An Overview of Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Based on V-I Trajectory Signature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review of NILM Based on V-I Trajectory
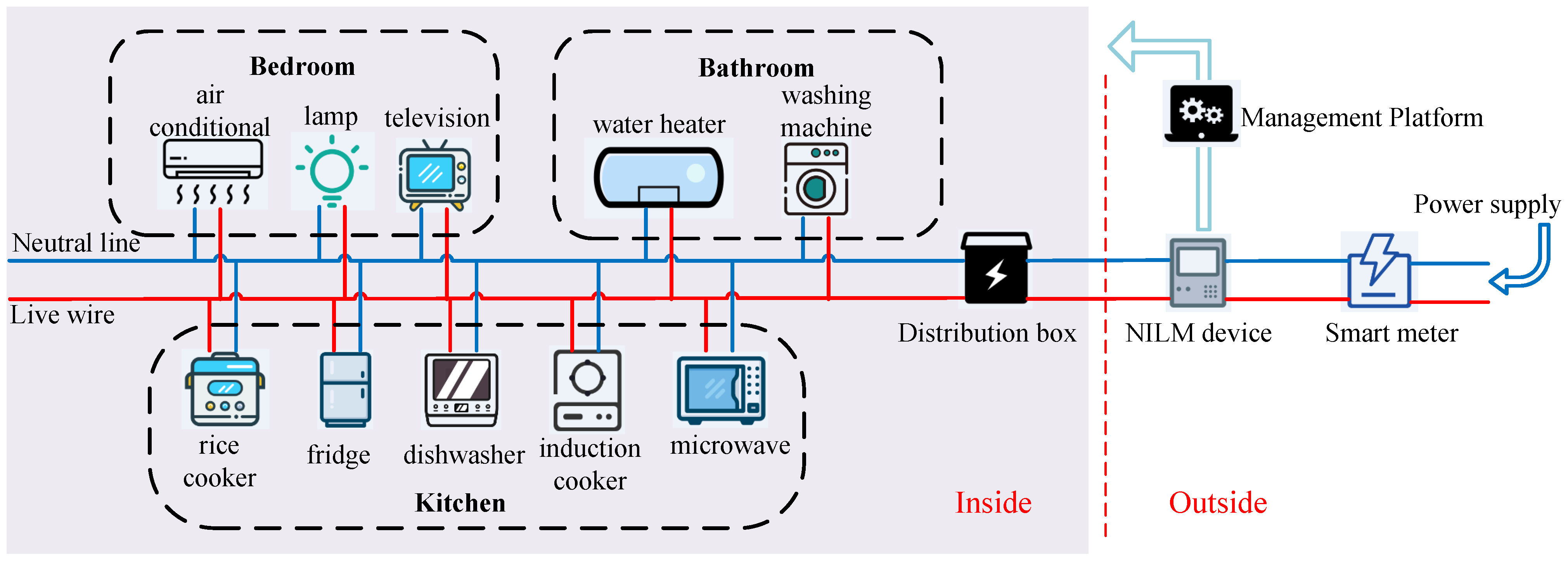
3. Datasets for the Study of V-I Trajectory Signature
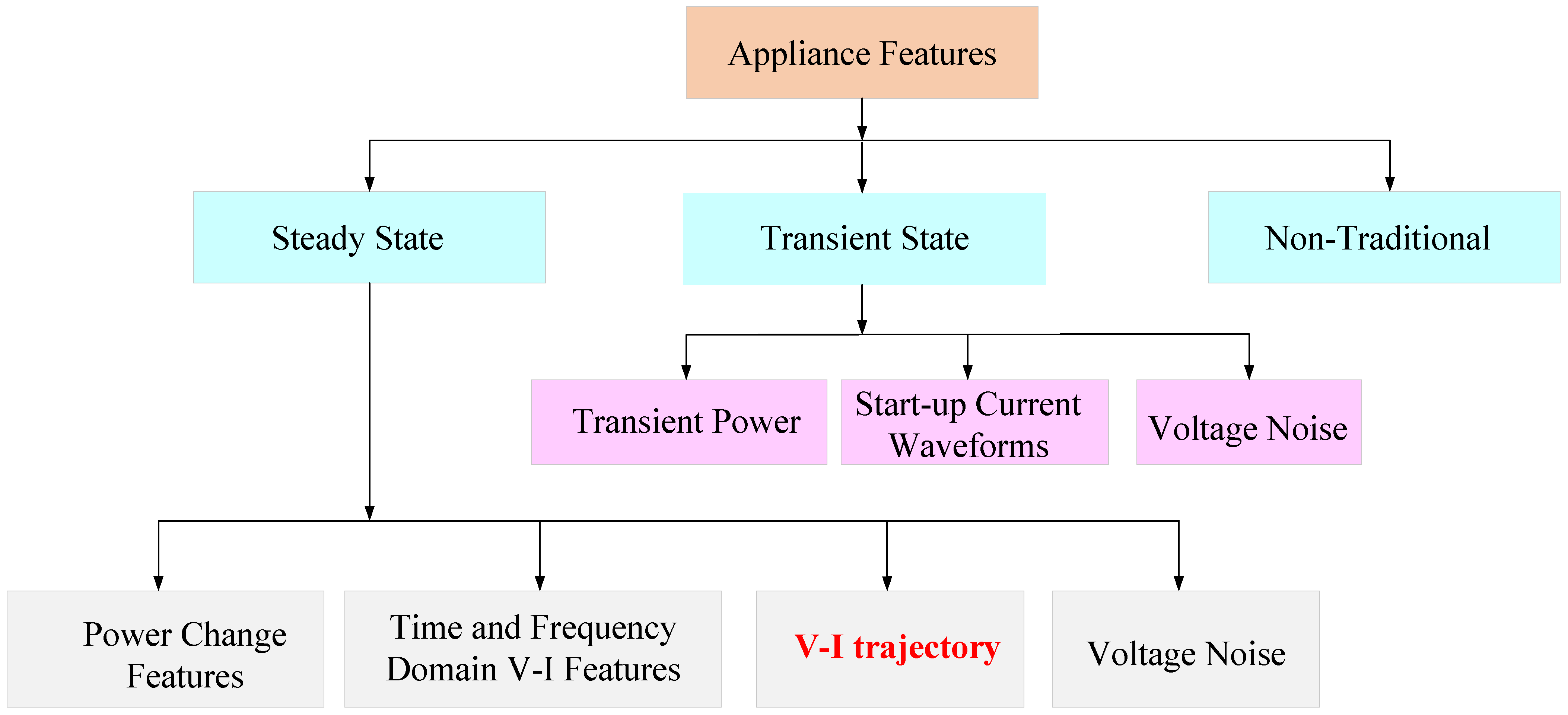
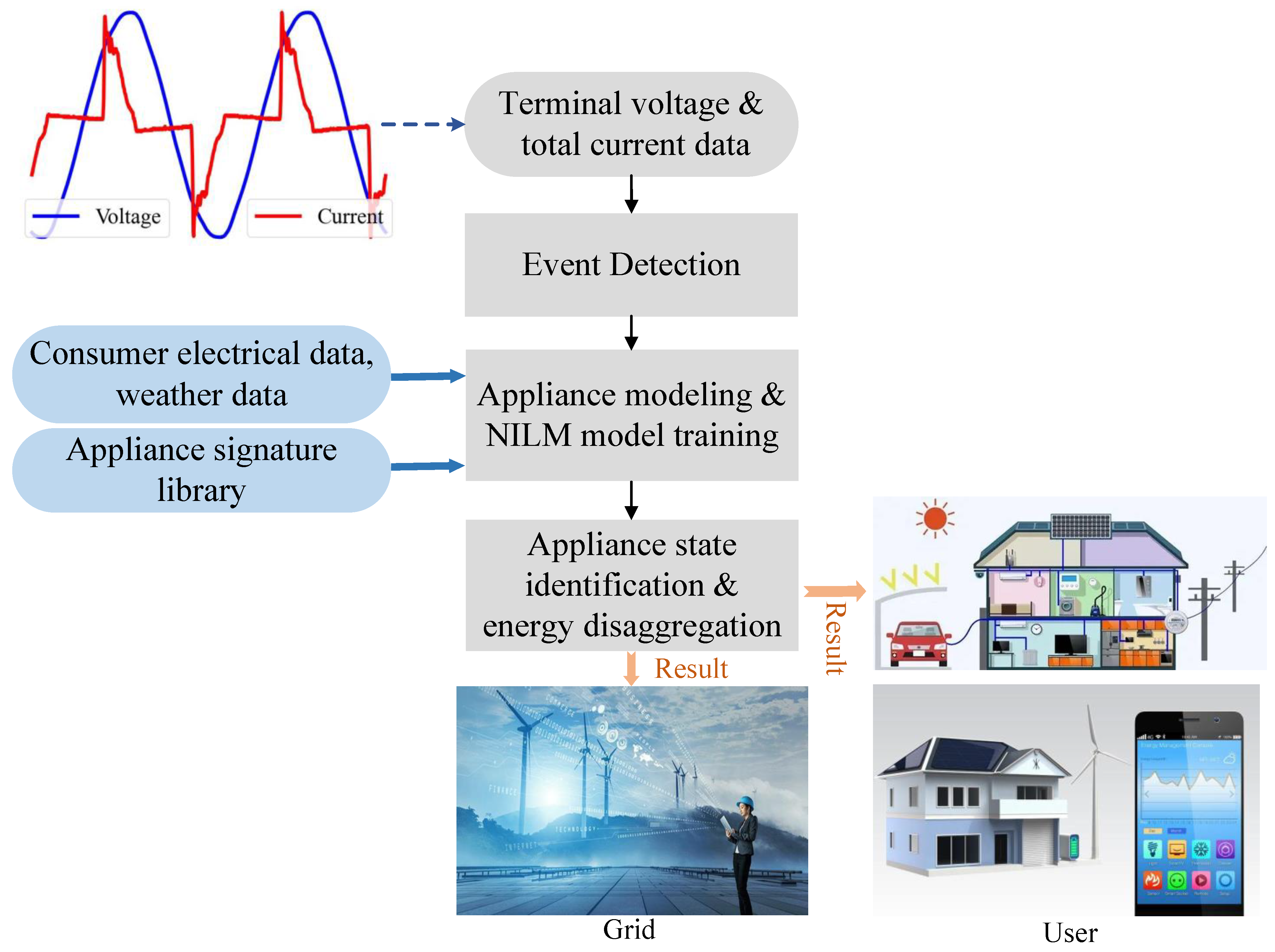
