Day-Ahead Hourly Solar Photovoltaic Output Forecasting Using SARIMAX, Long Short-Term Memory, and Extreme Gradient Boosting: Case of the Philippines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
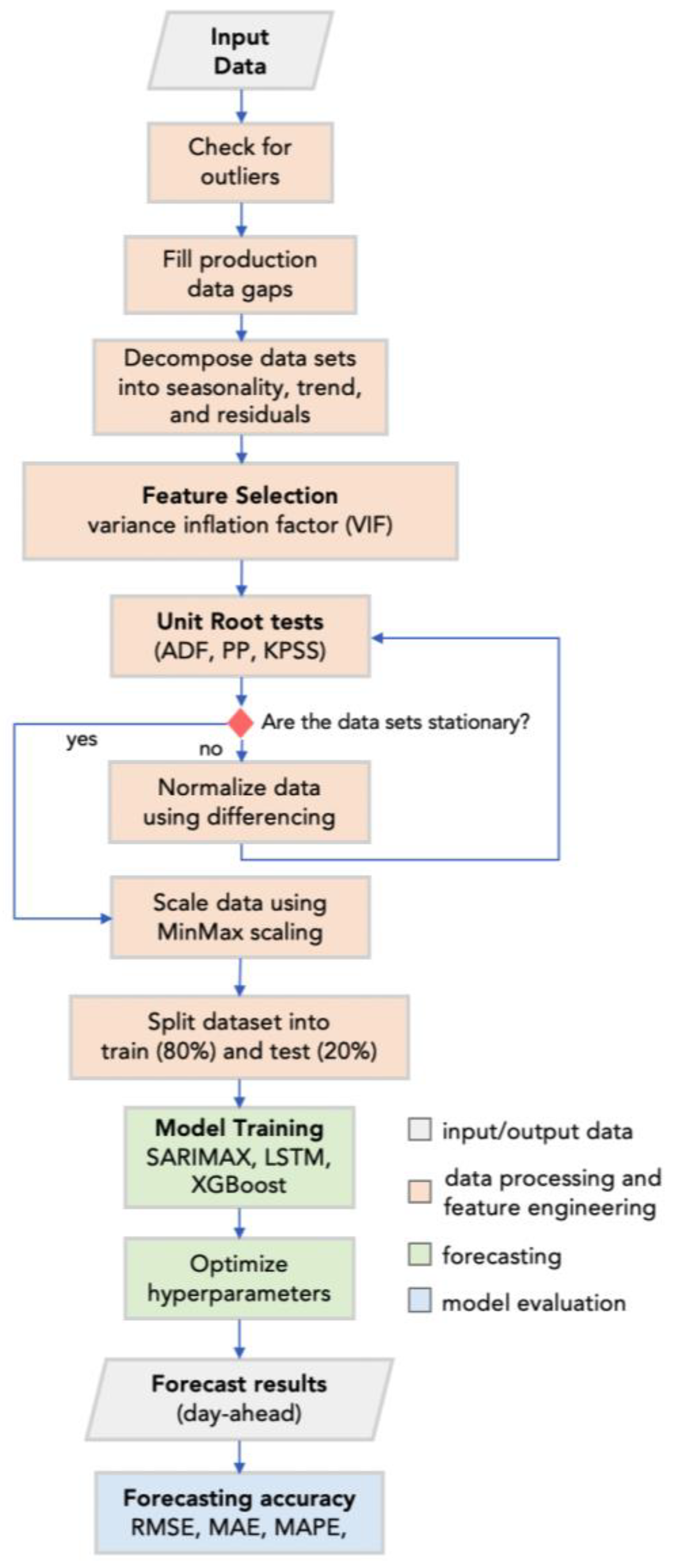
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Solar PV Output Data
2.1.2. Weather Parameters and Solar Irradiance
2.2. Data Processing and Feature Engineering
2.2.1. Outlier Detection and Data Gaps Filling
2.2.2. Decomposition
2.2.3. Feature Selection
2.2.4. Unit Root Testing
2.2.5. Data Splitting
2.3. Forecasting Techniques
2.3.1. SARIMAX
2.3.2. Long Short-Term Memory
2.3.3. Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost)
2.3.4. Hybrid Models
2.4. Model Evaluation
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Data Evaluation
3.2. Data Processing and Feature Engineering
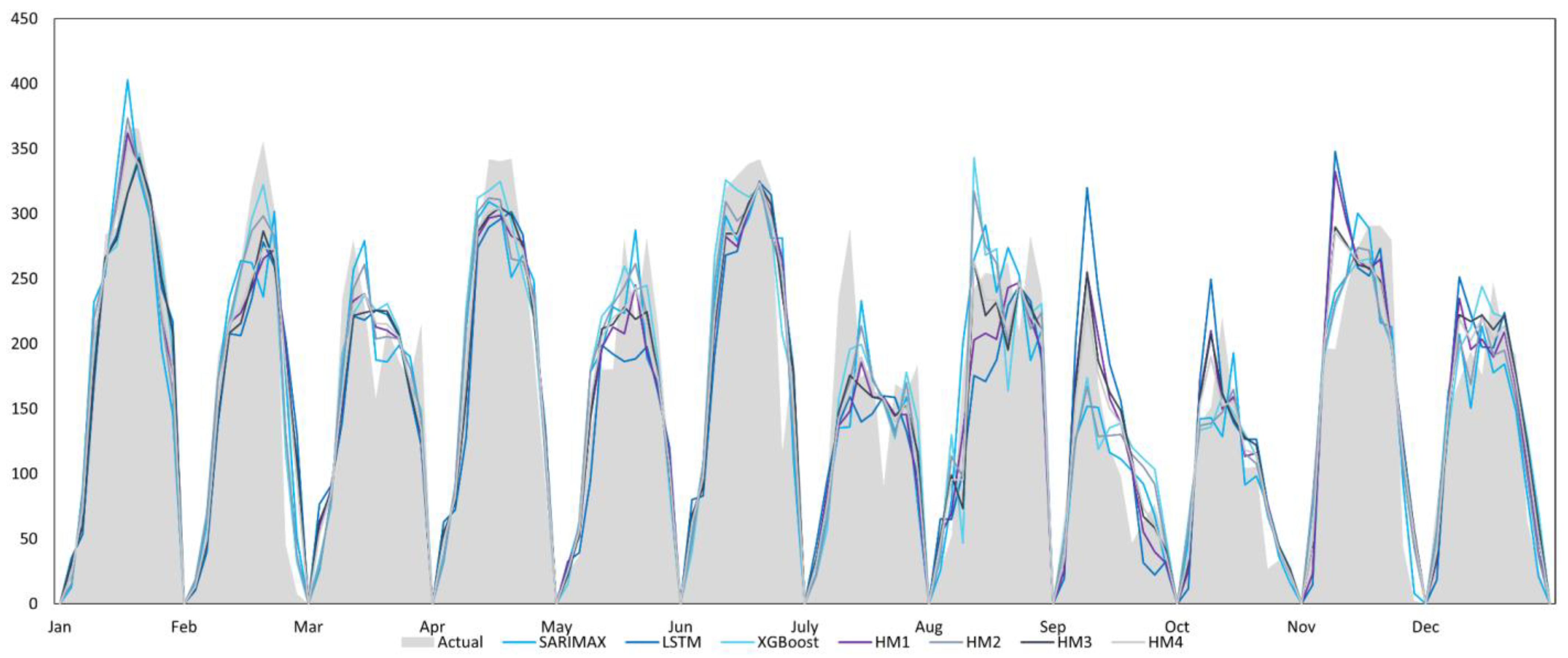
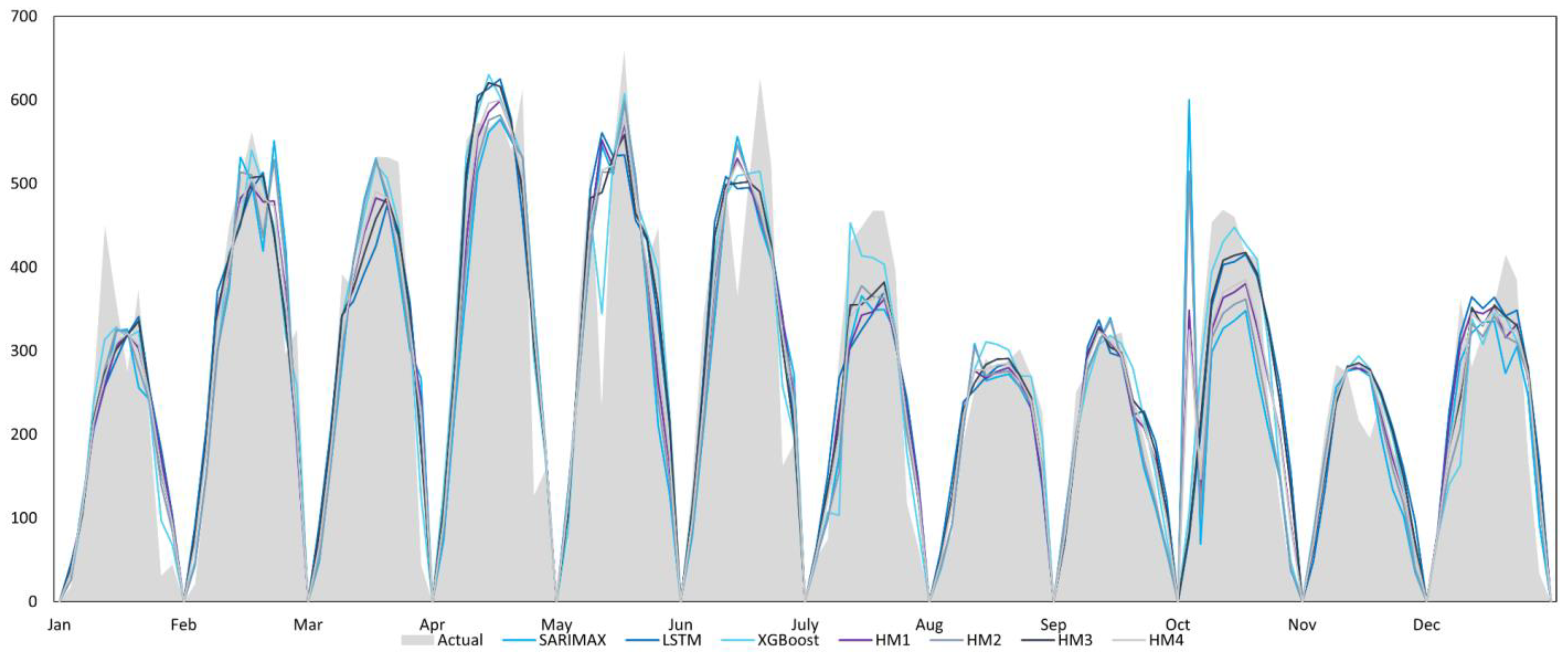
3.3. Forecasting
3.3.1. Plant 1
3.3.2. Plant 2
3.3.3. Plant 3
3.3.4. Model Performance for the Three Plants
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Model | SARIMAX | LSTM | XGBoost | HM1 | HM2 | HM3 | HM4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | |||||||
| Metrics | |||||||
| January | |||||||
| RMSE | 2.92 | 4.38 | 1.91 | 3.20 | 2.46 | 3.12 | 2.74 |
| MAE | 1.61 | 1.91 | 0.95 | 1.53 | 1.37 | 1.44 | 1.31 |
| MAPE | 7.52 | 8.93 | 4.29 | 6.40 | 6.25 | 6.80 | 5.57 |
| February | |||||||
| RMSE | 5.18 | 7.21 | 3.72 | 6.018 | 4.12 | 5.66 | 5.29 |
| MAE | 2.68 | 3.66 | 2.01 | 3.016 | 2.17 | 3.01 | 2.74 |
| MAPE | 10.94 | 13.93 | 8.16 | 11.68 | 9.01 | 11.44 | 10.57 |
| March | |||||||
| RMSE | 3.59 | 7.59 | 4.46 | 5.88 | 3.72 | 6.18 | 5.35 |
| MAE | 1.72 | 3.33 | 2.08 | 2.56 | 1.84 | 2.73 | 2.39 |
| MAPE | 4.82 | 7.57 | 5.00 | 5.89 | 4.77 | 6.15 | 5.49 |
| April | |||||||
| RMSE | 2.58 | 6.43 | 2.78 | 4.85 | 2.30 | 5.09 | 4.19 |
| MAE | 1.33 | 2.80 | 1.18 | 2.17 | 1.12 | 2.30 | 1.91 |
| MAPE | 3.58 | 7.56 | 2.90 | 5.94 | 2.98 | 6.18 | 5.18 |
| May | |||||||
| RMSE | 3.14 | 5.47 | 1.78 | 4.16 | 2.48 | 4.43 | 3.64 |
| MAE | 1.43 | 2.71 | 0.93 | 2.15 | 1.18 | 2.26 | 1.93 |
| MAPE | 4.63 | 8.33 | 2.64 | 6.86 | 3.93 | 6.92 | 6.12 |
| June | |||||||
| RMSE | 4.72 | 11.01 | 4.76 | 7.04 | 4.23 | 8.46 | 6.18 |
| MAE | 2.60 | 4.92 | 2.20 | 3.49 | 2.27 | 4.00 | 3.19 |
| MAPE | 9.13 | 14.63 | 5.83 | 11.17 | 7.33 | 11.75 | 9.99 |
| July | |||||||
| RMSE | 12.49 | 14.29 | 10.26 | 10.94 | 11.15 | 10.66 | 10.23 |
| MAE | 5.96 | 5.33 | 3.43 | 5.45 | 4.58 | 4.57 | 4.99 |
| MAPE | 17.29 | 16.00 | 8.11 | 15.84 | 12.17 | 12.78 | 14.00 |
| August | |||||||
| RMSE | 3.74 | 6.27 | 2.04 | 4.54 | 2.73 | 5.09 | 4.05 |
| MAE | 1.99 | 2.70 | 1.00 | 2.35 | 1.38 | 2.22 | 2.06 |
| MAPE | 10.41 | 15.01 | 4.90 | 12.84 | 7.03 | 12.25 | 11.19 |
| September | |||||||
| RMSE | 13.14 | 13.00 | 8.30 | 12.07 | 9.86 | 10.27 | 10.98 |
| MAE | 6.17 | 6.26 | 4.08 | 5.50 | 4.79 | 4.65 | 5.08 |
| MAPE | 24.31 | 21.35 | 14.70 | 20.81 | 17.95 | 16.48 | 19.09 |
| October | |||||||
| RMSE | 4.05 | 7.90 | 2.30 | 5.14 | 2.70 | 5.63 | 4.38 |
| MAE | 1.95 | 3.61 | 1.16 | 2.69 | 1.38 | 2.70 | 2.31 |
| MAPE | 19.39 | 21.80 | 12.35 | 17.94 | 12.34 | 18.34 | 15.67 |
| November | |||||||
| RMSE | 2.30 | 5.29 | 2.89 | 4.82 | 2.55 | 3.32 | 3.19 |
| MAE | 1.17 | 2.06 | 1.51 | 1.94 | 1.34 | 1.67 | 1.63 |
| MAPE | 6.31 | 53.16 | 51.77 | 48.12 | 43.61 | 52.28 | 49.64 |
| December | |||||||
| RMSE | 1.52 | 3.89 | 1.76 | 3.40 | 1.42 | 2.37 | 2.24 |
| MAE | 0.70 | 1.65 | 0.92 | 1.51 | 0.72 | 1.13 | 1.10 |
| MAPE | 3.47 | 21.74 | 29.02 | 18.75 | 20.87 | 25.70 | 24.06 |
