Biomass Origin Waste as Activators of the Polyurethane Foaming Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fillers’ Characteristics
2.2. Preparation of Rigid Polyurethane Foam Samples and Characterization of the Foaming Process
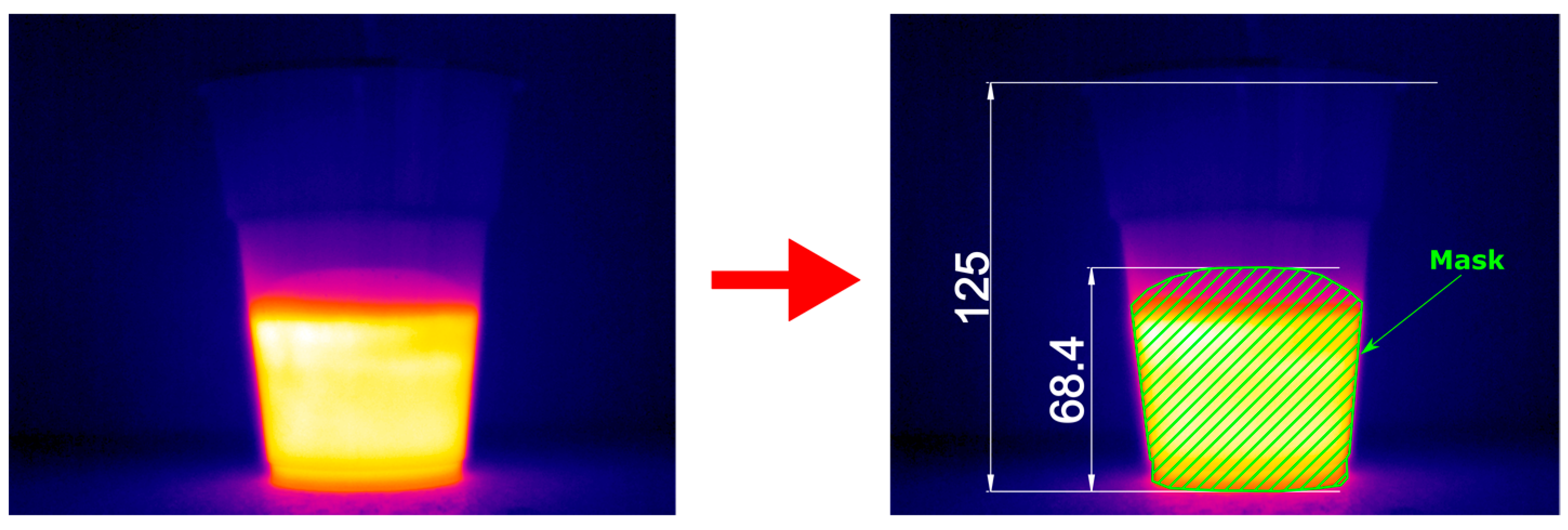
2.3. Temperature and Volume Measurements
3. Results
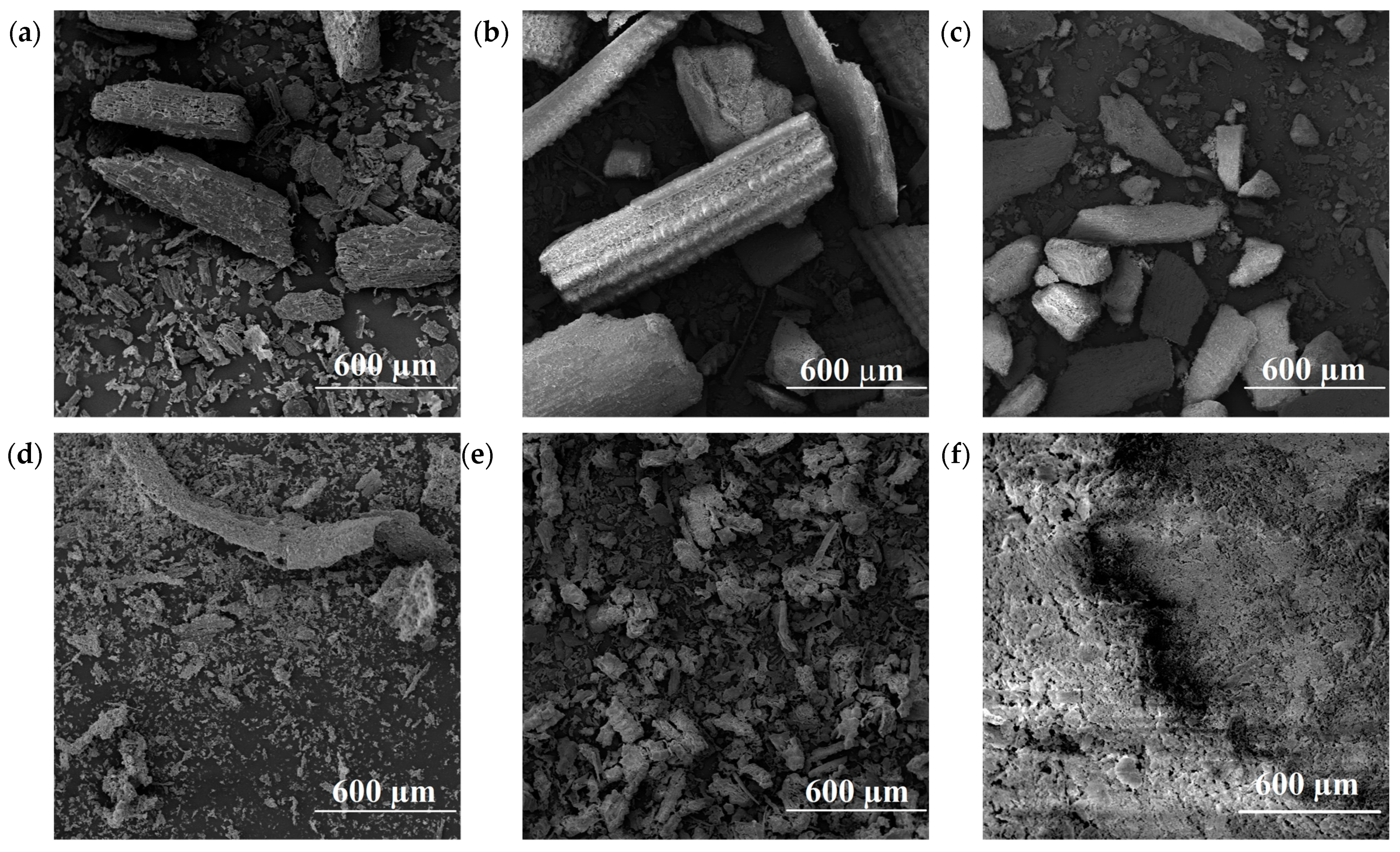
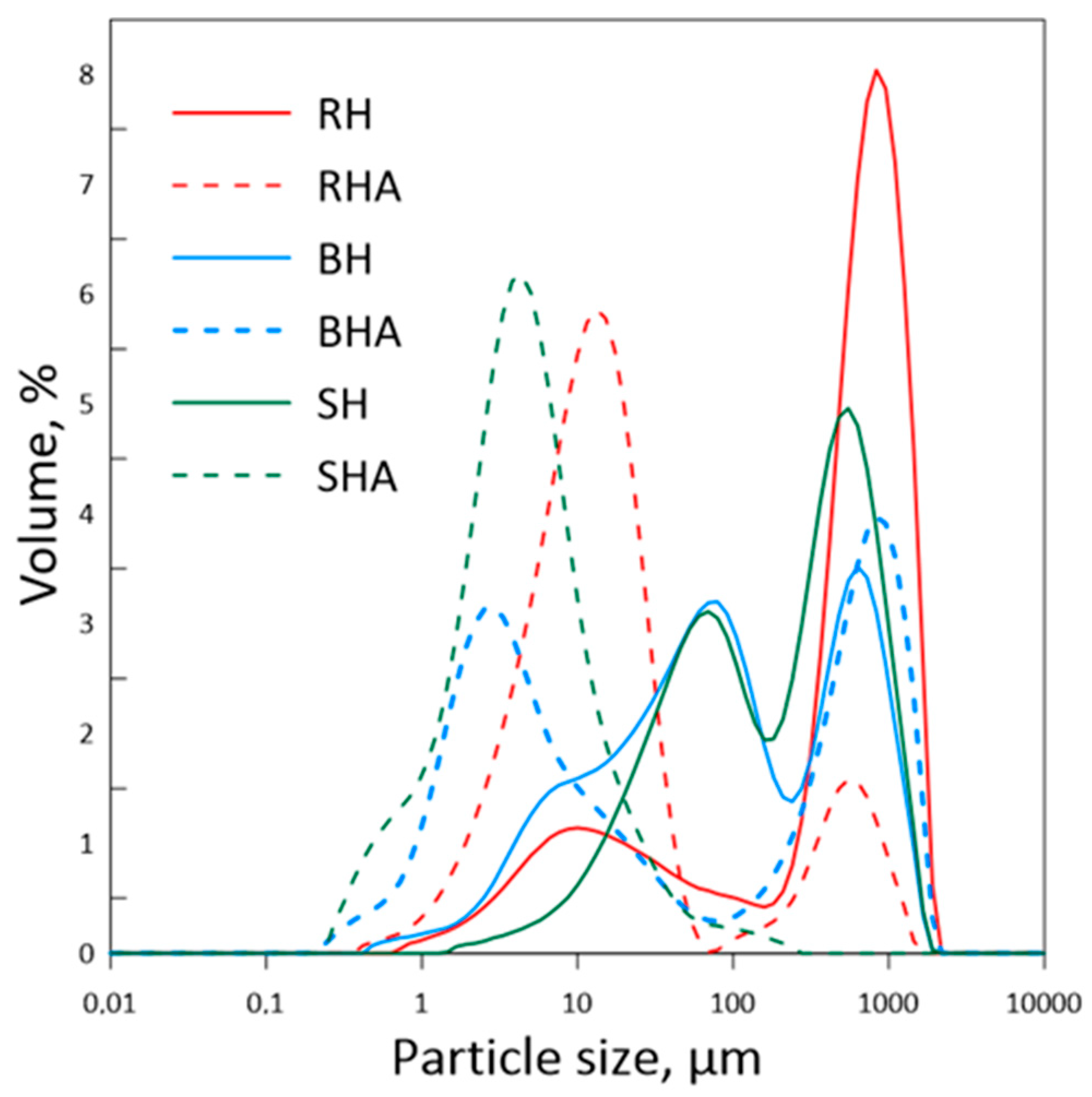
3.1. Fillers’ Characteristics
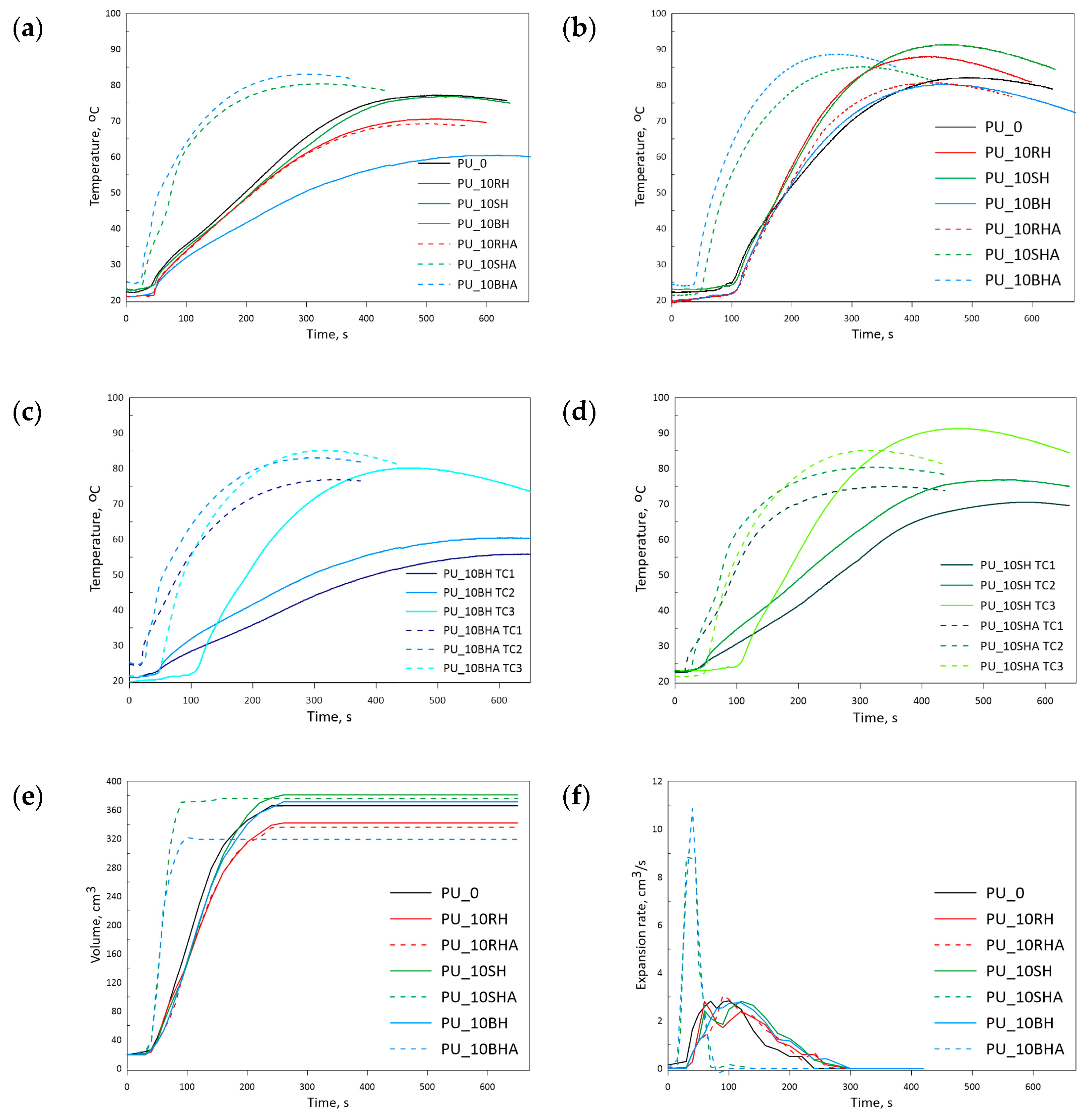
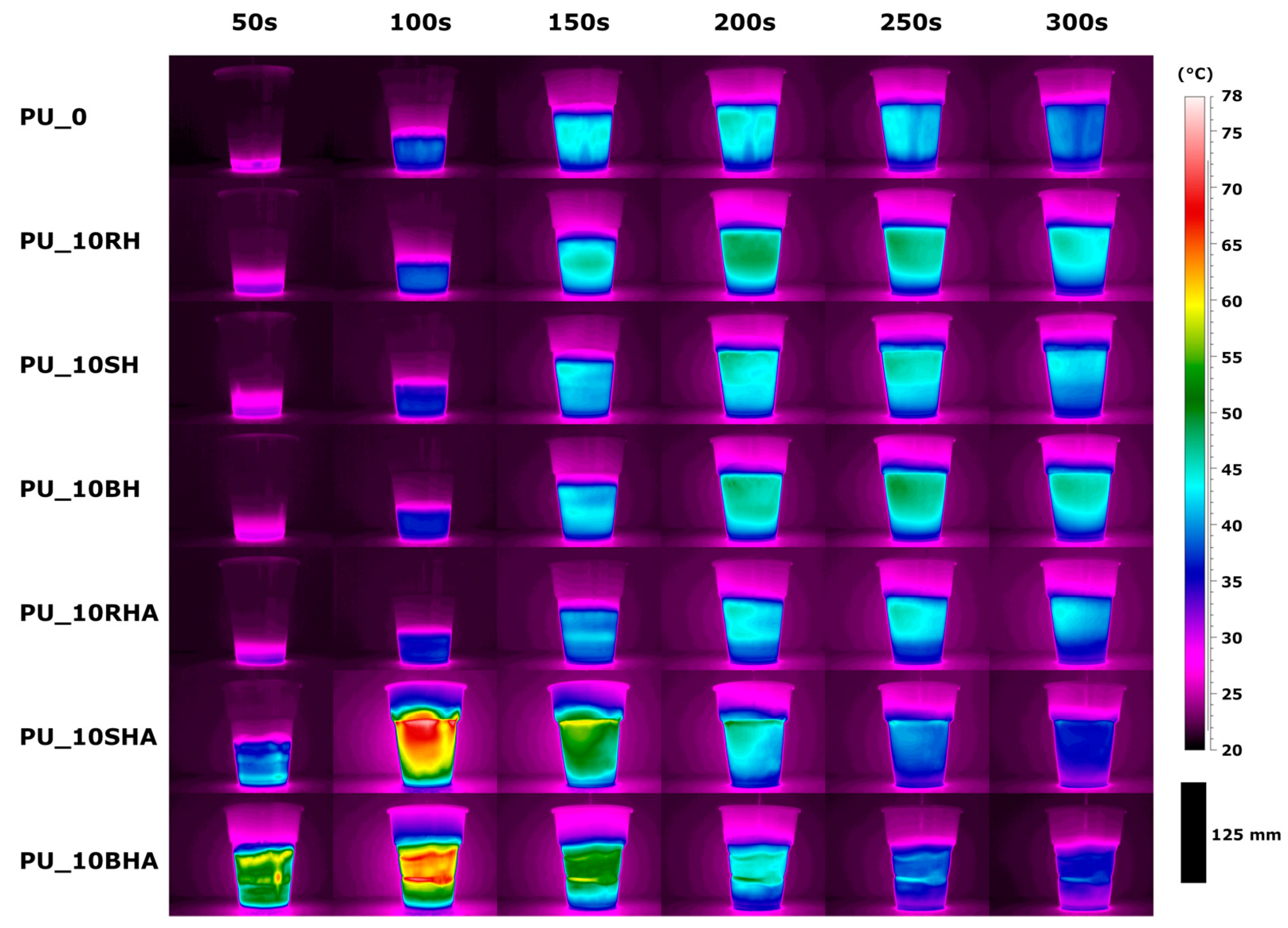
3.2. Polyurethane Foaming Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gama, N.V.; Ferreira, A.; Barros-Timmons, A. Polyurethane foams: Past, present, and future. Materials 2018, 11, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Członka, S.; Strąkowska, A.; Strzelec, K.; Kairytė, A.; Vaitkus, S. Composites of rigid polyurethane foams and silica powder filler enhanced with ionic liquid. Polym. Test. 2019, 75, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, G.; Xu, X.; Tian, X.; Wu, J.; He, X.; Xu, L.; Yunjun, Y. Synthesis and characterization of flame-retardant rigid polyurethane foams derived from gutter oil biodiesel. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 147, 110329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, B.; Qiu, Y. Quickly self-extinguishing flame retardant behavior of rigid polyurethane foams linked with phosphaphenanthrene groups. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Członka, S.; Bertino, M.F.; Strzelec, K. Rigid polyurethane foams reinforced with industrial potato protein. Polym. Test. 2018, 68, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, W.; Qian, L.; Huang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Li, L. Continuous flame-retardant actions of two phosphate esters with expandable graphite in rigid polyurethane foams. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 130, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Sun, S.