Abstract
The proliferation of renewable energy sources to achieve carbon neutrality has rapidly increased the adoption of photovoltaic (PV) systems. Consequently, specialized solar PV systems have emerged for various installation purposes. This study focuses on grid connecting vertically installed bifacial PV modules facing east and west by establishing a test bed within Republic of Korea. Based on weather and generation data collected in Republic of Korea, located in the middle of latitude 34.98° N, from January to July 2023, we analyzed and compared the generation patterns, peak generation, peak hours, and total generation of conventional and vertical PV systems. Moreover, PVsyst was used to model the solar PV generation and analyze the consistency and viability of vertical PV generation by comparing actual operational data with simulation results. The vertical PV system demonstrated a peak power generation of 89.1% compared with the conventional PV system with bifacial modules. Based on operational data from January to July, the power generation output of the vertical PV system decreased to 65.7% compared with that of the conventional system with bifacial modules. This corresponded to 78.8% to 80.2% based on the PVsyst simulation results. In particular, the investigations related to the peak generation levels and occurrence times of vertical PV systems provide insights into the practicality of vertical solar PV systems and their potential for improving the PV hosting capacity.
1. Introduction
Policies promoting the adoption of renewable energy sources to achieve carbon neutrality and energy efficiency have been implemented globally. Consequently, the solar photovoltaic (PV) industry has experienced rapid growth owing to competitive pricing and the increased participation of various market players.
In 2022, the market shares of bifacial solar modules accounted for 65%. The manufacturing process of the bifacial module is similar to that of existing monofacial modules, so the manufacturing cost is similar, and as the rear of bifacial modules receives light and generates electricity, the power generation efficiency is 4~8% higher for the Passivated Emitter and Rear Contact (PERC) solar cell, so the bifacial module is applied to most solar power generation projects [1].
In addition, owing to the characteristics of bifacial modules that can generate power from both sides, a vertical solar power generation model that functions as a fence and soundproof wall is emerging. This vertical solar power generation model that uses bifacial modules can be used for building railings, fences, canopies, etc. [2]
The Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO) implemented a renewable energy connection guarantee system in Republic of Korea on 31 October 2016. The system ensured the connection of distributed power sources of 1 MW or less, which significantly increased applications for grid connections. The system places a burden on KEPCO to reinforce power facilities to accommodate the grid connection of small-scale renewable energy sources.
The resulting surge in waiting lists for grid connections highlights the need for infrastructure expansion, including distribution lines. This poses a financial burden on KEPCO owing to the need for new line installations, raising concerns about potential opposition from nearby residents regarding the installation of new power infrastructure.
The situation necessitates research and development to explore alternatives to expand grid connection lines.
KEPCO has been conducting studies to improve its hosting capacity for PV generation. The aim of this research is to study the feasibility of vertical solar PV systems, which differ from conventional systems in terms of installation conditions, to improve the PV hosting capacity and line utilization rate.
Many studies have been conducted on vertical PV systems using bifacial modules. In particular, research on the characterization methods of indoor/outdoor vertical PV systems [3,4] and studies on the application of vertical solar power generation systems to roofs and agriculture, focusing on electricity generation and additional income, have been published [5,6]. Moreover, studies have addressed the conditions to increase vertical solar power generation globally [7]. With the ongoing research on vertical solar power generation, studies that analyze the advantages and economic feasibility of vertical solar power generation under specific conditions have also been presented [8]. However, while these studies primarily use electricity generation data to discuss efficiency improvements, the present study is based on the analysis of electricity generation patterns and peak generation using actual operational data from a vertical solar power generation system over a period of seven months. The data on peak generation is crucial for analyzing the integration capacity of solar power generation into the actual distribution grid, and we plan to use it directly, referring to a similar study conducted under Nordic conditions [9].
2. Methods
Solar PV systems directly convert solar energy into electrical energy by absorbing photons within solar panels and creating electron–hole pairs. When connected to a load, current flows owing to the electric field generated at the P–N junction of a solar cell [10]. The establishment of mass production systems has reduced the prices of PV modules and their related components by a considerable margin. The solar PV industry in Republic of Korea was expected to achieve grid parity by 2021.
