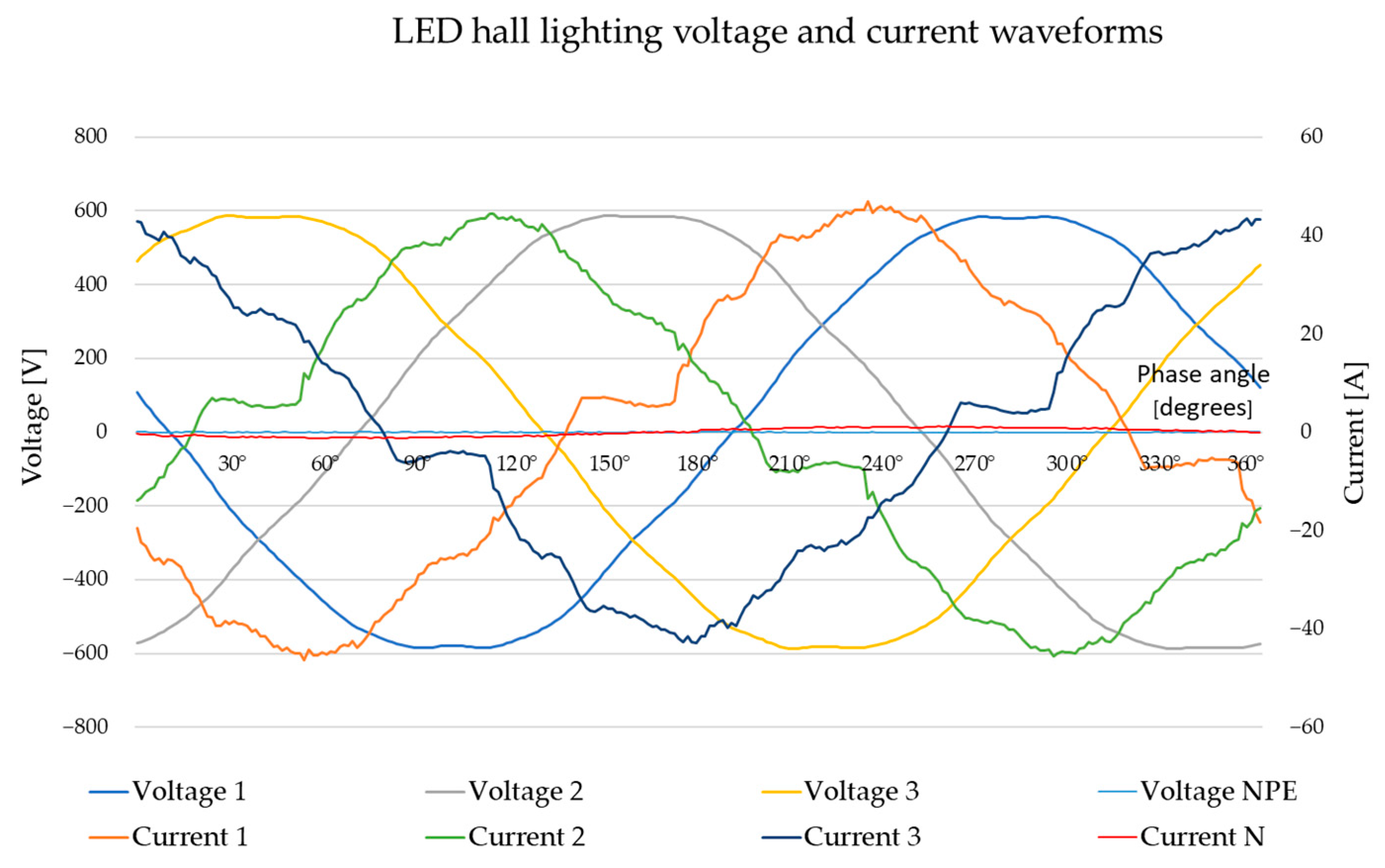
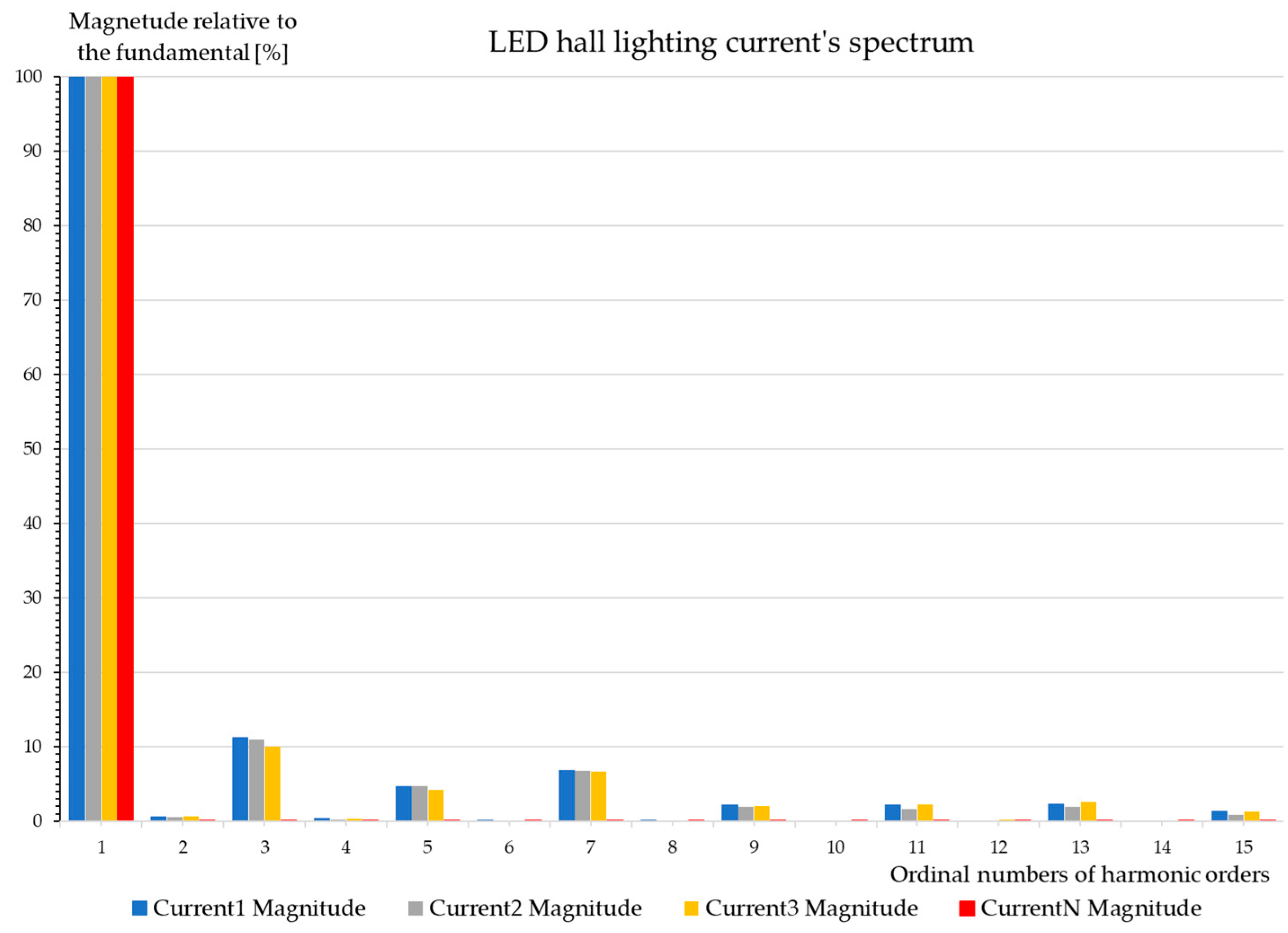
7.2. LED Lamp Built-In Passive Harmonic Filter Validation in the Case of Hall Lighting
7.3. Test Bench Built-In Active Harmonic Filter Validation
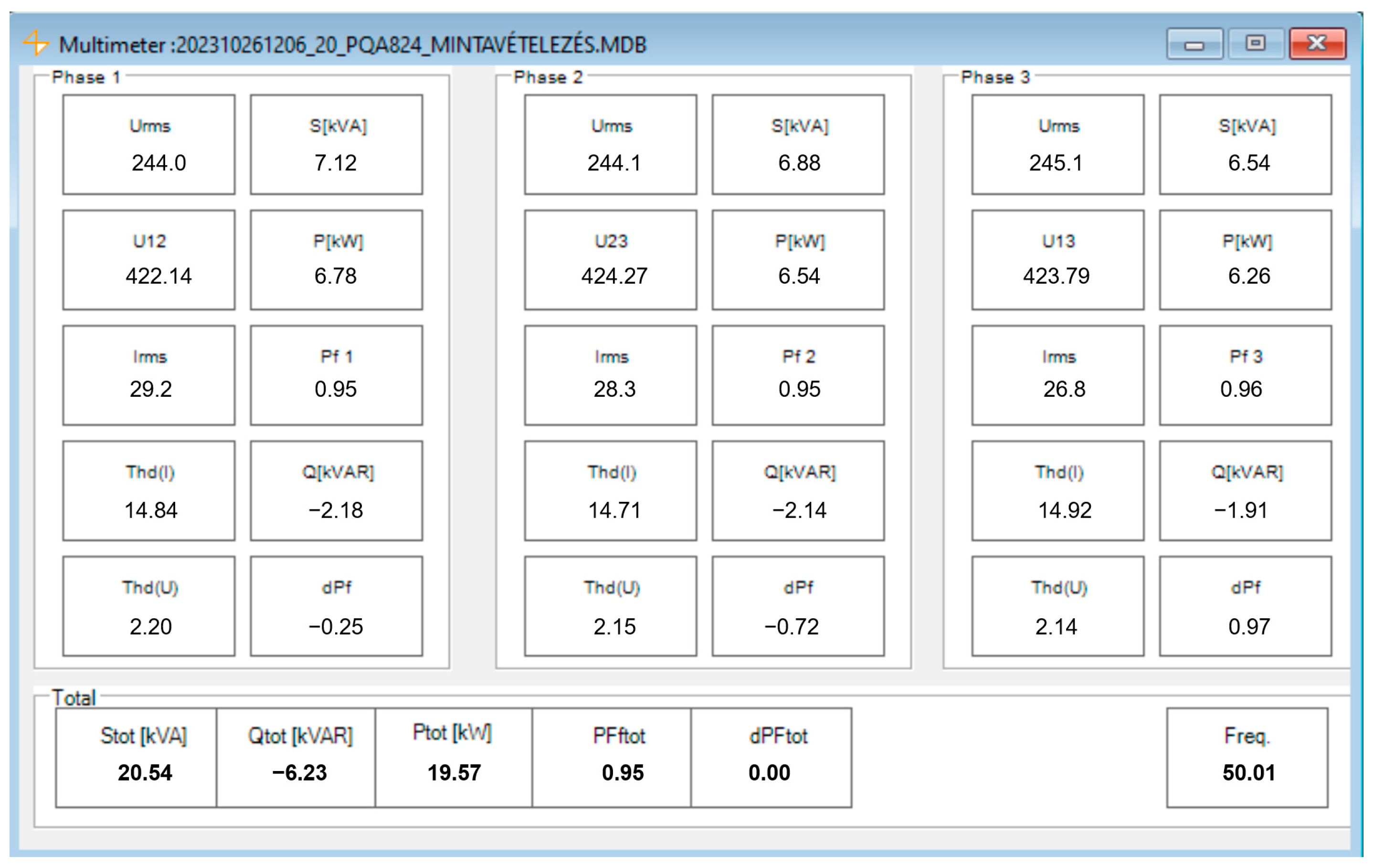
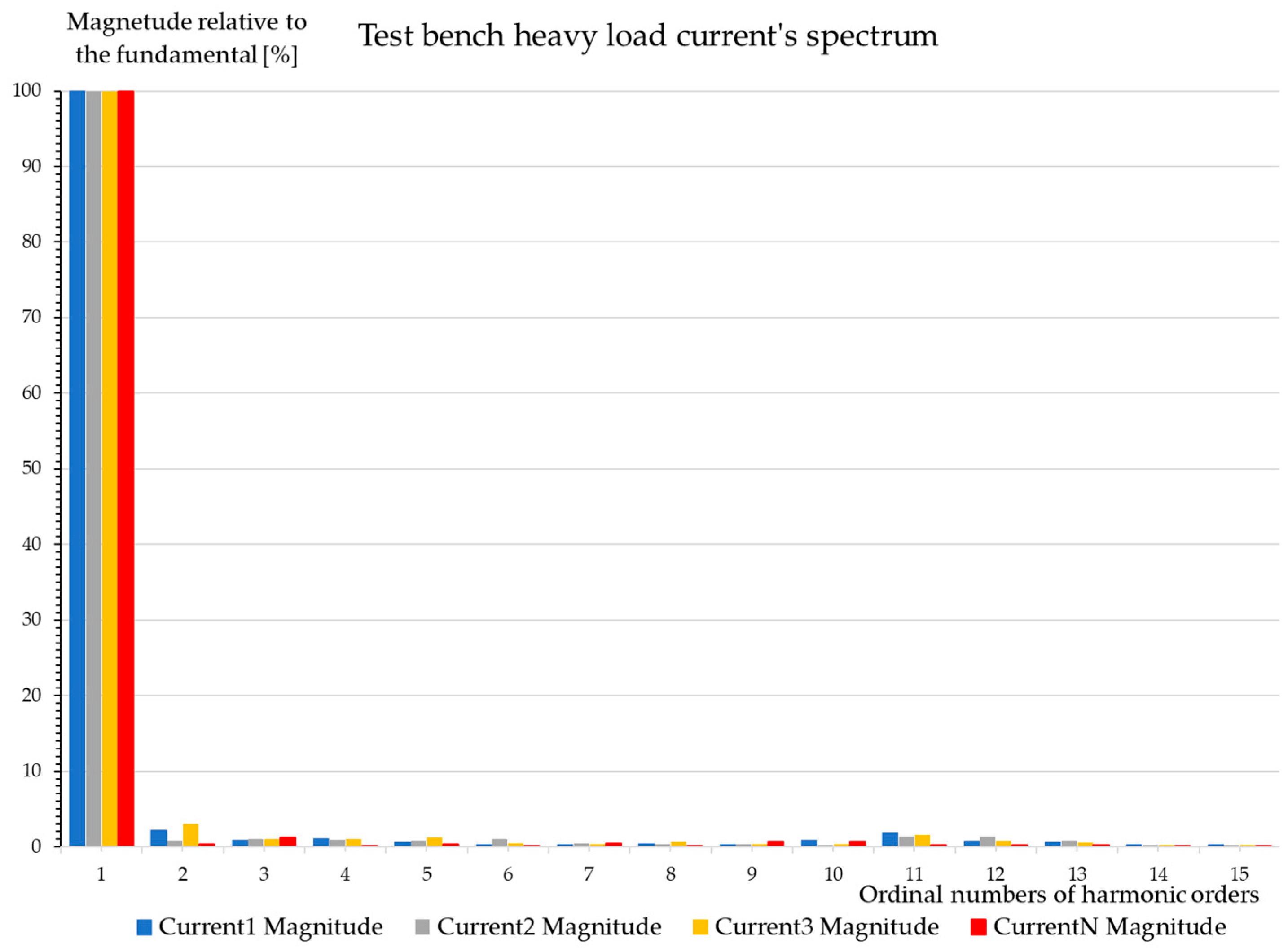
7.3.1. Test Bench at a Heavy Load
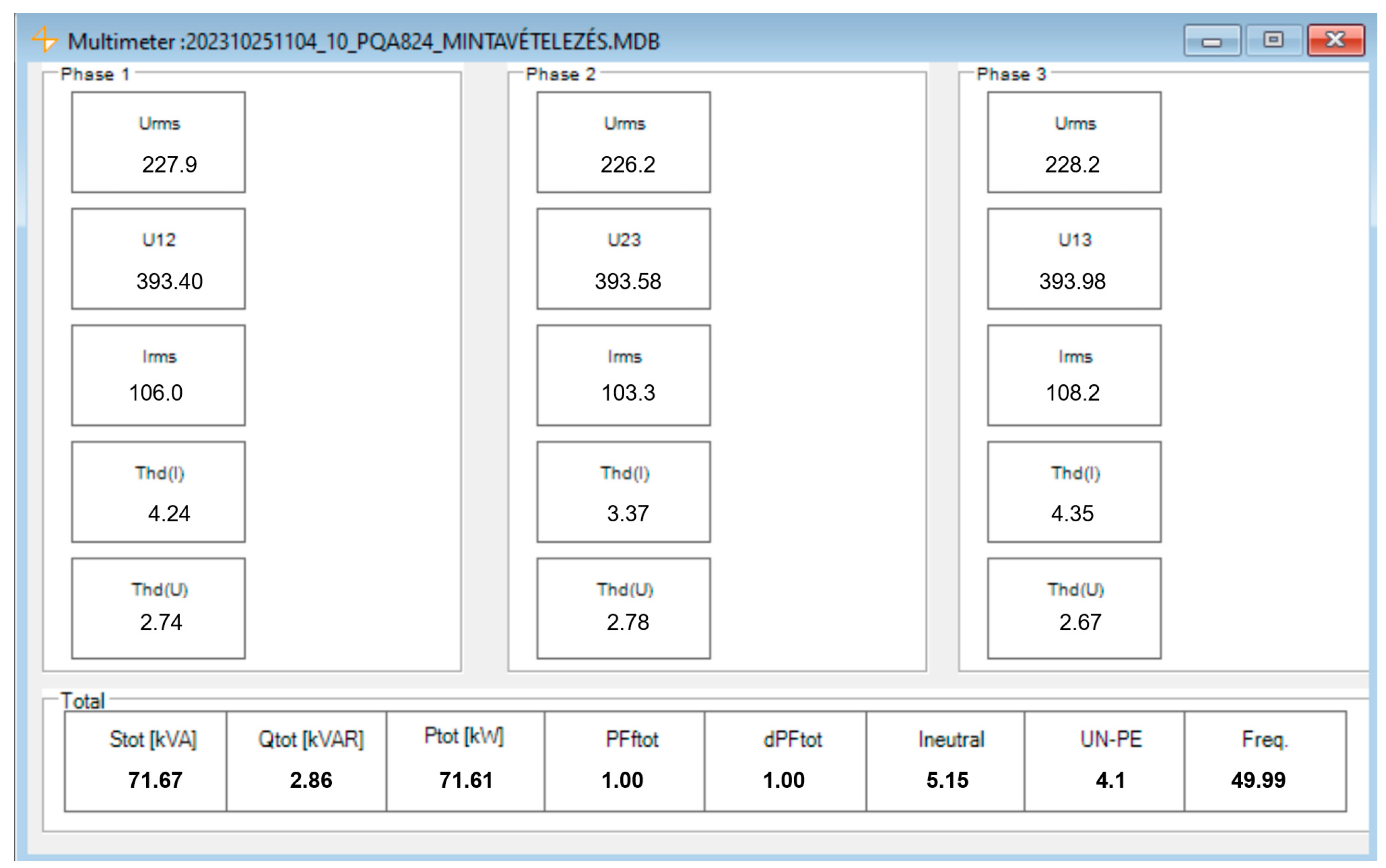
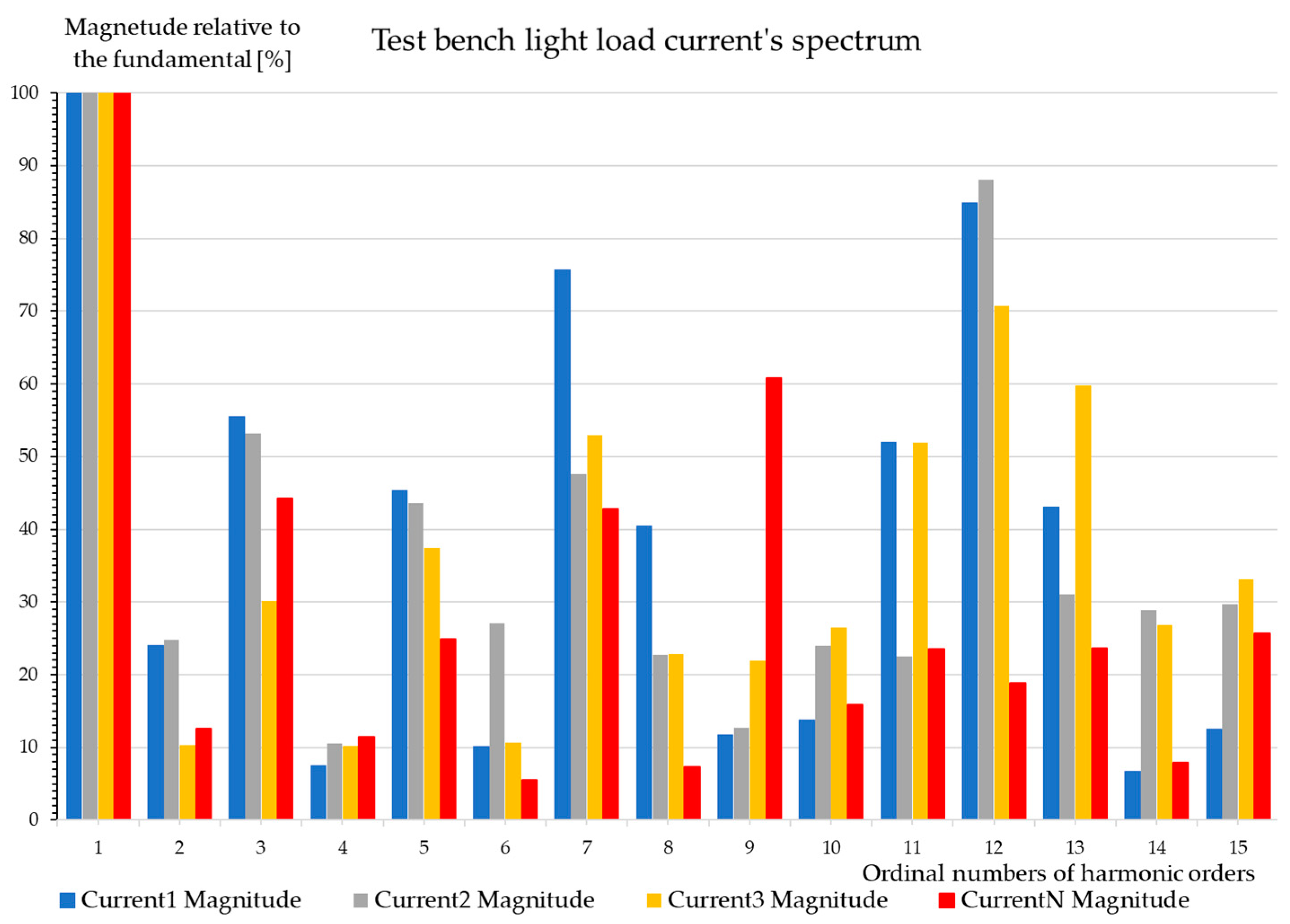
7.3.2. Test Bench at Light Load
7.4. Industrial Robot Built-In Active Harmonic Filter Validation
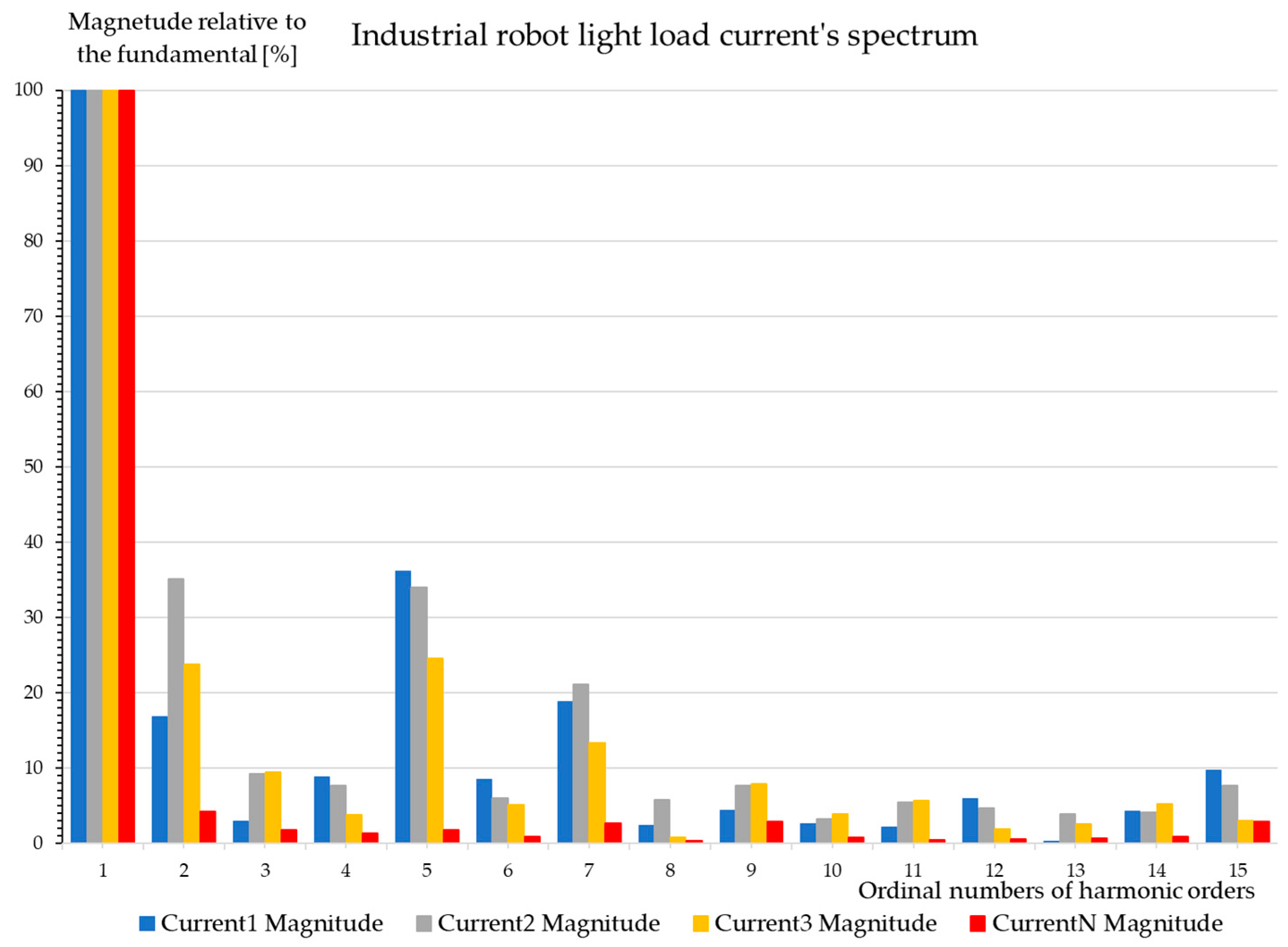
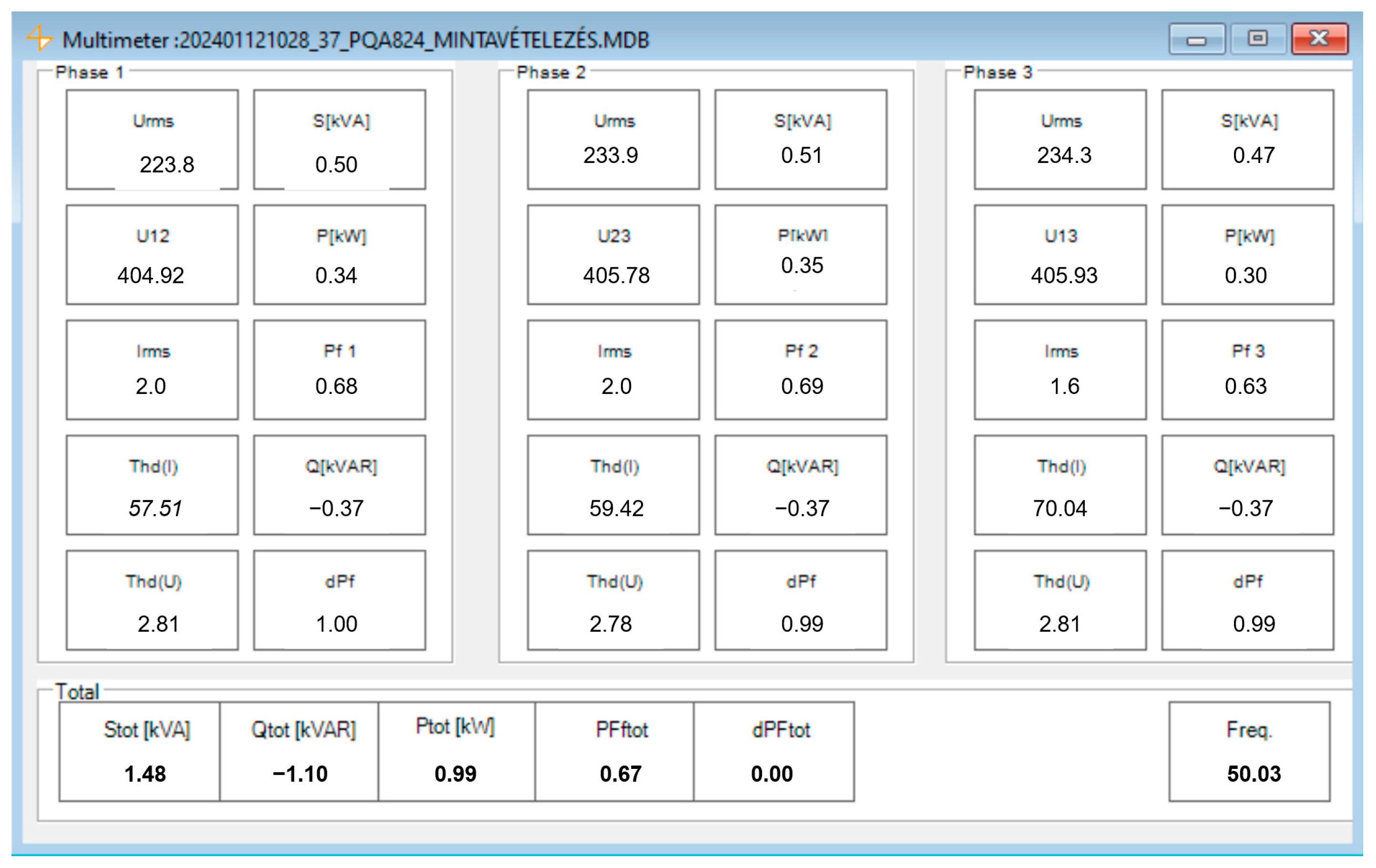
7.4.1. Industrial Robot at Light Load
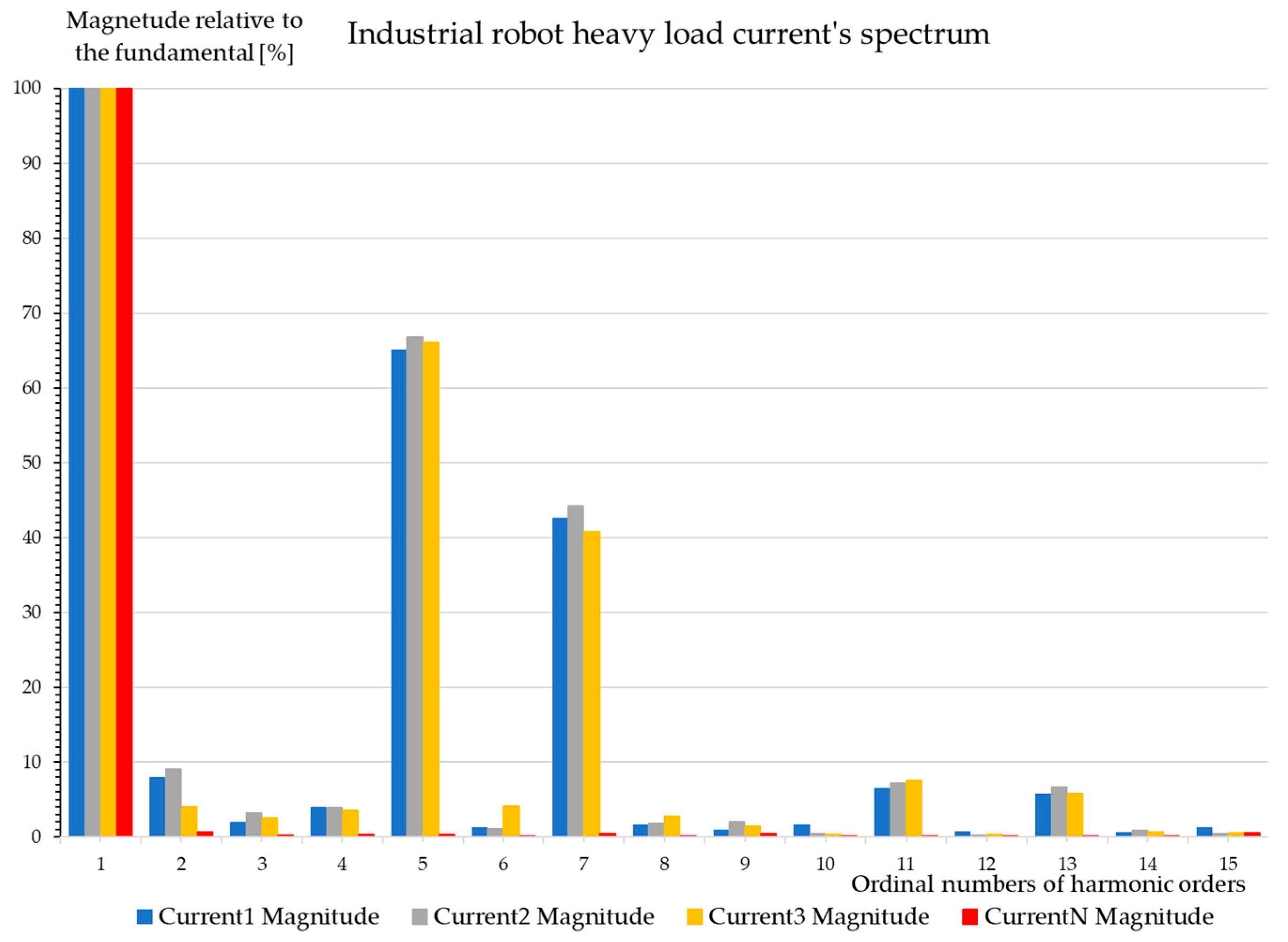
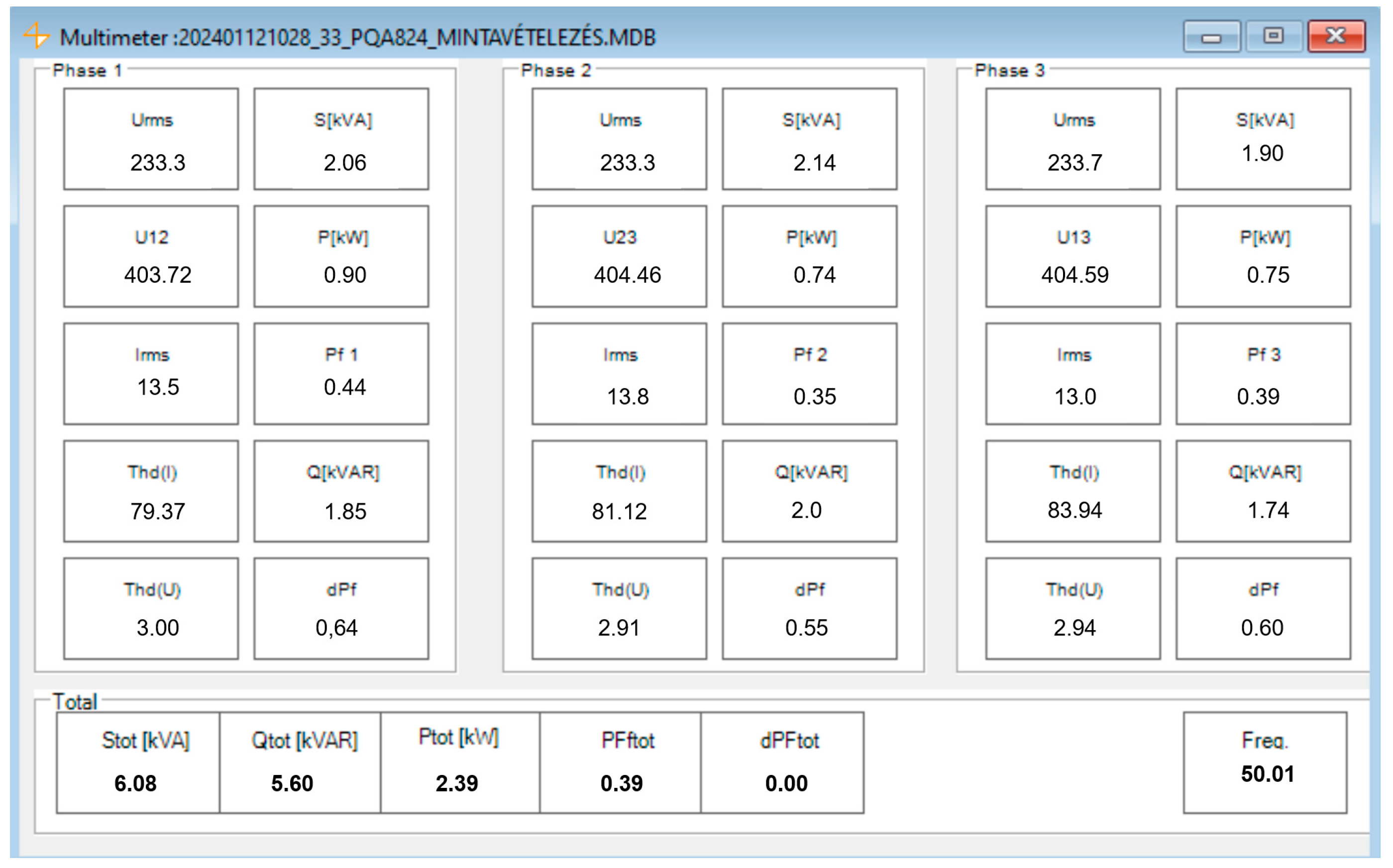
7.4.2. Industrial Robot at Heavy Load
8. Network Analysis of Different Locations of the Industrial Facility
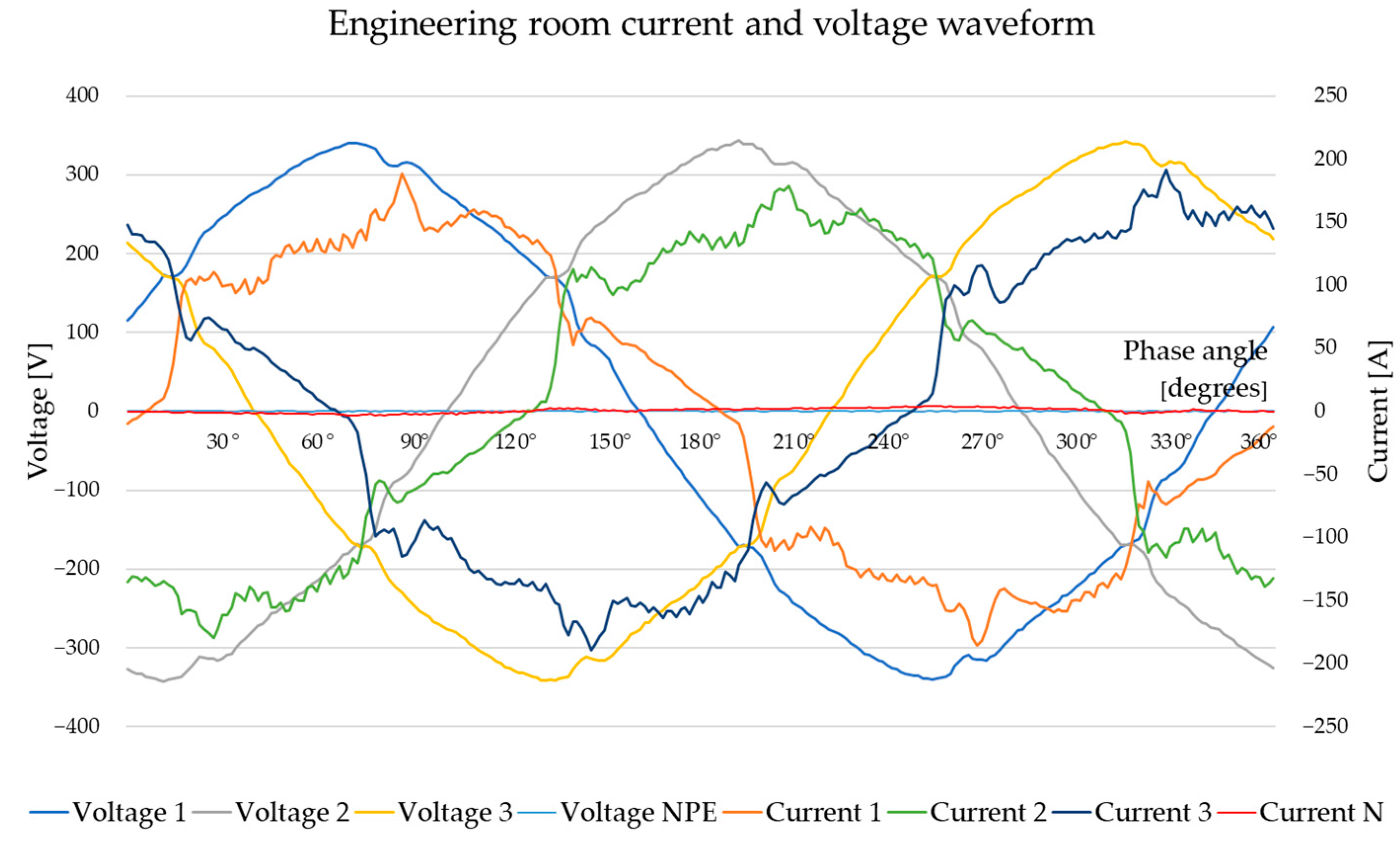
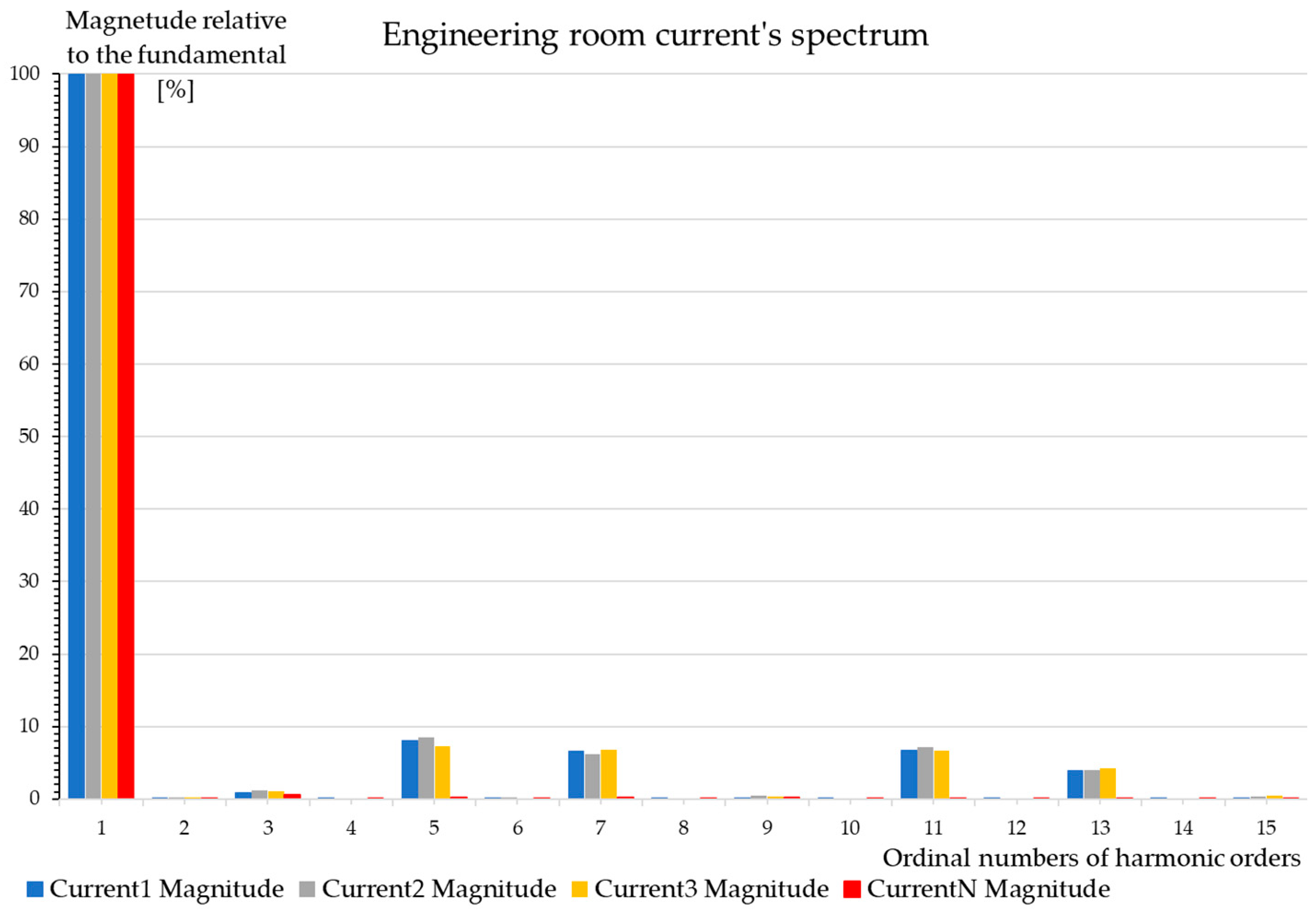
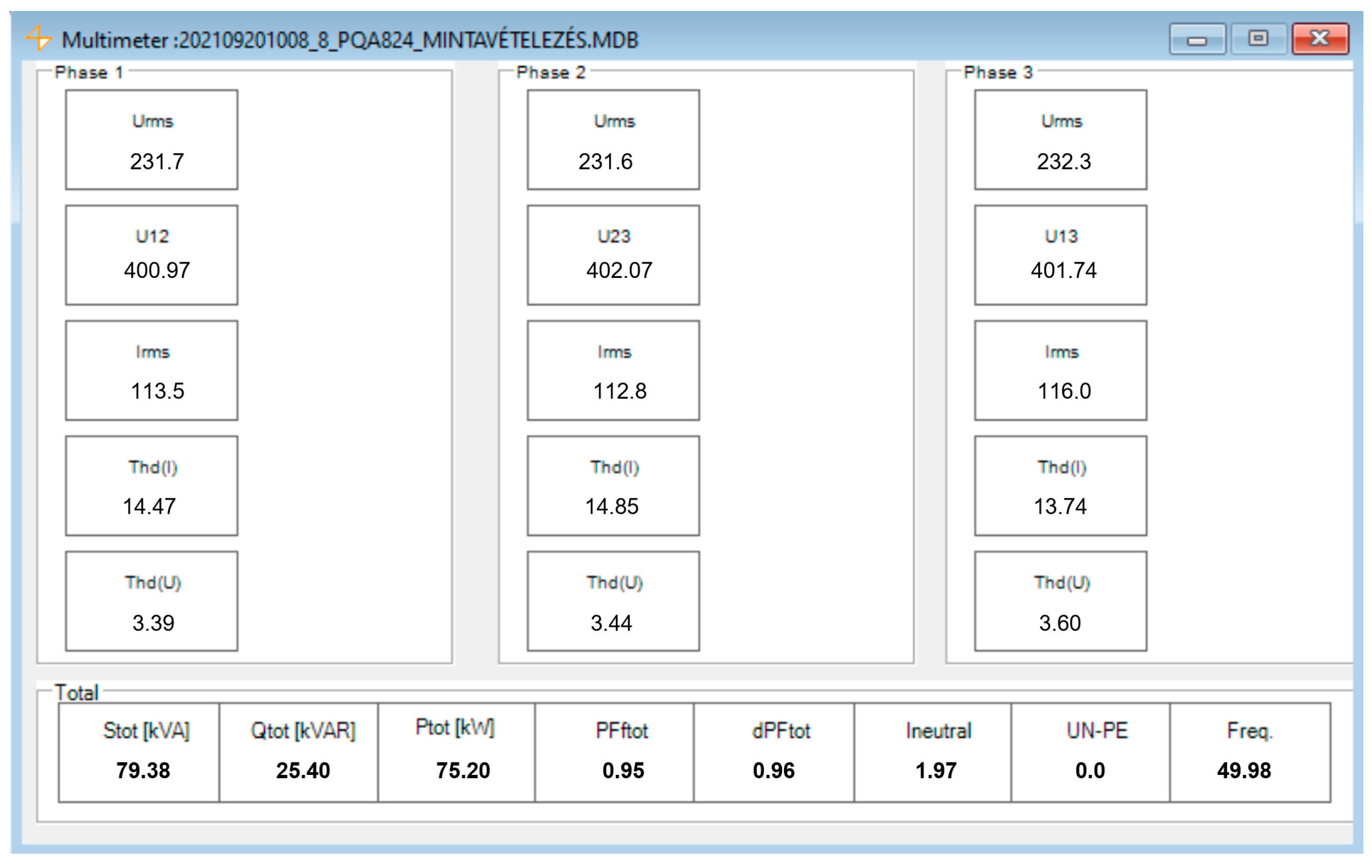
8.1. Engineering Room
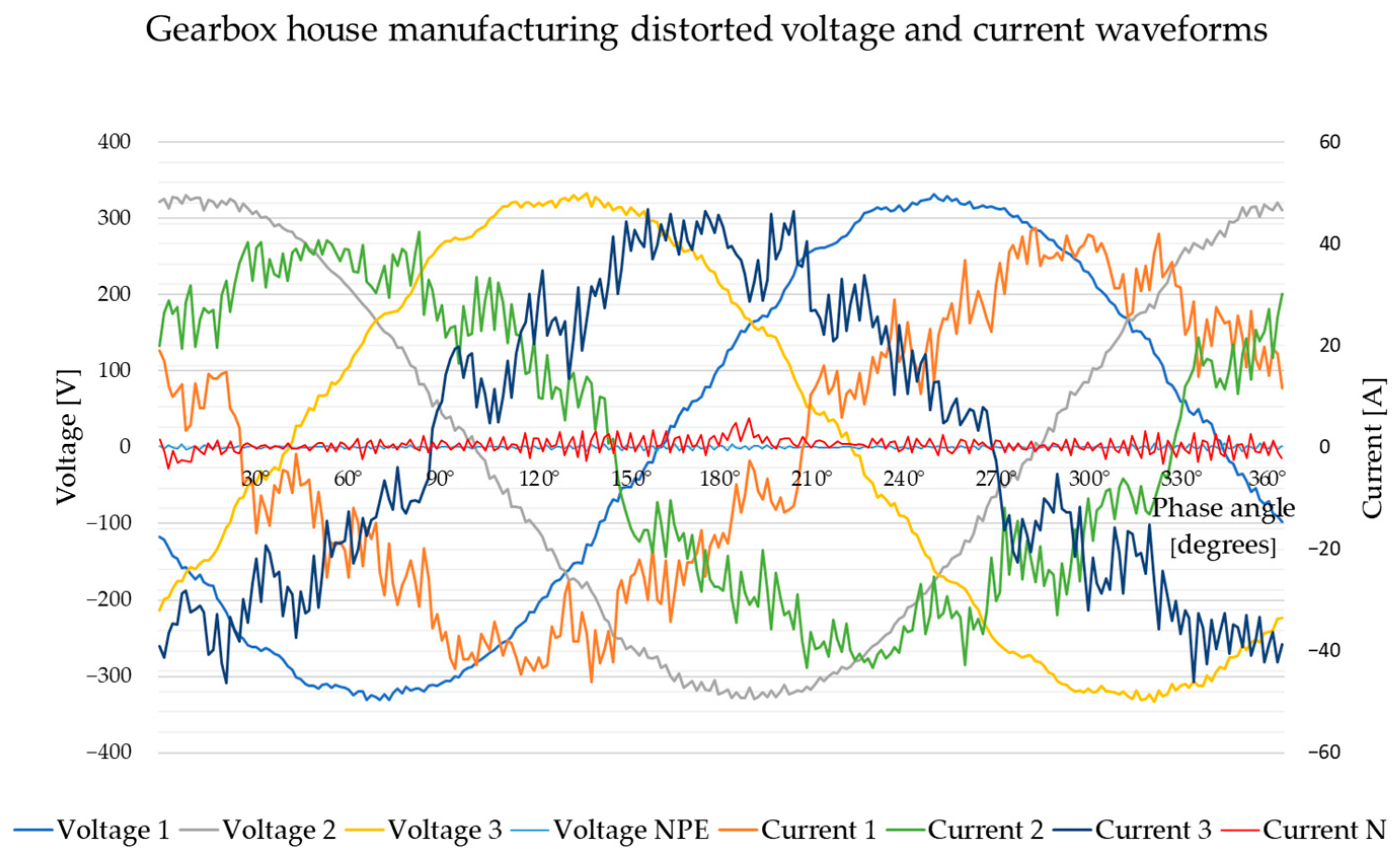
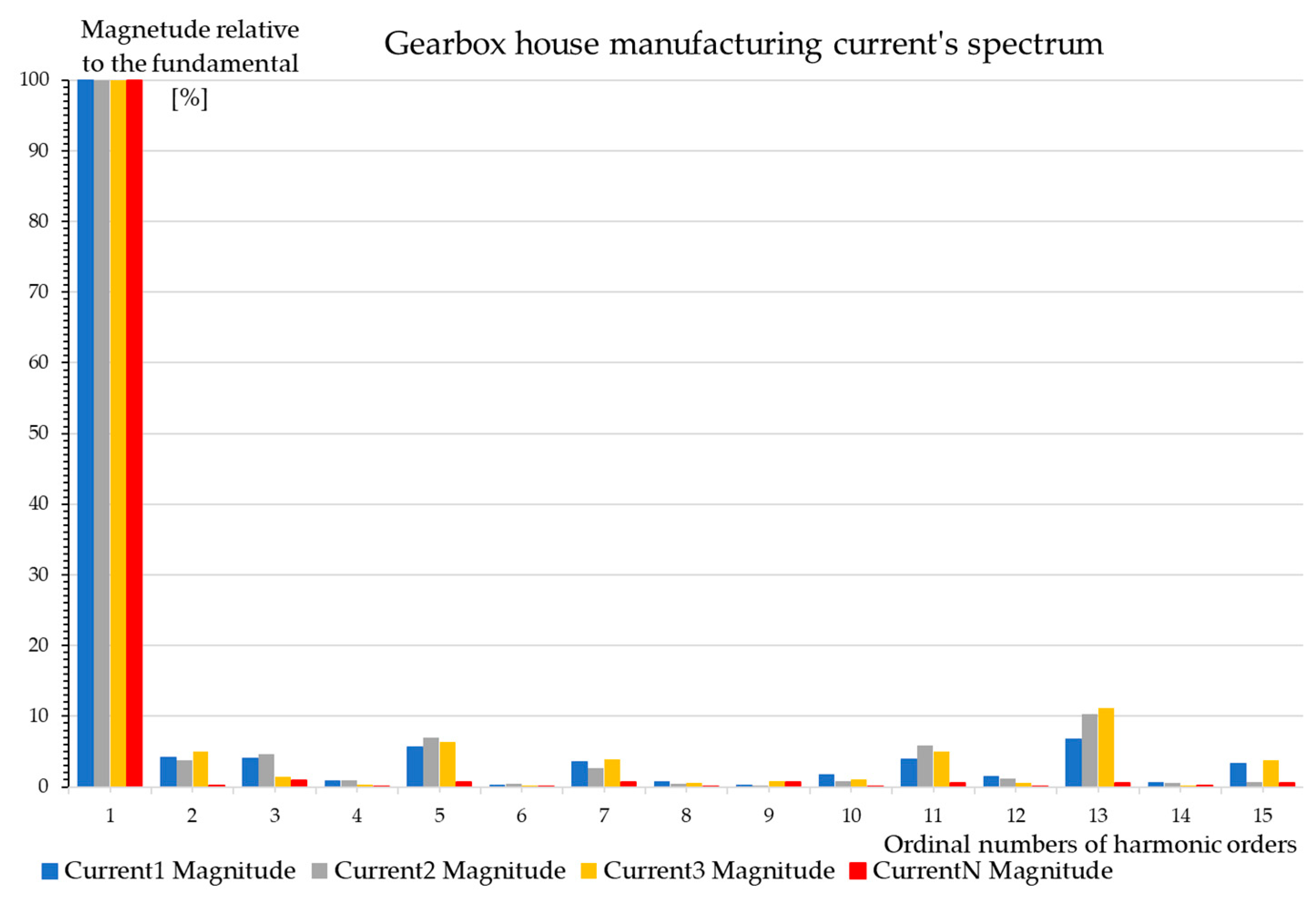
8.2. Gearbox House Machine Tool
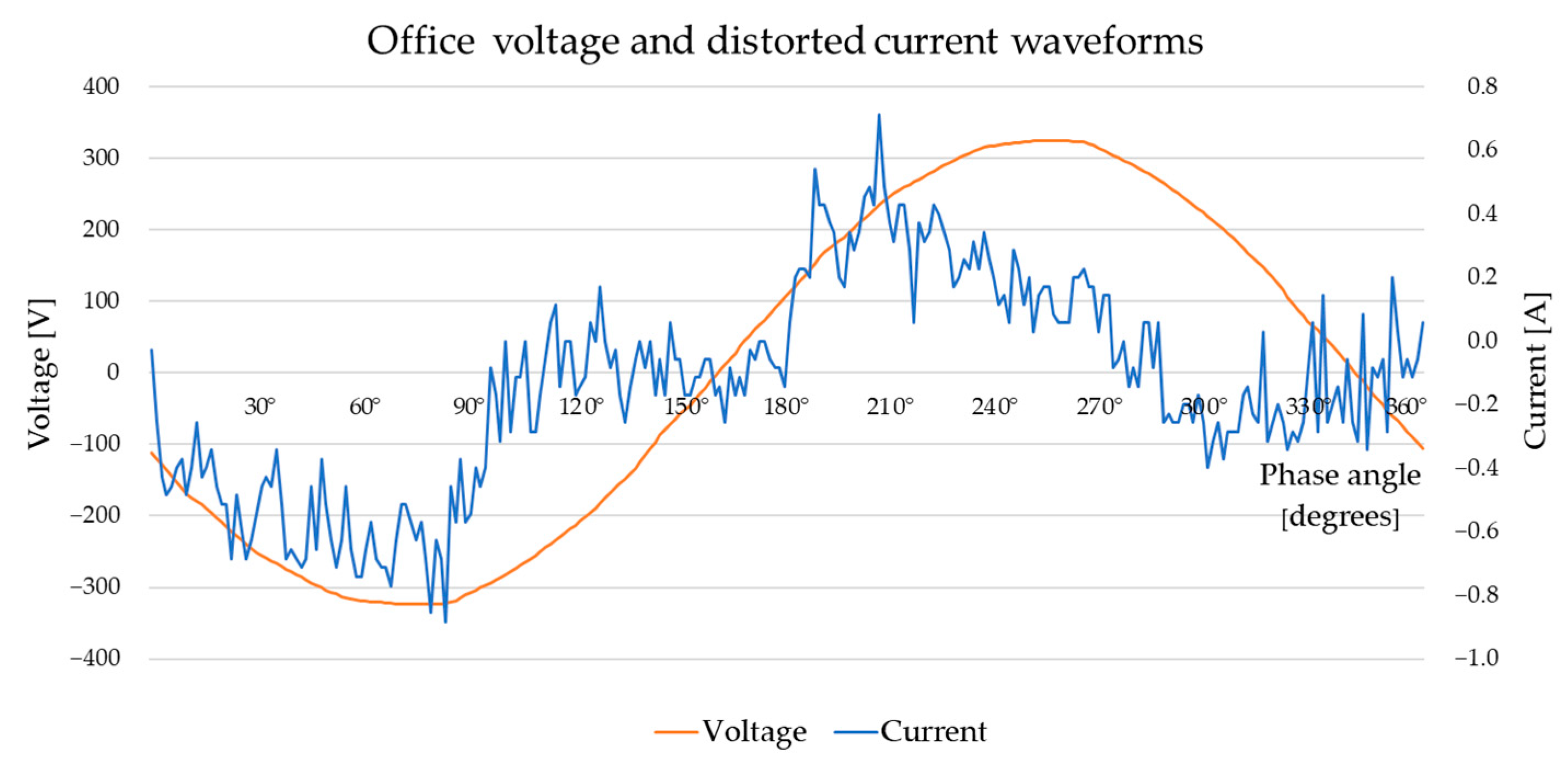
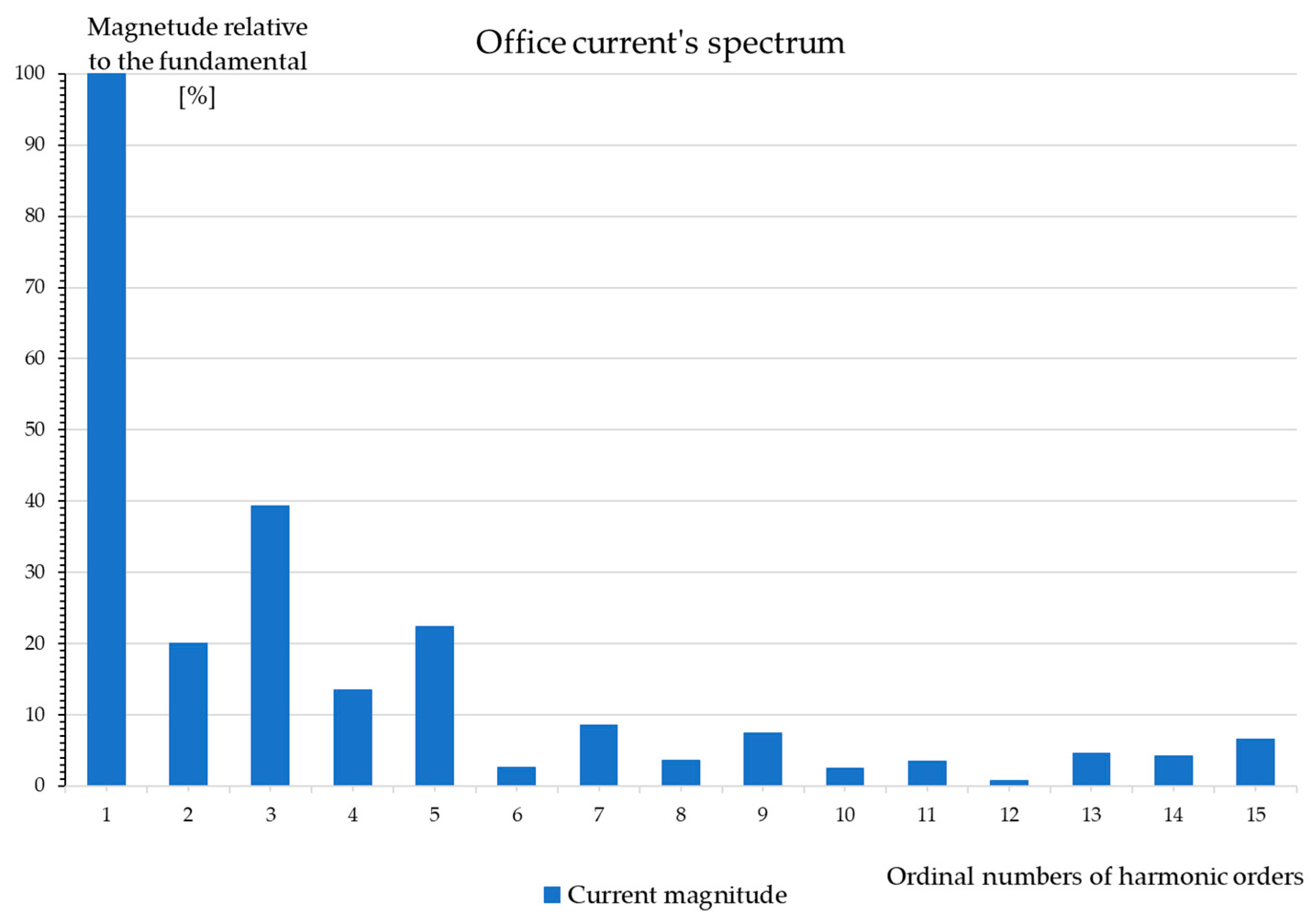
8.3. Office Room
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| THD | Total harmonic distortion |
| EMS | Energy Management System ISO 50001 |
| PHEV | Plug in hybrid vehicle |
| PLC | Programmable logic controller |
| CNC | Computer numerical control |
| LED | Light-emitting diodes |
