Abstract
This study provides an overview of new trends in the development of cooling systems for electric motors. It includes a summary of academic research and patents for cooling systems implemented by leading motor manufacturers at TRL9. New trends in the cooling management of air and liquid cooling systems are discussed and analyzed with a focus on temperature distribution and its influence on the power-to-dimension ratio of electric motors. The prevailing cooling method for synchronous and asynchronous motors is air cooling using external fins, air circulation ducts, air gaps, and fan impellers to enhance efficiency and reliability. Internal cooling with rotor and stator ducts, along with optimized air duct geometry, shows potential to increase the power-to-dimension ratio and reduce motor size. Liquid cooling systems offer a power-to-dimension ratio of up to 25 kW/kg, achieved through redesigned cooling ducts, stator heat exchangers, and cooling tubes. However, liquid cooling systems are complex, requiring maintenance and high ingress protection ratings. They are advantageous for providing high power-to-dimension ratios in vehicles and aircraft. Discussions on using different refrigerants to improve efficient motor cooling are underway, with ozone-friendly natural refrigerants like CO2 considered to be promising alternatives to low-pressure refrigerants with high global warming potential.
1. Introduction
The design of electric motors differs depending on the application, while the power varies in the range between 0.06 kW and 1000 kW (or even higher). The operation of electric motors is linked to loss in the form of thermal energy. One main reason is the electric current, which heats the conductive metal parts of the motor, including the windings and metal parts of the stator. An additional factor is friction from moving elements, for example, the rotor [1]. Such heat release can be considerable, particularly for high-speed motors in vehicles, aircraft, and industry, for example, the high-speed motors of turbocompressors. The winding temperature is also increased when on/off switching occurs frequently [2]. If the temperature of the windings is above the temperature limit (see standard requirements [3]), the electric motor can become inoperative in a short time. Exceeding the temperature limit leads to a decrease in electrical and mechanical performance.
As a consequence, the service life of the windings decreases by 50% for every 10 °C increase above the allowable temperature limit [4,5]. In addition, the temperature increase results in the reduction of motor efficiency and power. The motor’s power correlates with its dimensions (size and weight): high power means a large and heavy motor. At the same time, a high-power motor requires higher heat rejection to maintain the optimal operating temperature. This dependence generates technical limits in developing and producing high-power motors with small sizes and weights.
The basic trends in today’s motors are not only towards high efficiency but also towards a high power-to-dimension ratio (relation of motor power to motor weight, kW/kg), which is in agreement with the concepts of sustainable use of energy and resources and the circular economy [6]. The power-to-dimension ratio value becomes even more important when considering the necessary volume for motor installation. The higher such performance, the lower the volume and weight of the electric motor, which is important for vehicles and airplanes.
Table 1 summarizes the dependence among power (kW), the power-to-dimension ratio (kW/kg), and the application of electric motors in different areas. It can be observed that electric motors used in robotics, pumps, and power stations have the lowest power-to-dimension ratio irrespective of the total power of the electric motor (Figure 1). The value varies in the range between 0.02 and 0.65 kW/kg. At the same time, electric motors used in aviation and vehicles show power-to-dimension ratios in a wide range from 1.1 to 25.3 kW/kg. It should be noted that manufacturers of electric motors can declare the power-to-dimension ratio concerning the total size of the system (auxiliary pumps, compressors, fans, electronics, etc.) or the weight of the electric motor only. In Table 1, all data are normalized to the total size of the system.

Table 1.
The power-to-dimension ratios of modern electric motors.
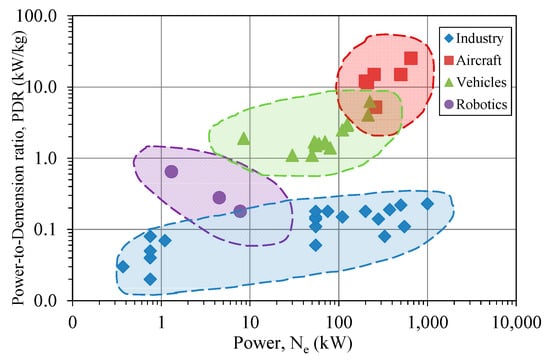
Figure 1.
The application areas of motor cooling systems.
Table 1 indicates that the power-to-dimension ratio also depends on the type of the cooling system. An efficient cooling system is one way to approach a high value for the power-to-dimension ratio when intensive heat rejection maintains the optimal temperature for the motor’s operation [28]. The type of cooling system strongly depends on the application area, ambient temperature, occurrence of partial load, off-design operation, etc. Modern trends in the development of new small-size and high-power motors require the development of advanced thermal management systems to support the motor’s sustainable operation. Hence, there is a strong need for an overview and analysis of the recent trends in thermal management and cooling methods for electric motors. The current review discusses the following topics:
- Overview of the temperature distribution in the electric motor;
- Comparative overview of the influence of the temperature on electric motor performance, especially on the power-to-dimension ratio;
- Overview and discussion of cooling methods and systems, including patent analysis and recent trends.
2. Analysis of the Temperature Influence on the Performance of Electric Motors
2.1. The Temperature Distribution in Electric Motors
Motor efficiency is always below 100% [10,11]. The difference between input and output represents the loss, which is transformed into heat. Heat losses for modern motors can be up to 10% of motor power. The heat distribution in electric motors is as follows: windings (copper in stator), 40–65%; rotor, 10–25%; and iron (metal plates in stator), 25–35% [29,30,31]. The total heat loss of the stator is the largest and accounts for up to 80–85%, which determines the cooling system design. At the same time, a temperature gradient occurs in electric motors due to the thermal resistance of the motor’s elements, with the highest temperatures observed at the rotor and winding elements (see Figure 2). The temperature field of the electric motor can be divided into several zones with respect to the heat loss:
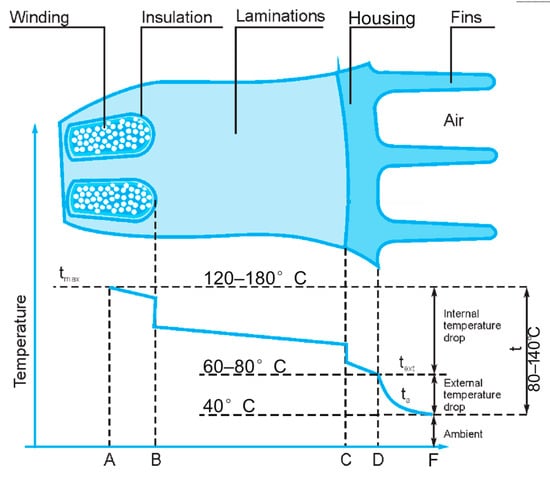
Figure 2.
Example of the temperature gradient of the motor’s stator and housing, adopted from [10].
A—Hotspot temperature, which determines the insulation class of the electric motor and operation parameters.
AB—Area of high heat transfer. The winding’s hottest spot is in the center of the slots where heat is generated as a result of losses in the conductors. A drop in temperature occurs due to heat transfer from the hottest spot to the outer wires.
B—Area of low heat transfer due to slot insulation and contact between the insulating material, conductors, and core laminations.
BC—Area of high heat transfer due to transmission through the stator’s lamination material.
C—Area of low heat transfer due to contact between the stator core and frame.
CD—Drop in temperature due to conduction through the frame’s thickness.
D—Temperature in the area of the outer surface of the housing.
DF—Drop in temperature due to convective heat transfer between the housing, fins, and ambient air.
F—Ambient temperature.
As can be seen from Figure 2, the internal temperature distribution in the electric motor’s stator occurs due to conduction and depends on the thermal properties and thicknesses of materials, including metals, insulation, air gaps, etc. The external temperature drop is influenced by convection and radiation. The main components of the electric motor are made of metal, which can tolerate high temperatures. However, the electric insulation, which is formed by organic polymers, is part of the windings (Point B in Figure 2). This area is exposed both to high temperatures and thermal stresses. Exceeding the temperature limit leads to degradation of the insulating material and a significant decrease in the working life of the motor [32]. Electric motors can be classified by insulation class with respect to the hotspot temperature. Motor standards specify a maximum allowed ambient temperature, as well as a maximum allowed temperature rise for each insulation class [32,33,34]. The allowable temperature profile for the hottest spot is shown for each insulation class in Table 2.

Table 2.
Temperature composition as function of insulation class, IEC 60034-1 [10].
The maximum permissible temperature rise of the windings is determined based on the thermal (insulation) class temperature limit due to the occurrence of hotspots in the windings, while the lower temperature limit (permissible temperature rise) is specified for the insulation material [35]. For example, the Marathon Electric Motors company [12,13] produces motors using insulation class F with a winding temperature rise in accordance with class B (max 80 K). This means that the motors have a temperature reserve of 25 K. This reserve can be utilized for short-term overload, higher ambient temperature (above 40 °C), supply voltage/frequency fluctuations, etc. These materials are specified in thermal classes referenced as Y, A, E, B, F, H, and C. Every thermal class has a temperature limit. Each material of a specific class needs to retain its mechanical and electrical properties within the temperature limit. Ambient temperature should not exceed 40 °C, as per the standard; above this value, working conditions are considered to be special operating conditions.
2.2. The Influence of Coolant Temperature on the Motor Power and Efficiency
The temperature regime significantly affects engine efficiency and service life [36]. The impact of the cooling system on the main motor parameters was determined and compared for asynchronous motors (motor power, 55 kW; speed, 1470–1488 rpm; IC code, IC411). These motors had insulation class F, the type of cooling system was IC411 (air cooling), and the basic design was identical. Data for analysis (relative power ratio, coolant temperature, ambient temperature, and other characteristics) were taken from sources published by motor manufacturers [7,8,10,13,14,17,37,38]. The nominal characteristics were given to an ambient temperature of 40 °C. Based on an analysis of the literature, the following dependences between power and efficiency were established (Figure 3). A clear trend toward an increase in efficiency with decreasing ambient temperature (Point F in Figure 2) was observed. For, example, a decrease in the coolant temperature (tc) by 10 °C resulted in an increase of the motor power (ΔNe) by 3–8%. The efficiency of the motor increased by 0.2–0.4% with a temperature (tc) decrease of 10 °C, respectively.
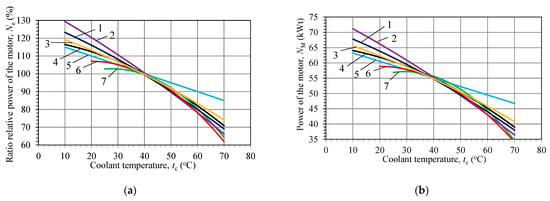
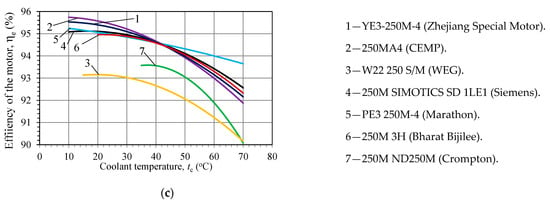
Figure 3.
