Application of Silver Nanoparticles Supported over Mesoporous Carbon Produced from Sustainable Sources as Catalysts for Hydrogen Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Catalytic Tests
2.4. Catalyst Reusability
3. Results/Discussions
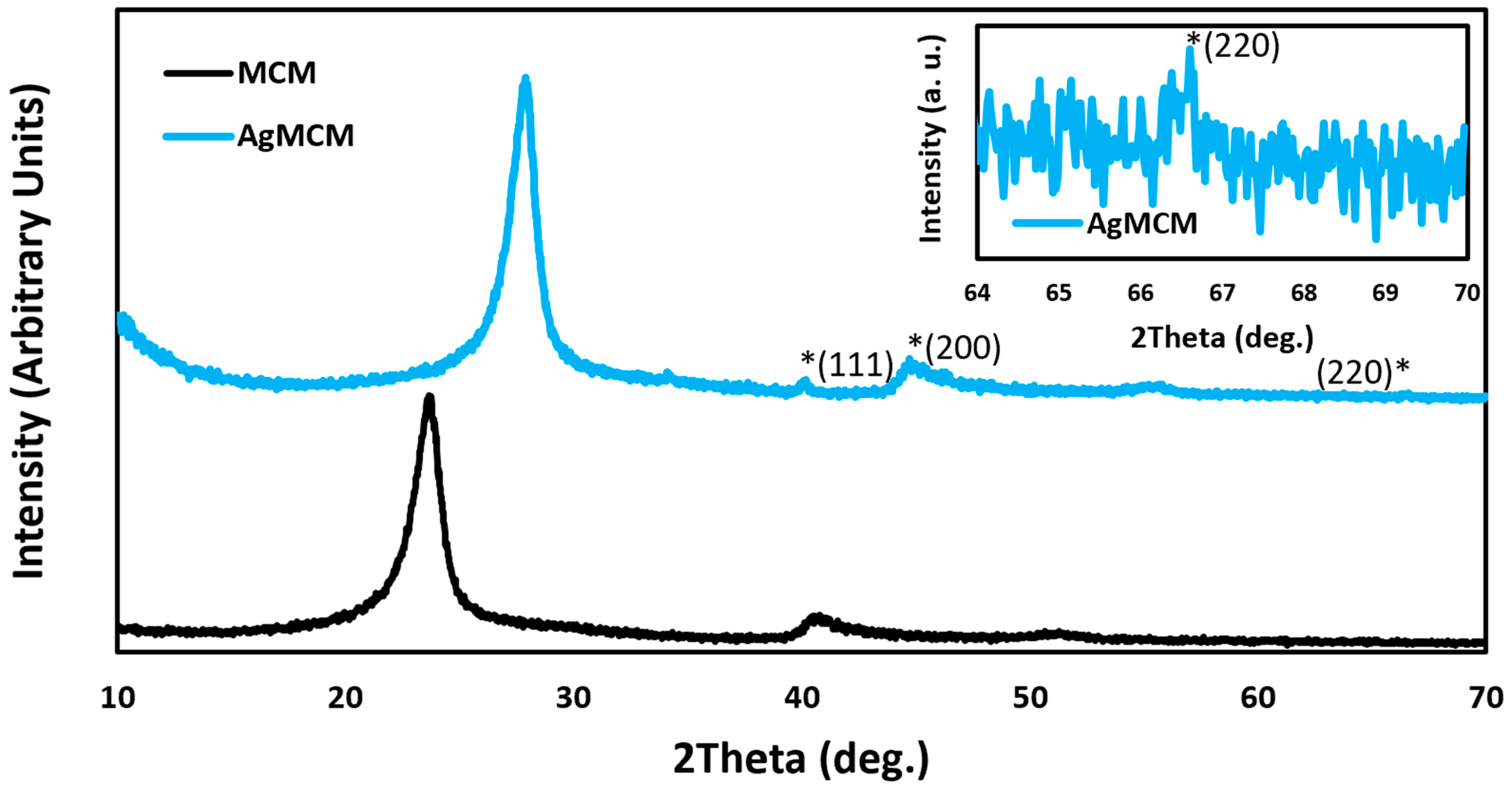
3.1. Catalyst Characterization
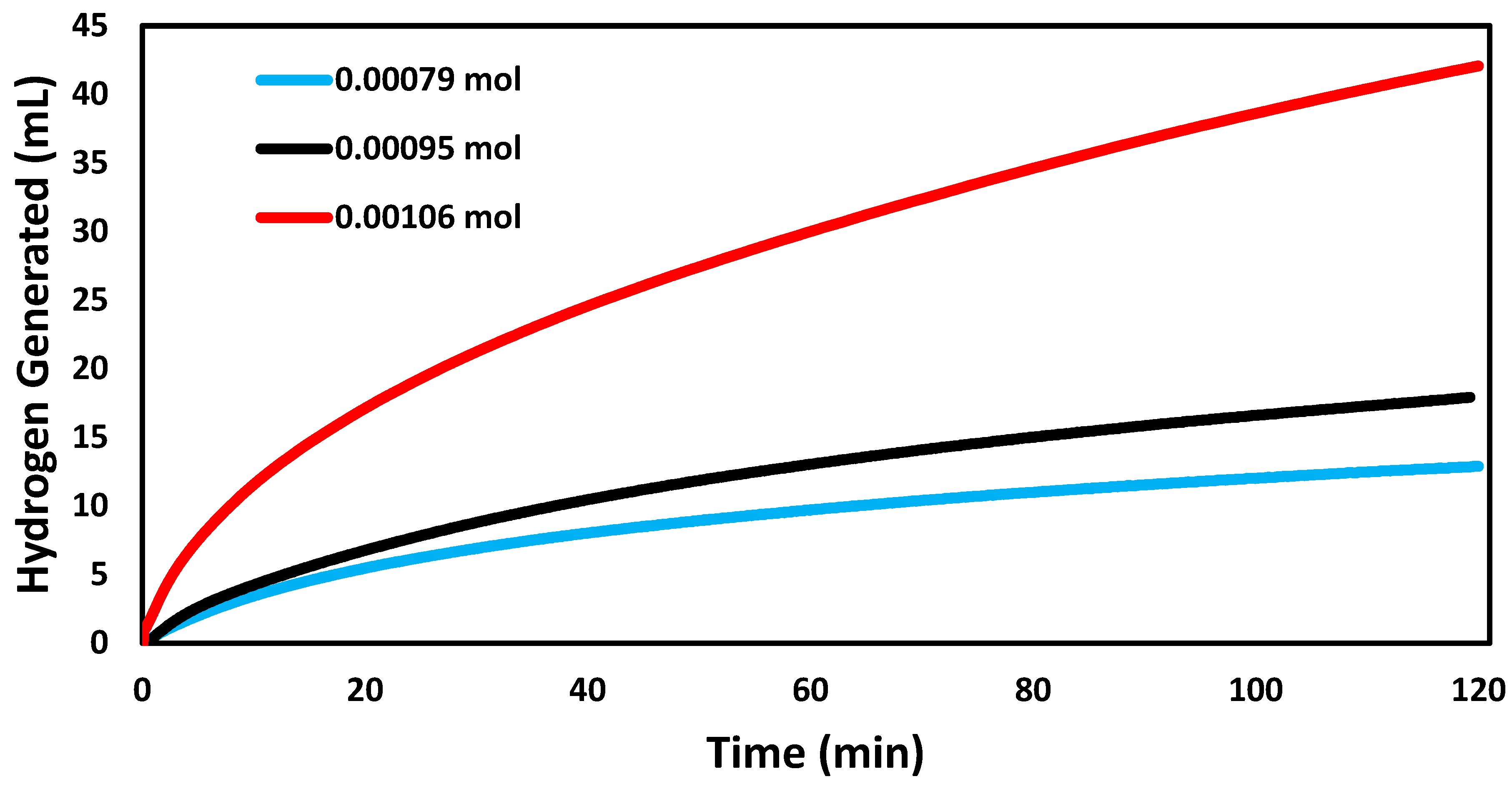
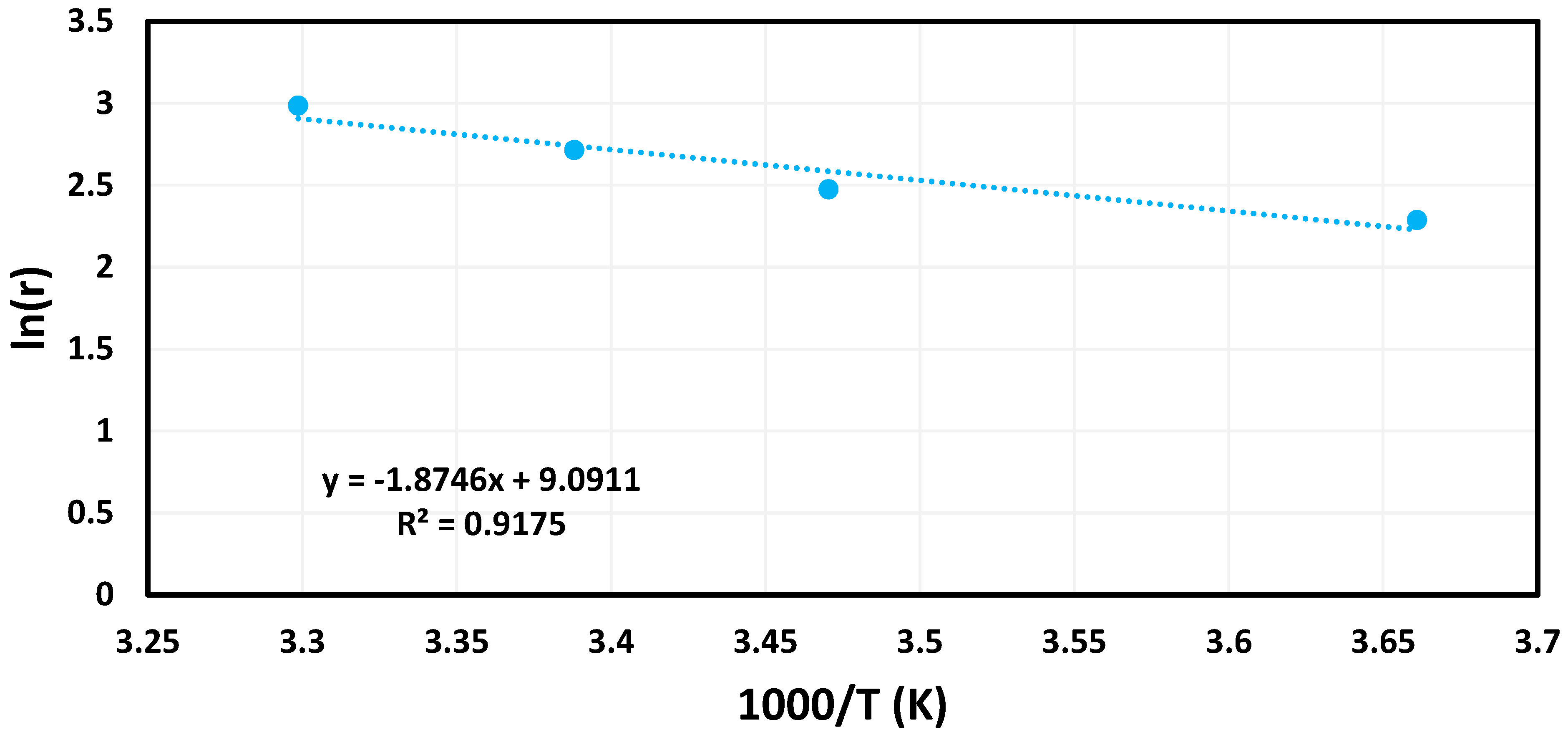
3.2. Catalytic Tests
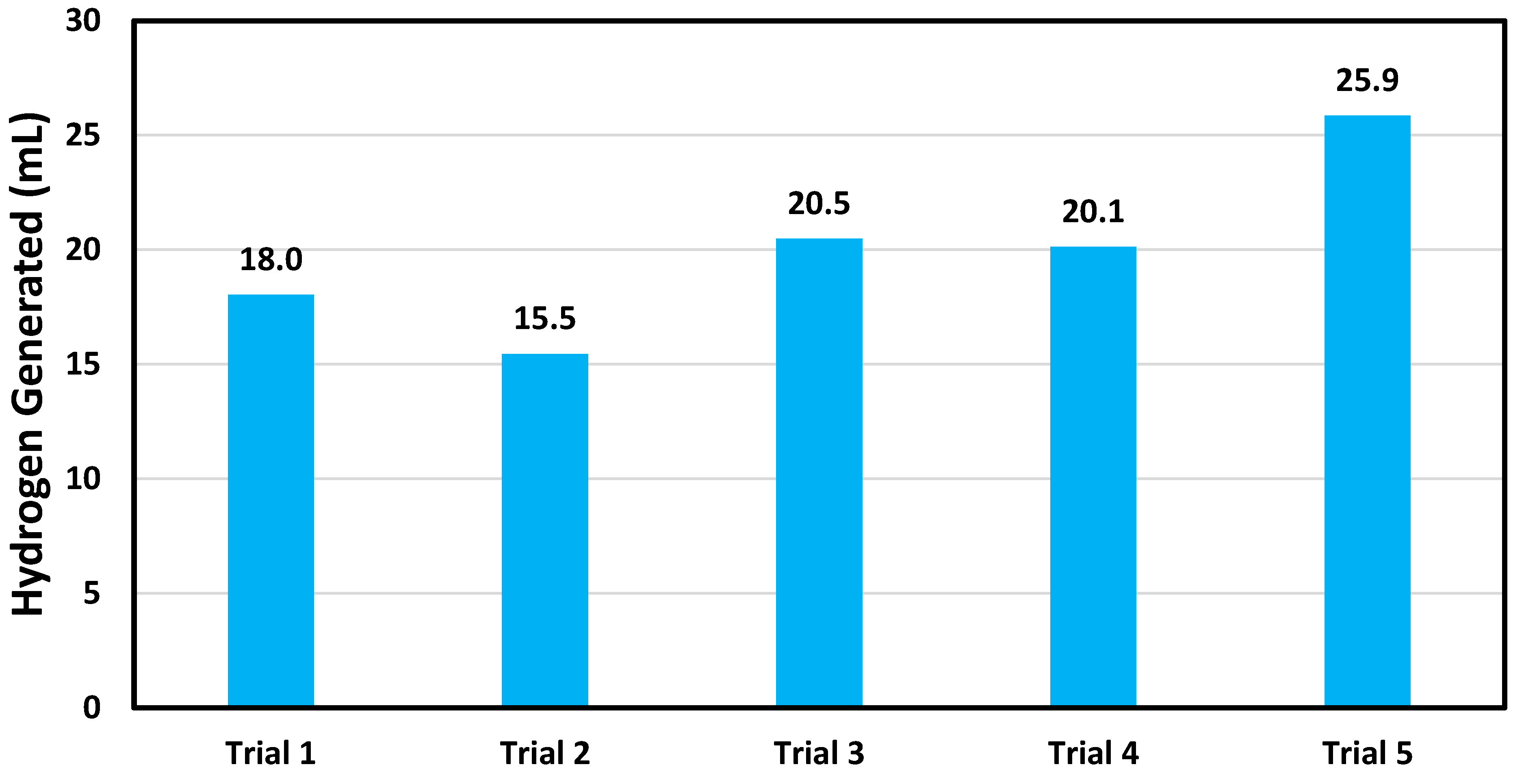
3.3. Catalytic Reusability Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Energy Council. World Energy Resources 2016 Report; Report No. 24; World Energy Council: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiee, S.; Topal, E. When will fossil fuel reserves be diminished? Energy Policy 2008, 37, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, M.R.; Marland, G.; Ciais, P.; Le Quéré, C.; Canadell, J.G.; Klepper, G.; Field, C.B. Global and regional drivers of accelerating CO2 emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10288–10293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veziroglu, T.N. 21st Century’s Energy: Hydrogen Energy System. Assess. Hydrog. Energy Sustain. Dev. NAPSC 2007, 4, 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yang, Z.; Mokaya, R. Simultaneous Control of Morphology and Porosity in Nanoporous Carbon: Graphitic Mesoporous Carbon Nanorods and Nanotubules with Tunable Pore size. Chem. Mater. 2005, 18, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Li, Z.; Dai, S. Mesoporous Carbon Materials: Synthesis and Modification. Angew. Chem. Int. 2008, 47, 3696–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, E.; Puskás, R.; Rémiás, R.; Mohl, M.; Kukovecz, Á.; Kónya, Z.; Kiriesi, I. A Novel Catalyst Type Containing Noble Metal Nanoparticles Supported on Mesoporous Carbon: Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic properties. Top Catal. 2009, 52, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Joo, S.H.; Pak, C. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous carbon for fuel cell applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 3078–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Mokaya, R. Generalized and Facile Synthesis Approach to N-Doped Highly Graphitic Mesoporous Carbon Materials. Chem Mater. 