Analysis of Air Pollutants for a Small Paintshop by Means of a Mobile Platform and Geostatistical Methods †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
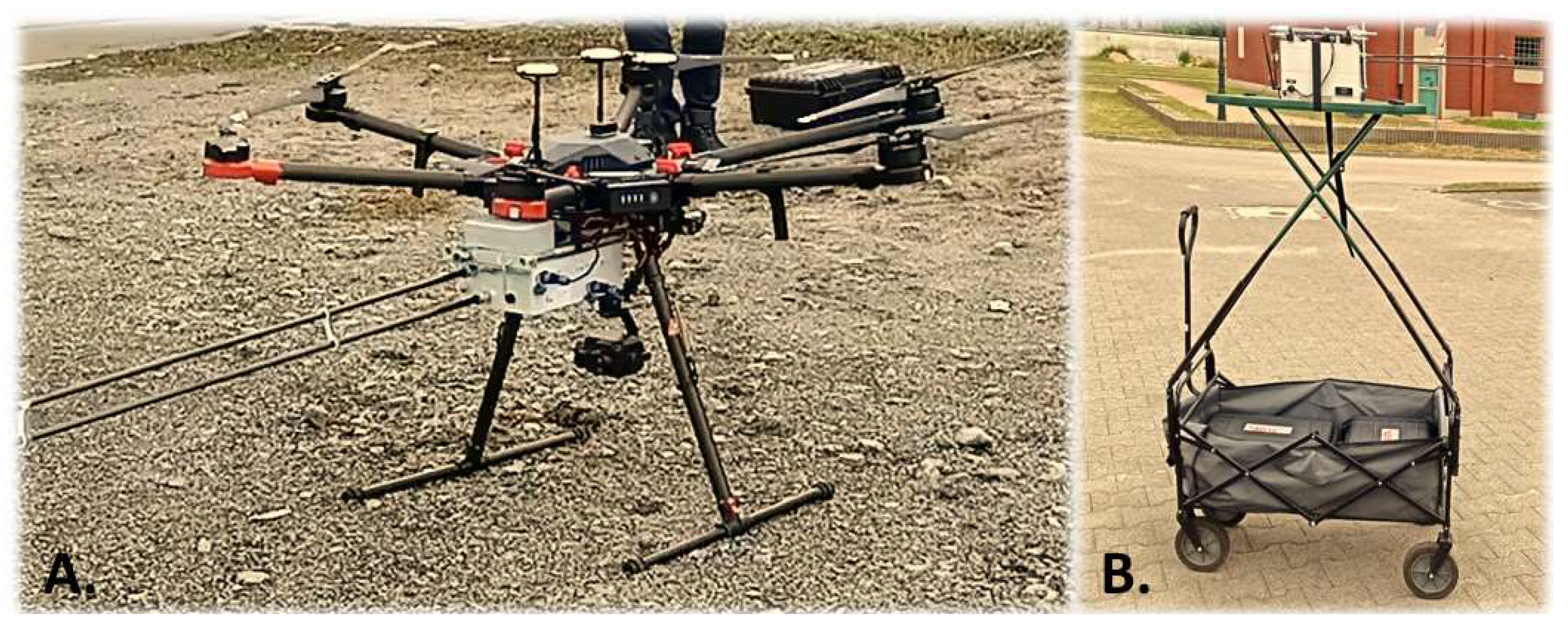
2.2. Sampling Methodology
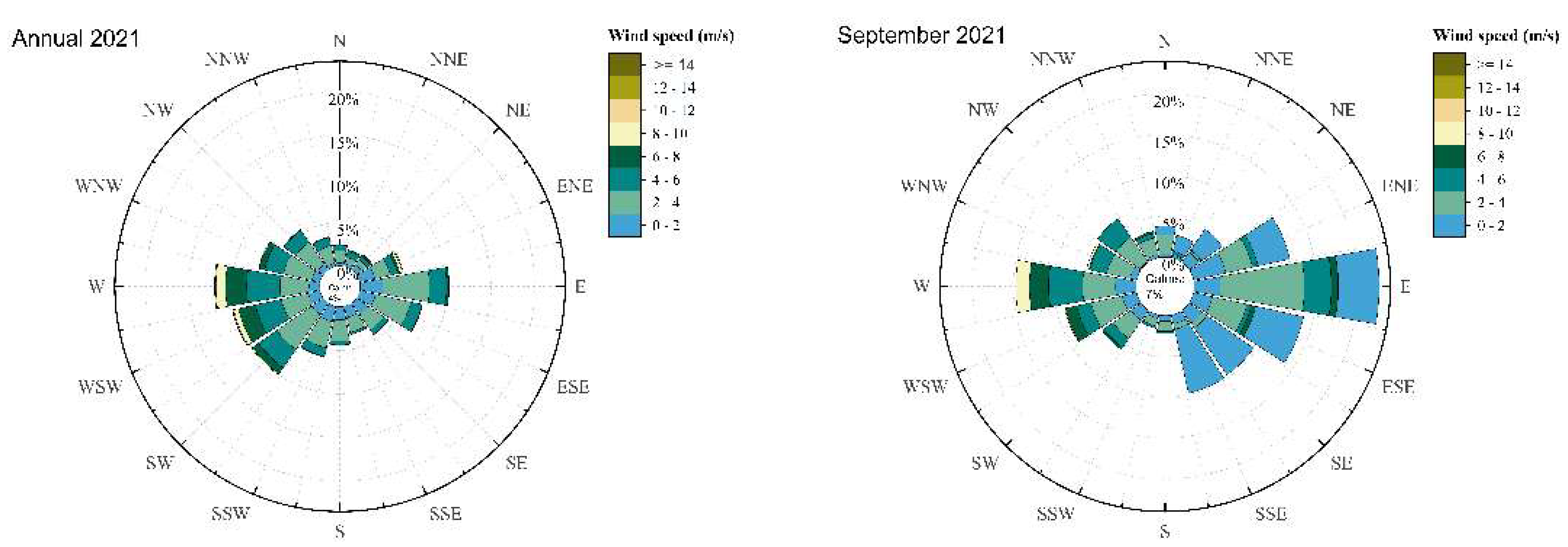
2.3. Meteorological Data
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
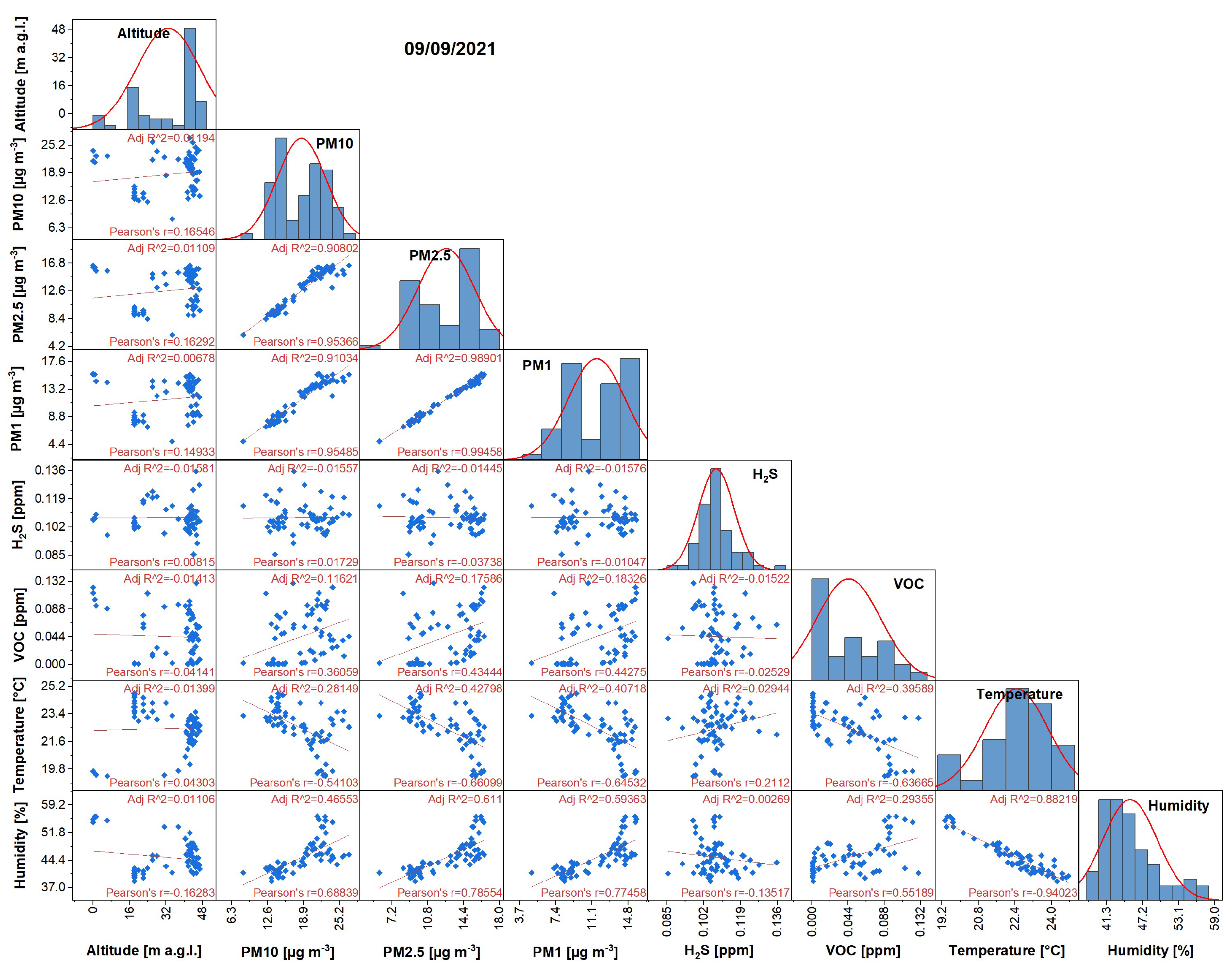
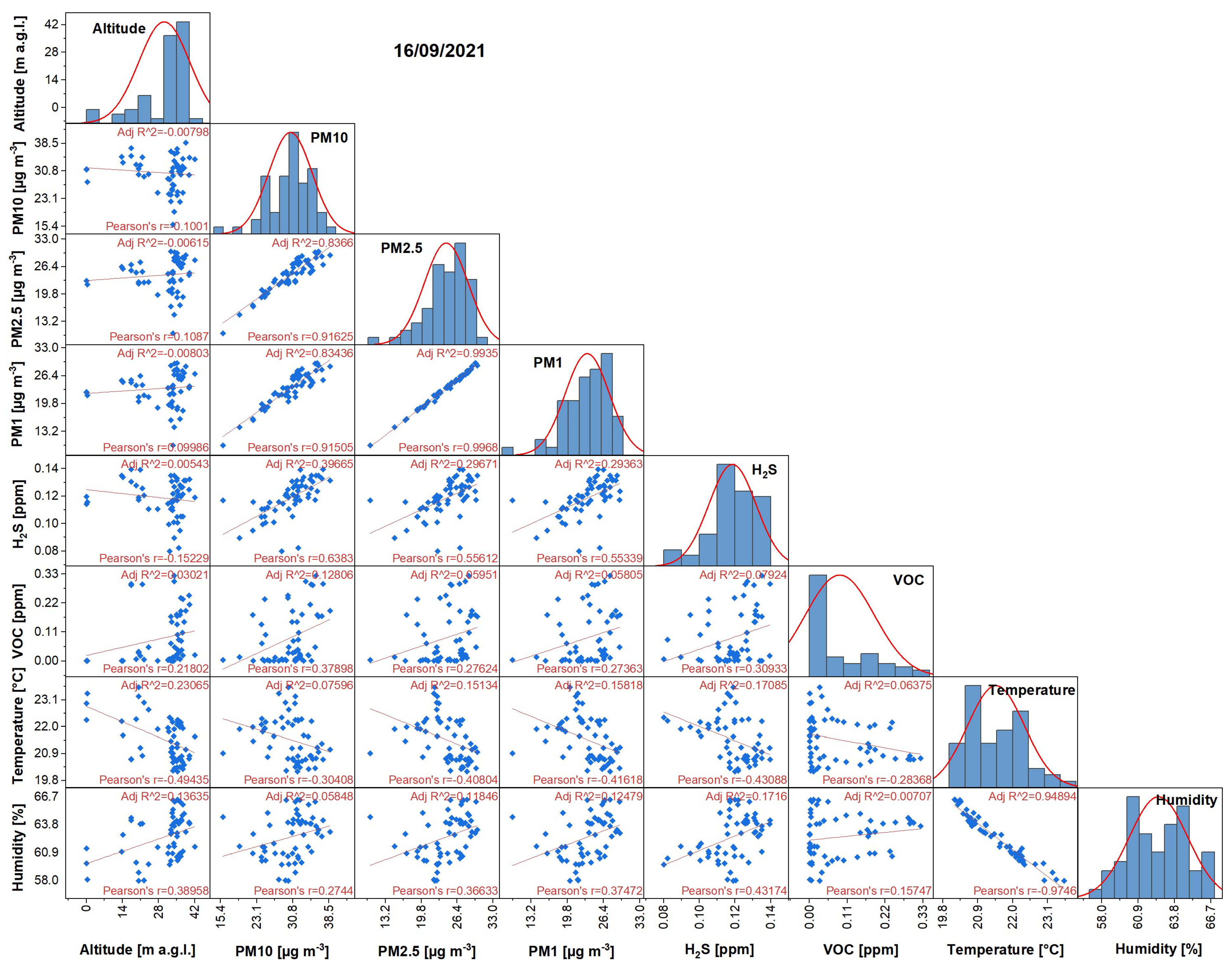
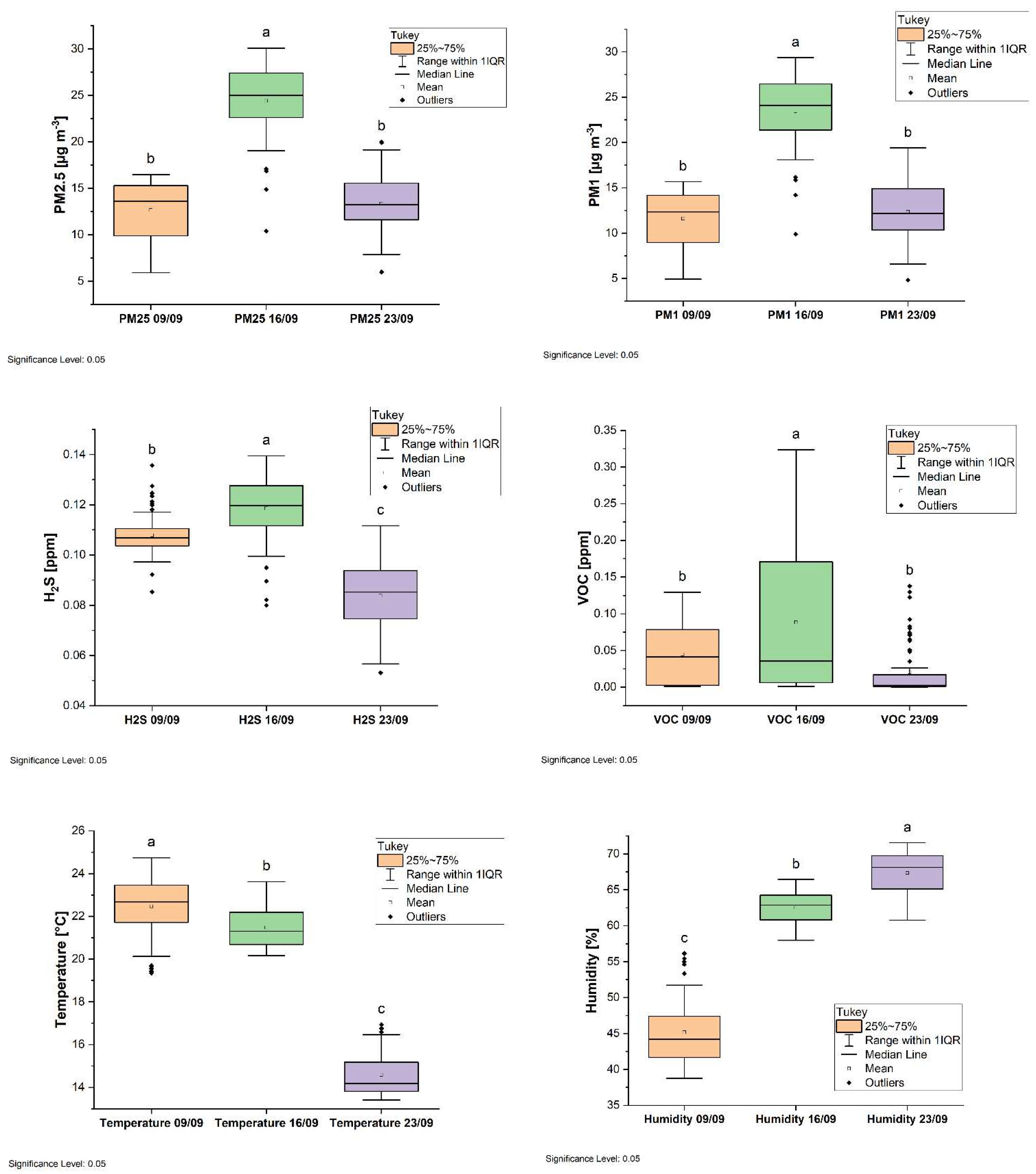
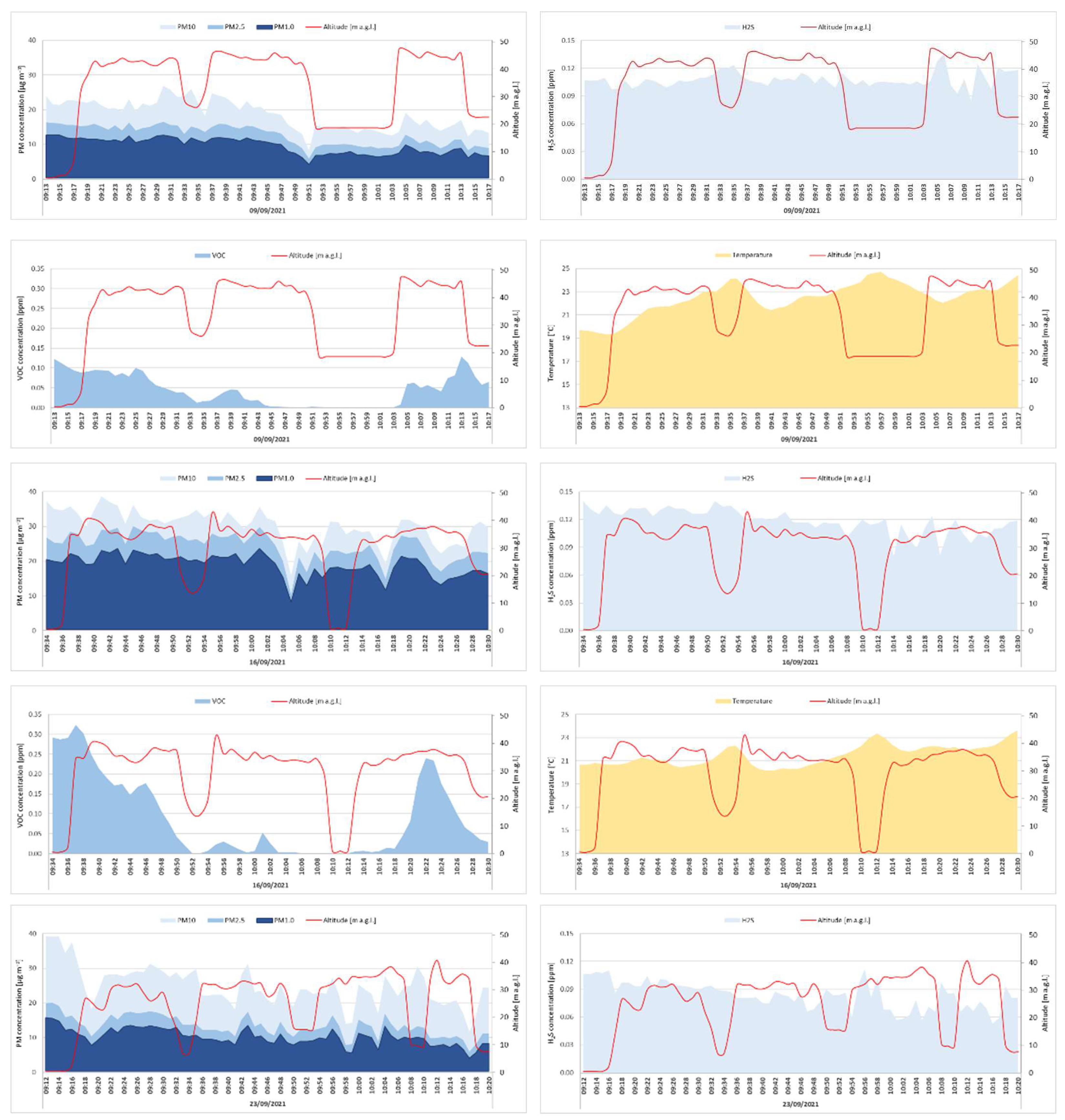
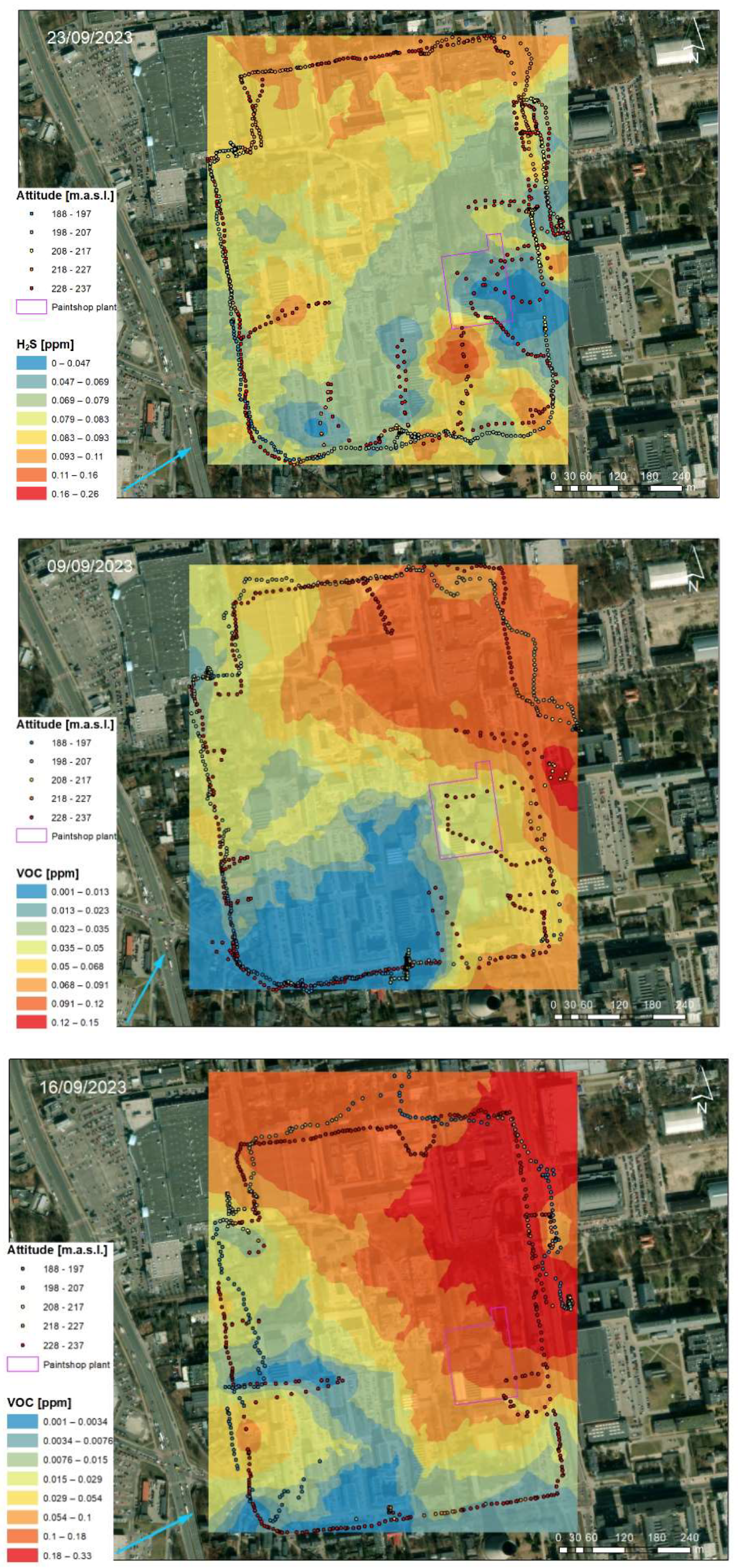
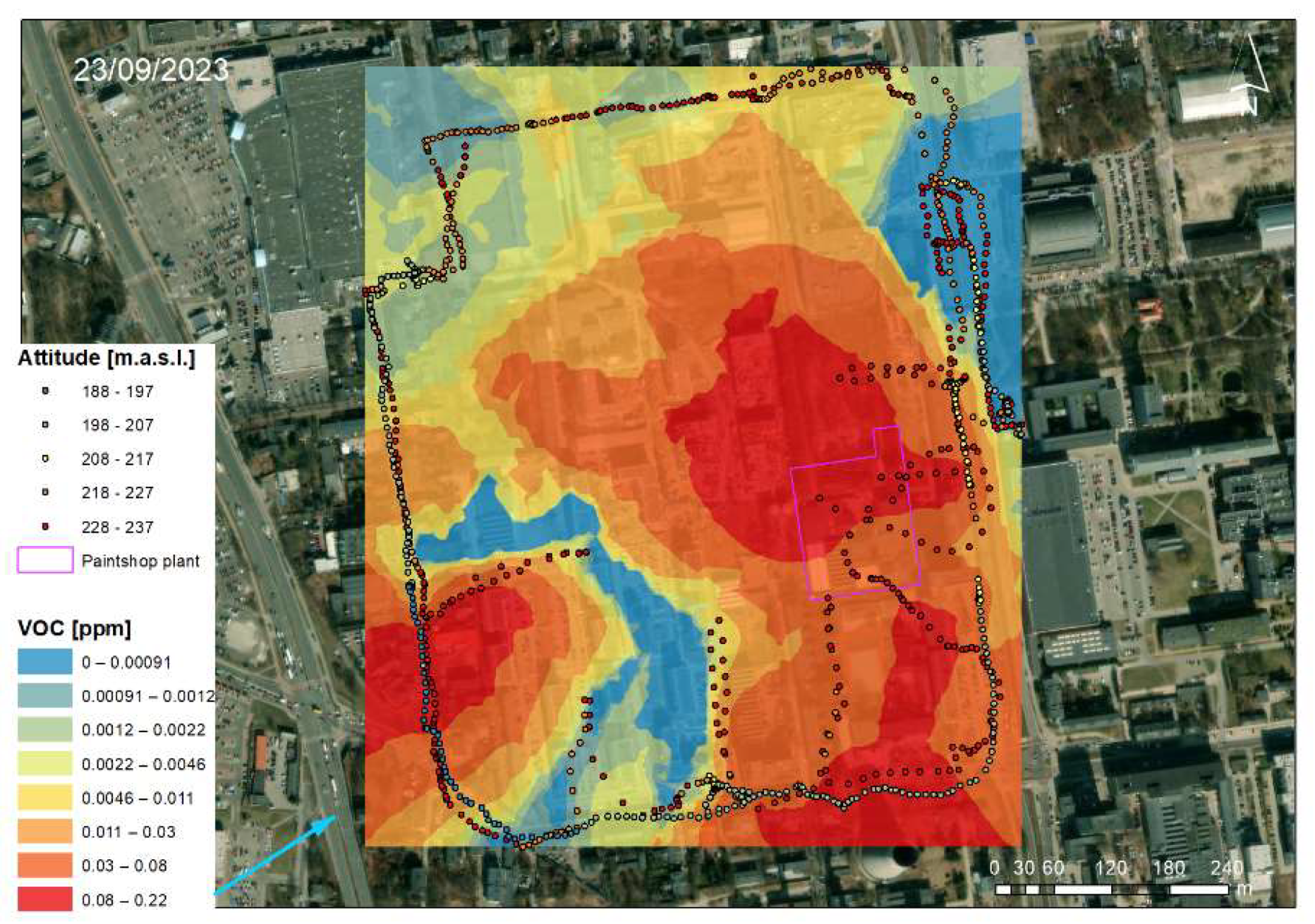
3.1. Analysis of the Measured Pollution Concentrations in Ambient Air
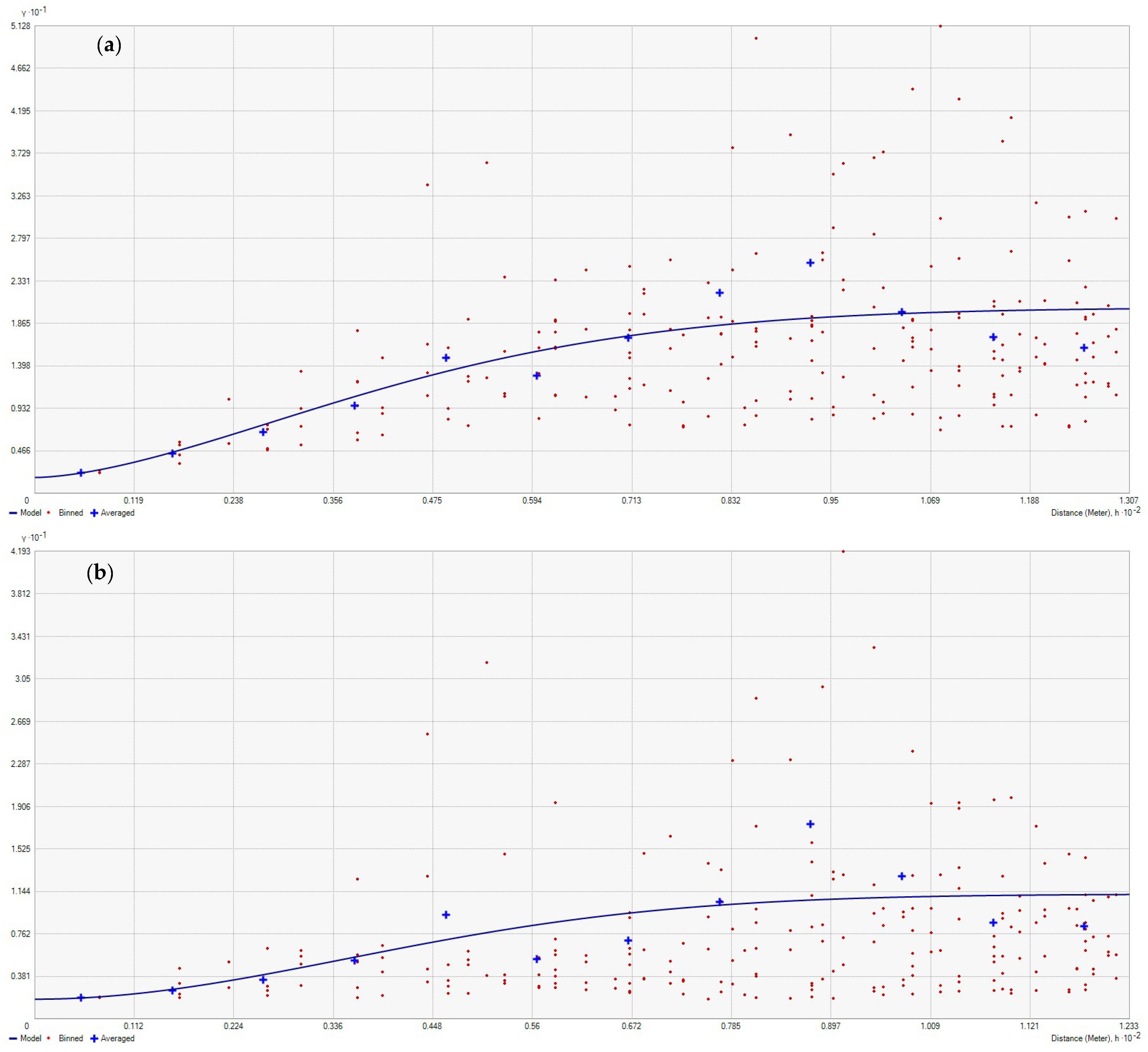
3.2. Geostatistical Analysis of Atmospheric Pollution Concentrations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


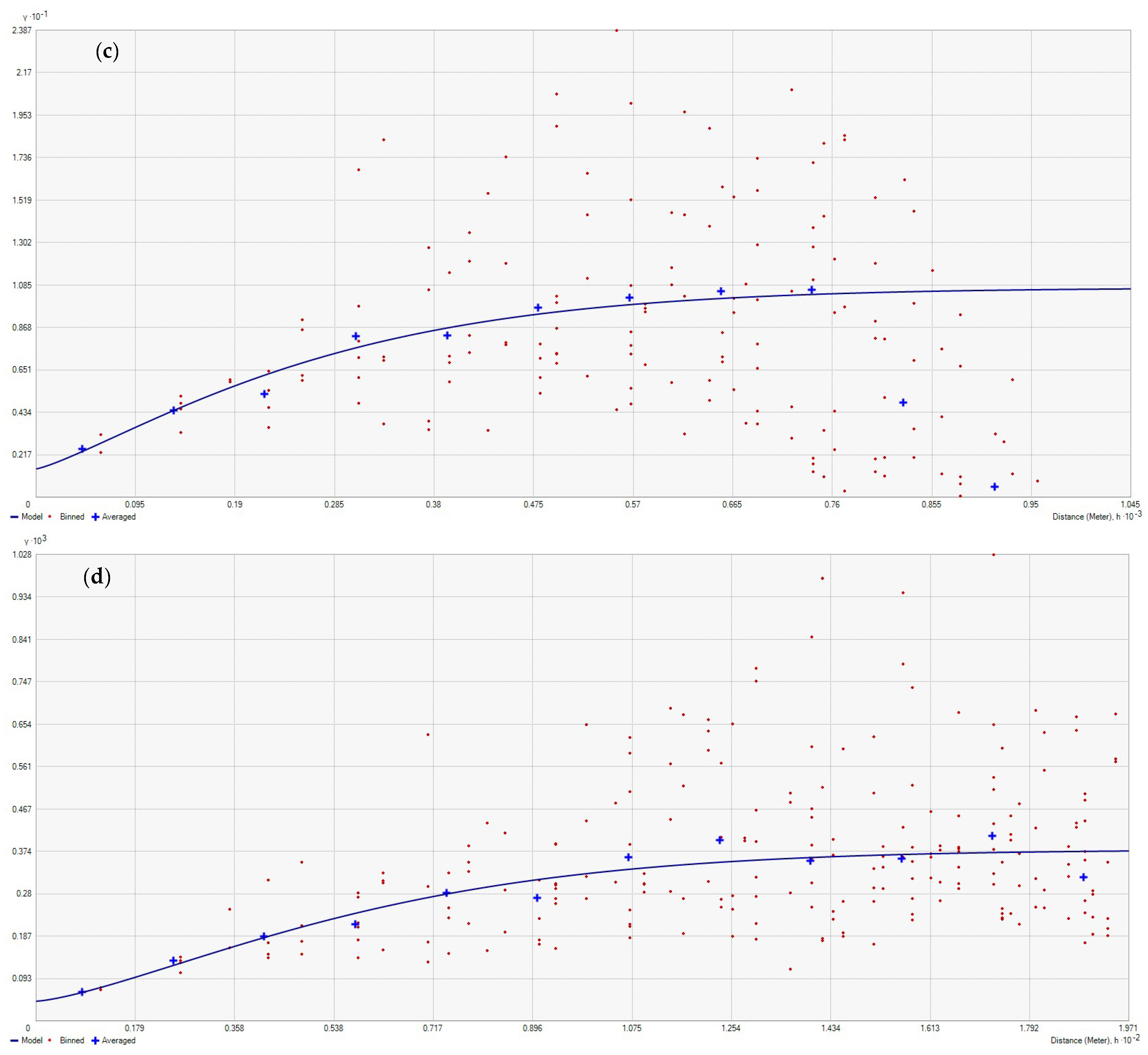
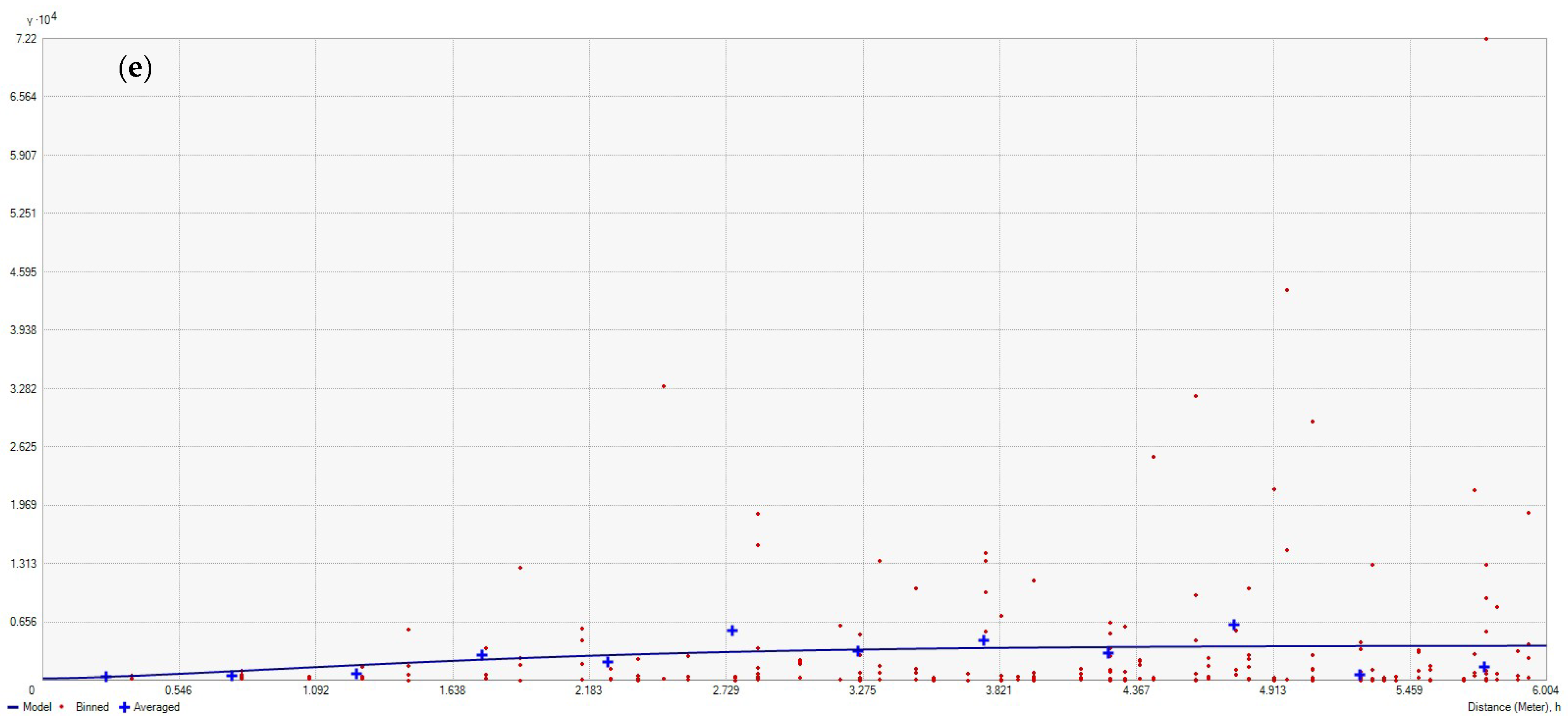
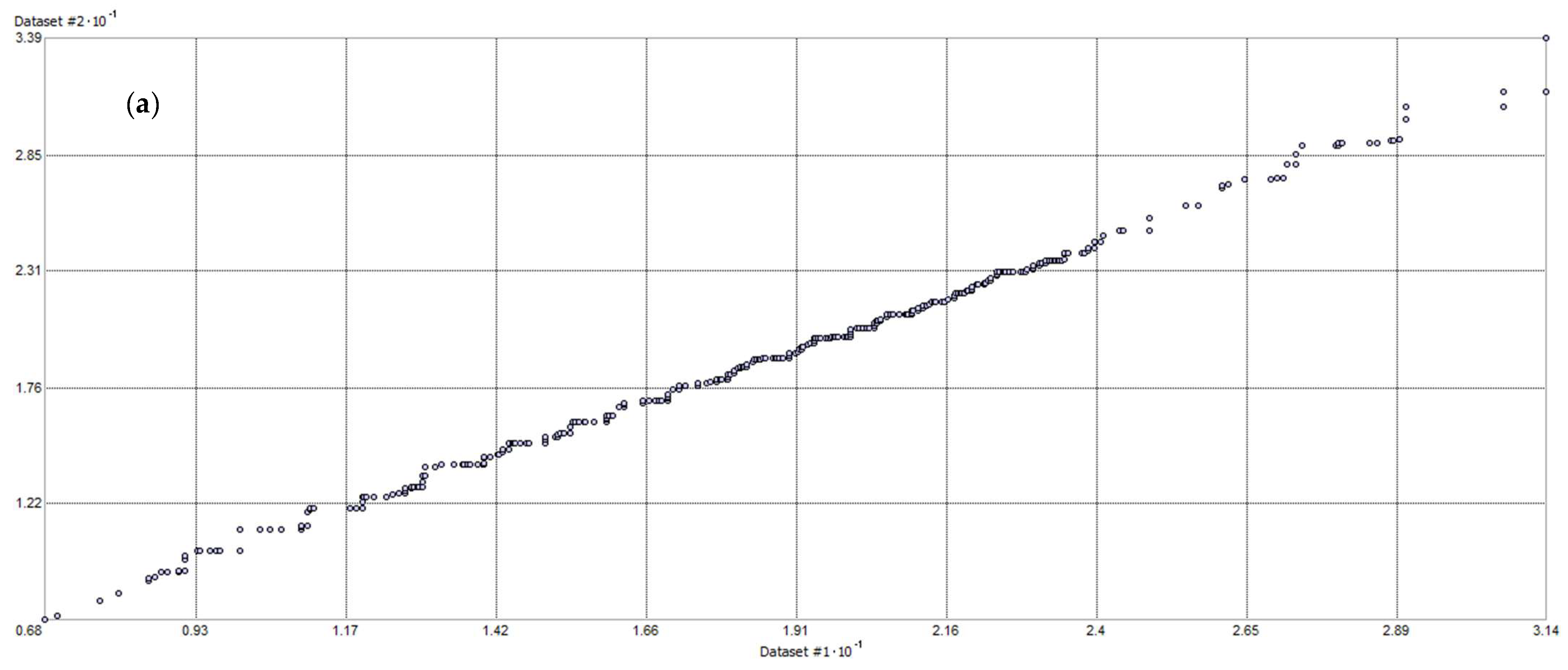
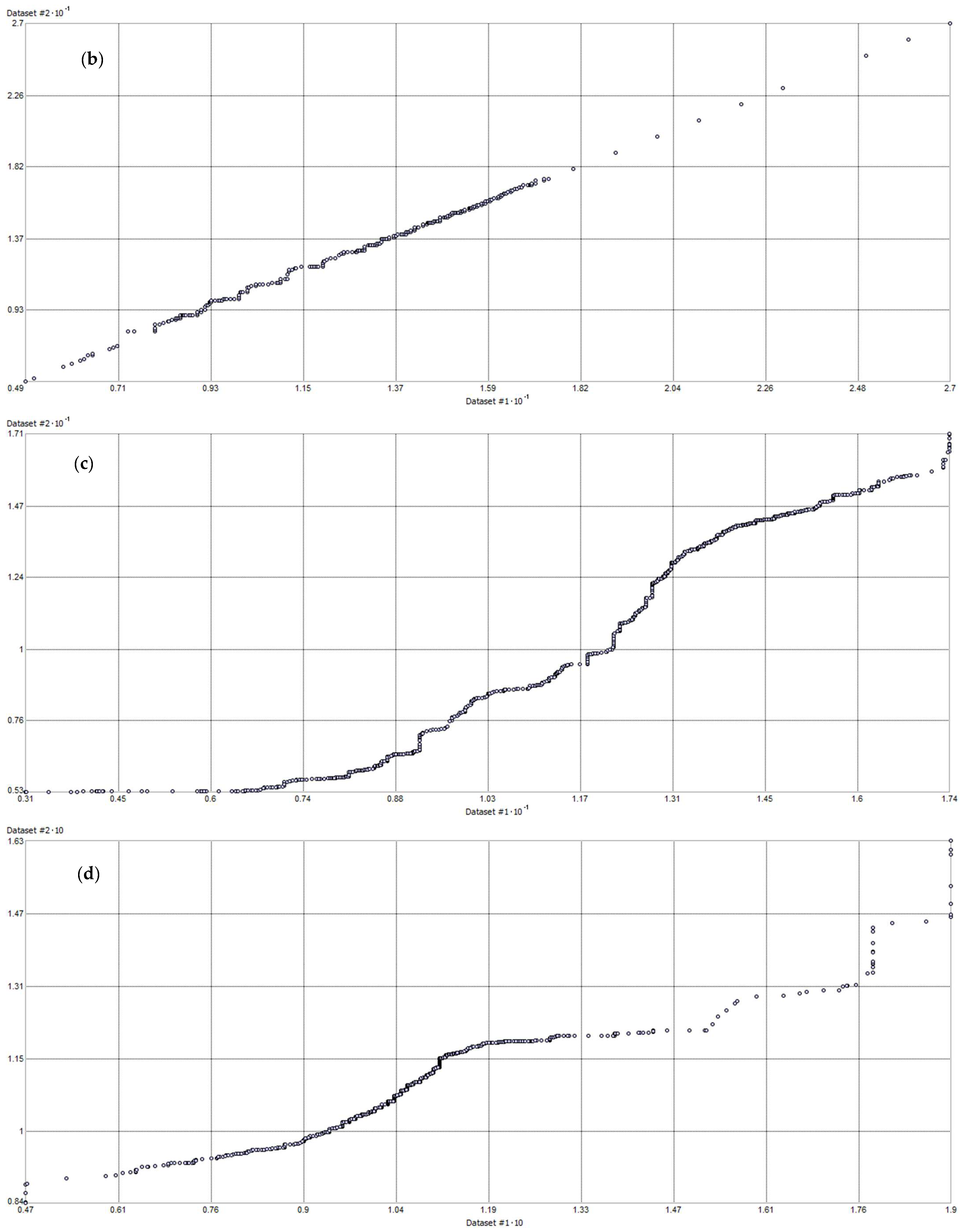
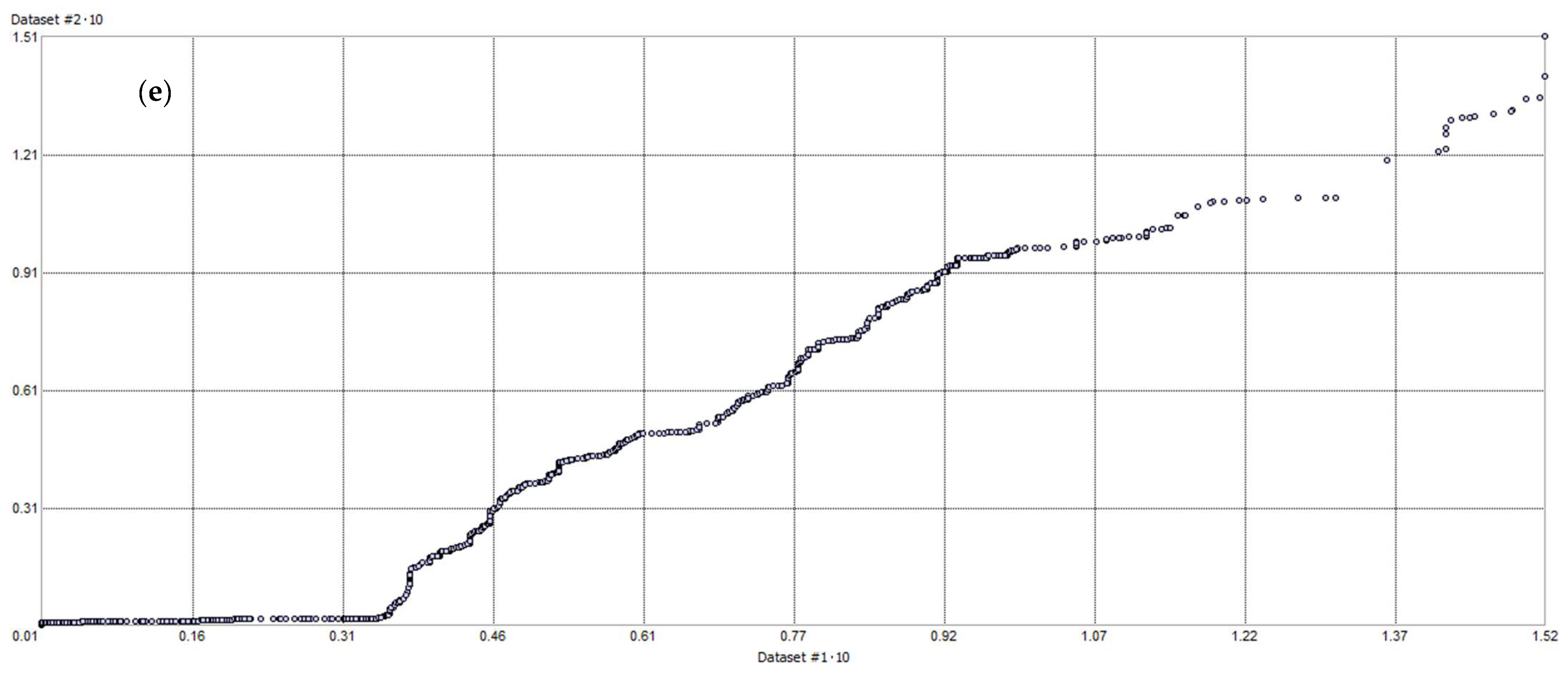
References
- Volatile Organic Compounds’ Impact on Indoor Air Quality. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/volatile-organic-compounds-impact-indoor-air-quality#Sources (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Wei, B.; Zhang, W.; Chao, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, T.; Noctor, G.; Liu, Y.; Han, Y. Functional analysis of the role of hydrogen sulfide in the regulation of dark-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtidis, K.; Kelesis, A.; Petrakakis, M. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in urban ambient air. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7476–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Paarticulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Recommendation from the Scientific Committee on Occupational Exposure Limits for Hydrogen Sulphide. 