Visualizing the Landscape and Evolution of Solar Energy-Integrated Desalination Systems via Scientometric Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Bibliometrics and Citation Analysis, History, and Previous Art
3. Visualization Algorithm and Discussion
- Data input: VosViewer can accept data from different sources primarily through:
- ○
- APIs—OpenAlex, Europe PMC, Semantic Scholar, Wikidata etc.
- ○
- Bibliographic database files from websites such as Web of Science, Scopus, Lens, PubMed etc.
- ○
- Reference manager files like RefWorks, EndNote, RIS etc.
- Citation network formation: This network forms the backbone of the bibliometric visualizations. Citation networks are created depending on the user requirement such as: authors, publication titles, keywords, countries, affiliations etc. They are identified as “nodes” or “labels” which are then interconnected with a series of lines which represents the citations between each respective node (author names, titles, keywords, countries etc.). Co-citation is also represented by the thickness of said lines (thicker lines between two nodes indicate frequent citation by other publications citing both “nodes” together).
- Bibliographic coupling: VOSviewer utilizes bibliographic coupling to arrange nodes in clusters. Based on the user’s input requirements, such as the focus on authors, countries, publication titles, or keywords, the nodes are grouped together if they share a similar or identical set of references. For instance, if two publications cite the same source, they will be bibliographically coupled, resulting in the closer proximity of their nodes in the visualization. The distance between two nodes indicates the number of shared references they possess, with a node being farther away indicating fewer shared references, and nodes closer together indicating numerous shared references.
- Thematic clustering and visualization: Combining both the citation network and bibliographic coupling, the software assigns a color scheme of differing colors to differentiate one theme from another, this color scheme can be manually overridden should the user wish to assign their own personal color schemes. Displaying the combined citation network and the bibliographic coupling as one scientometric map. The automated sizing of these nodes is conducted by the software based on their centrality or significance within the network.
3.1. Findings
3.2. Implications
3.3. Citation Analysis
3.4. Challenges
3.5. Limitations
4. Conclusions
- Leading countries in solar desalination research were China, USA, Egypt, India, and Saudi Arabia.
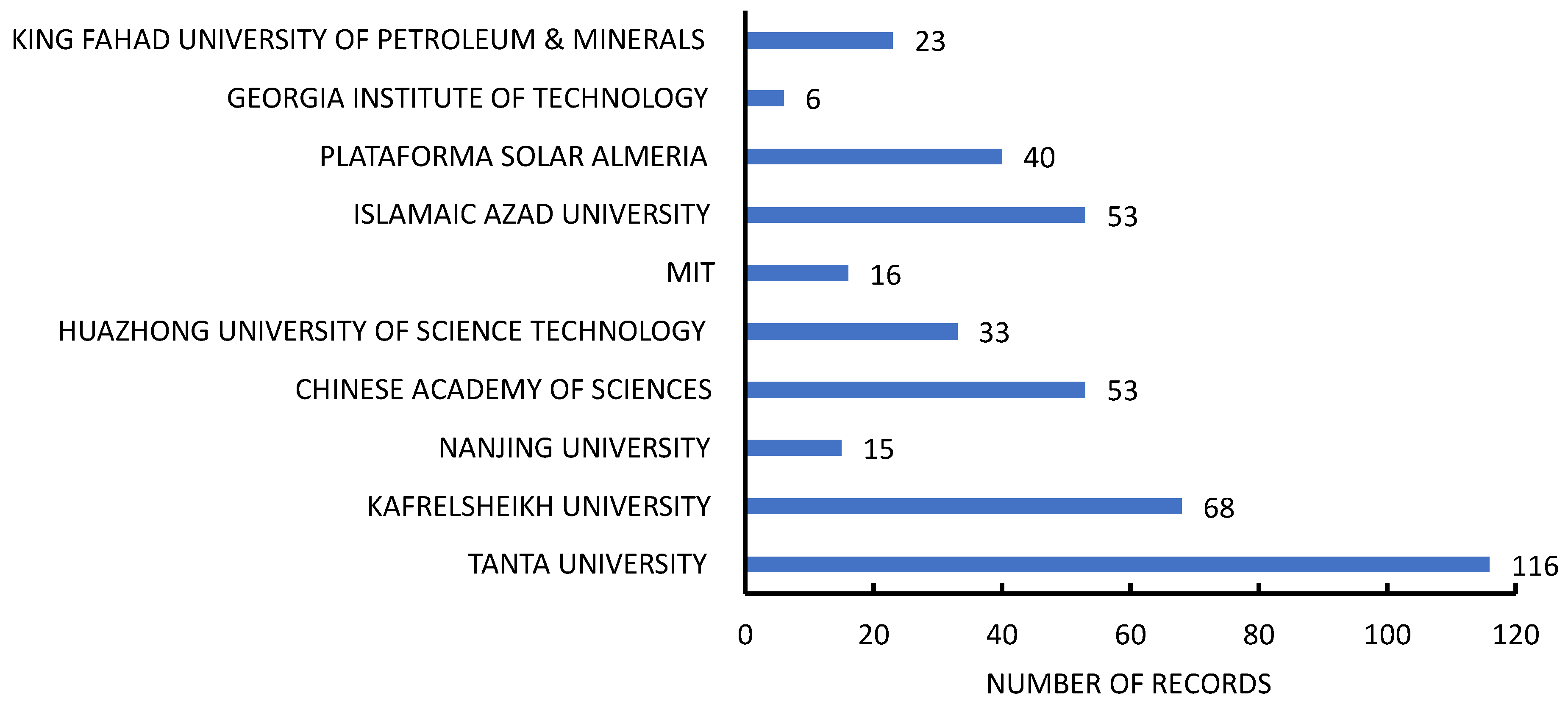
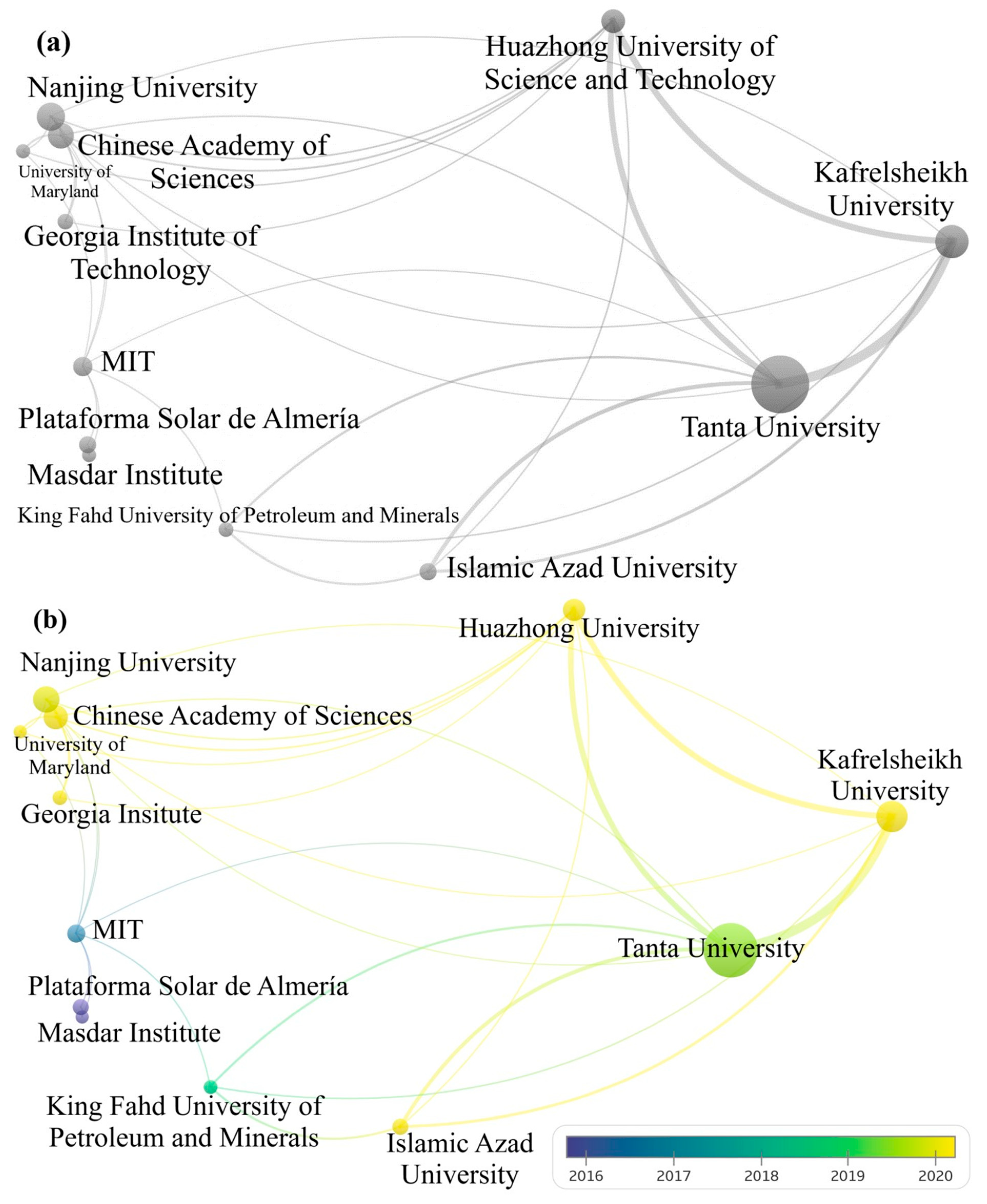
- Prominent research institutions according to the analysis performed in this manuscript were Tanta University, Kafrelsheikh University (Egypt), and Nanjing University (China).