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Zheng, J.; Lin, X.; Qin, Y.; Qiu, X. Successive organic solvent fractionation and homogenization of technical lignin for polyurethane foam with high mechanical performance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 221, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, M.; Magdziarz, A.; Zajemska, M.; Kuźnia, M. Syngas as a reburning fuel for natural gas combustion. Chem. Process Eng. Inz. Chem. Proces. 2014, 35, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerzak, W.; Kuźnia, M.; Szajding, A. Experimental Studies and the Chemical Kinetics Modelling of Oxidation of Hydrogen Sulfide Contained in Biogas. Procedia Eng. 2016, 157, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, L.; Barczewski, M.; Kosmela, P.; Marrero, M.D.; Ortega, Z. Giant Reed (Arundo donax L.) Fiber Extraction and Characterization for Its Use in Polymer Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 20, 2131687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Członka, S.; Strąkowska, A.; Kairytė, A.; Kremensas, A. Nutmeg filler as a natural compound for the production of polyurethane composite foams with antibacterial and anti-aging properties. Polym. Test. 2022, 86, 106479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strąkowska, A.; Członka, S.; Konca, P.; Strzelec, K. New Flame Retardant Systems Based on Expanded Graphite for Rigid Polyurethane Foams. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharsia, R.R.; Jerro, H.D. Enhancing tensile strength and toughness in syntactic foams through nanoclay reinforcement. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 454, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña, P.; Lin, X.; Calvo, M.S.; Shao, Z.; Pérez, N.; Villafañe, F.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.