Ratio of the relative power of the motor Ne = NM(tc)/NM (tc = 40 °C) (a), power NM (b), and efficiency of the motor ηe (c) versus the coolant temperature tc of the motor.
It is worth noting that the values of efficiency and power differed with respect to the motor’s design, even if the same type of cooling system was used. The greatest difference in efficiency was determined at low cooling temperatures. For example, at a temperature tc = 10 °C, the power increased by ΔNe = 15–30% (8–16 kW) when compared to that at tc = 40 °C (PE3 250M-4 and 250MA4, respectively). This occurred due to differences in heat rejection and vending temperatures, which occurred in the motor when the coolant temperature (tc) was 10 °C. Although the cooling method and type of cooling system was the same for all seven electric motors, the efficiency of the cooling system was different. Thus, an efficient cooling system is one of the key factors influencing the working parameters of electric motors. At the same time, the high temperature gradient inside the motor and limited heat transfer surface with ambient air creates significant challenges for efficient thermal management. As a result, a cooling system may consist of several cooling circuits and combine cooling with internal or external heat exchangers [22,36].
3. Overview of the Cooling Methods of Electric Motors and Their Application in Different Areas
The architecture of the thermal management system depends on the motor type and area of its use, as well as on the available cooling system type. Based on a literature analysis and technical information from manufacturers of modern motors, the following main trends in cooling systems were determined (Table 3).

Table 3.
Areas of application for motor cooling methods.
The data presented in Table 3 show that air cooling dominates motor thermal management when considering the areas of application. This method is the simplest in application, use, and maintenance, and is cheap in terms of running and investment costs [5]. External cooling has some limitations in terms of area of application, with fan cooling or self-cooling being the dominant solutions for this method. Passive air cooling occurs in most types of electric motors with a few exceptions, like when direct access to air is limited in the electric motor of a vehicle. Water and oil cooling are in second place in terms of use and research interest because they requires more complicated instrumentation and infrastructure. However, these methods allow the highest power-to-dimension ratio to be obtained when a compact system is a requirement [22]. The past 10 years have witnessed high interest in new internal cooling systems with different types of cooling agents. These have become the most used methods in all application areas. The use of cooling channels can be considered to be part of internal cooling systems. The method will be introduced separately in this paper to show the high importance of cooling channels reflected in recent research. The injection method of cooling is an efficient method due to direct contact between the coolant and the motor’s interior. Oil and refrigerant are the working fluids for this method, which creates significant challenges in terms of preventing leakage and return system.
The use of refrigerants for direct cooling purposes in electric motors is not well established due to the high risk of leakage and special requirements for pressure levels. At the same time, boiling and condensation provide the highest heat transfer rates, especially when internal cooling is applied [84].
4. Overview of Principle Solutions for Cooling Electric Motors
4.1. The Air Cooling System
Air cooling is the most common cooling method for synchronous and asynchronous motors. It should be noted that several cooling media can be utilized instead of air, like nitrogen, hydrogen, noble gases, etc., but air still dominates as a cooling media. Due to low convective heat transfer in air cooling, thermal management is applied both in the interior and exterior of the motor with the aim of increasing the heat exchange area. The design of the cooling system includes a few main elements alone and in different combinations: external fins on the motor housing, ducts for air circulation in the stator and rotor, an air gap between the rotor and stator, an air gap between the stator and housing, and internal and external fan impellers (Figure 4) [42]. The design and location of the elements is the subject of research and patent protection.
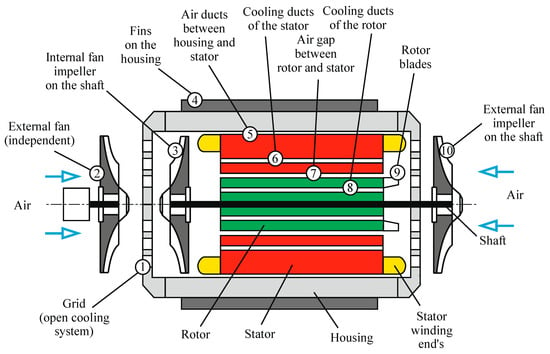
Figure 4.
The method of air cooling for electric motors.
The external cooling of motors occurs through the finned surface by natural or forced convention. Forced convection is provided by an external fan impeller installed on the rotor shaft, ensuring the movement of airflow along the finned surface ducts of the motor housing (Figure 3) [46,47,48]. In some cases, an independent fan impeller can be utilized for external cooling [15,89,133]. One-sided external cooling naturally results in uneven temperature distribution inside the electric motor [10]. Therefore, the fan characteristics and fin geometry of the motor housing are of great importance. Improved design and optimization of these elements can increase the cooling system efficiency in the range of 10–30% [44,45]. The fin geometry of the housing can be organized, for example, with axial or radial deployment [43]. The axial arrangement is the most efficient, while the radial arrangement is common for small-size electric motor [41,42]. Numeric modeling has been intensively used to improve the blade profile design of the external fan in order to reduce noise and increase the cooling air speed at the motor’s surface [31,55,56,59,61,89,134].
Kindl et al. [62] presented external cooling of the stator through the ducts in the housing of an electric motor (open system). This provided noise reduction due to changes in the configuration of the airflow circuit and an increase in the area of heat exchange.
Internal air circulation (in the motor’s interior) is provided by blades installed directly on the rotor. At the same time, the rotor’s blades or shaft impeller are common for closed electric motors [57,79]. This cools, in particular, the stator winding heads, the rotor winding, and the drive-end bearings. In the case of open electric motors, the fan impeller is utilized. Efficient heat transfer from the interior of the motor (heat from rotor) to the ambient air can be provided by air circulation in the gap between the stator and housing (closed system) [40].
Recent research has mostly focused on the intensification of internal cooling by including ducts in the structure of the rotor and stator. The air ducts (Figure 4) intensify internal heat transfer and, therefore, lower the working temperature in the motor and stabilize the temperature regime during motor operation [31]. The resulting reduction in thermal loading increases the operating reliability and prolongs the service life [33]. The internal airflow channels (see Figure 4, cooling ducts in the stator and rotor) increase the ventilation efficiency, which means that the external airflow can be reduced. The lower volumetric flow and optimized airflow of all guide channels result in a low level of fan noise. There are numerous solutions for the design and locations of ducts in the interior of electric motors when the air circulation is provided by rotor/shaft blades and/or internal/external fans.
Determining the air duct geometry for open-type motors can help to increase the power-to-dimension ratio and reduce the motor size by up to 5–10% [36,89]. For example, in one patent for invention [79], the axial duct between the rotor and shaft was utilized. There are designs in which the cooling air circulates through the axial channels in the rotor itself (see Figure 4, cooling ducts in the rotor) to increase the cooling efficiency of the rotor. The ducts in the rotor vary from a simple shape, like axial ducts with a circular cross-section [42], to complicated designs with multi-segments (for magnetic motors) [94]. The main aim of multi-segment designs is to increase the heat transfer area.
The study by Kung L. et al. [58] utilized a cooling circuit consisting of cooling ducts in the rotor with air distribution in the axial direction and through the radial ducts. The solution increased the cooling system efficiency by 10%. The air gap between the rotor and stator was used for air distribution. It should be noted that the air gap is utilized for cooling only for large-size electric motors (50.0 kW and more) when the gap exceeds 2.5 mm. A smaller size of the gap results in high pressure loss, which significantly reduces the airflow [1,33].
Ducts designed with a certain geometry using polycarbonate-aluminum flake for the windings can be used to increase the cooling efficiency. The use of three-dimensional printed direct winding heat exchanger (DWHX) technology provided good control of the stator temperature regime in motors with high power-to-dimension ratios [113].
Direct shaft cooling by airflow was reported. In this case, the internal design of the shaft included an air distribution system [71]. This method was applied when high loads (> 1 MW) were used at power plant generators.
For high-power motors with an open-type cooling system (Figure 4), a fan impeller is installed inside the motor housing, which is common for electric motors in vehicles. The fan impeller can be installed on the motor shaft or as a separate unit. The design of the fan impeller is a crucial part of efficient cooling. It was shown [55,56] that the use of axial fans with forward sweep and inclined blades reduced aerodynamic resistance, increased airspeed and, accordingly, reduced the stator winding temperature by 30%. More effective cooling was achieved by mounting a separate constant-speed fan, which was especially beneficial at low speeds. In recent years, there have been several attempts to improve such cooling systems [1,36]. Selecting the optimal fan motor speed and fan design to deliver a stronger cooling effect than that achieved with a standard motor at nominal speed can give an improved cooling effect over the entire speed range [14,15]. Figure 5 shows internal axial flux fan designs for rotor cooling, such as in the case of permanent magnet machines. The design with radial aerofoil blades was concluded to be more efficient when compared with other types. It provided a heat transfer coefficient for the cooling air of over 100 W/(m2∙K) at 1500 rpm (Figure 5) [60].
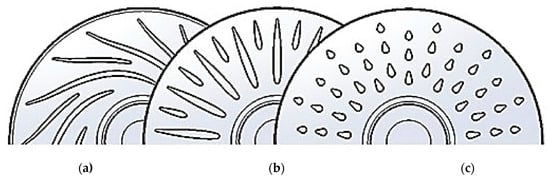
Figure 5.
Fan blade design selection with (a) backward-inclined aerofoil blade, (b) radial aerofoil blade, and (c) tear drop pillar blade [60].
Thermal management of the motor housing is focused on the number and geometry of the ventilation holes, as well as the distance between the fan and cover. These parameters are of great importance because they determine the turbulence airflow and, therefore, the air distribution and pressure drop in the ducts [36]. Proper design of the fan blades and wheels should ensure lower noise levels. For example, the noise levels of Sirocco redial fans are 5 dBA lower than those of other fans of the same type [135].
It is important to note that the use of one-circuit air cooling is not sufficient for efficient thermal management. Air cooling methods are used in combination. For example, dual-circuit cooling technology is one of the solutions that results in high motor power and better reliability [22,38,60,135]. The cooling system consists of primary and secondary circuits. The primary cooling circuit provides air cooling of the electric motor housing by the shaft-mounted external fan impellers, which direct the airflow over the stator body fins and cool the motor by forced convection and radiation (see Figure 4, external cooling (fan, self-cooling)). The secondary internal cooling circuit consists of a rotor with vent holes, aluminum rotor blades, and ventilating ducts on the inner side of the stator housing (see Figure 4, cooling ducts in the stator). The air inside the motor passes through the ventilating ducts in the stator, then the air passes through the rotor vents, absorbs heat, and the cycle repeats. The advantages of this technology include a lower temperature rise at the windings’ ends, reduced temperature gradient between the stator and windings’ ends due to uniform distribution of heat, and increased working life of the insulation and motor reliability.