2.1. Purpose of Research
Various solar power generation systems have emerged under different installation conditions. The peak generation of PV systems is influenced by installation conditions. In the case of vertical systems, modules cannot optimize sunlight exposure, which results in a lower peak generation relative to the installed capacity. Consequently, a standard of grid integration based on operational performance, specifically peak generation, should be established, rather than the current standard based on the installed capacity. To this end, we construct and operate both conventional and vertical PV systems in the environmental conditions of Republic of Korea. The goal is to acquire a track record and analyze generation data, including peak generation and generation patterns.
2.2. Status of Solar PV Integration in Republic of Korea
As of December 2021, Republic of Korea has an installed solar PV capacity of approximately 21.2 GW. This capacity includes participation from various sources, such as the Korea Power eXchange (KPX) market participants with 5.8 GW, KEPCO power purchase agreements with 13.2 GW, behind-the-meter (BTM) installations, and other sources with 2.4 GW (Table 1) [11,12,13].

Table 1.
Cumulative installed capacity of PV system in Republic of Korea.
2.3. Characteristics of Vertical Solar Photovoltaic Systems
Conventional PV systems are fixed solar power generation structures designed for maximizing solar power generation. The tilt of solar modules is typically 25–30 degrees, and the azimuth is set to a directly southward direction (0°) (these values are based on installation standards in Republic of Korea and may vary depending on the installation location). The vertical PV system, on the other hand, arranges solar power generation modules vertically (at 90°) for specific user purposes, and the azimuth angle may vary depending on site conditions and objectives.
A conventional PV system typically experiences peak generation at midday when the Sun’s altitude is at its highest. By contrast, vertical PV systems, which are installed to face the east (front) and west (rear) directions using bifacial modules, exhibit a twin-peak generation pattern, with concentrated generation in the morning and afternoon [14].
Figure 1 illustrates an example of the contrasting generation patterns between conventional and vertical (installed in an east–west orientation) PV systems. A comparison of the monthly generation data between conventional and vertical solar panels indicates that depending on the installation environment, either the vertical system yields a higher generation output, or both types generate similar levels [6,8]. However, the specific generation level can vary based on factors such as the solar altitude of the location, climatic conditions, and other environmental variables.
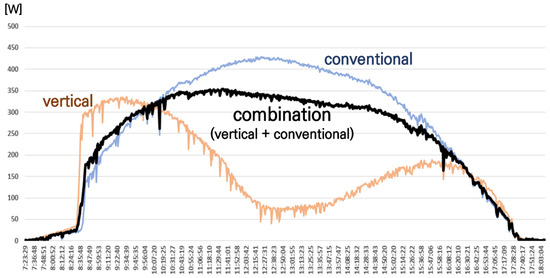
Figure 1.
Example of output patterns for conventional (blue line) PV, vertical PV (orange line), and combined with vertical and conventional PV (black line).
2.4. Trends in Vertical Solar Photovoltaic Generation
The concept of vertical installation with bifacial modules was first introduced by the German company Next2Sun in Supplementary Materials. The company has been conducting demonstrations at a scale of several MW. The system was implemented for various applications, including agricultural fencing, sound barriers, and building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV). Recently, research on improving the PV hosting capacity by combining vertical and conventional solar systems has been conducted [9].
In Republic of Korea, where mountains cover approximately 60% of the land area, vertical solar PV systems have emerged as a viable solution to be installed in various sites for specific purposes owing to the country’s unique topography. In addition, government initiatives and projects related to the technology are increasing.
2.5. Design of Vertical Solar Photovoltaic Systems
Designing a typical solar PV system is a vital step toward achieving optimal power generation by considering factors, such as weather conditions and transmission losses. To achieve this, various procedures are followed, including the selection of high-efficiency components, configuration of modules in series or parallel, and determining the spacing between arrays.
Supporting structures for solar panels are installed based on international standards, such as ISO 12006 [15], ensuring that they satisfy or exceed the required structural strength criteria. Electrical components and subsystems are designed in compliance with standard codes, such as IEC-60364 [16] and IEC-61936 [17], which determine the capacity of each electrical device, select appropriate cable and wire sizes, and establish grounding systems. In addition, practices in accordance with IEC-60909 [18] and IEC-61850 [19] are followed for grid integration and protection, including fault current calculations and protection relay coordination [20,21].
