Integrating Statistical Simulation and Optimization for Redundancy Allocation in Smart Grid Infrastructure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
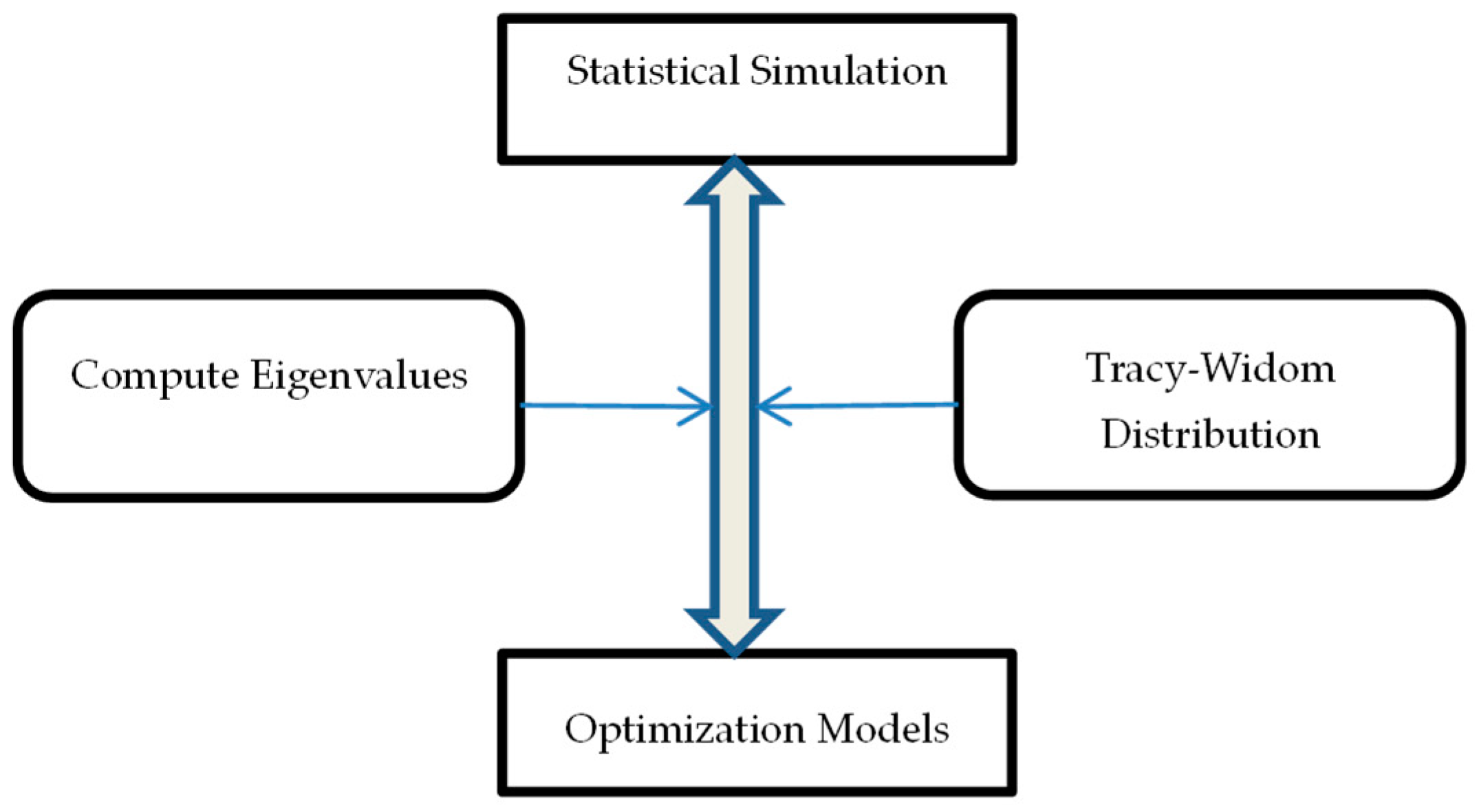
2.1. Statistical Simulation and Optimization Framework
| Algorithm 1. Statistical simulation–optimization framewor |
| 1 |
| 2 Generate eigenvectors V |
| 3 matrix |
| 4 Sort eigenvalues λ |
| 5 |
| 6 matrix |
| 7 matrix |
| 8 follows TW distribution |
| 9 Apply clustering method |
| 10 IP optimization |
| 11 Form the clusters |
| 12 Apply CNP reduction model |
| 13 Identify the critical nodes IP: |
| 14 Minimize total connectivity CNP: |
| 15 If (total connectivity is min.) Critical Nodes are found |
| 16 Allocate resources to improve resilience |
2.2. Optimization Model for Redundancy Allocation
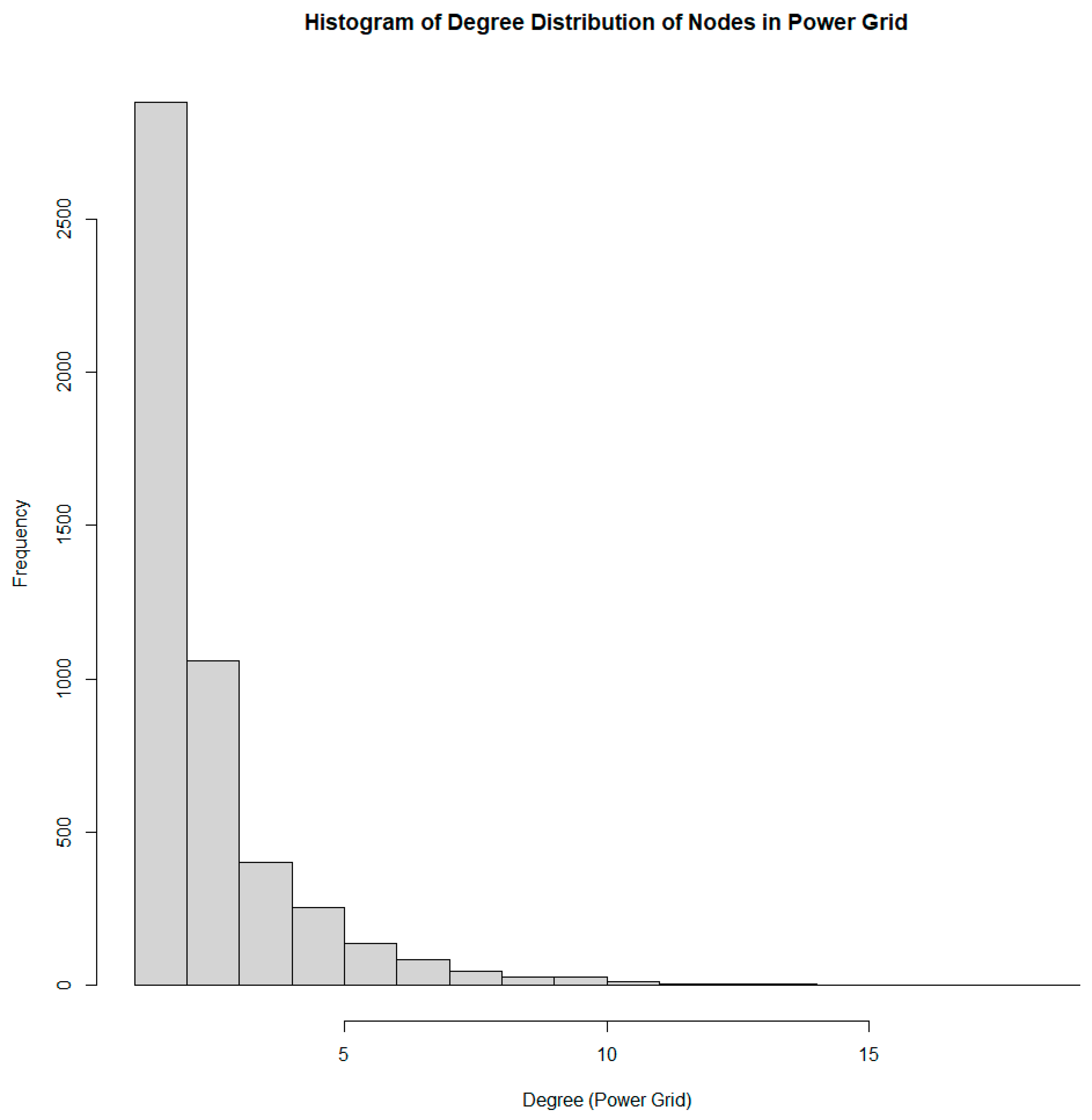
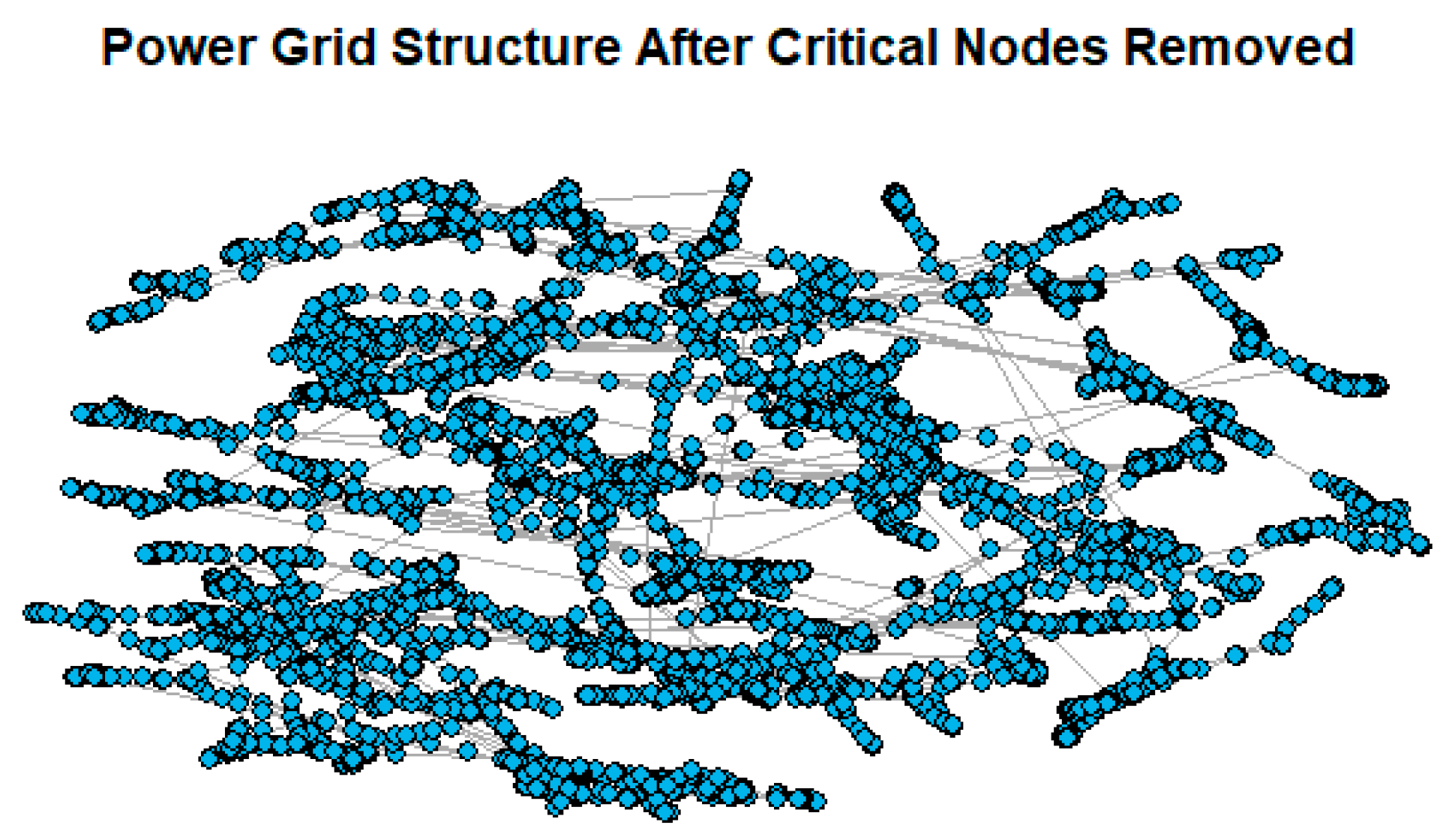
3. Results
4. Discussion
- Redundancy planning—Identify critical components in the smart grid infrastructure. Allocate redundancy by duplicating these components, ensuring backup systems are in place to seamlessly take over in case of failures;
- Risk assessment—Conduct a thorough risk analysis to understand potential failure points. Allocate redundancies to the most vulnerable areas identified during this assessment;
- Advanced monitoring—Implement real-time monitoring systems to detect anomalies and potential failures. Use data analytics to predict failure patterns and allocate redundancies accordingly.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Office of Nuclear Energy. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/ne/articles/department-energy-report-explores-us-advanced-small-modular-reactors-boost-grid (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Department of Energy, Office of Electricity. Available online: https://www.smartgrid.gov/the_smart_grid/smart_grid.html (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Saleem, M.U.; Shakir, M.; Usman, M.R.; Bajwa, M.H.T.; Shabbir, N.; Shams Ghahfarokhi, P.; Daniel, K. Integrating Smart Energy Management System with Internet of Things and Cloud Computing for Efficient Demand Side Management in Smart Grids. Energies 2023, 16, 4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Ker, P.J.; Mansor, M.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Al-Shetwi, A.Q.; Alghamdi, S.M.; Begum, R.A.; Tiong, S.K. Recent advancement of energy internet for emerging energy management technologies: Key features, potential applications, methods and open issues. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 3970–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, G.; Batta, R. Review of recent developments in OR/MS research in disaster operations management. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 230, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sharman, R.; Zionts, S. Functionality defense through diversity a design framework to multitier systems. Ann. Oper. Res. 2012, 197, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, R.K.; Josephkutty, J. An IOT based efficient energy management in smart grid using DHOCSA technique. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 79, 103727. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P.; Singh, G. Energy Management Systems in Sustainable Smart Cities Based on the Internet of Energy: A Technical Review. Energies 2023, 16, 6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.Z.; Ahmed, E.; Hakak, S.; Yaqoob, I.; Ahmed, A. Edge computing A survey. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 97, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavromoustakis, C.X.; Batalla, J.M.; Mastorakis, G.; Markakis, E.; Pallis, E. Socially Oriented Edge Computing for Energy Awareness in IoT Architectures. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, A.; Abozariba, R.; Patwary, M.; Aneiba, A.; Jindal, A. Clustering-based Redundancy Minimization for Edge Computing in Future Core Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 4th 5G World Forum (5GWF), Montreal, QC, Canada, 13–15 October 2021; pp. 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakarami, A.; Ghobaei-Arani, M.; Shahidinejad, A. A survey on the computation offloading approaches in mobile edge computing A machine learning-based perspective. Comput. Netw. 2020, 182, 107496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ma, X.; Fan, X.; Liu, J.; Gong, W. When deep learning meets edge computing. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 25th International Conference on Network Protocols (ICNP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 10–13 October 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, I. Small-World and Scale-Free Network Models for IoT Systems. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2017, 2017, 6752048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faloutsos, M.; Faloutsos, P.; Faloutsos, C. On power-law relationships of the Internet topology. In Proceedings of the Conference on Applications, Technologies, Architectures, and Protocols for Computer Communication, Cambridge, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bebortta, S.; Senapati, D.; Rajput, N.K.; Singh, A.K.; Rathi, V.K.; Pandey, H.M.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Qian, J.; Tiwari, P. Evidence of power-law behavior in cognitive IoT applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 16043–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-g.; Zhu, Y.-n.; Zhao, C.-p.; Dai, W.-b. A new constructing approach for a weighted topology of wireless sensor networks based on local-world theory for the Internet of Things (IOT). Comput. Math. Appl. 2012, 64, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsidis, A.; Dyśko, A.; Booth, C.; Rousis, A.O.; Kalliga, P.; Tzelepis, D. Digital Architecture for Monitoring and Operational Analytics of Multi-Vector Microgrids Utilizing Cloud Computing, Advanced Virtualization Techniques, and Data Analytics Methods. Energies 2023, 16, 5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, L.A.; Loeb, M.P. The Economics of Information Security Investment. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur. 2002, 5, 438–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.; Lee, J.-N.; Straub, D.W. Institutional influences on information systems security innovations. Inf. Syst. Res. 2012, 23 Pt 2, 918–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Bapna, S. The economic impact of cyber terrorism. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2013, 22, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chaudhury, A.; Rao, H.R. Research Note-A Value-at-Risk Approach to Information Security Investment. Inf. Syst. Res. 2008, 19, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, B.K. Entropy based spatial domain image watermarking and its performance analysis. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 9315–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veremyev, A.; Prokopyev, O.A.; Pasiliao, E.L. An integer programming framework for critical elements detection in graphs. J. Comb. Optim. 