2005, 17, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Zeng, J.; Bao, X.; Yu, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Zhao, X.S. Preparation and Characterization of Highly Ordered Graphitic Mesoporous Carbon as a Pt Catalyst Support for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3960–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, I.; Bernardo, M.; Neves, P.D.; Castanheiro, J.E.; Vital, J.; Fonseca, I.M. Mesoporous Carbon as effective and sustainable catalyst for fine chemistry. Bol. Grupo Español Carbón 2016, 39, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Budarin, V.; Clark, J.H.; Hardy, J.J.E.; Luque, R.; Milkowski, K.; Tavener, S.J.; Wilson, A.J. Starbons: New Starch-Derived Mesoporous Carbonaceous Materials with Tunable Properties. Angew. Int. Ed. 2007, 45, 3782–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biehler, E.; Quach, Q.; Abdel-Fattah, T. Screening study of Different Carbon Based Materials for Hydrogen. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2023, 12, 081002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuttleworth, P.S.; Budarin, V.; White, R.J.; Gun’ko, V.M.; Luque, R.; Clark, J.H. Molecular-Level Understanding of the Carbonistation of Polysaccharides. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 9351–9357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milkowski, K.; Clark, J.H.; Doi, S. New materials based on renewable resources: Chemically modified highly porous starches and their composites with synthetic monomers. Green Chem. 2004, 6, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Ihm, S. Synthesis, Characterization, and Hydrodesulfurization Activity of New Mesoporous Carbon Support Transition Metal Sulfide Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Slanac, D.A.; Kumar, P.; Wiggins-Camacho, J.D.; Kim, J.; Ryoo, R.; Stevenson, K.J.; Johnston, K.P. Highly Stable Pt/Ordered Graphitic Mesoporous Carbon Electrocatalysts for Oxidation Reduction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 10796–10805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, J. Core/Shell Pt/C Nanoparticle Embedded in Mesoporous Carbon as a Methanol-Tolerant Cathode Catalyst in Direct Methanol fuel Cells. J. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholoud, M.M.; El-Nour, A.; Eftaiha, A.; Al-Warthan, A.; Ammar, R.A.A. Synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles. Arabian J. Chem. 2010, 3, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Dushatinski, T.; Huff, C.