Á.; Wang, D. Synergistic effect of expandable graphite and phenylphosphonic-aniline salt on flame retardancy of rigid polyurethane foam. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 179, 109274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sethi, J.; Geng, S.; Berglund, L.; Frisk, N.; Aitomäki, Y.; Sain, M.M.; Oksman, K. Dispersion and reinforcing effect of carrot nanofibers on biopolyurethane foams. Mater. Des. 2016, 110, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husainie, S.M.; Deng, X.; Ghalia, M.A.; Robinson, J.; Naguib, H.E. Natural fillers as reinforcement for closed-molded polyurethane foam plaques: Mechanical, morphological, and thermal properties. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 27, 102187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuźnia, M.; Magiera, A.; Pielichowska, K.; Ziąbka, M.; Benko, A.; Sztkowski, P.; Jerzak, W. Fluidized bed combustion fly ash as filler in composite polyurethane materials. Waste Manag. 2019, 92, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuźnia, M.; Magiera, A.; Zygmunt-Kowalska, B.; Kaczorek-Chrobak, K.; Pielichowska, K.; Szatkowski, P.; Benko, A.; Ziąbka, M.; Jerzak, W. Fly ash as an eco-friendly filler for rigid polyurethane foams modification. Materials 2021, 14, 6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuźnia, M.; Zygmunt-Kowalska, B.; Szajding, A.; Magiera, A.; Stanik, R.; Gude, M. Comparative Study on Selected Properties of Modified Polyurethane Foam with Fly Ash. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuźnia, M. Reusing of fly ash from coal combustion in technology of polyurethane materials. Przemysł Chem. 2021, 1, 38–40. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zygmunt-Kowalska, B.; Pielichowska, K.; Trestka, P.; Ziąbka, M.; Kuźnia, M. The Effect of Ash Silanization on the Selected Properties of Rigid Polyurethane Foam/Coal Fly Ash Composites. Energies 2022, 15, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaukat, R.A.; Saqib, Q.M.; Khan, M.U.; Chougale, M.Y.; Bae, J. Bio-waste