Photometric Method to Determine Membrane Degradation in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Setup FER
2.2. Test Setup PEFC
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical Characterization
3.1.1. Performance Analysis
3.1.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3.2. Measurement of the FER
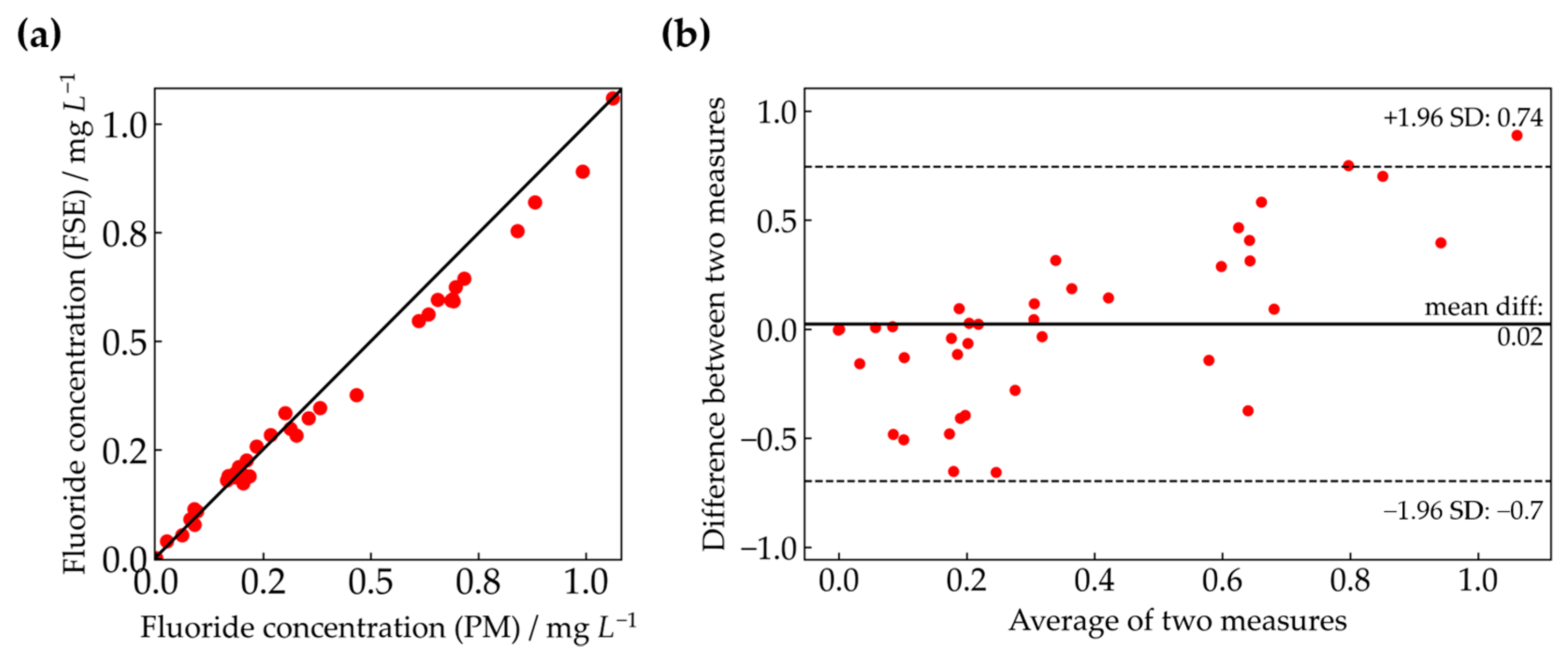
3.3. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuhnert, E.; Hacker, V.; Bodner, M. A Review of Accelerated Stress Tests for Enhancing MEA Durability in PEM Water Electrolysis Cells. Int. J. Energy Res. 2023, 2023, 3183108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, K.; Nagai, T.; Matsuzawa, K.; Kuroda, Y.; Mitsushima, S.; Ishihara, A. Green Hydrogen and Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells for Our Future Sustainable Growth. Meet. Abstr. 2019, 235, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, R.E.; Sulong, A.B.; Daud, W.R.W.; Zulkifley, M.A.; Husaini, T.; Rosli, M.I.; Majlan, E.H.; Haque, M.A. A Review of High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (HT-PEMFC) System. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 9293–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, V. Fuel Cells and Hydrogen; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; ISBN 978-0-12-811459-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, V.O.; Kunz, H.R.; Fenton, J.M. Membrane Degradation Mechanisms in PEMFCs. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, B652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V.O.; Russell Kunz, H.; Fenton, J.M. Is H2O2 Involved in the Membrane Degradation Mechanism in PEMFC? Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2006, 9, A299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Saito, M.; Hayamizu, K.; Okada, T. Degradation of Perfluorinated Ionomer Membranes for PEM Fuel Cells during Processing with H2O2. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, A967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Fuller, T.F. Modeling of H2O2 Formation in PEMFCs. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 3984–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Sui, P.C.; Wong, K.H.; Kjeang, E.; Knights, S.; Djilali, N. Modeling the Effect of Chemical Membrane Degradation on PEMFC Performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, F3328–F3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marocco, P.; Sundseth, K.; Aarhaug, T.; Lanzini, A.; Santarelli, M.; Barnett, A.O.; Thomassen, M. Online Measurements of Fluoride Ions in Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis through Ion Chromatography. J. Power Sources 2021, 483, 229179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodner, M.; Marius, B.; Schenk, A.; Hacker, V. Determining the Total Fluorine Emission Rate in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Effluent Water. ECS Trans. 2017, 80, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodner, M.; Cermenek, B.; Rami, M.; Hacker, V. The Effect of Platinum Electrocatalyst on Membrane Degradation in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Membranes 2015, 5, 