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Characterization of electrochemically deposited films from aqueous and ionic liquid cobalt precursors toward hydrogen evolution reactions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 385, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, K.K.R.; Reddy, B.V.S.; Ariga, K.; Vinu, A. Gold Nanoparticles Embedded in a Mesoporous Carbon Nitride Stabilizer for Highly Efficent Three-Component Coupling Reaction. Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 6097–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Liu, T.; Zhong, J.; Li, G. Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Electron Transfer Reactivity and the Catalytic Activity of Myoglobin. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 1686–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Shape-Dependent Catalytic Activity of Silver Nanoparticles for the Oxidation of Styrene. Chem. Asian J. 2006, 1, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; McCullen, S.B.; et al. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comotti, M.; Pina, C.D.; Matarrese, R.; Rossi, M. The Catalytic Activity of “Naked” Gold Particles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5812–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff, C.; Dushatinski, T.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Gold nanoparticle/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite as novel catalyst for hydrogen evolution reactions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 18985–18990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Sohn, K.; Bin Na, H.; Hyeon, T. Synthesis of Nanorattles Composed of Gold Nanoparticles Encapsulated in Mesoporous Carbon and Polymer Shells. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Su, R.; Qi, W.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; He, Z. Synthesis of well-dispersed Ag nanoparticles on eggshell membrane for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, N.; Janssens, T.V.W.; Clausen, B.S.; Xu, Y.; Mavrikakis, M.; Bligaard, T.; Nørskov, J.K. On the origin of the catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles for low-temperature CO oxidation. J. Catal. 2004, 223, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daté, M.; Okumura, M.; Tsubota, S.; Haruta, M. Vital Role of Moisture in the Catalytic Activity of Supported Gold Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2129–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Hwang, J.; Kim, J.; Jeong, Y.; Hwang, M.P.; Choi, J. Antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 4621–4629. [Google Scholar]