| Average | |||||||
| RMSE | 4.95 | 7.73 | 3.91 | 6.01 | 4.14 | 5.86 | 5.21 |
| MAE | 2.44 | 3.41 | 1.79 | 2.86 | 2.01 | 2.72 | 2.55 |
| MAPE | 10.15 | 17.50 | 12.47 | 15.19 | 12.35 | 15.59 | 14.71 |
| Model | SARIMAX | LSTM | XGBoost | HM1 | HM2 | HM3 | HM4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | |||||||
| Metrics | |||||||
| January | |||||||
| RMSE | 4.86 | 2.53 | 2.28 | 2.99 | 3.52 | 2.31 | 2.65 |
| MAE | 2.73 | 1.27 | 1.20 | 1.55 | 1.89 | 1.11 | 1.44 |
| MAPE | 8.41 | 7.49 | 4.25 | 5.46 | 5.56 | 5.70 | 5.12 |
| February | |||||||
| RMSE | 6.45 | 8.42 | 3.10 | 7.61 | 3.91 | 7.35 | 6.93 |
| MAE | 2.76 | 4.49 | 1.52 | 3.90 | 1.80 | 3.91 | 3.55 |
| MAPE | 39.40 | 90.31 | 21.98 | 74.67 | 26.64 | 76.94 | 67.04 |
| March | |||||||
| RMSE | 4.05 | 5.76 | 4.13 | 4.93 | 3.82 | 5.17 | 4.69 |
| MAE | 2.15 | 2.96 | 2.01 | 2.41 | 1.96 | 2.64 | 2.28 |
| MAPE | 7.23 | 14.65 | 6.36 | 10.95 | 6.23 | 12.04 | 9.81 |
| April | |||||||
| RMSE | 4.11 | 4.23 | 2.77 | 3.74 | 3.58 | 3.30 | 3.31 |
| MAE | 1.92 | 2.28 | 1.54 | 2.02 | 1.79 | 1.84 | 1.80 |
| MAPE | 5.30 | 9.23 | 4.23 | 6.98 | 4.88 | 7.00 | 5.96 |
| May | |||||||
| RMSE | 5.24 | 4.95 | 3.53 | 4.54 | 4.08 | 3.38 | 3.90 |
| MAE | 2.79 | 2.40 | 2.11 | 2.24 | 2.36 | 1.73 | 2.09 |
| MAPE | 11.06 | 8.25 | 10.93 | 8.39 | 10.04 | 6.64 | 7.82 |
| June | |||||||
| RMSE | 6.86 | 6.09 | 3.58 | 6.21 | 5.53 | 5.13 | 5.66 |
| MAE | 3.15 | 3.06 | 1.53 | 3.08 | 2.45 | 2.56 | 2.77 |
| MAPE | 11.50 | 13.11 | 5.29 | 12.23 | 8.87 | 10.65 | 10.87 |
| July | |||||||
| RMSE | 7.90 | 6.93 | 5.31 | 7.18 | 6.31 | 5.95 | 6.54 |
| MAE | 3.87 | 3.53 | 2.84 | 3.41 | 3.25 | 2.92 | 3.16 |
| MAPE | 13.69 | 14.02 | 11.47 | 12.23 | 12.32 | 11.01 | 11.20 |
| August | |||||||
| RMSE | 4.22 | 5.90 | 7.41 | 4.43 | 5.53 | 5.34 | 4.66 |
| MAE | 2.10 | 3.54 | 3.86 | 2.70 | 3.05 | 3.02 | 2.68 |
| MAPE | 6.94 | 15.65 | 17.04 | 11.89 | 13.04 | 14.69 | 12.85 |
| September | |||||||
| RMSE | 4.63 | 5.62 | 4.98 | 3.59 | 4.74 | 3.44 | 3.22 |
| MAE | 2.19 | 3.45 | 2.71 | 2.04 | 2.45 | 1.74 | 1.70 |
| MAPE | 14.53 | 22.82 | 18.22 | 15.95 | 16.13 | 13.95 | 13.49 |
| October | |||||||
| RMSE | 3.92 | 4.98 | 2.76 | 4.00 | 3.03 | 3.71 | 3.45 |
| MAE | 1.65 | 2.62 | 1.29 | 2.00 | 1.26 | 2.02 | 1.72 |
| MAPE | 13.16 | 22.32 | 13.13 | 17.73 | 12.25 | 18.51 | 16.11 |
| November | |||||||
| RMSE | 4.19 | 7.38 | 4.87 | 6.73 | 4.56 | 5.70 | 5.52 |
| MAE | 2.01 | 3.85 | 2.55 | 3.52 | 2.27 | 3.08 | 2.96 |
| MAPE | 17.59 | 104.18 | 99.17 | 91.45 | 75.68 | 100.77 | 94.01 |
| December | |||||||
| RMSE | 3.83 | 4.53 | 3.98 | 3.83 | 3.40 | 3.97 | 3.62 |
| MAE | 2.16 | 2.48 | 2.19 | 2.00 | 1.91 | 2.29 | 2.00 |
| MAPE | 9.11 | 15.10 | 16.53 | 11.13 | 9.31 | 15.71 | 13.01 |
| Average | |||||||
| RMSE | 5.02 | 5.61 | 4.06 | 4.98 | 4.33 | 4.56 | 4.51 |
| MAE | 2.46 | 2.99 | 2.11 | 2.57 | 2.20 | 2.41 | 2.34 |
| MAPE | 13.16 | 28.09 | 19.05 | 23.25 | 16.74 | 24.47 | 22.27 |
| Model | SARIMAX | LSTM | XGBoost | HM1 | HM2 | HM3 | HM4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | |||||||
| Metrics | |||||||
| January | |||||||
| RMSE | 5.14 | 5.08 | 3.16 | 5.03 | 4.42 | 4.46 | 4.65 |
| MAE | 2.57 | 2.51 | 1.49 | 2.54 | 2.19 | 2.20 | 2.33 |
| MAPE | 30.55 | 37.68 | 16.58 | 34.49 | 25.63 | 31.24 | 30.99 |
| February | |||||||
| RMSE | 4.64 | 3.55 | 2.05 | 3.50 | 3.93 | 2.98 | 3.11 |
| MAE | 2.57 | 1.93 | 1.09 | 1.85 | 2.16 | 1.56 | 1.68 |
| MAPE | 11.48 | 19.37 | 8.25 | 15.59 | 10.59 | 15.68 | 14.02 |
| March | |||||||
| RMSE | 5.34 | 4.59 | 2.42 | 4.70 | 4.57 | 3.72 | 4.26 |
| MAE | 2.36 | 2.39 | 1.20 | 2.11 | 2.04 | 1.84 | 1.93 |
