Examining the Spillover Effects of Renewable Energy Policies on China’s Traditional Energy Industries and Stock Markets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Research Methods
DY Spillover Index Model Construction
4. Data and Variable Description
5. Empirical Analysis
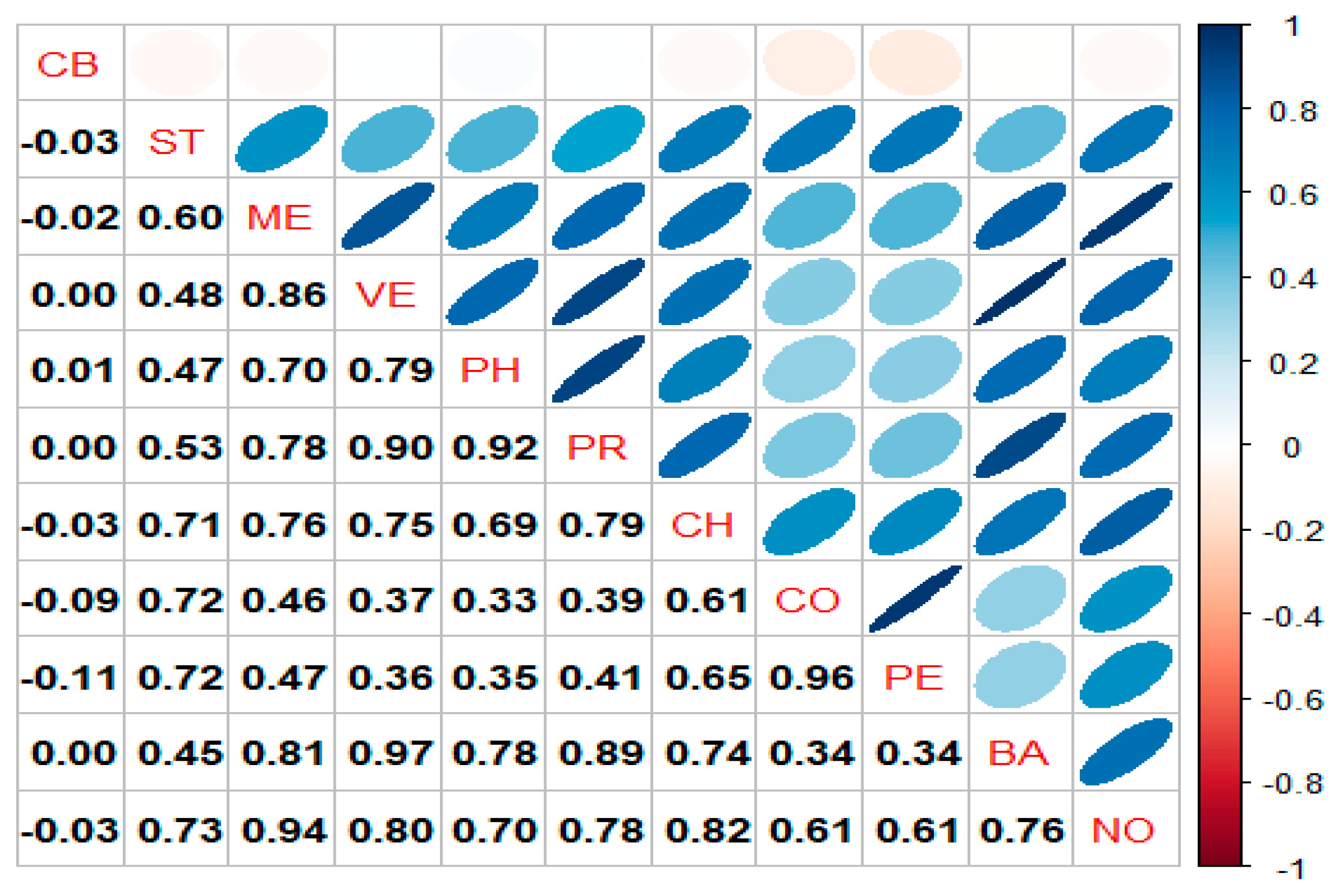
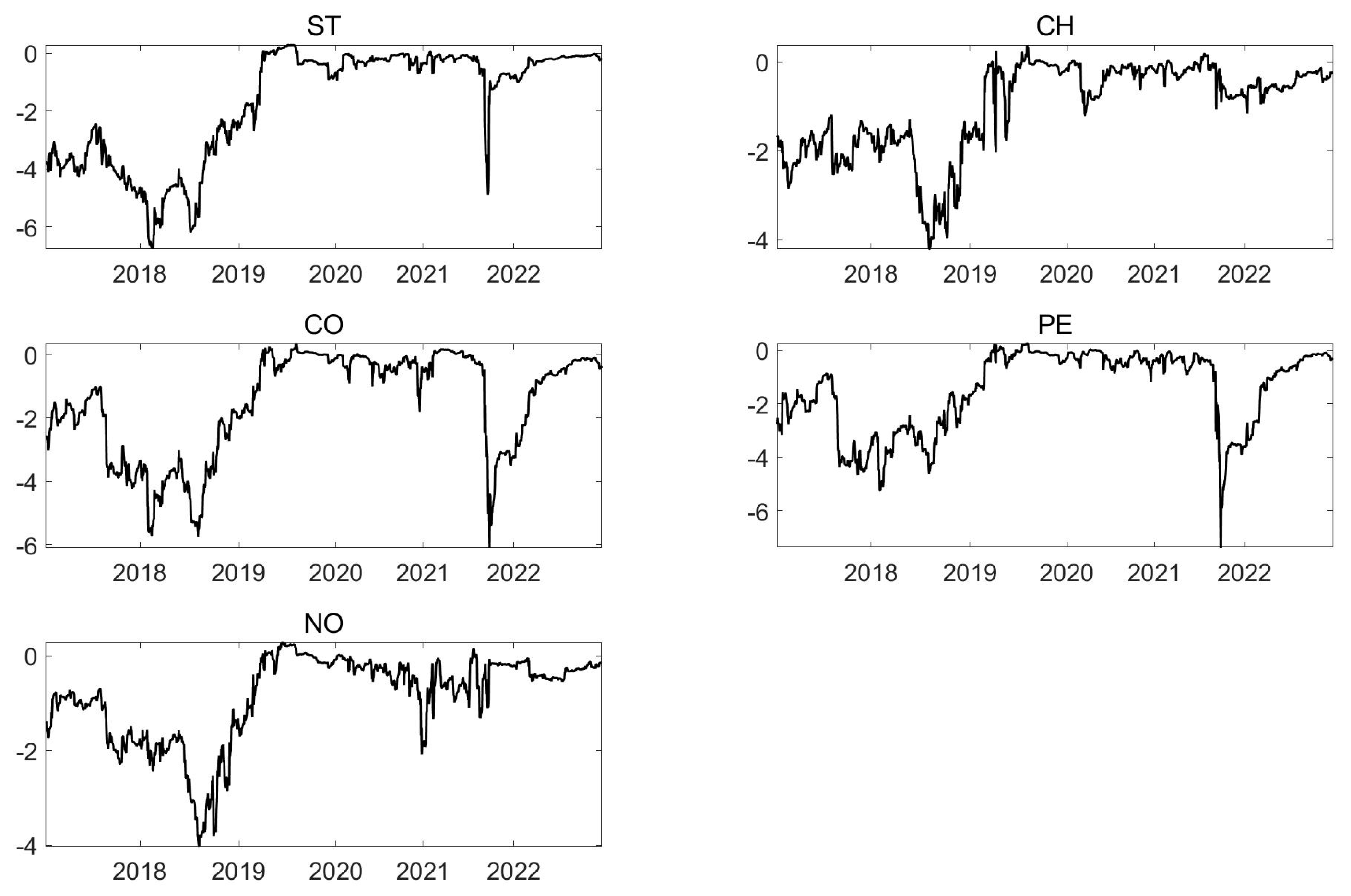
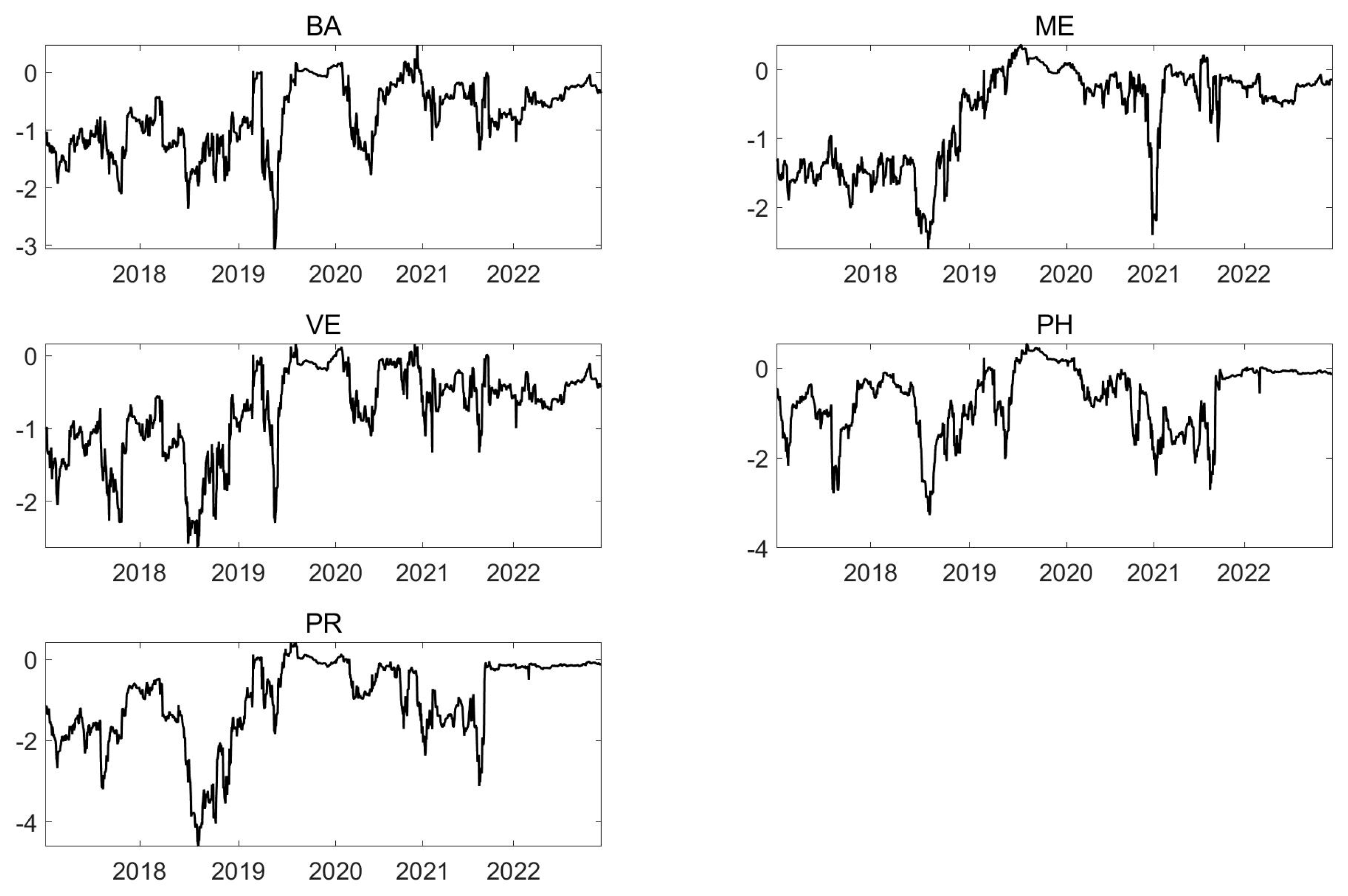
5.1. Static Spillover Index
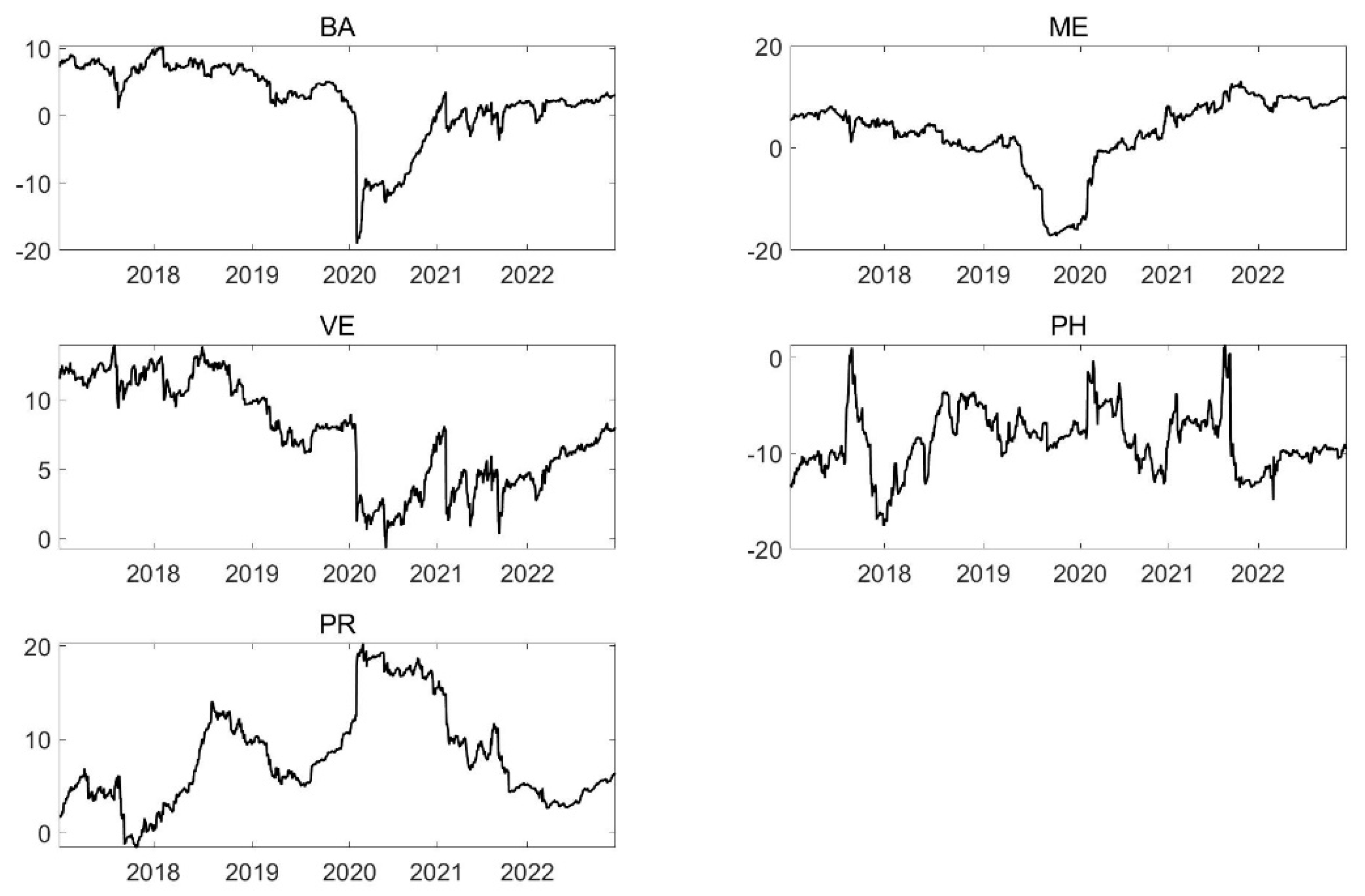
5.2. Dynamic Spillover Index
5.2.1. Total Spillover
5.2.2. Directional Spillover and Net Spillover
5.2.3. The Robustness of the Spillover Index
6. Implications and Conclusions
7. Recommendation
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diebold, F.X.; Yılmaz, K. On the network topology of variance decompositions: Measuring the connectedness of financial firms. J. Econom. 2014, 182, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Zhao, L.; He, S.; Yang, G. Asymmetric relationship between carbon emission trading market and stock market: Evidences from China. Energy Econ. 2020, 91, 104850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-H.; Ren, F.; Yang, M.-Y.; Lu, F.-Z.; Li, S.-P. Dynamic lead–lag relationship between Chinese carbon emission trading and stock markets under exogenous shocks. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2023, 85, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, K.; Huo, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhao, H.; Sun, J.; Guo, S. Research on spillover effect between carbon market and