Table 2 lists the other key design parameters and conditions. The vertical PV system, which utilizes both bifacial and monofacial modules, is designed with a variety of azimuth conditions, as listed in Table 3, with 45° intervals facing a direct southward direction. Monofacial and bifacial modules with a 25° installation angle were installed to compare the power generation characteristics of conventional and vertical solar PV systems. Module-level power optimizers were installed to enhance data acquisition and analysis efficiency.

Table 2.
Test-bed design overview.

Table 3.
Shade impact simulation conceptual diagram (based on winter solstice 2022).
Furthermore, power optimizers increase the current, which may have been reduced to normal module levels using the DC/DC converter functionality owing to effects such as individual module shading and module-to-module mismatch within a string. By doing so, it prevents a decrease in the overall power generation of the string, enabling the inverter to perform optimal maximum power point tracking (MPPT) and optimize solar power generation [22].
In vertical solar PV systems, solar radiation sensors are placed on the front and back of the solar modules, along with surface temperature sensors on the back. By contrast, solar radiation sensors are installed on the structures of conventional solar PV systems with a 25° installation angle.
Table 3 presents the results of shadow impact simulations conducted using the SolarPro program to optimize the placement of the test-bed, which includes both conventional and vertical solar power generation systems. The system is designed to ensure there is no shadow impact within the modules based on the winter solstice in Republic of Korea, from 10:00 AM to 3:00 PM. When analyzing the snapshots captured at 10:00 AM and 3:00 PM, as shown in the “Overall bird’s eye view” in Table 2, it is evident that there is no shadow interference caused by adjacent structures on individual structures.
2.6. Construction of a Photovoltaic Generation System Test Bed
The solar PV system is based in the Naju City, Jeollanam-do, with a total installed capacity of 28.5 kW. It comprises vertical solar PV panels with a 14.8 kW capacity, conventional solar panels (oriented to the south with a 25° installation angle) with an 11.0 kW capacity, and tracking solar panels with a 2.7 kW capacity. Gravel is spread across the ground at power generation facilities to inhibit the growth of weeds and unwanted vegetation. Figure 2 is the actual view of the completed test-bed. In the constructed PV system, analysis is performed using data from vertical PV system using bifacial modules marked with a red box and conventional PV system using monofacial/bifacial modules. To acquire various types of data within the limited site area, the front and rear sides of the modules were arranged by crossing them within the same structure of vertical PV.
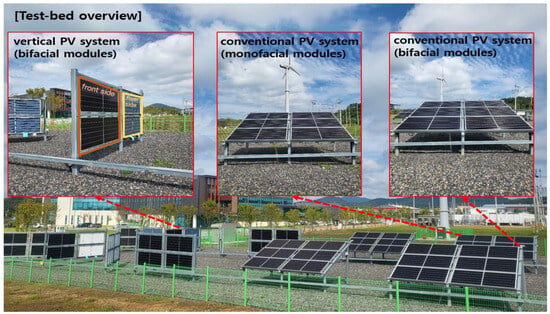
Figure 2.
Test-bed placement and data analysis targets (vertical and conventional PV which utilizes both bifacial and monofacial modules).
Monofacial and bifacial solar modules from Hanwha Q Cells with a 460 W rated power were used. For the bifacial modules, both the front and back sides had a 2 mm-thick glass to facilitate the output characteristic analysis. Table 4 and Table 5 list the specifications of the configured bifacial and monofacial modules, respectively.

Table 4.
Specifications of the bifacial module.

Table 5.
Specifications of the monofacial module.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Data Analysis of East–West-Facing Vertical Solar Photovoltaic System
The operating data under different installation conditions were monitored using the module-level voltage/current/power, inverter-level voltage/current/power, and weather sensors (solar radiation and temperature). Data were acquired at a minimum of 1-min intervals. However, data were analyzed at 1-h intervals. For example, the data recorded at 7 AM were the average values of the data acquired between 6 AM and 7 AM. Consequently, considering the differences in time resolution is necessary to compare the findings of this study with other cases based on a lower time resolution.
Data acquisition began in January 2023. For seven successive months, output analysis was performed based on days with clear skies and peak production days, as selected based on the daily average cloudiness data provided by the Korean Meteorological Administration (KMA) (Table 6). Slightly cloudy days were used as the basis for the analysis for July as there were no clear-sky days.