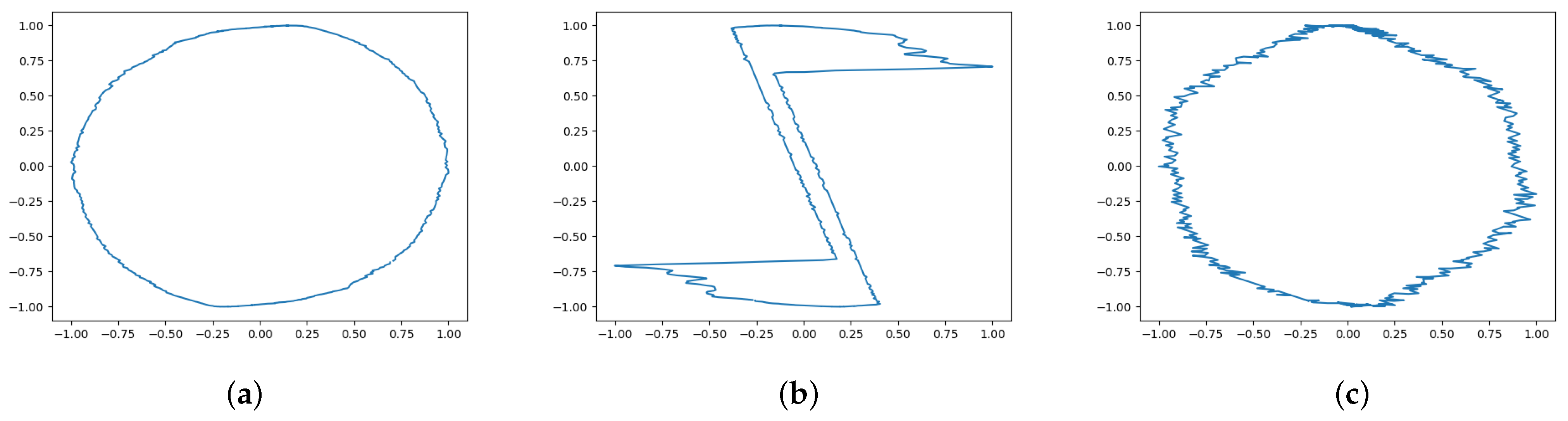
4. V-I Trajectory Extraction
5. Performance Metrics
6. Conclusions
- 1.
- At present, the V-I trajectory is obtained by normalizing the voltage and current data, which leads to the lack of energy information.
- 2.
- An appliance with continuously varying power is difficult to be represented by the V-I trajectory; examples are dimmers and tools.
- 3.
- When a new appliance is added, or the appliance works abnormally, it is necessary to detect these abnormal V-I trajectories.
- 4.
- Due to the difficulty in obtaining high-frequency data and the expensive data storage, it is necessary to reduce the necessary number of training data.
- 5.