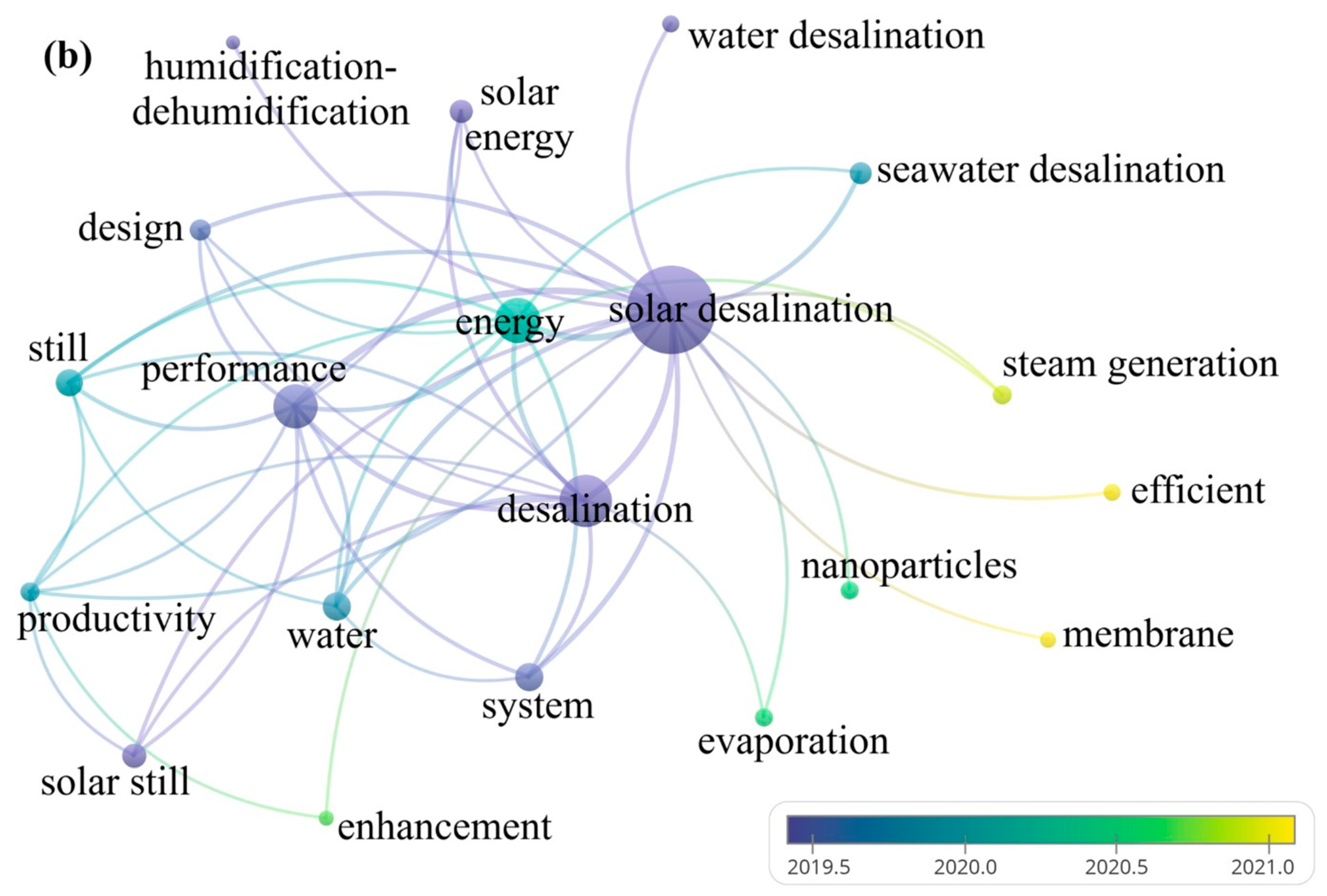
- Peak research activity from 2018 to 2022 used “stills” as the most frequent keyword; the keyword occurrence was 904.