Table 6.
Amount of cloud.
Table 7 presents the operational results for the vertical solar power system with a 90° azimuth facing east–west. The values were calculated using the DC output data of a single module in the optimizer to minimize the effect of the variables on the output characteristics of the vertical solar power system. Table 7 lists the monthly average daily power generation and monthly capacity factor for the days, excluding periods of the abnormal operation and maintenance of the test bed.

Table 7.
Comparison of power generation and capacity factor between vertical (east–west) PV and conventional PV using bifacial/monofacial modules.
For clear-sky days, the power generation was averaged based on dates provided by the KMA, ranging from 0 to 2. Notably, a few cloudy days were used as substitutes for the calculations for July 2023 as there were no clear-sky days.
The monthly average daily power generation for the east–west vertical solar power generation system ranged from 913 kWh to 1492 kWh. The monthly capacity factor from January to July ranged from 8.3% to 13.5%. The peak power generation (1st peak) for the vertical solar power generation system with an east-facing front occurred in the morning, followed by a second peak generation time in the afternoon, owing to the rear-facing west side of the modules. This resulted in a twin-peak generation pattern, as shown in Figure 3.
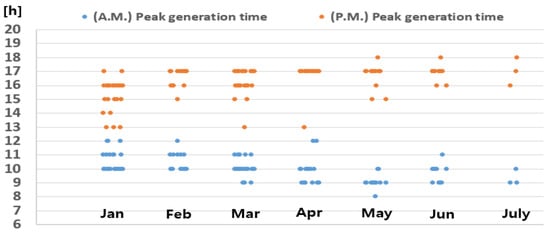
Figure 3.
Distribution of monthly concentrated power generation time for vertical PV in the east–west direction.
Figure 3 illustrates the distribution of the peak generation times in the morning and afternoon from January to July for the days that were either clear or had minimal cloud cover. In January, the peak generation occurred at 10–11 AM and 3–4 PM. As the analysis progressed toward July, peak generation was observed at approximately 9 AM and 5 PM. Table 8 lists the concentrated generation times on the peak days for each month.

Table 8.
Concentrated generation times (1st peak/secondary peak) of vertical PV.
The total energy generation and peak generation values must be considered for the hosting capacity. The monthly maximum output values listed in Table 9 indicate that the peak generation occurred in January at 89.1% of the installed capacity. Peak generation occurred on 25 January 2023.

Table 9.
Peak generation of vertical PV.
Several factors caused the relatively high peak generation on 25 January compared with the other months. On that day, the average temperature was −7.9 °C, according to the KMA, resulting in lower module heating effects. Additionally, as shown in Figure 4, there was a direct solar radiation of approximately 800 W/m2 during the concentrated generation hours for the vertical solar modules. This condition is conducive to the vertical solar panel generation during the winter months when the sun’s altitude is low.
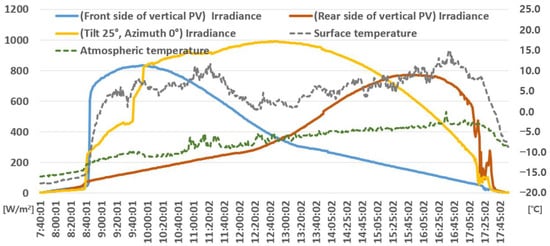
Figure 4.
Weather monitoring data for 25 January 2023.
The 25° installation angle for the structures also contributed to favorable conditions. The installed solar radiation sensor recorded daytime values of approximately 1000 W/m2, indicating excellent weather conditions.
In Figure 4, the blue and red solid lines represent the solar radiation measurements from the sensors installed on the front and back sides of the vertical solar modules, respectively. The yellow solid line represents the solar radiation measurement values from the sensors installed on the structures with a 25° installation angle. The grey and green dashed lines represent the atmospheric and module surface temperatures, respectively.
Furthermore, on that day, snow covered the ground, resulting in a high albedo of approximately 0.9 [23]. This high albedo indicated that a substantial amount of sunlight was reflected from the ground, increasing the front- and back-side generation of the module.
Peak generation in February started at 74% of the installed capacity and increased until April before gradually decreasing to 60.4% after May, influenced by changes in the sun’s altitude and weather conditions.
