Abstract
In this study, three-dimensional simulations were conducted on a new passive micromixer to assess the thermal and hydrodynamic behaviors of Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids subjected to low generalized Reynolds numbers (0.1 to 50) and shear-thinning properties. To acquire a more profound comprehension of the qualitative and quantitative fluctuations in fluid fraction using the CFD Fluent Code, the mass mixing index, rheological behavior, performance index, mixing energy cost, mass fraction distributions, temperature contours, and pressure drop were compared to illustrate the importance of the mixer geometry in the context of two miscible fluids with varying inlet temperatures. The selected geometry is characterized by a robust chaotic flow that substantially enhances thermal and hydrodynamic performance across all Reynolds numbers. A mass mixing exceeding 72.5% is obtained when Re = 5, reaching 93.5% when Re = 50. Furthermore, the evolution of thermal mixing for all behavior indexes reaches a step of 98% with minimal pressure losses. This work enabled the demonstration of a chaotic geometry in a highly efficient mixing system, leading to enhanced thermal performance for both Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids. The results of the hydrodynamic and thermal characterization of the mixing of shear-thinning fluids within the micromixers under investigation are conclusive.
1. Introduction
A fundamental and crucial aspect of microfluidic chip technology for research in microfluidic systems is mixing. A micromixer is an indispensable part of the microfluidic chip analysis system [1]. Active mixing and passive mixing are the two broad categories into which mixing may often be divided. Passive micromixers, also known as static micromixers, use chaotic advection and secondary flows to boost mixing efficiency at low Reynolds numbers. Passive micromixers, which rely on geometric modifications to enhance fluid mixing without external energy input, have been a focus of microfluidic research for decades. Early studies laid the groundwork by exploring the fundamental mechanisms that drive passive mixing, such as chaotic advection and secondary flows. Foundational studies often utilized simple geometries such as T-shaped and Y-shaped micromixers. These designs create mixing at the intersection of channels, where fluid streams interact and shear forces induce initial mixing [2]. The intersection of fluid streams generates shear forces that help in breaking up the fluid layers, promoting mixing through diffusion [3,4,5]. The introduction of serpentine micromixers with curved channels aimed to enhance mixing by inducing secondary flows known as Dean vortices. These vortices arise due to centrifugal forces acting on the fluid as it navigates through the curved paths [6]. The development of secondary flows enhances fluid particle trajectories, thereby improving mixing efficiency by increasing fluid interfacial contact [7]. One of the significant advancements was the development of staggered herringbone mixers. These designs incorporate periodic herringbone-shaped grooves on the channel floor, which disrupt the laminar flow and generate chaotic advection [2]. The grooves create transverse flows that repeatedly stretch and fold the fluid streams, significantly enhancing mixing by continuously disrupting the flow [8,9]. The basic construction and straightforward fabrication of the passive micromixers give them a distinctive significance; these micromixers can be further categorized as two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) [10,11]. Passive micromixers, in contrast to active micromixers, are energy-efficient devices that just require pressure to maintain constant fluid flows. They also do not require any moving parts. The fluid flows become chaotic by inducing obstacles and curvature in the channels [2,12,13,14,15].
Recent studies have focused on optimizing micromixer designs to achieve higher mixing efficiency and explore new applications in microfluidics. These innovations often involve more complex geometries and multi-layer designs to maximize chaotic advection and fluid interaction. For instance, in order to mix two fluids using Dean vortices, Chen and Shie [16] proposed a planar micromixer with many staggered curved segments; they looked and inspected how mixing efficiency changed with different Reynolds numbers and channel layouts. Kim et al. [17] demonstrated that inducing chaotic advection in laminar flow by altering the geometry and periodically arranging the inclined grooves and barriers at the top and bottom walls of a microchannel can significantly improve mixing efficiency.
Naas et al. [18] reported a novel passive micromixer which can be used to improve homogenization in various nano-non-Newtonian mechanisms with a minimal amount of energy, as it is characterized by a high thermal mixing rate of 0.99% and a mixing factor with a mass fraction of more than 0.93% with extremely low pressure losses. Based on the idea of unbalanced division and cross collision of the fluid flow, Wu et al. [19] developed a new passive microphone mixer. The micromixer exhibits attractive mixing for different width ratios of the two sub channels.
Mengeaud et al. [20] exhibited a Y-shaped zigzag microchannel. In a series of tests, the influence of the periodic step values on mass mixing was explored. Increasing the geometrical ratio s/w from 1 to 8 increased the mixing efficiency from 65% to 83.8% for Re = 0.26. The number of angles rose as s/w decreased, leading to the rise in effective width and a reduction in effective dimension. The more successful zigzag design with s = 800 m produced an overall mixing of 83.8% for the low Reynolds number flows.
By incorporating radial baffles inside a curving microchannel at only moderate diameters, Tsai et al. [21] developed a high-efficiency planar micromixer. With a short enough radius, an extra vortex occurs downstream of the second baffle in the C-shaped micromixer. Although the suggested micromixer works best at high Reynolds numbers, adding radial baffles in the curved channel wall improves mass mixing even with low Reynolds numbers. The same author also evaluated the mixing properties of water that was deionized and carboxyl methyl cellulose solutions using 3 serpentine-type micromixers made up of repeating C-shaped units [22]. A micromixer composed of semicircular repeating units in the shape of C with a smaller median line radius has a higher mixing efficiency than a micromixer composed of repetitive units of segments with a larger median line curvature radius. The vortex created by the curvature improves fluid mixing significantly.
Raza et al. [23] suggested a new 3D structure (SAR) passive micromixer with imbalanced collisions. In a wide range of Reynolds numbers spanning from 0.1 to 120, the mixing efficiency of three types of shapes was quantified. The micromixer arrangement with forward and backward facing steps in both sub channels demonstrated a higher mixing efficiency, with 0.86 for Re 20 and 0.95 for Re 50.
Alam et al. [24] developed another typical micromixer having eight circular chambers and two constricted channels connecting to the next chambers. Their results from simulations indicated that when diffusion dominated the fluidic mixture for low Reynolds number (Re = 0.1), this micromixer could attain an efficiency of 88%.
The micromixer with two layers of cross channels is among the best innovative passive micromixers for mixing miscible fluids. Two cross-channel layers make up this micromixer, which performs well at mixing in a variety of Reynolds numbers. Folding, recombination, doubling, and enlargement all contribute to the chaotic advection. Xia et al. [25] created the first micromixer of this type achieving an elevated mixing performance of 0.96 even at a low number of Reynolds with 0.2.
Hossain et al. [26] improved on the referred model of Xia et al., whose mixture can achieve an index of 0.99 via Reynolds numbers below 10. The advantage of this micromixer has been proven experimentally and numerically. Wang et al. [27] suggested a new micromixer with two crossed channel layers. A PMMA bond included into the crossings allows for the formation of chaotic advection and Dean vortices, which improves mass mixing at low Reynolds numbers. This micromixer provides high-quality mixing at Re ≤100, according to numerical and experimental data.
Afzal et al. [28] investigated the hydrodynamic behavior and mass mixing of Newtonian and non-Newtonian flows in the T-shaped microchannels of the right channel and the serpentine channel. The flow simulation took into account the characteristics of water and blood. It was discovered that the coil channel provides enhanced mixing performance across all flows, while the water pressure loss was lower than the blood pressure drop at similar flow rates.