2007. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/social/search.jsp?advSearchKey=hydrogen+sulphide&mode=advancedSubmit&langId=en (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- The European Parliament. European Council: On Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe 2008/50/EC. Available online: https://www.eumonitor.eu/9353000/1/j9vvik7m1c3gyxp/vhvvygrp44xc (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Atkinson, R.W.; Mills, I.C.; Walton, H.A.; Anderson, H.R. Fine particle components and health—A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological time series studies of daily mortality and hospital admissions. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougiatioti, A.; Kanakidou, M.; Mihalopoulos, N. Air Quality in European Cities. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 517–542. [Google Scholar]
- Jońca, J.; Pawnuk, M.; Bezyk, Y.; Arsen, A.; Sówka, I. Drone-Assisted Monitoring of Atmospheric Pollution—A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichowicz, R.; Dobrzański, M. 3D Spatial Analysis of Particulate Matter (PM10, PM2.5 and PM1.0) and Gaseous Pollutants (H2S, SO2 and VOC) in Urban Areas Surrounding a Large Heat and Power Plant. Energies 2021, 14, 4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambey, V.; Prasad, A.D. A Review on Air Quality Measurement Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; Xiong, Z.; Wu, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Du, Y. Investigating the vertical distribution patterns of urban air pollution based on unmanned aerial vehicle gradient monitoring. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 86, 104144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlagh, N.H.; Irjala, M.; Zuniga, A.; Lagerspetz, E.; Rantala, V.; Flores, H.; Nurmi, P.; Tarkoma, S. Toward Blue Skies: City-Scale Air Pollution Monitoring Using UAVs. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2023, 12, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guin, M.K.; Hiremath, S.; Shrishail, M.H. Semi-Autonomous UAV based Weather and Air Pollution Monitoring System. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1921, 012091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bossche, J.; Peters, J.; Verwaeren, J.; Botteldooren, D.; Theunis, J.; De Baets, B. Mobile monitoring for mapping spatial variation in urban air quality: Development and validation of a methodology based on an extensive dataset. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 105, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Chi, X.; Ding, A.; Yao, M.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Wu, M.; et al. Mobile monitoring of urban air quality at high spatial resolution by low-cost sensors: Impacts of COVID-19 pandemic lockdown. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 7199–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilt, U.; Barahona, B.; Buck, R.; Meyer, P.; Kappani, P.; Möckli, Y.; Meyer, M.; Schuetz, P. Low-Cost Sensor Node for Air Quality Monitoring: Field Tests and Validation of Particulate Matter Measurements. Sensors 2023, 23, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samad, A.; Alvarez Florez, D.; Chourdakis, I.; Vogt, U. Concept of Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) for 3D Investigation of Air Quality in the Atmosphere—Example of Measurements Near a Roadside. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumaah, H.J.; Kalantar, B.; Halin, A.A.; Mansor, S.; Ueda, N.; Jumaah, S.J. Development of UAV-Based PM2.5 Monitoring System. Drones 2021, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichowicz, R.; Dobrzański, M. Spatial Analysis (Measurements at Heights of 10 m and 20 m above Ground Level) of the Concentrations of Particulate Matter (PM10, PM2.5, and PM1.0) and Gaseous Pollutants (H2S) on the University Campus: A Case Study. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochwała, S.; Anweiler, S.; Deptuła, A.; Gardecki, A.; Lewandowski, P.; Przysiężniuk, D. Optimization of air pollution measurements with unmanned aerial vehicle low-cost sensor based on an inductive knowledge management method. Optim. Eng. 2021, 22, 1783–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohi, G.; Ejofodomi, O.; Ofualagba, G. Autonomous monitoring, analysis, and countering of air pollution using environmental drones. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babak, V.P.; Babak, S.V.; Eremenko, V.S.; Kuts, Y.V.; Myslovych, M.V.; Scherbak, L.M.; Zaporozhets, A.O. Monitoring the Air Pollution with UAVs. In Models and Measures in Measurements and Monitoring; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 191–225. [Google Scholar]
- Brander, L.M.; Bräuer, I.; Gerdes, H.; Ghermandi, A.; Kuik, O.; Markandya, A.; Navrud, S.; Nunes, P.A.L.D.; Schaafsma, M.; Vos, H.; et al. Using Meta-Analysis and GIS for Value Transfer and Scaling Up: Valuing Climate Change Induced Losses of European Wetlands. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2012, 52, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, J.E.; Wong, M.S.; Wang, J. A 3D aerosol and visibility information system for urban areas using remote sensing and GIS. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2501–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcaino, P.; Pistocchi, A. Use of a Simple GIS-Based Model in Mapping the Atmospheric Concentration of γ-HCH in Europe. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 720–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezyk, Y.; Sówka, I.; Górka, M.; Blachowski, J. GIS-Based Approach to Spatio-Temporal Interpolation of Atmospheric CO2 Concentrations in Limited Monitoring Dataset. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Heap, A.D. Spatial interpolation methods applied in the environmental sciences: A review. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 53, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, X.; Kalo, M.; Piltner, R. Spatiotemporal Interpolation Methods for the Application of Estimating Population Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter in the Contiguous U.S. A Real-Time Web Application. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matejicek, L. Spatial modelling of air pollution in urban areas with GIS: A case study on integrated database development. Adv. Geosci. 2005, 4, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristanović, B.; Cimbaljević, M.; Miljković, Đ.; Ostojić, M.; Fekete, R. GIS Application for Determining Geographical Factors on Intensity of Erosion in Serbian River Basins. Case Study: The River Basin of Likodra. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Super, I.; Dellaert, S.N.C.; Visschedijk, A.J.H.; Denier van der Gon, H.A.C. Uncertainty analysis of a European high-resolution emission inventory of CO2 and CO to support inverse modelling and network design. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1795–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. An enhanced dual IDW method for high-quality geospatial interpolation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesus, K.L.M.; Senoro, D.B.; Dela Cruz, J.C.; Chan, E.B. A Hybrid Neural Network–Particle Swarm Optimization Informed Spatial Interpolation Technique for Groundwater Quality Mapping in a Small Island Province of the Philippines. Toxics 2021, 9, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Xu, W.; Zhang, D.; Nie, F.; Sun, Q. Contrasting multiple deterministic interpolation responses to different spatial scale in prediction soil organic carbon: A case study in Mollisols regions. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Population. Statistical Office in Lodz. Available online: https://lodz.stat.gov.pl/ (accessed on 16 January 2022).
- City of Lodz. Statistical Office in Lodz. Available online: https://lodz.stat.gov.pl/vademecum/vademecum_lodzkie/portrety_miast/miasto_lodz.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2022).
- Chief Inspectorate for Environmental Protection. Annual Assessment of Air Quality in the Łódź Voivodeship. Provincial Report for 2021. Available online: https://powietrze.gios.gov.pl/pjp/rwms/publications/card/1684?lang=en (accessed on 11 August 2022).
- OpenStreetMap. Available online: https://www.openstreetmap.org (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Climate in Lódz, Poland. Available online: https://weather-and-climate.com/average-monthly-Rainfall-Temperature-Sunshine,lodz,Poland (accessed on 16 January 2022).
- Climate-Data.org. Available online: https://en.climate-data.org/europe/poland/lower-silesian-voivodeship-456/ (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- Weather Atlas. Monthly Weather Forecast and Climate Łódź, Poland. Available online: https://www.weather-atlas.com/en/poland/lodz-climate#uv_index (accessed on 16 January 2022).
- Climate and Average Weather Year Round at Lodz Lublinek Poland. Available online: https://weatherspark.com/y/150026/Average-Weather-at-Lodz-Lublinek-Poland-Year-Round (accessed on 16 January 2022).
- Meteorological Data. IMGW. Available online: https://danepubliczne.imgw.pl/data/dane_pomiarowo_obserwacyjne/dane_meteorologiczne/miesieczne/synop/2021/ (accessed on 16 January 2022).