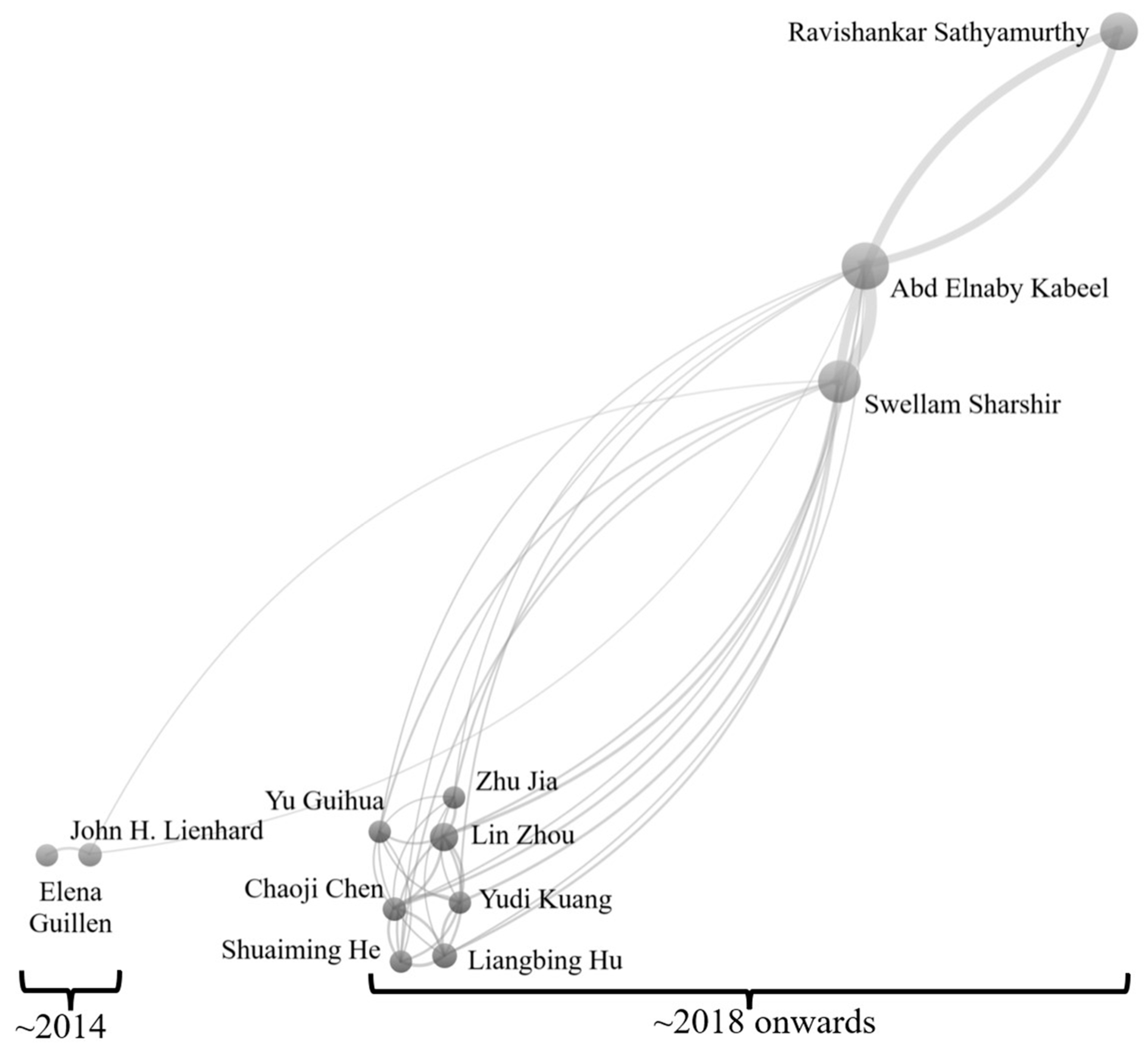
- Top cited researchers were A.E. Kabeel and Lin Zhou. Moreover, Lin Zhou had the highest cited paper on solar desalination with 1554 citations.
- The dominant research theme was modifications to material-based evaporators (graphene membranes and hydrogel channels).