888–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Zhang, H. The Investigation of Resin Degradation in Catalyst Layer of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellevold Malde, M.; Bjorvatn, K.; Julshamn, K. Determination of Fluoride in Food by the Use of Alkali Fusion and Fluoride Ion-Selective Electrode. Food Chem. 2001, 73, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.; Mehra, A.; Saikat, S.; Lynch, P. Human Exposure Assessment of Fluoride from Tea (Camellia sinensis L.): A UK Based Issue? Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamari, N.L.A.; Dohmann, J.F.; Raab, A.; Krupp, E.M.; Feldmann, J. Novel Non-Target Analysis of Fluorine Compounds Using ICPMS/MS and HPLC-ICPMS/MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2017, 32, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.M.; Patel, K.S.; Naik, M.L. Zr(Iv)-spadns Flow Analysis Procedure for Determination of Fluoride in Surface and Groundwater. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 1999, 56, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, N.; Benjamin, T.; Kopasz, J. DOE Fuel Cell Program: Durability Technical Targets and Testing Protocols. ECS Trans. 2007, 11, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AiDEXA GmbH eFLUORiX Product Description 2022. Available online: http://www.aidexa.com/products.html (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- European Commision; Joint Research Centre; De Marco, G.; Malkow, T.; Pilenga, A.; Tsotridis, G. EU Harmonised Test Protocols for PEMFC MEA Testing in Single Cell Configuration for Automotive Applications; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, H.; Avgouropoulos, G. Research Progress of Proton Exchange Membrane Failure and Mitigation Strategies. Materials 2021, 14, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Du, H.; Guo, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, D.; Ming, P.; Zhang, C. Experimental Study on the Effect of Flow Channel Parameters on the Durability of PEMFC Stack and Analysis of Hydrogen Crossover Mechanism. Energy 2023, 264, 