Islami et al. [29] conducted a computational analysis on the mixing of shear-thinning non-Newtonian fluids in six curved micromixers at lower Reynolds numbers and discovered that the micromixer shape has no significant effect on the mixing index for fluids with behavior indexes near to 1. This effect becomes significant as the behavior index is reduced. Furthermore, their findings revealed that when the Reynolds number and curvature radius increase, the amount of secondary flows increases. The mixing of Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids was also studied by them [30] in a curved micromixer with built-in grooves on the bottom half of the conduit. They demonstrated that while the dimensionless pressure drop was not significantly affected by the grooves, the grooves caused chaotic advection and improved mixing efficiency. Additionally, for all behavioral index values, grooves with a 30° angle had a greater mixing index.
The performance of mixing six 3D divided and recombined structure micromixers (SAR) has been numerically examined by He et al. [31], where the working fluids are power law fluids and water. According to their findings, the ideal micromixer, known as DBEM-3, has an outstanding mixing efficiency of over 95% for three types of fluids with behavioral indexes ranging from 0.69 to 1.
Mashaei et al. [32] conducted a numerical study to investigate the thermal and hydrodynamic behavior of a combination of non-Newtonian fluids in a T-junction 2D geometry; their findings revealed an enhancement in thermal mixing as a result of the rise in Reynolds number and fluid behavior index. Nonetheless, the increase in the characteristic index led to more heat mixing throughout the channel. The angle of the T-junction had no influence on the thermal mixing within the channel; however, as the angle of impact increased, this mixture improved in this location.
Maurya et al. [33] used a 2D T-junction micromixer to conduct a numerical examination of laminar and stationary power low fluid. The influence of behavior index (0.6–1), varying Reynolds number from 10 to 50, and differential temperature (∆T = 10 K) on shear-thinning fluid mixing behavior was investigated. In contrast, a faster reduction in the mixing index was seen in the impact zone. A significant mixing index was attained across a short distance by using elevated behavior indexes (n = 1); however, for low Reynolds numbers, the mixing index is relatively little influenced by the temperature difference and Nusselt number.
According to Naas et al. [34], the heat mass mixing of the shear-thinning fluids in C-shape and the straight channel geometries was investigated numerically for a wide range of Reynolds numbers between 200 and 50 as well as behavior index values between 0.5 and 1. They investigated thermal mixing quality in two geometries with two input portions, horizontal and vertical, into which the two fluids were pumped at 300 K and 330 K. Their findings suggest that the chaotic C-shape geometry outperforms the straight channel in terms of temperature homogenization. Furthermore, the mixing time in the C-shape geometry is less than one second, but it takes many minutes in the straight channel.
Kouadri et al. [35] recently examined the mixing degree across various cross-sectional areas using a Two-Layer Crossing Channels Micromixer (TLCCM) with a very short length of 3.75 mm. This design demonstrated superior mixing performance and operated in the laminar regime for both Newtonian and pseudoplastic fluids. Li et al. [36] have shown that under laminar flow regimes, the use of rectangular stirred tanks significantly improves chaotic mixing. They employed both computational and experimental techniques in their research, highlighting the potential of rectangular stirred tanks as a user-friendly and cost-effective solution for applications involving laminar mixing. In summary, most studies have focused on the mixing of Newtonian fluids in various microfluidic devices, with few studies addressing the mixing of non-Newtonian fluids. Many of these experiments and simulations utilized active micromixers, which are more expensive and complex at the microscale for viscous fluids and require external energy for the mixing process. In contrast, passive micromixers, with their revolutionary multi-layer designs, offer outstanding thermal performance and substantial mixing improvement, making them the ideal option.
To sum up, the fundamental aspect of microfluidic chip technology is efficient mixing, essential for various research applications. While passive micromixers, which rely on geometric modifications to enhance mixing without external energy, are significant due to their simple construction and energy efficiency, most existing research has focused on mixing Newtonian fluids using active micromixers. These active micromixers, although effective, are more complex and costly due to their need for external energy.
This study proposes a novel design of multi-layer micromixers with outstanding thermal performances and substantial mixing improvement. The mixing properties of Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids were studied. The homogeneity of fluid indexes and mixing energy cost will be examined for the purpose to achieve significant energy efficiency. The numerical findings reveal that the suggested micromixer performs well throughout a broad range of Reynolds values, from 0.1 to 50. This innovation contrasts with prior research by focusing on the energy-efficient passive mixing of non-Newtonian fluids, highlighting the potential for substantial energy savings and simpler design in microfluidic systems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Micromixer Design
The suggested micromixer, a Two-Layer Crossing Modified geometry (TLCM) micromixer, is presented in Figure 1a,b. The TLCM micromixer consists of two main twisted channels, one positioned above the other. These channels are twisted in a specific manner to create a complex flow path that enhances fluid mixing. The twisting of channels induces secondary flows and vortices, which disrupt the laminar flow and promote chaotic mixing. Between the upper and lower twisted channels, there are periodic chambers strategically placed to further enhance mixing. These chambers serve as intermediate mixing zones where the fluid streams from the upper and lower channels interact. Each periodic chamber contains two grooves on either side, designed to induce additional secondary flows within the chambers. The presence of grooves creates turbulence, which enhances the mixing process by continually disrupting the fluid layers. The last chamber features a larger groove compared to the other chambers, specifically designed to further disrupt the fluid flow as it exits the micromixer. This larger groove ensures thorough mixing before the fluid leaves the device. The functional mechanisms of the TLCM micromixer include the induction of secondary flows and chaotic advection. The grooves and the twisted nature of the channels generate secondary flows within the micromixer, creating complex fluid trajectories essential for chaotic advection. By promoting chaotic advection, the micromixer ensures that fluid particles follow irregular paths, significantly enhancing the mixing efficiency, especially at low Reynolds numbers where traditional mixing mechanisms are less efficient. The unique configuration of twisted channels and periodic chambers maximizes the interaction between the fluid streams. As the fluids pass through the micromixer, they are repeatedly split, stretched, and recombined, leading to a more homogeneous mixture. The design is optimized to handle both Newtonian (constant viscosity) and non-Newtonian (variable viscosity) fluids, ensuring effective mixing regardless of the fluid’s rheological properties. The combination of twisted channels, periodic chambers, and strategically placed grooves results in a micromixer that offers superior mixing performance. The design ensures that the fluids are thoroughly mixed by the time they exit the micromixer. The TLCM micromixer is effective across a broad range of Reynolds numbers (0.1 to 50), making it versatile for various microfluidic applications.
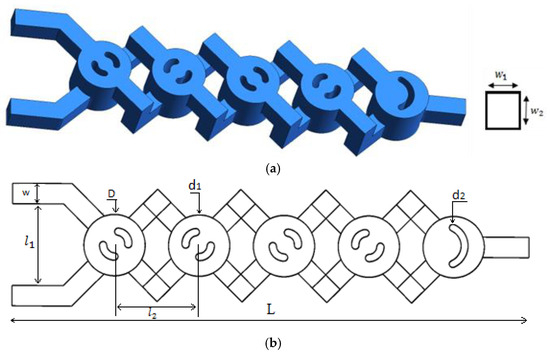
Figure 1.
(a) 3D-view design of the proposed micromixers, (b) geometric parameters.
The number of mixing chambers was 4 with D = 0.6 mm, l1 is fixed as 0.8 mm, and l2 is 0.82 mm; d1 and d2 are the groove diameters equaling 0.21 and 0.42 mm, respectively. The sizes of the inlet channels are w1 = 0.2 and w2 = 0.25 mm. L = 5.6 mm is the axial length of the geometry of the channel shown in Figure 1a,b.