| MAPE | 26.30 | 21.47 | 10.67 | 22.20 | 22.20 | 17.02 | 20.00 |
| April | |||||||
| RMSE | 6.10 | 5.12 | 3.73 | 5.38 | 5.44 | 4.51 | 4.90 |
| MAE | 2.89 | 2.63 | 1.68 | 2.63 | 2.57 | 2.24 | 2.39 |
| MAPE | 13.99 | 11.77 | 8.07 | 12.71 | 12.63 | 10.27 | 11.57 |
| May | |||||||
| RMSE | 7.95 | 6.97 | 3.05 | 7.33 | 7.10 | 5.59 | 6.54 |
| MAE | 3.87 | 2.80 | 1.62 | 3.27 | 3.44 | 2.38 | 2.90 |
| MAPE | 15.85 | 11.65 | 5.72 | 13.59 | 13.97 | 9.61 | 11.92 |
| June | |||||||
| RMSE | 7.11 | 5.52 | 4.57 | 6.33 | 6.54 | 5.03 | 5.88 |
| MAE | 3.95 | 2.75 | 2.32 | 3.34 | 3.61 | 2.44 | 3.10 |
| MAPE | 15.15 | 10.68 | 8.08 | 13.04 | 13.67 | 9.27 | 11.85 |
| July | |||||||
| RMSE | 5.28 | 5.57 | 4.32 | 5.33 | 4.80 | 4.61 | 4.80 |
| MAE | 3.06 | 3.28 | 2.09 | 3.19 | 2.77 | 2.81 | 2.90 |
| MAPE | 15.57 | 20.43 | 10.56 | 18.33 | 14.10 | 16.82 | 16.40 |
| August | |||||||
| RMSE | 2.10 | 2.43 | 1.29 | 2.14 | 1.93 | 1.85 | 1.82 |
| MAE | 1.11 | 1.17 | 0.74 | 1.09 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 0.94 |
| MAPE | 5.82 | 8.09 | 4.42 | 6.35 | 5.40 | 5.73 | 5.59 |
| September | |||||||
| RMSE | 1.51 | 2.33 | 1.38 | 1.78 | 1.34 | 1.89 | 1.57 |
| MAE | 0.83 | 1.35 | 0.74 | 0.97 | 0.71 | 1.02 | 0.81 |
| MAPE | 4.76 | 11.49 | 5.40 | 8.06 | 4.17 | 8.99 | 6.96 |
| October | |||||||
| RMSE | 11.43 | 5.00 | 2.06 | 7.00 | 9.56 | 4.41 | 6.43 |
| MAE | 5.36 | 2.77 | 1.04 | 3.89 | 4.51 | 2.45 | 3.60 |
| MAPE | 30.90 | 28.61 | 6.43 | 28.10 | 26.18 | 24.53 | 25.97 |
| November | |||||||
| RMSE | 2.59 | 2.66 | 2.44 | 2.32 | 2.40 | 2.46 | 2.31 |
| MAE | 1.46 | 1.44 | 1.21 | 1.19 | 1.29 | 1.25 | 1.16 |
| MAPE | 9.77 | 9.87 | 7.79 | 7.17 | 8.58 | 7.52 | 7.13 |
| December | |||||||
| RMSE | 3.87 | 3.90 | 5.25 | 3.69 | 4.60 | 4.25 | 4.07 |
| MAE | 2.02 | 1.94 | 2.71 | 1.90 | 2.43 | 2.20 | 2.16 |
| MAPE | 13.88 | 22.14 | 21.13 | 18.67 | 18.47 | 21.22 | 19.44 |
| Average | |||||||
| RMSE | 5.25 | 4.40 | 2.98 | 4.54 | 4.72 | 3.81 | 4.20 |
| MAE | 2.67 | 2.25 | 1.49 | 2.33 | 2.39 | 1.94 | 2.16 |
| MAPE | 16.17 | 17.77 | 9.42 | 16.52 | 14.63 | 14.83 | 15.15 |
References
- International Energy Agency. Global Energy Review 2021. 2021. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-review-2021/renewables (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- International Renewable Energy Agency. Renewable Energy and Climate Pledges: Five Years after the Paris Agreement. Abu Dhabi. Available online: https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2020/Dec/IRENA_NDC_update_2020.pdf?rev=cdad99bc95ce4bff98ee48e157847a9f (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- International Energy Agency. “Solar PV”, Paris, Sep. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/solar-pv (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Nwaigwe, K.; Mutabilwa, P.; Dintwa, E. An overview of solar power (PV systems) integration into electricity grids. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiullah; Ahmed, S.D.; Al-Sulaiman, F.A. Grid Integration Challenges and Solution Strategies for Solar PV Systems: A Review. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 52233–52257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaporozhets, A.; Sverdlova, A. Photovoltaic technologies: Problems, technical and economic losses, prospects. In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Information Technologies: Theoretical and Applied Problems, Ternopil, Ukraine, 16–18 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, M.Q.; Nadarajah, M.; Ekanayake, C. On recent advances in PV output power forecast. Sol. Energy 2016, 136, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, P.; Mithulananthan, N.; Raza, M.Q. Solar PV Power Forecasting Using Modified SVR with Gauss-Newton Method. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd Global Power, Energy and Communication Conference (GPECOM), Izmir, Turkey, 20–23 October 2020; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Suh, D.; Otto, M.-O.; Huh, J.-S. A Novel Hybrid Spatio-Temporal Forecasting of Multisite Solar Photovoltaic Generation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebyk, D.; Alcañiz, A.; Donker, J.C.; Zeman, M.; Ziar, H.; Isabella, O. Individual yield nowcasting for residential PV systems. Sol. Energy 2023, 251, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulescu, M.; Paulescu, E.; Gravila, P.; Badescu, V. Weather Modeling and Forecasting of PV Systems Operation; Green Energy and Technology; Springer: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrou, F.; Kadri, F.; Sun, Y.; Harrou, F.; Kadri, F.; Sun, Y. Forecasting of Photovoltaic Solar Power Production Using LSTM Approach. In Advanced Statistical Modeling, Forecasting, and Fault Detection in Renewable Energy Systems; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Singh, R.K. Short-term day-ahead photovoltaic output forecasting using PCA-SFLA-GRNN algorithm. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 1029449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.K.; Tey, K.S.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Mekhilef, S.; Idris, M.Y.I.; Van Deventer, W.; Horan, B.; Stojcevski, A. Forecasting of photovoltaic power generation and model optimization: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 912–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonanzas, J.; Osorio, N.; Escobar, R.; Urraca, R.; Martinez-De-Pison, F.J.; Antonanzas-Torres, F. Review of photovoltaic power forecasting. Sol. Energy 2016, 136, 78–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.J.; Gróf, G. Extensive comparison of physical models for photovoltaic power forecasting. Appl. Energy 2021, 283, 116239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Kleissl, J.; Gueymard, C.A.; Pedro, H.T.; Coimbra, C.F. History and trends in solar irradiance and PV power forecasting: A preliminary assessment and review using text mining. Sol. Energy 2018, 168, 60–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobri, S.; Koohi-Kamali, S.; Rahim, N.A. Solar photovoltaic generation forecasting methods: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 156, 459–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, R.H.; Pedro, H.T.; Coimbra, C.F. Solar forecasting methods for renewable energy integration. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2013, 39, 535–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Soni, S.; Paliwal, P.; Saboor, S.; Chaurasiya, P.K.; Sharifpur, M.; Khalilpoor, N.; Afzal, A. A novel long term solar photovoltaic power forecasting approach using LSTM with Nadam optimizer: A case study of India. Energy Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 2909–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.-J.; Wu, Y.-K. Short-Term Solar Power Forecasts Considering Various Weather Variables. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Symposium on Computer, Consumer and Control (IS3C), Taichung City, Taiwan, 13–16 November 2020; pp. 