- Cichowicz, R.; Dobrzański, M. Indoor and Outdoor Concentrations of Particulate Matter (PM10, PM2.5) and Gaseous Pollutants (VOC, H2S) on Different Floors of a University Building: A Case Study. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sówka, I.; Cichowicz, R.; Dobrzański, M.; Bezyk, Y. Application of mobile platform and geostatistical methods in the analysis of air quality in the selected area of the city of Lodz. In Proceedings of the 4th Symposium “Air Quality and Health”, Wrocław, Poland, 3–5 July 2023; Korzystka-Muskała, M., Kubicka, J., Sawiński, T., Drzeniecka-Osiadacz, A., Eds.; University of Wrocław: Wrocław, Poland, 2023; pp. 94–95. [Google Scholar]
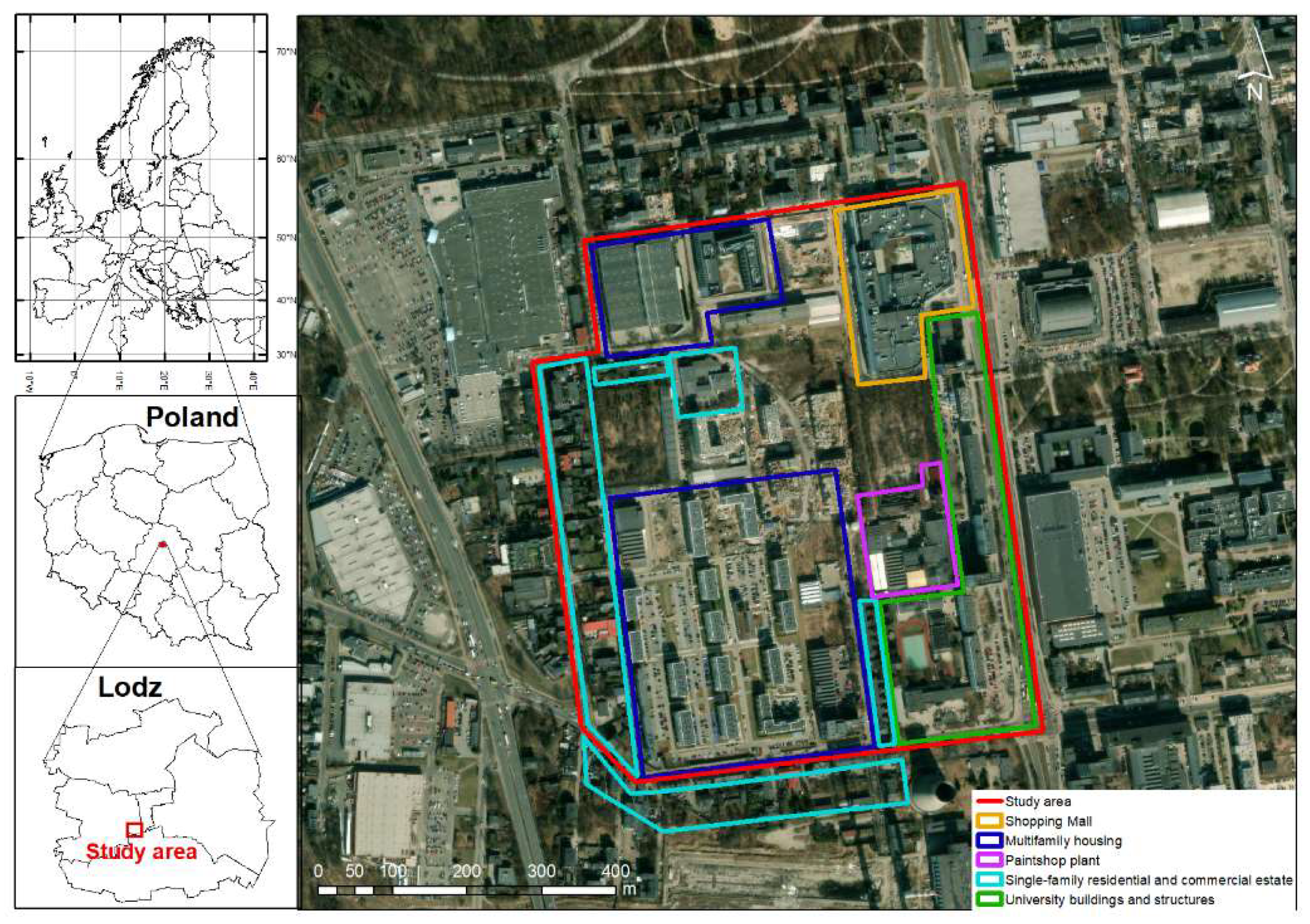


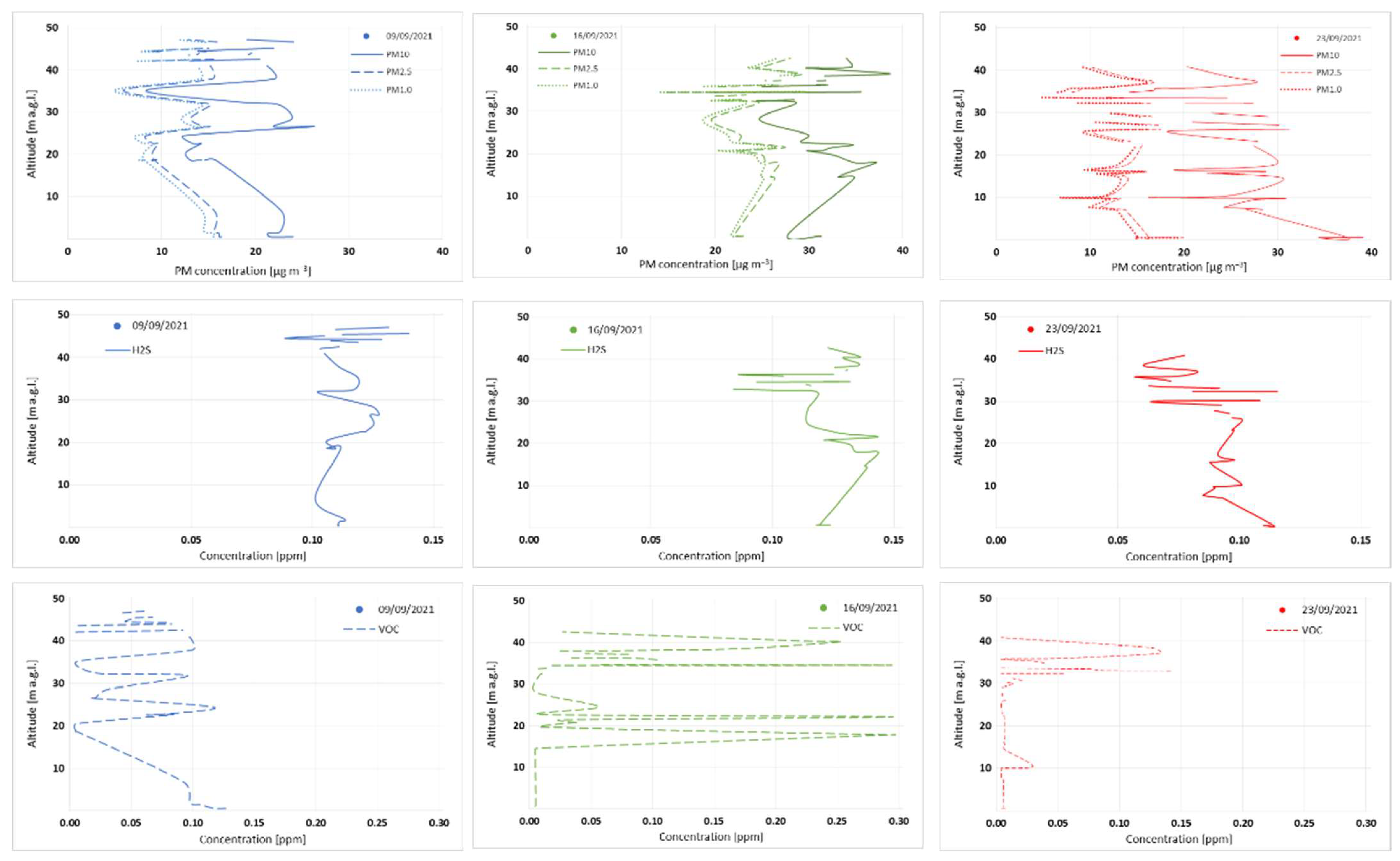

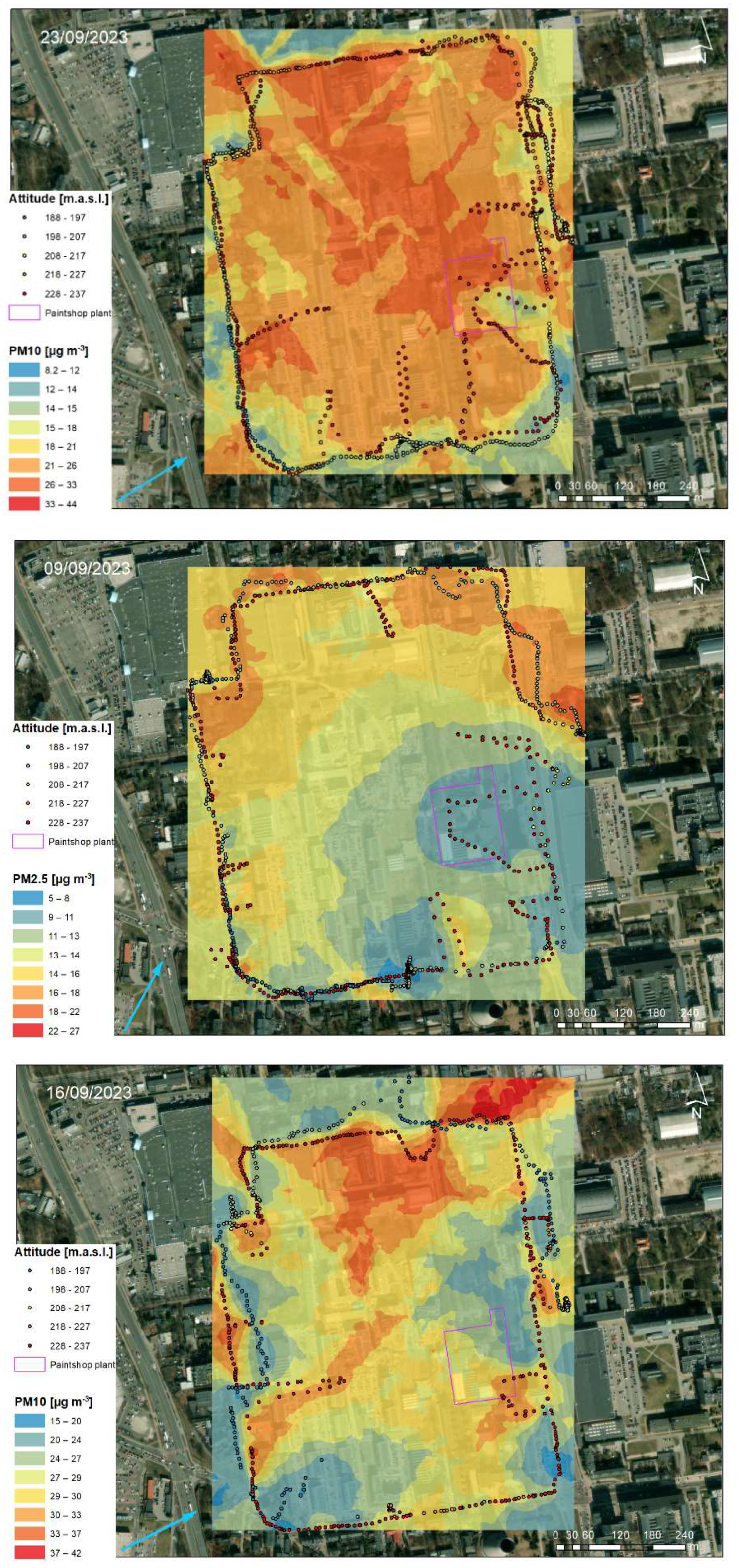
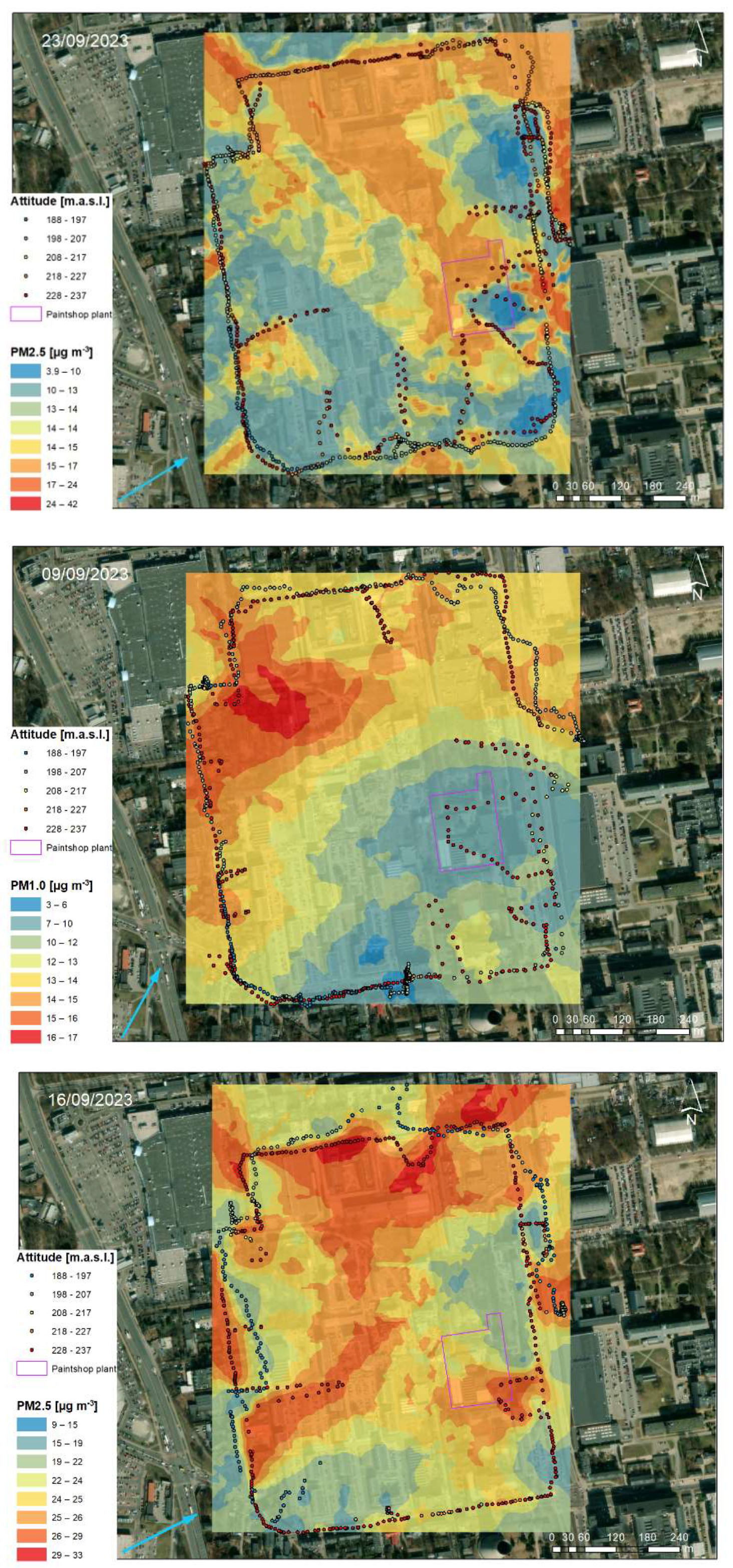
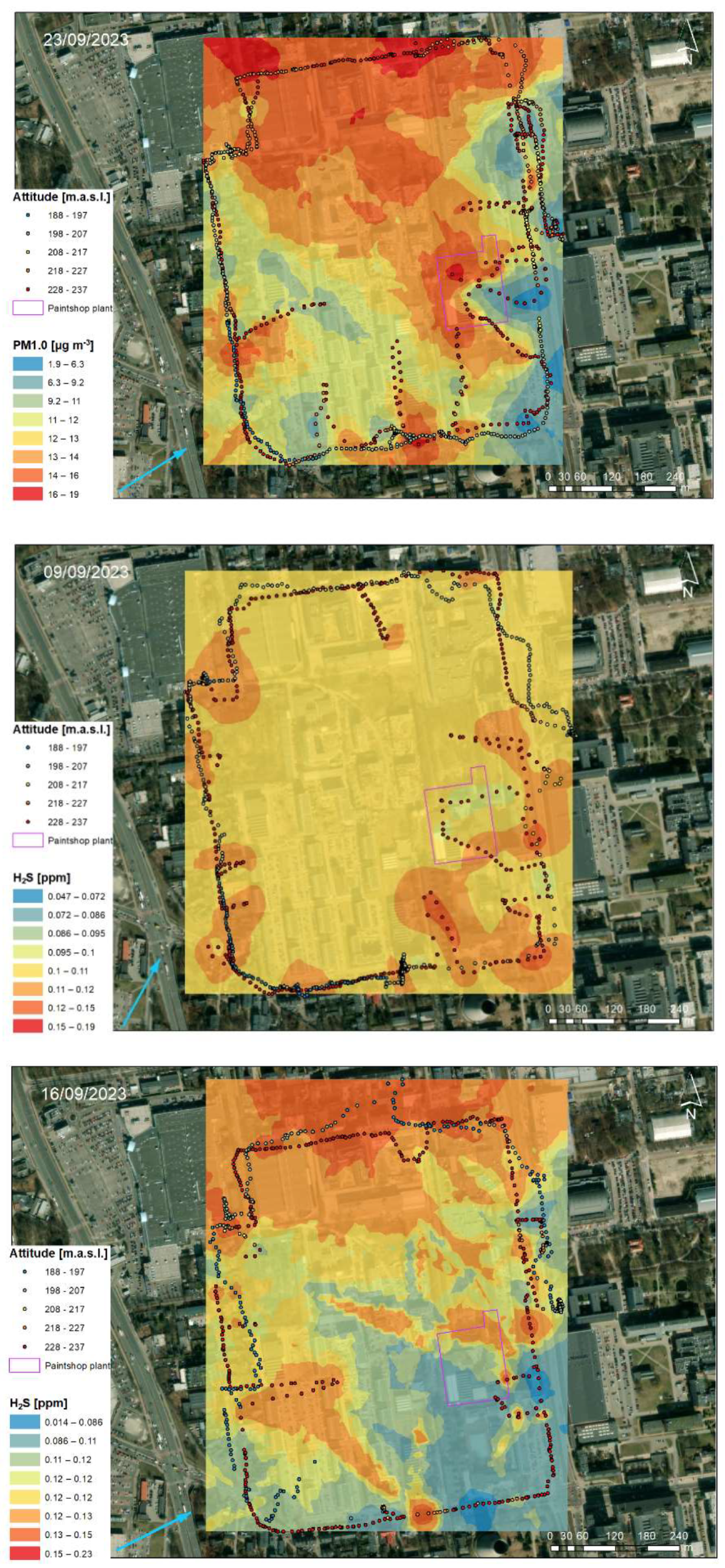
| Location in Relation to the Paintshop | Distance to the Paintshop [m] | Building Feature | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| North | 200–300 | Residential, multi-family, and commercial buildings | Dominated height of 15–30 m |
| South | 100–200 | Residential, multifamily buildings | Dominated height of 15–30 m |
| West | 100–200 | Single-family buildings and service facilities | Dominated height of 6–15 m |
| East | 100–300 | Facilities at the Łódź University of Technology and academic estate | Dominated height of 27–33 m |
| Campaigns | Air Temperature [°C] | Real Humidity [%] | Air Pressure [hPa] | Wind Speed [m·s–1] | Wind Direction [°] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 September 2021 | |||||
| Min. | 21.3 | 36.0 | 1018.2 | 2.0 | 176 |
