Silver-Nanoparticle-Decorated Fused Carbon Sphere Composite as a Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
2.2. Synthesis of Fused Carbon Spheres (FCS)
2.3. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Supported over Fused Carbon Spheres (AgNP-FCS)
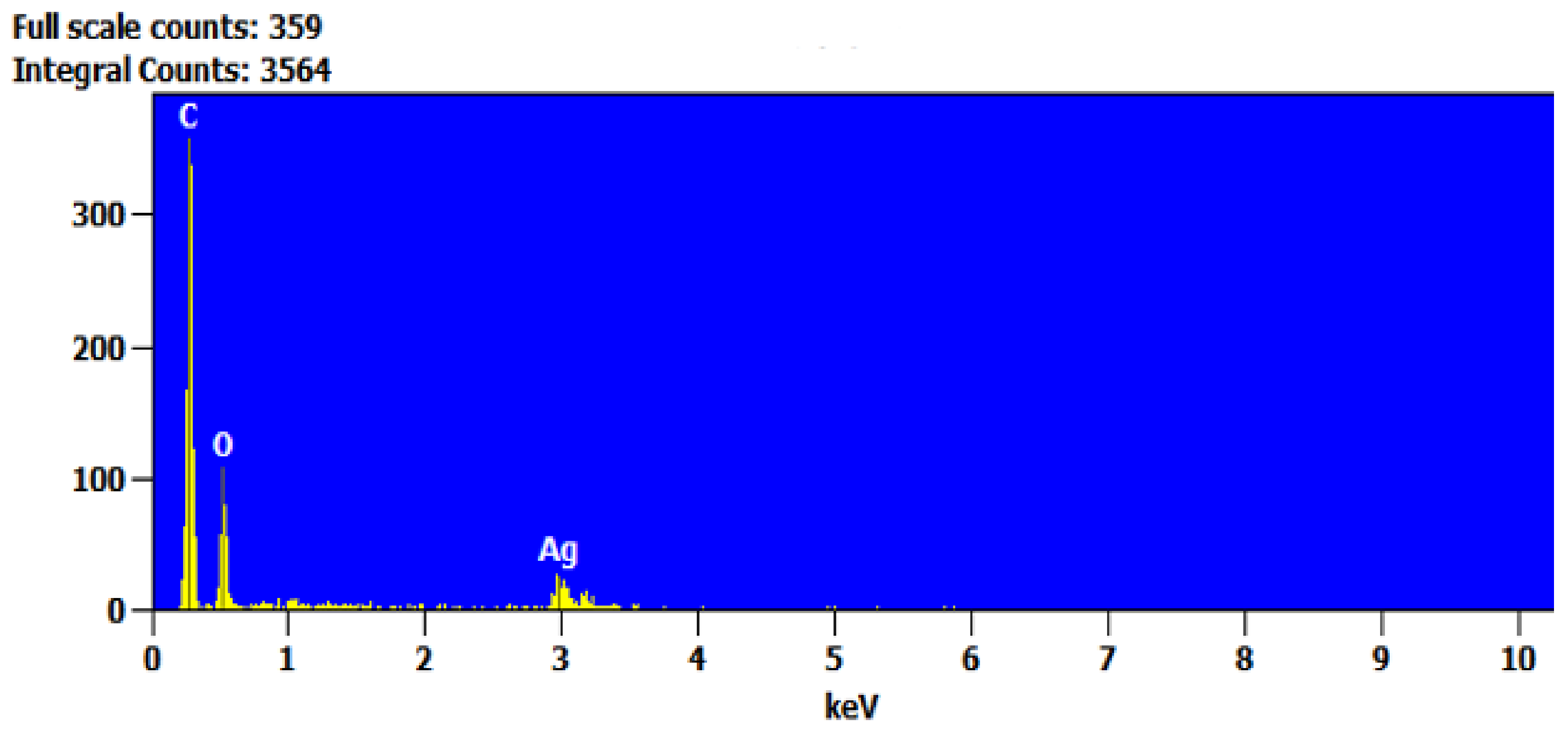
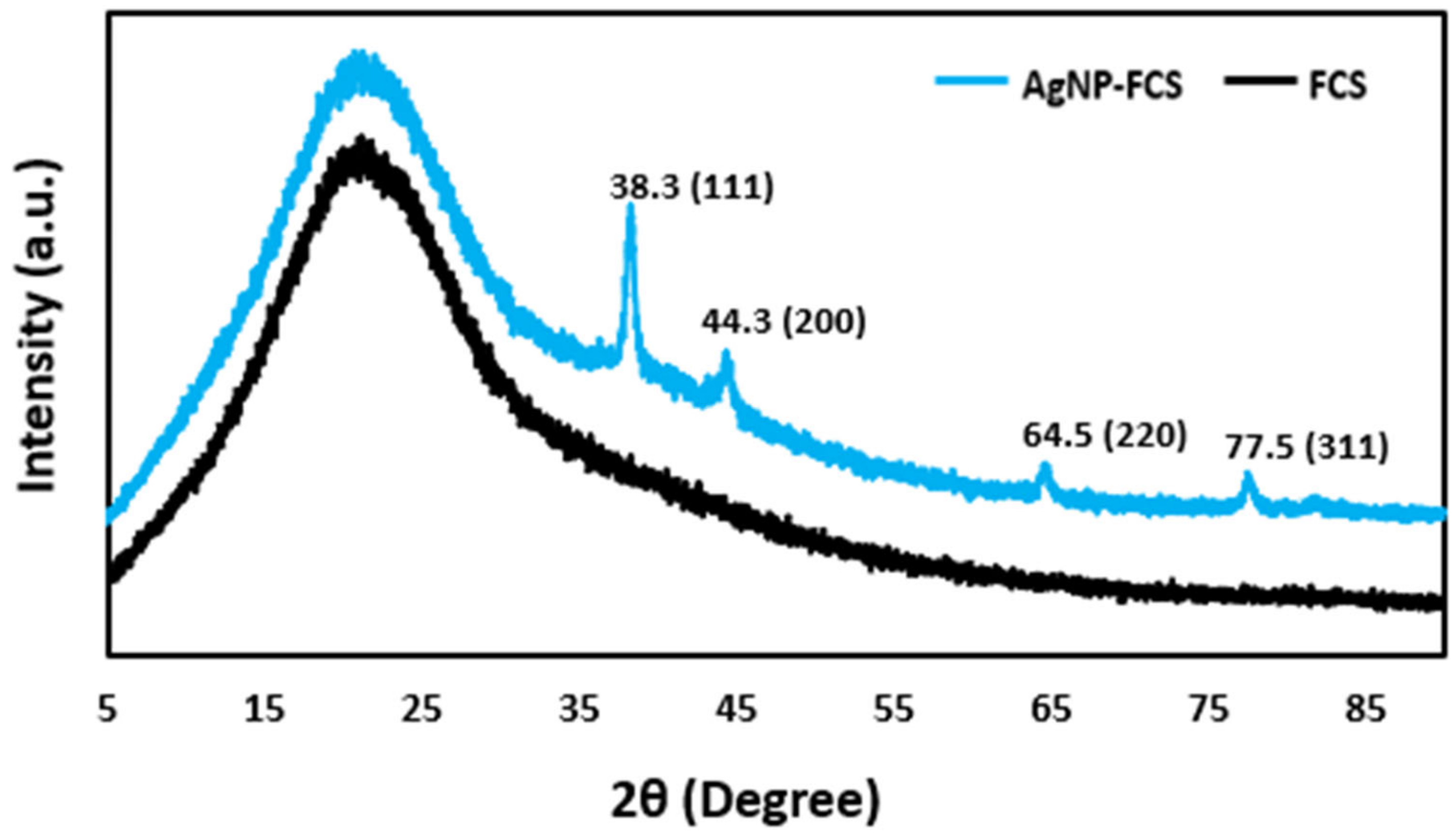
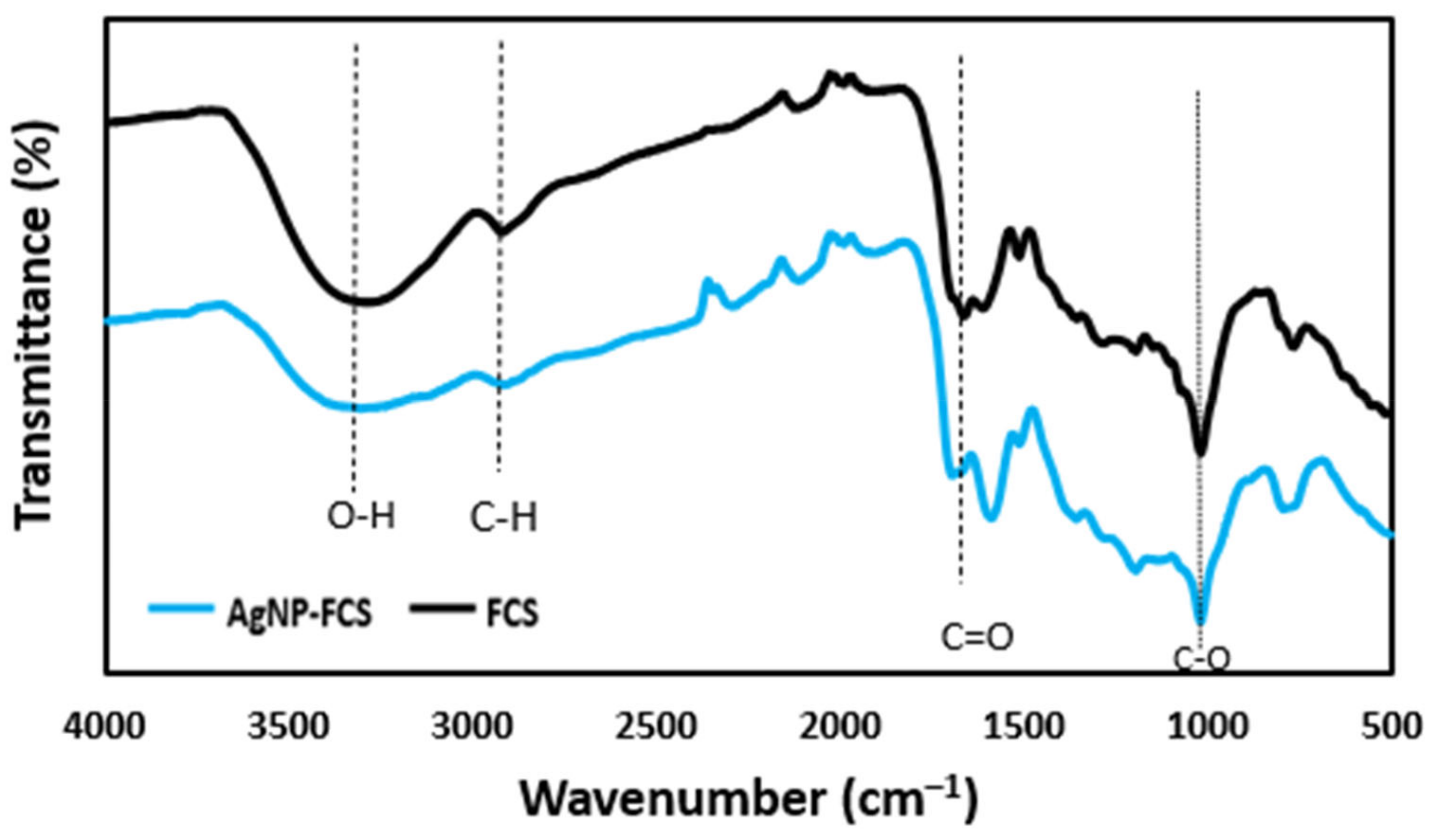
2.4. Characterization
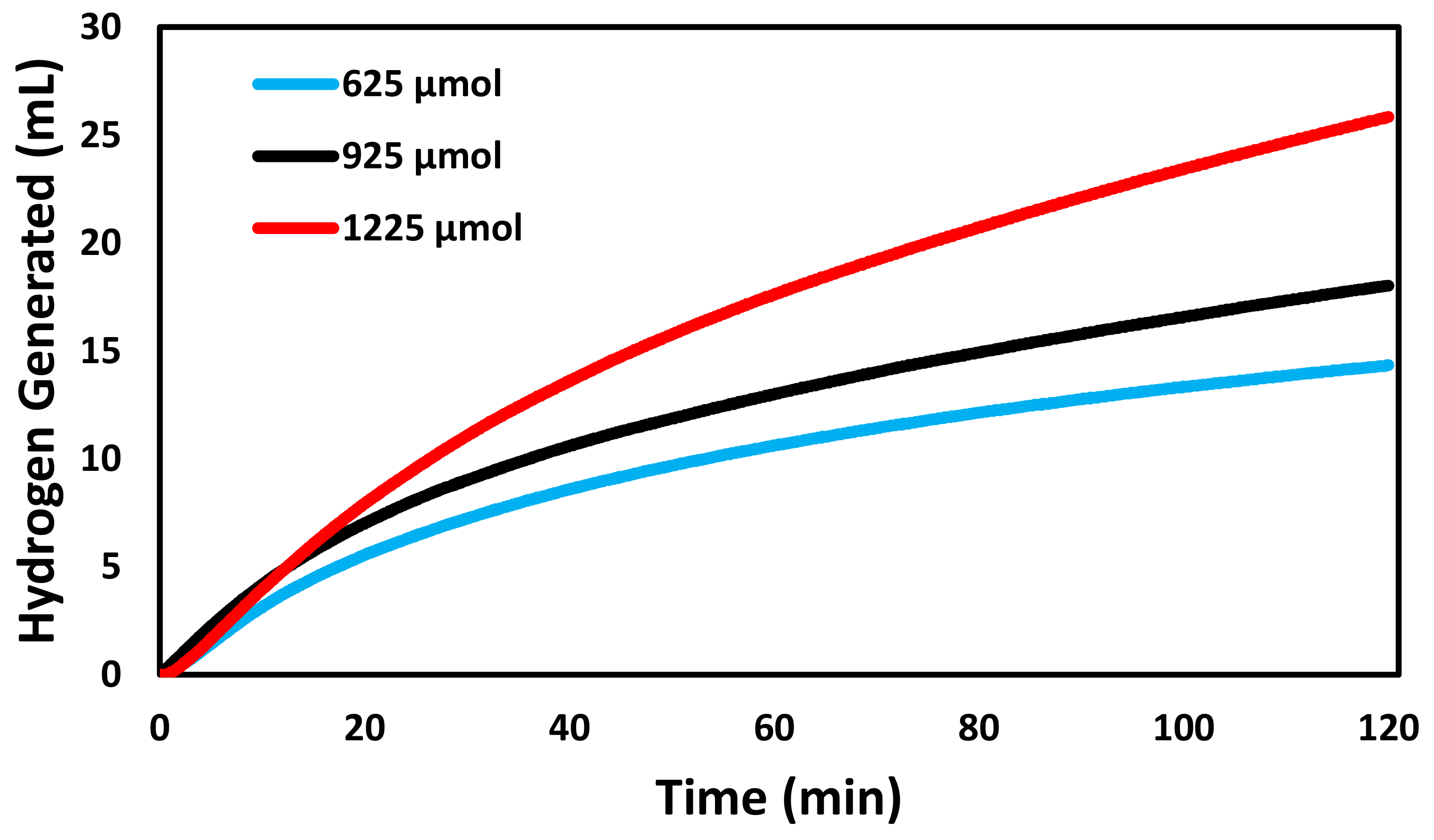
2.5. Catalysis
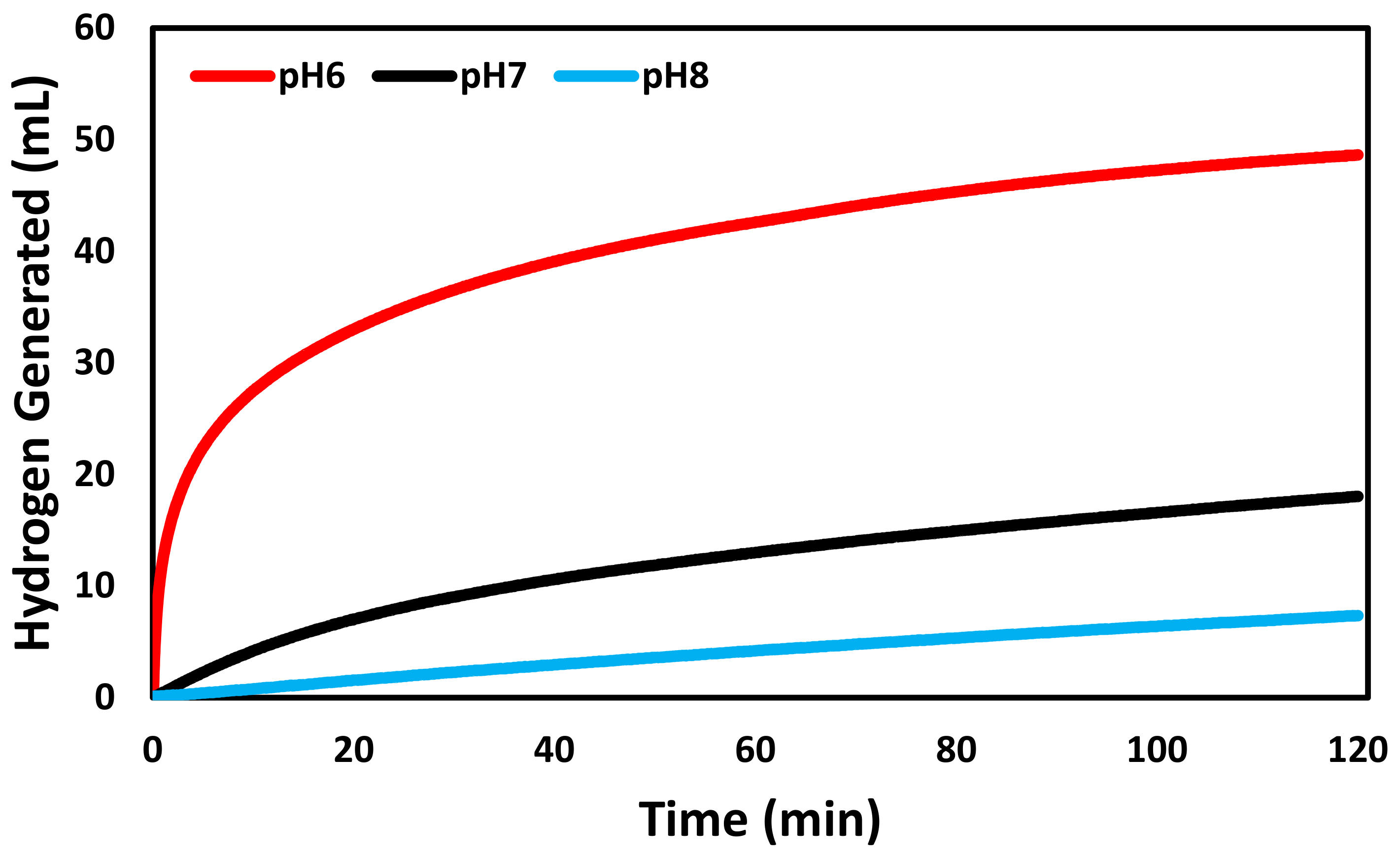
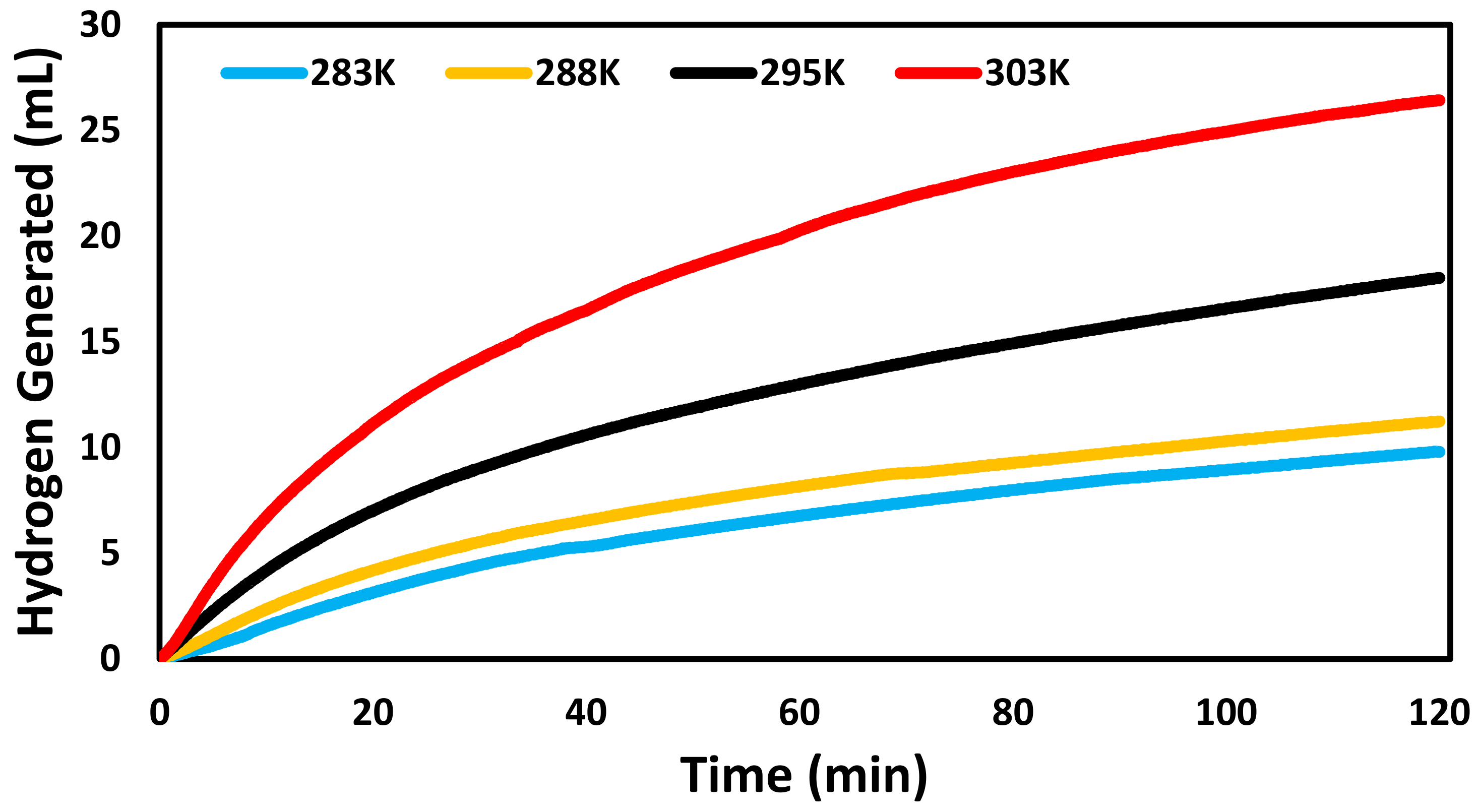
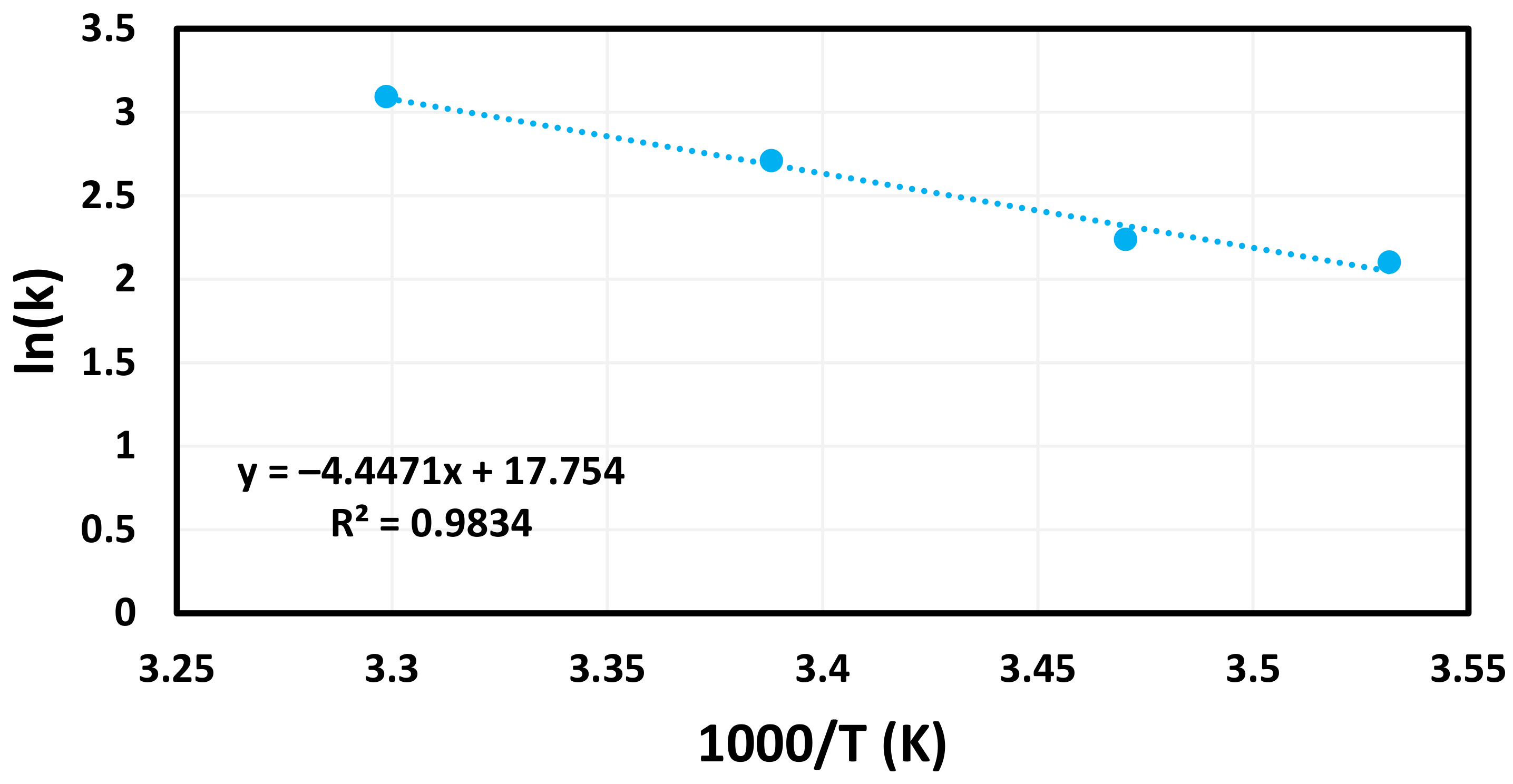
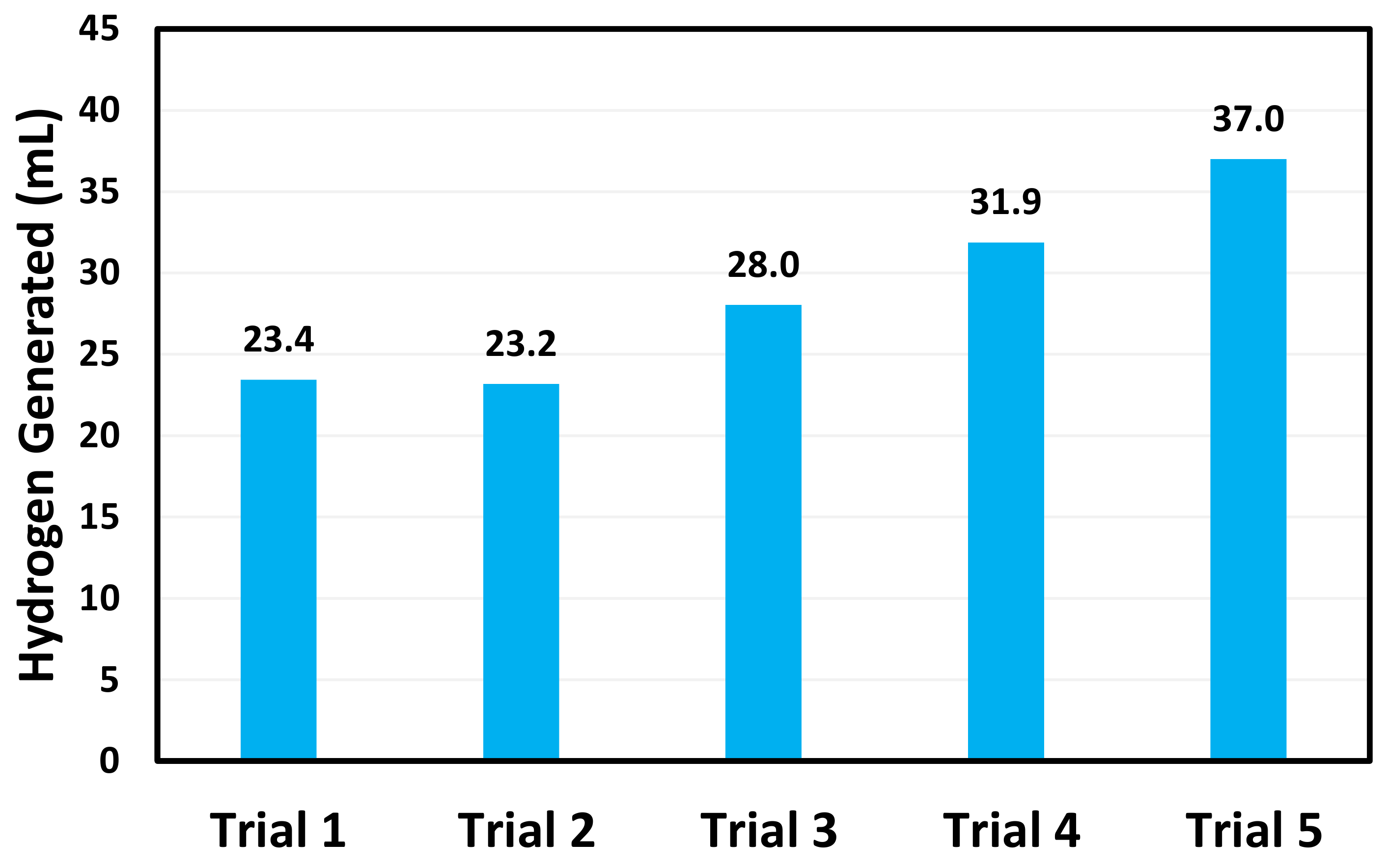
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M. Energy—Our World in Data. 2014. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/energy (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Rodhe, H.A. Comparison of the Contribution of Various Gases to the Greenhouse Effect. Science 1990, 248, 1217–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiee, S.; Topal, E. When Will Fossil Fuel Reserves Be Diminished? Energy Policy 2009, 37, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veziroglu, T.N. 21st Century’s Energy: Hydrogen Energy System. Assessment of Hydrogen Energy for Sustainable Development. In Assessment of Hydrogen Energy for Sustainable Development; NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C: Environmental Security; Sheffield, J.W., Sheffield, Ç., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Züttel, A. Hydrogen storage methods. Naturwissenschaften 2004, 91, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, H.I.; Brown, H.C.; Finholt, A.E.; Gilbreath, J.R.; Hoekstra, H.R.; Hyde, E.K. Sodium