Synthesis of 1-Hexanol/Hexyl hexanoate Mixtures from Grape Pomace: Insights on Diesel Engine Performances at High Bio-Blendstock Loadings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Catalyst Characterization
2.3. Hydrogenation Reactions
2.4. Engine Setup
3. Results
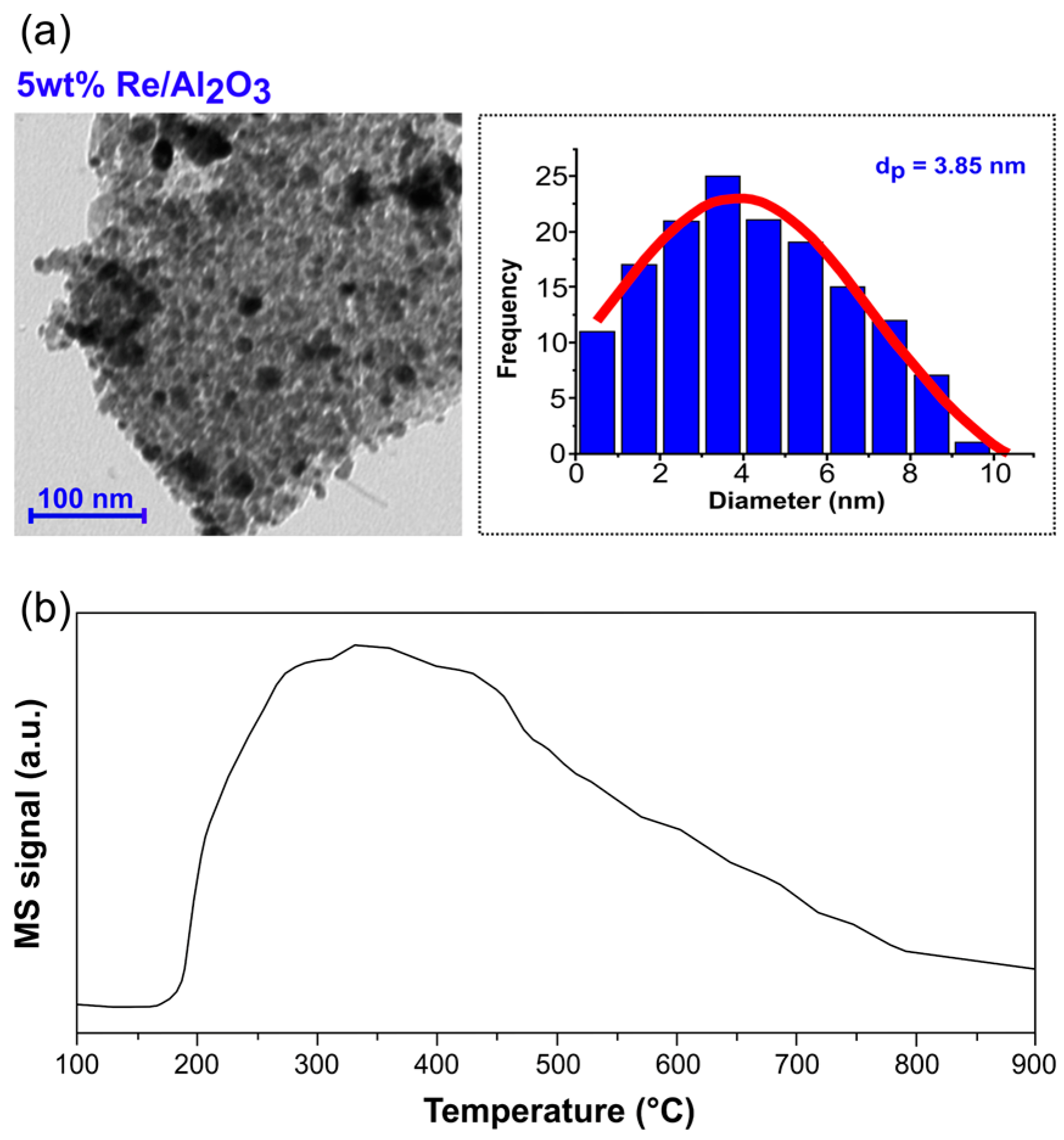
3.1. Hydrogenation of Hexanoic Acid with 5 wt% Re/γ-Al2O3
3.2. Additives Definition for Engine Tests
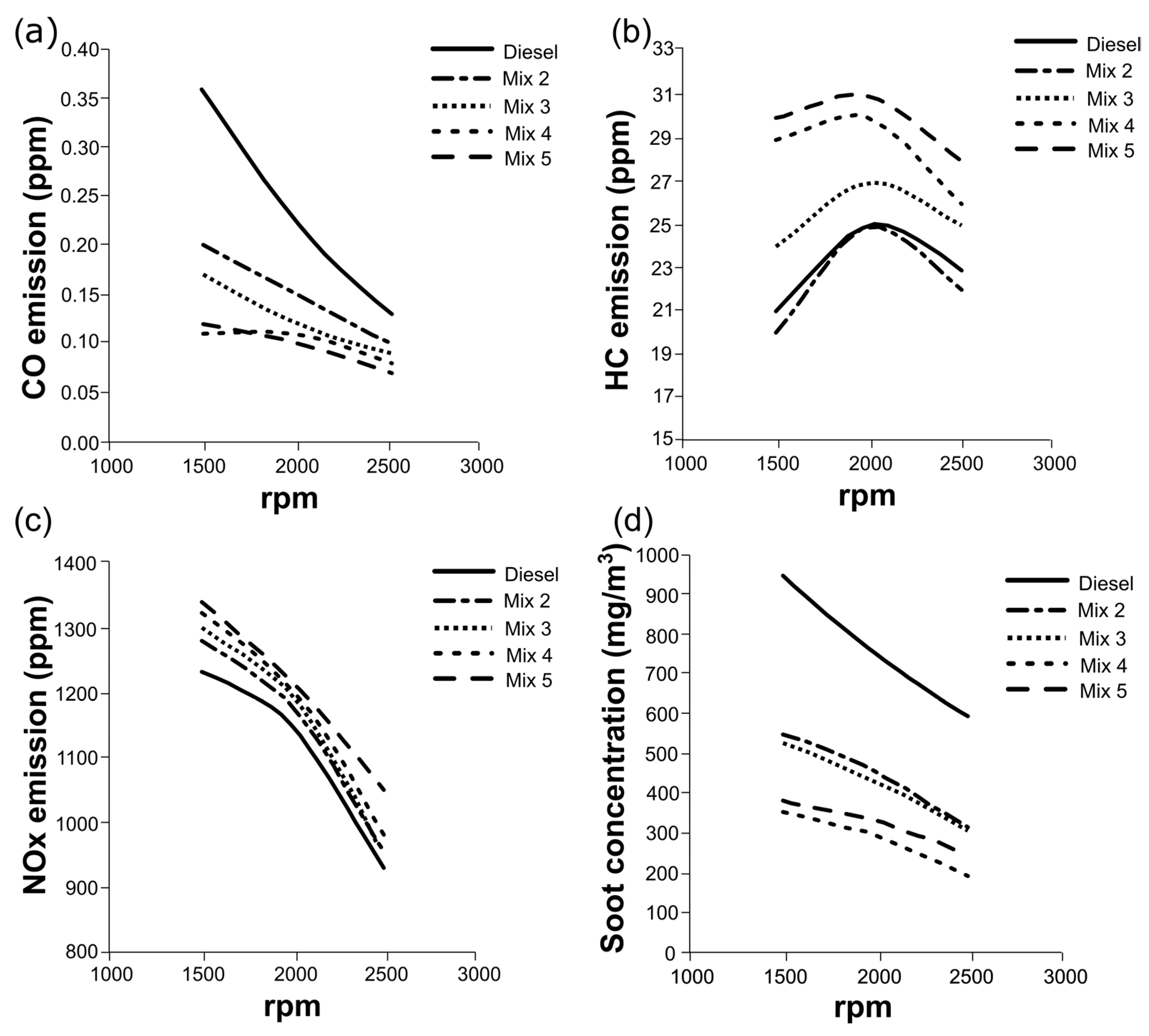
