Simulation of the Asphaltene Deposition Rate in Oil Wells under Different Multiphase Flow Condition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Models
2.1. Eulerian–Eulerian Gas–Liquid Two-Phase Flow Modeling
2.2. Asphaltene Particle Movement
2.3. Turbulence Model
3. Numerical Method
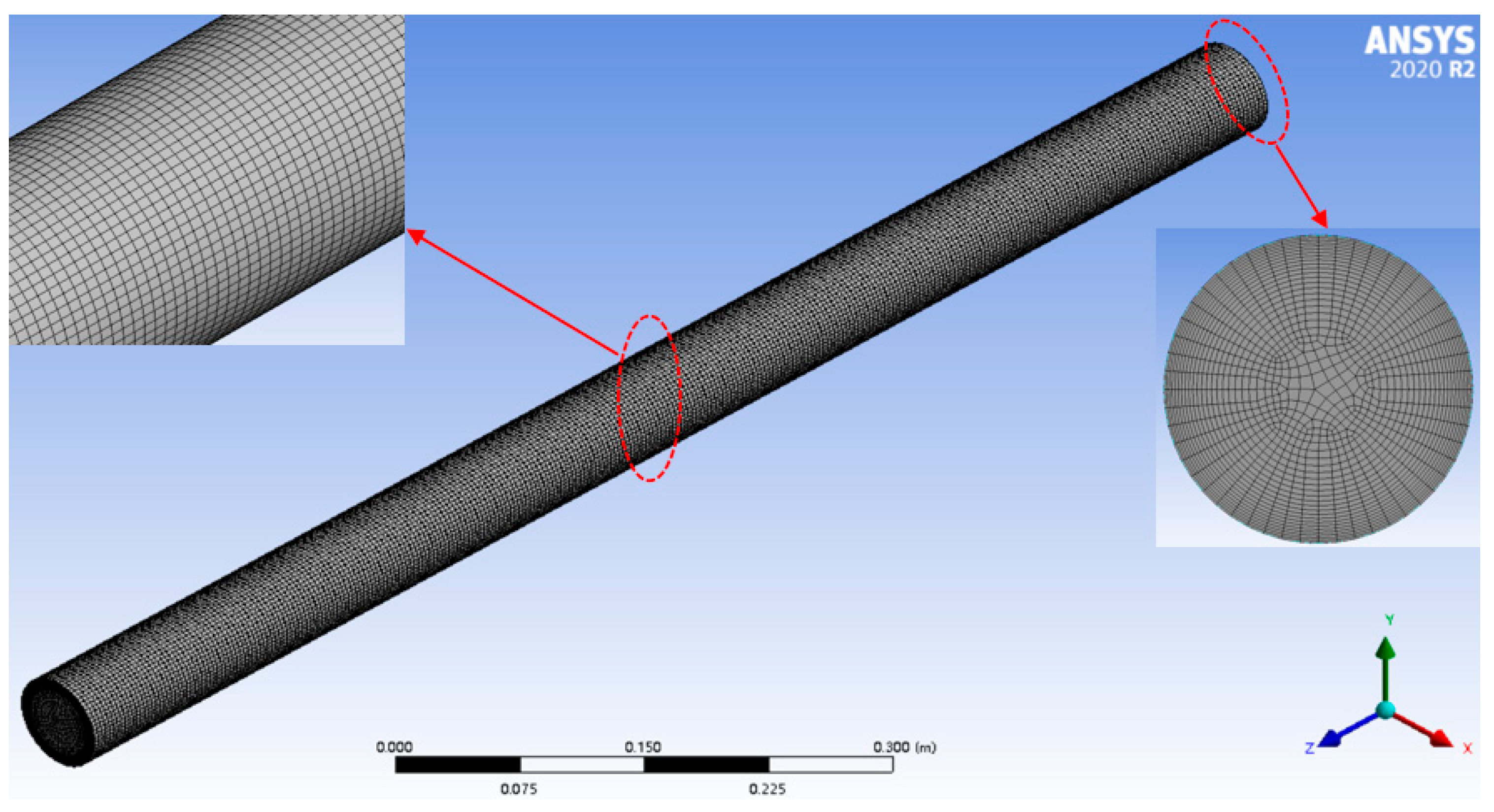
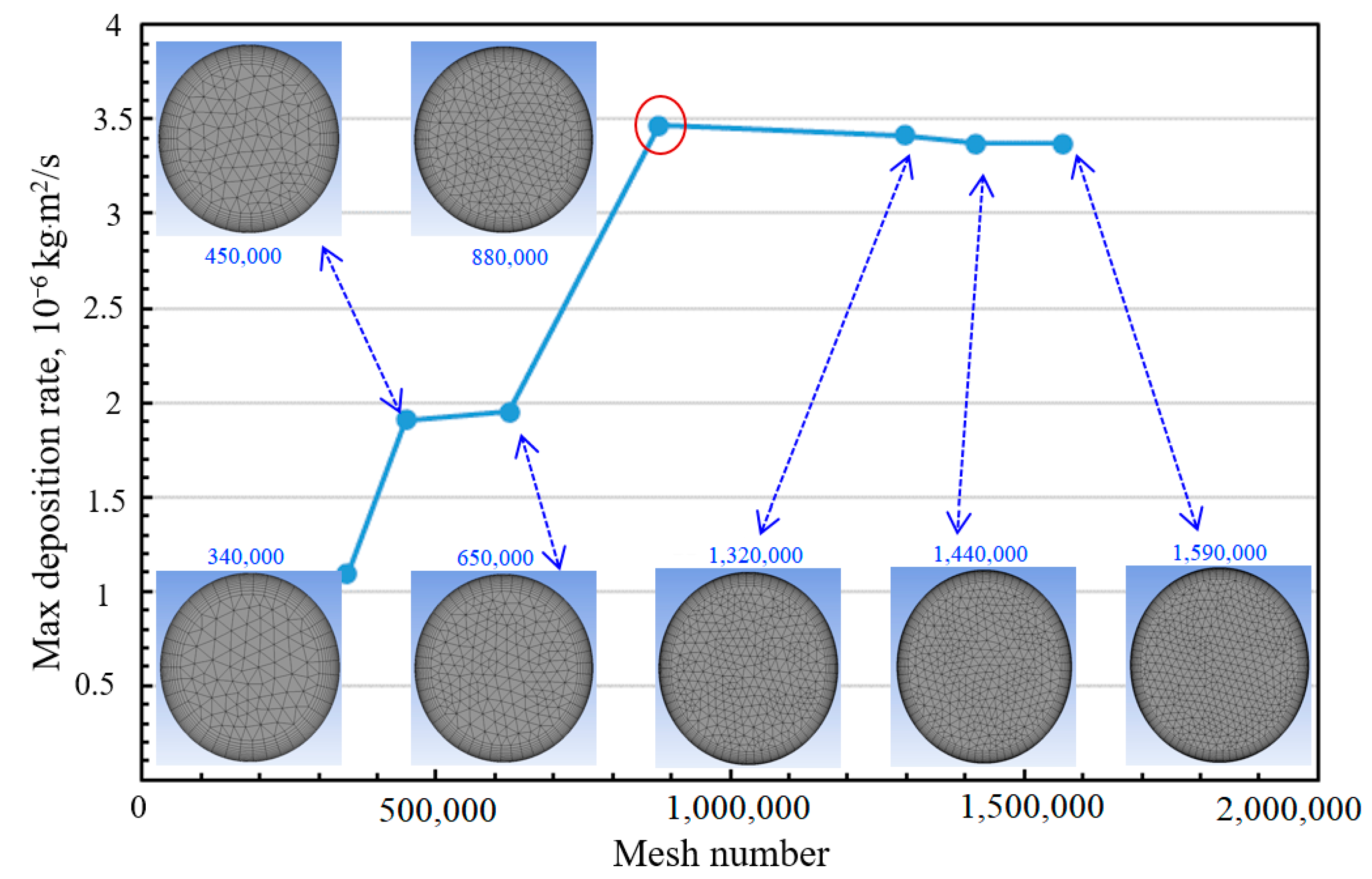
3.1. Geometry Generation and Mesh
3.2. Boundary Condition
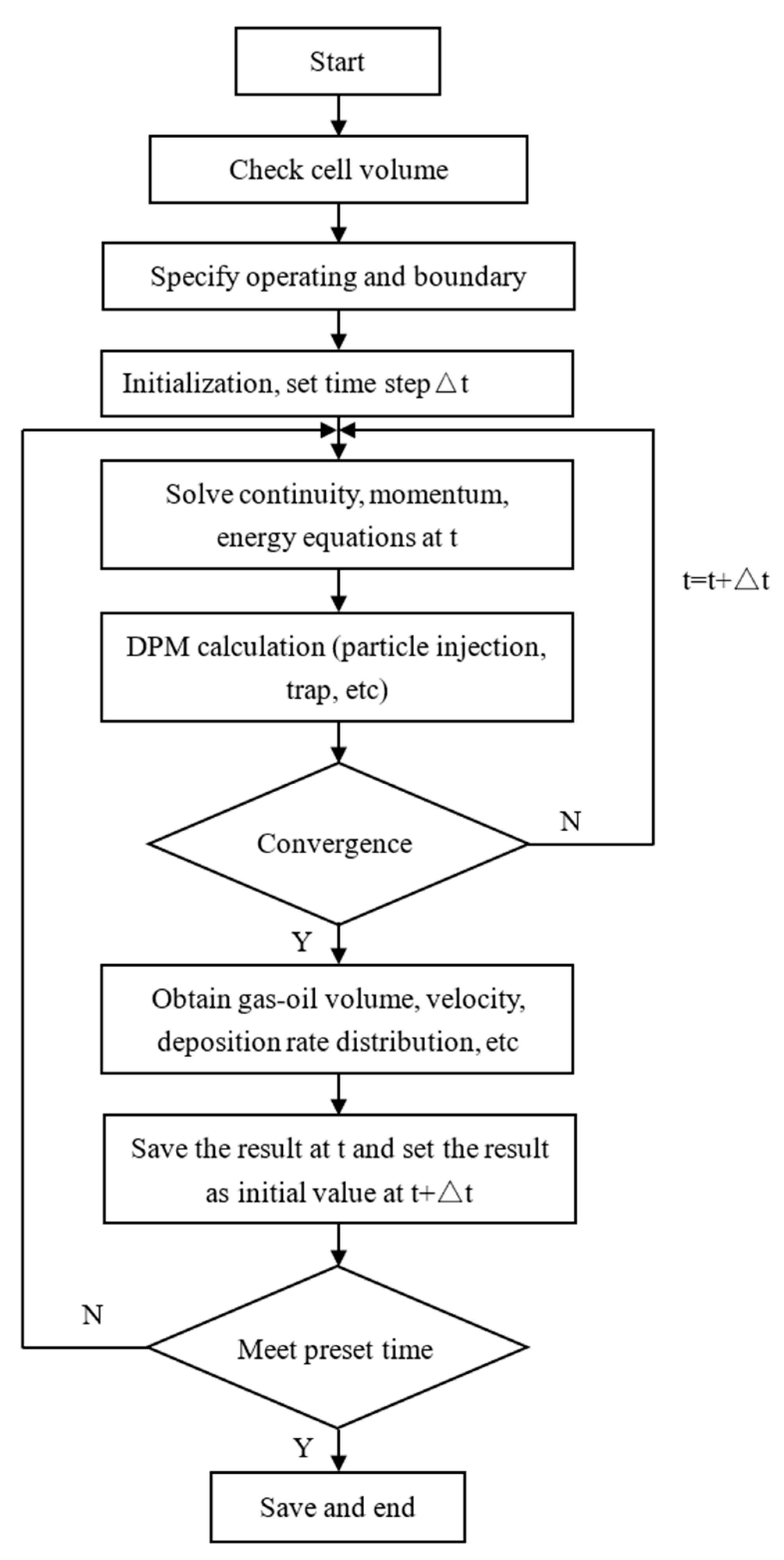
3.3. Calculation Method
4. CFD Simulation Results
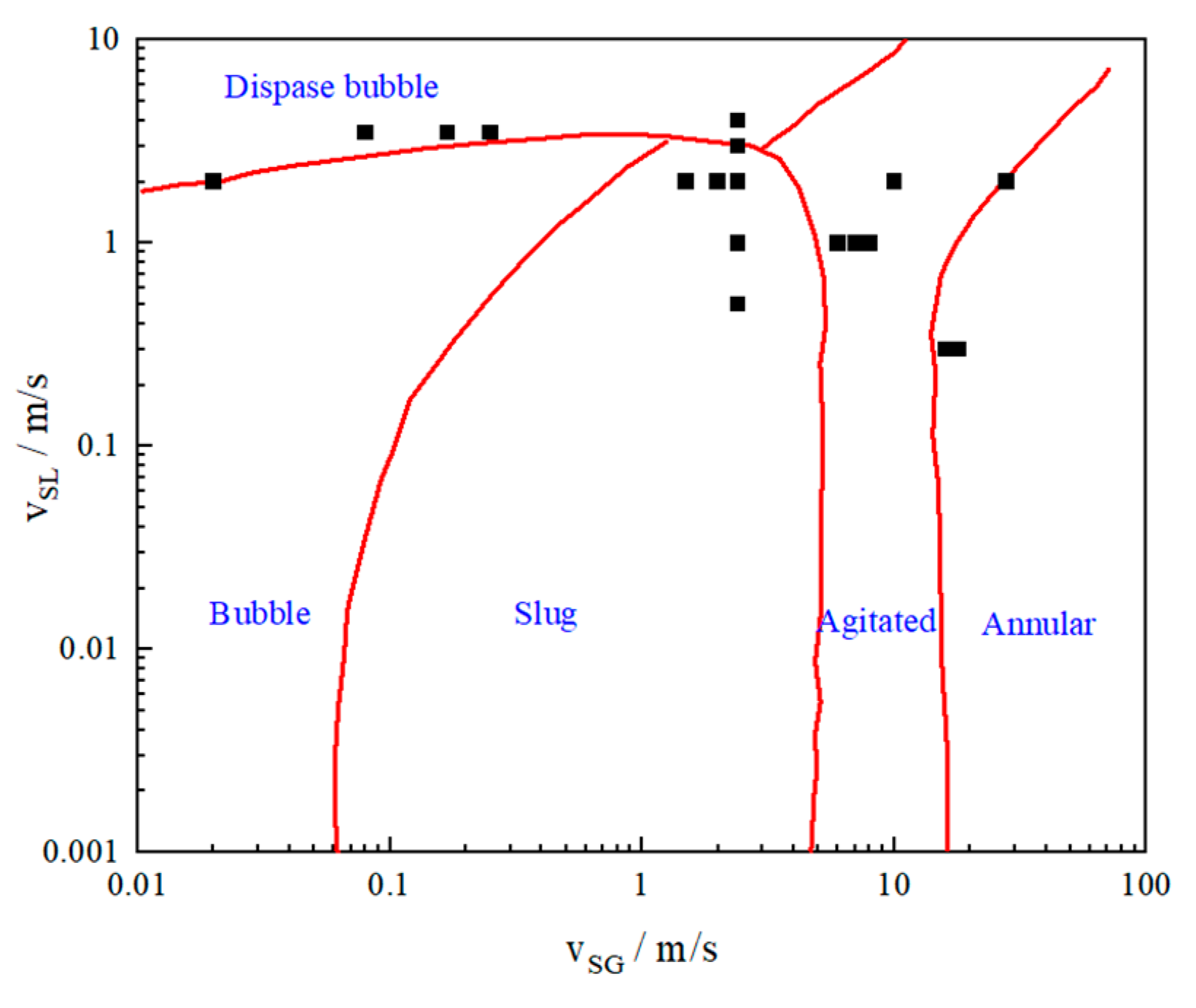