Table 10 presents detailed figures of the peak generation by time of day from January to July, as shown in Figure 5. In comparing the maximum outputs based on the operational performance between the bifacial vertical solar panels and conventional solar panels, Table 10 indicates that the peak generation of the vertical solar panels is lower. This difference can be attributed to the physical characteristics of the vertical solar panels based on their installation conditions.

Table 10.
Hourly peak generation results.
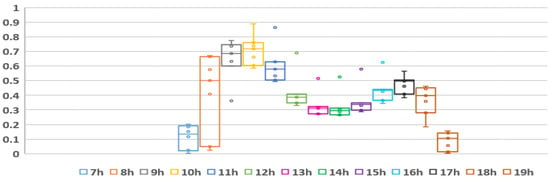
Figure 5.
Hourly Peak generation boxplot by time zone.
3.2. PVsyst Simulation Modeling
Simulations were performed using the PVsyst 7.3 program to predict the power generation of the solar PV systems. PVsyst is a specialized software used for annual power generation calculations and loss analysis of solar PV systems, including shading analysis. As shown in Figure 6, during the initial setup phase of the system, simple input variables were used to predict the installation angles, orientation-based effective surface area, and loss rates. In the simulation phase, system configuration and shading analyses were performed to calculate the loss rates and power generation [24].
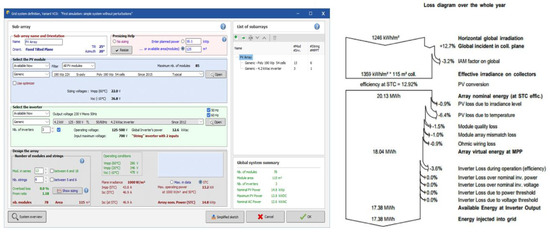
Figure 6.
Analysis conditions and results of PVsyst.
Key assumptions for the simulation of vertical PV systems included the modeling of vertical structures, the application of bifaciality for bifacial modules, and setting the albedo based on the actual ground conditions of the test site.
Table 11 lists the simulated conditions of the solar PV system used in this study.

Table 11.
Simulation conditions of the PVsyst program.
Weather data were obtained from Meteonorm 8.1 and KMA sources. Meteonorm 8.1 uses artificial satellite data in addition to ground-based observations, resulting in relatively low errors when calculating solar irradiance for domestic and international locations. KMA data are known for their high reliability with respect to domestic observation data; however, concerns may exist regarding errors when applied to locations far from the observation stations. As the KMA did not provide solar irradiance data for the Naju region, weather data for the Gwangju City were used for this research.
In the simulations, 6 kW systems were developed for the configurations, and mismatch losses were set to account for power loss caused by voltage and current mismatches between the modules and string voltage mismatches. For vertical PV systems, the module mismatch losses were set to 3%, and the string voltage mismatch was set to 0.2%. In addition, vertical PV systems, with a 90° installation angle and higher susceptibility to surface contaminant accumulation than conventional bifacial PV systems, had a module surface loss coefficient of 1.0%. A reference was made to experimental cases under similar overseas conditions to simulate a ground albedo similar to that of the actual test bed.
Table 12 lists the simulation results for each weather dataset. The table indicates that the power generation results from the KMA data under the same simulation conditions were slightly higher.

Table 12.
Power generation simulation results (kWh).
3.3. Comparison of PVsyst Simulation Results with Operational Data
Monthly power generation simulations were conducted for a solar PV system at the same location to compare the operational data and simulation results. The results were converted into monthly capacity factors based on the actual module ratings of 460 W.
Figure 7 and Figure 8 represent the capacity factor trends of the simulation results using two weather datasets and actual operational data from the test bed. For the conventional PV system, the operational data were higher than the simulation results from January to March and June. For the vertical PV system, the operational data closely matched the simulation results for January to March, but decreased thereafter. A slight decrease in the average capacity factor for the operational data in April and May was observed in both cases.
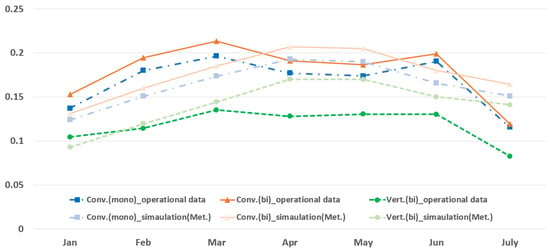
Figure 7.