electricity market: Evidence from Northern Europe. Energy 2023, 263, 126107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Chu, L.; Zhou, R.; Xu, H.; Yuan, S. How do carbon, stock, and renewable energy markets interact: Evidence from Europe. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 407, 137106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, T.-t.; Liu, L.-l.; Zhang, M.-x. How do the electricity market and carbon market interact and achieve integrated development?--A bibliometric-based review. Energy 2023, 265, 126308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-R.; Feng, T.-T.; Zhong, C. Effectiveness of CO2 cost pass-through to electricity prices under “electricity-carbon” market coupling in China. Energy 2023, 266, 126387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-W.; Pang, L.-D.; Qin, M.; Lobonţ, O.-R.; Umar, M. The spillover effects among fossil fuel, renewables and carbon markets: Evidence under the dual dilemma of climate change and energy crises. Energy 2023, 274, 127304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wang, B.; Wei, J.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. The role of carbon pricing in achieving energy transition in the Post-COP26 era: Evidence from China’s industrial energy conservation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 182, 113349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnik, K.; Hnydiuk-Stefan, A.; Li, Z.; Ma, Z. Short-term modeling of carbon price based on fuel and energy determinants in EU ETS. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 417, 137970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Feng, M. The dependence between European Union carbon market and crude oil market: A copula analysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 237, 042005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, M. Global transmission of returns among financial, traditional energy, renewable energy and carbon markets: New evidence. Energies 2021, 14, 7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Ren, X.; Shi, Y.; Mishra, T.; Yan, C. The marginal impacts of energy prices on carbon price variations: Evidence from a quantile-on-quantile approach. Energy Econ. 2021, 95, 105131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Xue, Q.; Zhao, R.; Wang, D. Renewable energy technological innovation, market forces, and carbon emission efficiency. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Abakah, E.J.A.; Gabauer, D.; Dwumfour, R.A. Dynamic spillover effects among green bond, renewable energy stocks and carbon markets during COVID-19 pandemic: Implications for hedging and investments strategies. Glob. Financ. J. 2022, 51, 100692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, Y. The time-frequency connectedness among metal, energy and carbon markets pre and during COVID-19 outbreak. Resour. Policy 2022, 77, 102763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Lie, J.; Mo, B. Dynamic dependence nexus and causality of the renewable energy stock markets on the fossil energy markets. Energy 2021, 233, 121191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Poletti, S.; Wen, L.; Sheng, M.S. Dynamic spillovers between the carbon, stock, and energy markets: A New Zealand case. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shen, Z.; Song, M.; Wei, W. Exploring the interconnectedness of China’s new energy and stock markets: A study on volatility spillovers and dynamic correlations. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 89, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirer, R.; Ferrer, R.; Shahzad, S.J.H. Oil price shocks, global financial markets and their connectedness. Energy Econ. 2020, 88, 104771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Sirichand, K.; Vivian, A.; Wang, X. How connected is the carbon market to energy and financial markets? A systematic analysis of spillovers and dynamics. Energy Econ. 2020, 90, 104870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta-Mensah, J. Commodity-linked bonds as an innovative financing instrument for African countries to build back better. Quant. Financ. Econ. 2021, 5, 516–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikiru, A.A.; Salisu, A.A. Hedging with financial innovations in the Asia-Pacific markets during the COVID-19 pandemic: The role of precious metals. Quant. Financ. Econ. 2021, 5, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ao, Z.; Mo, B. Revisiting the valuable roles of global financial assets for international stock markets: Quantile coherence and causality-in-quantiles approaches. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, B.; Meng, J.; Wang, G. Risk Dependence and Risk Spillovers Effect from Crude Oil on the Chinese Stock Market and Gold Market: Implications on Portfolio Management. Energies 2023, 16, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Mo, B.; Nie, H. The dynamics of crude oil future prices on China’s energy markets: Quantile-on-quantile and casualty-in-quantiles approaches. J. Futures Mark. 2023, 43, 1853–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Z. Multidimensional risk spillovers among carbon, energy and nonferrous metals markets: Evidence from the quantile VAR network. Energy Econ. 2022, 114, 106319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhu, J. Energy and carbon intensity in China during the urbanization and industrialization process: A panel VAR approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Shi, R.; Xu, J.; Lin, B. Analyzing spillover effects between carbon and fossil energy markets from a time-varying perspective. Appl. Energy 2021, 285, 116384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonakakis, N.; Gabauer, D. Refined measures of dynamic connectedness based on TVP-VAR. Munich Pers. RePEc Arch. 2017, 78282. Available online: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/78282/ (accessed on 12 April 2017).
- Huang, Y.; Dai, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, D. A hybrid model for carbon price forecasting using GARCH and long short-term memory network. Appl. Energy 2021, 285, 116485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargallo, P.; Lample, L.; Miguel, J.A.; Salvador, M. Co-movements between EU ETS and the energy markets: A VAR-DCC-GARCH approach. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, M.; Khan, H. Does carbon asset add value to clean energy market? Evidence from EU. Green Financ. 2021, 3, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alola, A.A.; Bekun, F.V. Pandemic outbreaks (COVID-19) and sectoral carbon emissions in the United States: A spillover effect evidence from Diebold and Yilmaz index. Energy Environ. 2021, 32, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, F.X.; Yilmaz, K. Better to give than to receive: Predictive directional measurement of volatility spillovers. Int. J. Forecast. 2012, 28, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, F.X.; Yilmaz, K. Measuring financial asset return and volatility spillovers, with application to global equity markets. Econ. J. 2009, 119, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

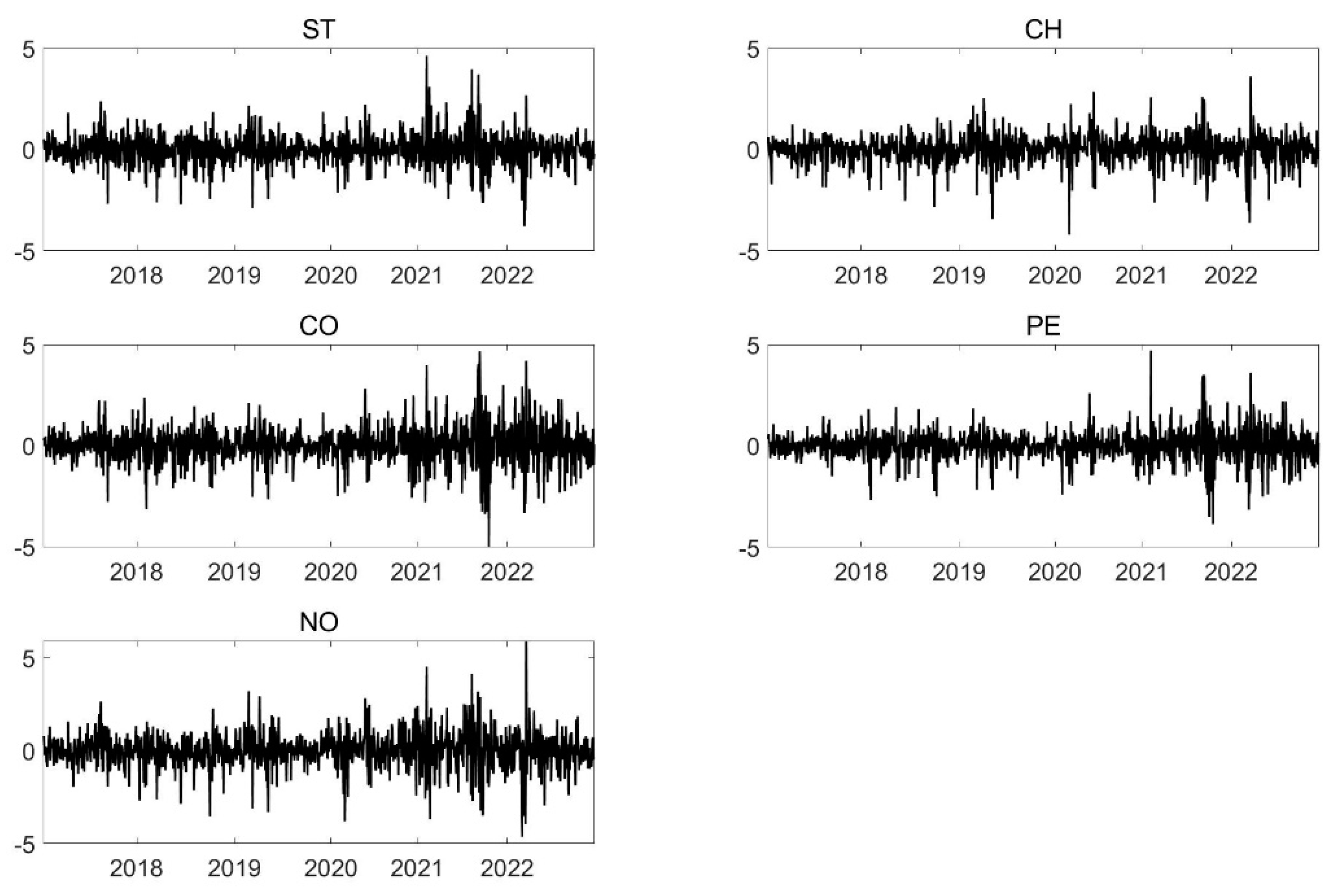
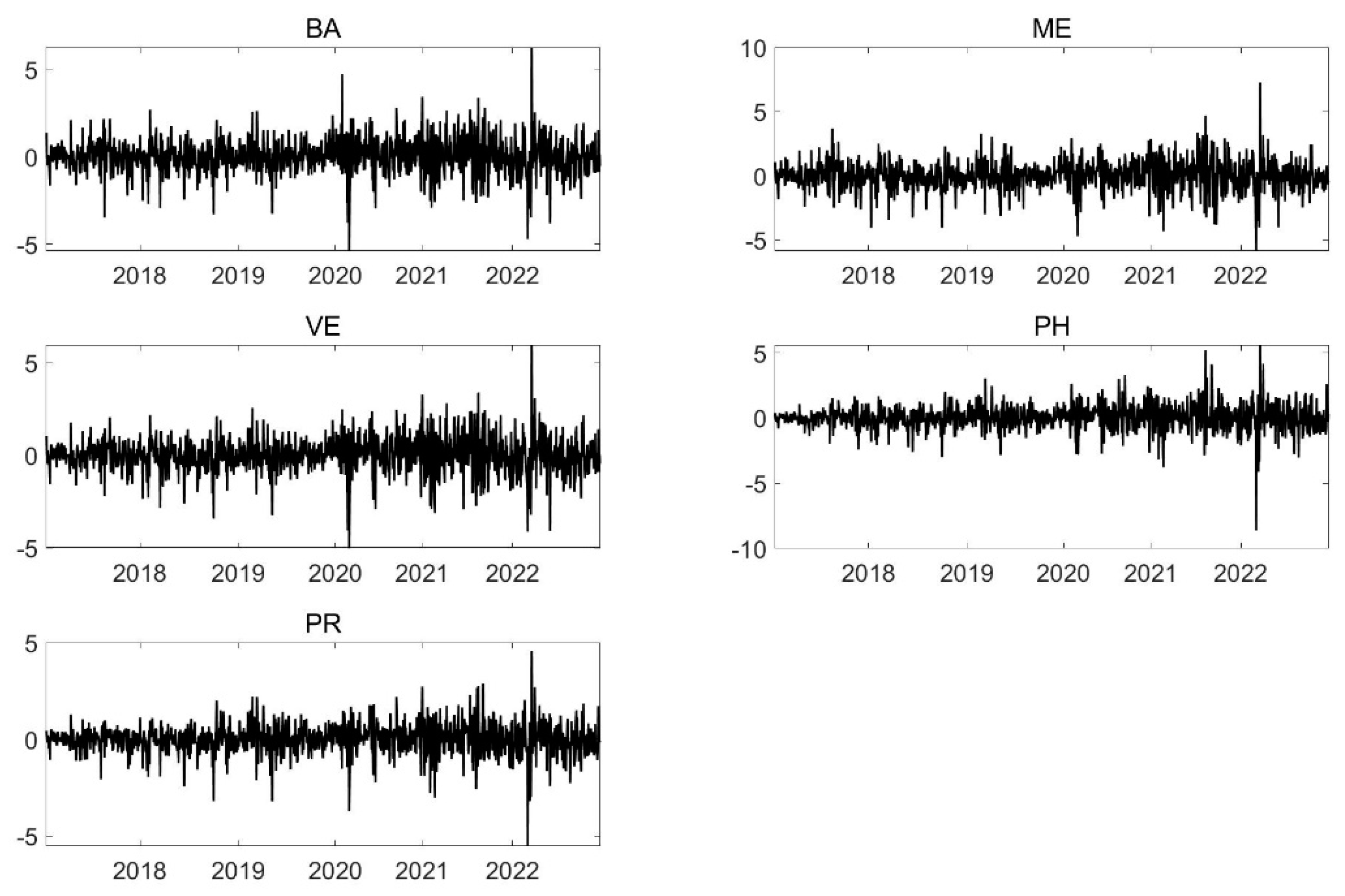



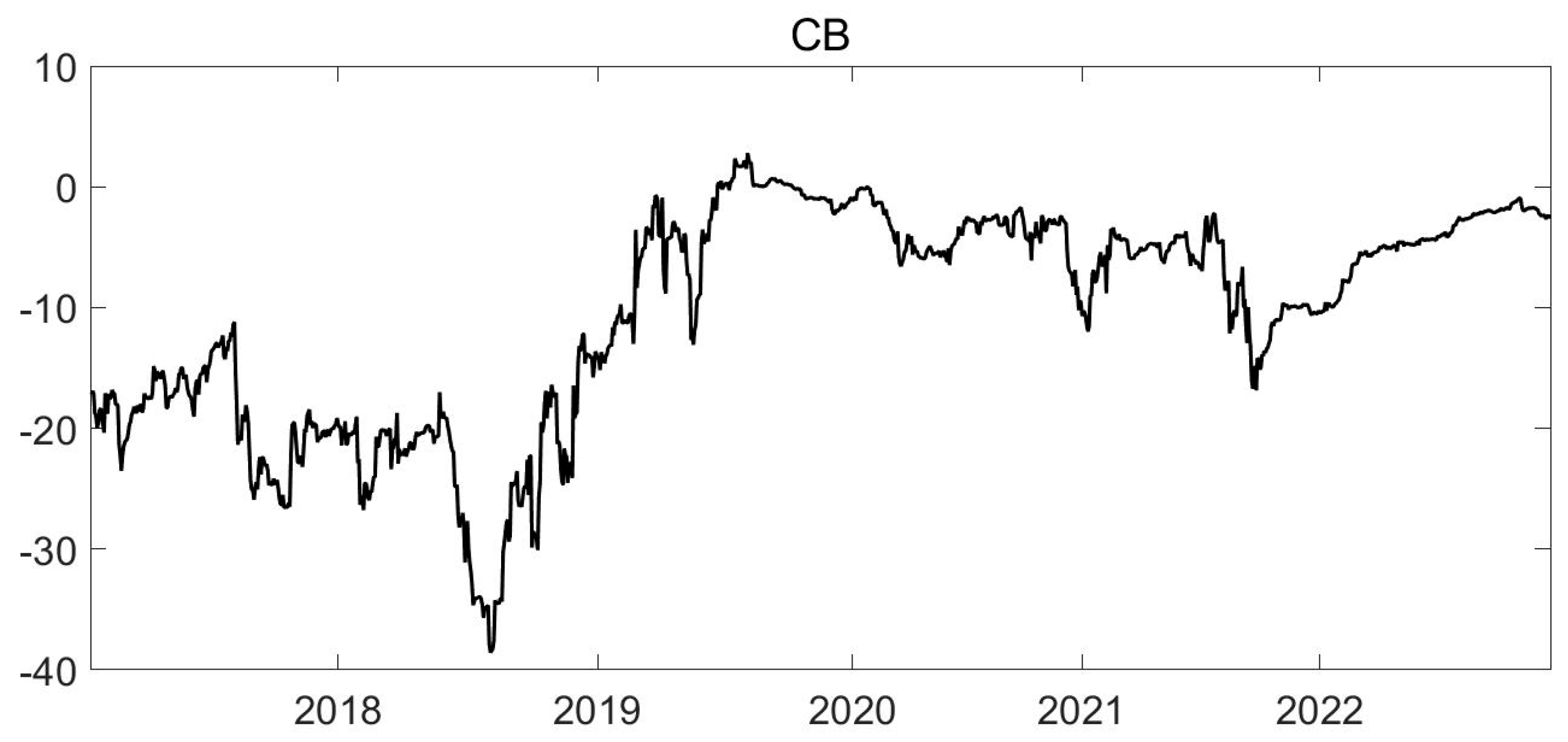


| Min | Max | Mean | S.D. | Skew | Kurt | JB | ADF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB | −120.412 | 146.344 | 0.0185 | 16.2630 | 0.320 | 15.458 | 12,519.191 *** | −57.053 *** |
| ST | −3.7848 | 4.6237 | 0.0004 | 0.7629 | 0.052 | 3.647 | 694.953 *** | −36.19 *** |
| ME | −5.8372 | 7.2720 | 0.0232 | 1.1247 | −0.143 | 3.300 | 572.476 *** | −34.378 *** |
| VE | −5.0393 | 5.9550 | 0.0193 | 0.9450 | −0.197 | 3.288 | 572.368 *** | −33.983 *** |