Borohydride, Its Hydrolysis and Its Use as a Reducing Agent and in the Generation of Hydrogen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1953, 75, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, J.; Horten, M.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Gold Nanoparticles Supported over Low-Cost Supports for Hydrogen Generation from a Hydrogen Feedstock Material. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 071004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C.; Long, J.M.; Aboulatta, A.; Heyman, A.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Silver Nanoparticle/Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Composite as Catalyst for Hydrogen Production. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2017, 6, M115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C.; Dushatinski, T.; Barzanji, A.; Abdel-Fattah, N.; Barzanji, K.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Pretreatment of Gold Nanoparticle Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Composites for Catalytic Activity toward Hydrogen Generation Reaction. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2017, 6, M69–M71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dushatinsk, T.; Huff, C.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Characterization of electrochemically deposited films from aqueous and ionic liquid cobalt precursors toward hydrogen evolution reactions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 385, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C.; Dushatinski, T.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Gold nanoparticle/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite as novel catalyst for hydrogen evolution reactions. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 18985–18990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C.; Long, J.M.; Heyman, A.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Palladium Nanoparticle Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Composite as Catalyst for Hydrogen Production by the Hydrolysis of Sodium Borohydride. FCS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 4635–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C.; Biehler, E.; Quach, Q.; Long, J.M.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Synthesis of Highly Dispersive Platinum Nanoparticles and their Application in a Hydrogen Generation Reaction. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 610, 125734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.; Poulose, E.K. Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanism of Antimicrobial Action, Synthesis, Medical Applications, and Toxicity Effects. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, Q.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Silver Nanoparticles Functionalized Nanosilica Grown over Graphene Oxide for Enhancing Antibacterial Effect. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudrik, S.G.; Chaki, N.K.; Chavan, V.B.; Chavan, S.P.; Chavan, S.P.; Sonawane, H.R.; Vijayamohanan, K. Silver Nanocluster Redox-Couple-Promoted Nonclassical Electron Transfer: An Efficient Electrochemical Wolff Rearrangement of α-Diazoketones. Chem.