Review of Concepts and Determinants of Grid Electricity Reliability
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Innovations and Contribution of the Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Step 1: Question Formulation
- How is the reliability concept understood with special focus on grid electricity reliability?
- What precursor factors influence grid electricity reliability?
- What are the measures or computational tools of grid electricity reliability?
- Which theories and methodologies are applied to study grid electricity reliability?
- What are the likely research gaps that need to be addressed in the future?
2.2. Step 2: Locating Studies
2.2.1. Database Selection
2.2.2. Journal Selection
2.3. Step 3: Selection and Evaluation of Studies (Content Collection)
2.3.1. Search Terms (Boolean Words)
2.3.2. The Criteria for Exclusion and Inclusion
- (i)
- Inclusion criteria
- (ii)
- Exclusion criteria
2.4. Step 4: Synthesis (Content Categorisation/Grouping)
3. Analysis and Synthesis
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Reviewed Articles
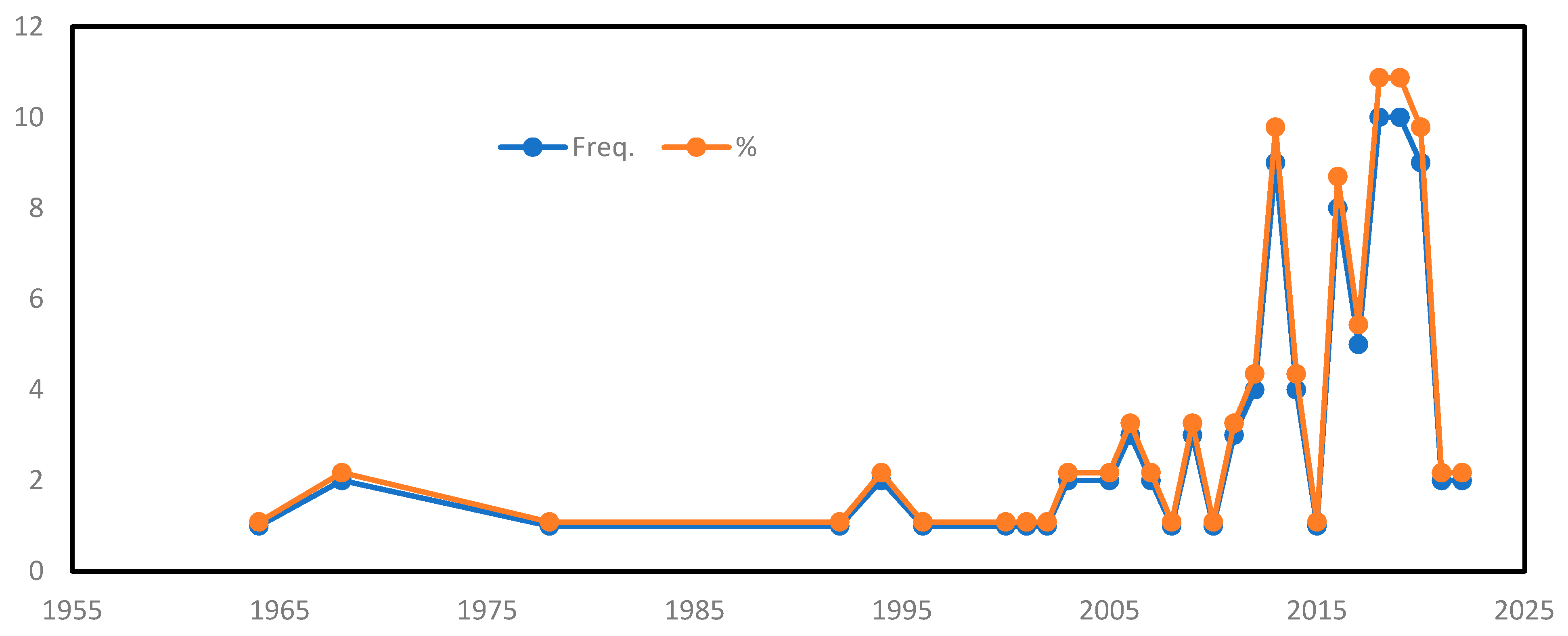
3.1.1. Distribution of Articles According to the Year of Publication
3.1.2. Distribution of the Studies by Region
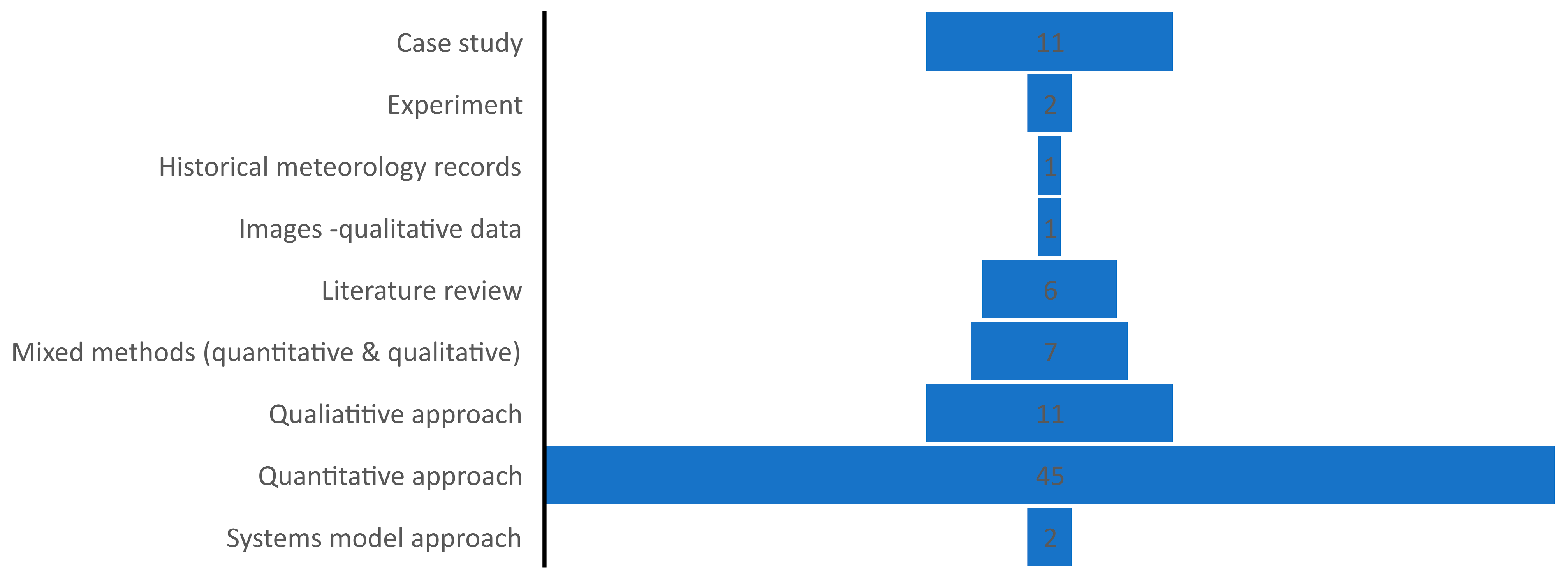
3.1.3. Publication by Research Design/Approach
3.1.4. Theories/Frameworks/Models
3.1.5. Publication by Journal/Publisher
3.1.6. Data Analytic Tools
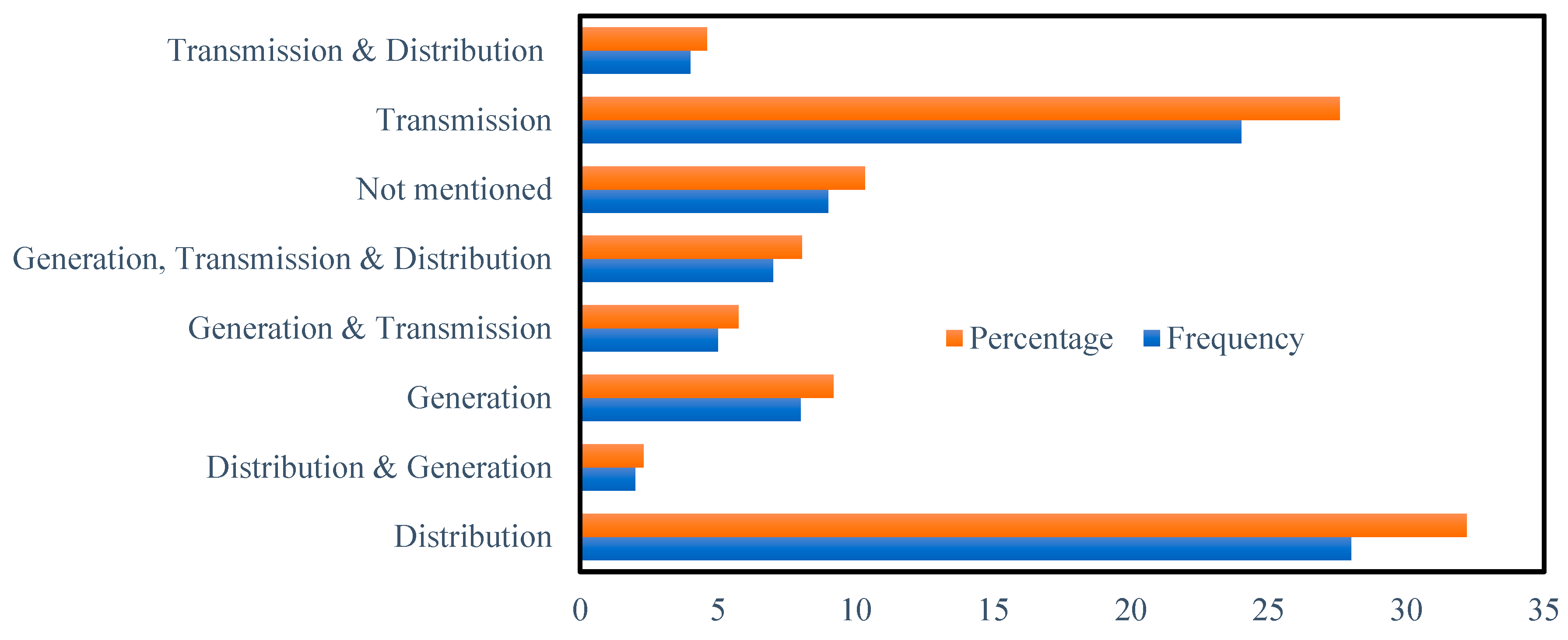
3.1.7. Subsystem of the Grid
3.2. Conceptualizing Grid Electricity Reliability
3.3. Parameters Used in the Measures of Grid Electricity Reliability
3.4. Measures/Computational Tools of Grid Electricity Reliability
3.5. Precursor Factors Influencing Grid Electricity Reliability
4. Discussion
4.1. Environmental/Weather Factors
4.2. Technical Factors
4.3. Organizational Factors
4.4. Security Factors (System Threats)
4.5. Other External Factors
4.6. Measurements of Grid Reliability
5. Conclusions
5.1. Summary of Results
5.2. Directions for Further Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Bank and S. Energy Sector Management Assistance Program (ESMAP), S4All. State of Electricity Access Report (SEAR); World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- EnergyAfrica. Fiscal Policy OptioNS for Solar Home Systems; final report; EnergyAfrica: Hastings, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- IEA. African Energy Outlook. 2019. Available online: https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/2f7b6170-d616-4dd7-a7ca-a65a3a332fc1/Africa_Energy_Outlook_2019.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Fashina, A.; Mundu, M.; Akiyode, O.; Abdullah, L.; Sanni, D.; Ounyesiga, L. The Drivers and Barriers of Renewable Energy Applications and Development in Uganda: A Review. Clean Technol. 2018, 1, 9–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamba, C. Effect of school electrification on learning outcomes: A subnational level analysis of students’ pass rate in English and mathematics in Ghana. Educ. Res. Policy Pract. 2018, 17, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blimpo, M.P.; Cosgrove-davies, M. Electricity Access in Sub-Saharan Africa: Uptake, Reliability, and Complementary Factors for Economic Impact. Africa Development Forum; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Borecki, M.; Ciuba, M.; Kharchenko, Y.; Khanas, Y. Substation reliability evaluation in the context of the stability prediction of power grids. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2020, 68, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, E.; Kirby, B. Bulk-Power Basics: Reliability and Commerce; Consulting in Electric-Industry Restructuring: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Osborn, J.G.; Kawann, C. Reliability of the U.S. Electricity System: Recent Trends and Current Issues. 2001. Available online: https://emp.lbl.gov/publications/reliability-us-electricity-system (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Ward, D.M. The effect of weather on grid systems and the reliability of electricity supply. Clim. Chang. 2013, 121, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentschler, J.; Kornejew, M.; Hallegatte, S.; Braese, J.; Obolensky, M. Underutilized Potential: The Business Costs of Unreliable Infrastructure in Developing Countries; World Bank Policy Research Working Papers; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martikainen, A.; Pykälä, M.; Farin, J. Recognizing Climate Change in Electricity Network Design and Construction; VTT Rsearch Center of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Veloza, O.P.; Santamaria, F. Analysis of major blackouts from 2003 to 2015: Classification of incidents and review of main causes. Electr. J. 2016, 29, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, L.N.; Sohn, M.D.; LaCommare, K.H.; Eto, J.H. Exploratory analysis of high-resolution power interruption data reveals spatial and temporal heterogeneity in electric grid reliability. Energy Policy 2019, 129, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherb, A.; Garrè, L.; Straub, D. Evaluating component importance and reliability of power transmission networks subject to windstorms: Methodology and application to the nordic grid. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 191, 106517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oseni, M.O.; Pollitt, M.G. Power Outages and the Costs of Unsupplied Electricity: Evidence from Backup Generation among Firms in Africa. 2013. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=ced66a3eb2d00a416501131cbbbf07483248c2f1 (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Moreno, R.; Panteli, M.; Mancarella, P.; Rudnick, H.; Lagos, T.; Navarro, A.; Ordonez, F.; Araneda, J.C. From Reliability to Resilience: Planning the Grid against the Extremes. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2020, 18, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ERA. Annual Report FY 2018-19. 2020, p. 172. Available online: https://www.era.go.ug/index.php/resource-centre/publications/annual-reports/548-annual-report-fy-2018-19/download (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Wabukala, B.M.; Otim, J.; Mubiinzi, G. Assessing wind energy development in Uganda: Opportunities and challenges. Wind. Eng. 2021, 45, 1714–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.U.; Omolola, S.A. A Study and Evaluation of Power Outages on 132 Kv Transmission Network In Nigeria for Grid Security. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2019, 8, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhelou, H.H.; Hamedani-Golshan, M.E.; Njenda, T.C.; Siano, P. A survey on power system blackout and cascading events: Research motivations and challenges. Energies 2019, 12, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, V.; Hilton, B. Electric grid reliability research. Energy Inform. 2019, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petticrew, M.; Roberts, H. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide. 2008. Available online: https://fcsalud.ua.es/en/portal-de-investigacion/documentos/tools-for-the-bibliographic-research/guide-of-systematic-reviews-in-social-sciences.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Aveyard, H.; Bradbury-Jones, C. An analysis of current practices in undertaking literature reviews in nursing: Findings from a focused mapping review and synthesis. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2019, 19, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, A.F.; Naveiro, R.M.; Aoussat, A.; Reyes, T. Systematic literature review of eco-innovation models: Opportunities and recommendations for future research. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 1278–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranfield, D.; Denyer, D.; Smart, P. Towards a Methodology for Developing Evidence-Informed Management Knowledge by Means of Systematic Review*. Br. J. Manag. 2003, 14, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayring, P. Qualitative Content Analysis. Forum: Qualitative Social Research. 2000, Volume 1. Available online: https://www.qualitative-research.net/index.php/fqs/article/view/1089/2386 (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Siva, V.; Gremyr, I.; Bergquist, B.; Garvare, R.; Zobel, T. The support of Quality Management to sustainable development: A literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 138, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.; Darko, E.; Seth, P.; Rud, J.-P. Job Creation Impact Study: Bugoye Hydropower Plant, Uganda. 2013. Available online: https://www.jobsanddevelopment.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/Job-Creation.-Impact-Study.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Baarsma, B.E.; Hop, J.P. Pricing power outages in the Netherlands. Energy 2009, 34, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoffman; Streit, D. United States Electricity Industry Primer, Office of Electricity Delivery and Energy Reliability, U.S. Department of Energy. In Off. Electr. Deliv. Energy Reliab. U.S. Dep. Energy, DOE/OE-0017; July 2015; pp. 1–94. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2015/12/f28/united-states-electricity-industry-primer.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Kornatka, M. The weighted kernel density estimation methods for analysing reliability of electricity supply. In Proceedings of the 2016 17th International Scientific Conference on Electric Power Engineering (EPE), Prague, Czech Republic, 16–18 May 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subcommittee, D. IEEE Guide for Electric Power Distribution Reliability Indices; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, E.; Roy, S.; Mohammad, N.; Nawar, N.; Dipta, D.R. Metrics and enhancement strategies for grid resilience and reliability during natural disasters. Appl. Energy 2021, 290, 116709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, J.H.; Lacommare, K.H.; Sohn, M.D.; Caswell, H.C. Evaluating the Performance of the IEEE Standard 1366 Method for Identifying Major Event Days. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiamarit, K.; Nuchprayoon, S. Modeling of renewable energy resources for generation reliability evaluation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 26, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi Nikzad, B. Shoorangiz Shams Shamsabad Farahani, Mohammad Bigdeli Tabar, Hossein Tourang, B.; Yousefpour Calculation of Generation System Reliability Index: Loss of Load Expectationا. Экoнoмика Региoна 2012, 9, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Mouhsen, M.A.; Tamtum, A.A. Loss of Load Expectation of Alkhoms Generating Units. In Proceedings of the First Conference for Engineering Sciences and Technology (CEST-2018), Libya, North Africa, 25–27 September 2018; Volume 1, pp. 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrylenko, O.; Strzelecki, R.; Denysiuk, S.; Derevianko, D. Main features of the stability and reliability enhancement of electricity grid with DG in Ukraine based on IEEE standards. Техн. Електрoдинаміка 2013, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Billinton, R.; Wangdee, W. Predicting bulk electricity system reliability performance indices using sequential Monte Carlo simulation. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2006, 21, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaburi, J.; Bazilian, M.; Kincer, J.; Moss, T. Measuring “Reasonably Reliable” access to electricity services. Electr. J. 2020, 33, 106828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosyadi, G.; Syahputra, R.; Mujaahid, F. Electrical Power Distribution Network Reliability: A Case Study in Wates Substation, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. J. Electr. Technol. UMY 2018, 2, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jooshaki, M.; Karimi-Arpanahi, S.; Lehtonen, M.; Millar, R.J.; Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M. Reliability-Oriented Electricity Distribution System Switch and Tie Line Optimization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 130967–130978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravorti, S. Key issues pertaining to aging, maintenance and reliability of electricity infrastructure. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Power and Energy Conference, Putra Jaya, Malaysia, 28–29 November 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-alvarado, M.S. Power System Reliability and Maintenance Evolution: A Critical Review and Future Perspectives. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 51922–51950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, A.; Tekin, E.; Khodaei, A.; Khator, S.K.; Han, Z. System Hardening and Condition-Based Maintenance for Electric Power Infrastructure under Hurricane Effects. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2016, 65, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.A.; Liu, H.; Sarpong, I.K.; Sparks, P.; Rosowsky, D.V. Electric Power Distribution System Performance in Carolina Hurricanes. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2003, 4, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, P.; Apt, J.; Talukdar, S. Large blackouts in North America: Historical trends and policy implications. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 5249–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, V.; Kwasinski, A. Characterization of power system outages caused by hurricanes through localized intensity indices. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–25 July 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwasinski, A.; Weaver, W.W.; Chapman, P.L.; Krein, P.T. Telecommunications power plant damage assessment for hurricane katrina-site survey and follow-up results. IEEE Syst. J. 2009, 3, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Singh, C. A methodology for evaluation of hurricane impact on composite power system reliability. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, A.F.; Duenas-Osorio, L. Outage predictions of electric power systems under Hurricane winds by Bayesian networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Probabilistic Methods Applied to Power Systems (PMAPS), Durham, UK, 7–10 July 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepyne, D.L. Topology and cascading line outages in power grids. J. Syst. Sci. Syst. Eng. 2007, 16, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.; Dueñas-Osorio, L.; Stein, R.; Subramanian, D. Performance assessment of topologically diverse power systems subjected to hurricane events. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2010, 95, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamov, D.; Perzhabinsky, S. Influence of failures of overhead lines on reliability of autonomous power supply system. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 69, 02015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papic, M.; Agarwal, S.; Allan, R.N.; Billinton, R.; Dent, C.J.; Ekisheva, S.; Gent, D.; Jiang, K.; Li, W.; Mitra, J.; et al. Outage Events in Power Systems: A Review. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Guikema, S.D.; Nateghi, R.; Quiring, S.M.; Staid, A.; Reilly, A.C.; Gao, M. Predicting Hurricane Power Outages to Support Storm Response Planning. IEEE Access 2014, 2, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero Pulido, D.F.; Ten Kortenaar, M.V.; Hurink, J.L.; Smit, G.J.M. The role of off-grid houses in the energy transition with a case study in the Netherlands. Energies 2019, 12, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.W. Power line failures and catastrophic wildfires under extreme weather conditions. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 35, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, A.; Vinogradova, A.; Bolshev, V. Analysis of the quantity and causes of outages in LV/MV electric grids. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 6, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, S.; Pahwa, A. A probabilistic approach for animal-caused outages in overhead distribution systems. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Probabilistic Methods Applied to Power Systems, Stockholm, Sweden, 11–15 June 2006; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras, B.A.; Reynolds-Barredo, J.M.; Dobson, I.; Newman, D.E. Validating the OPA cascading blackout model on a 19402 bus transmission network with both mesh and tree structures. In Proceedings of the Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), Wailea, HI, USA, 8–11 January 2019; pp. 3494–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koks, E.; Pant, R.; Thacker, S.; Hall, J.W. Understanding Business Disruption and Economic Losses Due to Electricity Failures and Flooding. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2019, 10, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Sun, L.; Cai, J.; Hu, T. uR = I nout toutJIInollf; no. Ciced. In Proceedings of the China International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CICED 2014), Shenzhen, China, 23–26 September 2014; pp. 