Comparison of operational data and Meteonorm-based simulation results.
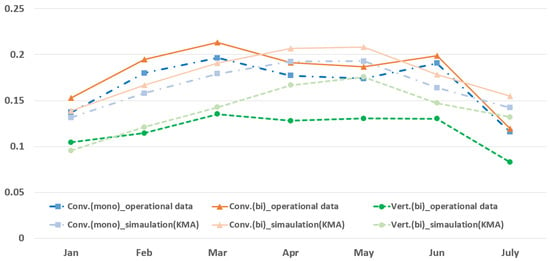
Figure 8.
Comparison of operational data and KMA-based simulation results.
Figure 9 shows the ratio of solar irradiance in 2023 to the monthly average solar irradiance from 1981–2022, as provided by the KMA [26]. The solar irradiance in 2023 was approximately 20% higher than the average from 1981 to 2022, but showed a similar pattern in April and May. This suggests that the operational data patterns for conventional PV systems were similar to those expected for normal operation on the test bed. However, for vertical PV systems, the significant decrease in power generation compared with the simulation results may have occurred because the PVsyst program does not calculate electrical losses when shading occurs on the rear side of the bifacial modules, and losses from reflected and diffused solar radiation owing to shading are limited.
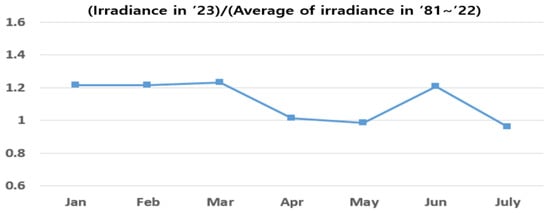
Figure 9.
Ratio of irradiance in 2023 compared to irradiance from 1981–2022.
4. Conclusions
This study aimed to acquire peak generation data track records of a vertical PV system, which are essential for analyzing the voltage stability and thermal capacity of the interconnected lines owing to solar power generation integration. Moreover, it aims to analyze the hourly generation peak and total generation.
To this end, a vertical solar PV system, designed and constructed using bifacial modules facing east (front) and west (rear), was analyzed based on operational data obtained from January to July 2023 in Republic of Korea.
The vertical PV system exhibited a peak power generation of 89.1% compared with the conventional PV system using bifacial modules. Based on operational data from January to July, the power generation output of the vertical PV system decreased to 65.7% compared with that of the conventional system with bifacial modules, corresponding to 78.8% to 80.2% based on the PVsyst results. However, power generation can be improved based on albedo in areas with heavy snowfall.
Vertical PV systems exhibit concentrated power generation in the morning and afternoon, which could enable an optimal power supply during peak demand times within a smart grid. In addition, owing to the concentrated power generation during sunrise and sunset, an output shift occurs, which could lead to the replacement effect of energy storage systems (ESS) and prevent power grid issues, such as the curtailment of renewable energy output [27].
Furthermore, considering the low peak power generation characteristics compared with conventional PV, a new grid connection method based on operational data can be developed to increase the PV hosting capacity and line utilization rate.