-Eur. J. 2006, 12, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudome, T.; Mikami, Y.; Mori, H.; Arita, S.; Mizugaki, T.; Jitsukawa, K.; Kaneda, K. Supported Silver Nanoparticle Catalyst for Selective Hydration of Nitriles to Amides in Water. Chem. Commun. 2009, 2009, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudome, T.; Mikami, Y.; Funai, H.; Mizugaki, T.; Jitsukawa, K.; Kaneda, K. Oxidant-Free Alcohol Dehydrogenation Using a Reusable Hydrotalcite-Supported Silver Nanoparticle Catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C.; Long, J.M.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Beta-cyclodextrin-assisted synthesis of silver nanoparticle network and its application in a hydrogen generation reaction. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Science 2013, 298, 2176–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xin, Q.; Sun, G.; Yi, B. Studies on Performance Degradation of a Direct Methanol Fuel Cell (DMFC) in Life Test. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2004, 6, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, T.M.; Wixtrom, A.; Zhang, K.; Baumgart, H. Highly Uniform Self-Assembled Gold Nanoparticles over High Surface Area Dense ZnO Nanorod Arrays as Novel Surface Catalysts. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, M61–M64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, T.M.; Wixtrom, A. Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol Using Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Carbon Nanotubes. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, M18–M20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wu, Z.; Dai, W.