4.1. Model Validation for Gas–Oil Two Phases
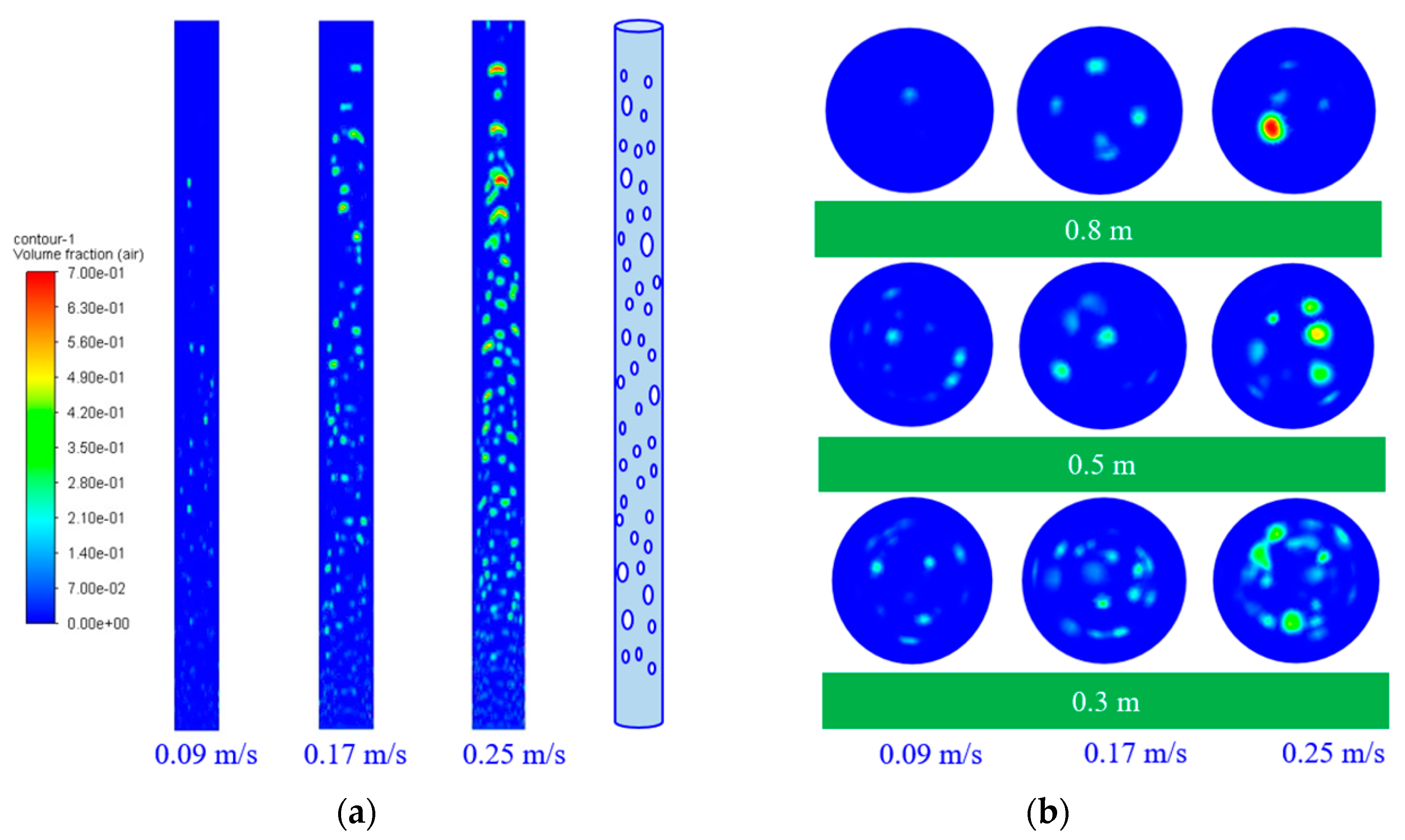
4.1.1. Bubbly Flow
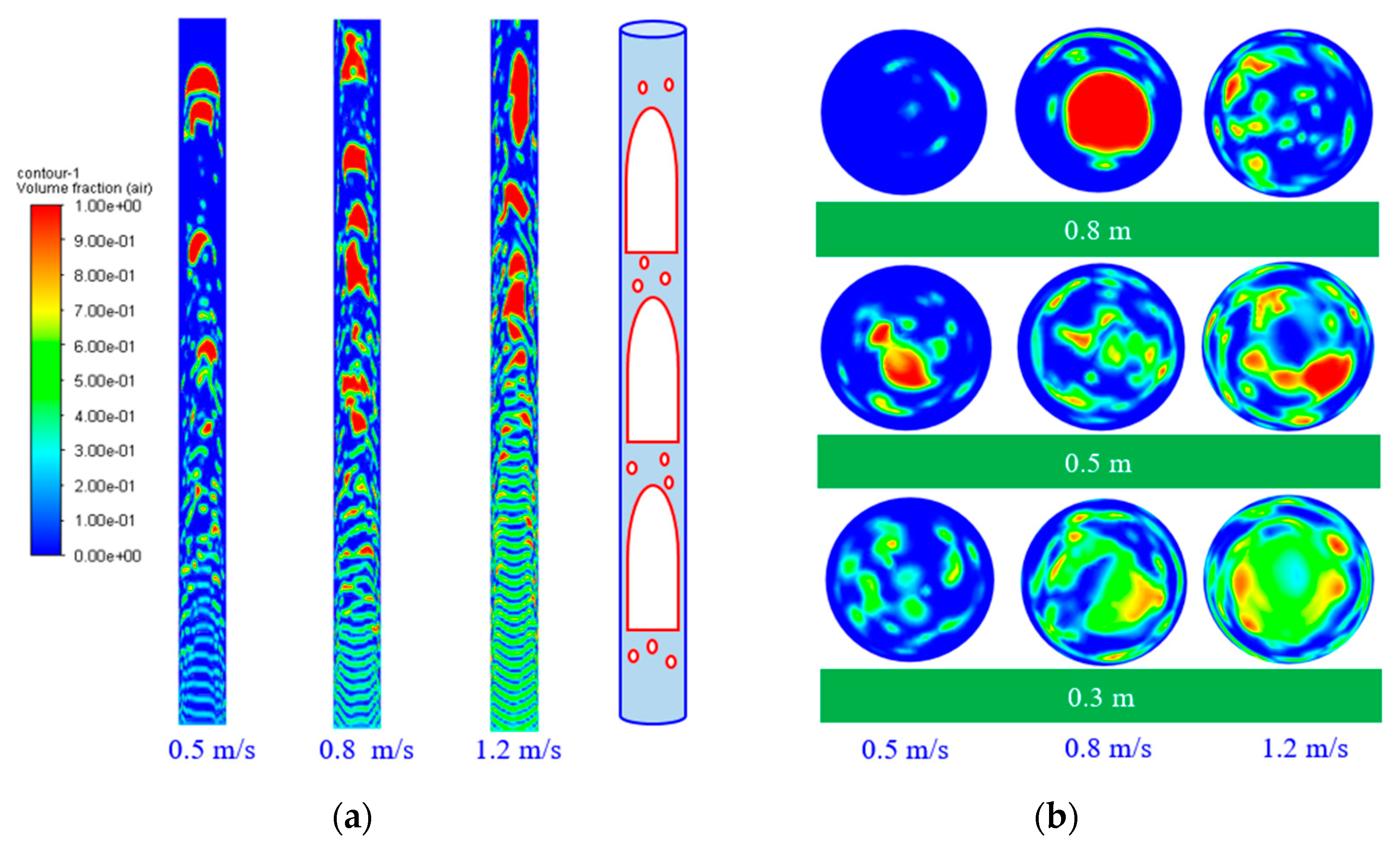
4.1.2. Slug Flow
4.1.3. Agitated Flow
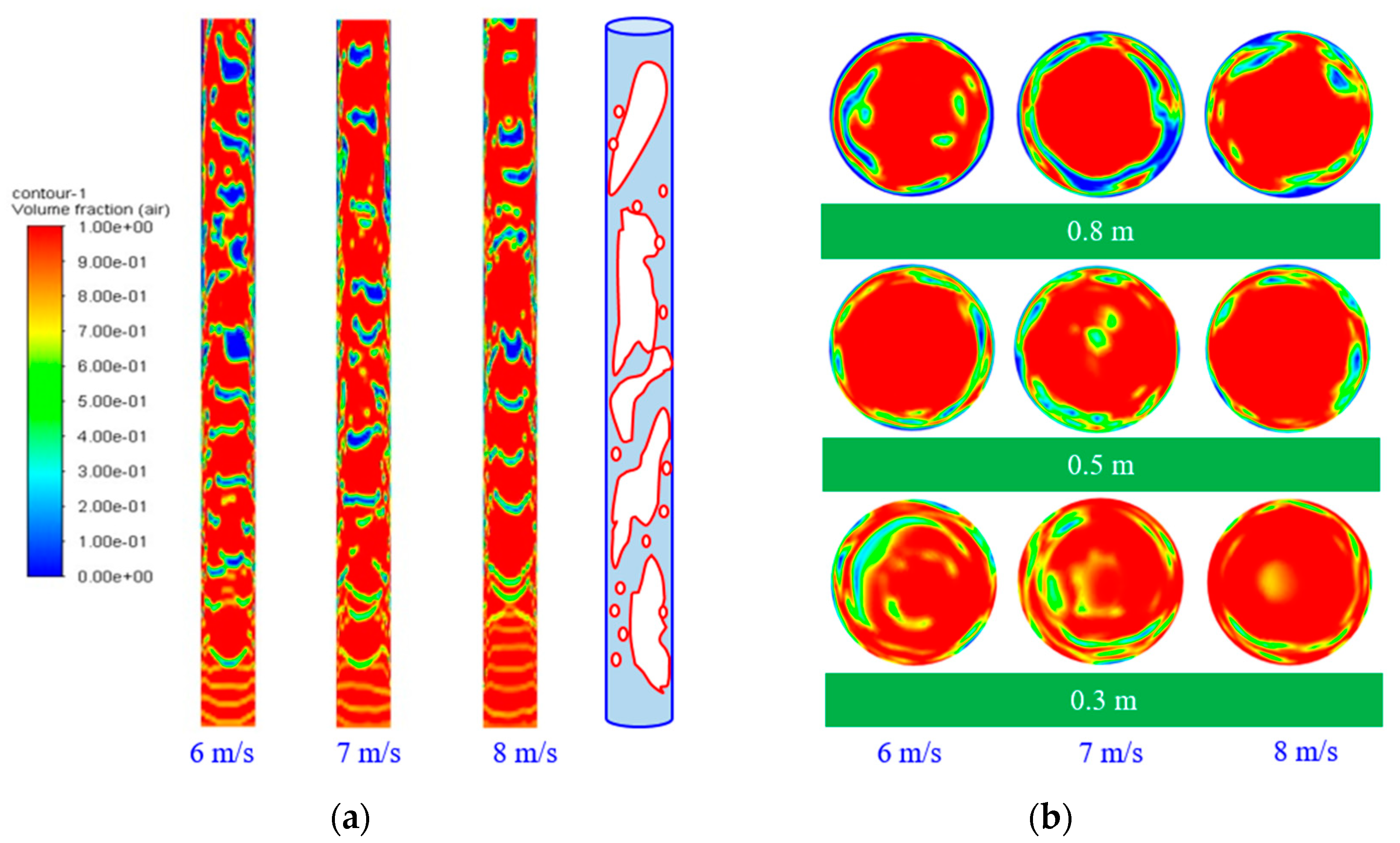
4.1.4. Annular Flow