sunflower husks powder based recycled triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubitto, M.A.; Gentili, R.A. Bioremediation of Crude Oil-Contaminated Soil by Immobilized Bacteria on an Agroindustrial Waste—Sunflower Seed Husks. Bioremediat. J. 2015, 19, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehlen, G.S.; Nogueira, A.P.G.; Carlevaris, D.; Barros, L.Y.; Poletto, J.C.; Lasch, G.; Straffelini, G.; Ferreira, N.F.; Neis, P.D. Tribological assessment of rice husk ash in eco-friendly brake friction materials. Wear 2023, 516, 204613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel Tinoco, M.; Gouvêa, L.; de Cássia Magalhães Martins, K.; Dias Toledo Filho, R.; Aurelio Mendoza Reales, O. The use of rice husk particles to adjust the rheological properties of 3D printable cementitious composites through water sorption. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 130046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.; Andres, Y.; Blel, W.; Gad, A.; Ahmed, A. Effect of VS organic loads and buckwheat husk on methane production by anaerobic co-digestion of primary sludge and wheat straw. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 117, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szycher, M. Structure–Property Relations in Polyurethanes. In Szycher’s Handbook of Polyurethanes, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 37–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimavilla-Román, P.; Pérez-Tamarit, S.; Santiago-Calvo, M.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.Á. Influence of silica aerogel particles on the foaming process and cellular structure of rigid polyurethane foams. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 135, 109884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Abraham, T.; Ference, D.; MacOsko, C.W. Rigid polyurethane foams from a soybean oil-based Polyol. Polymer 2011, 52, 2840–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Calvo, M.; Pérez-Tamarit, S.; Tirado-Mediavilla, J.; Villafañe, F.