3.3. Engine Tests with HexOH or HexHex with Diesel Fuel
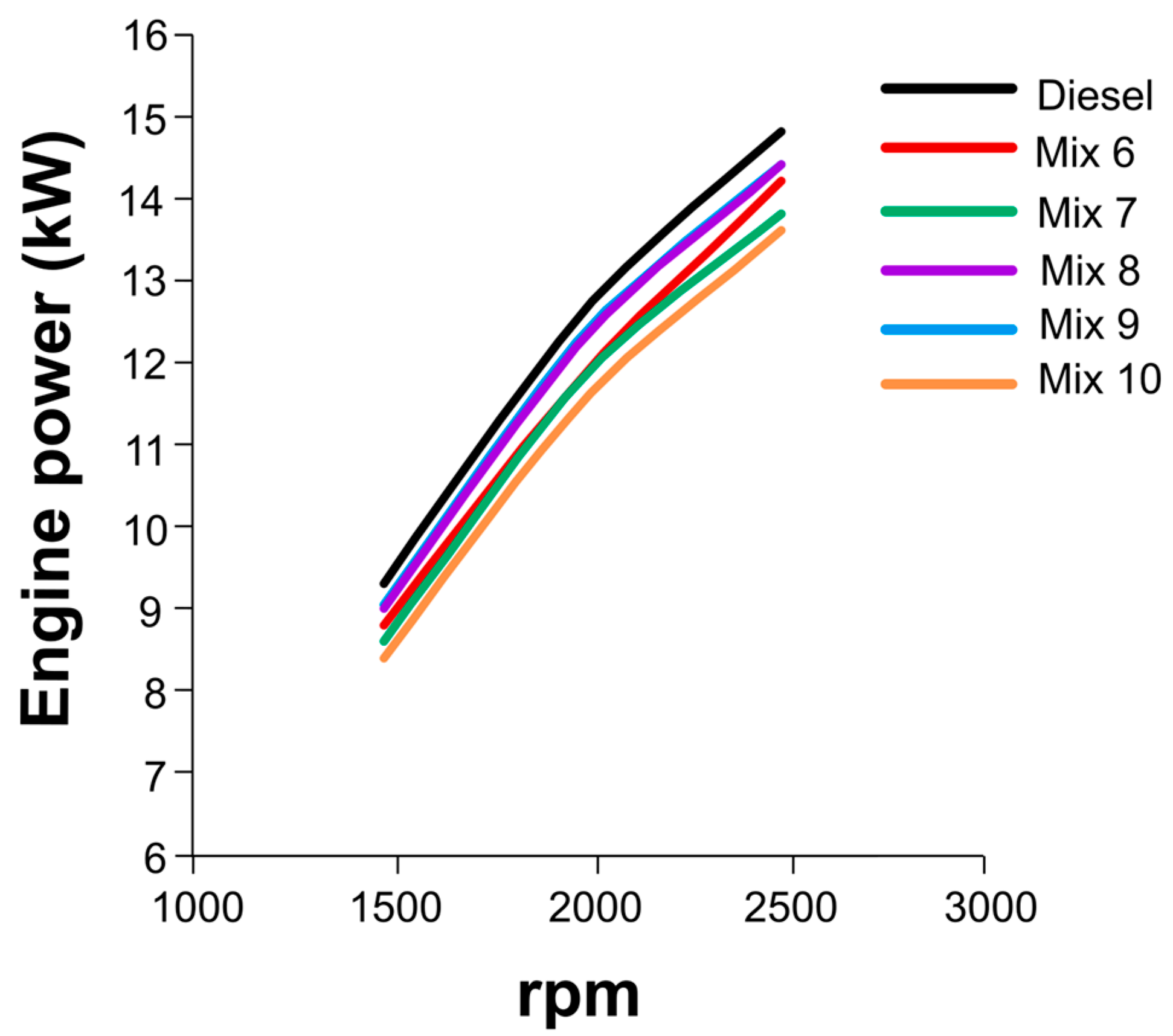
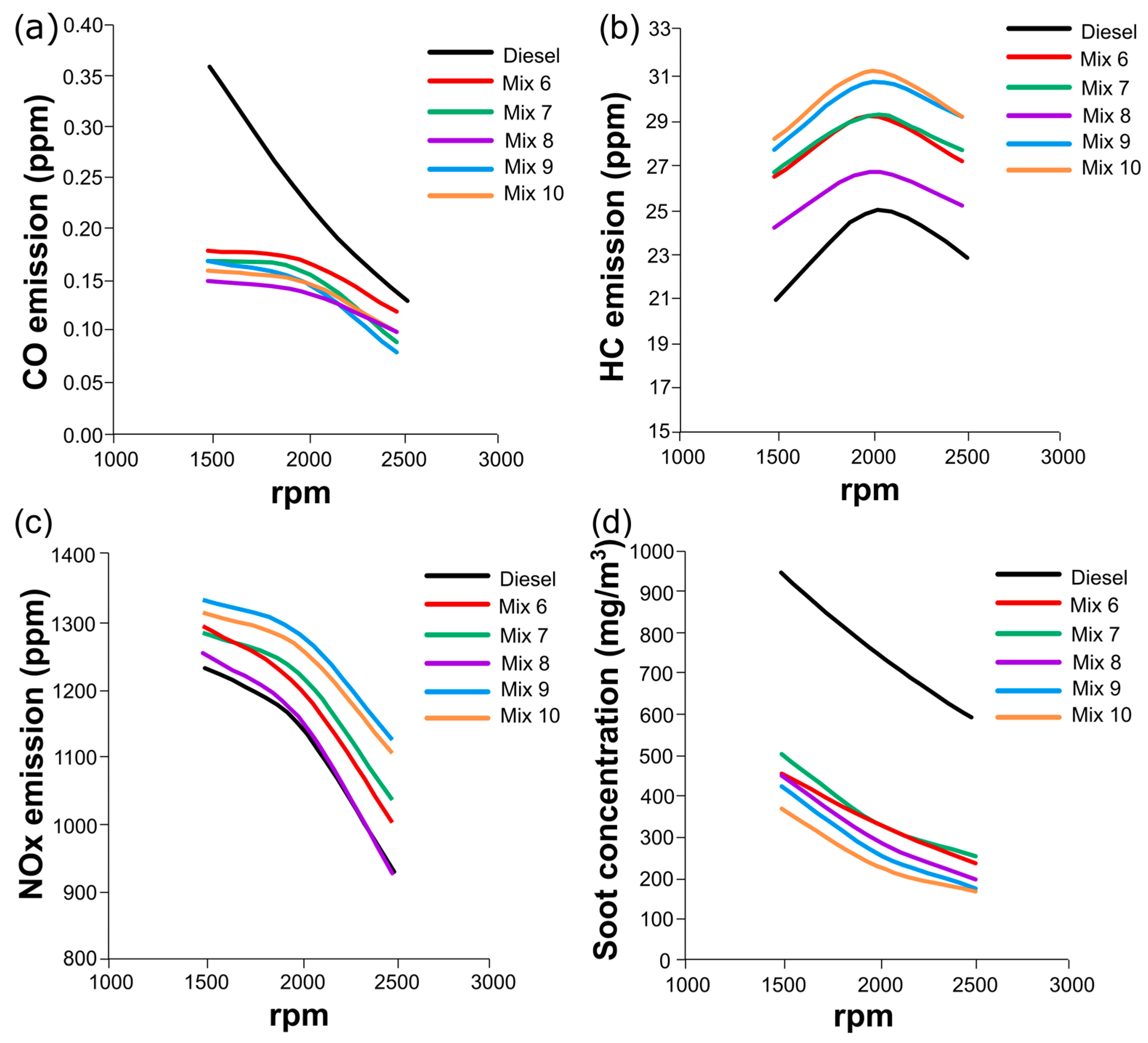
3.4. Engine Tests with Mixtures of HexOH/HexHex with Diesel Fuel
3.5. Engine Combustion Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| CA° | crank angle |
| CCD | charge coupled device |
| CN | cetane number |
| COVimep | coefficient of variation of the indicated mean effective pressure |
| GC-FID | gas chromatography–flame ionization detector |
| GC-MS | gas chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| HC | hydrocarbon |
| HexHex | hexyl hexanoate |
| HexOH | 1-hexanol |
| ICEs | internal combustion engines |
| ICP-OES | inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectroscopy |
| ISG | integrated starter generator |
| LHV | lower heating value |
| MFB50 | mass fraction burned 50% |
| NbPO | niobium phosphate |
| TCD | temperature conductivity detector |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| TPD | temperature-programmed desorption |
References
- Volumetric Energy Density of Lithium-Ion Batteries Increased by More Than Eight Times between 2008 and 2020. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/eere/vehicles/articles/fotw-1234-april-18-2022-volumetric-energy-density-lithium-ion-batteries (accessed on 30 August 2023).