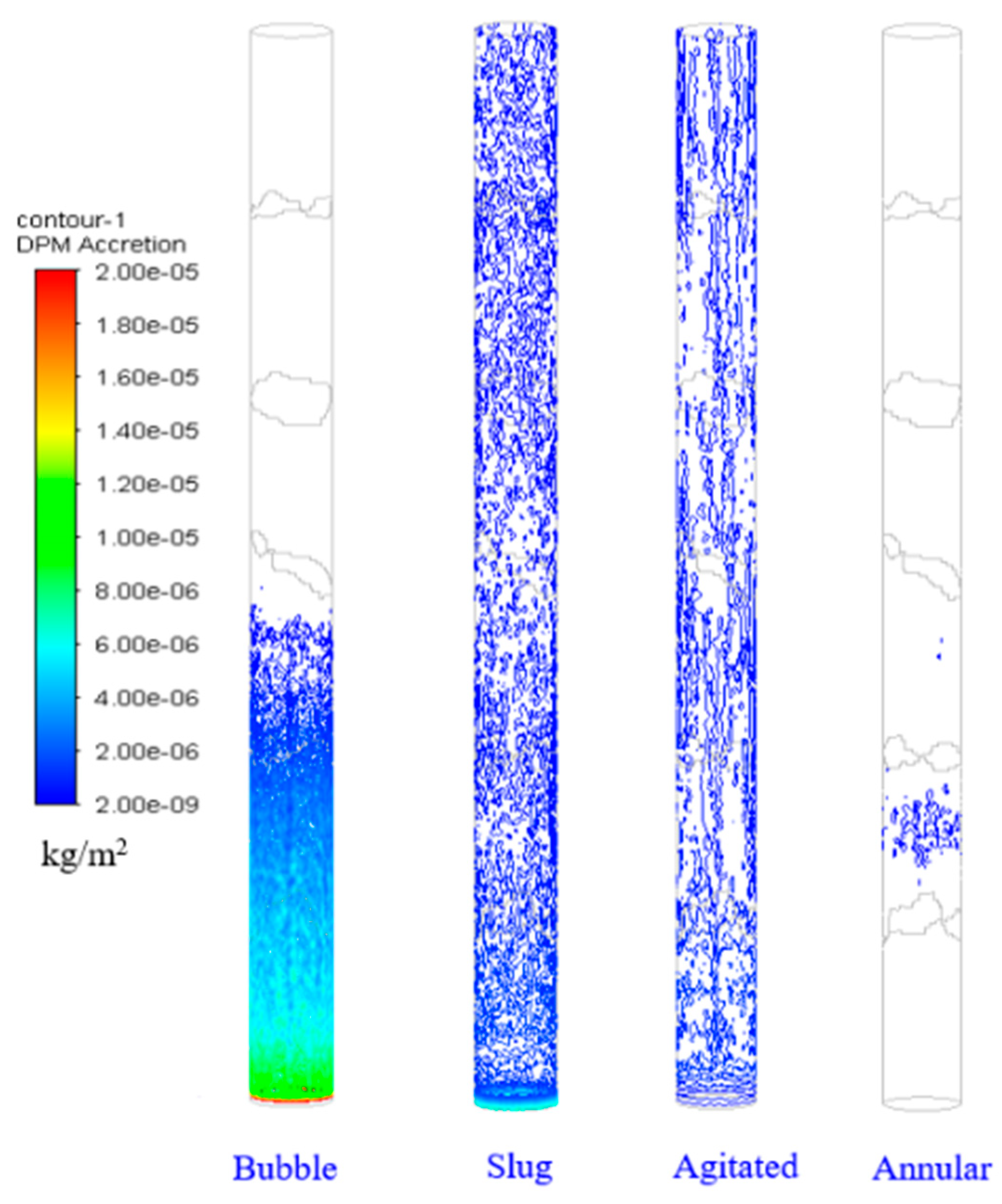
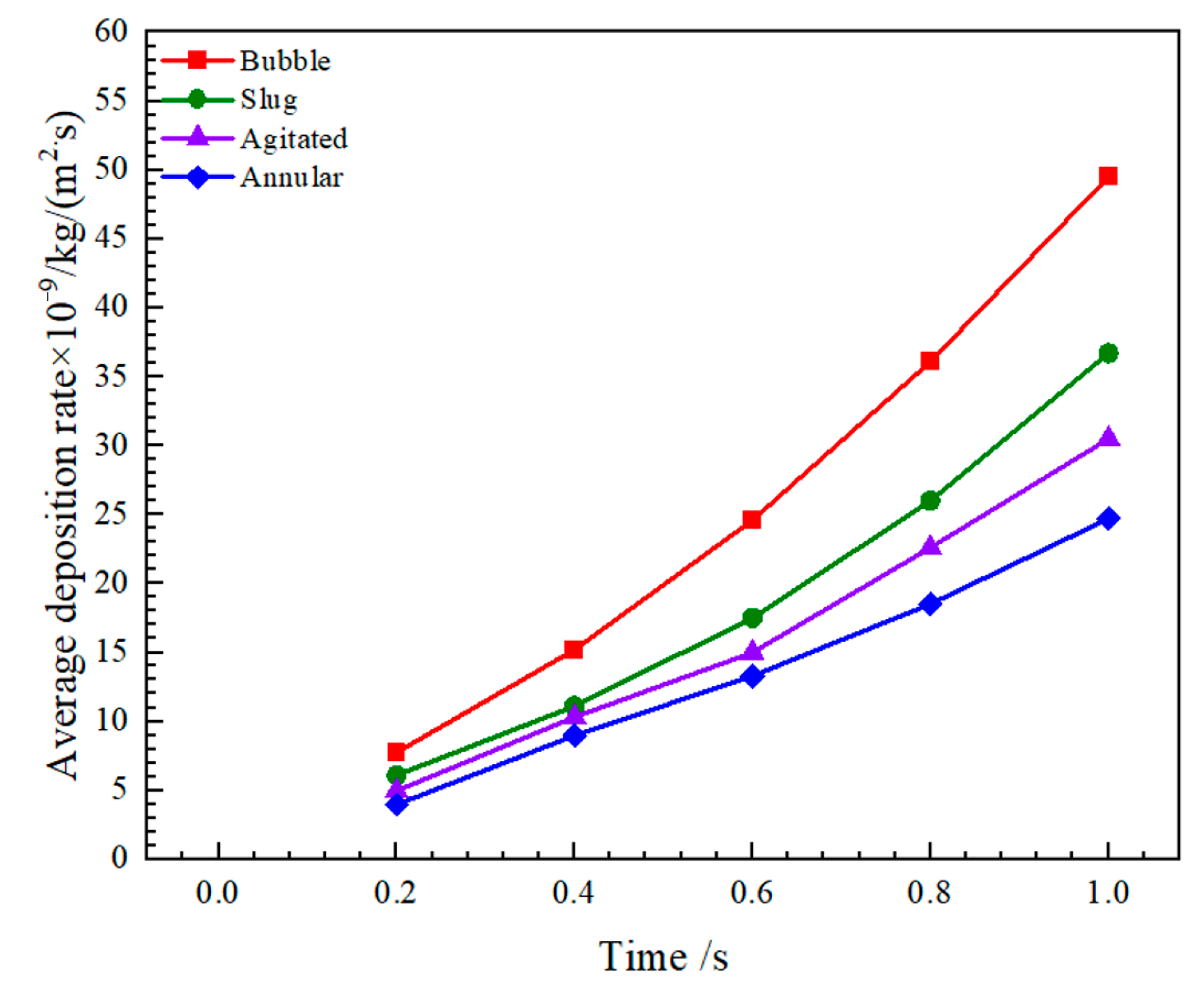
4.2. Comparison of Deposition Rates in Different Flow Patterns
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
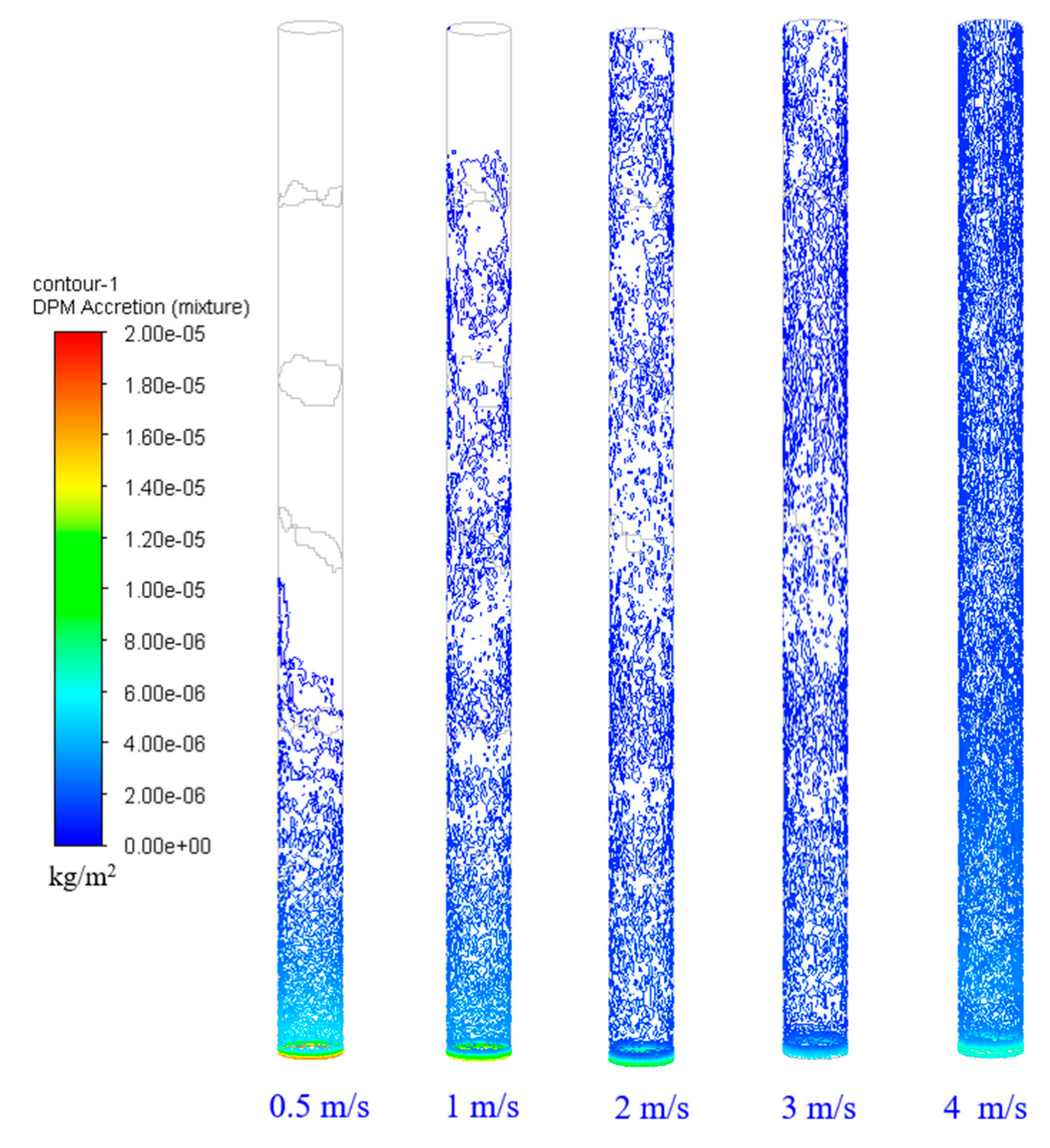
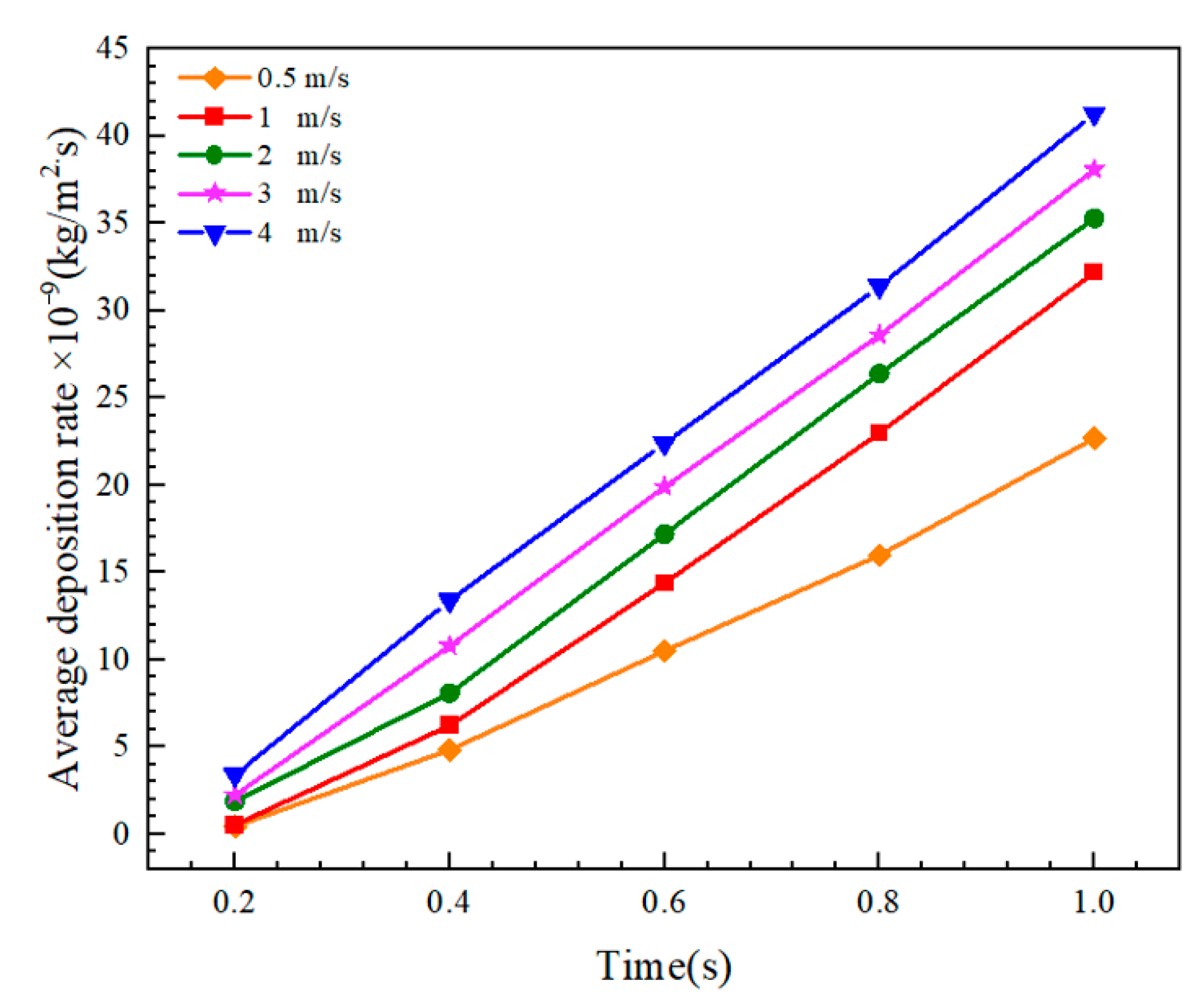