| Max. | 24.3 | 55.0 | 1019.4 | 4.0 | 197 |
| Avg. | 23.1 | 44.0 | 1018.9 | 3.3 | 191 |
| St. Dev. | 1.3 | 8.0 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 10 |
| 16 September 2021 | |||||
| Min. | 20.0 | 70.0 | 1011.3 | 3.0 | 212 |
| Max. | 23.3 | 82.0 | 1011.9 | 4.0 | 254 |
| Avg. | 21.8 | 77.0 | 1011.7 | 3.5 | 232 |
| St. Dev. | 1.4 | 5.1 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 17 |
| 23 September 2021 | |||||
| Min. | 13.2 | 81.0 | 1014.3 | 4.0 | 228 |
| Max. | 14.9 | 88.0 | 1017.4 | 6.0 | 248 |
| Avg. | 14.3 | 83.0 | 1015.9 | 5.25 | 237 |
| St. Dev. | 0.8 | 3.4 | 1.4 | 1.0 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sówka, I.; Cichowicz, R.; Dobrzański, M.; Bezyk, Y. Analysis of Air Pollutants for a Small Paintshop by Means of a Mobile Platform and Geostatistical Methods. Energies 2023, 16, 7716. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16237716
Sówka I, Cichowicz R, Dobrzański M, Bezyk Y. Analysis of Air Pollutants for a Small Paintshop by Means of a Mobile Platform and Geostatistical Methods. Energies. 2023; 16(23):7716. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16237716
Chicago/Turabian StyleSówka, Izabela, Robert Cichowicz, Maciej Dobrzański, and Yaroslav Bezyk. 2023. "Analysis of Air Pollutants for a Small Paintshop by Means of a Mobile Platform and Geostatistical Methods" Energies 16, no. 23: 7716. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16237716
APA StyleSówka, I., Cichowicz, R., Dobrzański, M., & Bezyk, Y. (2023). Analysis of Air Pollutants for a Small Paintshop by Means of a Mobile Platform and Geostatistical Methods. Energies, 16(23), 7716. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16237716