The abovementioned advantages of dual-circuit cooling technology are utilized in train transport [129] in which an external fan impeller and system of closed cooling ducts are used (metro trains, locomotives, and high-speed electric trains). This method is applied when it is necessary to provide high acceleration in a short time, with high peak torques and power-to-dimension ratios and relatively low noise levels. The speed range in modern trains can be in the range of 200–350 km/h. For example, aiming to keep the rotor speed below 6500 rpm, the resulting gear ratios are in the range of 2.6–4.5. Such gear ratios result in higher torque levels for a given tractive effort, which necessitates continuous forced ventilated cooling. Despite the drawback of decreased cooling at lower speeds (<1000 rpm) and higher noise levels at high speeds (>4000 rpm), open self-ventilation is a popular cooling method for trains.
Increasing the cooling efficiency can be achieved by replacing the primary circuit by indirect cooling when the hot air from the interior of the motor is cooled down in the external heat exchanger on top of the motor housing. In this case, heat exchange is not limited by the geometry of the motor itself. This allows high specific power values for the motor to be achieved, which is of great importance for electric vehicle motors of all types [94]. For example, this concept is used in the BMW i3 (IPMSM motor), Toyota Prius (IPSMSM motor), Sonata (PMSM motor), Tesla Roadster (AC IM motor), and Nissan Leaf (IPMSM motor), making it possible to increase the power-to-dimension ratio by up to 2.5–2.7 kW/kg.
Different motor types are used for transport, in particular, outer-rotor motors. In such motors, in addition to air cooling, water and oil cooling of the rotor can also be used, which effectively increase the power-to-dimension ratio. At the same time, it is important to correctly determine the cooling duct’s geometric characteristics [92,93].
4.2. Liquid Cooling Systems
Liquid cooling systems in their various types have one common element—an external heat exchanger with liquid circulation provided by a pump. The design and type of the external heat exchanger strongly depends on the motor application area and size. For example, for car motors, the design of such heat exchangers is similar to that of standard radiators in the cooling systems of classic petrol and diesel engines. The literature does not pay great attention to this element of cooling systems. However, the design of the external heat exchanger can potentially influence the heat rejection from the motor interior and the performance of electric motors.
The thermal management of electric motors is organized via systems of ducts, channels, pipes, and gaps between the motor’s elements (Figure 6). The simplest and most common liquid cooling method is a housing jacket or “water jacket” [136]. The housing jacket is made of different alloys, and liquid distribution inside the jacket is provided by axial or tangential cooling ducts with rectangular cross-sections [42,104,105,106]. The most common technology used to manufacture the housings of such motors is casting using aluminum alloys [137]. The design utilizing an axial arrangement of the ducts decreases the motor’s temperature, but the load on the circulation pump is greater due to greater hydraulic losses (pressure drop) in the ducts (Figure 7) [35,102,103]. At the same time, the hydraulic resistance for axial channels is 10–15% higher than that for tangential ones.
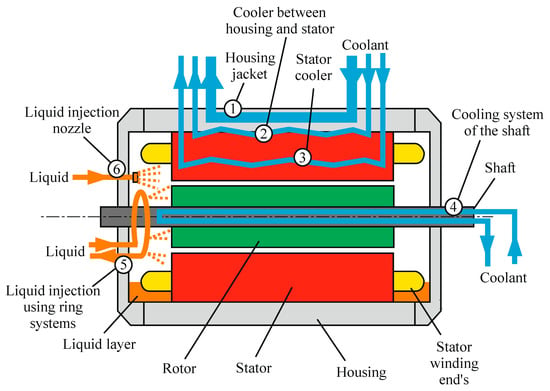
Figure 6.
The method of liquid cooling for electric motors.
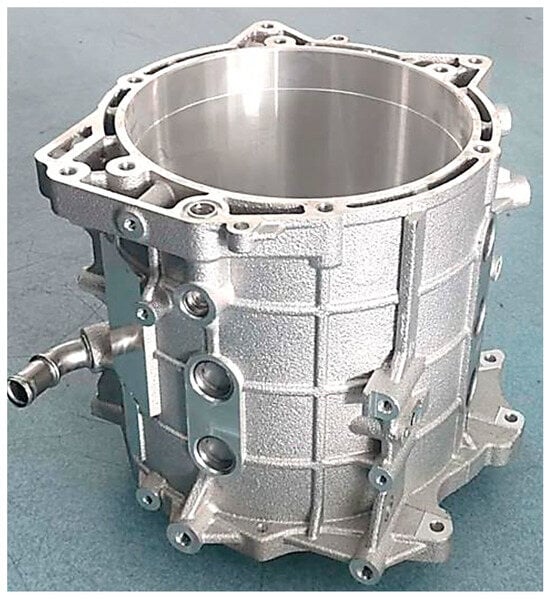

Figure 7.
The design of the motor housing with a cooling jacket [137].
The housing jacket cooling performance depends less on the power load and rpm of the shaft than it does in air cooling systems with rotor blades, thus guaranteeing the high performance of electric motors in a large range of operations when compared with air cooling only. The study by Zheng et al. reported that a circular 12-duct water cooling system reduced the stator winding temperature by 13 °C [138]. The power-to-dimension ratio increased as a result.
It is important to note that air circulation is necessary in the interior of the motor when a housing jacket is applied (Figure 7). Thus, most housing cooling solutions can be considered to be combined cooling systems [81,82,133]. This combination is widely used for electric cars, motors, and cars with a hybrid installation [2,22,100,101]. The use of specially shaped ducts in the body of the BMW i3 IPMSM motor to distribute coolant flow is considered to be one of the most effective from the point of view of ensuring intensive heat transfer [20]. A motor housing jacket cooled by oil is used in the Toyota Prius IPSMSM [21,99]. Thermal management is utilized in the Sonata PMSM motor [139]. Combined air cooling (internal and external forced ventilation with heat transfer intensification) is used in the Tesla Roadster AC IM motor, which showed a 4.1 kW/kg power-to-dimension ratio for this motor [22]. Ethylene glycol [140,141] can also be used as a coolant in the cooling system using a housing jacket, and such a system is successfully used in the Equipmake APM 200 (2018), Rimac C (2018) [1], and Nissan Leaf IPMSM [23] motors.
Housing jackets are used in variable-speed motors since cooling is optimized even at reduced speeds and where space is limited motor placement [10]. Water-cooled electric motors for marine vessels are an example of this effect at a large scale, with the motor operating for a long time at very low speeds (Figure 8) [10,11]. In addition, this solution significantly reduces the noise level (decreasing from 80–85 dBA to 40 dBA or less) and virtually eliminates heat transfer from the motor to the environment, as compared to fan cooling, resulting in a uniform temperature distribution inside the motor [96,130]. It is reported that motors of Norwegian Electric Systems vessels successfully utilize the IC7A1W7 cooling system for heavy-duty marine applications in which space is limited and natural ventilation is one of the key factors [130]. These electric motors create five times less noise than conventional air-cooled motors.

Figure 8.
The WGM motor type with a water cooling system (WEG).
Several studies have investigated the replacement of ducts in the housing by tubes. The small-diameter heat exchange tubes helped to increase the power-to-dimension ratio by 2.76 times when maintaining the set (standard) temperature regime. The suggested diameter of tubes varied from 4 to 8 mm with respect to the permanent magnet linear motor’s design and power. The use of capillary tubes inside the jacket was also proposed. The temperature withstanding capacity of a 1.1 kW (test prototype), three-phase, 50 Hz squirrel cage induction motor at 1450 rpm was decreased by 15.5% (reduction of 8 °C) [142]. In the work by Deriszadeh and Monte [143], it was proposed to use nanofluids in the cooling coil in the housing jacket. The study showed an increase in heat transfer by 40%. However, the placement of tubes inside the housing jacked is still not well developed for commercial purposes.
Instead, the installation of pipes and tubes in the stator is more common (Figure 6, Point 3). This reduces the weight and increases the power-to-dimension ratio when compared with other housing jacket solutions. The tube coils are installed directly in the stator on the outer or inner surface of the stator or between the stator’s winding coils. The cooling tubes installed between the windings and at the inner surface of the stator are shown in Figure 9 [110].

Figure 9.
Cooling of the synchronous motor using coil cooling ducts: coolant flow path through the whole motor (a); around a single tooth (b); main ducts for installing cooling tubes (c).
The installation of a cooling coil between the housing and inner surface of the stator helped to maintain the permanent magnet temperature of the in-wheel motor (25 kW) at 156.9 °C [144]. The coil tubes could be equipped with vortex generators to increase the convective heat transfer coefficient from the inner side of tubes (up 23%), which could increase the thermal performance of the heat exchanger by 6.5%. However, the pipes, tubes, and microchannels in(at) the stator required internal air cooling. For example, the study by Sikora et al. [30] suggested a cooling method in which the stator for a small induction motor (7.5 kW) was cooled by a coil-type tubular heat exchanger, which was installed in special slots at the outer surface of the stator (Figure 10). Air circulated in the gap between the stator and rotor and then passed into the gap between the stator and housing. The stator from the outer side was equipped with fins, which enhanced the air cooling by the coil-type tubular heat exchanger. The combined solution provided lower temperatures at high motor loads when compared with air cooling only. The rotor temperature decreased from 130 to 80 °C and the temperature of the stator windings decreased from 155 to 80 °C as a result.
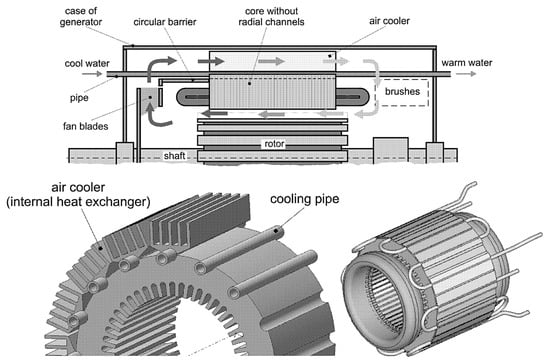
Figure 10.
The scheme of water cooling [30].