| DC | Direct current |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| TDD | Total current demand distortion |
| PCC | Point of common coupling |
| FFT | Fast Fourier transform |
| TN | Three-phase neutral system |
| AC | Alternating current |
| MV | Medium voltage |
| LV | Low voltage |
| APLC | Active power line conditioning |
| PWM | Pulse-width modulation |
| NPC | Neutral point clamped |
| IGBT | Insulated-gate bipolar transistor |
References
- Ghorbani, M.J.; Mokhtari, H. Impact of harmonics on power quality and losses in power distribution systems. Int. J. Electr. Comp. Eng. 2015, 5, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, I. Power quality issues-a distribution company perspective. Power Eng. J. 2001, 15, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmehr, M.; Farhangi, S.; Nasiri, A. Effects of power quality distortions on electrical drives and transformer life in paper industries: Simulations and real time measurements. In Proceedings of the Pulp and Paper Industry Technical Conference, Appleton, WI, USA, 18–23 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.H.; Chen, C.S.; Moo, C.S.; Hsu, C.T. Harmonic analysis for industrial customers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1994, 30, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, A.; Grady, W.M.; Staats, P.T. Predicting the net harmonic currents produced by large numbers of distributed single-phase computer loads. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1995, 10, 2001–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoum, M.A.S.; Fuchs, E.F. Power Quality in Power Systems and Electrical Machines, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization). ISO Central Secretariat. ISO 50001:2018. Vernier, Geneva, Switzerland. 2018. Available online: https://www.iso.org/files/live/sites/isoorg/files/store/en/PUB100400.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Pinyol, R. Harmonics: Causes, Effects and Minimization. Salicru White Papers. 2015. Available online: https://www.salicru.com/files/pagina/72/278/jn004a01_whitepaper-armonics_(2).pdf (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Das, J.C. Power System Harmonics and Passive Filter Designs. Power System Harmonics and Passive Filter Designs, 1st ed.; Wiley-IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wenqian, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Longwei, X.; Chao, Z.; Xinsheng, M. Harmonic loss analysis of low-voltage distribution network integrated with distributed photovoltaic. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumaryadi, D.; Gumilang, H.; Suslilo, A. Effect of power system harmonic on degradation process of transformer insulation syste. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Conference on the Properties and Applications of Dielectric Materials, Harbin, China, 19–23 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiee-Rad, M.; Kazerooni, M.; Ghorbany, J.; Mokhtari, H. Analysis of the grid harmonics and their impacts on distribution transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power and Energy Conference, Champaign, IL, USA, 24–25 February 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Aktif. Problems Caused by Harmonics in Electrical Plants. Available online: https://aktif.net/en/problems-caused-by-harmonics-in-electrical-plants/# (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Szűcs, V.; Fodor, A.; Görbe, P. Examination of nonlinear distortion of IT power supplies in low voltage grid from the current quality point of view. Acta Phys. Pol. 2018, 134, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo, E.J.; Romero, A.A.; Zini, C.H. Assessment of the harmonic distortion in residential distribution networks. Ing. Investig. 2017, 37, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, A.; Grebe, T.; Gunther, E.; Hopkins, L.; Marz, M.B.; Mahseredjian, J.; Xu, W. Modeling and simulation of the propagation of harmonics in electric power networks. Part I: Concepts, models, and simulation techniques. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1996, 11, 452–465. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, S.; Shareef, H.; Mohamed, A. Power quality performance of energy-efficient low-wattage LED lamps. Measurement 2013, 46, 3783–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplawski, T.; Kurkowski, M. Nonlinear Loads in lighting installations—Problems and threats. Energies 2023, 16, 6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.; Mesas, J.J.; Mesbahi, N.; Sainz, L. LED lamp modelling for harmonic studies in distribution systems. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, W.; Qian, K.; Meng, S. Modelling of ampacity and temperature of MV cables in presence of harmonic currents due to EVs charging in electrical distribution networks. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 112, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouybari-Moghaddam, H.; Alimardani, A.; Hosseinian, S.H. Influence of electric vehicle charging rates on transformer derating in harmonic-rich battery charger applications. Arch. Electr. Eng. 2012, 61, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarian, T.; Joorabian, M.; Reza, A. The effect of plug-in electric vehicles on harmonic analysis of smart grid. Int. J. Emerg. Electr. Power Syst. 2015, 16, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, A.A.; Malik, P.O. Harmonics in Electric Distribution Systems. In Electric Distribution Systems, 2nd ed.; El-Hawary, M.E., Ed.; Wiley-IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; Chapter 14; pp. 379–402. [Google Scholar]
- Fourier Analysis. Carl von Ossietzky University Oldenburg—Faculty V—Institute of Physics. Module Introductory Laboratory Course Physics—Part I. Available online: https://uol.de/f/5/inst/physik/ag/physikpraktika/download/GPR/pdf/E_Fourieranalyse.pdf?v=1666712279 (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Emanuel, A.E.; Janczak, J.; Pileggi, D.J.; Gulachenski, E.M.; Root, C.E.; Breen, M.; Gentile, T.J. Voltage distortion in distribution feeders with nonlinear loads. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1994, 9, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.H.; Liao, S.H.; Leou, R.C. Three-phase harmonic analysis method for unbalanced distribution systems. Energies 2014, 7, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What is True-RMS? Available online: https://www.fluke.com/en-us/learn/blog/electrical/what-is-true-rms (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Magadum, P.K. Effects of nonlinear loading on power quality. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Advances in Computing, Control, and Telecommunication Technologies, Hyderabad, India, 27–28 June 2022; Volume 8, pp. 1119–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Tarnik, I. Villamos Hálózati Zavarok/Electrical Network Disturbances. 2008. Available online: https://www.muszeroldal.hu/measurenotes/tarmikcikk.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Peng, F.Z. Harmonic sources and filtering approaches. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2001, 7, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, T.I.A.H.; Cabral, S.H.L.; Almaguer, H.A.D.; Meyer, L.H.; Puchale, L.H.B.; Vier, G.B.; Cereja, J.E. Analysis of the Behavior of the 5th Harmonic over Power Transmission Lines. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 400–405. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8566407 (accessed on 11 August 2024).