2014, 28, 233–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlikov, K. Improved formulations for minimum connectivity network interdiction problems. Comput. Oper. Res. 2018, 97, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventresca, M. Global search algorithms using a combinatorial unranking-based problem representation for the critical node detection problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2012, 39, 2763–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Jin, L.; Song, M.; Li, Z. A new approach for evaluating node importance in complex networks via deep learning methods. Neurocomputing 2022, 497, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Chow, T.W.S.; Sun, Y.; Shan, J.; Lau, B.C.P. Kuiper test and autoregressive model-based approach for wireless sensor network fault diagnosis. Wirel. Netw. 2015, 21, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, C.A.; Widom, H. On orthogonal and symplectic matrix ensembles. Commun. Math. Phys. 1996, 177, 727–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulturel-Konak, S.; Smith, A.E.; Coit, D.W. Efficiently Solving the Redundancy Allocation Problem Using Tabu Search. IIE Trans. 2003, 35, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.B.M. Optimal redundancy allocation for information technology disaster recovery in the network economy, Dependable and Secure Computing. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2005, 2, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattrysse, D.G.; Wassenhove, L.N.V. A survey of algorithms for the generalized assignment problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1992, 60, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öncan, T. A survey of the generalized assignment problem and its applications. INFOR Inf. Syst. Oper. Res. 2007, 45, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Garg, H.; Garg, D. A review of redundancy allocation problem for two decades bibliometrics and future directions. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 7457–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Alidaee, B.; Ortiz, J.; Wang, W. The multi-skilled multi-period workforce assignment problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 59, 5477–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huo, D.; Alidaee, B. Position Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in the Mobile Ad Hoc Network. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2014, 74, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alidaee, B.; Gao, H.; Wang, H. A note on task assignment of several problems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2010, 59, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G. Cross-Utilization of Workers Whose Capabilities Differ. Manag. Sci. 1999, 45, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G.M.; Diaby, M. Developing and evaluation of an assignment heuristic for allocating cross-trained workers. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 138, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadatdiynov, K.; Cui, L.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.Z.; Salloum, S.; Mahmud, M.S. A review of optimization methods for computation offloading in edge computing networks. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2022, 9, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zeadally, S.; Chen, Z.; Labiod, H.; Wang, L. A survey on computation offloading modeling for edge computing. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2020, 169, 102781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alidaee, B.; Kochenberger, G.; Wang, H. Theorems Supporting r-flip Search for Pseudo-Boolean Optimization. Int. J. Appl. Metaheuristic Comput. 2010, 1, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Alidaee, B. Unrelated Parallel Machine Selection and Job Scheduling with the Objective of Minimizing Total Workload and Machine Fixed Costs. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2018, 15, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavero, S.; Pardo, E.G.; Glover, F.; Martí, R. Strategic oscillation tabu search for improved hierarchical graph drawing. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 243, 122668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of “small-world” networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauset, A.; Shalizi, C.R.; Newman, M.E.J. Power-Law Distributions in Empirical Data. SIAM Rev. 2009, 51, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copper Development Association. Available online: https://www.copper.org/environment/sustainable-energy/transformers/education/trans_life_cycle.html (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Electricity Delivery and Energy Reliability. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/articles/economic-benefits-increasing-electric-grid-resilience-weather-outages (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Volodarsky, M. The Smart Grid, A Smart Investment. Available online: https://esg.wharton.upenn.edu/news/the-smart-grid-a-smart-investment/ (accessed on 1 July 2023).