| PH | −8.6209 | 5.5933 | 0.0257 | 0.9481 | −0.398 | 8.210 | 3556.668 *** | −36.305 *** |
| PR | −5.5193 | 4.5705 | 0.0061 | 0.7776 | −0.419 | 4.623 | 1153.262 *** | −35.188 *** |
| CH | −4.2021 | 3.6064 | 0.0032 | 0.7152 | −0.553 | 3.704 | 780.364 *** | −34.606 *** |
| CO | −5.0241 | 4.6636 | 0.0214 | 0.9124 | 0.014 | 3.286 | 563.529 *** | −34.52 *** |
| PE | −3.8627 | 4.7001 | 0.0080 | 0.7388 | 0.102 | 4.743 | 1177.173 *** | −36.423 *** |
| BA | −5.3829 | 6.2398 | 0.0293 | 0.9801 | −0.094 | 3.505 | 643.055 *** | −34.38 *** |
| NO | −4.6367 | 5.9044 | 0.0125 | 0.9422 | −0.135 | 3.790 | 753.673 *** | −36.196 *** |
| CB | ST | ME | VE | PH | PR | CH | CO | PE | BA | NO | FROM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB | 84.58 | 1.88 | 1.03 | 1.26 | 1.26 | 1.25 | 1.47 | 2.29 | 2.14 | 1.31 | 1.53 | 15.42 |
| ST | 0.35 | 21.29 | 7.64 | 5.65 | 5.47 | 6.91 | 10.83 | 12.79 | 12.71 | 5.01 | 11.36 | 78.71 |
| ME | 0.34 | 6.41 | 16.85 | 12.53 | 8.04 | 10.25 | 9.69 | 4.83 | 4.95 | 11.15 | 14.97 | 83.15 |
| VE | 0.27 | 4.85 | 11.99 | 16.04 | 9.94 | 12.91 | 9.66 | 4.11 | 4.26 | 15.21 | 10.75 | 83.96 |
| PH | 0.3 | 5.45 | 9.13 | 11.62 | 18.68 | 15.58 | 9.68 | 4.3 | 4.7 | 11.38 | 9.18 | 81.32 |
| PR | 0.23 | 5.74 | 9.73 | 12.72 | 13.17 | 15.8 | 10.63 | 4.6 | 5.04 | 12.5 | 9.85 | 84.2 |
| CH | 0.38 | 8.57 | 9.55 | 9.76 | 8.31 | 10.85 | 16.58 | 7.29 | 7.91 | 9.38 | 11.42 | 83.42 |
| CO | 0.6 | 13.13 | 5.71 | 4.79 | 4.36 | 5.61 | 9.51 | 22.3 | 20.24 | 4.09 | 9.67 | 77.7 |