2.2. Numerical Simulations
The CFD simulations were conducted using ANSYS Fluent version 16.0. The specific settings and parameters within ANSYS Fluent were tailored to accurately model the fluid dynamics in our micromixer design. An unstructured mesh with uniform tetrahedral cells was employed for the CFD simulations. This type of grid is particularly suitable for capturing the complex geometries and flow patterns in the micromixer. The unstructured mesh allows for greater flexibility in meshing irregular domains and ensures that the numerical solutions are accurate and stable. The mesh density was optimized through a mesh independence study to balance computational efficiency and solution accuracy.
2.2.1. Properties of Fluids
Water and carboxy methyl cellulose (CMC) solution were utilized in this work to simulate non-Newtonian and Newtonian flows. Shear-thinning behavior appears in the fluid simulating. Table 1 summarizes the rheological parameters of the CMC solutions utilized in this study [37,38]:

Table 1.
Flow parameters of fluids.
2.2.2. Governing Equations
The governing equations for three-dimensional, incompressible, steady, and laminar flows are the equations for continuity, momentum, and the convection diffusion equation [39]:
The shear stress tensor is given by:
where is the shear rate tensor.
For Newtonian fluids, the viscosity is constant, and for non-Newtonian fluids, the apparent viscosity is determined as [40]:
To define the viscous impact of a non-Newtonian fluid in a microchannel, the generalized Reynolds number (Reg) of the shear-thinning fluid is expressed as [41,42]:
where k is the consistency index, n is the power law index, and is a dimensionless geometrical parameter. This geometrical parameter is necessary to define the generalized Reynolds number. For circular ducts, Metzner and Reed concluded that ξ = 8 [41], whereas for rectangular ducts of aspect ratio 0.5, Delplace and Leuliet [42] proposed = 7.774. In this study, this latter value was adopted to account for the rectangular cross-section of the micromixer channels, ensuring the Reynolds number calculation reflects the actual flow dynamics.
The hydraulic diameter has been determined by:
where A is the cross-sectional area of the flow and P is the wetted perimeter of the cross-section.
For rectangular ducts:
The sizes of the inlet channels are and :
The mixing index is computed to compare the mixing effectiveness of micromixers with different flow conditions and geometrical characteristics by [43]:
where the following expression denotes the standard deviation of the mole fraction in the transverse section:
The standard deviation can be written as:
where n represents the overall sample count, indicates the mole fraction at a particular location on the section under consideration, and corresponds to the average value of .
2.3. Characterization of the Thermal Mixing
The thermal mixing index (TMI) of the two fluids (cold and hot) is an acceptable measure for quantifying thermal mixing, and it can be characterized as follows [44]:
where N is the cross-section’s number of points, denotes the temperature at node I, and is the cross-section’s mean temperature; moreover denotes the inlet section’s standard deviation. The values range from 0 (no mixing) to 1 (complete mixing).
The performance index (PI) is obtained by dividing the mixing index by the pressure drop [45]:
The mixing energy cost (MEC), which is derived by combining pressure loss and mixing degree, has been employed to measure the efficiency of the micromixer, as shown below [46]:
The matching flow rate (m3/s) is denoted by Q. It is measured in Watts or W.
2.4. Boundary Conditions and Mesh-Independent Test
The governing equations were numerically solved with no-slip boundary conditions along the walls; all walls are adiabatic. The adiabatic wall condition assumes no heat transfer through the walls of the micromixer, which is reasonable given the negligible heat loss to the ambient environment in microfluidic systems. This assumption simplifies the thermal analysis and is validated by previous studies indicating minimal thermal exchange in similar setups. The accuracy of this condition is supported by comparing our results with experimental data, showing consistent thermal behavior. At the channel exit, there is no static pressure, and the velocity profile and gradient pressure are established. Furthermore, the mass fractions were set to be 1 at the first input and 0 at the other, and the temperatures of two fluids (hot and cold) were set to be 330 K and 290 K, respectively.
To verify that the result was mesh independent, the number of meshes was gradually raised until there were no noticeable differences in the numerical result. To identify the ideal number of meshes for the current geometry, several meshes were performed for the mixing index. Table 2 displays the outcomes of this test. As can be noticed, a mesh size of around 652,463 was selected to provide a good combination of computational cost and numerical precision.

Table 2.
Mesh-independent test.
Figure 2 presents the results of the mesh sensitivity test, showing the variation of the mixing index with different mesh densities. The study reveals that beyond a certain mesh density, the changes in the mixing index become negligible, indicating mesh independence. This validation step confirms that the chosen mesh density provides a reliable representation of the flow characteristics in the micromixer.
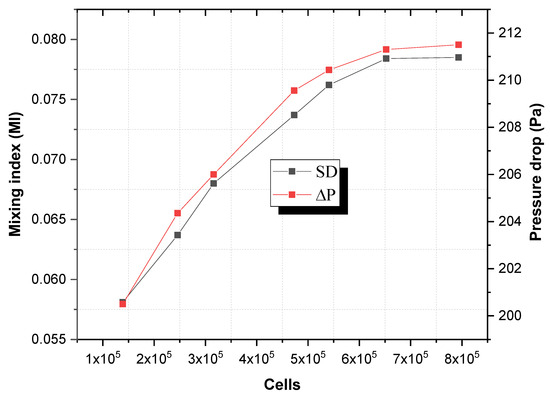
Figure 2.
Mesh sensitivity test: evolutions of standard deviation (SD) and the pressure drop.
3. Results and Discussion
The thermal and hydrodynamic behaviors of mixing Newtonian and non-Newtonian flows are studied in depth inside an innovative micromixer that is contrasted to prospective micromixers recently employed in the literature. For numerous low generalized Reynolds numbers ranging from 0.1 to 50, temperature, thermal mixing, pressure drop, and fluid mass mixing processes are explored.
3.1. CFD Validation Case
To validate the results obtained using the CFD code, a quantitative comparison was performed under the same conditions, using the mass standard deviation developments along the TLCM micromixer as reported by Naas et al. [18]. In their study, Naas et al. explored the mixing performance of a micromixer design that shares fundamental principles with the current study, specifically focusing on inducing chaotic advection through geometric modifications. While the two geometric shapes differ in the number and placement of grooves, both designs aim to enhance mixing efficiency by promoting chaotic flows and secondary vortices within the micromixer.
The model used in this study and the one used by Naas et al. belong to the same category of passive micromixers that utilize similar mechanisms to disrupt fluid streams and enhance mixing. By comparing the mass standard deviation, which is a critical parameter in assessing mixing performance, the reliability and consistency of the simulation results with established findings in the literature are ensured. The quantitative comparison shows a strong correlation between the simulation results and those reported by Naas et al., confirming the accuracy and validity of the CFD model.
Furthermore, the comparability of the models is enhanced by the similar operating conditions, including Reynolds numbers and fluid properties. This alignment underscores the robustness of the approach and validates the effectiveness of the TLCM micromixer design. The successful validation against Naas et al.’s study provides confidence that the findings are accurate and relevant to the broader field of microfluidic mixing. This validation step is crucial as it ensures that the innovative design can be reliably compared to and benchmarked against existing micromixer technologies, thereby reinforcing the significance of the contributions to enhancing passive micromixing efficiency. Thus, the numerical solution approach for mass mixing capabilities has been provided and completely evaluated by a quantitative comparison of the current results with the outcomes of Naas et al. [18] for a Reynolds number equal to 0.2, as seen in Figure 3.