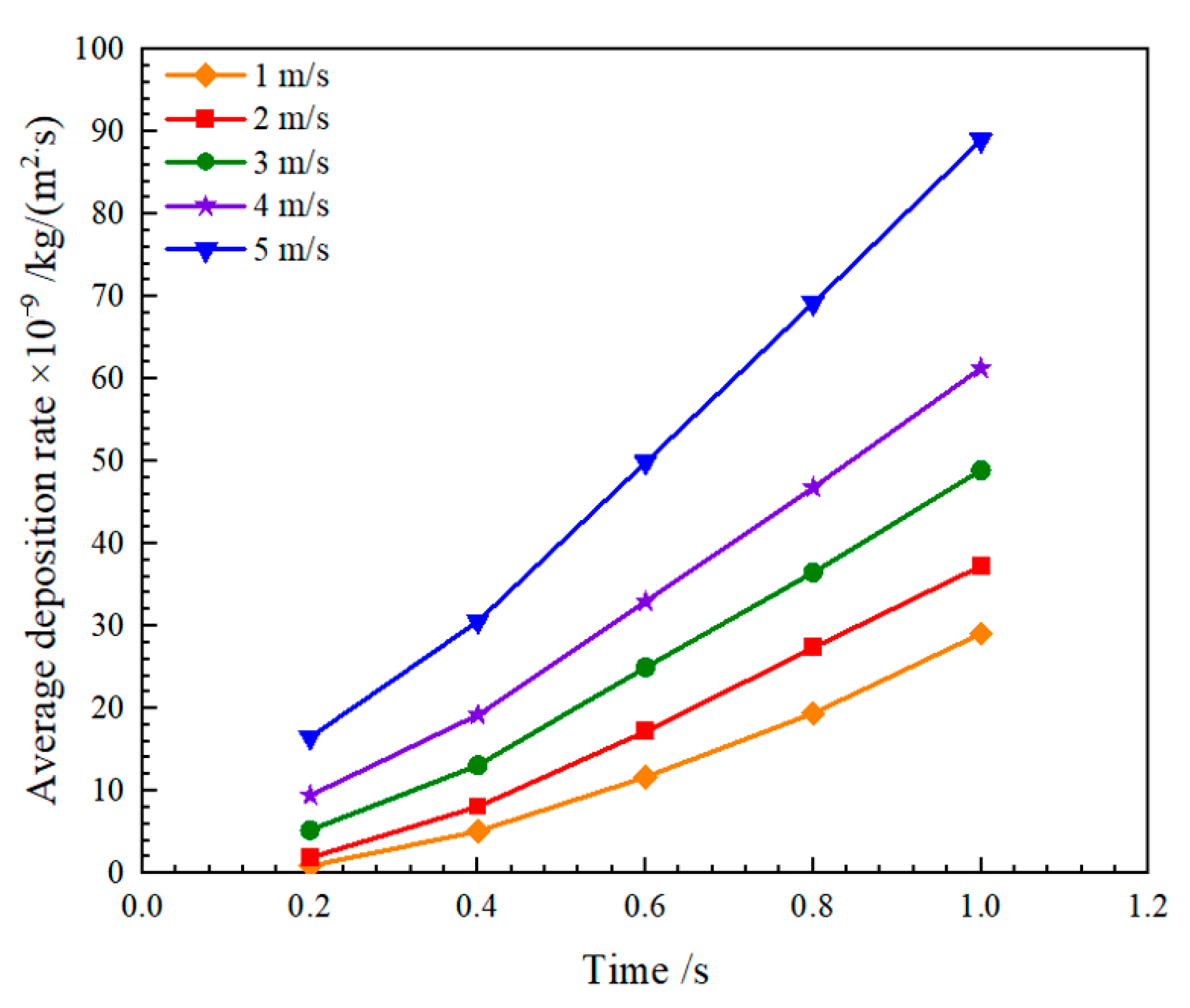
4.3.1. Effect of Gas Superficial Velocity on Deposition Rate
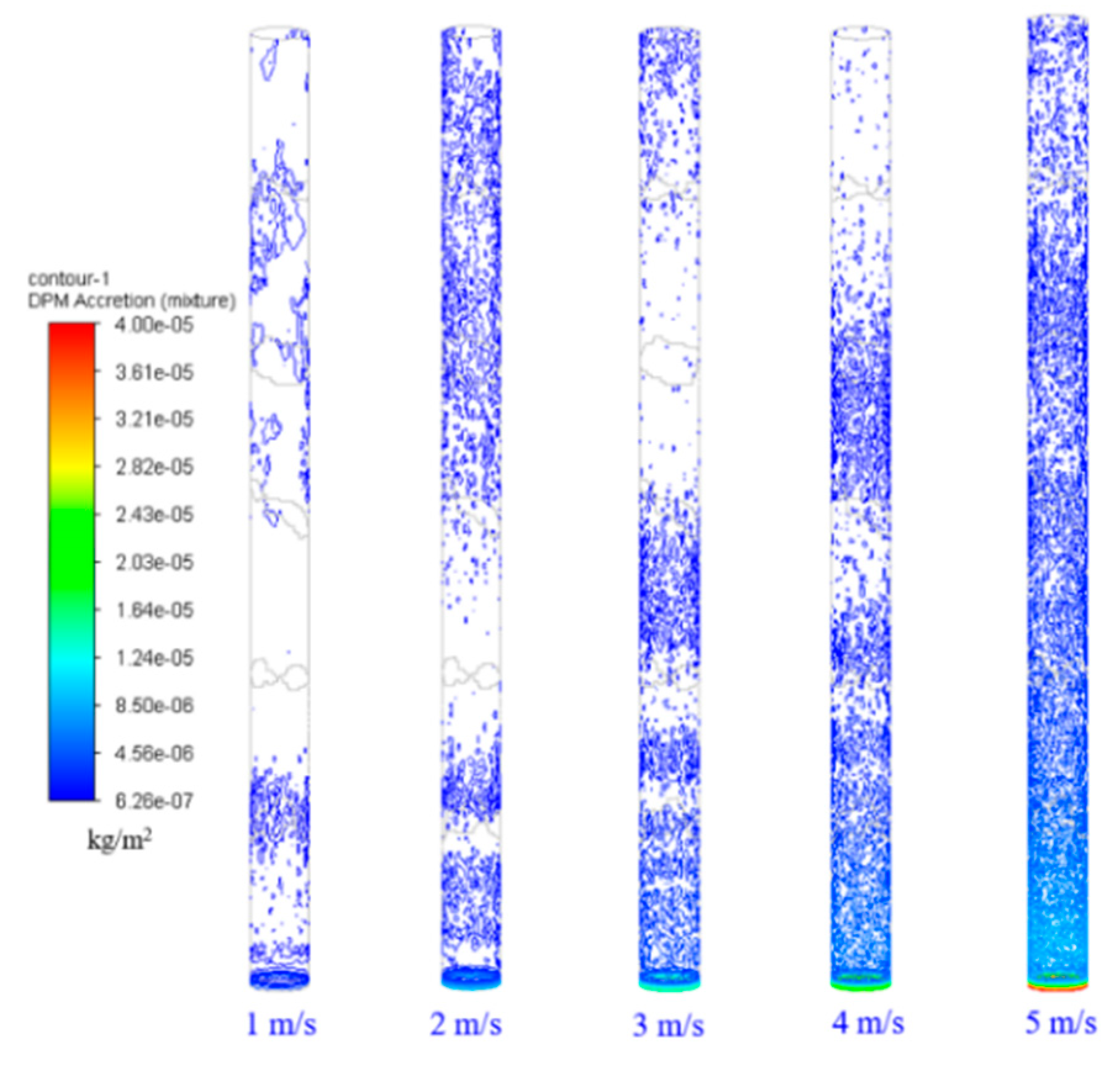
4.3.2. Effect of Liquid Superficial Velocity on Deposition Rate
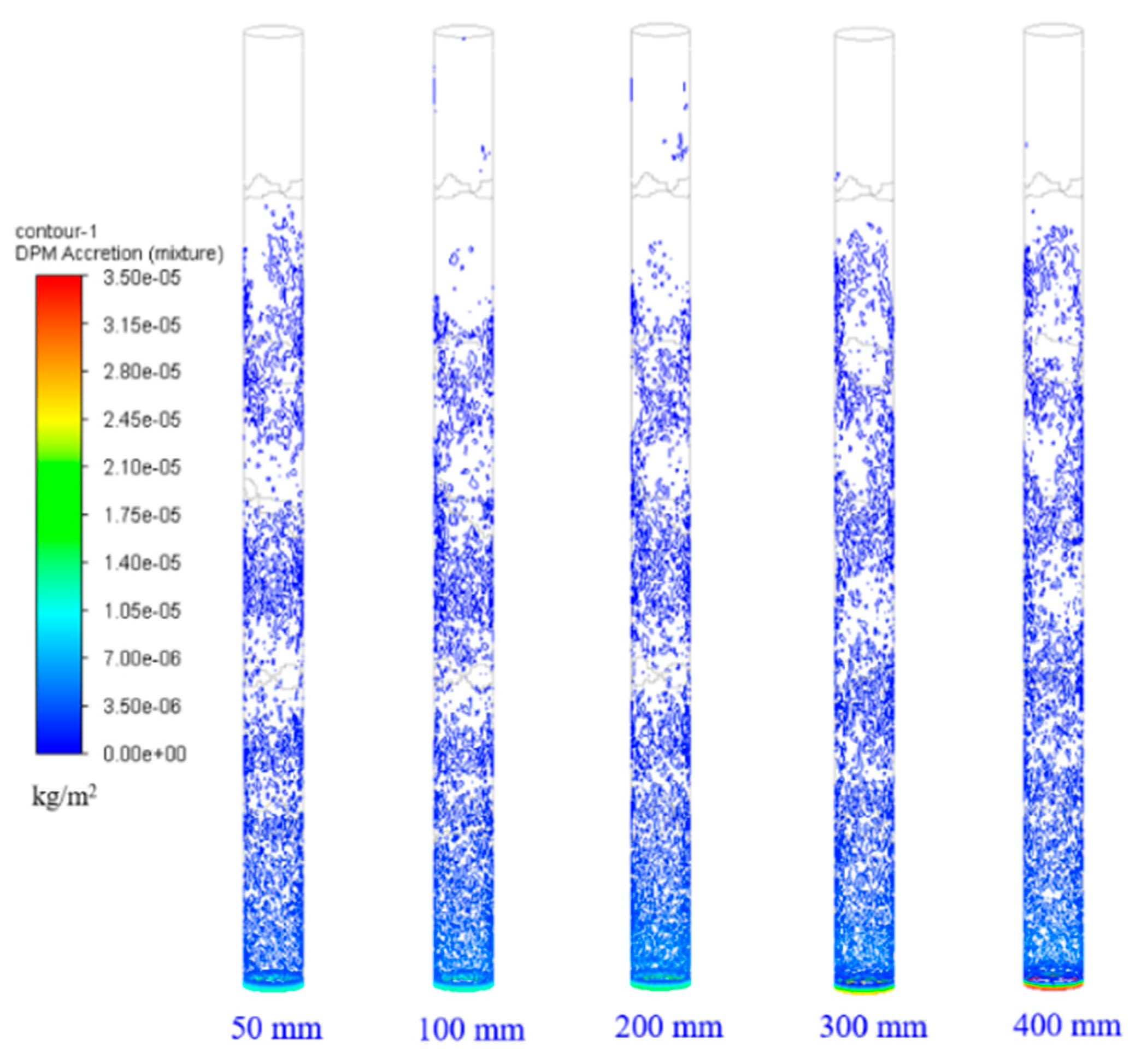
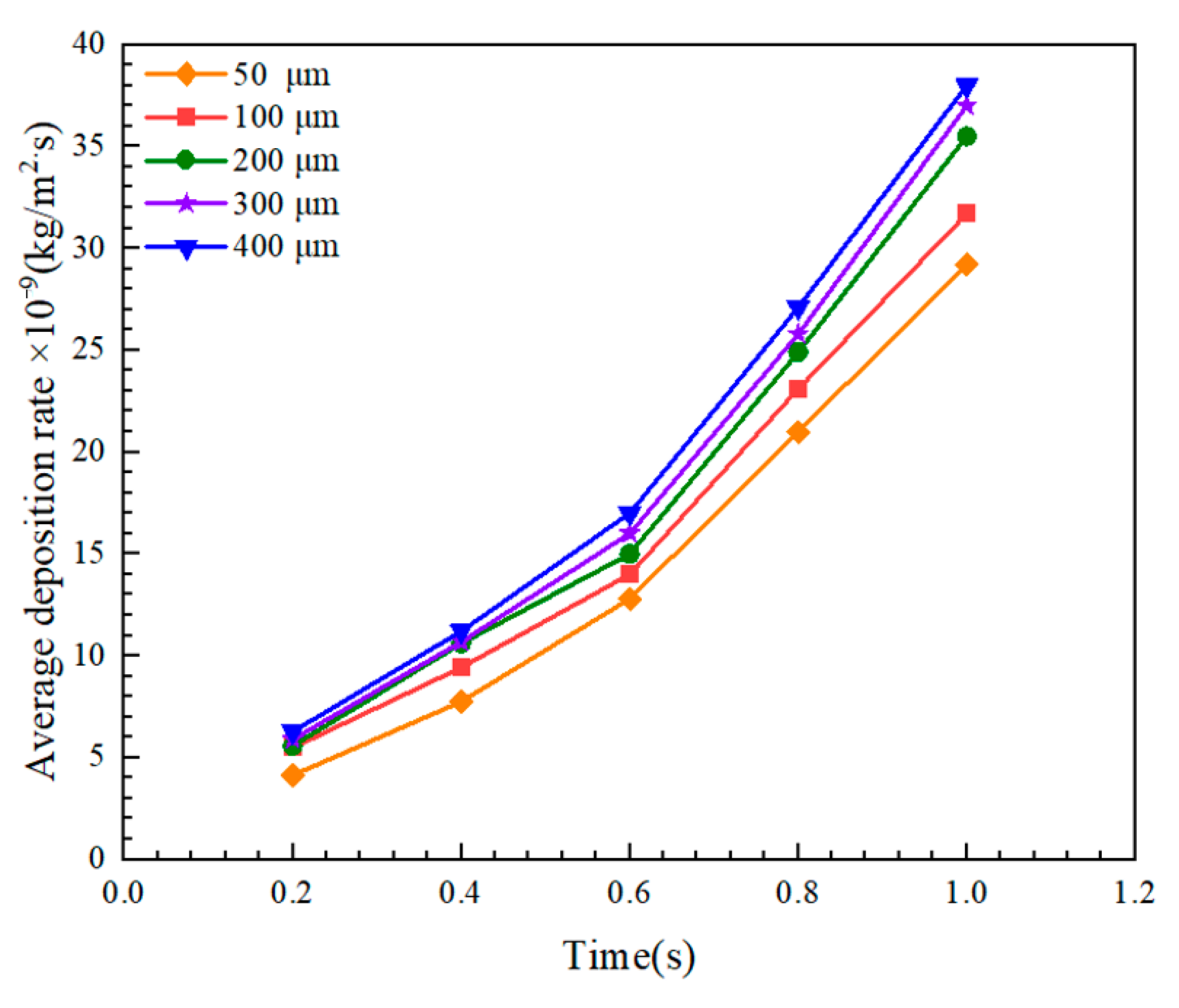