126286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodner, M.; Schenk, A.; Salaberger, D.; Rami, M.; Hochenauer, C.; Hacker, V. Air Starvation Induced Degradation in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells 2017, 17, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, M.; Kinumoto, T.; Kiriake, M.; Umebayashi, R.; Tasaka, A.; Ogumi, Z. Gas Crossover and Membrane Degradation in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 5746–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D. Statistical Methods for Assessing Agreement between Two Methods of Clinical Measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
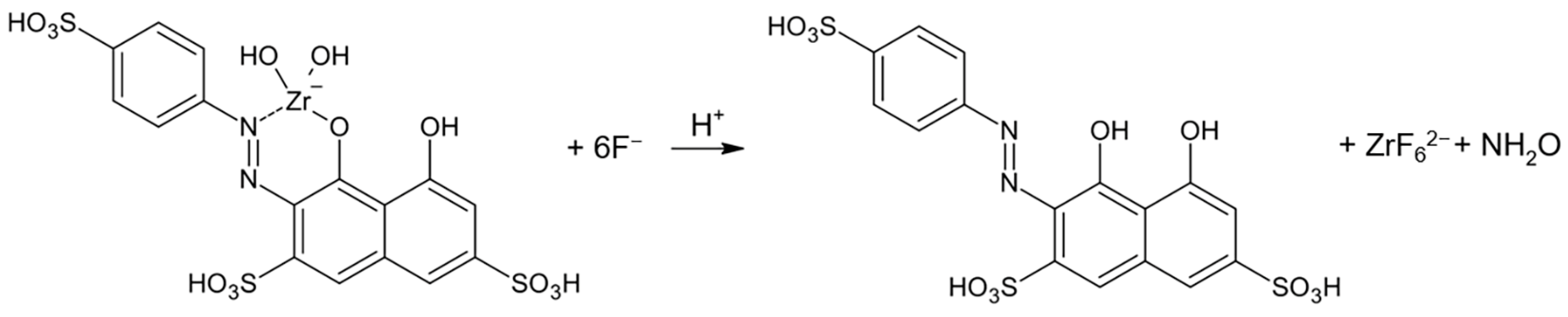
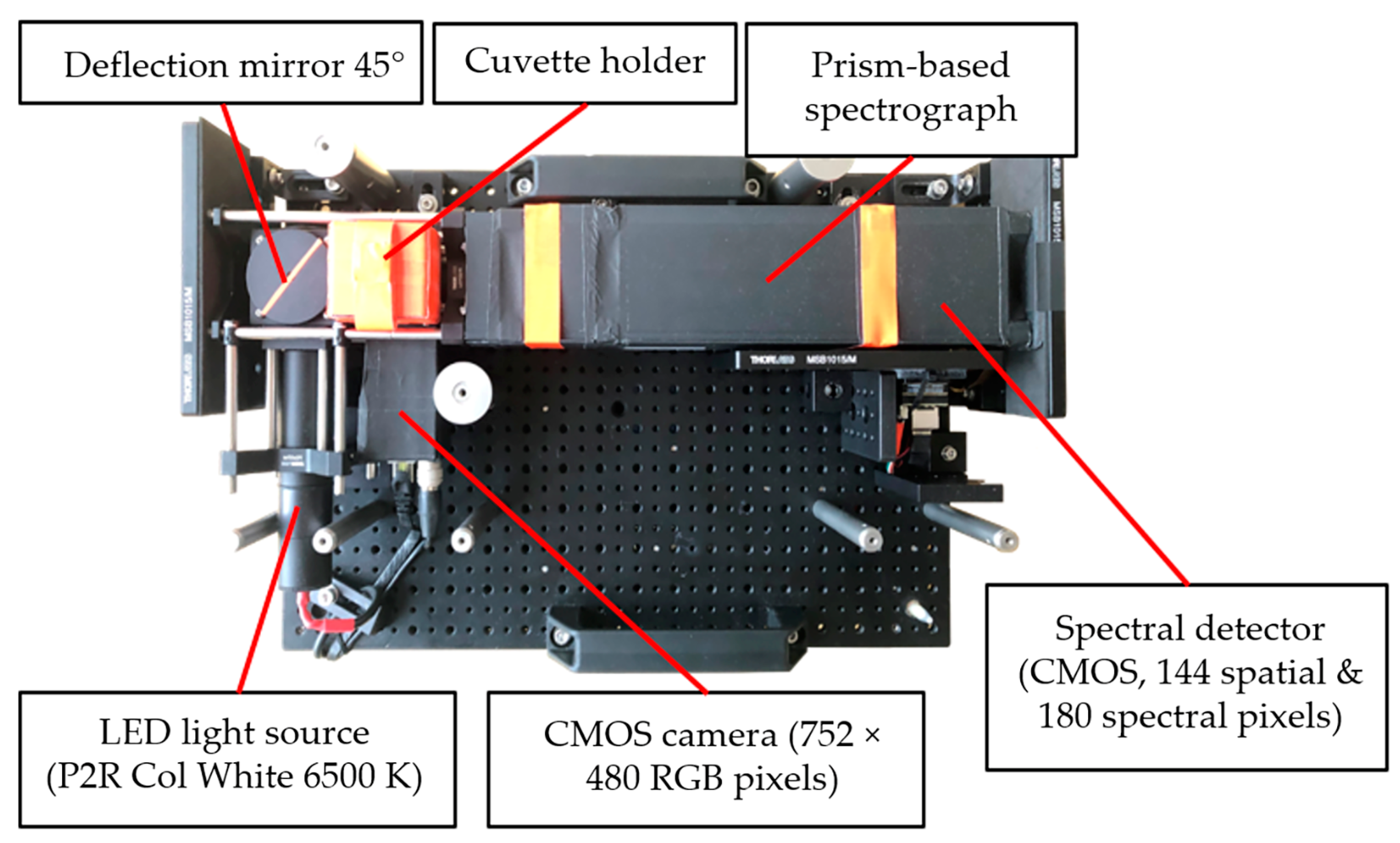
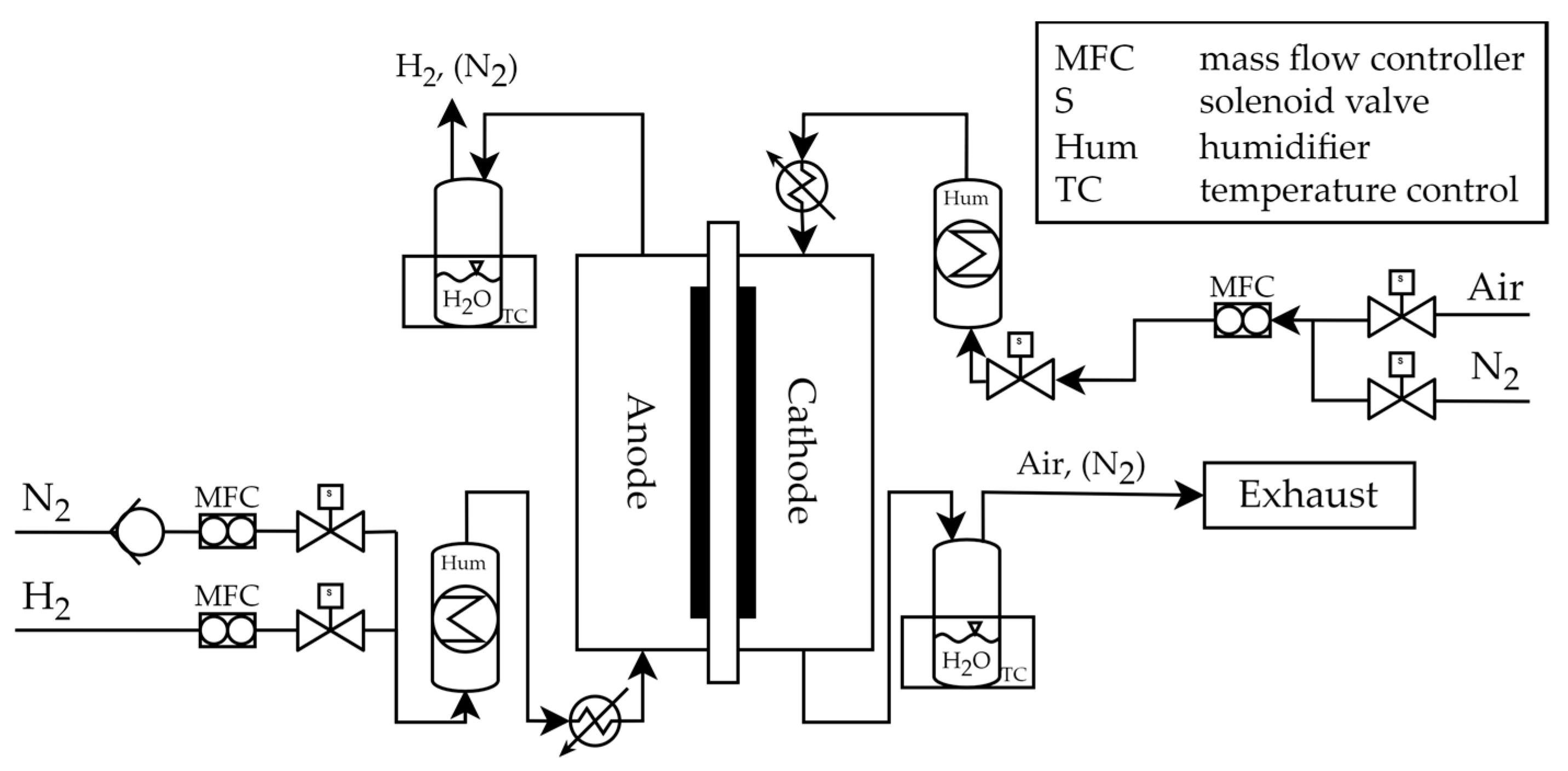
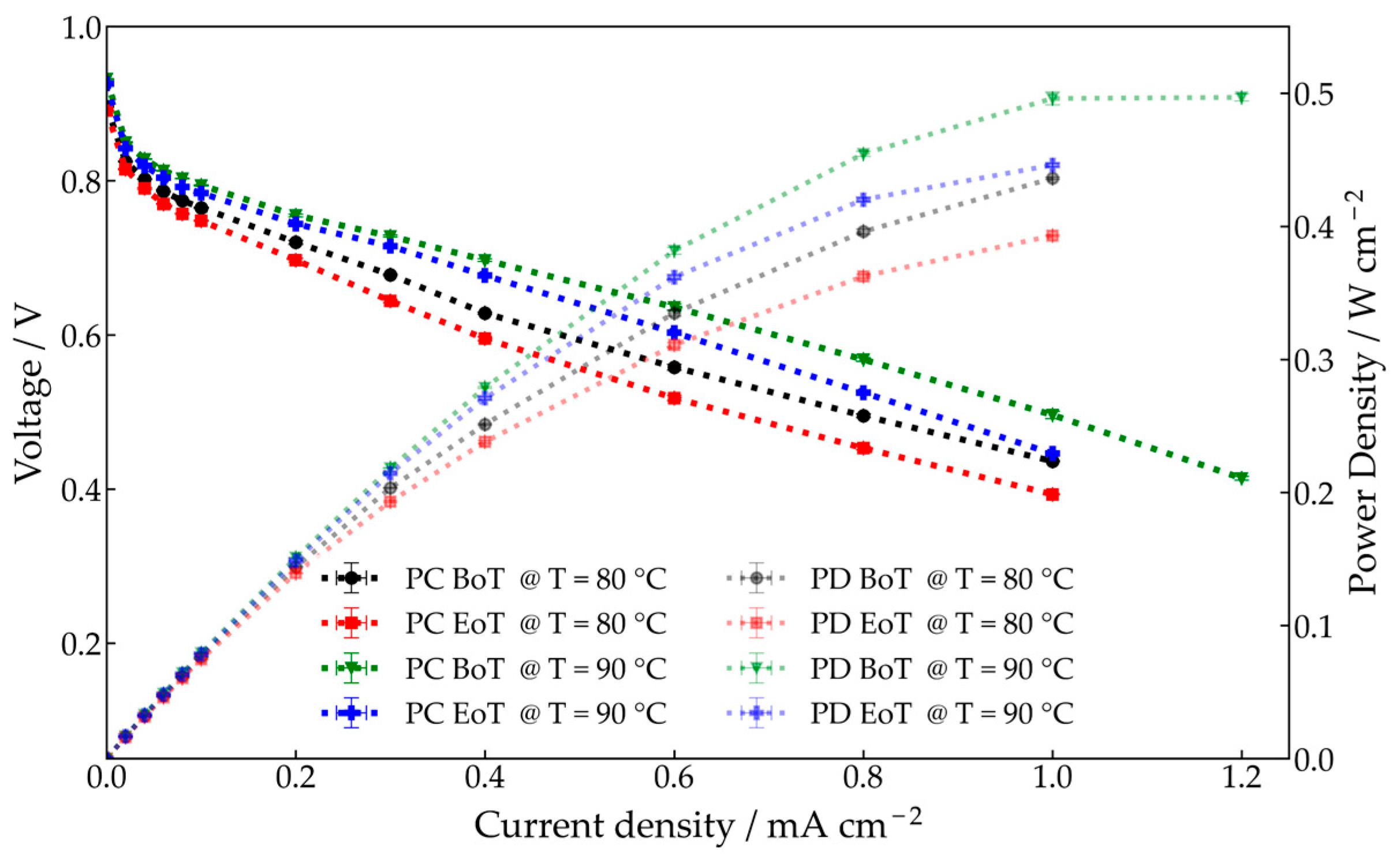
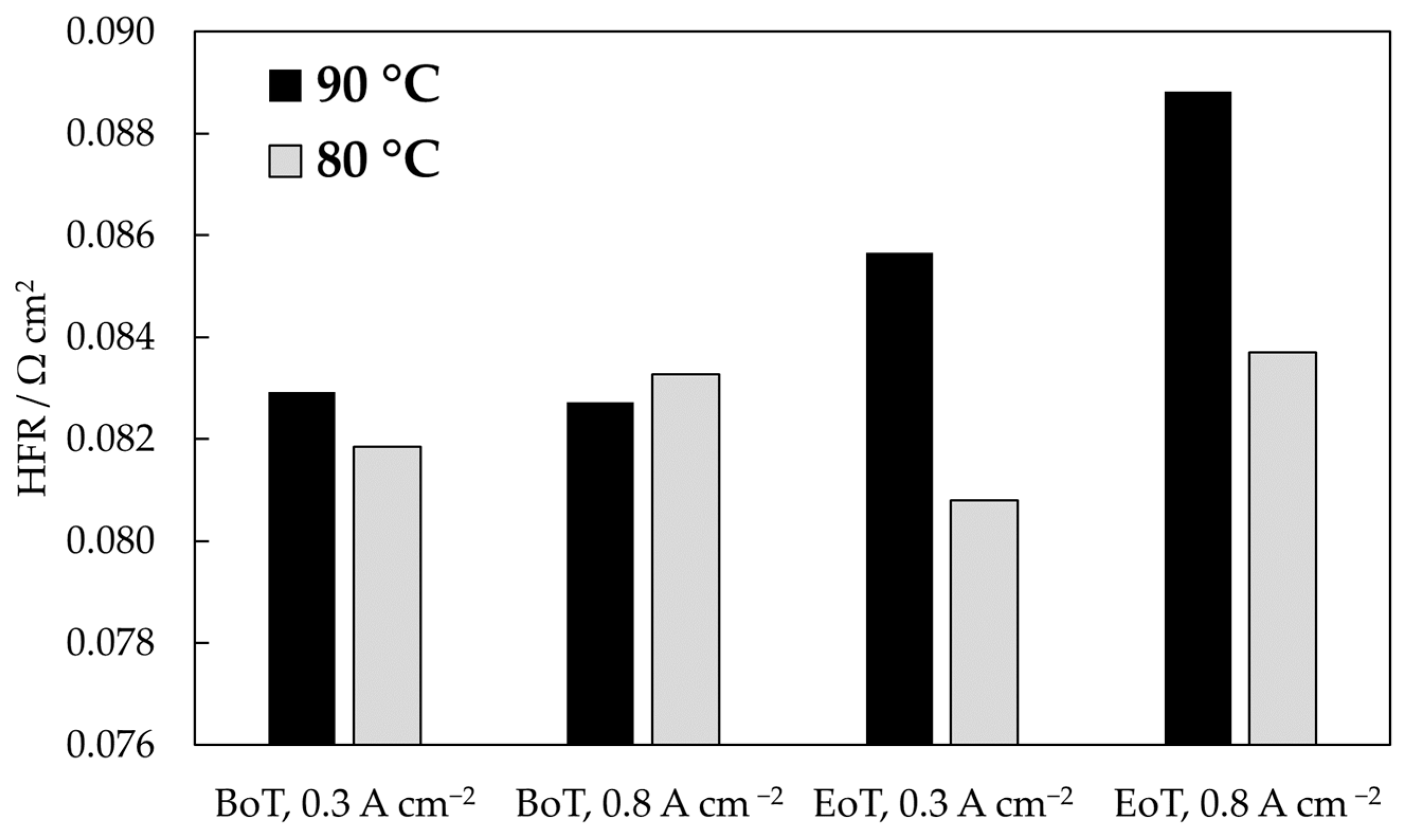
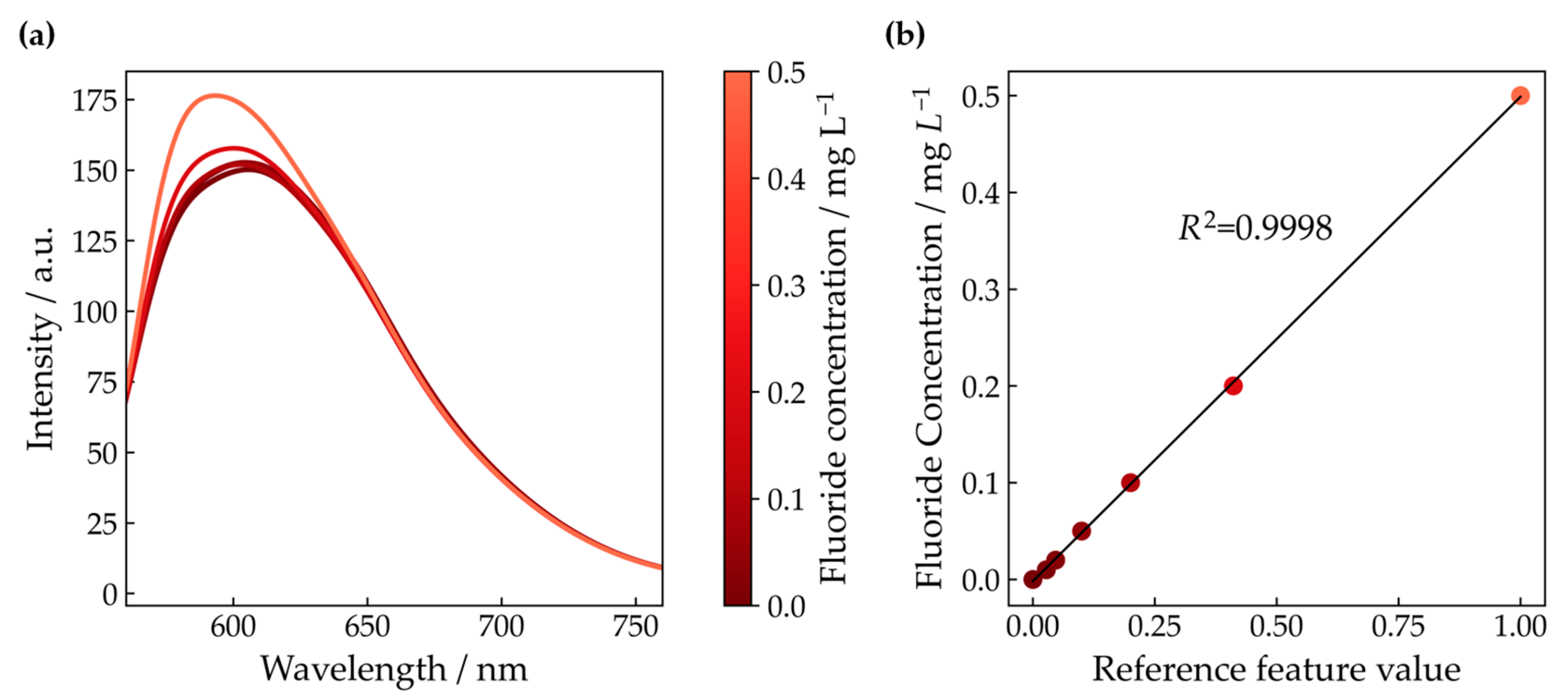
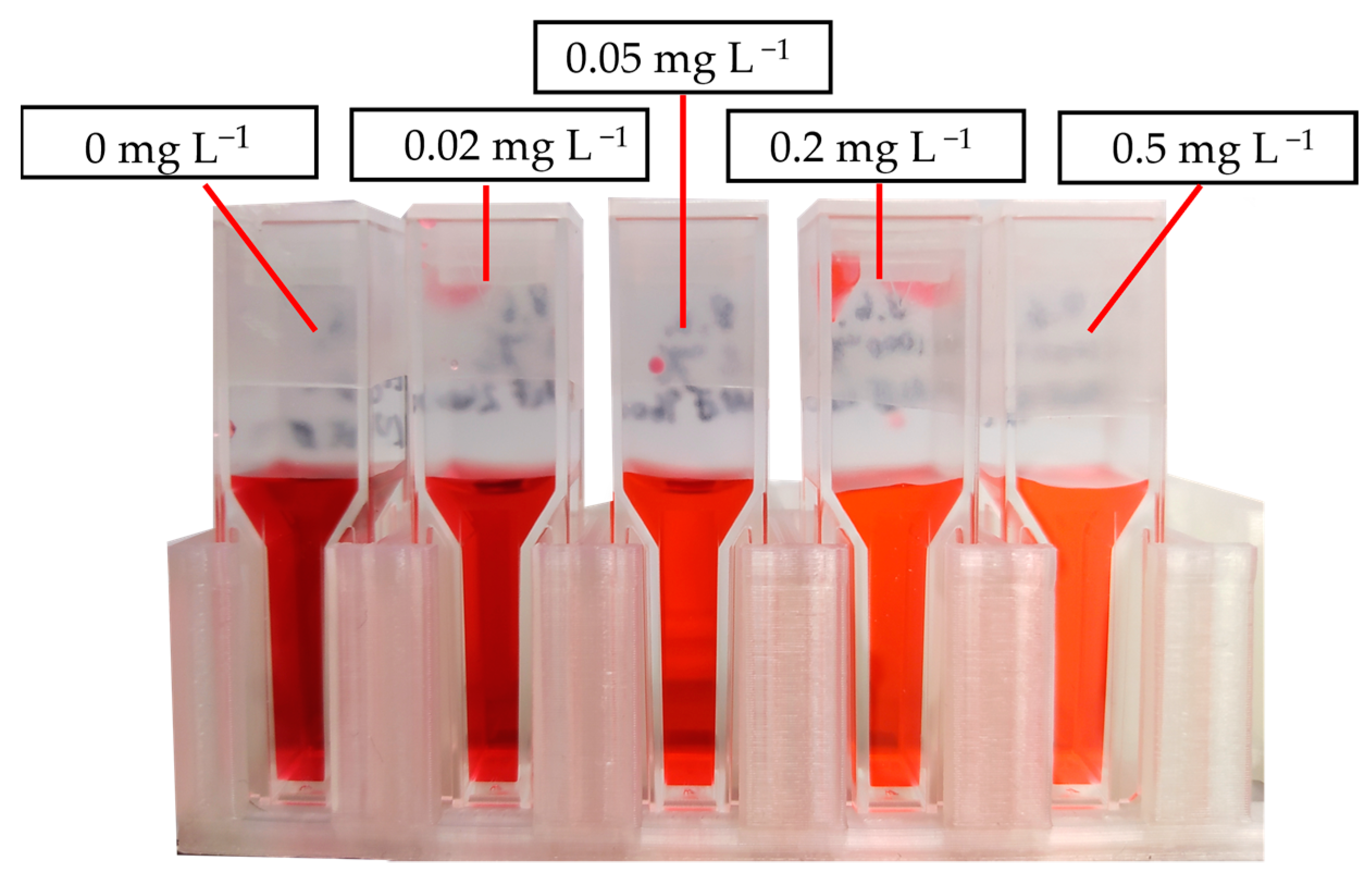
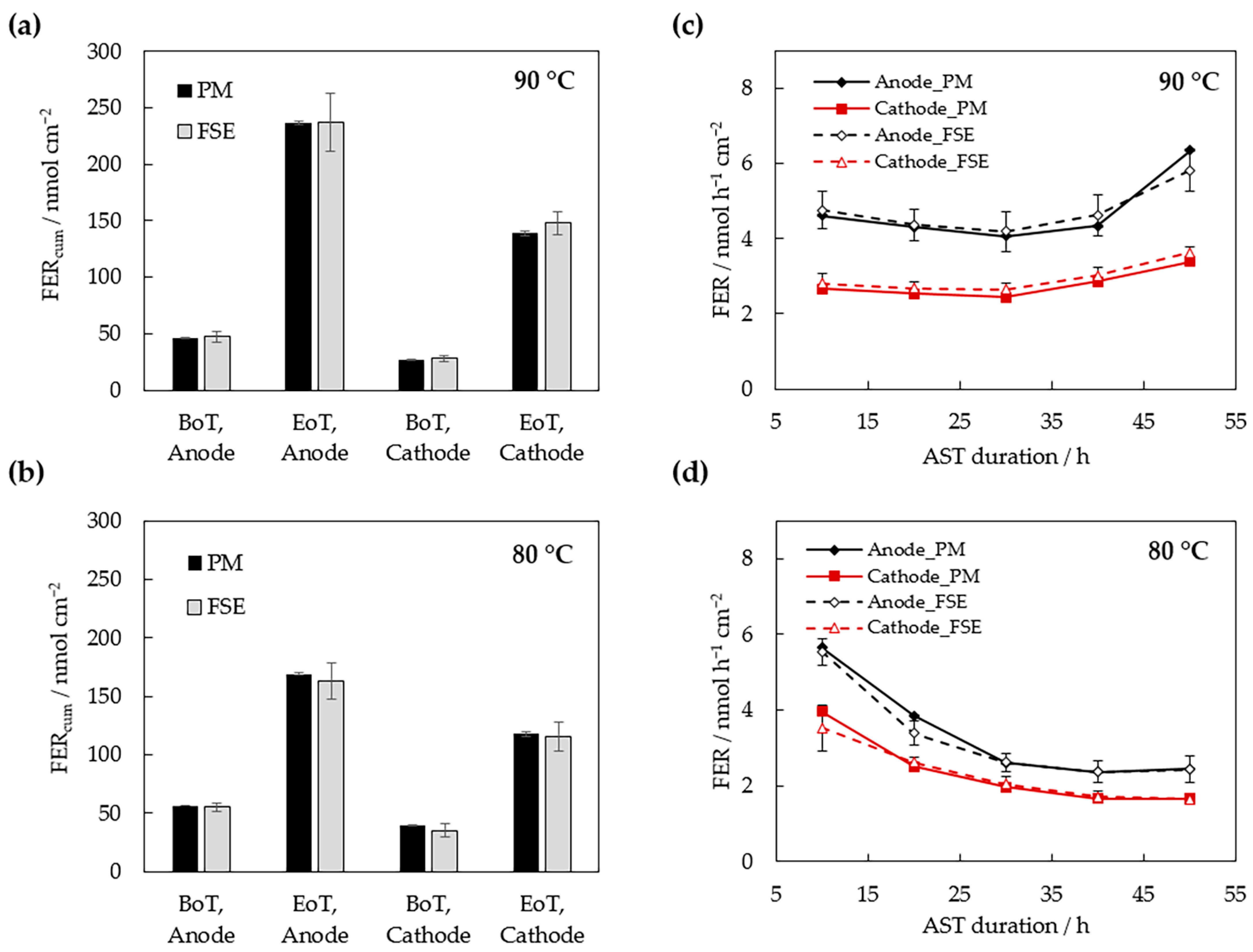