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Su, X.; Teng, Z. Synthesis of multiple Ag nanoparticles loaded hollow mesoporous carbon spheres for highly efficient and recyclable catalysis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 314, 110856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Laguna, J.; Mollar-Cuni, A.; Ventura-Espinosa, D.; Martin, S.; Caballero, A.; Mata, J.A.; Perez, P.J. Gold nanoparticle-catalysed functionalization of carbon–hydrogen bonds by carbene transfer reactions. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 5250–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Guan, L.; Jiao, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhao, F.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Pt, Ag and Au Nanoparticles on Hollow Carbon Spheres as Cathode ORR. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2023, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovskii, A.L. Graphene-Based and Graphene-Like Materials. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2012, 81, 571–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, H.; Hu, M.; Zhang, S. Classification and carbon structural transformation from anthracite to natural coaly graphite by XRD, Raman spectroscopy, and HRTEM. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 249, 119286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temgire, M.K.; Joshi, S.S. Optical and structural studies of silver nanoparticles. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2004, 71, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Peng, Z.; Gong, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, P.; Kong, L. Mechanism of a green graphene oxide reduction with reusable potassium carbonate. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 11966–11972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciplak, Z.; Yildiz, N.; Calimli, A. Investigation of Graphene/Ag Nanocomposites Synthesis Parameters for Two Different Synthesis Methods. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 2014, 23, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, C.M.; Sen, B. Hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of sodium tetrahydroborate: Effects of acids and transition metals and their salts. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1985, 2, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakap, M.; Özkar, S. Hydroxyapatite-supported cobalt(0) nanoclusters as efficient and cost-effective catalyst for hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of both sodium borohydride and ammonia-borane. Catal. Today 2012, 183, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Fan, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F. A highly efficient heterogeneous catalyst of Ru/MMT: Preparation, characterization, and evaluation of catalytic effect. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 140–141, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Liu, X.; Jiang, J. Synthesis of loofah sponge carbon supported bimetallic silver-cobalt nanoparticles with enhanced catalytic activity towards hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride hydrolysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 625, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C.; Quach, Q.; Long, J.M.