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, D.A. Electric utility distribution analysis for extreme winds. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2008, 96, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, P.D.H.; Dobson, I.; Rezaei, P. Cascading Power Outages Propagate Locally in an Influence Graph That is Not the Actual Grid Topology. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germany, M.S.; Dressler, A.; Hollmach, D. A new grid driven approach to guarantee reliable communication during power outages. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference and Exhibition on Electricity Distribution (CIRED 2013), Stockholm, Sweden, 10–13 June 2013; pp. 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Schaller, J.; Ekisheva, S. Leading causes of outages for transmission elements of the North American bulk power system. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Boston, MA, USA, 17–21 July 2016; Volume 2016-Novem, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthathip, N.; Bhasaputra, P.; Pattaraprakorn, W. Outage cost assessment for investment-benefit model of smart grid in Thailand. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Cogeneration, Small Power Plants and District Energy (ICUE), Bangkok, Thailand, 14–16 September 2016; pp. 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diendorfer, G.; Pichler, H.; Achleitner, G.; Broneder, M. Lightning caused outages in the Austrian Power Grid transmission line network. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Lightning Protection (ICLP), Shanghai, China, 11–18 October 2014; pp. 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapin, Y.; Ekisheva, S.; Papic, M.; Zarikas, V. Outage Data Analysis of the Overhead Transmission Lines in Kazakhstan Power System. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Probabilistic Methods Applied to Power Systems (PMAPS), Liege, Belgium, 18–21 August 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.E. Electric Power Distribution Reliability, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, A.W. Dependent Mode Outages in analysis and prediction of multiple outage states. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 July 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekisheva, S.; Papic, M.; Pakeltis, M.J.; Brantley Tillis, G.; King, D.J. Assessment of north american transmission outages by fault type. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Montreal, QC, Canada, 2–6 August 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpay, B.A.; Wanik, D.; Watson, P.; Cerrai, D.; Liang, G.; Anagnostou, E. Dynamic Modeling of Power Outages Caused by Thunderstorms. Forecasting 2020, 2, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, E.; Guikema, S.D.; Quiring, S.M. Predicting Thunderstorm-Induced Power Outages to Support Utility Restoration. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 4370–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewhart, W.A.; Wilks, S.S. System Reliability Theory; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y. Identification of cascading failures based on overload character of transmission lines. In Proceedings of the 2008 Third International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies, Nanjing, China, 6–9 April 2008; pp. 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhuis, A.J.; Leach, M.; Yang, A. The impact of increased decentralised generation on the reliability of an existing electricity network. Appl. Energy 2018, 215, 479–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaver, D.P.; Montmeat, F.E.; Patton, A.D. Power System Reliability I—Measures of Reliability and Methods of Calculation. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1964, 83, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaohui, Y.E.; Wuzhi, Z.; Xinli, S.; Guoyang, W.U.; Tao, L.I.U.; Zhida, S.U. Review on Power System Cascading Failure Thoeries and Studies. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Probabilistic Methods Applied to Power Systems (PMAPS), Beijing, China, 16–20 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Faruqui, A.; Harris, D.; Hledik, R. Unlocking the €53 billion savings from smart meters in the EU: How increasing the adoption of dynamic tariffs could make or break the EU’s smart grid investment. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 6222–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, F.A.; Alam, M.S.; Asghar, M.S.J.; Ahmad, F. Blackout Mitigation of Voltage Stability Constrained Transmission Corridors through Controlled Series Resistors. Recent Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. (Former. Recent Pat. Electr. Electron. Eng.) 2017, 11, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampurkar, V.; Pentayya, P.; Mangalvedekar, H.A.; Kazi, F. Cascading Failure Analysis for Indian Power Grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.V.F.; Balu, N.J.; Member, S.; Objectives, A.; System, P. Composite Generation/Transmission Reliability Evaluation. Proc. IEEE 1992, 80, 470–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaipia, T.; Peltoniemi, P.; Lassila, J.; Salonen, P.; Partanen, J. Impact of low voltage DC system on reliability of electricity distribution. In Proceedings of the CIRED 2009—20th International Conference and Exhibition on Electricity Distribution—Part 1, Prague, Czech Republic, 8–11 June 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimtsios, A.M.; Safigianni, A.S. Optimization of a medium voltage power distribution network’s reliability indices. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering (EEEIC), Florence, Italy, 7–10 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatziargyriou, N.D.; Andersson, G.; Donalek, P.; Farmer, R.; Hatziargyriou, N.; Kamwa, I.; Kundur, P.; Martins, N.; Paserba, J.; Pourbeik, P. Causes of the 2003 Major Grid Blackouts in North America and Europe, and Recommended Means to Improve System Dynamic Performance Causes of the 2003 Major Grid Blackouts in North America and Europe, and Recommended Means to Improve System Dynamic Perform. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2005, 20, 1922–1928. [Google Scholar]