- Sudrik, S.G.; Chaki, N.K.; Chavan, V.B.; Chavan, S.P.; Chavan, S.P.; Sonawane, H.R.; Vijayamohanan, K. Silver Nanocluster Redox-Couple-Promoted Nonclassical Electron Transfer: An Efficient Electrochemical Wolff Rearrangement of α-Diazoketones. Chem.—Eur. J. 2006, 12, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsudome, T.; Mikami, Y.; Mori, H.; Arita, S.; Mizugaki, T.; Jitsukawa, K.; Kaneda, K. Supported Silver Nanoparticle Catalyst for Selective Hydration of Nitriles to Amides in Water. Chem. Commun. 2009, 2009, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsudome, T.; Mikami, Y.; Funai, H.; Mizugaki, T.; Jitsukawa, K.; Kaneda, K. Oxidant-Free Alcohol Dehydrogenation Using a Reusable Hydrotalcite-Supported Silver Nanoparticle Catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff, C.; Long, J.M.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Beta-cyclodextrin-assisted synthesis of silver nanoparticle network and its application in a hydrogen generation reaction. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, Z.S.; Kamat, P.V. What Factors Control the Size and Shape of Silver Nanoparticles in the Citrate Ion Reduction Method? J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C.; Dushatinski, T.; Barzanji, A.; Abdel-Fattah, N.; Barzanji, K.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Pretreatment of Gold Nanoparticle Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Composites for Catalytic Activity toward Hydrogen Generation Reaction. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2017, 6, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolini, E.; Cardellini, F. Formation of carbon supported PtRu alloys: An XRD analysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 315, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, H.I.; Brown, H.C.; Finholt, A.E.; Gilbreath, J.R.; Hoekstra, H.R.; Hyde, E.K. Sodium borohydride, its hydrolysis and its use as a reducing agent and in the generation of hydrogen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1953, 75, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, C.M.; Sen, B. Hydrogen Generation by Hydrolysis of Sodium Tetrahydroborate: Effects of Acids and Transition Metals and Their Salts. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1985, 1985, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C.; Long, J.M.; Aboulatta, A.; Heyman, A.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Silver Nanoparticle/Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Composite as Catalyst for Hydrogen Production. ECS J. Solid State Sc. 2017, 6, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C.; Long, J.M.; Heyman, A.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Palladium Nanoparticle Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Composite as Catalyst for Hydrogen Production by the Hydrolysis of Sodium Borohydride. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 4635–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, Q.; Biehler, E.; Elzamzami, A.; Huff, C.; Long, J.M.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Catalytic Activity of Beta-Cyclodextrin-Gold Nanoparticles Network in Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Catalysts 2021, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C.; Biehler, E.; Quach, Q.; Long, J.M.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Synthesis of Highly Dispersive Platinum Nanoparticles and their Application in a Hydrogen Generation Reaction. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 610, 125734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Shen, P.K.; Wei, Z. Accurately measuring the hydrogen generation rate for hydrolysis of sodium borohydride on multi-walled carbon nanotubes/Co-B catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 7110–7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.U.; Kim, R.K.; Cho, E.A.; Kim, H.-J.; Nam, S.-W.; Oh, I.-H.; Hong, S.-A.; Kim, S.H. A study on hydrogen generation from NaBH4 solution using the high-performance Co-B catalyst. J. Power Sources 2005, 144, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.; Brown, J.B.; Lyons, C.J. Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Sodium Borohydride. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1960, 52, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, J.; Roy, B.; Sharma, P. Efficient hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride hydrolysis using silica sulfuric acid catalyst. J. Power Sources 2015, 275, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Dai, H.