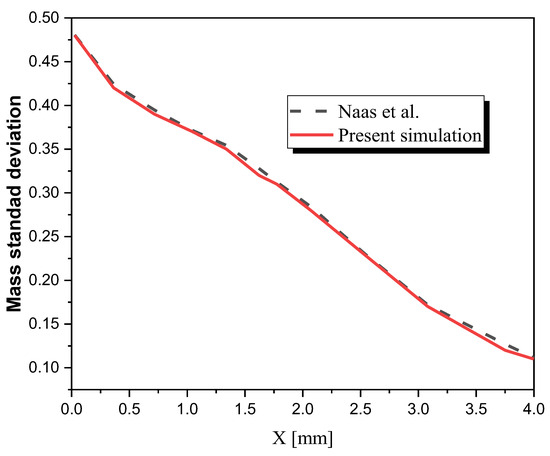
Figure 3.
Evolution of standard deviations along the micromixer [34].
The current data and the literature values of the mass standard deviation show great agreement. It clearly illustrates the strong correlation between the simulation findings with the CFD code and the findings of Naas et al., confirming their accuracy.
3.2. Analysis of the Newtonian Fluid
Micromixer Mixing Performance
Figure 4 shows the evolution of the mixing index along the micromixer, more precisely in transverse planes, for different values of Reynolds number. It can be observed that MI steadily increases and approaches the output level in all situations. It is worth noting that the highest value of Re corresponds to the highest value of the mixing index. Thus, the proportional relationship can be seen between the evolution of the mixing index and Reynolds, for Re = 0.1, for which the evolution of the mass mixing process is superior than for Re = 1 where molecular diffusion dominated.
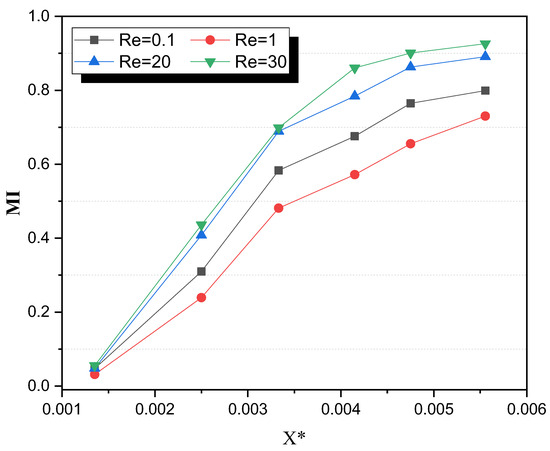
Figure 4.
Evolution of the mixing index along the micromixer with different values of Reynolds number for the Newtonian fluid.
The flow regime significantly influences the mixing index through different mechanisms that operate at various Reynolds numbers. At low Reynolds numbers, the flow is predominantly laminar, and mixing occurs primarily through molecular diffusion. As the Reynolds number increases, the flow transitions to an advection-dominated regime where inertial effects become more pronounced, leading to enhanced mixing through chaotic advection and the formation of vortices. At very low Reynolds numbers (Re < 1), the mixing process is slow and inefficient due to the dominance of viscous forces and the lack of turbulence. In this regime, molecular diffusion is the primary mechanism driving mixing, and the mixing index remains relatively low. The flow remains orderly, and fluid layers do not interact significantly, resulting in poor homogenization.
As the Reynolds number increases to intermediate values (Re = 1 to 10), the influence of inertial forces begins to compete with viscous forces, and the flow starts to exhibit more complex behavior. In this transitional regime, the onset of secondary flows, such as Dean vortices, enhances mixing efficiency. These secondary flows create cross-sectional mixing by continually disrupting the fluid layers, leading to an increase in the mixing index. However, the mixing process is still not fully optimized due to the limited chaotic advection.
At higher Reynolds numbers (Re > 10), the flow regime is characterized by pronounced chaotic advection. In this regime, the inertial forces dominate, and the flow becomes highly dynamic and turbulent. The twisting of channels and the presence of grooves in the micromixer induce strong secondary flows and vortices, which significantly enhance mixing. These chaotic flow patterns ensure that fluid particles follow irregular and intersecting paths, leading to rapid homogenization of the fluid streams. Consequently, the mixing index reaches its highest values in this regime, as observed in the study.
Specifically, for the TLCM micromixer, the combination of twisted channels and periodic chambers with grooves amplifies the chaotic advection, further boosting the mixing efficiency. The grooves and twists generate intense secondary flows that continuously disrupt and rearrange the fluid layers, promoting extensive fluid interaction and mixing. This results in a substantial increase in the mixing index as the Reynolds number increases. The presence of larger grooves in the final chamber further enhances this effect by creating additional disturbances that maximize fluid mixing before exiting the micromixer.
The observed relationship between the Reynolds number and the mixing index is consistent with the theoretical understanding of fluid dynamics in microchannels. The transition from a diffusion-dominated regime at low Reynolds numbers to an advection-dominated regime at higher Reynolds numbers explains the significant improvement in the mixing index. The CFD simulations accurately capture these phenomena, demonstrating that the TLCM micromixer is highly effective in leveraging chaotic advection to achieve superior mixing performance across a broad range of Reynolds numbers.
In brief, the highest value of the mixing index corresponds to the highest value of Reynolds number due to the shift from molecular diffusion to chaotic advection and the formation of vortices, which are more effective at higher Reynolds numbers. The design of the TLCM micromixer, with its twisted channels and periodic chambers, is optimized to take advantage of these flow dynamics, resulting in enhanced mixing efficiency for both Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids.
Figure 5 shows the mass fraction distribution of the Newtonian fluid in a C-micromixer for five values of Re from 0.1 to 50 where the mixing arises after the fluid has traveled a short distance. It was observed that mass fraction profiles were developed greatly after the area of the first element and this effect can be seen up to 30% at the second element of the mixer.
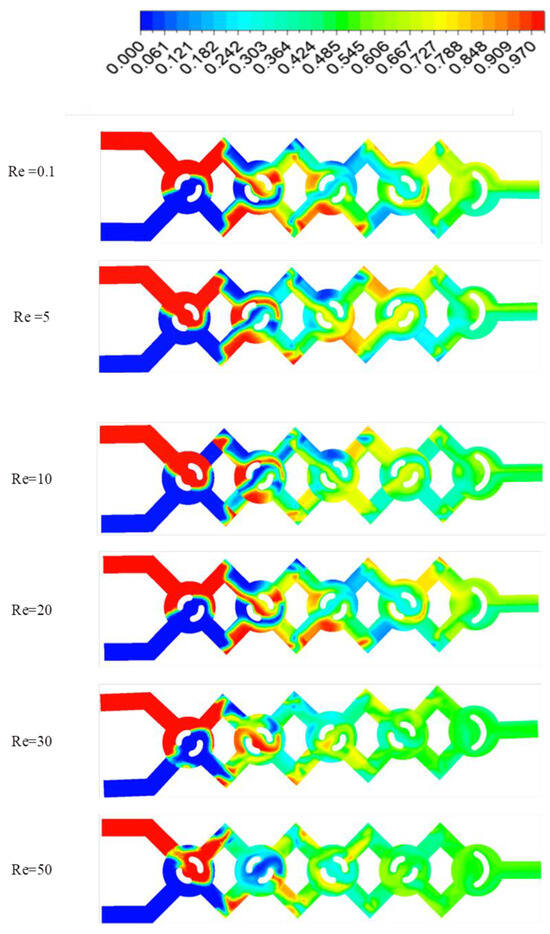
Figure 5.
Mass fraction distributions of Newtonian fluid in the micromixer.