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.A. Infrared expandometry: A novel methodology to monitor the expansion kinetics of cellular materials produced with exothermic foaming mechanisms. Polym. Test. 2018, 66, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurańska, M.; Prociak, A. The influence of rapeseed oil-based polyols on the foaming process of rigid polyurethane foams. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 89, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Alonso, S.; Solórzano, E.; Estravís, S.; Rodríguez-Perez, M.A.; de Saja, J.A. In situ evidence of the nanoparticle nucleating effect in polyurethane-nanoclay foamed systems. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 11262–11270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Calvo, M.; Blasco, V.; Ruiz, C.; París, R.; Villafañe, F.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.Á. Synthesis, characterization and physical properties of rigid polyurethane foams prepared with poly(propylene oxide) polyols containing graphene oxide. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 97, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mar Bernal, M.; Pardo-Alonso, S.; Solórzano, E.; Lopez-Manchado, M.Á.; Verdejo, R.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.Á. Effect of carbon nanofillers on flexible polyurethane foaming from a chemical and physical perspective. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 20761–20768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczewski, M.; Sałasińska, K.; Szulc, J. Application of sunflower husk, hazelnut shell and walnut shell as waste agricultural fillers for epoxy-based composites: A study into mechanical behavior related to structural and rheological properties. Polym. Test. 2019, 75, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, T.; Kataoka, T.; Nishimura, T.; Sakai, T. Relative viscosities of polymer melts filled with inorganic fillers. Rheol. Acta 1980, 19, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, N.; Unsen, M.; López, H.; Giansiracusa, C.; Roether, J.A.; Boccaccini, A.R. Ash from sunflower husk as raw material for ceramic products. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño, A.A.B.; Lassalle, V.L.; Horst, M.F. Magnetic hydrochar nanocomposite obtained from sunflower husk: A potential material for environmental remediation. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1239, 130509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamanikandan, T.; Banumathi, S.; Karthikeyan, B.; Palanisamy, R.; Bajaj, M.; Zawbaa, H.M.; Kamel, S. Investigation of dielectric and mechanical properties of Lignocellulosic Rice Husk Fibril for high and medium voltage electrical insulation applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, J.; Liang, C. Natural biomass-derived porous carbons from buckwheat hulls used as anode for lithium-ion batteries. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2021, 119, 108553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.E.; El-Refaey, A.A.; Mahmoud, A.H. Effectiveness of Sunflower Seed Husk Biochar for Removing Copper Ions from Wastewater: A Comparative Study. Soil Water Res. 2016, 11, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun, M.; Arslan, H.; Saleh, M.; Yalvac, M.; Dizge, N. Optimization of Silica Extraction from Rice Husk Using Response Surface Methodology and Adsorption of Safranin Dye. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2022, 16, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trestka, P.; Zygmunt-Kowalska, B.; Kuźnia, M.; Olesy, M. Blackcurrant pomace as a biodegradable filler for rigid polyurethane foams. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovations in Energy Engineering & Cleaner Production (IEECP’22), Oxford, UK, 21–22 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczewski, M.; Kurańska, M.; Sałasińska, K.; Michałowski, S.; Prociak, A.; Uram, K.; Lewandowski, K. Rigid polyurethane foams modified with thermoset polyester-glass fiber composite waste. Polym. Test. 2020, 81, 106190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, W.J.; Park, J.H.; Sung, Y.T.; Hwang, D.H.; Kim, W.N.; Lee, H.S. Properties of water-blown rigid polyurethane foams with reactivity of raw materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 2334–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Cho, S.H.; Seo, H.W.; Nam, J.; Suhr, J. Natural cork agglomerate enabled mechanically robust rigid polyurethane foams with outstanding viscoelastic damping properties. Polymer 2021, 217, 123437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczewski, M.; Kurańska, M.; Sałasińska, K.; Aniśko, J.; Szulc, J.; Szafraniak-Wiza, I.; Prociak, A.; Polaczek, K.; Uram, K.; Surmacz, K.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of the Influence of Expanded Vermiculite on the Foaming Process and Selected Properties of Composite Rigid Polyurethane Foams. Polymers 2022, 14, 4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, G.; Khakhar, D.V. Modeling the dynamics of reactive foaming and film thinning in polyurethane foams. AIChE J. 2010, 56, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniowski, W.; Taler, J.; Wang, X.; Kalemba-Rec, I.; Gajek, M.; Mlonka-Mędrala, A.; Nowak-Woźny, D.; Magdziarz, A. Investigation of biomass, RDF and coal ash-related problems: Impact on metallic heat exchanger surfaces of boilers. Fuel 2022, 326, 125122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Filler | Description | C, % | H, % | N, % | SSABET, m2/g | Ash Content, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH | Sunflower husk | 48.75 | 5.67 | 0.82 | 0.39 | 3.36 |