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Nanocomposite Catalyst Derived from Ultrafine Platinum Nanoparticles and Carbon Nanotubes for Hydrogen Generation. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 101008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, Q.; Biehler, E.; Elzamzami, A.; Huff, C.; Long, J.M.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Catalytic Activity of Beta-Cyclodextrin-Gold Nanoparticles Network in Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Catalysts 2021, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehler, E.; Quach, Q.; Huff, C.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Organo-Nanocups Assist the Formation of Ultra-Small Palladium Nanoparticle Catalysts for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Materials 2022, 15, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deraedt, C.; Salmon, L.; Gatard, S.; Ciganda, R.; Hernandez, E.; Ruiz, J.; Astruc, D. Sodium borohydride stabilizes very active gold nanoparticle catalysts. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14194–14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.B.; Huang, C.P.; Doong, R.-A. Enhanced catalytic reduction of nitrophenols by sodium borohydride over highly recyclable Au@graphitic carbon nitride nanocomposites. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 240, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Catalyst | Ea (kJ mol−1) | Temperature (K) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | 71 | 273–308 | [32] |
| Raney-Nickel | 63 | 273–308 | [32] |
| Co | 75 | 273–308 | [32] |
| Co nanoclusters | 50 | 288–318 | [33] |
| Ru/MMT | 54.7 | 283–303 | [34] |
| LSC/AgCo | 49.3 | 293–323 | [35] |
| Pt/MWCNTs | 46.2 | 283–303 | [36] |
| Ag/MWCNTs | 44.5 | 273–303 | [8] |
| Pd/MWCNTs | 62.7 | 273–303 | [10] |
| Au/MWCNTs | 21.1 | 273–303 | [37] |
| PtNPs | 39.2 | 283–303 | [11] |
| BCD-AuNP | 54.7 | 283–303 | [9] |
| PdNPs | 58.9 | 273–303 | [38] |
| AgNP-FCS | 37.0 | 283–303 | This Work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biehler, E.; Quach, Q.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Silver-Nanoparticle-Decorated Fused Carbon Sphere Composite as a Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation. Energies 2023, 16, 5053. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135053
Biehler E, Quach Q, Abdel-Fattah TM. Silver-Nanoparticle-Decorated Fused Carbon Sphere Composite as a Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation. Energies. 2023; 16(13):5053. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135053
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiehler, Erik, Qui Quach, and Tarek M. Abdel-Fattah. 2023. "Silver-Nanoparticle-Decorated Fused Carbon Sphere Composite as a Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation" Energies 16, no. 13: 5053. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135053
APA StyleBiehler, E., Quach, Q., & Abdel-Fattah, T. M. (2023). Silver-Nanoparticle-Decorated Fused Carbon Sphere Composite as a Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation. Energies, 16(13), 5053. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135053