- How to obtain the power consumption information of an appliance through the identification of the V-I trajectory is still an open work.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Desley, V.; Laurie, B.; Peter, M. The effectiveness of energy feedback for conservation and peak demand: A literature review. Open J. Energy Effic. 2013, 2013, 28957. [Google Scholar]
- Bonfigli, R.; Principi, E.; Fagiani, M.; Severini, M.; Squartini, S.; Piazza, F. Non-intrusive load monitoring by using active and reactive power in additive Factorial Hidden Markov Models. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 1590–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoha, A.; Gluhak, A.; Imran, M.A.; Rajasegarar, S. Non-intrusive load monitoring approaches for disaggregated energy sensing: A survey. Sensors 2012, 12, 16838–16866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.; Bergés, M. An energy estimation framework for event-based methods in non-intrusive load monitoring. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 90, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridi, A.; Gisler, C.; Hennebert, J. A survey on intrusive load monitoring for appliance recognition. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014; pp. 3702–3707. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, G.W. Nonintrusive appliance load monitoring. Proc. IEEE 1992, 80, 1870–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiu, J.; Ma, J. SAMNet: Toward Latency-Free Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring via Multi-Task Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 13, 2412–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruano, A.; Hernandez, A.; Ureña, J.; Ruano, M.; Garcia, J. NILM techniques for intelligent home energy management and ambient assisted living: A review. Energies 2019, 12, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parson, O.; Ghosh, S.; Weal, M.; Rogers, A. Non-intrusive load monitoring using prior models of general appliance types. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Toronto, ON, Canada, 22–26 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Marwah, M.; Arlitt, M.; Lyon, G.; Han, J. Unsupervised disaggregation of low frequency power measurements. In Proceedings of the 2011 SIAM international Conference on Data Mining, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11–14 December 2011; pp. 747–758. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Kamoto, K.M.; Liu, X.; Sun, M.; Linge, N. Low-complexity non-intrusive load monitoring using unsupervised learning and generalized appliance models. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2019, 65, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, J.; Zeng, X.; Stankovic, V.; Stankovic, L.; Xiao, C.; Shi, Q. Transfer learning for multi-objective non-intrusive load monitoring in smart building. Appl. Energy 2023, 329, 120223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Yu, M.; Lu, L.; Wang, B.; Bao, Z. Adaptive Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Based on Feature Fusion. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 6985–6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Hong, T.; Kang, C. Review of smart meter data analytics: Applications, methodologies, and challenges. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 10, 3125–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Luan, W.; Yang, J.; Yu, Y. The Balanced Window based Load Event Optimal Matching for NILM. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 4690–4703. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.L.; Chen, B.X.; Wang, C.G.; Hua, D. Non-intrusive load monitoring algorithm based on features of V–I trajectory. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 157, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Kara, E.C.; Giri, S.; Bergés, M. A feasibility study of automated plug-load identification from high-frequency measurements. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Orlando, FL, USA, 14–16 December 2015; pp. 220–224. [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath, R.; Kumar, M.; Joshua, C.P.C.; Srinivas, K. Energy management using non-intrusive load monitoring techniques–State-of-the-art and future research directions. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, M.B.; Almeida, A.d.; Ribeiro, B. An experimental study on electrical signature identification of non-intrusive load monitoring (nilm) systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Adaptive and Natural Computing Algorithms, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 14–16 April 2011; pp. 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, H.; Ting, K.; Lee, W.; Fung, G. An analytical understanding on voltage-current curve of electrical load. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Boumerdes, Algeria, 13–15 December 2006; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, H.Y.; Fung, G.; Lee, W. A novel method to construct taxonomy electrical appliances based on load signaturesof. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2007, 53, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, T.; Javed, F.; Arshad, N. An empirical investigation of VI trajectory based load signatures for non-intrusive load monitoring. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 5, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iksan, N.; Sembiring, J.; Haryanto, N.; Supangkat, S.H. Appliances identification method of non-intrusive load monitoring based on load signature of VI trajectory. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Information Technology Systems and Innovation (ICITSI), Bandung, Indonesia, 16–19 November 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.; He, D.; Harley, R.G.; Habetler, T.G. Electric load classification by binary voltage–current trajectory mapping. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 7, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baets, L.; Develder, C.; Dhaene, T.; Deschrijver, D. Automated classification of appliances using elliptical fourier descriptors. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Dresden, Germany, 23–26 October 2017; pp. 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- De Baets, L.; Ruyssinck, J.; Develder, C.; Dhaene, T.; Deschrijver, D. Appliance classification using VI trajectories and convolutional neural networks. Energy Build. 2018, 158, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baets, L.; Dhaene, T.; Deschrijver, D.; Develder, C.; Berges, M. VI-based appliance classification using aggregated power consumption data. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), Sicily, Italy, 18–20 June 2018; pp. 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Baptista, D.; Mostafa, S.S.; Pereira, L.; Sousa, L.; Morgado-Dias, F. Implementation strategy of convolution neural networks on field programmable gate arrays for appliance classification using the voltage and current (VI) trajectory. Energies 2018, 11, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baets, L.; Develder, C.; Dhaene, T.; Deschrijver, D. Detection of unidentified appliances in non-intrusive load monitoring using siamese neural networks. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 104, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulinari, B.M.; de Campos, D.P.; da Costa, C.H.; Ancelmo, H.C.; Lazzaretti, A.E.; Oroski, E.; Lima, C.R.; Renaux, D.P.; Pottker, F.; Linhares, R.R. A new set of steady-state and transient features for power signature analysis based on VI trajectory. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference-Latin America (ISGT Latin America), Gramado City, Brazil, 15–18 September 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Jiao, D.; Liang, K.; Han, X. A fast online load identification algorithm based on VI characteristics of high-frequency data under user operational constraints. Energy 2019, 188, 116012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; You, W. Non-intrusive load monitoring by voltage–current trajectory enabled transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 10, 5609–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustine, A.; Pereira, L.; Klemenjak, C. Adaptive weighted recurrence graphs for appliance recognition in non-intrusive load monitoring. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 12, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Guo, L.; Xu, D. Non-intrusive load identification based on the improved voltage-current trajectory with discrete color encoding background and deep-forest classifier. Energy Build. 2021, 244, 111043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Li, Y.; Du, Z.; Xu, J.; Yin, B. Non-intrusive load identification using reconstructed voltage–current images. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 77349–77358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Han, Y. Non-intrusive load monitoring based on deep pairwise-supervised hashing to detect unidentified appliances. Processes 2021, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huo, Y.; Zhao, Q. Non-intrusive load monitoring by voltage–current trajectory enabled asymmetric deep supervised hashing. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2021, 15, 3066–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, K.; Feng, H.; Zhao, Q. Non-intrusive load monitoring based on semi-supervised smooth teacher graph learning with voltage–current trajectory. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolter, J.Z.; Johnson, M.J. REDD: A public data set for energy disaggregation research. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Data Mining Applications in Sustainability (SIGKDD), San Diego, CA, USA, 21–24 August 2011; Volume 25, pp. 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Giri, S.; Kara, E.C.; Bergés, M. Plaid: A public dataset of high-resoultion electrical appliance measurements for load identification research: Demo abstract. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM Conference on Embedded Systems for Energy-Efficient Buildings, Memphis, TN, USA, 4–6 November 2014; pp. 198–199. [Google Scholar]
- Baets, L.D.; Develder, C.; Dhaene, T.; Deschrijver, D.; Berges, M. Handling imbalance in an extended PLAID. In Proceedings of the 2017 Sustainable Internet and ICT for Sustainability (SustainIT), Funchal, Portugal, 6–7 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Medico, R.; De Baets, L.; Gao, J.; Giri, S.; Kara, E.; Dhaene, T.; Develder, C.; Bergés, M.; Deschrijver, D. A voltage and current measurement dataset for plug load appliance identification in households. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, M.; Haq, A.U.; Kriechbaumer, T.; Jacobsen, H.A. Whited-a worldwide household and industry transient energy data set. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 14–15 May 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Meziane, M.N.; Picon, T.; Ravier, P.; Lamarque, G.; Le Bunetel, J.C.; Raingeaud, Y. A measurement system for creating datasets of on/off-controlled electrical loads. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering (EEEIC), Florence, Italy, 7–10 June 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kahl, M.; Krause, V.; Hackenberg, R.; Haq, A.U.; Horn, A.; Jacobsen, H.A.; Kriechbaumer, T.; Petzenhauser, M.; Shamonin, M.; Udalzow, A. Measurement system and dataset for in-depth analysis of appliance energy consumption in industrial environment. Tech. Mess. 2019, 86, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.; Ocneanu, A.; Benitez, D.; Carlson, D.; Rowe, A.; Berges, M. Blued: A fully labeled public dataset for event-based nonintrusive load monitoring research. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Data Mining Applications in Sustainability (SustKDD), Beijing, China, 12–16 August 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]

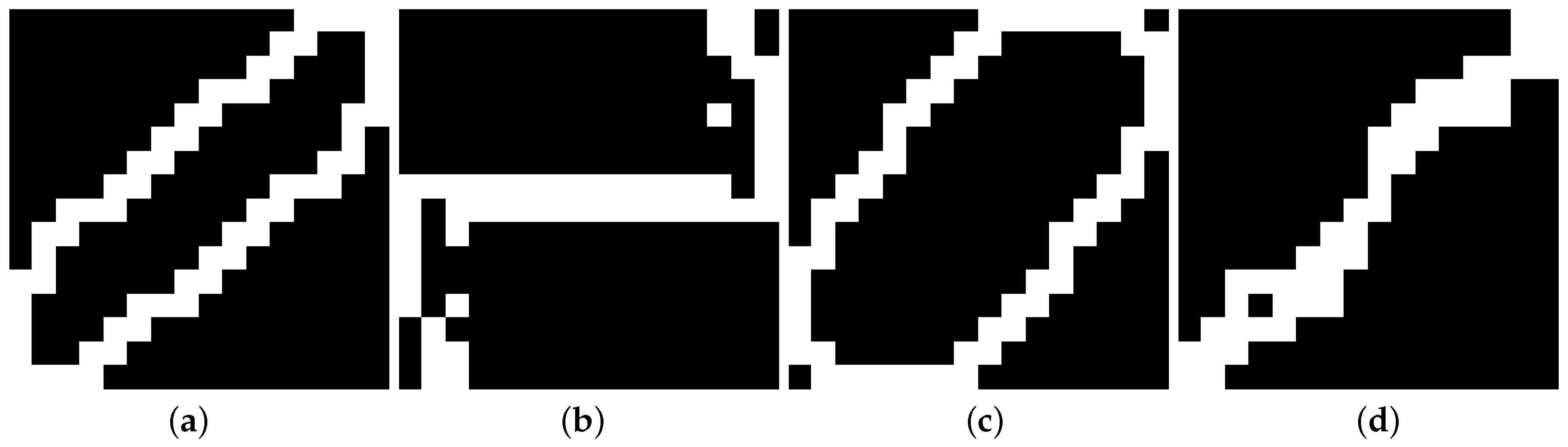
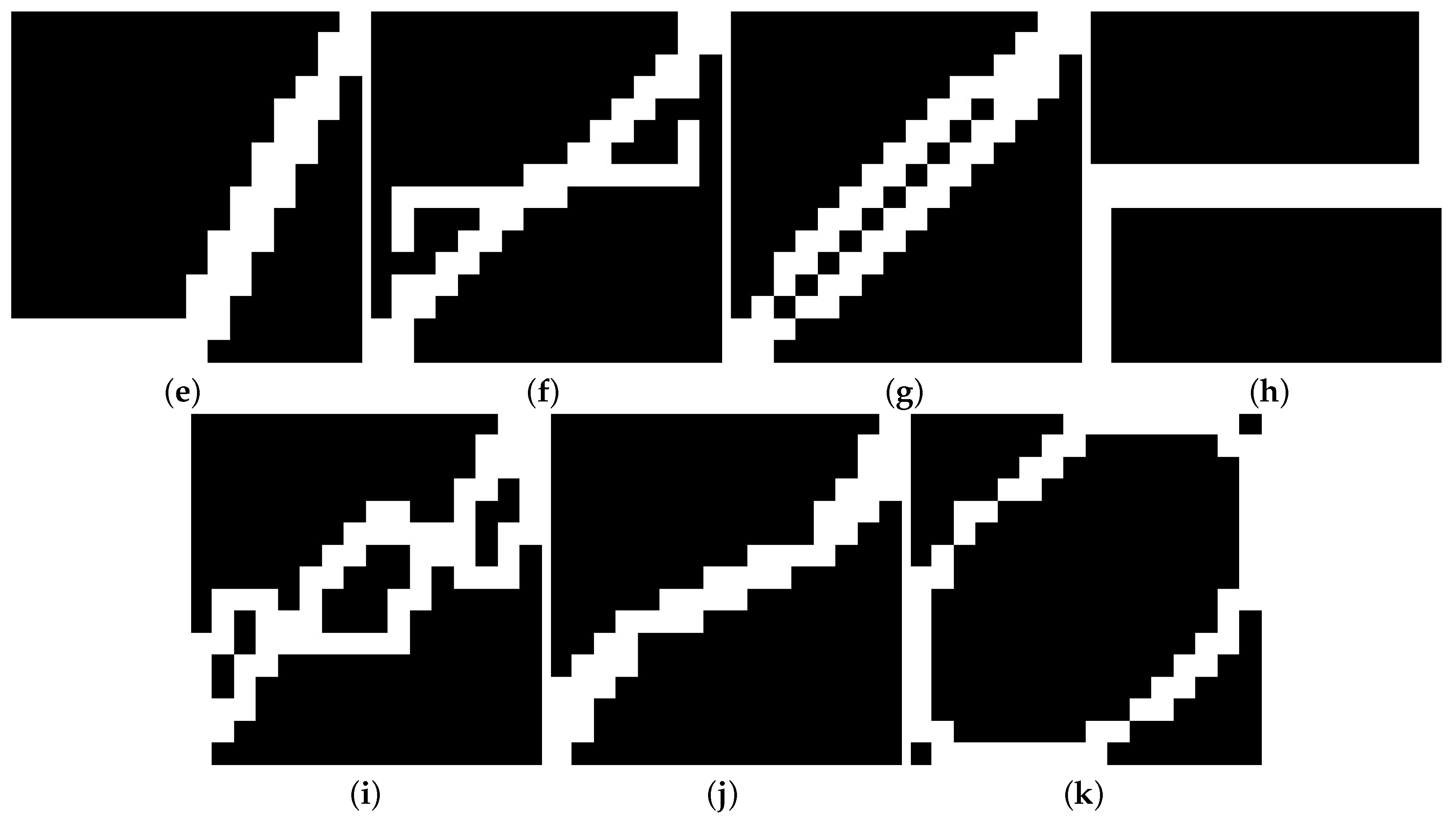
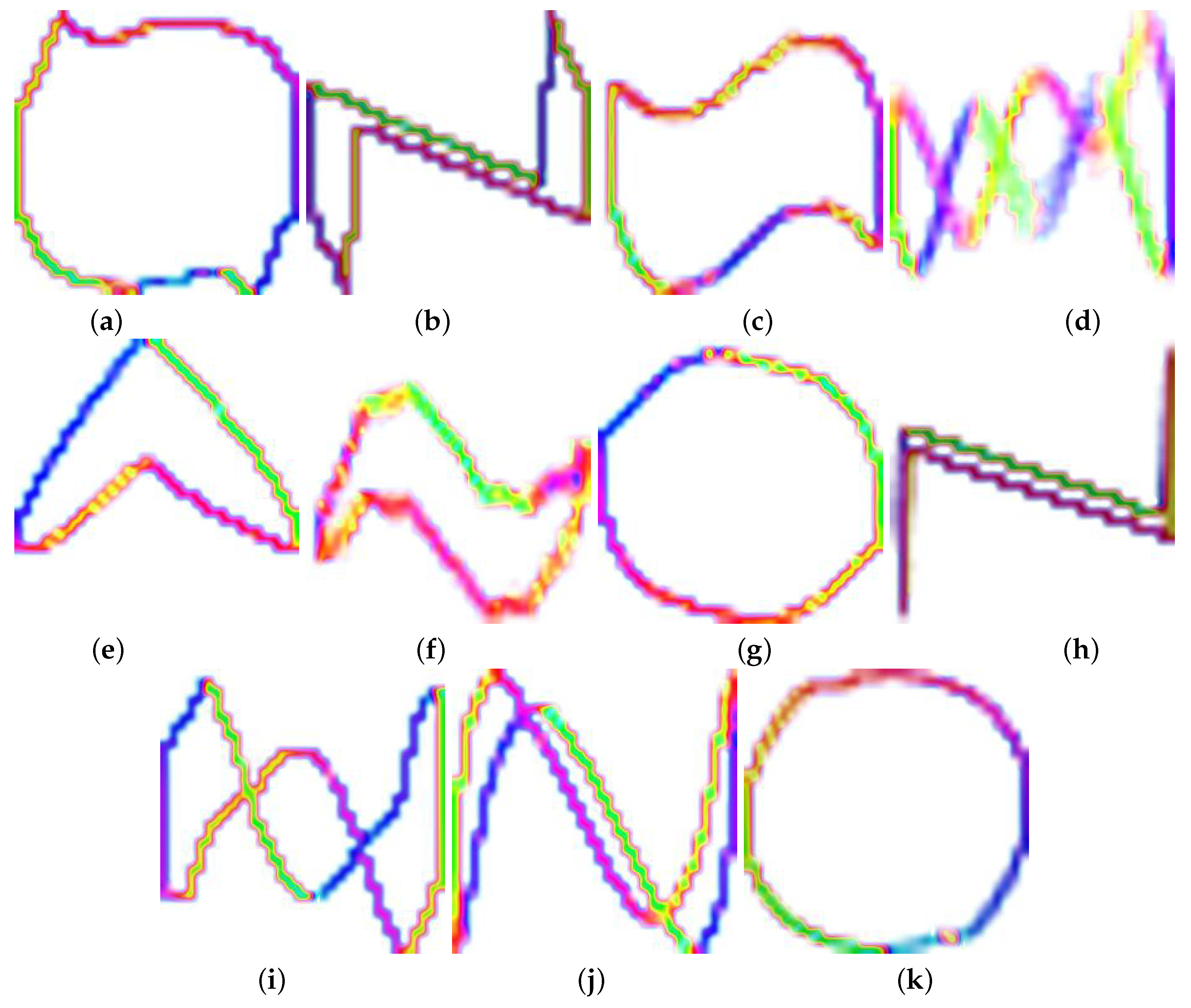
| Reference | Prediction | |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | |
| Positive | True Positive (TP) | False Negative (FN) |
| Negative | False Positive (FP) | True Negative (TN) |
| Methods | Year of Publication | Dataset | Frequency | Number of Appliances | Metrics | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [20] | 2006 | - | - | - | - | - |
| [21] | 2007 | - | - | - | - | - |
| [22] | 2013 | REDD | 16.5 kHz | 22 | Precision | 0.909 |
| [17] | 2015 | PLAID | 30 kHz | 11 | Accuracy | 0.8603 |
| [23] | 2015 | REDD | 16.5 kHz | 22 | Accuracy | 0.9134 |
| [24] | 2016 | private | 30.72 kHz | 23 | Accuracy | 0.99 |
| [25] | 2017 | PLAID | 30 kHz | 11 | Accuracy | 0.8175 |
| [26] | 2018 | PLAID | 30 kHz | 11 | F-measure | 0.7760 |
| [26] | 2018 | WHITED | 44 kHz | 22 | F-measure | 0.7546 |
| [27] | 2018 | PLAID(2018) | 30 kHz | 12 | F-measure | 0.8795 |
| [28] | 2018 | PLAID | 30 kHz | 11 | F-measure | 0.7816 |
| [16] | 2018 | REDD | 16.5 kHz | 22 | F-measure | 0.9643 |
| [29] | 2018 | PLAID | 30 kHz | 11 | RI | 0.996 |
| [29] | 2018 | WHITED | 44 kHz | 22 | RI | 0.879 |
| [30] | 2019 | COOLL | 100 kHz | 42 | Accuracy | 0.99 |
| [31] | 2019 | BLUED | 20 kHz | 22 | Accuracy | 0.90 |
| [31] | 2019 | Laboratory data | - | 12 | Accuracy | 0.90 |
| [32] | 2019 | PLAID | 30 kHz | 11 | F-macro | 0.9540 |
| [32] | 2019 | WHITED | 44 kHz | 54 | F-macro | 0.9866 |
| [33] | 2020 | PLAID | 30 kHz | 12 | F-macro | 0.9777 |
| [33] | 2020 | LILACD | 50 kHz | 16 | F-macro | 0.9833 |
| [34] | 2021 | PLAID | 30 kHz | 11 | Accuracy | 0.985 |
| [35] | 2021 | PLAID | 30 kHz | 11 | F-macro | 0.9736 |
| [35] | 2021 | IDOUC | 30 kHz | 23 | F-macro | 0.9878 |
| [36] | 2021 | REDD | 16.5 kHz | 10 | F-macro | 0.984 |
| [36] | 2021 | PLAID | 30 kHz | 6 | F-macro | 0.969 |
| [37] | 2021 | REDD | 16.5 kHz | 10 | F-macro | 0.974 |
| [37] | 2021 | PLAID | 30 kHz | 6 | F-macro | 0.961 |
| [38] | 2022 | PLAID | 30 kHz | 11 | F-macro | 0.928 |
| [38] | 2022 | WHITED | 44 kHz | 54 | F-macro | 0.9838 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, J.; Zhao, R.; Liu, B.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z. An Overview of Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Based on V-I Trajectory Signature. Energies 2023, 16, 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020939
Lu J, Zhao R, Liu B, Yu Z, Zhang J, Xu Z. An Overview of Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Based on V-I Trajectory Signature. Energies. 2023; 16(2):939. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020939
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Jiangang, Ruifeng Zhao, Bo Liu, Zhiwen Yu, Jinjiang Zhang, and Zhanqiang Xu. 2023. "An Overview of Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Based on V-I Trajectory Signature" Energies 16, no. 2: 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020939
APA StyleLu, J., Zhao, R., Liu, B., Yu, Z., Zhang, J., & Xu, Z. (2023). An Overview of Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Based on V-I Trajectory Signature. Energies, 16(2), 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020939