The housing jacket cooling method can be combined with tubing installed in the stator (Figure 6). In the study by Madonna et al. [112], the end-winding cooling method was combined with housing jacket cooling. Multi-shaped tubes were installed on the stator windings’ frontal parts (inside the windings). This method helped to increase the overall cooling performance and decreased the hotspot temperature by 25%. By reducing the hotspot temperature, the electric current density could be increased whilst maintaining the wire insulation thermal limit, preserving the machine’s lifetime. Also, it was shown that the developed torque could be increased by 11.4% while keeping the same machine geometry, or the machine axial length could be reduced by 10% while maintaining the same torque. The axial arrangement of the coil heat exchanger at the inner surface of the stator and simultaneous cooling by water in the housing jacket of the automotive switched reluctance motor held the peak winding and stator temperatures below 90 °C, while the average stator and winding temperatures decreased to 65 °C and 90 °C, respectively [111]. Oil can easily replace water as a cooling media. For example, a synchronous motor stator was cooled by liquid circulating through coaxially arranged tubes installed between the stator windings [84]. A comparison was performed when the 60 kW electric motor (AFMM) was cooled using three different liquid cooling methods. The reference case utilized housing jacket cooling combined with cooling by a coil installed at the surface of the stator, using water as the cooling media. The other two cases utilized the cooling coil (4 mm diameter) installed directly between the winding wires, with polyalphaolefin oil and water used as the cooling media. The results revealed that the reference case had a maximum temperature in the windings of 137 °C, while the water and oil cases showed 57 and 86 °C, respectively [145]. The direct integration of the cooling coil inside the windings reduced the system’s weight and ensured motor compactness when compared with the water-cooled housing jacket [146].
Direct winding heat exchanger (DWHX) technology uses a heat exchanger with microchannels, which are installed between the stator winding bundles. This cooling method increases the power-to-dimension ratio by providing heat transfer coefficients of up to 30,000 W/(m2∙K). This technology was applied to permanent magnet synchronous motors. It was claimed that the method helped to achieve a current density of 40 A/mm2, reduced the hotspots, and significantly increased the steady-state and transient current density limits [147].
In the case of small-size motors, cooling of the rotor can be provided via cooling pipes mounted inside the motor shaft only (Figure 6, Point 4). One of the most effective methods of cooling motors in modern electric vehicles is simultaneous cooling of the motor housing and shaft (rotor), which is utilized in the Tesla S60 AC IM motor (Figure 11) [96,114]. The same principle was applied in the Audi e-tron (2018), Mercedes EQC (2019), and Audi e-tron S (2020) motors [1]. The SFD study by Arbab et al. proved the efficiency of shaft cooling a 10 kW electric motor combined with the housing jacket cooling method (circular ducts used in both methods). However, the method did not secure the temperature of the windings at the frontal part of the stator [80].
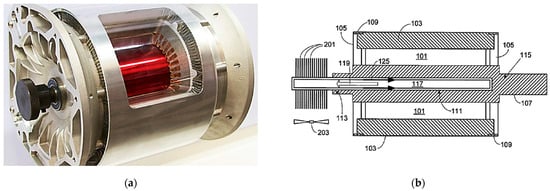
Figure 11.
The cooling of the Tesla S AC IM motor (a); coaxially cooled stator and rotor (b) [96].
Direct liquid cooling assumes direct contact between the liquid coolant and the interior of the electric motor (Figure 6). It was reported that a power plant of 300 MW combined liquid cooling of the rotor with air cooling of the stator [72]. The liquid cooler (water) was delivered to the rotor section via a system of pipes in the shaft from one side. It is important to note that the construction of high-power motors allows separation of the rotor from the stator by a wall (sleeve) due to the large gap between the rotor and stator (water does not have direct contact with the stator). The return flow of water was also provided via a pipe system in the motor’s shaft. Direct intensive cooling of the rotor windings was combined with partial cooling of the inner surface of the stator through the separation wall. Air was circulated in the gap between the housing and stator by centrifugal fans. Cooling of the frontal parts of the stator windings also occurred.
Mineral oil is utilized as a cooling liquid for most applications due to its safety and dielectric properties [116,118,119,120,127,145]. The oil can circulate in the channels of the stator (between the stator and housing) or it can be sprayed directly into the interior of the motor (Figure 6, Points 5 and 6 and liquid layer). In both cases, the hot oil is removed from the motor through passes at the bottom.
Contact cooling by liquid injection is a solution for closed systems. It includes nozzles, liquid (oil), a buffer tank for the liquid, and a high-pressure pump [148]. A significant disadvantage of such systems is the uneven temperature distribution, which is associated with the number and location of nozzles and spraying systems [149]. Therefore, it is advisable to use high-pressure nozzles for highly viscous liquids. For example, oil injection by high-pressure nozzles multiplied the dissipation power by a factor of 2.5 to 5.0 [116]. High-pressure injection allows the spray droplets to cover the surface more uniformly, which increases the oil film’s cooling impact. Oil spray cooling provided better cooling performance and temperature uniformity when compared with air cooling and indirect oil cooling methods [117]. Similar oil injection systems for cooling electric motors have been applied in aircraft power systems [131].
One of the methods used to increase oil spraying cooling efficiency is the use of injection through tubular rings (Figure 12) to cool the lower part of the stator and rotor windings [121]. The use of this method significantly intensifies the heat transfer process at high values of motor relative power. Oil spray cooling of the stator and rotor ends was implemented using a relatively simple system for the “wound field synchronous motor” (190.55 Nm, 79.6 kW, 4000 rpm). Coiled copper piping with one closed end was connected to the pump system. The spray hole system consisted of two sets of 16 holes (1.15 mm diameter) offset by 30 degrees, with one set cooling the rotor end windings and the other cooling the stator end windings [117,119,120].
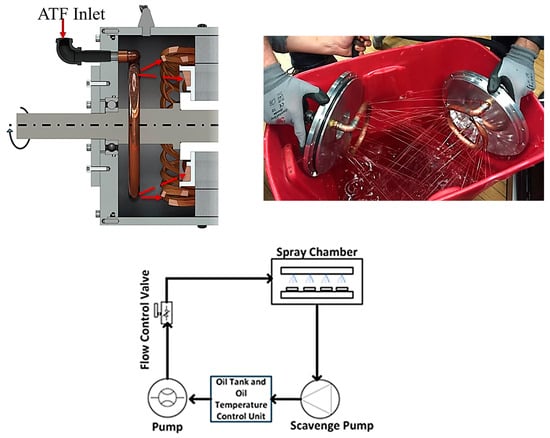
Figure 12.
Spray cooling of rotor and stator end windings [121].
The work by Xu et al. [150] presented the concept of semi-flooded direct oil cooling for a high-speed aircraft motor. The oil was injected in the specified gap between the stator and rotor to divide the electric machine into a stationary submerged part of the stator and a dry rotor part. The use of oil for contact cooling allowed not only high values of specific power to be obtained but also ensured high efficiency and reliability during operation [118].
Sindjui et al. [95] suggested the design of a system with simultaneous water cooling (housing jacket) and oil injection. A significant decrease in the coil end-winding temperature (around 50 °C) was observed at an operating point of 6000 rpm (partial load) and 50 kW power.
Both direct and indirect oil cooling can also be used for hybrid car motors. It was suggested to inject oil through the ducts located between the stator and housing [115], but oil return was complicated in such a design. Making 2 mm channels between the stator and housing decreased the produced torque by only 1%. But the average temperature rise was decreased by 1.5–3.0 °C when compared with indirect liquid cooling. Therefore, direct cooling enables higher current loading capacity of the electric machine and, as a result, higher power density. For example, for the GE Global Research motor, the power-to-dimension ratio at maximum speed (14,000 rpm, 30 kW) was doubled using this method [109]. However, this required a new rotor design, the “squirrel cage,” which ensured good distribution of oil in the interior of the motor at different loads. In addition, use of this new rotor design required more frequent maintenance, especially when the motor was operated at partial loads for a long time. The combined use of a motor housing cooling jacket (water), direct liquid injection cooling (oil), and intensive forced air cooling of the rotor are involved in the cooling system of the Porsche Panamera E-Hybrid 416 horsepower motor [96], which allows the temperature regime to be maintained while doubling the power of the electric motor when compared to the previous model of the hybrid car. Similar to air cooling of the “squirrel cage” rotor, contact cooling by oil injection can be used to cool the wheel motor [125,126].
One study investigated the evaporative cooling mechanism for an outer-rotor permanent magnet machine, revealing that the principle of the heat pipe can be utilized when the stator acts as an evaporator and the rotor acts as a condenser. Methanol and propanol were suggested as the working fluids [126]. It should be noted that heat pipe-based thermal management of electrical machines has received significant attention in recent years as it enables targeted heat removal from motor subassemblies and has been used in wide range of applications, including vehicles and aircraft. Such technology allows current densities of up to 20 A/mm2 to be achieved. However, this high level of cooling system integration imposes several issues associated with electrical, electromagnetic, thermal, and mechanical compatibility [28].
4.3. Overview of Patents for Cooling of Electric Motors
Selected patents for the cooling of electric motors are presented in Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6. A significant number of patents also include a secondary cooling system.

Table 4.
Selected invention patents for liquid cooling systems.

Table 5.
Selected invention patents for air cooling systems.

Table 6.
Selected invention patents for cooling systems using refrigerant.
The patents related to liquid cooling systems (Table 4) include methods and technical solutions related to the housing jacket, stator, rotor, and shaft. Liquid injection is also of interest. Water and oil are mainly used as the coolants. Liquid cooling is utilized for vehicles and aircraft mainly due to the need to increase the power-to-dimension ratio. At the same time, liquid cooling systems are relatively expensive in service as they include additional elements like pumps, compressors, filters, etc., and require higher ingress protection ratings (IP) for the electric motor.
Robotics and industrial electric motors mainly utilize forced air cooling, with the cooling method or design of the fan, stator, and rotor being the main subjects of patents (Table 5).
A characteristic feature of refrigerant cooling systems is the direct evaporative cooling of the stator and rotor via injection (Table 6). This cooling method requires an additional refrigeration unit to maintain cooling of the electric motor.
4.4. The Cooling Systems Using Refrigerant
Direct evaporation of cooling media from the hot surfaces of electric motors is beneficial in terms of a high heat transfer coefficient. The following properties should be considered when using refrigerant as cooling media for the electronics of hybrid vehicles: dielectric strength, dielectric constant, flammability, auto-ignition temperature, lower explosive limit, atmospheric lifetime, ozone depletion potential, and global warming potential. One method is direct injection and spraying of the refrigerant in the motor’s interior, (Figure 13, Points 1 and 2). It can also be organized as described by Metheny at al. [51] for a hermetic motor. R11 was supplied through both ends of the motor (at vicinity of vending) and dispersed by the rotation of the fan blades. The flow of refrigerant through the stator was organized via a system of axial ducts, then the refrigerant was radially exhausted through an orifice at the axial center of the motor. The temperature of the refrigerant was at the boiling point. There was no membrane between the rotor and stator [51].