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitropoulos, N.; Sofias, N.; Kapsalis, P.; Mylona, Z.; Marinakis, V.; Primo, N.; Doukas, H. Forecasting of short-term PV production in energy communities through Machine Learning and Deep Learning algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2021 12th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems & Applications (IISA), Chania Crete, Greece, 12–14 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.L.; García-Santiago, X.; Camarero, F.E.; Gil, G.B.; Ortega, P.C. Application of Temporal Fusion Transformer for Day-Ahead PV Power Forecasting. Energies 2022, 15, 5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Guo, W.; Gong, X. Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Output Prediction Based on k-Fold Cross-Validation and an Ensemble Model. Energies 2019, 12, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, F.; Jia, L. Short-Term Load Forecasting Based on SARIMAX-LSTM. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Power and Renewable Energy (ICPRE), Shanghai, China, 12–14 September 2020; pp. 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotto, M.; Bauzon, M.; Cañete, J.; Principe, J. AHI-8 SWR Adjustment using CLOT-derived Correction Factor for Solar PV Power Potential Assessment in the Philippines. In Proceedings of the 31st IIS Forum Earth Observation, Disaster Monitoring and Risk Assessment from Space, Tokyo, Japan, 6–7 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Principe, J.; Takeuchi, W. Assessment of solar PV power potential over Asia Pacific region with remote sensing considering meteorological factors. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2019, 11, 013502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Biavati, G.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Thépaut, J.N. ERA5 hourly data on single levels from 1979 to present. In Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS); European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Knowledge Base. ERA5: How to Calculate Wind Speed and Wind Direction from u and v Components of the Wind?—Copernicus Knowledge Base—ECMWF Confluence Wiki, May 16. 2022. Available online: https://confluence.ecmwf.int/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=133262398 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Alduchov, O.A.; Eskridge, R.E. Improved Magnus’ form approximation of saturation vapor pressure. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1996, 35, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, C.; Petitta, M.; Wagner, J.; Belluardo, G.; Moser, D.; Castelli, M.; Zebisch, M.; Tetzlaff, A. Wind Effect on PV Module Temperature: Analysis of Different Techniques for an Accurate Estimation. Energy Procedia 2013, 40, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterworth, D.; Armstrong, A. Southerly winds increase the electricity generated by solar photovoltaic systems. Sol. Energy 2020, 202, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Nahid-Al-Masood; Razee, I.A.; Zunaed, M. Solar PV Power Forecasting Using Traditional Methods and Machine Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Kansas Power and Energy Conference (KPEC), Manhattan, KS, USA, 19–20 April 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, V.; Janik, P.; Rezmer, J.; Leonowicz, Z. Forecasting Solar PV Output Using Convolutional Neural Networks with a Sliding Window Algorithm. Energies 2020, 13, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Puri, V.; Mahajan, S.; Abualigah, L.; Abu Zitar, R.; Gandomi, A.H. Solar power forecasting beneath diverse weather conditions using GD and LM-artificial neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essam, Y.; Ahmed, A.N.; Ramli, R.; Chau, K.