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molden, D. Scarcity of water or scarcity of management? Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2020, 36, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Wahid, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Fujita, D.; Basra, S.M. Plant drought stress: Effects, mechanisms and management. Sustain. Agric. 2009, 29, 153–188. [Google Scholar]
- Balligand, P.; Denis, P.; De Cachard, M.; Gouzy, A.; Berger, R. Serres a dessalement solaire. Desalination 1979, 31, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Hatzell, K.B. Technoeconomic analysis of solar thermal desalination. Desalination 2020, 474, 114168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abutayeh, M.; Yogi Goswami, D.; Stefanakos, E.K. Theoretical and experimental simulation of passive vacuum solar flash desalination. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2013, 135, 021013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariman, H.; Shafieian, A.; Khiadani, M. Small scale desalination technologies: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2023, 567, 116985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez, L.; Delgado-Torres, A.M. Renewable Energy-Driven Desalination: New Trends and Future Prospects of Small Capacity Systems. Processes 2022, 10, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmenkov, D.M.; Struchalin, P.G.; Olkhovskii, A.V.; Yunin, V.S.; Kutsenko, K.V.; Balakin, B.V. Solar-driven desalination using nanoparticles. Energies 2021, 14, 5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnu, S.; Bigham, S. Multiple-effect desiccant-based zero liquid discharge desalination systems. Desalination 2021, 502, 114942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Limón, N.; López-Zavala, R.; Hernández-Callejo, L.; Aguilar-Jiménez, J.A.; Ojeda-Benítez, S.; Ríos-Arriola, J. Study of a hybrid solar absorption-cooling and flash-desalination system. Energies 2020, 13, 3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Piao, G.; Han, D.S.; Shon, H.K.; Park, H. Solar desalination coupled with water remediation and molecular hydrogen production: A novel solar water-energy nexus. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcovecchio, M.G.; Mussati, S.F.; Aguirre, P.A.; Nicolás, J. Optimization of hybrid desalination processes including multi stage flash and reverse osmosis systems. Desalination 2005, 182, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meindertsma, W.; Van Sark, W.; Lipchin, C. Renewable energy fueled desalination in Israel. Desalination Water Treat. 2010, 13, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Xia, D.; Liu, J. Seawater desalination with solar-energy-integrated vacuum membrane distillation system. J. Water Reuse Desalination 2017, 7, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sebaey, M.S.; Ellman, A.; Hegazy, A.; Essa, F.A. Experimental study with thermal and economical analysis for some modifications on cylindrical sector and double slope, single basin solar still. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 49, 103310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sebaey, M.S.; Hegazy, A.; Essa, F.A. Performance enhancement of a tubular solar still by using stepped basins: An experimental approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 437, 140746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyamurthy, R.; Ali, H.M.; Said, Z.; El-Sebaey, M.S.; Gopalsamy, S.; Nagaraj, M.; Almasoud, N.; Alomar, T.S. Enhancing solar still thermal performance: The role of surface coating and thermal energy storage in repurposed soda cans. J. Energy Storage 2024, 77, 109807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Kang, N.; Ahmed, A.; Zong, Y.; Tu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X. Graphene-based membranes for water desalination: A literature review and content analysis. Polymers 2022, 14, 4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A. IAAM’s Pledge for Global Climate Resilience at COP 28. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2024, 15, 2402-1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Waltman, L. Large-scale analysis of the accuracy of the journal classification systems of Web of Science and Scopus. J. Informetr. 2016, 10, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, I.D. Bibliometrics basics. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. JMLA 2015, 103, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, B.I.; Baker, K.L.; Davis, M.T.; Diwersy, M.A.; Haque, E.; Harriman, R.M.; Hoppe, T.A.; Leicht, S.A.; Meyer, P.; Santangelo, G.M. The NIH Open Citation Collection: A public access, broad coverage resource. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, F.; Ghazali, K.H.; Muda, R.; Johari, N.H.; Dennis, J.O.; Tamam, N.; Sulieman, A.; Ji, Y. Magnetoresistance and magneto-plasmonic sensors for the detection of cancer biomarkers: A bibliometric analysis and recent advances. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2023, 6, 100172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, O.; Hagiwara, Y.; Hong, T.J.; Lih, O.S.; Acharya, U.R. Deep learning for healthcare applications based on physiological signals: A review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 161, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Daya, M.; Hassini, E.; Bahroun, Z. Internet of things and supply chain management: A literature review. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 4719–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, M.; Joss, S.; Schraven, D.; Zhan, C.; Weijnen, M. Sustainable–smart–resilient–low carbon–eco–knowledge cities; making sense of a multitude of concepts promoting sustainable urbanization. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 109, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzaabi, M.S.A.; Mezher, T. Analyzing existing UAE national water, energy and food nexus related strategies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 144, 111031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, W. The Role of Desalination in an Increasingly Water-Scarce World; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Alegre, H.; Baptista, J.M.; Cabrera, E., Jr.; Cubillo, F.; Duarte, P.; Hirner, W.; Merkel, W.; Parena, R. Performance Indicators for Water Supply Services; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, L.; He, T.; Chen, S.; Gao, C.; Zhang, L. Seawater desalination technology and engineering in China: A review. Desalination 2021, 498, 114728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of India. Current Notices. 2015. Available online: https://mnre.gov.in/notice/information-related-to-decentralized-solar-schemes-implemented-by-mnre/ (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Chandrashekara, M.; Yadav, A. Water desalination system using solar heat: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 1308–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.J.; Ng, Z.C.; Hubadillah, S.K.; Goh, P.S.; Lau, W.J.; Othman, M.; Ismail, A.F.; Hilal, N. Fouling mitigation in forward osmosis and membrane distillation for desalination. Desalination 2020, 480, 114338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh H, D.E.; Lichtfouse, E. How the COVID-19 pandemic has changed research? Env. Chem Lett. 2022, 29, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsheikh, A.H.; Sharshir, S.W.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Kabeel, A.E.; Guilan, W.; Haiou, Z. Modeling of solar energy systems using artificial neural network: A comprehensive review. Sol. Energy 2019, 180, 622–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tan, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Cai, W.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J. 3D self-assembly of aluminium nanoparticles for plasmon-enhanced solar desalination. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meho, L.I.; Yang, K. Impact of data sources on citation counts and rankings of LIS faculty: Web of Science versus Scopus and Google Scholar. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2007, 58, 2105–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Winter, J.C.; Zadpoor, A.A.; Dodou, D. The expansion of Google Scholar versus Web of Science: A longitudinal study. Scientometrics 2014, 98, 1547–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Martín, A.; Orduna-Malea, E.; Thelwall, M.; López-Cózar, E.D. Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Scopus: A systematic comparison of citations in 252 subject categories. J. Informetr. 2018, 12, 1160–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfield, E. Citation analysis as a tool in journal evaluation: Journals can be ranked by frequency and impact of citations for science policy studies. Science 1972, 178, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easterbrook, P.J.; Gopalan, R.; Berlin, J.; Matthews, D.R. Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet 1991, 337, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, W.; Tang, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J. Graphene oxide-based efficient and scalable solar desalination under one sun with a confined 2D water path. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13953–13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, F.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, G. A hydrogel-based antifouling solar evaporator for highly efficient water desalination. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsinger, D.M.; Swaminathan, J.; Guillen-Burrieza, E.; Arafat, H.A. Scaling and fouling in membrane distillation for desalination applications: A review. Desalination 2015, 356, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Chen, C.; He, S.; Hitz, E.M.; Wang, Y.; Gan, W.; Mi, R.; Hu, L. A high-performance self-regenerating solar evaporator for continuous water desalination. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1900498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Chen, C.; Kuang, Y.; Mi, R.; Liu, Y.; Pei, Y.; Kong, W.; Gan, W.; Xie, H.; Hitz, E. Nature-inspired salt resistant bimodal porous solar evaporator for efficient and stable water desalination. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Goswami, Y.; Stefanakos, E. Solar assisted sea water desalination: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 136–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Liu, K.