The mechanism of the chaotic mixture was qualitatively investigated by visualizing global fracture profiles at different Reynolds numbers. From Figure 5, the liquid gradually splits into several smaller layers as the flow continues. Thus, the inter-liquid interface area is enlarged, and the performance of the mixture is clearly improved. Hence, a high homogeneous mixture is obtained at the last mini-mixer for all values of Re; regardless of the increase in the value of the Reynolds, the mixing efficiency in this micromixer increases.
3.3. Analysis of the Non-Newtonian Fluid
This part of the research focused on the influence of the Reynolds number in a behavioral liquid with index n on the mixing efficiency of the proposed C-micromixer. Numerical simulations were performed using generalized Reynolds numbers as low as 0.1 to 50. The non-Newtonian fluids used are the sheer thinner by a behavior index ranging from 0.49 to 0.9. The efficiency of the mixture is evaluated by calculating the mixture index (MI) and thermal mixture (TMI) at various cross-sections and numbers of Reynolds. To analyze the numerical simulation results, mass fraction profiles, pressure drop, and temperature contours at different levels and locations are presented.
3.3.1. Micromixer Mixing Performance
Figure 6 depicts the mixer’s performance for non-Newtonian fluid over the analyzed range of Reynolds numbers. It can be appreciated that the mixing efficiency is affected by the concentration level and the advection regime for high and moderate generalized Reynolds numbers. This figure further illustrates that the mixing index rises as Reynolds number increases after creeping flow, whereas the diffusion was dominant for Re ≤ 5. At higher Reynolds numbers, however, the highest n gives the best performance. The augmentation of n (diminution in viscosity) brings low shear rates into the flow; low shear rates improve mixing efficacy.
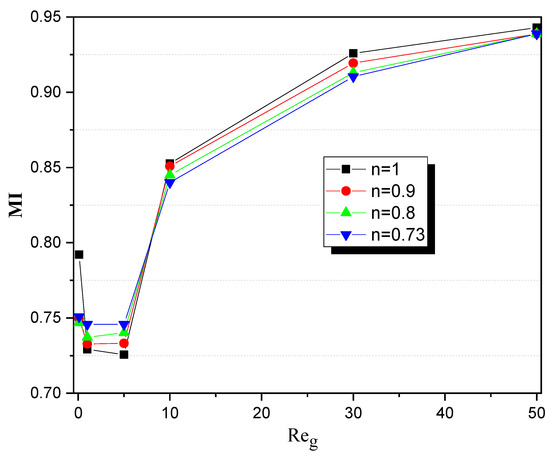
Figure 6.
Improvement of mixing efficiency for various Reynolds numbers with a different number (n) for non-Newtonian fluid.
To determine the thermal efficiency of the mixture, the behavioral effects, and the generalized Reynolds number, Figure 7 illustrates the evolution of the TMI score as a function of the generalized Reynolds number for each of the proposed n power index. In fine mixing, stirring is more noticeable due to chaotic lags as well as the presence of sealing areas and high flow pressure. This characteristic substantially adds to the improvement of thermal mixing performance, and as mentioned earlier, higher ratios; as the Reynolds number approaches the highest, the tendency to accelerate sharply increases, and all values approach TMI = 1.
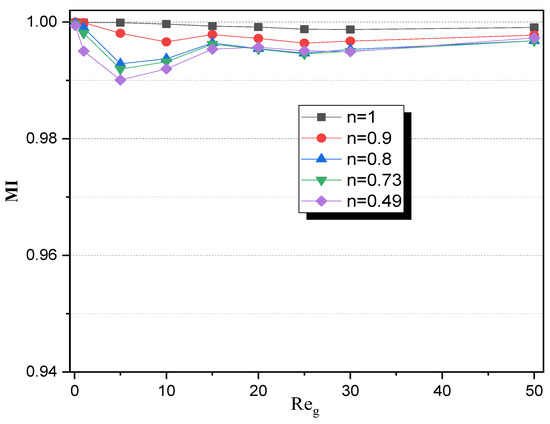
Figure 7.
Evolution of thermal mixing behavior for various Reg values and power law indexes (n).
Because of their small dimensions and improved fluidic properties at the microscale, mixing efficiency is typically high. The small size allows for rapid heat transfer between fluids, resulting in efficient mixing and thermal homogeneity, as well as diffusion at low generalized Reynolds values, and chaotic advection and Dean vortices enhance thermal mixing. The non-Newtonian fluids with high viscosities or shear-thinning behavior have higher flow rates to achieve highly efficient heat transfer.
For the thermal mixing index (TMI), the results show a similar trend to the MI, with TMI values improving as Re increases. At low Re values (e.g., Re = 0.1), the TMI is lower, indicating initial thermal mixing. At higher Re values (e.g., Re = 50), the TMI approaches 1, demonstrating excellent thermal homogenization. This improvement is attributed to the enhanced chaotic advection and increased turbulence at higher Reynolds numbers.
3.3.2. Pressure Drop and Performance Index
The found pressure drop patterns imply that pressure drop increases with increasing Re, resulting in richer mixing. Figure 8 depicts the differences in pressure drop in a micromixer as a result of the generalized Reynolds number. The ideal mixture is typically associated with a decrease in pressure. A large pressure drop results in a large energy loss, an important property in the design of the micromixer. Pressure drops increase rapidly and non-linearly as the low power index (n) increases. This quick increase in the drop of pressure is mostly due to the establishment of recycling processes and interactions of particles and fluids with walls that result from secondary flows generated within the geometry. It is mainly necessary that the higher values of generalized Reynolds numbers, which mainly give excellent MI values, take the highest values of pressure loss.
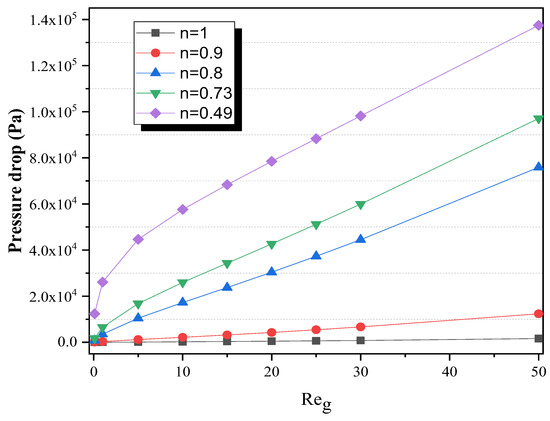
Figure 8.
Pressure drop evolution with Reg for various behavior indexes.
The quantitative analysis shows that ΔP increases with the Reynolds number. For example, at Re = 0.1, the pressure drop is minimal for all behavior indexes. As Re increases to 50, the pressure drop rises sharply. Although higher pressure drops are observed at increased Reynolds numbers, the corresponding improvements in mixing efficiency justify the energy expenditure, particularly in applications where high mixing performance is critical.
A good microdevice performance index must have a high value of mixing indexes and a low value of pressure loss in order to measure the perfection of a micromixer. A high PI score indicates superior overall performance.
In Figure 9, the performance index drops as the Reynolds number increases, and it rises in proportion to the n power low index value. At all Reynolds numbers tested here, the performance indexes with n = 1 are higher than those with non-Newtonian micromixers. This improved performance is owing to a decrease in pressure drop.