| RH | Rice husk | 40.82 | 5.20 | 0.50 | 0.51 | 1.53 |
| BH | Buckwheat husk | 47.96 | 5.67 | 0.62 | 0.28 | 14.25 |
| SHA | Sunflower husk ash | 5.68 | 0.76 | 0.11 | 4.13 | - |
| RHA | Rice husk ash | 1.35 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 3.91 | - |
| BHA | Buckwheat husk ash | 7.09 | 0.89 | 0.14 | 6.57 | - |
| Foam | Description | Cream Time, s | Rise Time, s | Tack-Free Time, s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PU_0 | Foam without fillers | 8.37 | 170 | 932 |
| PU_10SH | Foam with 10% SH | 8.46 | 164 | 799 |
| PU_10RH | Foam with 10% RH | 8.83 | 180 | 695 |
| PU_10BH | Foam with 10% BH | 8.60 | 178 | 863 |
| PU_10SHA | Foam with 10% SHA | 8.63 | 51 | 14 |
| PU_10RHA | Foam with 10% RHA | 8.98 | 196 | 573 |
| PU_10BHA | Foam with 10% BHA | 8.42 | 55 | 28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zakrzewska, P.; Zygmunt-Kowalska, B.; Kuźnia, M.; Szajding, A.; Telejko, T.; Wilk, M. Biomass Origin Waste as Activators of the Polyurethane Foaming Process. Energies 2023, 16, 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031354
Zakrzewska P, Zygmunt-Kowalska B, Kuźnia M, Szajding A, Telejko T, Wilk M. Biomass Origin Waste as Activators of the Polyurethane Foaming Process. Energies. 2023; 16(3):1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031354
Chicago/Turabian StyleZakrzewska, Patrycja, Beata Zygmunt-Kowalska, Monika Kuźnia, Artur Szajding, Tadeusz Telejko, and Małgorzata Wilk. 2023. "Biomass Origin Waste as Activators of the Polyurethane Foaming Process" Energies 16, no. 3: 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031354
APA StyleZakrzewska, P., Zygmunt-Kowalska, B., Kuźnia, M., Szajding, A., Telejko, T., & Wilk, M. (2023). Biomass Origin Waste as Activators of the Polyurethane Foaming Process. Energies, 16(3), 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031354