- Vaiman, M.; Bell, K.; Chen, Y.; Chowdhury, B.; Dobson, I.; Hines, P.; Papic, M.; Miller, S.; Zhang, P. Risk assessment of cascading outages: Methodologies and challenges. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 27, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overholt, P. Recent power outages and reliability initiatives. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Power Engineering Society Winter Meeting. Conference Proceedings (Cat. No.01CH37194), Columbus, OH, USA, 28 January–1 February 2001; pp. 2013–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, G.W. Challenges and opportunities in smart grid: A position article. Proc. IEEE 2011, 99, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran Hendi, R.; Seyed-Shenava, S.J. Customer interruption cost minimization based on graph theory in smart distribution grid. In Proceedings of the 2013 Smart Grid Conference (SGC), Tehran, Iran, 17–18 December 2013; pp. 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy Bilinton, R.N.A. Reliabilty Evaluation of Power Systems; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Vianna, E.A.L.; Abaide, A.R.; Canha, L.N.; Miranda, V. Substations SF6 circuit breakers: Reliability evaluation based on equipment condition. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 142, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numan, M.; Baig, M.F.; Yousif, M. Reliability evaluation of energy storage systems combined with other grid flexibility options: A review. J. Energy Storage 2023, 63, 107022. [Google Scholar]
- Moraski, J.W.; Popovich, N.D.; Phadke, A.A. Leveraging rail-based mobile energy storage to increase grid reliability in the face of climate uncertainty. Nat. Energy 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuangpishit, S.; Katiraei, F.; Chalamala, B.; Novosel, D. Mobile Energy Storage Systems: A Grid-Edge Technology to Enhance Reliability and Resilience. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2023, 21, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrai, D.; Wanik, D.W.; Bhuiyan, A.E.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Frediani, M.E.B.; Anagnostou, E.N. Predicting Storm Outages Through New Representations of Weather and Vegetation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 29639–29654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olugbenga, T.K.; Jumah, A.A.; Phillips, D.A. The current and future challenges of electricity market in Nigeria in the face of deregulation process. Afr. J. Eng. Res. 2013, 1, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kabanda, P.; Ttondo, S.S. Patrick Kabanda Technical Strategy to Curb Transformer Oil Theft on Distribution Networks: Case of Uganda’s Power Distribution Network. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2018, V7, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnpaul, A.; Adella, K.; Mwikirize, C.; Okou, R. A Surveillance System to Counter Vandalism of Transmission Line Equipment. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Advances in Human-oriented and Personalized Mechanisms, Technologies, and Service, Nice, France, 12–16 October 2014; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuna, M.; Muumbo, A.; McLean, J. Pylon Anti-Vandalism Monitoring System using Machine Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE PES/IAS PowerAfrica, Nairobi, Kenya, 25–28 August 2020; pp. 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kithinji Kirunguru, E. Design and Implementation of a Transformer Vandalism Monitoring System. Int. J. Sens. Sens. Netw. 2017, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.K. Cybersecurity and Confidentiality in Smart Grid for Enhancing Sustainability and Reliability. Recent Res. Rev. J. 2023, 2, 215–241. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.K.; Habib, A.A.; Shukur, Z.; Ibrahim, F.; Islam, S.; Razzaque, M.A. Review on cyber-physical and cyber-security system in smart grid: Standards, protocols, constraints, and recommendations. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2023, 209, 103540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueck, J.D.; Kirby, B.J.; Overhold, P.N.; Markel, L.C. Measurement Practices for Reliability and Power Quality; Ornl/Tm-2004/91; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2004. Available online: https://info.ornl.gov/sites/publications/Files/Pub57467.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Salimian, M.R.; Aghamohammadi, M.R. A Three Stages Decision Tree-Based Intelligent Blackout Predictor for Power Systems Using Brittleness Indices. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 5123–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, S.S.S.; Nikzad, M.; Tabar, M.B.; Tourang, H.; Yousefpour, B. STATCOM control using a PSO-based IP controller. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 4, 768–774. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.D.; Ringlee, R.J. System Reliability Calculations: I-Generation System Model. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1968, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, M.; Ghadimi, N.; Ahmadinia, E. An analytical methodology for reliability assessment and failure analysis in distributed power system. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Country | Freq. | Country | Freq. | Country | Freq. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | 3 | Libya | 1 | USA | 25 |