This study was based on seven months of empirical data. Therefore, economic analysis and further analysis on the impact of vertical PV systems on the power grid will be conducted based upon the availability of annual data to provide insights into improving the PV hosting capacity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/en16196971/s1, Agrivoltaics based on vertical bifacial PV by the German company Next2Sun.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.-S.K. and S.-H.Y.; methodology, W.-Y.L.; formal analysis, S.-M.L.; investigation, E.-C.L.; data curation, J.-H.L.; visualization, S.-M.L.; supervision, J.-S.H.; project administration, S.-M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Research Fund for the KEPCO Research Institute (R22EA03).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fregosi, D. Bifacial PV Perfomance Modeling. EPRI, U.S. In Proceedings of the IEEE 48th Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC), Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jouttijärvi, S.; Lobaccaro, G.; Kamppinen, A.; Miettunen, K. Benefits of bifacial solar cells combined with low voltage power grids at high latitudes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 161, 112354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.O.; Aberle, A.G.; Walsh, T.M. Electrical characterization method for bifacial photovoltaic modules. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 127, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.A.; Quispe, G.R.; Zamudio, M.A.; Conde, L.A.; Angulo, J.E.; Berastain, A.E.; Töfflinger, J.A. Outdoor I-V characterization of tilted and vertical bifacial PV modules. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2538, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, T.; Carigiet, F.; Knecht, R.; Klenk, M.; Dreisiebner, A.; Nussbaumer, H.; Baumgartner, F. Performance analysis of vertically mounted bifacial pv modules on green roof system. In Proceedings of the 35th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition (EU PVSEC 2018), Brussels, Belgium, 24–28 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Reker, S.; Schneider, J.; Gerhards, C. Integration of vertical solar power plants into a future German energy system. Smart Energy 2022, 7, 100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Khan, M.R.; Deline, C.; Alam, M.A. Optimization and Performance of Bifacial Solar Modules: A Global Perspective. Appl. Energy 2018, 212, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudinzow, D.; Nagel, S.; Gusewell, J.; Eltrop, L. Vertical bifacial photovoltaics—A complementary technology for the European electricity supply? Appl. Energy 2020, 264, 114782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouttij, S.A.; Thorning, J.; Manni, M.; Huerta, H.; Ranta, S.; Di Sabatino, M.; Lobaccaro, G.; Miettunen, K. A comprehensive methodological workflow to maximize solar energy in low-voltage grids: A case study of vertical bifacial panels in Nordic conditions. Sol. Energy 2023, 262, 111819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honsberg, C.; Bowden, S. PV CDROM; Photovoltaic Education Network: Solar Power Labs, Arizona State University: Tempe, AZ, USA, 2016; pp. 71–155. [Google Scholar]
- KNREC. Available online: https://www.knrec.or.kr/biz/statistics/supply/supply03_01_list.do (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- KEPCO. Available online: https://home.kepco.co.kr/kepco/KO/ntcob/list.do?boardCd=BRD_000097&menuCd=FN05030101 (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- KPX. Available online: https://epsis.kpx.or.kr/epsisnew/selectEkifBoardList.do?menuId=080200&boardId=020000 (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Khanb, M.R.; Hannaa, A.; Sunb, X.; Alam, M.A. Vertical bifacial solar farms: Physics, design, and global optimization. Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 12006-2:2015; Building Construction—Organization of Information about Construction Works. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- IEC 60364-1:2005; Low-Voltage Electrical Installations-Part 1: Fundamental Principles, Assessment of General Characteristics, Definitions. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- IEC 61936-2:2023; Power Installations Exceeding 1 kV AC and 1,5 kV DC-Part 2: DC. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- IEC 60909-0:2016; Short-Circuit Currents in Three-Phase A.C. Systems-Part 0: Calculation of Currents. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- IEC 61850:2023; SER, Communication Networks and Systems for Power Utility Automation-All Parts. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Dunlop, E.D.; Gracia Amillo, A.; Salis, E.; Sample, T.; Taylor, N. Standards for the Assessment of the Environmental Performance of Photovoltaic Modules, Power Conditioning Components and Photovoltaic Systems. European Union, Luxembourg. 2018. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/168398814.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Sarkar, S.; Bhaskar, M.S.; Rao, K.U.; Prema, V.; Almakhles, D.; Subramaniam, U. Solar PV network installation standards and cost estimation guidelines for smart cities. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firstsilicon. Available online: http://www.firstsilicon.co.kr/bbs/content.php?co_id=PowerOptimizer (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Cleantechnica. Available online: https://cleantechnica.com/2019/02/18/nrel-builds-first-solar-database-for-bifacial-albedo/ (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Gi-Cheol, K.; Min-Seok, O.; Kyu-Hong, H.; Seong-Ryong, R. Comparative Analysis for Vertical Photovoltaic System Based on Light-receiving Efficiency and Solar Installation Area. J. Korean Inst. Archit. Sustain. Environ. Build. Syst. 2022, 16, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, B. Ground Albedo Field Measurements. In Proceedings of the NREL Bifacial PV Workshop 2018. SUNPOWER, Lakewood, CO, USA, 10–11 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Woo-young, L.; Seoul 04789, Republic of Korea. Personal communication, 2023.
- Obara, S.; Konno, D.; Utsugi, Y.; Morel, J. Analysis of output power and capacity reduction in electrical storage facilities by peak shift control of PV system with bifacial modules. Appl. Energy 2014, 128, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).