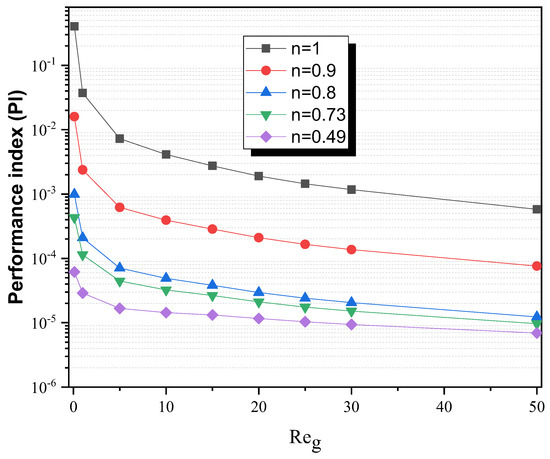
Figure 9.
Performance index variation with the generalized Reynolds number for various behavior indexes.
3.3.3. Mixing Energy Cost
The cost of mixing energy signifies overall improved capacity, and low values suggest that the specific micromixer has superior mixing efficiency. The device’s design has a considerable impact on pressure loss, and this in turn affects the mixing energy cost. The pressure decrease is exactly proportional to the energy input employed in the mixing operation. Figure 10 shows that when Re increases, the MEC within the micromixers grows larger since the fluid flow becomes more sheared.
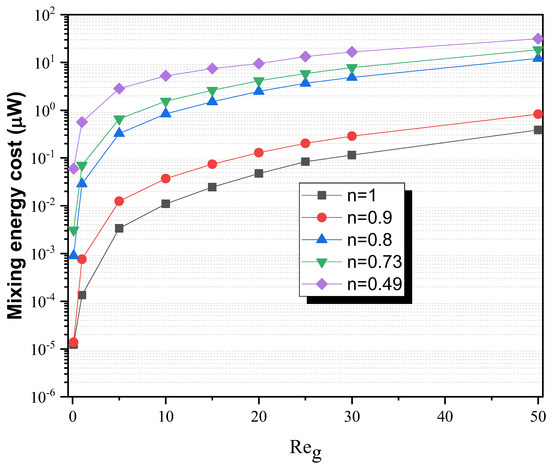
Figure 10.
Development of power mixing cost in terms of generalized Reynolds number change (μW).
Table 3 compares the mixing energy cost of the suggested micromixer with several recent micromixers for a variety of Reynolds numbers in Newtonian flow.

Table 3.
Mixing energy cost of micromixers.
The results indicate that while the MEC increases with Re due to the higher ΔP, the significant improvements in MI at higher Re values offset this cost. For instance, at Re = 5, the MEC is relatively low, reflecting the balance between moderate pressure drop and good mixing efficiency. At Re = 50, the MEC is higher, but the substantial increase in MI makes it a cost-effective solution for applications requiring high-quality mixing. When compared to existing micromixers, the micromixer presented here offers a low mixing energy cost for very low Reynolds numbers. In general, this micromixer has a good economical mixing energy cost.
3.3.4. Mass Distribution of the Non-Newtonian Fluids
The influence of Reynolds number and behavior indexes on the liquid process was analyzed, showing the fracture profiles of the bulk mixture in the different transverse planes P1–P5 and at the outlet with a power law index n = 0.9 and a generalized Reynolds range from 0.1 to 50 (Figure 11).
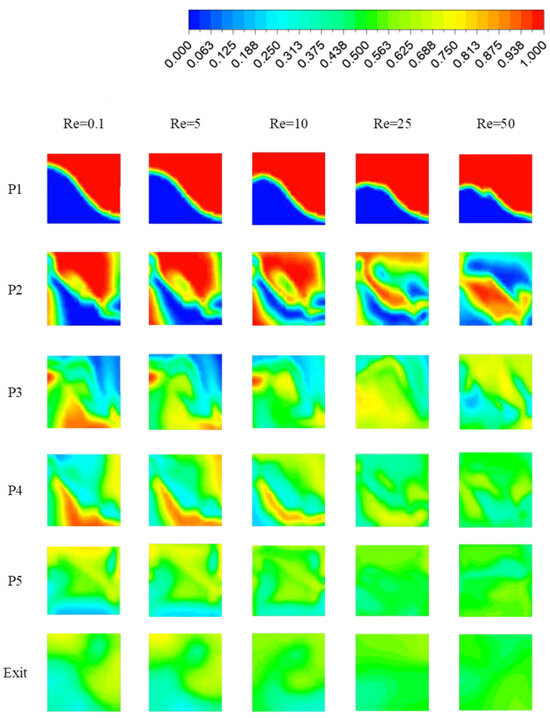
Figure 11.
Partial mass distribution of the non-Newtonian fluid micromixer with n = 0.8.
The effectiveness has been defined by various mixing mechanisms, which includes split and recombines caused by obstructions, chaotic advection, and separation vortices caused by secondary flow, thereby expanding the interfacial region of the fluid streams. At very low Re, mixing is controlled by molecular diffusion. However, with an increase in the Reynolds number to Re = 5, the residence time becomes lower, and the mass mixing barely decreases caused by the insufficient formation of separation vortices. By increasing the Reynolds number in a range of 10–50, convection takes over the mass mixing process, and the enhanced secondary flow and circulation induced by the baffles improves mixing efficiency. It is evident that when the Reynolds number and axial distance in the flow direction increase, mass mixing increases.
Next, the Reynolds number was fixed at Re = 10, and three power law indexes were used, namely, 0.9, 0.73, and 0.46, to visualize the flow of mass fraction in the mini mixer as shown in Figure 12. It can be observed that the fluid mixing increases with the length of the micromixer for all fluid behavior index n and the liquid gradually splits into several finer layers as the flow continues. Therefore, the inter-liquid interface area is expanded, and the performance of the mixture is clearly improved with whatever Reynolds values and behavior index are contained in the liquid, which confirms the effectiveness of the mini mixer.
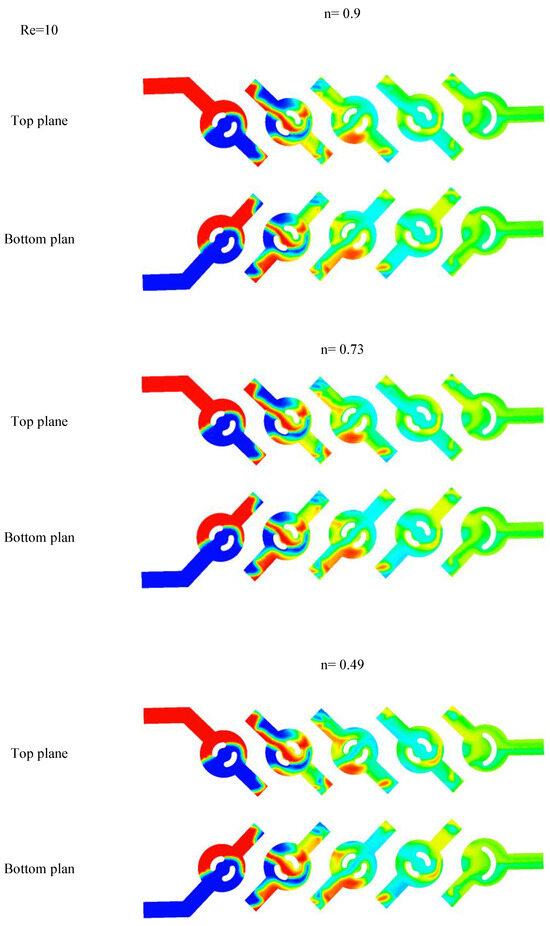
Figure 12.
Mass fraction distributions of the non-Newtonian fluid micromixer.