-W.; Ibrahim, M.S.I.; Sherif, M.; Sefelnasr, A.; El-Shafie, A. Investigating photovoltaic solar power output forecasting using machine learning algorithms. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2022, 16, 2002–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Jung, J.; Kim, B.; Han, S. Long short-term memory recurrent neural network for modeling temporal patterns in long-term power forecasting for solar PV facilities: Case study of South Korea. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, I.B.; Ibañez, J.A.; Lumabad, C.D.; Cañete, J.M.; Reyes, F.N.D.L.; Principe, J.A. A novel data gaps filling method for solar PV output forecasting. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2023, 15, 046102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, D.A.; Fuller, W.A. Likelihood Ratio Statistics for Autoregressive Time Series with a Unit Root. Econometrica 1981, 49, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.C.B.; Perron, P. Testing for a unit root in time series regression. Biometrika 1988, 75, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, D.; Phillips, P.C.B.; Schmidt, P.; Shin, Y. Testing the null hypothesis of stationarity against the alternative of a unit root: How sure are we that economic time series have a unit root? J. Econom. 1992, 54, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamy; Kreinovich, V.; Kosheleva, O. Why 70/30 or 80/20 Relation between Training and Testing Sets: A Pedagogical Explanation Departmental Technical Reports (CS), Feb. 2018. Available online: https://scholarworks.utep.edu/cs_techrep/1209 (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- Manigandan, P.; Alam, M.D.S.; Alharthi, M.; Khan, U.; Alagirisamy, K.; Pachiyappan, D.; Rehman, A. Forecasting Natural Gas Production and Consumption in United States-Evidence from SARIMA and SARIMAX Models. Energies 2021, 14, 6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, J.; Saldaña, J., Jr.; Spanswick, B.; Santerre, J. Forecasting Power Consumption in Pennsylvania During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A SARIMAX Model with External COVID-19 and Unemployment Variables. SMU Data Sci. Rev. 2020, 3, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.; Sandels, C.; Zhu, K.; Nordström, L. A seasonal ARIMA model with exogenous variables for elspot electricity prices in Sweden. In Proceedings of the 2013 10th International Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM), Stockholm, Sweden, 27–31 May 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.G. Pmdarima: ARIMA Estimators for Python, alkaline-ml, Sep. 03. 2017. Available online: https://alkaline-ml.com/pmdarima/modules/generated/pmdarima.arima.auto_arima.html#pmdarima-arima-auto-arima (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Bamisile; Ejiyi, C.J.; Osei-Mensah, E.; Chikwendu, I.A.; Li, J.; Huang, Q. Long-Term Prediction of Solar Radiation Using XGboost, LSTM, and Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th Asia Energy and Electrical Engineering Symposium (AEEES), Chengdu, China, 25–28 March 2022; pp. 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the KDD ’16: 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcañiz, A.; Grzebyk, D.; Ziar, H.; Isabella, O. Trends and gaps in photovoltaic power forecasting with machine learning. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 447–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study | Year | Location | Methodology | Train-Test Ratio | Error Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | 2023 | Netherlands and Belgium | XGBoost | 50–50 | MAE MAPE RMSE |