| Cell Temperature | Sampling Location | AST Time /h | Fluoride Emission Rate/nmol h−1 cm−2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photometry | FSE | |||
| 80 °C | Anode | 10 | 5.65 ± 0.03 | 5.54 ± 0.35 |
| 20 | 3.85 ± 0.02 | 3.39 ± 0.32 | ||
| 30 | 2.60 ± 0.02 | 2.62 ± 0.25 | ||
| 40 | 2.37 ± 0.02 | 2.37 ± 0.29 | ||
| 50 | 2.46 ± 0.02 | 2.43 ± 0.34 | ||
| Cathode | 10 | 3.96 ± 0.03 | 3.53 ± 0.60 | |
| 20 | 2.52 ± 0.04 | 2.62 ± 0.15 | ||
| 30 | 1.96 ± 0.03 | 2.04 ± 0.20 | ||
| 40 | 1.66 ± 0.04 | 1.71 ± 0.16 | ||
| 50 | 1.67 ± 0.04 | 1.65 ± 0.15 | ||
| 90 °C | Anode | 10 | 4.62 ± 0.03 | 4.76 ± 0.49 |
| 20 | 4.31 ±0.03 | 4.36 ± 0.43 | ||
| 30 | 4.07 ±0.03 | 4.19 ± 0.53 | ||
| 40 | 4.34 ± 0.03 | 4.63 ± 0.55 | ||
| 50 | 6.35 ± 0.03 | 5.81 ± 0.55 | ||
| Cathode | 10 | 2.67 ± 0.06 | 2.81 ± 0.27 | |
| 20 | 2.54 ± 0.05 | 2.68 ± 0.17 | ||
| 30 | 2.44 ± 0.04 | 2.65 ± 0.16 | ||
| 40 | 2.86 ± 0.05 | 3.02 ± 0.23 | ||
| 50 | 3.39 ± 0.04 | 3.63 ± 0.14 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heidinger, M.; Kuhnert, E.; Mayer, K.; Sandu, D.; Hacker, V.; Bodner, M. Photometric Method to Determine Membrane Degradation in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Energies 2023, 16, 1957. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041957
Heidinger M, Kuhnert E, Mayer K, Sandu D, Hacker V, Bodner M. Photometric Method to Determine Membrane Degradation in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Energies. 2023; 16(4):1957. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041957
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeidinger, Mathias, Eveline Kuhnert, Kurt Mayer, Daniel Sandu, Viktor Hacker, and Merit Bodner. 2023. "Photometric Method to Determine Membrane Degradation in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells" Energies 16, no. 4: 1957. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041957
APA StyleHeidinger, M., Kuhnert, E., Mayer, K., Sandu, D., Hacker, V., & Bodner, M. (2023). Photometric Method to Determine Membrane Degradation in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Energies, 16(4), 1957. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041957