3.3.5. Temperature Contours
Figure 13 shows the temperature profiles at different Y-dimension levels. Secondary flow vectors of fluid particles are shown in specific regions in the proposed geometry. For the sake of clarity, the positions of the planes in the micromixer are listed in Table 4.
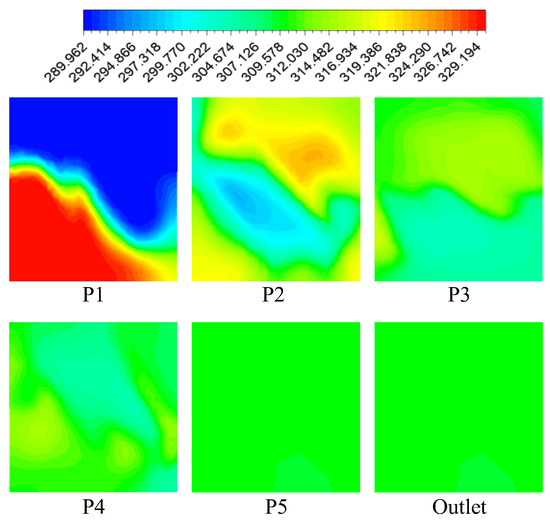
Figure 13.
Temperature contours.

Table 4.
Positions of the planes in the micromixer.
The simulation results are obtained by assuming the temperature of the first liquid is 290 K and the second liquid is 330 K. It is worth noting that there has been a marked improvement in heat exchange over time. Thermal transfer is closely related to the imposed temperature. The inter-liquid interface area is expanded, and the performance of the thermal mixture is clearly improved.
3.3.6. Average Fluid Temperature
Two indicators are used to evaluate the heat transfer efficiency by chaotic mixing. The first indicator is the mean temperature Tm, while the second is the standard deviation. Figure 14a shows the homogeneous mixture obtained at the port in the mini mixer. Figure 14b clearly shows that the temperature standard deviation dissolution rate is relatively large at the start, which confirms the homogeneity of thermal mixing.
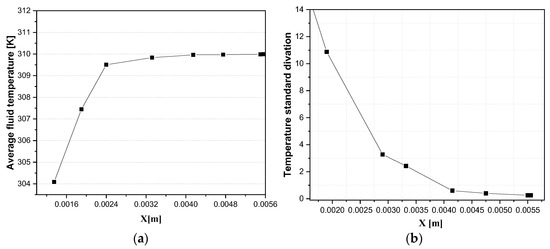
Figure 14.
Evolution of the mean mixing temperature of the fluid (a) and temperature standard deviation (b).
4. Conclusions
In this work, the mixing process is analyzed and numerically characterized exclusively in steady state using the CFD numerical tool, ANSYS Fluent 16.0, to characterize the mixing of fluids with shear-thinning behavior. The fluids considered are solutions of carboxyl methyl cellulose (CMC) in the geometries of a two-layer micromixer containing cylindrical chambers with fin-shaped obstructions. The inlet section is composed of two parts, through which the fluids are injected at 290 K and 330 K.
A power law describes the viscosity, with the behavior index (n) ranging from 0.49 to 1 and the generalized Reynolds number ranging from 0.1 to 50. Characteristic quantities of micromixers such as mixing index, thermal mixing, mixing cost, average fluid temperature, standard deviation, pressure drop, MI/ΔP ratio, and contours were presented and investigated numerically with this novel micromixer. It should be noted that the behavior index (n) in liquids has an important influence on the performance of the mixture.
The results indicate that the TLCM micromixer achieves high mixing efficiency and temperature homogenization across a wide range of Reynolds numbers. The induced chaotic advection and secondary flows within the micromixer significantly enhance the mixing process for both Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids. The mixing index and thermal mixing index show marked improvements with increasing Reynolds numbers, underscoring the micromixer’s capability to handle diverse fluid dynamics efficiently.
The hydrodynamic and thermal characterization of this micromixer demonstrates its high efficiency in terms of mixing quality and temperature homogenization. The successful validation of the simulation results against established studies provides confidence in the accuracy and relevance of the findings.
These results pave the way for various promising future opportunities in the areas of microfluidics and bioenergy. Further investigation could focus on enhancing the efficiency of the twisted channels in micromixers and exploring untapped grooves within them. Expanding the micromixer design and assessing its efficiency can enhance its practical implementation in processing biological fluids on a microscale. Ultimately, the combined optimization of several factors, such as micromixer shape and fluid characteristics, continues to be an appealing problem within an integrated strategy.
Future research could also explore the integration of the TLCM micromixer with other microfluidic components to develop comprehensive lab-on-a-chip systems. Investigating the micromixer’s performance with different types of non-Newtonian fluids, including those with varying rheological properties, could further enhance its applicability. Additionally, experimental validation of the numerical findings and real-world testing in various applications would provide deeper insights and reinforce the potential of the TLCM micromixer as a versatile and efficient tool for advanced fluid mixing.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M. and N.T.T.; methodology, A.M., R.K. and N.T.T.; software, A.M. and N.T.T.; validation, N.T.T., R.K. and A.A.-K.; formal analysis, A.M., R.K.A.-K. and E.M.C.-C.; investigation, R.K., A.A.-K. and E.M.C.-C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M., R.K. and A.A.-K.; writing—review and editing, R.K.A.-K., E.M.C.-C. and A.A.-K.; visualization, R.K.A.-K. and E.M.C.-C.; supervision, A.A.-K. and R.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Raúl Kassir Al-Karany was employed by the company Aeronautical Services. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| Symbol | Description |
| ∇ | Gradient operator |
| c | Concentration |
| C | Average mole fraction |
| ci | Mole fraction at a specific location |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| CMC | Carboxy methyl cellulose |
| D | Diffusion coefficient |
| d1, d2 | Diameter of grooves |
| Dh | Hydraulic diameter |
| k | Consistency index |
| L | Axial length of channel |
| l1, l2 | Length of grooves |
| MEC | Mixing energy cost |
| MI | Mixing index |
| n | Power law index |
| N | Number of nodes in the cross-section. |
| P | Pressure |
| PI | Performance index |
| Q | Flow rate |
| Reg | Generalized Reynolds number |
| T | Cross-section mean temperature |
| Ti | Temperature at the i-th node |
| TMI | Thermal mixing index |
| u | Velocity vector |
| w1, w2 | Width of inlet channels |
| γ | Shear rate tensor |
| ΔP | Pressure drop |
| Μ | Dynamic viscosity |
| μa | Apparent viscosity (for non-Newtonian fluids) |
| ξ | Dimensionless geometrical parameter |
| ρ | Fluid density |
| σ | Standard deviation |
| σ0 | Standard deviation at inlet section |
| τ | Shear stress tensor |
References
- Chen, X.; Shen, J. Design and Simulation of a Chaotic Micromixer with Diamond-Like Micropillar Based on Artificial Neural Network. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2017, 15, 20160039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroock, A.D.; Dertinger, S.K.W.; Ajdari, A.; Mezić, I.; Stone, H.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Chaotic Mixer for Microchannels. Science 2002, 295, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, M.; Azimi, N.; Parsamogadam, M.A.; Rahimi, A.; Masahy, M.M. Mixing Performance of T, Y, and Oriented Y-Micromixers with Spatially Arranged Outlet Channel: Evaluation with Villermaux/Dushman Test Reaction. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 3117–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.-T.; Wu, Z. Micromixers—A Review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2005, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessel, V.; Löwe, H.; Schönfeld, F. Micromixers—A Review on Passive and Active Mixing Principles. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 2479–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasgow, I.; Aubry, N. Enhancement of Microfluidic Mixing Using Time Pulsing. Lab Chip 2003, 3, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, T.; Zeng, H.; Hu, Z.; Fu, B. Numerical and Experimental Investigation on Micromixers with Serpentine Microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 98, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X. Optimized Modular Design and Experiment for Staggered Herringbone Chaotic Micromixer. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2015, 13, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianovska, M.A.; Mulder, P.P.M.F.A.; Verpoorte, E. Development of Small-Volume, Microfluidic Chaotic Mixers for Future Application in Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 9090–9099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, T.J.; Foresti, D.; Lewis, J.A. Active Mixing of Complex Fluids at the Microscale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12293–12298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The, H.L.; Ta, B.Q.; Thanh, H.L.; Dong, T.; Thoi, T.N.; Karlsen, F. Geometric Effects on Mixing Performance in a Novel Passive Micromixer with Trapezoidal-Zigzag Channels. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 094004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-K.; Yang, R.-J. Electroosmotic Flow Mixing in Zigzag Microchannels. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.H.; Stremler, M.A.; Sharp, K.V.; Olsen, M.G.; Santiago, J.G.; Adrian, R.J.; Aref, H.; Beebe, D.J. Passive Mixing in a Three-Dimensional Serpentine Microchannel. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2000, 9, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanka, S.P.; Luo, G.; Winkler, C.M. Numerical Study of Scalar Mixing in Curved Channels at Low Reynolds Numbers. AIChE J. 2004, 50, 2359–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Ross, D.; Locascio, L.E. Rapid Microfluidic Mixing. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Shie, Y.S. Interfacial Configurations and Mixing Performances of Fluids in Staggered Curved-Channel Micromixers. Microsyst. Technol. 2012, 18, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, T.H.; Ahn, C.H. A Serpentine Laminating Micromixer Combining Splitting/Recombination and Advection. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeb, N.T.; Hossain, S.; Khan, A.H.; Mostefa, T.; Kim, K.-Y. Evaluation of Hydrodynamic and Thermal Behaviour of Non-Newtonian-Nanofluid Mixing in a Chaotic Micromixer. Micromachines 2022, 13, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-J.; Hsu, H.-C.; Feng, W.-J. Novel Design and Fabrication of a Geometrical Obstacle-Embedded Micromixer with Notched Wall. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 097201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengeaud, V.; Josserand, J.; Girault, H.H. Mixing Processes in a Zigzag Microchannel: Finite Element Simulations and Optical Study. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 4279–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, R.-T.; Wu, C.-Y. An Efficient Micromixer Based on Multidirectional Vortices Due to Baffles and Channel Curvature. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 014103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, R.-T.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-Y.; Kuo, M.-Y. Mixing Behaviors of Shear-Thinning Fluids in Serpentine-Channel Micromixers. Int. J. Aerosp. Mech. Eng. 2015, 9, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, W.; Kim, K.-Y. Unbalanced Split and Recombine Micromixer with Three-Dimensional Steps. Ind Eng Chem Res 2020, 59, 3744–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Kim, K.-Y. Mixing Performance of a Planar Micromixer with Circular Chambers and Crossing Constriction Channels. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 176, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.M.; Wan, S.Y.M.; Shu, C.; Chew, Y.T. Chaotic Micromixers Using Two-Layer Crossing Channels to Exhibit Fast Mixing at Low Reynolds Numbers. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Lee, I.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, K.-Y. A Micromixer with Two-Layer Serpentine Crossing Channels Having Excellent Mixing Performance at Low Reynolds Numbers. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Li, X.; He, F.; Ma, X. A Micromixer with Two-Layer Crossing Microchannels Based on PMMA Bonding Process. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2019, 17, 20180265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A.; Kim, K.-Y. Flow and Mixing Analysis of Non-Newtonian Fluids in Straight and Serpentine Microchannels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 116, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baheri Islami, S.; Khezerloo, M.; Gharraei, R. The Effect of Chaotic Advection on Mixing Degree and Pressure Drop of Non-Newtonian Fluids Flow in Curved Micromixers. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2017, 39, 813–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baheri Islami, S.; Khezerloo, M. Enhancement of Mixing Performance of Non-Newtonian Fluids Using Curving and Grooving of Microchannels. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2017, 10, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, M.Q.; Zhang, J. Numerical Investigation on the Efficient Mixing of Overbridged Split-and-Recombine Micromixer at Low Reynolds Number. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 3447–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaei, P.R.; Hosseinalipour, S.M.; Esmailpour, K. Numerical Investigation of Thermal Mixing of Shear Thinning Fluids in One-Way Opposing Jets. J. Comput. Appl. Res. Mech. Eng. 2014, 3, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, A.; Tiwari, N.; Chhabra, R.P. Thermal Mixing of Impinging Laminar Streams of Shear-Thinning Fluids. Heat Transf. Eng. 2020, 41, 1576–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naas, T.T.; Lasbet, Y.; Aidaoui, L.; Boukhalkhal, A.L.; Loubar, K. High Performance in Terms of Thermal Mixing of Non-Newtonian Fluids Using Open Chaotic Flow: Numerical Investigations. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, 16, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouadri, A.; Douroum, E.; El Ouederni, A.R.; Benazza, A.; Laouedj, S.; Khelladi, S. Assessment of Mixing Behaviors of Non-Newtonian Pseudoplastic Fluids in Short Microdevices. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 155, 107500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yao, Y.; Tang, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, P.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Tao, C.; et al. Experimental and Computational Investigation of Chaotic Advection Mixing in Laminar Rectangular Stirred Tanks. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellouah, H.; Castelain, C.; Ould-El-Moctar, A.; Peerhossaini, H. The Dean Instability in Power-Law and Bingham Fluids in a Curved Rectangular Duct. J. Non-Newton Fluid Mech. 2010, 165, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, F.T.; Whitelaw, J.H. Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids in a Pipe. J. Non-Newton Fluid Mech. 1990, 34, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-C.; Li, Z.-H.; Zheng-Hua, L. Finite Element Analysis of Non-Newtonian Flow: Theory and Software; Springer: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Byron Bird, R.; Armstrong, R.C.; Hassager, O. Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids, Volume 1: Fluid Mechanics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Metzner, A.B.; Reed, J.C. Flow of Non-newtonian Fluids—Correlation of the Laminar, Transition, and Turbulent-flow Regions. AIChE J. 1955, 1, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delplace, F.; Leuliet, J.C. Generalized Reynolds Number for the Flow of Power Law Fluids in Cylindrical Ducts of Arbitrary Cross-Section. Chem. Eng. J. Biochem. Eng. J. 1995, 56, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahammedi, A.; Tayeb, N.T.; Kim, K.-Y.; Hossain, S. Mixing Enhancement of Non-Newtonian Shear-Thinning Fluid for a Kenics Micromixer. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasbet, Y.; Auvity, B.; Castelain, C.; Peerhossaini, H. Thermal and Hydrodynamic Performances of Chaotic Mini-Channel: Application to the Fuel Cell Cooling. Heat Transf. Eng. 2007, 28, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidde, R.R.; Pawar, P.M.; Ronge, B.P.; Shinde, A.B.; Misal, N.D.; Wangikar, S.S. Flow Field Analysis of a Passive Wavy Micromixer with CSAR and ESAR Elements. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, L.; Commenge, J.-M. Performance Comparison of Micromixers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidde, R.R.; Pawar, P.M. Flow Feature and Mixing Performance Analysis of RB-TSAR and EB-TSAR Micromixers. Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 26, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).