- Jewel, W.; Miller, W.L.; Casey, T. Filtering dispersed harmonic sources on distribution. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2000, 15, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D. Application Note—Harmonics: Causes and Effects, 2nd ed.; European Copper Institute: Brussels, Belgium, 2011; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Calvas, L. Electrical Disturbances in LV, 1st ed.; Cahier Technique No. 141; Schneider Electric: Claix, France, 2000; Available online: https://www.tekdok.dk/files/cahiers_techniques/Electrical_disturbances_in_LV.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Wagner, V.E.; Balda, J.C.; Griffith, D.C.; McEachern, A.; Barnes, T.M.; Hartmann, D.P.; Phileggi, D.J.; Emannuel, A.E.; Horton, W.F.; Reid, W.E.; et al. Effects of harmonics on equipment. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1993, 8, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, A.E.; Orr, J.A.; Cyganski, D.; Gulachenski, E.M. A survey of harmonic voltages and currents at distribution substations. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1991, 6, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, W.M.; Samotyj, M.J.; Noyola, A.H. Minimizing network harmonic voltage distortion with an active power line conditioner. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1991, 6, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketabi, A.; Farshadnia, M.; Malekpour, M.; Feuillet, R. A new control strategy for active power line conditioner (APLC) using adaptive notch filter. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 47, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperix: Neutral Point Clamped Inverter (NPC). Available online: https://imperix.com/doc/implementation/neutral-point-clamped-inverter (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Wu, J.-C.; Jou, H.-L.; Hsaio, H.-H.; Xiao, S.-T. A new hybrid power conditioner for suppressing harmonics and neutral-line current in three-phase four-wire distribution power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2014, 29, 1525–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE 519-2022; IEEE Standard for Harmonic Control in Electric Power Systems. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022. Available online: https://standards.ieee.org/ieee/519/10677/ (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Caramia, P.; Carpinelli, G.; Rossi, F.; Verde, P. Probabilistic iterative harmonic analysis of power systems. IEE Proc.-Gener. Transm. Distrib. 1994, 141, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, A.; Segundo, J.; Ribeiro, P.; Xu, W.; Lian, K.L.; Chang, G.W.; Watson, N.R. Harmonic analysis in frequency and time domain. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2013, 28, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HT Italia. Available online: https://www.ht-instruments.com/en/ (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- HT Italia: Management Software Topview. Available online: https://www.ht-instruments.com/en/accessories/topview/ (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Karim, F.A.; Ramdhani, M.; Kurniawan, E. Low pass filter installation for reducing harmonic current emissions from LED lamps based on EMC standard. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Control, Electronics, Renewable Energy and Communications, Bandung, Indonesia, 13–15 September 2016; pp. 132–135. [Google Scholar]
- Lakervi, E.; Holmes, E.J. Electricity Distribution Network Design, 2nd ed.; Peter Peregrinus LTD, Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]




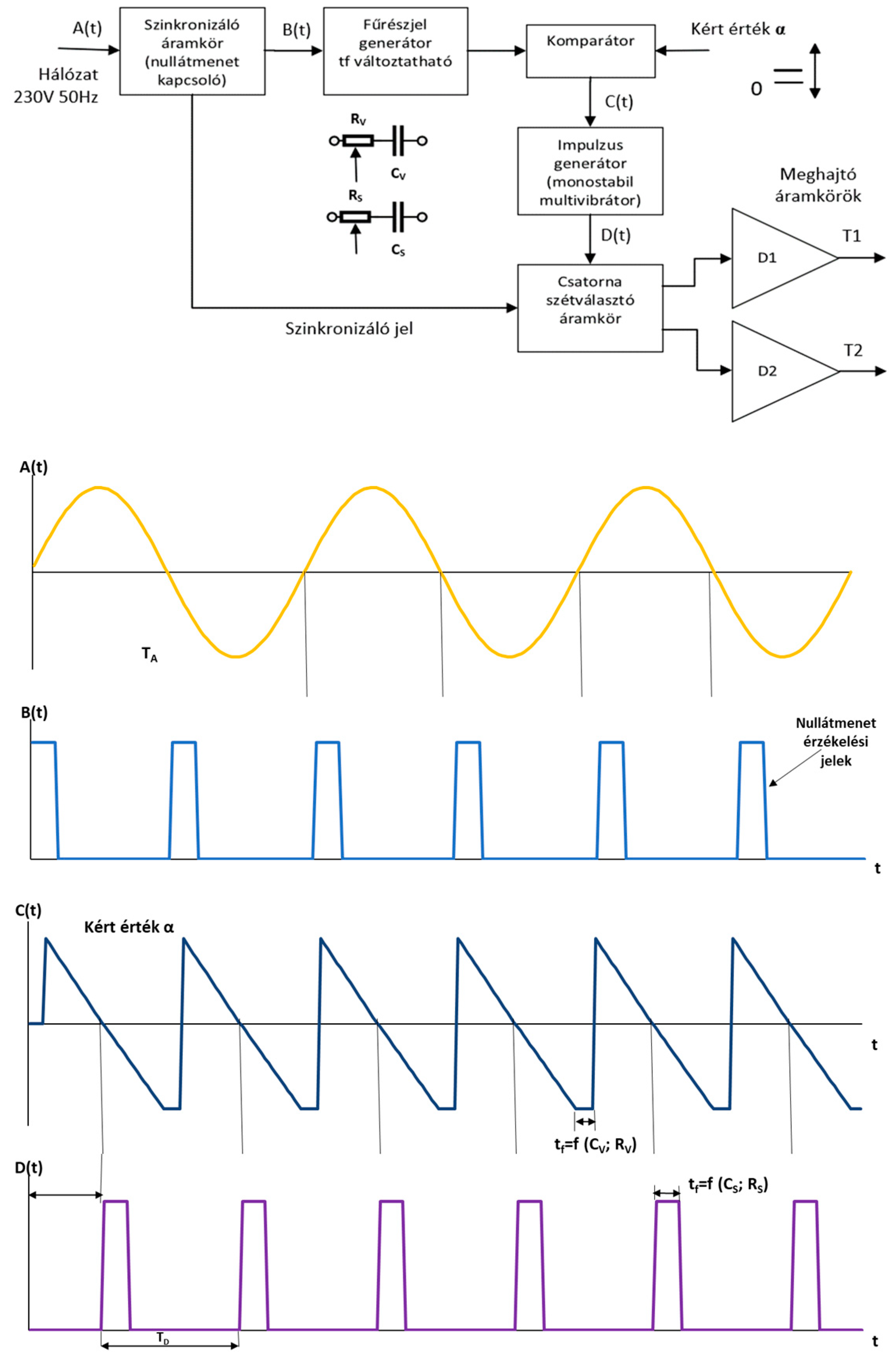
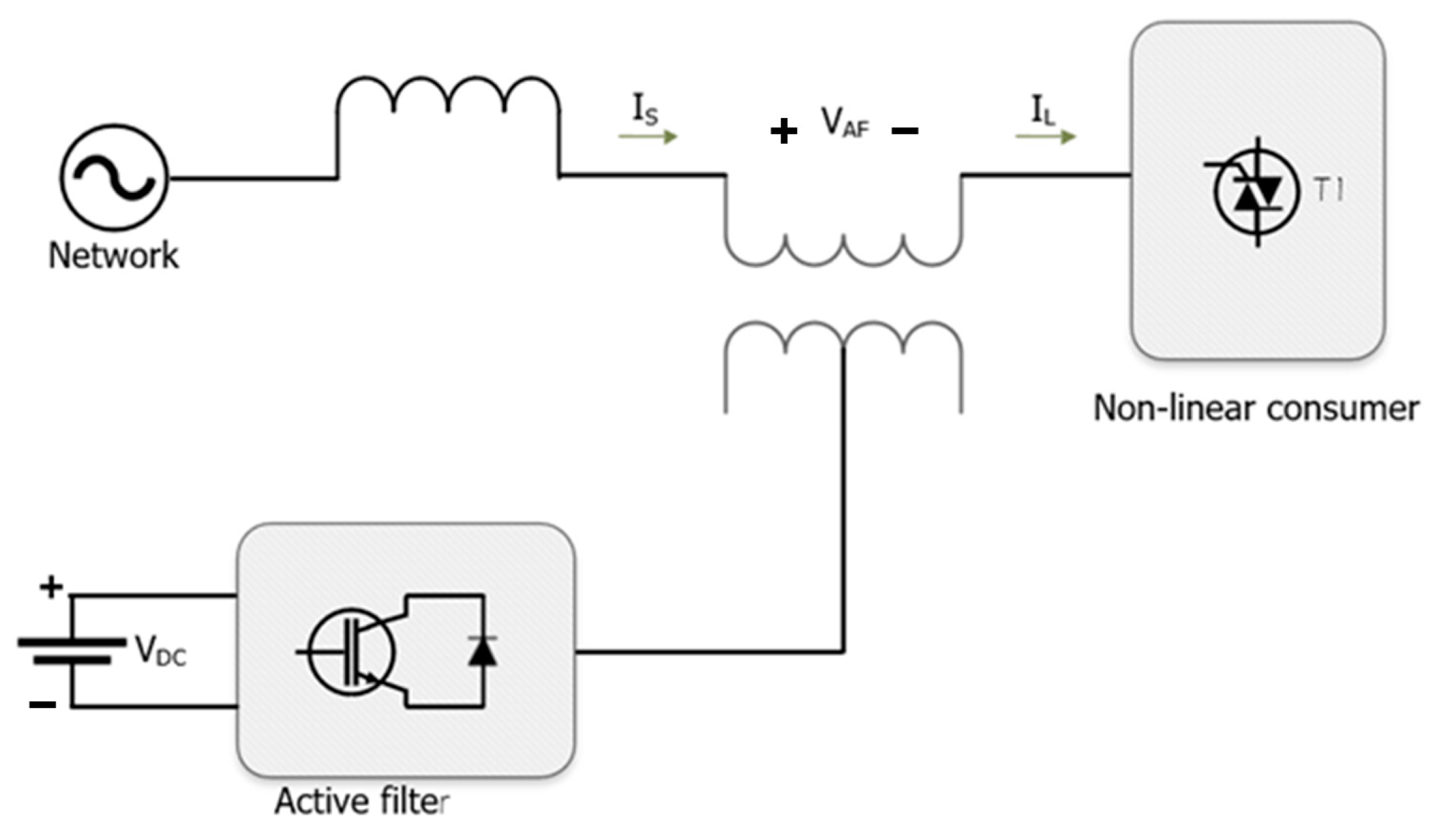
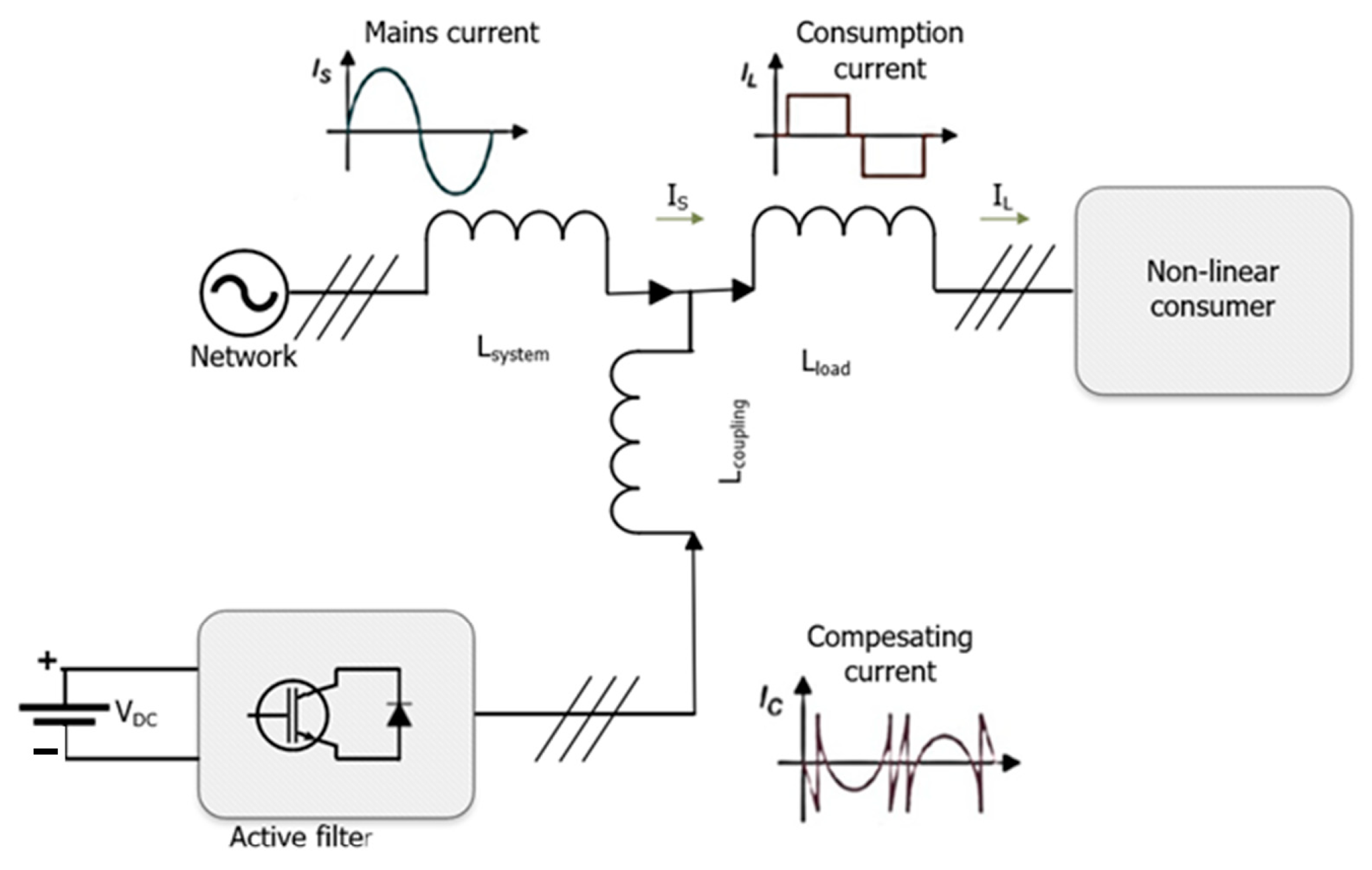
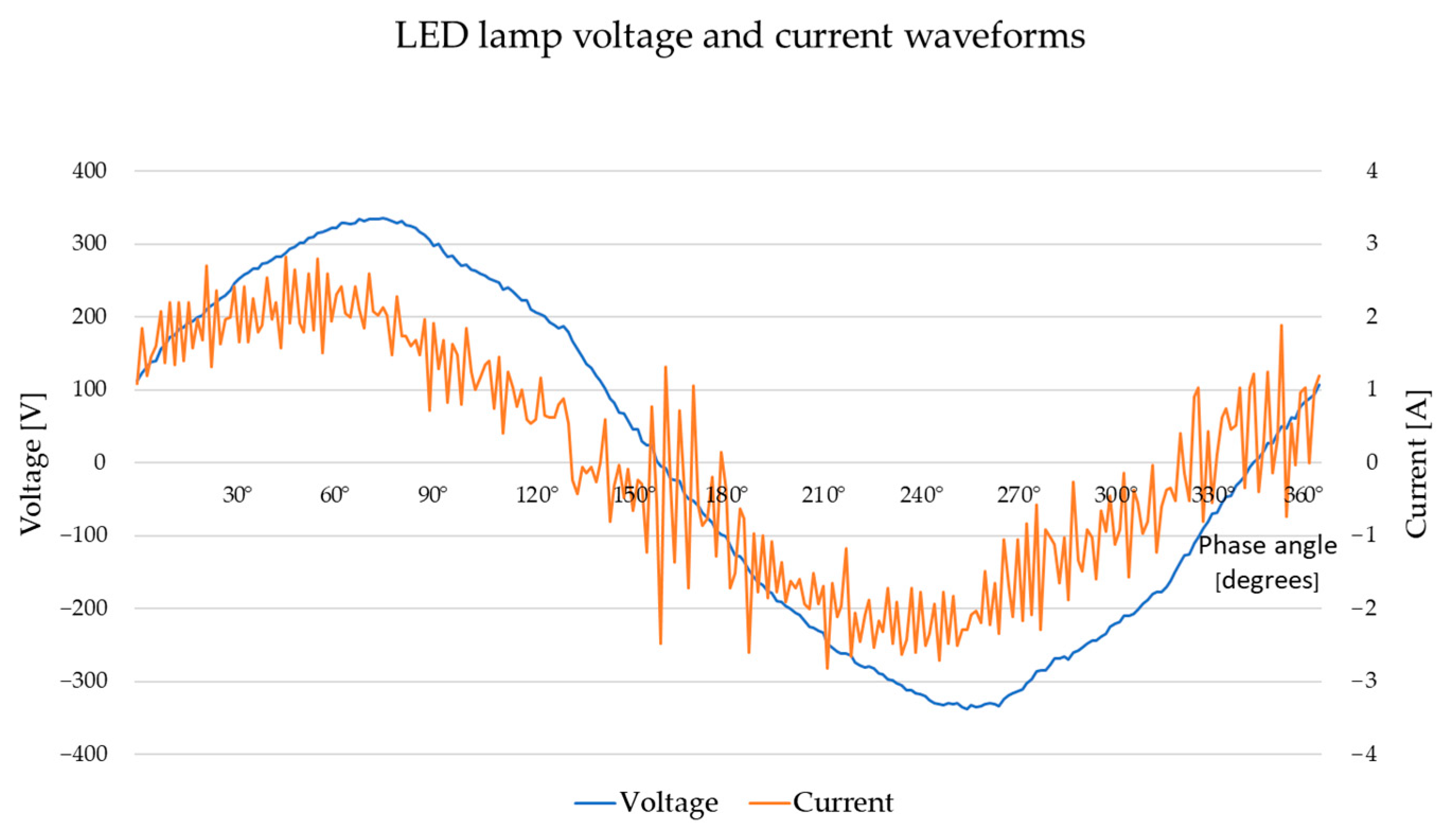








| Bus Voltage V at PCC (kV) | Individual Harmonic (%) | Total Harmonic Distortion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| V ≤ 1.0 | 5.0 | 8.0 |
| 1 < V ≤ 69 | 3.0 | 5.0 |
| 69 < V ≤ 161 | 1.5 | 2.5 |
| 161 < V | 1.0 | 1.5 1 |
| ISC/IL | Individual Harmonic Order (Odd Harmonics) 1,2 Maximum Harmonic Current Distortion in Percent of IL | Total Current Demand Distortion (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 ≤ h < 11 | 11 ≤ h < 17 | 17 ≤ h < 23 | 23 ≤ h < 35 | 35 ≤ h < 50 | ||
| <20 3 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 5.0 |
| 20–50 | 7.0 | 3.5 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 8.0 |
| 50–100 | 10.0 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 1.5 | 0.7 | 12.0 |
| 100–1000 | 12.0 | 5.5 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 15.0 |
| >1000 | 15.0 | 7.0 | 6.0 | 2.5 | 1.4 | 20.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovács, A.; Somogyiné Molnár, J.; Jármai, K. Electrical Transients in Industrial Facilities. Energies 2024, 17, 4215. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174215
Kovács A, Somogyiné Molnár J, Jármai K. Electrical Transients in Industrial Facilities. Energies. 2024; 17(17):4215. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174215
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovács, Attila, Judit Somogyiné Molnár, and Károly Jármai. 2024. "Electrical Transients in Industrial Facilities" Energies 17, no. 17: 4215. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174215
APA StyleKovács, A., Somogyiné Molnár, J., & Jármai, K. (2024). Electrical Transients in Industrial Facilities. Energies, 17(17), 4215. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174215