4.3.3. Effect of Particle Diameter on Deposition Rate
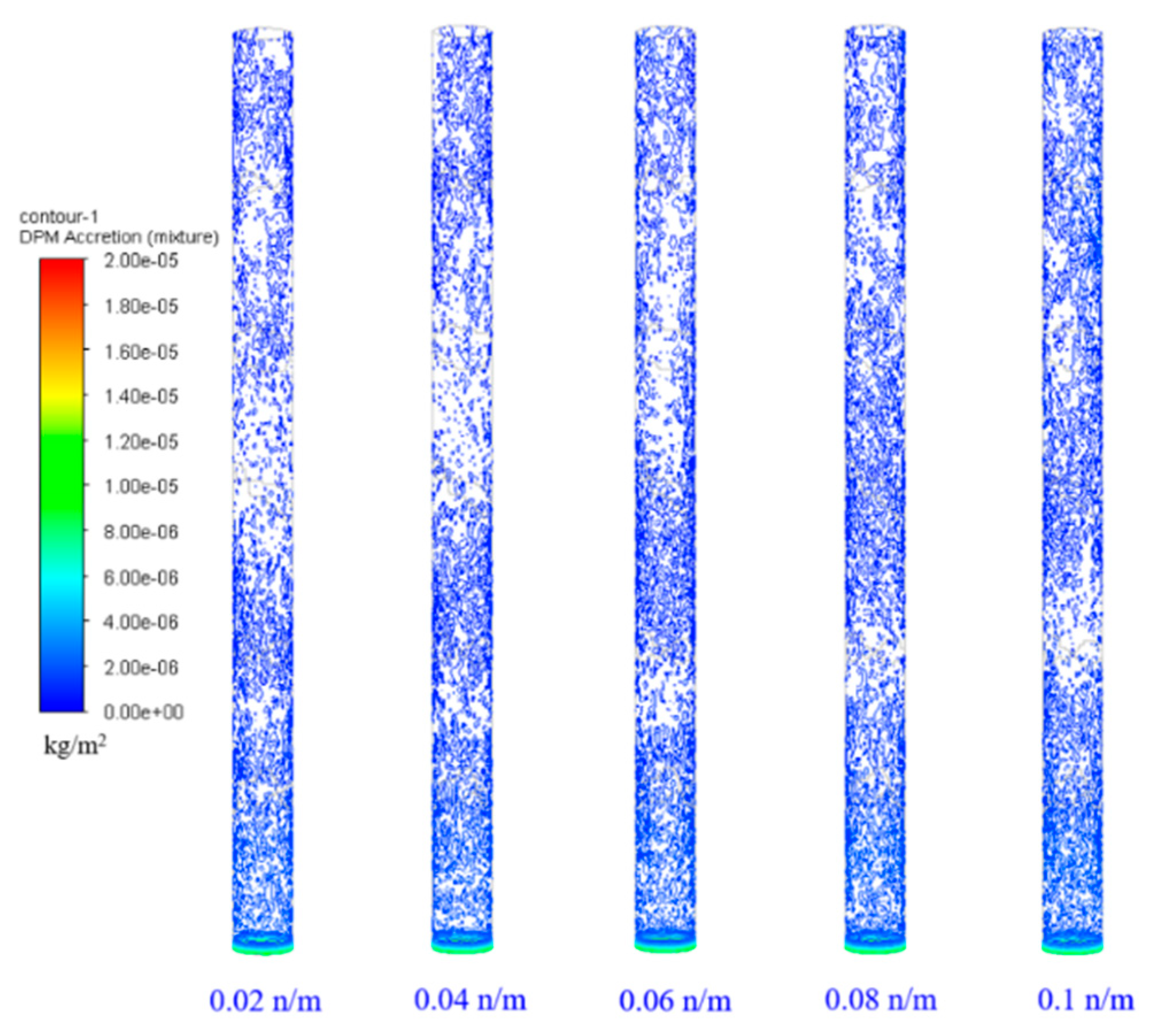
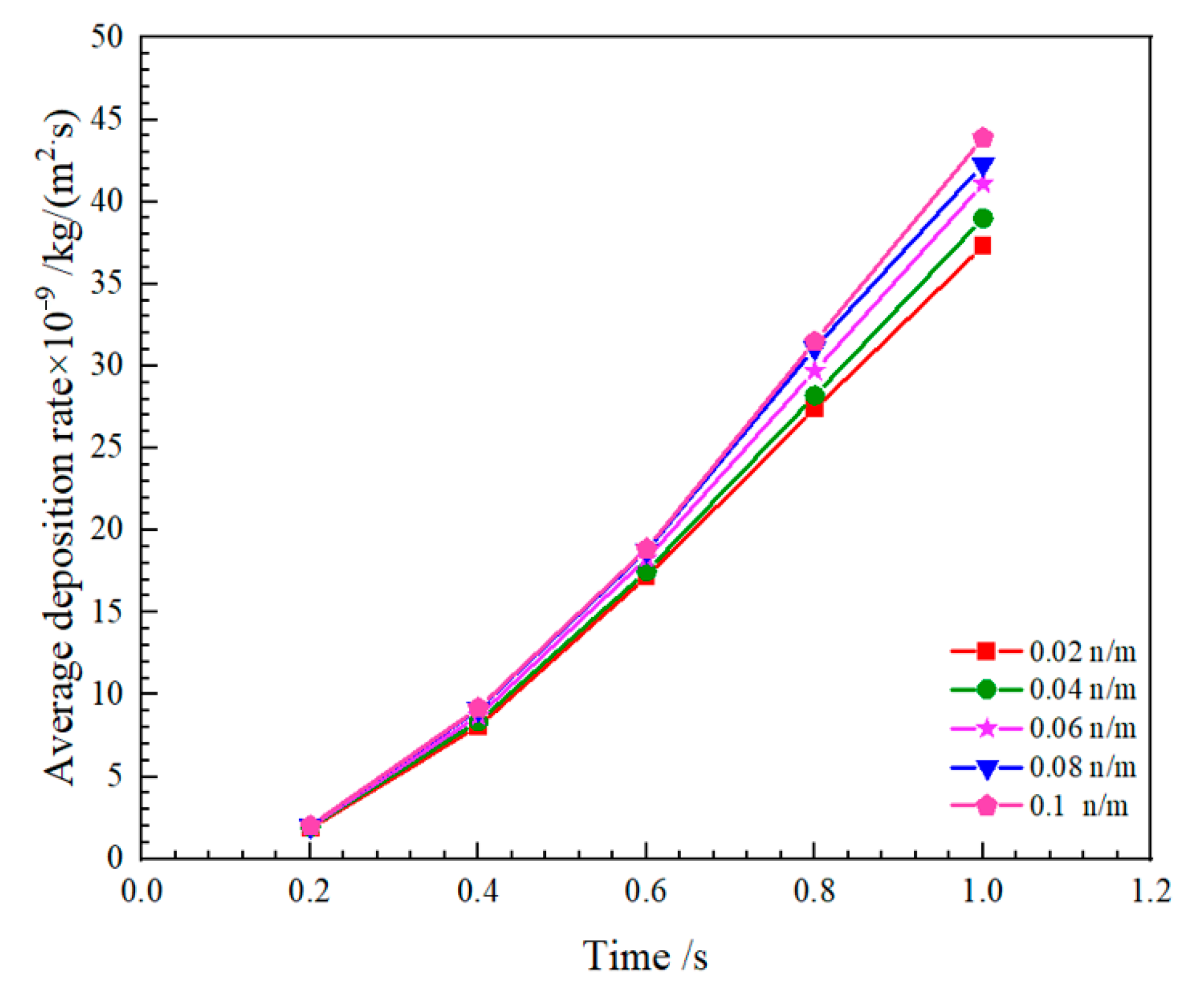
4.3.4. Effect of Interfacial Tension on Deposition Rate
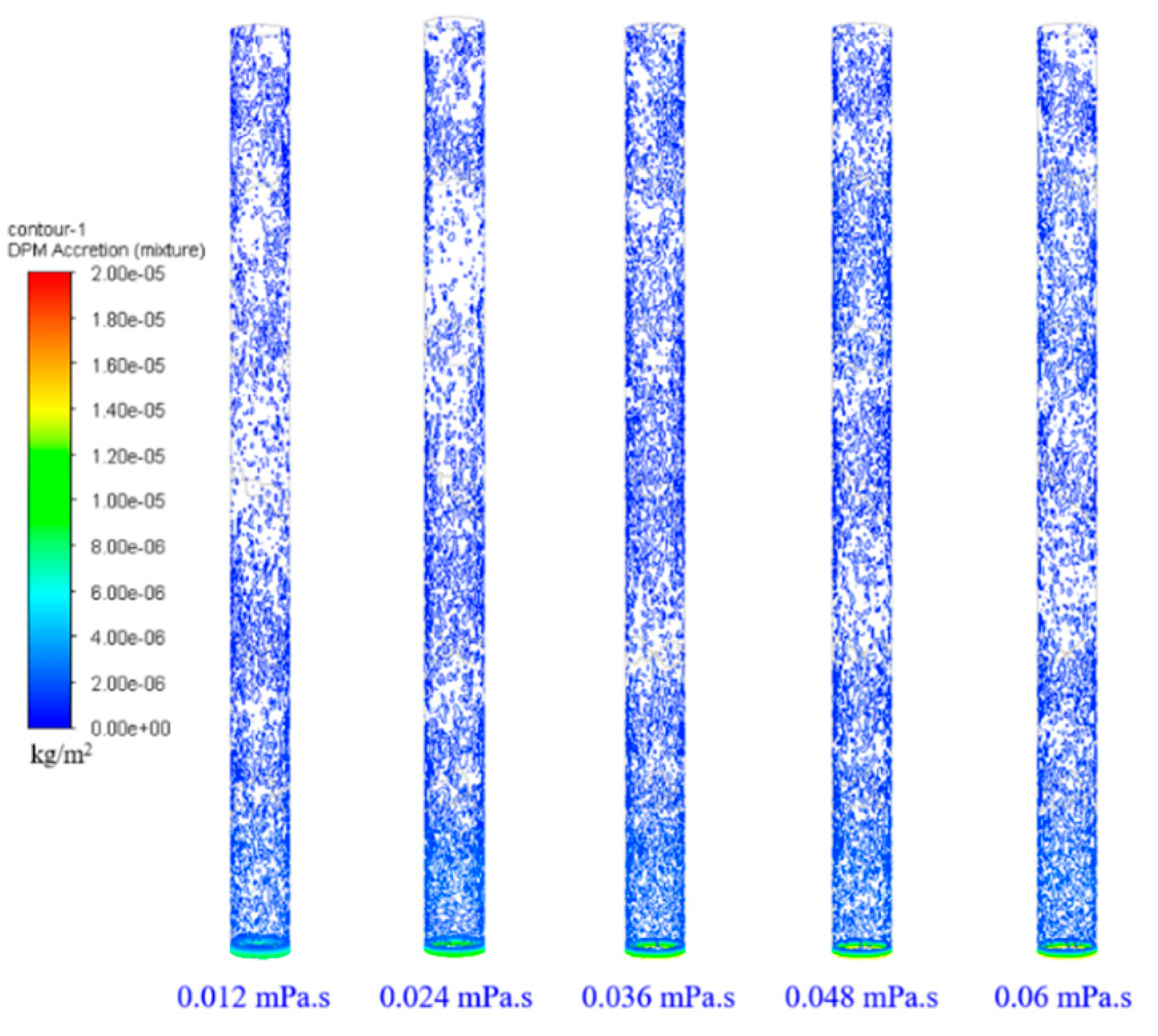
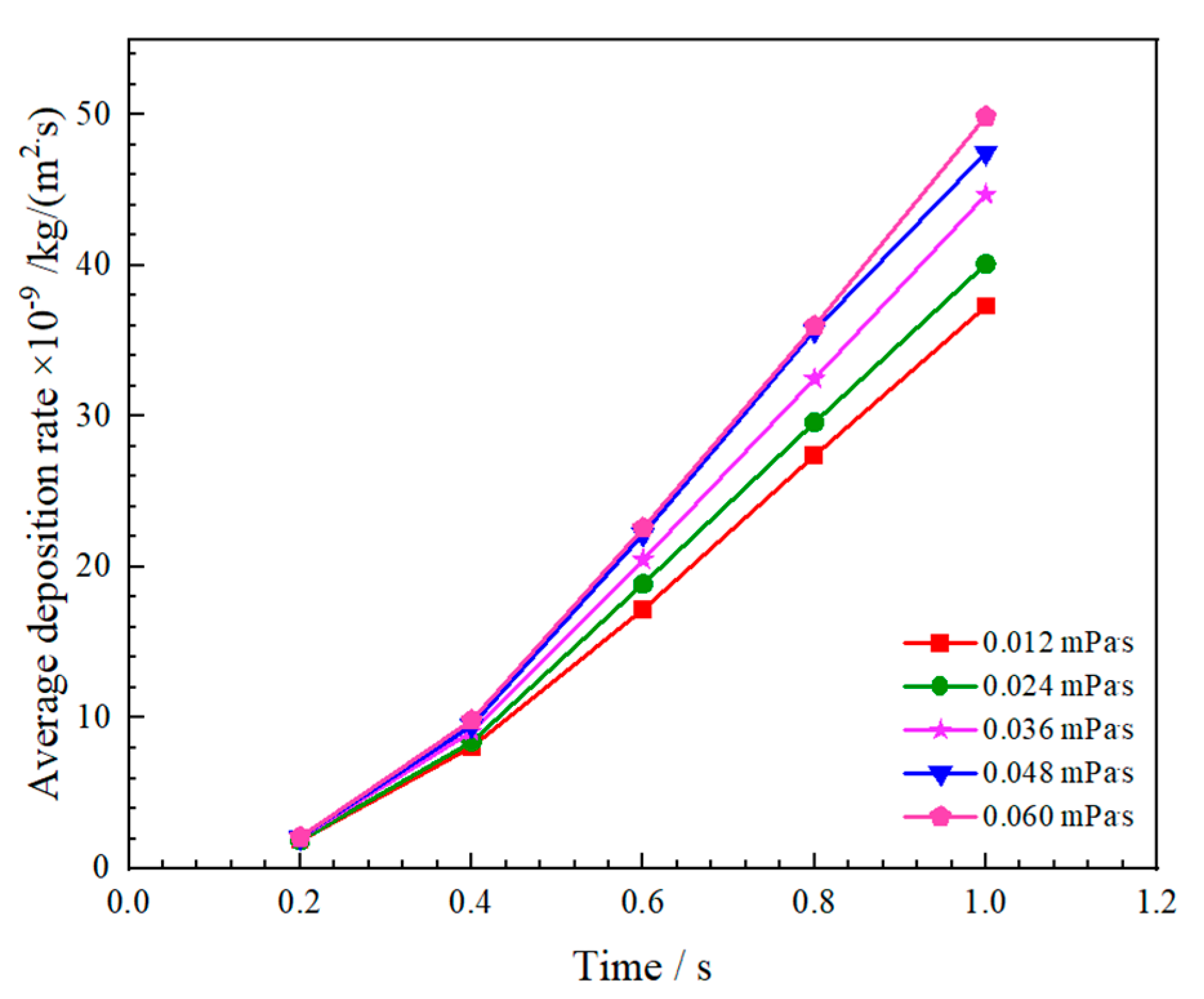
4.3.5. Effect of Oil Viscosity on Deposition Rate
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The deposition rates of asphaltene particles in the four flow patterns are observed to follow the order of bubble flow > slug flow > agitated flow > annular mist flow.