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Duan, J.; Xue, G.; Xu, Z.; Xie, W.; Zhou, J. Solar-driven simultaneous steam production and electricity generation from salinity. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1923–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, C.; Tian, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.; Yin, X.; Que, W. A hydrophobic surface enabled salt-blocking 2D Ti 3 C 2 MXene membrane for efficient and stable solar desalination. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 16196–16204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, F.; Bae, J.; Rosenberger, B.; Yu, G. Synergistic energy nanoconfinement and water activation in hydrogels for efficient solar water desalination. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 7913–7919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gude, V.G.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Deng, S. Renewable and sustainable approaches for desalination. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 2641–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.E.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. Solar powered desalination–Technology, energy and future outlook. Desalination 2019, 453, 54–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahian, O.; Kianifar, A.; Heris, S.Z.; Wen, D.; Sahin, A.Z.; Wongwises, S. Nanofluids effects on the evaporation rate in a solar still equipped with a heat exchanger. Nano Energy 2017, 36, 134–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Torres, A.M.; García-Rodríguez, L. Analysis and optimization of the low-temperature solar organic Rankine cycle (ORC). Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 2846–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, T.; Yang, Z.; Chen, C.; Kuang, Y.; Song, J.; Jia, C.; Hitz, E.M.; Yang, B.; Hu, L. Graphene oxide-based evaporator with one-dimensional water transport enabling high-efficiency solar desalination. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cáceres González, R.A.; Hatzell, M.C.; Hatzell, K.B. Challenges and Roadmap for Solar-Thermal Desalination. ACS EST Eng. 2023, 3, 1055–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, J.H.; Alhalabi, W. Solar-thermal powered desalination: Its significant challenges and potential. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 48, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.; Qadir, M.; van Vliet, M.T.; Smakhtin, V.; Kang, S.-m. The state of desalination and brine production: A global outlook. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1343–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Thi, H.T.; Pasztor, T.; Fozer, D.; Manenti, F.; Toth, A.J. Comparison of desalination technologies using renewable energy sources with life cycle, PESTLE, and multi-criteria decision analyses. Water 2021, 13, 3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeb, A.; Abdollahi, A.; Rejeb, K.; Treiblmaier, H. Drones in agriculture: A review and bibliometric analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Rank | Country | Collective Citations | Number of Records |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 23,621 | 625 |
| 2 | USA | 10,903 | 185 |
| 3 | Egypt | 7906 | 219 |
| 4 | India | 6665 | 286 |
| 5 | Saudi Arabia | 5510 | 176 |
| 6 | Iran | 4633 | 158 |
| 7 | Spain | 3306 | 78 |
| 8 | Australia | 2770 | 71 |
| 9 | United Arab Emirates | 2308 | 38 |
| 10 | England | 1976 | 57 |
| Rank | Affiliation | Citation Count | Number of Records |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tanta University | 5808 | 116 |
| 2 | Kafrelsheikh University | 3355 | 68 |
| 3 | Nanjing University | 2877 | 15 |
| 4 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | 2625 | 53 |
| 5 | Huazhong University of Science Technology | 2380 | 33 |
| 6 | MIT | 2002 | 16 |
| 7 | Islamic Azad University | 1751 | 53 |
| 8 | Plataforma Solar Almeria | 1720 | 40 |
| 9 | Georgia Institute of Technology | 1608 | 6 |
| 10 | King Fahad University of Petroleum & Minerals | 1494 | 23 |
| Author Name | Citations | Publications |
|---|---|---|
| Abd Elnaby Kabeel | 3419 | 54 |
| Lin Zhou | 2826 | 10 |
| Zhu Jia | 2763 | 5 |
| Swellam Sharshir | 1876 | 38 |
| Yudi Kuang | 1483 | 5 |
| Chaoji Chen | 1461 | 6 |
| Liangbing Hu | 1455 | 7 |
| John H. Lienhard | 1237 | 6 |
| Yu Guihua | 1146 | 5 |
| Shuaiming He | 1129 | 5 |
| Keyword | Occurrences |
|---|---|
| solar desalination | 924 |
| desalination | 501 |
| energy | 425 |
| performance | 411 |
| water | 244 |
| system | 242 |
| still | 231 |
| solar still | 203 |
| solar energy | 195 |
| seawater desalination | 182 |
| Solar Methodologies | Occurrences |
|---|---|
| still | 231 |
| solar still | 203 |
| nanoparticles | 145 |
| membrane | 125 |
| humidification-dehumidification | 114 |
| photovoltaic | 19 |
| Rank | Title | Citation | Broad Theme | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3D self-assembly of aluminum nanoparticles for plasmon-enhanced solar desalination (Zhou et al., 2016) [37] | 1554 | Plasmonic enhanced absorber | Modified Material Based Evaporator |
| 2 | Graphene oxide-based efficient and scalable solar desalination under one-sun with a confined 2D water path (Li et al., 2016) [43] | 907 | Foldable Graphene Oxide Film absorber | |