| Canada | 3 | Multicountry | 13 | Sweden | 1 |
| China | 7 | Nigeria | 3 | Ukraine | 1 |
| Tajikistan | 1 | Not indicated | 12 | Kenya | 2 |
| Finland | 1 | Poland | 2 | Uganda | 2 |
| Germany | 2 | Bulgaria | 1 | Iran | 2 |
| Great Britain | 1 | Russia | 1 | Thailand | 2 |
| Greece | 1 | Switzerland | 1 | Indonesia | 1 |
| India | 2 | South Australia | 1 |
| Models/Frameworks/Theories | Freq. | Models/Frameworks/Theories | Freq. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kolmogorov–Smirnov theory | 1 | Load model | 3 |
| Predictive modeling | 1 | Localized intensity indices | 1 |
| Weighted kernel density Eestimation method | 1 | Sensitive outage prediction framework | 1 |
| OPA cascading blackout model | 2 | Markov modeling | 8 |
| Abstract cascading failure model | 1 | Theory of HVDC protection and control system | 1 |
| Aggregated restoration model | 1 | MILP model | 1 |
| Automatic generator model | 1 | Motter–Lai model | 1 |
| Bayesian model | 1 | Multiregional supply–use model (MRIA model) | 1 |
| Bayesian networks DC-flow model | 1 | Negative binomial regression models | 1 |
| Three stages blackout predictor decision tree | 1 | Noisy OR-gate model | 1 |
| Calibrated hurricane wind speed model | 1 | Not indicated | 34 |
| Cascading line outage model | 1 | Operational reliability theory | 1 |
| Complex network theory | 2 | Optimization model | 1 |
| Component fragility model | 2 | Physical damage model | 1 |
| Composite risk index (CRI) assessment model | 1 | Climate models (ECHAM4-OPYC3 & HadAM3-H) | 1 |
| Optimal power flow (OPF) model | 1 | Power-flow model | 2 |
| Bathtub curve | 2 | Power network model | 1 |
| Consequence path and consequence box | 1 | Power system blackout model | 2 |
| Cost–benefit model | 1 | Power system simulation theory | 1 |
| Google Inception deep convolutional object detection model | 1 | Predictive models | 1 |
| Customer interruption cost model | 1 | Generalized linear model | 1 |
| DC load-flow model | 1 | Reliability and cost model | 1 |
| Deterministic model | 1 | Reliability assessment model | 3 |
| Distribution feeder model | 1 | Renewable generation model | 1 |
| Distribution network model & formulas | 1 | Sandpile model | 1 |
| Drawing theory | 1 | Self-organized critical theory | 1 |
| Two-stage mixture models (QRF, RF, BT or SVM, SVDD-QRF) | 1 | Infrastructure hardening and condition-based maintenance scheduling model | 1 |
| Entropy-based metric model | 1 | State space model | 1 |
| Spatial random field model | 1 | Synergetic predictive model | 1 |
| Generation capacity and system model | 3 | The dynamic model | 1 |
| Graph theory | 3 | Two-state Markov model | 1 |
| Hazard model | 1 | Two-state model | 1 |
| Hidden failure model | 1 | Two-state weather model | 1 |
| Investment–benefit model | 1 | Under-frequency load | 1 |
| AIRS & ANN Model | 1 | Weather stochastic model | 1 |
| Graph model | 1 | Three-state model | 3 |
| Journals | FREQ. | Journals | FREQ. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Africa | 1 | IEEE on Transactions on power Apparatus and systems | 3 |
| African Journal of Engineering Research | 1 | The Electricity Journal | 2 |
| Applied Energy | 3 | IEEE Systems Journal | 1 |
| Bulletin of Electrical Engineering And Informatics | 1 | IEEE Transactions on Power delivery | 1 |
| Bulletin of The Polish Academy of Sciences Technical Sciences | 1 | IEEE Transactions on Power Systems | 6 |
| CSEE Journal of Power And Energy Systems | 2 | Electrical Power and Energy Systems | 1 |
| Electric Power Systems Research | 1 | Applied Sciences | 1 |
| Electrical & Electronic Engineering | 1 | IEEE Transactions on Reliability | 2 |
| Energies | 1 | IEEE Transactions on a smart grid | 1 |
| Energy Policy | 1 | International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology | 1 |
| Engineering Failure Analysis | 1 | Int J Disaster Risk Sci | 1 |
| Forecasting | 1 | International Journal of Sensors and Sensor Networks | 1 |
| Green Energy and Smart Grids | 1 | International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management. | 1 |
| IEEE Access | 1 | International Journey of Engineering and Science | 1 |
| IEEE Milan Power Tech | 1 | Journal of Electrical Technology UMY | 1 |
| IEEE Power & Energy Society Section | 1 | Natural Hazards Review | 1 |
| IEEE Systems Journal | 1 | PES T&D 2012 | 1 |
| Reliability Engineering and System Safety | 3 | The International Journal of Engineering and Science | 1 |
| Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews | 1 | Life Science Journal | 2 |
| Climatic Change | 1 |
| Conferences and Meetings | Freq. | Conferences and Meetings | Freq. |
|---|---|---|---|
| China International Conference on Electricity Distribution | 1 | International Conference on Lightning Protection | 1 |
| Proceedings of the IEEE | 2 | Smart grid conference | 1 |
| Electrical and Computer Engineering Conference Papers, Posters and Presentations. | 1 | International Conference on Probalistic Methods Applied to Power | 5 |
| Electrical Engineering Faculty Conference | 1 | International conference on Signals and Electronic Systems | 1 |
| IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting | 2 | International Conference on System and Science | 1 |
| International conference on Advances in human-oriented and Personalized Mechanism | 1 | International Society Conference on Electric Power Engineering | 1 |
| IEEE Power Engineering Society Winter Meeting | 1 | Conference for Engineering Sciences and Technology | 1 |