- IEA. Global EV Outlook 2022. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2022 (accessed on 30 August 2023).
- Abdellatief, T.M.M.; Ershov, M.A.; Kapustin, V.M. New recipes for producing a high-octane gasoline based on naphtha from natural gas condensate. Fuel 2020, 276, 118075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shebli, M.N.; Raj, A.; Elkadi, M.; Anjum, D.; Pena, G.D.J.; Prabhu, A. Fuel oxygenation as a novel method to reduce sooting propensity of fuels: An investigation with gasoline surrogate fuels. Fuel 2022, 324, 124562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatief, T.M.M.; Ershov, M.A.; Kapustin, V.M.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Kamil, M.; Olabi, A.G. Recent trends for introducing promising fuel components to enhance the anti-knock quality of gasoline: A systematic review. Fuel 2021, 291, 120112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, K. Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rodionova, M.V.; Poudyal, R.S.; Tiwari, I.; Voloshin, R.A.; Zharmukhamedov, S.K.; Nam, H.G.; Zayadan, B.K.; Bruce, B.D.; Hou, H.J.M.; Allakherdiev, S.I. Biofuel production: Challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 8450–8461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florin, M.J.; van de Ven, G.W.J.; van Ittersum, M.K. What drives sustainable biofuels? A review of indicator assessments of biofuel production systems involving small holder farmers. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 37, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Verma, P. Biomass-based biorefineries: An important architype towards a circular economy. Fuel 2021, 288, 119622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlNazr, H.A.; Ahmad, N.; Ahmed, U.; Mohan, B.; Jameel, A.G.A. Predicting physical properties of oxygenated gasoline and diesel range fuels using machine learning. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 76, 193–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, A.; Sinha, A.; Chaubey, K.K.; Hariharan, S.; Dayal, D.; Bachheti, R.K.; Bachheti, A.; Chandel, A.K. Second-generation bio-fuels: Strategies for employing degraded land for climate change mitigation meeting United Nation-sustainable development goals. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalwan, H.A.; Alminshid, A.H.; Aljaafari, H.A.S. Promising evolution of biofuel generations. Subject review. Renew. Energy Focus 2019, 28, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugapoopathi, S.; Ramachandran, T.; Rajaganapathy, C. Theoretical performance on energy and exergy analysis of methyl esters of rubber seed oil fuelled on supercharged VCR engine. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, V.; Venkatkarthick, R.; Jayashree, S.; Chuetor, S.; Dharmaraj, S.; Kumar, G.; Chen, W.H.; Ngamcharussrivichai, C. Recent advances in lignocellulosic biomass for biofuels and value-added bioproducts—A critical review. Biores. Technol. 2022, 344, 126195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çelebi, Y.; Aydın, H. An overview on the light alcohol fuels in diesel engines. Fuel 2019, 236, 890–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargün, M.; Özsezen, A.N. Evaluation of the effect of the fuel injection phase on the combustion and exhaust characteristics in a diesel engine operating with alcohol-diesel mixtures. Energy 2023, 270, 126975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musyoka, S.K.; Khalil, A.S.G.; Ookawara, S.A.; Elwardany, A.E. Effect of C4 alcohol and ester as fuel additives on diesel engine operating characteristics. Fuel 2023, 341, 127656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Miao, C.; Zhuang, X.; Li, W.; Tan, X.; Yang, T. Physicochemical characterization of levulinate esters with different alkyl chain lengths blended with fuel. Energy Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, C.; Xueqin, L.; Zhiwei, W.; Yantao, Y.; Tanglei, S.; Taoli, H.; Peng, L.; Yanling, L.; Youqing, W.; Tingzhou, L.; et al. Techno-economic and whole life cycle assessment of ester fuels production from agricultural waste via hydrothermal liquefaction. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 192, 116096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartling, A.W.; Benavides, P.T.; Phillips, S.D.; Hawkins, T.; Singh, A.; Wiatrowski, M.; Tan, E.C.D.; Kinchin, C.; Ou, L.; Cai, H.; et al. Environmental, economic, and scalability considerations of selected bio-derived blendstocks for mixing-controlled compression ignition engines. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 6699–6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Dai, J.; Liu, Z.; Lee, T.H.; Zhang, C. Optical study on spray, combustion and flame characteristics of n-hexanol/diesel blends under various diesel engine-like conditions. Fuel 2022, 325, 124941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Gao, S.; Zhao, W.; Lee, T.H. Study of combustion and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with diesel, butanol-diesel and hexanol-diesel mixtures under low intake pressure conditions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 243, 114273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, K.; Kumar, G.N. Effect of injection time on combustion, performance and emission characteristics of direct injection CI engine fuelled with equi-volume of 1-hexanol/diesel blends. Energy 2021, 214, 118984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, M.; Sun, Z.; El-Seesy, A.I.; Li, X. Experimental evaluation of the performance and emissions of a direct-injection compression-ignition engine fueled with n-hexanol–diesel blends. Fuel 2021, 302, 121144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.J.; Sabu, V.R.; Basrin, G.; Nagarajan, G. Hexanol: A renewable low reactivity fuel for RCCI combustion. Fuel 2021, 286, 119294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Poures, M.V.; Sathiyagnanam, A.P.; Rana, D.; Kumar, B.R.; Saravanan, S. 1-hexanol as a sustainable biofuel in DI diesel engines and its effect on combustion and emissions under the influence of injection timing and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR). Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 113, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelam, N.; Gugulothu, S.K.; Reddy, R.V.; Burra, B. Influence of hexanol/hydrogen additives with diesel fuel from CRDI diesel engine with exhaust gas recirculation technique: A special focus on performance, combustion, gaseous and emission species. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.J.; Manojkumar, C.V.; Sabu, V.R.; Nagarajan, G. Development and validation of a reduced chemical kinetic model for used vegetable oil biodiesel/1-hexanol blend for engine application. Fuel 2020, 273, 117780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioroni, G.; Fouts, L.; Luecke, J.; Vardon, D.; Huq, N.; Christensen, E.; Huo, X.; Alleman, T.; McCormick, R.; Kass, M.; et al. Screening of potential biomass-derived streams as fuel additives for mixing controlled compression ignition combustion. SAE Int. J. Adv. Curr. Prac. Mobil. 2019, 1, 1117–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayagopal, R.; Curran, S.; Deter, D.; Longman, D. Evaluating Class 6 Delivery Truck Fuel Economy and Emissions using Vehicle System Simulations for Conventional and Hybrid Powertrains and Co-Optima Fuel Blends; SAE Technical Paper 2022-01-1156; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, M.D.; Janke, C.J.; Connatser, R.M.; Lewis, S. Compatibility of biologically derivable alcohols, alkanes, esters, ketones, and an ether as diesel blendstocks with fuel system elastomers. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 4979–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, M.; Janke, C.; Nafziger, E. Impact of Biodiesel, Renewable Diesel, 1-Octanol, Dibutoxymethane, n-Undecane, Hexyl Hexanoate and 2-Nonanone with Infrastructure Plastics as Blends with Diesel; SAE Technical Paper 2022-01-0487; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzeteu, C.O.; Trego, A.C.; Abram, F.; O’Flaherty, V. Reproducible, high-yielding, biological caproate production from food waste using a single-phase anaerobic reactor system. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzola, G.; Braguglia, C.M.; Crognale, S.; Gallipoli, A.; Mininni, G.; Piemonte, V.; Rossetti, S.; Tonanzi, B.; Gianico, A. Biorefining of food waste through the anaerobic conversion of endogenous lactate into caproate: A fragile balance between microbial substrate utilization and product inhibition. Waste Manag. 2022, 150, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, Y.K.; Vidal-Antich, C.; Dosta, J.; Mata-Álarez, J. Volatile fatty acid production from mesophilic acidogenic fermentation of organic fraction of municipal solid waste and food waste under acidic and alkaline pH. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 35509–35522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duber, A.; Jaroszynski, L.; Zagrodnik, R.; Chwialkowska, J.; Juzwa, W.; Ciesielski, S.; Oleskowicz-Popiel, P. Exploiting the real wastewater potential for resource recovery—n-caproate production from acid whey. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 3790–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Arroyo, J.M.; Candry, P.; Andersen, S.J.; Props, R.; Seviour, T.; Ganigué, R.; Rabaey, K. Granular fermentation enables high rate caproic acid production from solid-free thin stillage. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, G.A.; Puccio, S.; Domingos, J.M.B.; Morselli, E.; Gioia, C.; Marchese, P.; Raspolli Galletti, A.M.; Celli, A.; Fava, F.; Bertin, L. Upgrading grape pomace contained ethanol into hexanoic acid, fuel additives and a sticky polyhydroxyalkanoate: An effective alternative to ethanol distillation. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 2882–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchiocchi, R.; De Maron, J.; Tabanelli, T.; Bianchi, D.; Cavani, F. Supported rhenium catalysts for the hydrogenation of levulinic acid derivatives: Limits and potential. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2023, 7, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothe, M.L.; Silva, K.L.C.; Figueredo, A.L.; Fiorio, J.L.; Rozendo, J.; Manduca, B.; Simizu, V.; Freire, R.S.; Garcia, M.A.S.; Vidinha, P. Rhenium–A tuneable player in tailored hydrogenation catalysis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 39, 4043–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licursi, D.; Raspolli Galletti, A.M.; Antonetti, C.; Martinez, G.A.; Jones, E.; Bertin, L.; Di Fidio, N.; Fulignati, S.; Pasini, G.; Frigo, S. Tunable production of diesel bio-blendstock by rhenium-catalysed hydrogenation of crude hexanoic acid from grape pomace fermentation. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonetti, C.; Gori, S.; Licursi, D.; Pasini, G.; Frigo, S.; López, M.; Parajó, J.C.; Raspolli Galletti, A.M. One-pot alcoholysis of the lignocellulosic Eucalyptus nitens biomass to n-butyl levulinate, a valuable additive for diesel motor fuel. Catalysts 2020, 10, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigo, S.; Pasini, G.; Caposciutti, G.; Antonelli, M.; Raspolli Galletti, A.M.; Gori, S.; Costi, R.; Arnone, L. Utilisation of advanced biofuel in CI internal combustion engines. Fuel 2021, 297, 120742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulignati, S.; Antonetti, C.; Wilbers, E.; Licursi, D.; Heeres, H.J.; Raspolli Galletti, A.M. Tunable HMF hydrogenation to furan diols in a flow reactor using Ru/C as catalyst. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 100, 390.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchave, G.J.; de S. Netto, L.D.; Almeida, J.M.A.R.; Aranda, D.A.G. Synthesis of fatty alcohols by hydrogenation of palm esters using rhenium-based catalysts supported on niobia, alumina and titania. Int. J. Develop. Res. 2020, 10, 42266–42278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, D.; Anand, R. Effect of biodiesel-diesel-n-pentanol and biodiesel-diesel-n-hexanol blends on diesel engine emission and combustion characteristics. Energy 2017, 133, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Huq, N.A.; Stunkel, J.; Cleveland, N.S.; Starace, A.K.; Settle, A.E.; York, A.M.; Nelson, R.S.; Brandner, D.G.; Fouts, L.; et al. Tailoring diesel bioblendstock from integrated catalytic upgrading of carboxylic acids: A “fuel property first” approach. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 5813–5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuff, A.S.; Dada, T.; Olateju, I.I.; Azeez, T.M.; Azeez, S.O. Experimental investigation of influence of methyl, ethyl and methyl-ethyl ester blends of used cooking oil engine performances and emissions. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2023, 17, 100346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.R.; Saravanan, S. Use of higher alcohol biofuels in diesel engines: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 84–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, J.B. Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Herreros, J.M.; Jones, A.; Sukjit, E.; Tsolakis, A. Blending lignin-derived oxygenate in enhanced multi-component diesel fuel for improved emissions. Appl. Energy 2014, 116, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.C.K.; Karmakar, S.; Basu, S. Atomization characteristics and instabilities in the combustion of multi-component fuel droplets with high volatility differential. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasheras, J.C.; Fernandez-Pello, A.C.; Dryer, F.L. Experimental observations on the disruptive combustion of free droplets of multicomponent fuels. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1980, 22, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Engine Type | Lombardini 9LD 625/2 |
| Number of cylinders | 2 |
| Cooling system | Forced air |
| Displacement (cm3) | 1248 |
| Bore (mm) | 95 |
| Stroke (mm) | 88 |
| Compression ratio | 17.5:1 |
| Max rotational speed (rpm) | 3000 |
| Power @ 3000 rpm (kW) | 21 |
| Max Torque @ 2200 rpm (Nm) | 29.4 |
| Fuel injection system | Direct-Mechanic |
| Mix | HexOH (vol%) | HexHex (vol%) | Diesel (vol%) | HexOH/HexHex (mol/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | Not applicable |
| 2 | 10 | 0 | 90 | Not applicable |
| 3 | 0 | 10 | 90 | Not applicable |
| 4 | 20 | 0 | 80 | Not applicable |
| 5 | 0 | 20 | 80 | Not applicable |
| 6 | 5.2 | 4.8 | 90 | 2/1 |
| 7 | 3.5 | 6.5 | 90 | 1/1 |
| 8 | 2.1 | 7.9 | 90 | 1/2 |
| 9 | 7 | 13 | 80 | 1/1 |
| 10 | 4.2 | 15.8 | 80 | 1/2 |
| Diesel | HexOH | HexHex | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm3) | 0.837 | 0.815 | 0.863 |
| Cinematic Viscosity (at 40 °C—cSt) | ≈2.7 | 3.64 | 2.37 |
| Self-Ignition Temperature (°C) | ≈300 | 285 | NA a |
| Latent Heat of Vaporization (kJ/kg) | 270–375 | 486 | NA a |
| Flash Point (°C) | 55 | 63 | 99 |
| Cetane number (CN) | >50 | 23 | 40 |
| Boiling point @1barA (°C) | 180–360 | 157 | 245 |
| Lower Heating Value (MJ/kg) | ≈43 | 39 | 35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frigo, S.; Raspolli Galletti, A.M.; Fulignati, S.; Licursi, D.; Bertin, L.; Martinez, G.A.; Pasini, G. Synthesis of 1-Hexanol/Hexyl hexanoate Mixtures from Grape Pomace: Insights on Diesel Engine Performances at High Bio-Blendstock Loadings. Energies 2023, 16, 6789. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196789
Frigo S, Raspolli Galletti AM, Fulignati S, Licursi D, Bertin L, Martinez GA, Pasini G. Synthesis of 1-Hexanol/Hexyl hexanoate Mixtures from Grape Pomace: Insights on Diesel Engine Performances at High Bio-Blendstock Loadings. Energies. 2023; 16(19):6789. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196789
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrigo, Stefano, Anna Maria Raspolli Galletti, Sara Fulignati, Domenico Licursi, Lorenzo Bertin, Gonzalo Agustin Martinez, and Gianluca Pasini. 2023. "Synthesis of 1-Hexanol/Hexyl hexanoate Mixtures from Grape Pomace: Insights on Diesel Engine Performances at High Bio-Blendstock Loadings" Energies 16, no. 19: 6789. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196789
APA StyleFrigo, S., Raspolli Galletti, A. M., Fulignati, S., Licursi, D., Bertin, L., Martinez, G. A., & Pasini, G. (2023). Synthesis of 1-Hexanol/Hexyl hexanoate Mixtures from Grape Pomace: Insights on Diesel Engine Performances at High Bio-Blendstock Loadings. Energies, 16(19), 6789. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196789