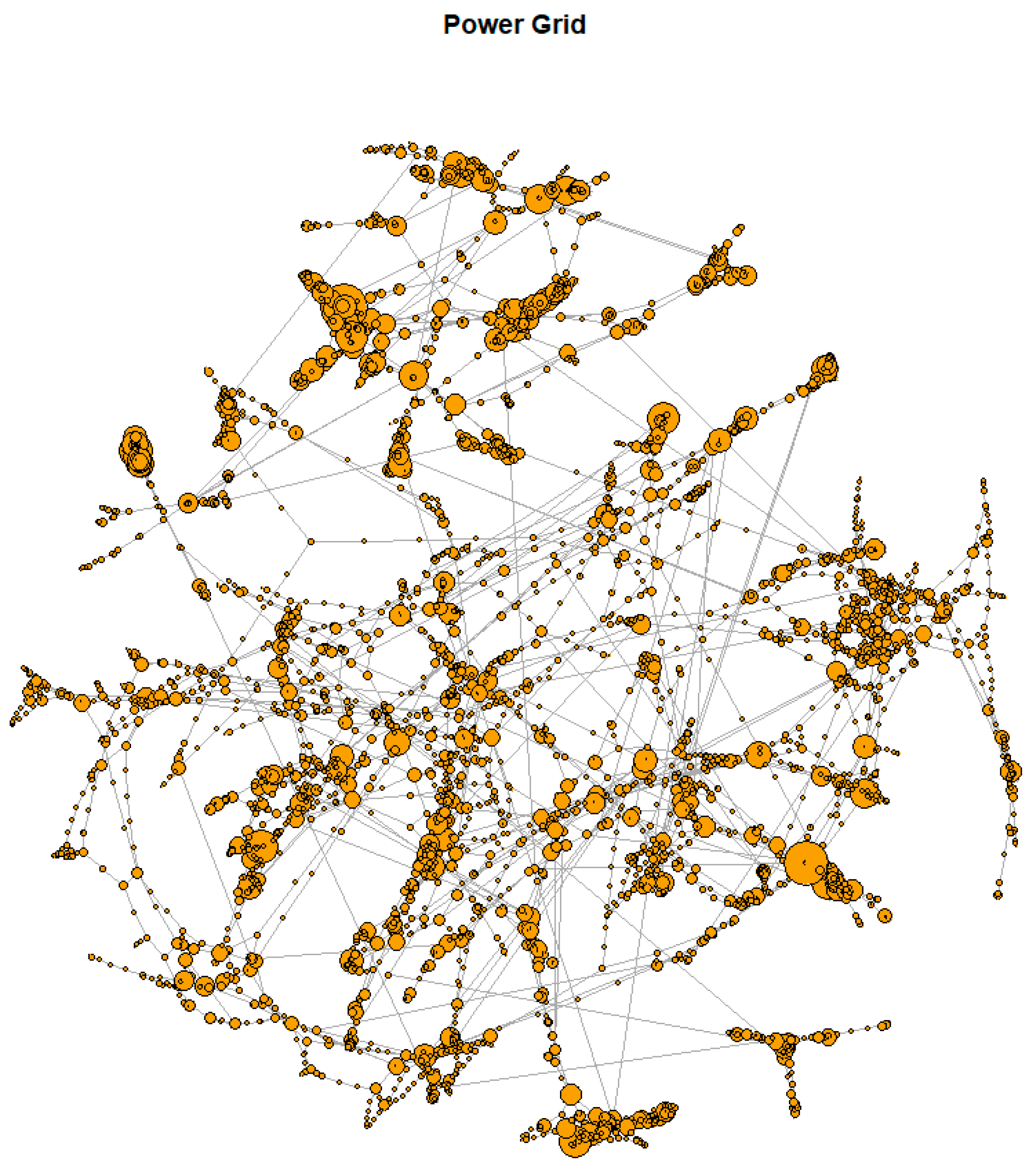
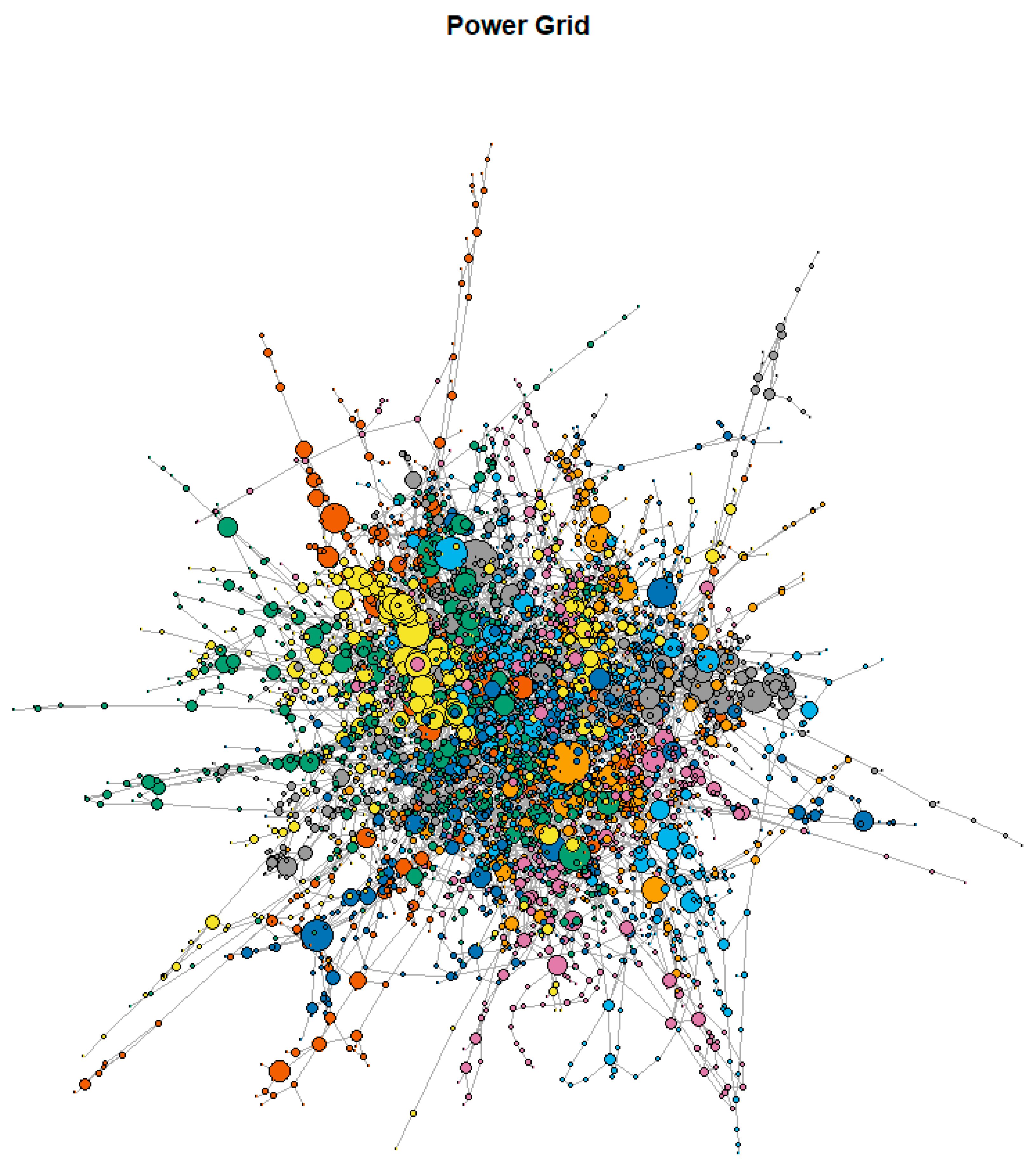


| Class | Methods | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Entropy-based | Graph neural network | [23] |
| NodedDeletion | Mixed integer programming | [24] |
| Network interdiction | Mixed integer linear programming | [25] |
| Maximum k-cut problem | Simulated annealing | [26] |
| Class | Methods | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Model-based | Structure–mechanics | [28] |
| Distribution-based | Tracy–Widom distribution | [29] |
| Number of Removed Critical Nodes | Connectivity |
|---|---|
| 5 | 0.0615851 |
| 10 | 0.0605954 |
| 15 | 0.0592443 |
| PowerGrid | Size | Critical Nodes | Cost of Redundancy (USD) | Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Carolina cities | 500 | 13 | 13,744,377 | 99.74% |
| Texas cities | 2000 | 17 | 19,378,002 | 99.66% |
| Texas state | 6717 | 31 | 47,454,580 | 99.63% |
| Midwest | 24,000 | 59 | 104,646,071 | 99.61% |
| West-East US | 80,000 | 156 | 312,855,059 | 98.79% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alidaee, B.; Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Sua, L.S. Integrating Statistical Simulation and Optimization for Redundancy Allocation in Smart Grid Infrastructure. Energies 2024, 17, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17010225
Alidaee B, Wang H, Huang J, Sua LS. Integrating Statistical Simulation and Optimization for Redundancy Allocation in Smart Grid Infrastructure. Energies. 2024; 17(1):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17010225
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlidaee, Bahram, Haibo Wang, Jun Huang, and Lutfu S. Sua. 2024. "Integrating Statistical Simulation and Optimization for Redundancy Allocation in Smart Grid Infrastructure" Energies 17, no. 1: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17010225
APA StyleAlidaee, B., Wang, H., Huang, J., & Sua, L. S. (2024). Integrating Statistical Simulation and Optimization for Redundancy Allocation in Smart Grid Infrastructure. Energies, 17(1), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17010225