| PE | 0.65 | 12.72 | 5.71 | 4.88 | 4.63 | 6.01 | 10.13 | 19.7 | 21.63 | 4.26 | 9.66 | 78.37 |
| BA | 0.31 | 4.5 | 11.21 | 16.07 | 10.26 | 13.37 | 9.71 | 3.73 | 3.92 | 16.95 | 9.98 | 83.05 |
| NO | 0.32 | 8.53 | 13.82 | 10.33 | 7.53 | 9.61 | 10.65 | 7.19 | 7.36 | 9.16 | 15.49 | 84.51 |
| TO | 3.75 | 71.77 | 85.52 | 89.61 | 72.96 | 92.35 | 91.95 | 70.83 | 73.24 | 83.44 | 98.37 | 833.79 |
| NET | −11.67 | −6.94 | 2.37 | 5.66 | −8.35 | 8.15 | 8.53 | −6.87 | −5.13 | 0.4 | 13.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Yu, M.; Meng, J.; Jiang, Y. Examining the Spillover Effects of Renewable Energy Policies on China’s Traditional Energy Industries and Stock Markets. Energies 2024, 17, 2563. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17112563
Zhao H, Yu M, Meng J, Jiang Y. Examining the Spillover Effects of Renewable Energy Policies on China’s Traditional Energy Industries and Stock Markets. Energies. 2024; 17(11):2563. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17112563
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Haiwen, Miao Yu, Juan Meng, and Yonghong Jiang. 2024. "Examining the Spillover Effects of Renewable Energy Policies on China’s Traditional Energy Industries and Stock Markets" Energies 17, no. 11: 2563. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17112563
APA StyleZhao, H., Yu, M., Meng, J., & Jiang, Y. (2024). Examining the Spillover Effects of Renewable Energy Policies on China’s Traditional Energy Industries and Stock Markets. Energies, 17(11), 2563. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17112563