| International Conference on Cogeneration, Small Power Plants and District Energy | 1 | International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering | 1 |
| International conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies | 2 | International Conference and Exhibition on Electric Distribution. | 1 |
| International Power and Energy Conference | 1 | International Conference on Electricity Distribution. | 1 |
| E3S Web of Conferences. | 1 |
| Analysis Tools | Freq. | Analysis Tools | Freq. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poisson distribution | 2 | Not indicated | 4 |
| Root cause analysis | 1 | Observation analysis | 2 |
| Bayesian networks | 2 | OPENCV a python computer vision library | 1 |
| Beta distributions | 1 | Periodic reviews | 1 |
| Binomial distribution | 1 | Crash indices | 1 |
| Cause–consequence analysis | 1 | Power-flow analysis | 1 |
| Chi square distribution | 1 | Principal components analysis (PCA) | 2 |
| Comparative analysis | 1 | Probability simulations | 5 |
| Cost–benefit analysis | 2 | Conditional probability analysis | 3 |
| DC-flow analysis | 1 | Geometric analysis | 1 |
| Descriptive analysis | 22 | Qualitative discussion | 18 |
| Localised intensity indices | 1 | Slow and fast dynamic simulations | 1 |
| Event tree analysis | 1 | RAM analysis | 1 |
| Exploratory analysis | 1 | Reactive power resources | 1 |
| Exponential distribution | 3 | Rectangular distribution | 1 |
| Failure probabilities | 2 | Regression analysis | 1 |
| Failures of overhead lines | 1 | Reliability analysis | 5 |
| Fuzzy inference systems | 2 | Sensitivity analysis | 7 |
| Gamma distribution | 3 | State probabilities | 1 |
| Gumbel distribution | 1 | Statistical analysis | 4 |
| Loading analysis | 1 | Step analysis | 1 |
| Log normal distribution | 3 | Stochastic processes | 1 |
| Markov decision processes | 4 | System brittleness indices | 1 |
| Monte Carlo-based simulation approach | 14 | The method of moments | 1 |
| Negative binomial regression analysis | 2 | Theoretical reliability analysis | 1 |
| Network reliability analysis (RDA and MSR) | 1 | Uniform distribution | 1 |
| Normal distribution | 5 | Weibull distribution | 7 |
| Description | Source |
|---|---|
| 1. Reliability is about an uninterrupted supply of electricity. | Scott et al. [29] |
| 2. Reliability of the electricity supply implies lack of power outages. | World Bank (2017) [1] |
| 3. “The ability of the electric grid to deliver electricity to customers without degradation or failure.” | [7,9,30,31] |
| 4. “The degree to which the performances of the elements of the electric system result in power being delivered to consumers within accepted standards and in the amount desired.” | Hirst & Kirby (2000) [8] |
| 5. “The reliability of electricity supply is very often defined in terms of the number and duration of interruptions in a customer’s voltage supply.” | Kornatka [32] |
| 6. ‘‘The probability that a system will perform its intended functions without failure, within design parameters, under specific operating conditions, and for a specific period of time’’ | IEEE (2012) [33] |
| 7. “The reliability of electricity supply is very often defined in terms of the number and duration of interruptions in a customer’s voltage supply.” | Hossain et al. (2021) [34] |
| 8. The interruption of electricity or as a sequence of successive observations reporting at least one grid user without service at a definite point location. | Eto et al. (2017) [35] |
| Parameter | Freq. | Parameter | Freq. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of outages | 20 | Frequency of outages | 17 |
| Failure rates | 8 | Mean time to repair rates | 7 |
| Availability | 3 | Mean duration of reserve states | 1 |
| Mean time to failure | 3 | Load level | 2 |
| Unavailability | 5 | Power network system | 1 |
| Load duration curve | 1 | Forced outage rate | 6 |
| Capacity credit | 1 | Size of blackout | 2 |
| Redundancy/reserve margin | 3 | Failure characteristics | 1 |
| Failure criticalness | 1 | Probability that a customer will be off service | 1 |
| Measures of Grid Reliability | Freq | Measures of Grid Reliability | Freq |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average service availability index (ASAI) | 4 | Monetary average interruption frequency index (MAIFI) | 3 |
| Average system interruption duration index (ASIDI) | 1 | Peak load carrying capability (PLCC) | 1 |
| Average system interruption frequency index (ASIFI) | 1 | Energy index of reliability (EIR) | 1 |
| Average service unavailability index (ASUI) | 2 | Equivalent forced outage rate (EFOR) | 2 |
| Customer total average interruption duration index (CTAIDI) | 1 | Expected interruption cost (EIC) | 1 |
| Delivery point unreliability index (DPUI) | 1 | Average duration of load curtailments (ADLCs) | 1 |
| Expected cost of unserved energy (ECOST) | 1 | Customer average interruption duration index (CAIDI) | 4 |
| Expected demand not supplied (EDNS) | 3 | Customer average interruption frequency index (CAIFI) | 6 |
| Loss of load duration (LOLD) | 3 | Customer experiencing long duration interruptions (CELIDs) | 1 |
| Loss of load expectation (LOLE) | 4 | Customers experiencing multiple interruptions (CEMIs) | 1 |
| Loss of load frequency (LOLF) | 1 | Value of lost load | 1 |
| Loss of load probability (LOLP) | 6 | Expected energy not supplied (EENS) | 2 |
| Index of reliability (IOR) | 1 | Frequency & duration (F & D) | 2 |
| Energy not supplied (ENS) | 2 | Loss of energy expectation (LOEE) | 3 |
| Forced outage rate (FOR) | 1 | Systems average interruption duration index (SAIDI) | 16 |
| Interrupted energy assessment rate (IEAR) | 1 | Systems average interruption frequency index (SAIFI) | 13 |
| System average RAM frequency index (SARFI) | 1 | System instantaneous average RAM frequency index (SIAFRI) | 1 |