-B.; Ma, L.-P.; Wang, P.; Cheng, H.-M. Hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride solution using a ruthenium supported graphite catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 3023–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Delgass, W.N.; Fisher, T.S.; Gore, J.P. Kinetics of Ru-catalyzed sodium borohydride hydrolysis. J. Power Sources 2007, 164, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Patton, B.; Zanchetta, C.; Fernandes, R.; Guella, G.; Kale, A.; Miotello, A. Pd-C power and thin film catalysts for hydrogen production by hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Alonso, R.; Sicurelli, A.; Callone, E.; Carturan, G.; Raj, R. A picoscale catalyst for hydrogen generation from NaBH4 for fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 165, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehler, E.; Quach, Q.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Synthesis of Platinum Nanoparticles Supported on Fused Nanosized Carbon Spheres Derived from Sustainable Source for Application in a Hydrogen Generation Reaction. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehler, E.; Quach, Q.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Silver-Nanoparticle-Decorated Fused Carbon Sphere Composite as a Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation. Energies 2023, 16, 5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, Q.; Biehler, E.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Synthesis of Palladium Nanoparticles Supported over Fused Graphene-like Material for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehler, E.; Quach, Q.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Gold Nanoparticles AuNP Decorated on Fused Graphene-like Materials for Application in a Hydrogen Generation. Materials 2023, 16, 4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quach, Q.; Biehler, E.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles Supported over Graphene-like Material Composite as a Catalyst for Hydrogen Evolution. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deraedt, C.; Salmon, L.; Gatard, S.; Ciganda, R.; Hernandez, E.; Ruiz, J.; Astruc, D. Sodium borohydride stabilizes very active gold nanoparticle catalysts. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14194–14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Fattah, T.M.; Biehler, E. Carbon Based Supports for Metal Nanoparticles for Hydrogen Generation Reactions Review. Adv. Carbon J. 2024, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Catalyst | Ea (kJ mol−1) | Temperature (K) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| MWCNT supported Co | 40.4 | 298–333 | [45] |
| Co-B | 64.9 | 283–303 | [46] |
| CoCl2 | 17.5 | 293–308 | [47] |
| Silica sulfuric acid | 17 | 298–343 | [48] |
| Ru/Graphite | 61.1 | 398–318 | [49] |
| Ru/C | 67 | 298–358 | [50] |
| Pd/C | 28 | 298–328 | [51] |
| Pt–Pd/CNTs | 19 | 302–332 | [52] |
| Au/MWCNTs | 21.1 | 273–303 | [26] |
| Ag/MWCNTs | 44.5 | 273–303 | [41] |
| Pd/MWCNTs | 62.7 | 273–303 | [42] |
| BCD-AuNP | 54.7 | 283–303 | [43] |
| PtNPs | 39.2 | 283–303 | [44] |
| PtFCS | 53.0 | 283–303 | [53] |
| AgNP-FCS | 37.0 | 273–303 | [54] |
| PdFGLM | 45.1 | 283–303 | [55] |
| AuFGLM | 45.5 | 283–303 | [56] |
| CuGLM | 46.8 | 283–303 | [57] |
| Ag-MCM | 15.6 | 273–303 | This Work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biehler, E.; Quach, Q.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Application of Silver Nanoparticles Supported over Mesoporous Carbon Produced from Sustainable Sources as Catalysts for Hydrogen Production. Energies 2024, 17, 3327. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133327
Biehler E, Quach Q, Abdel-Fattah TM. Application of Silver Nanoparticles Supported over Mesoporous Carbon Produced from Sustainable Sources as Catalysts for Hydrogen Production. Energies. 2024; 17(13):3327. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133327
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiehler, Erik, Qui Quach, and Tarek M. Abdel-Fattah. 2024. "Application of Silver Nanoparticles Supported over Mesoporous Carbon Produced from Sustainable Sources as Catalysts for Hydrogen Production" Energies 17, no. 13: 3327. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133327
APA StyleBiehler, E., Quach, Q., & Abdel-Fattah, T. M. (2024). Application of Silver Nanoparticles Supported over Mesoporous Carbon Produced from Sustainable Sources as Catalysts for Hydrogen Production. Energies, 17(13), 3327. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133327