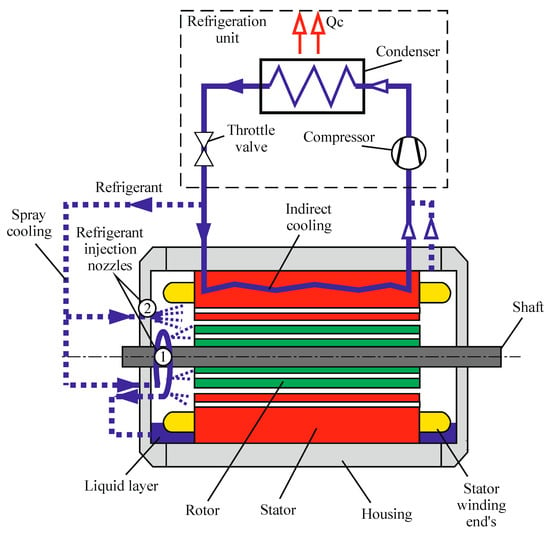
Figure 13.
Structure of spray cooling and indirect cooling system for electric motors [84,85,86,88].
The main problem with evaporative cooling in large machines is leakage of the refrigerant through the rotor’s bearings. The proposed solution used a hermetic fiberglass sleeve, which was installed in the gap between the rotor and stator and provided good sealing. An alternative solution utilized the magnetic sealing of the shaft and bearing when the sleeve was not needed. In pilot tests, R113 was sprayed through the distribution system on the windings’ ends (evaporation temperature 47.6 °C) and the vapor was removed by the condenser via radial ducts in the stator. The sub-cooled refrigerant was sprayed in the motor’s interior and formed a thin film on the surface, which increased the heat transfer of evaporation [84,85]. In the case of magnetic sealing of the bearing, the bottom part of the motor was filled with refrigerant. The stator winding and end-winding temperatures were 72.9 and 70.2 °C, respectively [86].
Spray volumetric flux has the strongest effect on heat rejection among other factors. The study by Nategh et al. [127] stated that two-phase spray cooling (R134a) had heat transfer values that greatly exceeded the heat flux anticipated in a hybrid vehicle (150–200 W/cm2). Submerging power electric devices for hybrid electric vehicles in R134a allowed a heat flux of 114 W/cm2 to be reached. No damage to the devices was observed during 300 days of operation [82].
It should be noted that oil, which is normally used in refrigeration systems, can decrease the dielectric strength of the environment inside the motor [32,83]. Therefore, indirect cooling systems are preferable. The direct use low-temperature refrigerating machines for motor cooling is relatively rare. Gordon L. Mount and James W. Endress invented a refrigeration system in which the low- and high-pressure sides were connected to the casing of a hermetically enclosed electric motor [88]. The liquid refrigerant was supplied by gravity in the interior of the motor and maintained at a predetermined level. The distribution of the refrigerant in the interior of the motor was maintained by a pump when the part of the refrigerant was sprayed on the rotor.
The potential use of several refrigerants to achieve efficient cooling of electric motors in aircraft was recently discussed, for which a high power-to-dimension ratio is appreciated [83]. The proposed cooling solution utilized thermal pipes, ducts, and microchannel. The high potential of low-pressure refrigerants like R236fa, R245fa, and R134a was discussed, as they can provide low weights for the cooling infrastructure. However, the high GWP of the abovementioned refrigerants complicates their use at industrial scales. The authors mentioned the high potential of CO2 as a working fluid. They noted that the high working pressure can be a significant issue when applying CO2 for the cooling of electric motors. However, this makes it possible to achieve a higher power-to-dimension ratio by, for example, reducing the size of the compressor and its working volume by more than 50% compared to more common systems using R134a [83].
An industrial solution for the use of refrigerant in motor cooling was presented by HERMETIC-Pumpen GmbH (Gundelfingen, Germany) [198]. An electric motor cooling system using the pumped refrigerant was proposed for refrigeration pumps (R717, R744, R290, R404A, etc.) with no physical separation between the motor and pump. The rotor was directly connected to the hollow shaft. As a result, the hollow shaft and impellers rotated automatically as soon as the rotor turned. The stator lay outside the liquid area and was separated from the rotor by a so-called rotor lining. The liquid refrigerant was introduced into the pump housing, where the motor was located, filling the entire space inside. The coolant cooled the motor elements by circulating through the gap between the stator and rotor and through the cooling duct inside the shaft. This solution enabled the pump size to be reduced by 50% compared to the classic design.
5. Conclusions
Analysis of the presented data shows that the cooling system’s effectiveness significantly impacts electric motor performance. Decreasing the cooling temperature by 10 °C allows for increases in power by 3–8% and efficiency by 0.2–0.4%. At the same time, a significant characteristic is the power-to-dimension ratio, which rises with improved cooling system efficiency. On the other hand, increasing the winding temperature by 10 °C over the high-temperature limit decreases the operation life by 50%. When applying similar cooling systems for motors with different designs and operation conditions, the effects on the performance of the motor are different. Therefore, the efficiency of cooling is not only a question of the cooling system or method but a combination of system design, motor operation, and environmental conditions.
The design of the cooling system depends on the application area of the motor. For example, air cooling systems are utilized in industrial and household appliance electric motors. Meanwhile, for vehicles and aircraft motors, there is a trend toward using liquid cooling systems.
Advanced air cooling systems include forced ventilation in which the stator and rotor are simultaneously cooled by air ducts of different designs and locations. These systems decrease operational and maintenance costs. In addition, this measure increases the power-to-dimension ratio by up to 10%. The air gap between the stator and rotor can be also used for cooling, but only for motors with power above 50 kW.
New trends in external cooling are focused on the development of efficient fans. For example, fans with forward-swept blades allow a large rise in air velocity and, as a result, decrease the stator winding temperature by 30%. Fans with radial blades were found to be even more efficient and could provide a heat transfer coefficient of over 100 W/(m2∙K).
Self-ventilation (self-cooling) is the most popular cooling technology for the motors of electric trains. However, such methods are not common for vehicles because of the limited volume of the motor area and heat rejection via external heat exchangers. However, air cooling systems provide relatively low power-to-dimension ratios (up to 0.65 kW/kg) due to low efficiency and the impossibility of ensuring a cooling temperature below ambient temperature. Therefore, a combined system consisting of air and liquid cooling systems is applied. It provides more intensive heat removal from all elements of the motor. This provides the opportunity to increase the power-to-dimension ratio up to 2.7 kW/kg. Water, oil, and glycol are common coolants for such cooling systems.
New liquid cooling systems allow a power-to-dimension ratio of up to 25 kW/kg to be achieved. The new trends in liquid cooling systems include new designs for cooling ducts in the housing jacket of the motor, installation of a heat exchanger in the stator, and cooling the rotor using ducts in the rotor shaft. The position and geometry of the ducts in the jacket housing can be different and a tangential position is preferable due to less hydraulic resistance (lowered by 10–15%). The use of cooling tubes with a small diameter, installed in the stator or between the stator and housing, allows the power-to-dimension ratio to be increased by over than 2 times due to significant decreases in the temperature of the rotor and stator windings. Also, cooling tubes can be installed on the stator windings’ ends, which allows the winding temperature to be reduced by 25%. It should be noted that liquid systems are relatively complex, requiring expanded maintenance and high ingress protection ratings. However, such systems allow the largest power-to-dimension ratio to be achieved, which is very important for vehicles and aircraft.
Much effort has been devoted in recent years to the development of contact cooling by injecting liquid oil or low-boiling liquids (refrigerant). Oil spray cooling provides better cooling performance and a lower temperature gradient when compared with air cooling and indirect liquid cooling. The temperature of the stator windings can be reduced by 50 °C. Direct cooling requires the application of a refrigeration machine and the development of a specially designed heat exchanger. On the other hand, this enables a high cooling capacity and low-temperature regime to be achieved, while direct evaporative cooling excludes bulky equipment from the design of the cooling system. In this case, the use of ozone-friendly and environmentally efficient natural refrigerants, such as CO2, is promising. The use of CO2 can provide a higher power-to-dimension ratio by up to 50% when compared with other working fluids by reducing the size of the compressor and working volume.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.K. and I.T.; methodology, D.K. and I.T.; formal analysis, D.K. and I.T.; writing—original draft, D.K. and I.T.; writing—review and editing, D.K., I.T., T.M.E. and A.H.; investigation, D.K., I.T., H.K., M.R. and A.R.; resources, I.T., D.K., M.R. and A.R.; supervision, D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gronwald, P.O.; Kern, T.A. Traction Motor Cooling Systems: A Literature Review and Comparative Study. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 2892–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriero, A.; Locatelli, M.; Ramakrishnan, K.; Mastinu, G.; Gobbi, M. A Review of the State of the Art of Electric Traction Motors Cooling Techniques; SAE Technical Papers; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- IEC 60034-1:2022; Rotating Electrical Machines—Part 1: Rating and Performance. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; p. 161.
- Bonnett, A.H.; Soukup, G.C. Cause and Analysis of Stator and Rotor Failures in Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1992, 28, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipo, T. Introduction to AC Machine Design; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDG17). Division for Sustainable Development Goals Department of Economic and Social Affairs United Nations Secretariat. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal17 (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- ABB. Low Voltage Motors. Motor Guide, 4th ed.; ABB: Zurich, Switzerland, 2019; p. 112. [Google Scholar]
- ABB. Low Voltage Process Performance Motors According to EU MEPS; ABB: Zurich, Switzerland, 2014; p. 124. [Google Scholar]
- Turncircles, s.r.o. Ultra Light Custom Electric Motor. Available online: https://turncircles.com/ (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- WEG. Specification of Electric Motors; WEG: Jaraguá do Sul, Brazil, 2020; p. 68. [Google Scholar]
- W22 Three-Phase Electric Motor; WEG: Jaraguá do Sul, Brazil, 2011; p. 44.