| 3 | A hydrogel-based antifouling solar evaporator for highly efficient water desalination (Zhou et al., 2018) [44] | 614 | Hybrid hydrogel (with capillary channels), antifouling properties | |
| 4 | Scaling and fouling in membrane distillation for desalination applications: A review (Warsinger et al., 2015) [45] | 580 | Discusses crystalline fouling, causes, prevention, and future research | Review |
| 5 | A High-Performance Self-Regenerating Solar Evaporator for Continuous Water Desalination (Kuang et al., 2019) [46] | 579 | Self-regenerating natural wood substrate evaporator | Modified Material-Based Evaporator |
| 6 | Nature-inspired salt resistant bimodal porous solar evaporator for efficient and stable water desalination (He et al., 2019) [47] | 436 | Balsa wood-based evaporator, bimodal and porous interconnected channels | |
| 7 | Solar assisted sea water desalination: A review (Li et al., 2013) [48] | 362 | Discusses solar desalination research, suggests modifications | Review |
| 8 | Solar-driven simultaneous steam production and electricity generation from salinity (Yang et al., 2017) [49] | 352 | PV-Blue energy system, using carbon nanotube filter paper with commercial Nafion membrane | Hybrid System |
| 9 | A hydrophobic surface enabled salt-blocking 2D Ti3C2 MXene membrane for efficient and stable solar (Zhao et al., 2018) [50] | 337 | Usage of a hydrophobic Mxene membrane, covered with a Ti3C2 nanosheet | Modified Material-Based Evaporator |
| 10 | Synergistic Energy Nanoconfinement and Water Activation in Hydrogels for Efficient Solar Water Desalination (Guo et al., 2019) [51] | 315 | Light-absorbing sponge-like hydrogel evaporator | |
| 11 | Renewable and sustainable approaches for desalination (Gude et al., 2010) [52] | 313 | Discusses detailed financial assessment on desalination systems | Review |
| 12 | Solar powered desalination—Technology, energy, and future outlook (Ahmed et al., 2019) [53] | 311 | Discusses RO hybrid systems, new advances in solar desalination | |
| 13 | Nanofluids effects on the evaporation rate in a solar still equipped with a heat exchanger (Mahian et al., 2017) [54] | 311 | Effects of heat exchanger on solar still performance indices | Modified Solar Collector |
| 14 | Analysis and optimization of the low-temperature solar organic Rankine cycle (ORC) (Delgado-Torres and García-Rodríguez, 2010) [55] | 302 | Expands upon theoretical research by a solar ORC through Solar Collectors | |
| 15 | Graphene oxide-based evaporator with one-dimensional water transport enabling high-efficiency solar desalination (Li et al., 2017) [56] | 298 | porous carbon black/graphene oxide (CB/GO) composite layer-based evaporator | Modified Material-based Evaporator |
| Challenges | Description |
|---|---|
| high startup costs | When implementing at large industrial scales, the startup costs are very high to maximize the light collected (especially solar stills) (Zheng et al., 2023, Reif and Alhalabi, 2015) [57,58] |
| low efficiency compared to non-solar | The need for further optimization and the energy loss from solar is high, more research and funding are needed to remediate this (Zheng et al., 2023, Reif and Alhalabi, 2015) [57,58] |
| massive brine disposal | The increase in desalination plants, brine generation (highly concentrated saline water) increases which is costly and has detrimental environmental effects (Jones et al., 2019) [59] |
| lack of cost efficiency | The high initial costs drive the payback period to become unfeasible, factoring construction and maintenance costs into account especially when compared to other non-solar derived methodologies (Reif and Alhalabi, 2015) [58] |
| (with regards to PV) energy storage | Systems that make use of photovoltaic cells run into the issues of inefficient storage of harnessed energy through batteries, diminishing the cost-effectives of such systems (Reif and Alhalabi, 2015) [58] |
| lower system operation uptime | Concentrated solar stills/Fresnel concentrators require a lot of upkeep as well as higher end materials to drive the efficiency to acceptable rates, usage of lower quality materials results in less operational uptime (Zheng et al., 2023, Reif and Alhalabi, 2015) [57,58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berana, Y.; Saleem, M.W.; Ali, H.; Mohmmed, A. Visualizing the Landscape and Evolution of Solar Energy-Integrated Desalination Systems via Scientometric Analysis. Energies 2024, 17, 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122857
Berana Y, Saleem MW, Ali H, Mohmmed A. Visualizing the Landscape and Evolution of Solar Energy-Integrated Desalination Systems via Scientometric Analysis. Energies. 2024; 17(12):2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122857
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerana, Yvhan, Muhammad Wajid Saleem, Hassan Ali, and Abdalellah Mohmmed. 2024. "Visualizing the Landscape and Evolution of Solar Energy-Integrated Desalination Systems via Scientometric Analysis" Energies 17, no. 12: 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122857
APA StyleBerana, Y., Saleem, M. W., Ali, H., & Mohmmed, A. (2024). Visualizing the Landscape and Evolution of Solar Energy-Integrated Desalination Systems via Scientometric Analysis. Energies, 17(12), 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122857