- (2)
- The deposition rate is observed to be the highest in bubble flow, while it is the lowest in annular flow. Specifically, the deposition rates in bubble flow are 1.35, 1.62, and 2 times greater than those in slug flow, churning flow, and annular mist flow, respectively.
- (3)
- The average deposition rate of asphaltene is escalated with a rise in the gas phase superficial velocity, liquid phase superficial velocity, particle size, oil–gas interfacial tension, and crude oil viscosity. The gas phase apparent velocity, particle diameter, and interfacial tension increase the deposition rate through changes in fluid kinetic energy. Conversely, the liquid phase apparent velocity and crude oil viscosity contribute to an increase in the deposition rate by amplifying the asphaltene content.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tavakkoli, M.; Panuganti, S.R.; Taghikhani, V.; Pishvaie, M.R.; Chapman, W.G. Understanding the polydisperse behavior of asphaltenes during precipitation. Fuel 2014, 117, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokal, S.L.; Sayegh, S.G. Asphaltenes: The cholesterol of petroleum. In Middle East Oil Show; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1995; Available online: https://www.onepetro.org/conference-paper/SPE-29787-MS (accessed on 25 November 2023).
- Decanio, S.J.; Nero, V.P.; DeTar, M.M.; Storm, D.A. Determination of the molecular weights of the Ratawi vacuum residue fractions- a comparison of mass spectrometric and vapour phase osmometry techniques. Fuel 1990, 69, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancheyta, J.; Centeno, G.; Trejo, F.; Marroquín, G.; García, J.A.; Tenorio, E.; Torres, A. Extraction and characterization of asphaltenes from different crude oils and solvents. Energy Fuels 2002, 16, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Takanohashi, T.; Tanaka, R. Molecular weight calibration of asphaltenes using gel permeation chromatography/mass spectrometry. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1991–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, R.; Khamehchi, E.; Ghaffarzadeh, M.; Kardani, N. Static and dynamic evaluation of a novel solution path on asphaltene deposition and drag reduction in flowlines: An experimental study. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 205, 108833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Yang, C.; Shan, H. Structure and Reactivity of Iranian Vacuum Residue and Its Eight Group-Fractions. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 8072–8086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schucker, R.; Kewwshan, R. Reactivity of Cold Lake asphaltenes. Am. Chem. Soc. Div. Fuel Chem. 1980, 25, 327–346. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, H.H.; Idem, O.R. Interrelationships between asphaltene precipitation inhibitor effectiveness, asphaltenes characteristics, and precipitation behavior during n-heptane (light paraffin hydrocarbon)-induced asphaltene precipitation. Energy Fuels 2004, 18, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Guo, J.; An, N.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Q. Study of asphaltene dispersion and removal for high-asphaltene oil wells. Pet. Sci. 2021, 9, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.; Bennion, D.; Hunter, B. Experimental and theoretical studies of solids precipitation from reservoir fluid. J. Can. Petrol. Technol. 1992, 31, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, A.; Phelps, C.H.; Monger-McClure, T.; Little, T.M. Asphaltene precipitation from live oils: An experimental investigation of onset conditions and reversibility. Energy Fuels 2000, 14, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.I. Effect of precipitation temperature on the composition of n-heptane asphaltenes. Fuel Sci. Technol. Int. 1994, 12, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskett, C.E.; Tartera, M. A Practical Solution to the Problem of Asphaltene Deposits Hassi Messaoud Field, Algeria. J. Pet. Technol. 1965, 17, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkafeef, S.F.; Al-Medhadi, F.; Al-Shammari, A.D. A Simplified Method to Predict and Prevent Asphaltene Deposition in Oilwell Tubings: Field Case. SPE Prod. Oper. 2005, 20, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creek, J.L. Freedom of Action in the State of Asphaltenes: Escape from Conventional Wisdom. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1212–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, F.M. Modeling of Asphaltene Precipitation and Arterial Deposition; Rice University: Houston, TX, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Dong, P.; Chen, X.; Nkok, L.Y.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, Y. CFD modeling of virtual mass force and pressure gradient force on deposition rate of asphaltene aggregates in oil wells. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2022, 40, 995–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broseta, D.; Robin, M.; Savvidis, T.; Fejean, C.; Durandeau, M.; Zhou, H. Detection of asphaltene deposition by capillary flow measurements. In SPE/DOE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium; Society of Petroleum Engineer: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ekholm, P.; Blomberg, E.; Claesson, P.; Auflem, I.H.; Sjöblom, J.; Kornfeldt, A. A quartz crystal microbalance study of the adsorption of asphaltenes and resins onto a hydrophilic surface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 247, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zougari, M.; Hammami, A.; Broze, G.; Fuex, N. Live oils novel organic solid deposition and control device: Wax and asphaltene deposition validation. In SPE Middle East Oil and Gas Show and Conference; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vilas Bôas Fávero, C.; Hanpan, A.; Phichphimok, P.; Binabdullah, K.; Fogler, H.S. Mechanistic investigation of asphaltene deposition. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 8915–8921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jing, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Yu, X. Simulations of deposition rate of asphaltene and flow properties of oil-gas-water three-phase flow in submarine pipelines by CFD. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Science & Information Technology, Chengdu, China, 9–11 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Haghshenasfard, M.; Hooman, K. CFD modeling of asphaltene deposition rate from crude oil. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 128, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyedbagheri, H.; Mirzayi, B. CFD modeling of high inertia asphaltene aggregates deposition in 3D turbulent oil production wells. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 150, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emani, S.; Shaari, R. Discrete phase-CFD simulations of asphaltenes particles deposition from crude oil in shell and tube heat exchangers. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 149, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyushev, D.A. Modeling and prediction of asphaltene-resin-paraffinic substances deposits in oil production wells. Georesursy 2020, 22, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syuzev, A.V.; Lekomtsev, A.V.; Martyushev, D.A. Complex method of selecting reagents to delete asphaltenosmolaparinine deposits in mechanized oil-producing wells. Bull. Tomsk. Polytech. Univ. Geo Assets Eng. 2018, 329, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Parsi, M.; Agrawal, M.; Srinivasan, V.; Vieira, R.E.; Torres, C.F.; McLaury, B.S.; Shirazi, S.A. CFD simulation of sand particle erosion in gas-dominant multiphase flow. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 27, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsi, M.; Kara, M.; Agrawal, M.; Kesana, N.; Jatale, A.; Sharma, P.; Shirazi, S. CFD simulation of sand particle erosion under multiphase flow conditions. Wear 2017, 15, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, L. Numerical Simulation on the Flow Pattern of a Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Swirl Flow. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 2679–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerne, G.; Petelin, S.; Tiselj, I. Coupling of the interface tracking and the two-fluid models for the simulation of incompressible two-phase flow. J. Comput. Phys. 2001, 171, 776–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghobashi, S. Particle-laden turbulent flows: Direct simulation and closure models. Appl. Sci. Res. 1991, 48, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Levenspiel, O. Drag Coefficient and Terminal Velocity of Spherical and Nonspherical Particles. Powder Technol. 1989, 58, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PSaffman, G. The lift on a small sphere in a slow shear flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1965, 22, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnea, D. A unified model for predicting flow-pattern transitions for the whole range of pipe inclinations. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1987, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhosano, A.; Daraboina, N. Effect of multi-phase flow on asphaltene deposition: Field case application of integrated simulator. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 206, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Source | Composition/wt% | Metal Content (μg/g) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | N | O | S | Fe | Ni | V | |
| Iraq [3] | 82.7 | 8.4 | 1.2 | 7.7 | 145 | 308 | ||
| Kuwait [4] | 81.62 | 7.26 | 1.46 | 1.02 | 8.46 | 320.2 | 1509.2 | |
| Iran [5] | 83.2 | 6.8 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 5.9 | 390 | 1200 | |
| Maya [4] | 83.96 | 11.8 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 3.57 | 53.4 | 298.1 | |
| Isthmus [4] | 85.4 | 12.68 | 0.14 | 0.33 | 1.45 | 10.2 | 52.7 | |
| Olmeca [4] | 85.91 | 12.8 | 0.07 | 0.23 | 0.99 | 1.6 | 8 | |
| Iran [6] | 80.3 | 10.99 | 1.99 | 3.07 | 3.43 | 0.12 | 0.08 | |
| Iran [7] | 85.14 | 12.12 | 0.23 | 2.52 | 19.1 | 63.1 | ||
| Cold Lake [8] | 80.64 | 7.64 | 1.6 | 1.84 | 7.95 | 815 | 310 | |
| Canada [9] | 83.6 | 6.95 | 1.06 | 2.6 | 4.64 | 79 | 100 | 140 |
| China [10] | 82.89 | 8.32 | 0.69 | 3.25 | 2.56 | 13.6 | 0.5 | 8 |
| Parameter | Numerical Value |
|---|---|
| Diameter, m | 0.62 |
| Length, m | 1 |
| Crude oil density, m3/d | 866 |
| Inlet pressure, MPa | 30 |
| Outlet pressure, MPa | 29.5 |
| Asphaltene particle density, kg/m3 | 1100 |
| Apparent velocity of liquid phase, m/s | 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| Gas phase superficial velocity, m/s | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 |
| Particle diameter, μm | 50, 100, 200, 300, 400 |
| Interfacial tension, n/m | 0.02, 0.04, 0.06, 0.08, 0.1 |
| Crude oil viscosity, mPa·s | 0.012, 0.024, 0.036, 0.048, 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Dong, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Chen, S.; Tian, M.; Cui, Y. Simulation of the Asphaltene Deposition Rate in Oil Wells under Different Multiphase Flow Condition. Energies 2024, 17, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17010121
Wang X, Dong P, Zhang Y, Gao X, Chen S, Tian M, Cui Y. Simulation of the Asphaltene Deposition Rate in Oil Wells under Different Multiphase Flow Condition. Energies. 2024; 17(1):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17010121
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoming, Pingchuan Dong, Youheng Zhang, Xiaodong Gao, Shun Chen, Ming Tian, and Yongxing Cui. 2024. "Simulation of the Asphaltene Deposition Rate in Oil Wells under Different Multiphase Flow Condition" Energies 17, no. 1: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17010121
APA StyleWang, X., Dong, P., Zhang, Y., Gao, X., Chen, S., Tian, M., & Cui, Y. (2024). Simulation of the Asphaltene Deposition Rate in Oil Wells under Different Multiphase Flow Condition. Energies, 17(1), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17010121