- Marathon Electric Motors. Commercial & Industrial Motor Solutions; Marathon Electric Motors: Eibergen, Netherlands, 2018; p. 318. [Google Scholar]
- Marathon Electric Motors. IEC IE3 Motor Range; Marathon Electric Motors: Eibergen, Netherlands, 2014; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- SIMOTICS GP, SD, XP, DP Low-Voltage Motors, 12/2021 ed.; Siemens AG: Alpharetta, GA, USA; Erlangen, Germany, 2021; p. 706. Available online: https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/document/109763390/catalog-d-81-2-usa-edition-2022?dti=0&pnid=13308&lc=en-NO" (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- SIMOTICS NEMA Motors. Low Voltage AC Motors Selection and Pricing Guide. Edition 2022 ed.; Siemens AG: Alpharetta, GA, USA, 2019; p. 293. Available online: https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/document/109749197/catalog-d-81-1-simotics-gp-sd-xp-dp-low-voltage-motors-september-2023?dti=0&pnid=13308&lc=en-NO (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- Brook Cromoton. Series 10 IE3. Frame size 80 to 355; Brook Cromoton: West Yorkshire, UK, 2015; Volume 2.1, p. 22. Available online: http://www.brookcrompton.com/upload/20151E_Series10_IE3_issue_2_1.pdf (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- Brook Cromoton. Series 10. Frame size 56 to 450; Brook Cromoton: West Yorkshire, UK, 2012; Volume 2, p. 30. Available online: http://www.brookcrompton.com/upload/20121E_issue2_Series10.pdf (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- Brook Cromoton. W Cast Iron motors. Frame size 80 to 355, 08/16 ed.; Brook Cromoton: West Yorkshire, UK, 2011; Volume 4, p. 30. Available online: http://www.brookcrompton.com/upload/20113E_W_Cast_Iron_issue4.pdf (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- Schneider Electric. Catalog Lexium 32 Servo Drives BMH BSH Servo Motors: France, 2021. p. 61. Available online: https://www.se.com/ (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- Burress, T. Electrical Performance, Reliability Analysis, and Characterization; Project ID: EDT087; U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Burress, T.A.; Campbell, S.L.; Coomer, C.; Ayers, C.W.; Wereszczak, A.A.; Cunningham, J.P.; Marlino, L.D.; Seiber, L.E.; Lin, H.-T. Evaluation of the 2010 Toyota Prius Hybrid Synergy Drive System; Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL): Oak Ridge, TN, USA; Power Electronics and Electric Machinery Research Facility: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2011; p. 88. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, Y.; Kimiabeigi, M.; Chuan Chong, Y.; Widmer, J.D.; Deng, X.; Popescu, M.; Goss, J.; Staton, D.A.; Steven, A. Cooling of automotive traction motors: Schemes, examples, and computation methods. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burress, T. Benchmarking State-of-the-Art Technologies; Project ID: APE006; US DOE Hydrogen and Fuel Cells Program and Vehicle Technologies Program Annual Merit Review and Peer Evaluation Meeting: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2013; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Limited, I.P. Electric Powertrain. Available online: https://ehelix.com/electric-powertrains/ (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- EMRAX. EMRAX 268 Technical Data. Available online: https://emrax.com/e-motors/emrax-268/#1482059435741-232ed37a-accc (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- H.X.T., Inc. High Performance Electric Propulsion Systems. Available online: https://www.h3x.tech/ (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- Frank, A. eAircraft: Hybrid-elektrische Antriebe für Luftfahrzeuge. In Proceedings of the 14 Tag der Deutschen Luft- und Raumfahrtregionen, Potsdam, Germany, 10 September 2019; p. 37. [Google Scholar]
- Wrobel, R. A technology overview of thermal management of integrated motor drives—Electrical Machines. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2022, 29, 101222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarev, P.; Polikarpova, M.; Pyrhönen, J. Thermal modeling of directly-oil-cooled permanent magnet synchronous machine. In Proceedings of the 2012 20th International Conference on Electrical Machines, ICEM 2012, Marseille, France, 2–5 September 2012; pp. 1882–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Sikora, M.; Vlach, R.; Navrátil, P. The unusial water cooling applied on small asynchronous motor. Eng. Mech. 2011, 18, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, Y.C. Thermal Analysis and Air Flow Modelling of Electrical Machines. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, G.C.; Culbert, I.; Boulter, E.A.; Dhirani, H. Electrical Insulation for Rotating Machines: Design, Evaluation, Aging, Testing, and Repair, 2nd ed.; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 9781118057063, pp. 1–643. [Google Scholar]
- Toliyat, H.A.; Kliman, G.B. Handbook of Electric Motors, 2nd ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 120. [Google Scholar]
- IEC 60034-6: 1991; Rotating electrical machines—Part 6: Methods of Cooling (IC Code). International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 1991; p. 39.
- Kral, C.; Haumer, A.; Bäuml, T. Thermal model and behavior of a totally-enclosed-water-cooled squirrel-cage induction machine for traction applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 3555–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, C. Cool Facts About Cooling Electric Motors: Improvements in Applications That Fall Outside the Normal Operating Conditions. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2015, 21, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Three-Phase Asynchronous Motors; ABB Technical Application Papers No. 7; Generalities and ABB Proposals for the Coordination of Protective Devices; ABB: Bergamo, Italy, 2008; p. 48.
- Bharat Bijlee. Low Voltage Motors; Bharat Bijlee: Mumbai, India, 2016; p. 86. [Google Scholar]
- Qandil, M.M.; Ray, R.B. Immersible Motor System. U.S. Patent US6183208, 6 February 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kanei, N.; Haga, S.; Horiuchi, K.; Sonoyama, K. Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled Motor. U.S. Patent US7629717B2, 8 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ulbrich, S.; Kopte, J.; Proske, J. Cooling fin optimization on a TEFC electrical machine housing using a 2-D conjugate heat transfer model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staton, D.A.; Cavagnino, A. Convection heat transfer and flow calculations suitable for electric machines thermal models. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 3509–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilson, G.M.; Raminosoa, T.; Pickering, S.J.; Gerada, C.; Hann, D.B. A combined electromagnetic and thermal optimisation of an aerospace electric motor. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Electrical Machines, ICEM 2010, Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela, M.A.; Tapia, J.A. Heat transfer and thermal design of finned frames for TEFC variable-speed motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 3500–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güvenç, A.; Yüncü, H. An experimental investigation on performance of fins on a horizontal base in free convection heat transfer. Heat Mass Transf. 2001, 37, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, T.; Bonnett, A.H. Motor temperature considerations for pulp and paper mill applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 1701–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bante, K.G.; Tarnekar, S.G.; Tutakane, D.R. AC Motor cooling system Analysis Based on Application Case Study. Int. J. Eng. Invent. 2013, 2, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnett, A.H. Operating temperature considerations and performance characteristics for IEEE 841 motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2001, 37, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, L.; Raguideau, J.-L.; Raguin, B. Ventilation Device and Rail Traction Electric Motor Equipped wth Such a Device. U.S. Patent US6570276, 27 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Early, J.; Evon, T.S.; Grant, E.D.; Melfi, M.J.; Smith, P.L.; Stelzner, D.J. Electric Motor Having Frame Adaptable for Enclosed and Open Motor Cooling. U.S. Patent US5998896, 7 December 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Metheny, L.; Sudhoff, D.; Thompson, A.; Budzynski, R. Integrated electric Motor and Drive System with Auxiliary Cooling Motor and Asymivietric Heat Sink. U.S. Patent US5763969, 9 June 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lenz, H.G. Castable Rotor Having Radially Venting Laminations. U.S. Patent US3684906, 15 August 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Lukens, A.F. Heat Transfer System for Dynamo-Electric Machine. U.S. Patent US3725706, 3 April 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Baumann, F.; Rosenberry, G. Ventilated Dynamoelectric Machines. U.S. Patent US3749953, 31 July 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Nakahama, T.; Biswas, D.; Kawano, K.; Ishibashi, F. Improved cooling performance of large motors using fans. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2006, 21, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahama, T.; Ishibashi, F.; Sato, K.; Kawano, K. Effects of fan blade forward-swept and inclined amounts in electric motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cezário, C.A.; Oliveira, A.A.M. Electric motor internal fan system CFD validation. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Electrical Machines, ICEM’08, Vilamoura, Portugal, 6–9 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, L.; Bikle, U.; Popp, O.; Jakoby, R. Improvement of the cooling performance of symmetrically self-ventilated induction machines in the 2–15 MW range. In Proceedings of the IEMDC 2001—IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference, Cambridge, MA, USA, 17–20 June 2001; pp. 673–680. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno, S.; Noda, S.; Matsushita, M.; Koyama, T.; Shiraishi, S. Development of a totally enclosed fan-cooled traction motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzal, A.S.; Cirstea, R.M.; Gyftakis, K.N.; Woolmer, T.J.; Dickison, M.; Blundell, M. Fan Performance Analysis for Rotor Cooling of Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 3295–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.V.R.S.; Rao, D.V.V.S. Design of cooling fan for noise reduction using CFD. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2011, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kindl, V.; Pechanek, R.; Bouzek, L. Cooling of new designed machine. In Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Mechatronics, MECHATRONIKA 2010, Trencianske Teplice, Slovakia, 2–4 June 2010; pp. 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Glahn, A.; Baumgartner, J.; Jung, M. Generatorkühlung mit Kühlernachlaufmischung. Patent EU EP1006643A3, 29 January 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara, M.; Yasuo, H.; Takashi, H.; Motoyasu, M. Cooling Structure for Rotor Core in Electric Rotating Machine. U.S. Patent US8080908, 20 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, V. Electric Machine with Rotor Cooling and Corresponding Cooling Method. U.S. Patent US7646119B2, 12 January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.A. Self-Cooled for an Electrical Machine. U.S. Patent US7514827B2, 7 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kylander, G.; Leijon, M. Axial Cooling of a Rotor. U.S. Patent US6369470B1, 6 April 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Arbanas, V.; Zysset, E. Driving unit Including a Liquid Cooled Electric Motor and a Planetary Gear. U.S. Patent US6329731, 11 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Masahiro Hasebe, Y. Motor Cooling Circuit. U.S. Patent US5889342, 30 March 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Armor, A.; Morgan, J. Flexible Serrated Abradable Stator Mounted Air Gap Baffle for a Dynamoelectric Machine. U.S. Patent US4264834, 28 April 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Wieland, H. External Rotor Motor Having a Cooling System. U.S. Patent US4574210, 4 March 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Johnsen, T.A. Cooling of a Rotor for a Rotary Electric Machine. U.S. Patent US6727609B2, 27 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, J. Generatorkühlung mit Kühlernachlaufmischung. EU Patent EP1006643A2, 7 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nagayama, T.; Kitamura, M.; Shiraishi, S. Fully-Enclosed Fan-Cooled Motor. U.S. Patent US7462964, 9 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- VanLuik, R.; Prosser, E.; Deitt, E. Semi-Enclosed AC Motor. U.S. Patent US7459817, 2 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Ye, Y.; Zhu, Z.Q. Modeling and Investigation of Thermal Characteristics of a Water-Cooled Permanent-Magnet Linear Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 2086–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zysset, E. Liquid Cooled Asynchronous Electric Machine. U.S. Patent US6191511B1, 20 February 2001. [Google Scholar]
- RD 34.45.507; Model Guidelines for Operation of Large Electric Motors with Water Cooling of Rotor for Feed Pump Drives. Soyuztechenergo: Moscow, Russia, 1989; p. 41.