| [20] | 2022 | India | LSTM ARIMA SARIMA | Variable from 75–25 to 90–10 | RMSE MSE |
| [21] | 2021 | Taiwan | ANN LSTM XGBoost | 60–40 | MAPE RMSE NRMSE |
| [9] | 2021 | Incheon, Busan, and Yeongam | SARIMAX linear SVR LSTM DNN RF SARIMAX-LSTM | 75–25 | MAE RMSE sMAPE MBE Cv |
| [22] | 2021 | Undisclosed location | LSTM SVR MLR XGBoost | 80–20 | Rsq. RMSE |
| [23] | 2022 | Germany and Australia | TFT ARIMA LSTM MLP XGBoost | 70–20–20 | RMSE MAE MASE Rsq. QuantileLoss |
| [24] | 2019 | China | MLP GRU XGBoost Ensemble | 80–10 (random sampling) | MAE MAPE RMSE |
| Variable | Unit | Short Name | Related Literature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wind speed | m·s−2 | WS | [31,32] |
| Wind direction | Cardinal direction | WD | [9,33] |
| Ambient temperature | °C | T | [32,34] |
| Relative humidity | % | RH | [32,35] |
| Total precipitation | mm | TP | [36,37] |
| Cloud cover (low, medium, high, total) | okta | LCC, MCC, HCC, TCC | [9] |
| Solar irradiance | W·m−2 | R’ | [9,12] |
| Hyperparameter | Plant 1 | Plant 2 | Plant 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| p | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| d | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| q | 0 | 5 | 1 |
| P | 5 | 3 | 5 |
| D | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Q | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Hyperparameter | Plant 1 | Plant 2 | Plant 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optimizer | Adam | Adam | Adam |
| Learning rate 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Epochs 2 | 500 | 500 | 500 |
| Loss function | MAE | MAE | MAE |
| Hidden layers | |||
| LSTM | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| LSTM units | 32 | 32 | 32 |
| Activation | tanH | tanH | tanH |
| Output layers | |||
| Layer | Dense | Dense | Dense |
| Activation | Linear | Linear | Linear |
| Hyperparameter | Plant 1 | Plant 2 | Plant 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| learning_rate | 0.3 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| n_estimators | 1000 | 2000 | 2000 |
| subsample | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| colsample_bytree | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| colsample_bylevel | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| min_child_weight | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| max_depth | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| objective | reg:squarederror | reg:squarederror | reg:squarederror |
| Model Name | Algorithm |
|---|---|
| HM1 | SARIMAX + LSTM |
| HM2 | SARIMAX + XGBoost |
| HM3 | LSTM + XGBoost |
| HM4 | SARIMAX + LSTM + XGBoost |
| Plant Number | Major Island | Location | Installed Capacity (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Luzon | Pangasinan | 40.92 |
| 2 | Visayas | Negros Occidental | 605.00 |
| 3 | Mindanao | Davao del Norte | 1110.00 |
| Parameter | Plant 1 | Plant 2 | Plant 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| R’ | 0.98 * | 0.78 * | 0.75 * |
| WS | 0.10 | 0.34 | 0.30 |
| WD | −0.08 | 0.11 | −0.31 |
| RH | −0.66 * | −0.78 * | −0.72 * |
| T | 0.73 * | 0.78 * | 0.76 * |
| TP | −0.09 | −0.13 | −0.04 |
| HCC | −0.05 | 0.09 | −0.11 |
| LCC | −0.08 | 0.09 | −0.02 |
| MCC | −0.09 | −0.06 | −0.05 |
| TCC | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.06 |
| Parameter | Plant 1 | Plant 2 | Plant 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | |
| R’ | 1.55 | 1.55 | 1.85 | 1.85 | 1.68 | 1.58 | 1.58 | 1.46 |
| WS | 1.12 | 1.12 | 1.11 | 1.11 | 1.09 | 1.12 | 1.12 | 1.07 |
| WD | 1.28 | 1.27 | 1.20 | 1.19 | 1.10 | 1.10 | 1.10 | 1.09 |
| RH | 2.57 | 2.55 | 5.39 | 5.39 | 1.88 | 9.40 | 9.40 | 1.69 |
| T | 2.03 | 2.02 | 5.45 | 5.45 * | rmvd | 10.02 | 10.02 * | rmvd |
| TP | 1.31 | 1.27 | 1.13 | 1.13 | 1.13 | 1.22 | 1.20 | 1.20 |
| HCC | 15.59 | 1.31 | 10.38 | 1.21 | 1.21 | 16.03 | 1.16 | 1.16 |
| LCC | 1.41 | 1.24 | 1.26 | 1.13 | 1.12 | 1.35 | 1.19 | 1.19 |
| MCC | 1.73 | 1.30 | 1.27 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.56 | 1.44 | 1.43 |
| TCC | 17.82 * | rmvd | 10.73 * | rmvd | - | 16.99 * | rmvd | - |
| Model | SARIMAX | LSTM | XGBoost | HM1 | HM2 | HM3 | HM4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics | |||||||
| RMSE | 4.95 | 7.73 | 3.91 | 6.01 | 4.14 | 5.86 | 5.21 |
| MAE | 2.44 | 3.41 | 1.79 | 2.86 | 2.01 | 2.72 | 2.55 |
| MAPE | 10.15 | 17.50 | 12.47 | 15.19 | 12.35 | 15.59 | 14.71 |
| Model | SARIMAX | LSTM | XGBoost | HM1 | HM2 | HM3 | HM4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics | |||||||
| RMSE | 5.02 | 5.61 | 4.06 | 4.98 | 4.33 | 4.56 | 4.51 |
| MAE | 2.46 | 2.99 | 2.11 | 2.57 | 2.20 | 2.41 | 2.34 |
| MAPE | 13.16 | 28.09 | 19.05 | 23.25 | 16.74 | 24.47 | 22.27 |
| Model | SARIMAX | LSTM | XGBoost | HM1 | HM2 | HM3 | HM4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics | |||||||
| RMSE | 5.25 | 4.40 | 2.98 | 4.54 | 4.72 | 3.81 | 4.20 |
| MAE | 2.67 | 2.25 | 1.49 | 2.33 | 2.39 | 1.94 | 2.16 |
| MAPE | 16.17 | 17.77 | 9.42 | 16.52 | 14.63 | 14.83 | 15.15 |
| Month | Plant 1 | Plant 2 | Plant 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | XGBoost | XGBoost | XGBoost |
| February | XGBoost | XGBoost | XGBoost |
| March | HM2 | HM2 | XGBoost |
| April | XGBoost | XGBoost | XGBoost |
| May | XGBoost | HM3 | XGBoost |
| June | XGBoost | XGBoost | XGBoost |
| July | XGBoost | HM3 | XGBoost |
| August | XGBoost | SARIMAX | XGBoost |
| September | XGBoost | HM4 | HM2 |
| October | HM2 | HM3 | XGBoost |
| November | SARIMAX | SARIMAX | HM4 |
| December | SARIMAX | SARIMAX | SARIMAX |
| Annual Average | SARIMAX | SARIMAX | XGBoost |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benitez, I.B.; Ibañez, J.A.; Lumabad, C.I.D.; Cañete, J.M.; Principe, J.A. Day-Ahead Hourly Solar Photovoltaic Output Forecasting Using SARIMAX, Long Short-Term Memory, and Extreme Gradient Boosting: Case of the Philippines. Energies 2023, 16, 7823. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16237823
Benitez IB, Ibañez JA, Lumabad CID, Cañete JM, Principe JA. Day-Ahead Hourly Solar Photovoltaic Output Forecasting Using SARIMAX, Long Short-Term Memory, and Extreme Gradient Boosting: Case of the Philippines. Energies. 2023; 16(23):7823. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16237823
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenitez, Ian B., Jessa A. Ibañez, Cenon III D. Lumabad, Jayson M. Cañete, and Jeark A. Principe. 2023. "Day-Ahead Hourly Solar Photovoltaic Output Forecasting Using SARIMAX, Long Short-Term Memory, and Extreme Gradient Boosting: Case of the Philippines" Energies 16, no. 23: 7823. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16237823
APA StyleBenitez, I. B., Ibañez, J. A., Lumabad, C. I. D., Cañete, J. M., & Principe, J. A. (2023). Day-Ahead Hourly Solar Photovoltaic Output Forecasting Using SARIMAX, Long Short-Term Memory, and Extreme Gradient Boosting: Case of the Philippines. Energies, 16(23), 7823. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16237823