| System monetary average RMS variation frequency index (SMARFI) | 1 | Customers experiencing multiple sustained interruptions (CEMSIs) | 1 |
| Loss of load occurrence (LLO) | 1 | Probability of load curtailments (PLCs) | 1 |
| Expected frequency of load curtailments (EFLCs) | 1 | Energy index of unreliability (EIU) | 1 |
| NH2 | 1 | Component reliability (COMREL) | 1 |
| Reliability evaluation complex systems (RECSs) | 1 | Coordinated outage restoration algorithm (CORAL) | 1 |
| Transmission reliability evaluation of large-scale systems (TRELSSs) | 1 | Coordinated planning for multienergy power systems (CPMEPS) | 1 |
| Cognitive reliability and error analysis method (CREAM) | 1 | DIGSILENT | 1 |
| Outage scheduling and reliability analysis of electric power system (OSCAR) | 1 | Operational scheduling decision support platform based on reliability assessment (OSDSP-RA) | 1 |
| System reliability risk model (SRRM) | 1 | Short-term assessment of risk and flexibility index (STARFI) | 1 |
| Bulk electricity system reliability evaluation–tsinghua (BESRE_TH) | 1 | Transmission contingency analysis and reliability evaluation (TransCARE) | 1 |
| Probabilistic composite system evaluation program (PROCOSE) | 1 | GATOR | 1 |
| Environment/Weather Factors (77) | Technology Factors (117) |
|---|---|
| Damage from falling trees and tree contacts and other tree characteristics (10) | Insulation (1) |
| Lightning (6) | Tripping lines circuits and generators, network failure/technological breaks (7) |
| Heat storms (5) | System topology (6) |
| Thunderstorms (3) | Fuel and gas (SF 6) supply disruptions (4) |
| Thermal conductivity of soil, soil moisture and other soil characteristics (3) | Arcing (1) |
| High wind and gust wind speed (9) | Grid equipment contact (1) |
| Ice and snow storms (2) | Load level (11) |
| Rainfall (4) | Interchange levels (1) |
| Floods (2) | Reactive power levels (5) |
| Landslides (1) | Meshed and radial grid (2) |
| Hurricanes (10) | Flow time (1) |
| Land cover type for example crops (1) | System inertia (1) |
| Animal (large and small) contact, for example (5) | Synchronous reserve (1) |
| El Nino/La Nina (1) | Voltage levels (11) |
| Earthquake (3) | Stability levels (2) |
| Duration of stormy weather (2) | Oscillatory transients (1) |
| Weather season (1) | Protection systems (7) |
| Time of the day (1) | Equipment failure (10) |
| Catastrophic days and major event days (1) | Frequency levels (2) |
| Dust storms (1) | Tie lines (2) |
| Others (6) | System condition (4) |
| Contingencies (1) | |
| System faults (3) | |
| Phases affected (1) | |
| Switch closing (1) | |
| Current transducers (1) | |
| Line capacity (2) | |
| Line segments (2) | |
| Power system variables (number of transformers, poles, switches, overhead and underground lines, length of lines) (6) | |
| System collapse behavior and disturbances (1) | |
| Computer software failures (3) | |
| Energy storage (1) | |
| Overlapping component outages (1) | |
| Reserve capacity usage (1) | |
| Design of power system (1) | |
| Capacity credit (2) | |
| Independent failures (1). | |
| Transient and technical faults for example bus faults (3) | |
| Aging of equipment (5) | |
| Operating conditions (1) | |
| Organizational factors (56) | Security factors (malicious damage/attacks)—(24) |
| System operations (6) | Collision with objects (for example, vehicle accidents) (4) |
| Measuring reliability metrics (1) | Other security issues (2) |
| Reporting reliability metrics (1) | Vandalism (9) |
| Inconsistencies (1) | Cyberattacks (2) |
| Vegetation management (5) | Theft of power grid equipment (5) |
| Outage management system (1) | Fire (2) |
| Controlling operation parameters (2) | Other factors (12) |
| Modern smart metering (1) | Load curtailment policies (1) |
| Planned maintenance (5) | Loadshedding policies (2) |
| Human errors (3) | Foreign IEEE standards (1) |
| Maintenance levels (9) | Renewable energy penetration (1) |
| Frequency of inspection/monitoring of equipment (3) | Over demand (1) |
| Periodic/technical reviews (3) | Requests for dig ins for parties outside the utility firm(s) (1) |
| Use of technical staff/adequate understanding of the system and support from the system coordinator (2) | Geographical/spatial variability (1) |
| Reduction in cost of spare parts (1) | Hidden failures (5) |
| Level of operation (2) | |
| Planned outages and unplanned (2) | |
| Level of situation awareness (1) | |
| Islanding (1) | |
| Outage data management (1) | |
| Improper relay coordination (1) | |
| Planning of repair and replacement activities (4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Migisha, A.G.; Ntayi, J.M.; Buyinza, F.; Senyonga, L.; Abaliwano, J.; Adaramola, M.S. Review of Concepts and Determinants of Grid Electricity Reliability. Energies 2023, 16, 7220. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16217220
Migisha AG, Ntayi JM, Buyinza F, Senyonga L, Abaliwano J, Adaramola MS. Review of Concepts and Determinants of Grid Electricity Reliability. Energies. 2023; 16(21):7220. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16217220
Chicago/Turabian StyleMigisha, Adella Grace, Joseph M. Ntayi, Faisal Buyinza, Livingstone Senyonga, Joyce Abaliwano, and Muyiwa S. Adaramola. 2023. "Review of Concepts and Determinants of Grid Electricity Reliability" Energies 16, no. 21: 7220. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16217220
APA StyleMigisha, A. G., Ntayi, J. M., Buyinza, F., Senyonga, L., Abaliwano, J., & Adaramola, M. S. (2023). Review of Concepts and Determinants of Grid Electricity Reliability. Energies, 16(21), 7220. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16217220