- Onjanow, N. Dynamoelectric Machine with Improved. U.S. Patent US3610975, 5 October 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Arbab, N.; Wang, W.; Lin, C.; Hearron, J.; Fahimi, B. Thermal Modeling and Analysis of a Double-Stator Switched Reluctance Motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tüysüz, A.; Meyer, F.; Steichen, M.; Zwyssig, C.; Kolar, J.W. Advanced Cooling Methods for High-Speed Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 2077–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, R.; Künzler, M.; Moullion, M.; Gauterin, F. Comparison of Commonly Used Cooling Concepts for Electrical Machines in Automotive Applications. Machines 2022, 10, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.B.; Tolbert, L.M.; Ayers, C.W.; Ozpineci, B.; Lowe, K.T. Two-phase cooling method using the R134a refrigerant to cool power electronic devices. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2007, 43, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deisenroth, D.C.; Ohadi, M. Thermal management of high-power density electric motors for electrification of aviation and beyond. Energies 2019, 12, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenguo, L.; Lin, R. Optimization design of the spray evaporative-cooling large electrical machine. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, ICEMS 2016, Chiba, Japan, 13–16 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Ruan, L.; Tang, L. Heat transfer characteristics of spray evaporative cooling system for large electrical machines. In Proceedings of the 2015 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, ICEMS 2015, Pattaya, Thailand, 25–28 October 2015; pp. 1740–1743. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Fu, D.; Guo, J.; Gu, G.; Xiong, B. Study on spraying evaporative cooling technology for the large electrical machine. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, ICEMS 2009, Tokyo, Japan, 15–18 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mount, G.; Endress, J. Refrigerant Cooling System for Electric Motor. U.S. Patent US3645112, 29 February 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Nakahama, T.; Suzuki, K.; Hashidume, S.; Ishihashi, F.; Hirata, M. Cooling airflow in unidirectional ventilated open-type motor for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2006, 21, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dames, M.; Ballmann, J.M.; Cruce, P.; Fee, D. Liqiuid Cooled Permanent Magnet Rotor. U.S. Patent US8022582B2, 20 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Iund, T.N.; Wookey, R.; Dames, M. Electrical Machine Having a Liquid-Cooled Rotor. U.S. Patent US7834492B2, 16 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, F.; Tang, Y.; Pei, Y.; Liang, P.; Gao, H. Temperature field accurate modeling and cooling performance evaluation of direct-drive outer-rotor air-cooling in-wheel motor. Energies 2016, 9, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrell, D.G.; Hsieh, M.F.; Popescu, M.; Evans, L.; Staton, D.A.; Grout, V. A review of the design issues and techniques for radial-flux brushless surface and internal rare-earth permanent-magnet motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 3741–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimiabeigi, M.; Long, R.; Widmer, J.D.; Gao, Y. Comparative Assessment of Single Piece and Fir-Tree-Based Spoke Type Rotor Designs for Low-Cost Electric Vehicle Application. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindjui, R.; Zito, G.; Zhang, S. Experimental Study of Systems and Oils for Direct Cooling of Electrical Machine. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2022, 14, 051007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.; Staton, D.A.; Boglietti, A.; Cavagnino, A.; Hawkins, D.; Goss, J. Modern Heat Extraction Systems for Power Traction Machines—A Review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Jahns, T.M. Coupled Electromagnetic-Thermal Analysis of Electric Machines Including Transient Operation Based on Finite-Element Techniques. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 1880–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricchi, F.; Crescimbini, F.; Di Napoli, A.; Marcheggiani, M. Prototype of electric vehicle drive with twin water-cooled wheel direct drive motors. In Proceedings of the PESC Record—IEEE Annual Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Baveno, Italy, 23–27 June 1996; pp. 1926–1932. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, S.; Yashiro, T.; Takizawa, K.; Mizutani, T. Development of new motor for compact-class hybrid vehicles. World Electr. Veh. J. 2016, 8, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikarpova, M. Liquid Cooling Solutions for Rotating Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. Ph.D. Thesis, Lappeenranta University of Technology, Lappeenranta, Finland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hari, D.; Brace, C.; Vagg, C.; Akehurst, S.; Ash, L.; Strong, R. Development and Testing of a Low Cost High Performance Hybrid Vehicle Electric Motor; SAE Technical Papers; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bennion, K. Electric Motor Thermal Management R&D; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2016; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Jia, N.; Li, L.; Liu, T.; Xue, M.; Li, M. Cooling System Design Optimization of a High Power Density PM Traction Motor for Electric Vehicle Applications. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2021, 16, 3061–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechanek, R.; Bouzek, L. Analyzing of two types water cooling electric motors using computational fluid dynamics. In Proceedings of the 15th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference and Exposition, EPE-PEMC 2012 ECCE Europe, Novi Sad, Serbia, 4–6 September 2012; pp. LS2e.41–LS42e.45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Qu, R.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Fan, X.; Chen, Y. Thermal Model of Totally Enclosed Water-Cooled Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines for Electric Vehicle Application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3020–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, D.P.; Rupertus, G.; Chen, E. Experimental investigation of contact resistance for water cooled jacket for electric motors and generators. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2012, 27, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funieru, B.; Binder, A. Thermal design of a permanent magnet motor used for gearless railway traction. In Proceedings of the 2008 34th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics, Orlando, FL, USA, 10–13 November 2008; pp. 2061–2066. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Gu, G. Temperature characteristics in the stator model of a permanent magnet motor by water-cooling and evaporative cooling. In Proceedings of the ICEMS 2005 8th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Nanjing, China, 27–29 September 2005; pp. 2408–2410. [Google Scholar]
- El-Refaie, A.M.; Alexander, J.P.; Galioto, S.; Reddy, P.B.; Huh, K.K.; De Bock, P.; Shen, X. Advanced high-power-density interior permanent magnet motor for traction applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3235–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefer, M.; Doppelbauer, M. Indirect slot cooling for high-power-density machines with concentrated winding. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference, IEMDC 2015, Coeur d’Alene, ID, USA, 10–13 May 2015; pp. 1820–1825. [Google Scholar]
- Rhebergen, C.; Bilgin, B.; Emadi, A.; Rowan, E.; Lo, J. Enhancement of electric motor thermal management through axial cooling methods: A materials approach. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, ECCE 2015, Montreal, ON, Canada, 20–24 September 2015; pp. 5682–5688. [Google Scholar]
- Madonna, V.; Giangrande, P.; Walker, A.; Galea, M. On the Effects of Advanced End-Winding Cooling on the Design and Performance of Electrical Machines. In Proceedings of the 2018 23rd International Conference on Electrical Machines, ICEM 2018, Alexandroupoli, Greece, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 311–317. [Google Scholar]
- Sixel, W.; Liu, M.; Nellis, G.; Sarlioglu, B. Cooling of Windings in Electric Machines via 3-D Printed Heat Exchanger. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 4718–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Garbuio, L.; Gerbaud, L.; Chazal, H. Modeling and design analysis of the Tesla Model S induction motor. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electrical Machines, ICEM 2020, Gothenburg, Sweden, 23–26 August 2020; pp. 495–501. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Nategh, S.; Lassila, V.; Alaküla, M.; Yuan, J. Direct oil cooling of traction motors in hybrid drives. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Electric Vehicle Conference, IEVC 2012, Greenville, SC, USA, 4–8 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Davin, T.; Pellé, J.; Harmand, S.; Yu, R. Experimental study of oil cooling systems for electric motors. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 75, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahfarokhi, P.S.; Podgornovs, A.; Kallaste, A.; Marques Cardoso, A.J.; Belahcen, A.; Vaimann, T. The Oil Spray Cooling System of Automotive Traction Motors: The State of the Art. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 9, 428–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahfarokhi, P.S.; Podgornovs, A.; Kallaste, A.; Vaimann, T.; Belahcen, A.; Cardoso, A.J.M. Oil Spray Cooling with Hairpin Windings in High-Performance Electric Vehicle Motors. In Proceedings of the 2021 28th International Workshop on Electric Drives: Improving Reliability of Electric Drives, IWED 2021, Moscow, Russia, 27–29 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bennion, K. Electric Motor Thermal Management R&D; NREL/PR-5400-63004; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2021; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Gerada, D.; Xu, Z.; Chong, Y.C.; Michon, M.; Goss, J.; Li, J.; Gerada, C.; Zhang, H. Estimation of Oil Spray Cooling Heat Transfer Coefficients on Hairpin Windings with Reduced-Parameter Models. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludois, D.C.; Brown, I. Brushless and Permanent Magnet Free Wound Field Synchronous Motors for EV Traction; DE-EE0006849; University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA; Illinois Institute of Technology: Chicago, IL, USA, 2017; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Xu, Z.; Gerada, D.; Li, J.; Gerada, C.; Chong, Y.C.; Popescu, M.; Goss, J.; Staton, D.; Zhang, H. Experimental Investigation on Oil Spray Cooling with Hairpin Windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 7343–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaviva, A.; Skoog, S.; Grunditz, E.; Thiringer, T. Electromagnetic and Calorimetric Validation of a Direct Oil Cooled Tooth Coil Winding PM Machine for Traction Application. Energies 2020, 13, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chong, Y.C.; Michon, M.; Goss, J.; Gerada, D.; Xu, Z.; Gerada, C.; Zhang, H. Model Calibration of Oil Jet and Oil Spray Cooling in Electrical Machines with Hairpin Windings. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, ECCE 2021, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–14 October 2021; pp. 3813–3820. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.H.; Kim, S.C. Thermal characteristics and effects of oil spray cooling on in-wheel motors in electric vehicles. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 152, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, R.; McCulloch, M. Investigation of an Integrated Evaporative Cooling Mechanism for an Outer-Rotor Permanent Magnet Machine. Heat Transf. Eng. 2014, 36, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nategh, S.; Huang, Z.; Krings, A.; Wallmark, O.; Leksell, M. Thermal modeling of directly cooled electric machines using lumped parameter and limited cfd analysis. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2013, 28, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudawar, I.; Bharathan, D.; Kelly, K.; Narumanchi, S. Two-phase spray cooling of hybrid vehicle electronics. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 2009, 32, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nategh, S.; Boglietti, A.; Liu, Y.; Barber, D.; Brammer, R.; Lindberg, D.; Aglen, O. A Review on Different Aspects of Traction Motor Design for Railway Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 2148–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwegian Electric System. Motors: Double Jacket Water Cooled Motors; Norwegian Electric System: Bergen, Norway, 2017; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.X.; Li, Y.Z.; Yu, X.K.; Li, G.C.; Ji, X.Y. Investigation of heat transfer mechanism of low environmental pressure large-space spray cooling for near-space flight systems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 119, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Fujiwara, S.; Mochizuki, T.; Nagashima, Y. Motor Cooling Apparatus for Refrigerator. U.S. Patent US4669279, 2 June 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Winkelmann Elektromotoren. Cooling Methods for Motors; Winkelmann Elektromotoren: Uelzen, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rama Krishna, S.; Rama Krishna, A.; Ramji, K. An experimental study on the reduction of motor-fan noise by modification of the blade and shroud configuration. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2010, 224, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, C. Cool facts about cooling electric motors. In Proceedings of the Industry Applications Society 60th Annual Petroleum and Chemical Industry Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 23–25 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Borges, S.S.; Cezario, C.A.; Kunz, T.T. Design of water cooled electric motors using CFD and thermography techniques. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Electrical Machines, ICEM’08, Vilamoura, Portugal, 6–9 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cui, W.; Sun, C. Design of low-pressure sand casting process for water-cooled motor shell in electric vehicle. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2101, 012052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Liu, R.; Thelin, P.; Nordlund, E.; Sadarangani, C. Research on the cooling system of a 4QT prototype machine used for HEV. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2008, 23, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burress, T. Benchmarking Competitive Technologies; Project ID: APE006; U.S. Deparment of Energy Hydrogen and Fuel Cells Program and Vehicle Technologies Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, Y.; Kimiabeigi, M.; Widmer, J.D.; Chong, Y.C.; Goss, J.; Sanandres, U.; Staton, D.A. Shaft cooling and the influence on the electromagnetic performance of traction motors. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference, IEMDC 2017, Miami, FL, USA, 21–24 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chasiotis, I.D.; Karnavas, Y.L. Design, Optimization and Modelling of High Power Density Direct-Drive Wheel Motor for Light Hybrid Electric Vehicles. In Hybrid Electric Vehicles; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, B.; Goyal, A.; Kumar Chobey, A. Improving thermal withstanding capacity of three phase induction motor using NWCC method. Int. J. Res. GRANTHAALAYAH 2014, 2, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deriszadeh, A.; de Monte, F. On heat transfer performance of cooling systems using nanofluid for electric motor applications. Entropy 2020, 22, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.C.; Cho, H.R.; Yadav, S.; Kim, S.C. Cooling Effect of Water Channel with Vortex Generators on In-Wheel Driving Motors in Electric Vehicles. Energies 2022, 15, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindh, P.; Petrov, I.; Jaatinen-Varri, A.; Gronman, A.; Martinez-Iturralde, M.; Satrústegui, M.; Pyrhonen, J. Direct Liquid Cooling Method Verified with an Axial-Flux Permanent-Magnet Traction Machine Prototype. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 6086–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindh, P.; Petrov, I.; Pyrhonen, J.; Scherman, E.; Niemela, M.; Immonen, P. Direct Liquid Cooling Method Verified with a Permanent-Magnet Traction Motor in a Bus. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 4183–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semidey, S.A.; Mayor, J.R. Experimentation of an electric machine technology demonstrator incorporating direct winding heat exchangers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5771–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.H.; Kim, S.C. Thermal performance of oil spray cooling system for in-wheel motor in electric vehicles. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 63, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Gerada, D.; Xu, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Zou, T.; Chong, Y.C.; Gerada, C. A Thermal Modeling Approach and Experimental Validation for an Oil Spray-Cooled Hairpin Winding Machine. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 2914–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Rocca, A.L.; Arumugam, P.; Pickering, S.J.; Gerada, C.; Bozhko, S.; Gerada, D.; Zhang, H. A semi-flooded cooling for a high speed machine: Concept, design and practice of an oil sleeve. In Proceedings of the IECON 2017—43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Beijing, China, 29 October–1 November 2017; pp. 8557–8562. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, E.; Rigney, R.; Tracy, R. Induced Vaporization Cooling of Rotary Electrical Machines. U.S. Patent US3294991, 27 December 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson, J.M. Liquid-Cooled Dynamoelectric Machine Rotor. U.S. Patent US3569752, 9 March 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, P.; Ying, S.-C.; Luzader, J. Water Cooled Rotor for dynamoelectric Machines. U.S. Patent US3740595, 19 June 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Barnhardt, S.B. Cooling Arrangement for an Integrated Drive-Generator System. U.S. Patent US4284913, 18 August 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Staub, F.; Richter, E. Motor Cooling Using a Liquid Cooled Rotor. U.S. Patent US5223757A, 29 June 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg, F.A. Electric Induction Motor and Related Method of Cooling. U.S. Patent US5519269, 21 May 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi, Y.; Idoguchi, R. Cooling System for Electric Motor of Vehicle. U.S. Patent US7156195B2, 2 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Kalayjian, N.R.; Cutler, G.D.; Augenbergs, P.K. Liquid Cooled Rotor Assembley. U.S. Patent US7489057B2, 10 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jockel, A. Electric Motor wth Permanent Magnet Excitation and Rotor Cooling. U.S. Patent US7816824B2, 19 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lambka, C.; Anderson, E. System for Cooling an Electrical Machine. EU Patent EP2264870A2, 22 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bradfield, M. Electric Machine Cooling System. U.S. Patent US8269383, 18 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sagawa, K. Electric Motor Cooling Apparatus. Japan Patent JP2015226363A, 14 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Masahiro, M.; Toshifumi, M. Electric Motor Provided with Cooling Structure. U.S. Patent US2015295474A1, 15 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Renjun, S.; Timing, Q.; Song, P.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Hong, Z. Rotatory Heat Section of Thick Bamboo Structure Suitable for Superconductive Electric Motor Rotor Coil Cooling. PRC Patent CN204615616U, 2 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pinkley, G.A.; Nelson, D.F.; Fong, W.R.; Heines, S.; Pearce, J. Pressurized and Gravity-Fed Liquid Cooling of Electric Motor. U.S. Patent US10439477B2, 6 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Reves, S.M.; Dellal, B.; Yang, B.; Tomas, M.; Swint, E.; Fedoseyev, L.; Bellemare, E.; Olsen, L.E.; Hain, A. Electric Motor Cooling System. WIPO Patent WO2017214232A1, 14 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Puls, R.; Puls, O. Cooling Housing for an Electric Motor. WIPO Patent WO2017211360A1, 14 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin, B.D.A.; Norbert, S.; Jomon, K.; Clemens, B.; Sailors, T., Jr. Cooling system for an electric motor. U.S. Patent US10516320B2, 24 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, N.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. Internal Water Cooling Electric Motor Rotor. PRC Patent CN206349829U, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka, K. Cooling Device of Electric Motor. Japan Patent JP2019221054A, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, K. Vehicle Electric Motor Cooling System. Japan Patent JP2019216515A, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ledieu, C.; Brodnik, J. Rotor for an Electric Motor Provided with a Cooling Circuit. WIPO Patent WO2021240101A1, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Assaad, B.; Negre, E. System for Oil Cooling an Electric Motor. WIPO Patent WO2021209285A1, 21 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhee, S.; Hombsch, M. Electric Motor Cooling System. U.S. Patent US11515756B2, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ledieu, C. Electric Motor Provided with a Cooling Circuit. WIPO Patent WO2021176158A1, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Saiki, M.; Niwa, Y.; Arai, K. Cooler-Equipped Electric Motor. Japan Patent JP2022069694A, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Oechslen, S.; Koenen, C. Electric Motor Vehicle Traction Motor. U.S. Patent US2022385133A1, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Freddi, R. Casing for Electric Motor, Electric Motor Comprising the Casing and Method for the Production. WIPO Patent WO2022248429A1, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Södö, N.J.A.; Keski-Kujala, T.; Yli-Rahnasto, T. Method for Cooling a Device Such as an Electric Motor Drive or a General Power Converter for Performing the Cooling Method. U.S. Patent US2022361364A1, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Christians, M.; Wortzler, D.; Gersten, R.; Spuller, S.; Jielniewski, M.; Bler, W.; Hoeller, T.; Hall, K. Cooling Device for cooling Stator of Electric Motor. PRC Patent CN114649885A, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Tian, J.; Shao, X.; Huang, H. Electric Motor Stator Cooling Device, Cooling Medium Discharge Structure for Double Stator Electric Motor, and Electric Motor. WIPO Patent WO2022142483A1, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lennart, N.A. Air Cooled Rotor for Dynamo-Electric Machine. U.S. Patent US3558943, 26 January 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Rausch, H. Cooled Electric Motor Protecting Components from Coolant. U.S. Patent US5081384, 14 January 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, B.; Kurt, H.R.; Ross, B.K. Alternator with Internal and External Fans. U.S. Patent US5751079, 12 May 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Harald, N. Luftgekühlte Elektrische Maschine. EU Patent EP2086091A2, 5 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ikaheimo, J.; Kolehmainen, J.; Pekola, J.; Ryyppii, T. Cooling Arrangement for Electrical Machine. U.S. Patent US8134261, 13 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, G.F.; Beresewicz, P.; Guidry, M.; Mason, J.; Johnson, R.; Sontag, J. Electric Motor Driven Compressor with Double Directionality Cooling Liquid Passages. Japan Patent JP2015209845A, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shouyuan, L.; Wenbo, Y.; Yang, Z. Nature Air Cooling Motor Casing for Electric Motor Car. PRC Patent CN206775289U, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani, P.; Leli, F.; Lettich, M.; Cataldi, M. Electric Motor Having a Tangential Architecture with improved air cooling. U.S. Patent US10560000B2, 11 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Benali, B. Electric Motor Including External Cooler and Multiple Cooling Circuits. Japan Patent JP2017201878A, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gerstler, W.D.; Hoefler, F.S.; Chan, M.A.C. Electric Motor Having an Integrated Cooling System and Methods of Cooling an Electric Motor. U.S. Patent US10784750B2, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, D.; Herman, E.; Mehner, R.; Pfister, M.; Schulz, J.; Röding, A.; Schoele, R. Electric Motor and Cooling Fan. EU Patent EP3512077A1, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Akihiro, O. Cooling Fan, Electric Motor, Electric Motor Assembly, Water Supply Device, and Inverter Replacement Method. Japan Patent JP2021197846A, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hirosawa, Y. Electric Motor, Blower, and Air Conditioning Device. WIPO Patent WO2022259453A1, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ginier, G.; Lagoin, B.; Antoine, K. Cooling Device of Electric Motor, Related Power Assembly and Vehicle. PRC Patent CN114844281A, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, R. High Speed Liquid Cooled Motors. U.S. Patent US3479541, 18 November 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Gerstler, W.D.; El-Refaie, A.M.; Lokhandwalla, M.; Alexander, J.P. Cooling System for Rotating Machine. U.S. Patent US7994668B2, 9 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- HERMETIC-Pumpen GmbH. HERMETIC Refrigeration Pumps. Available online: https://kaelte.hermetic-pumpen.com/en/pump-types (accessed on 24 March 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).