Grid Integration of Livestock Biogas Using Self-Excited Induction Generator and Spark-Ignition Engine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Selection and Modification of a Spark-Ignition Engine
2.2. Assesment of Possible Power Conversion Topologies
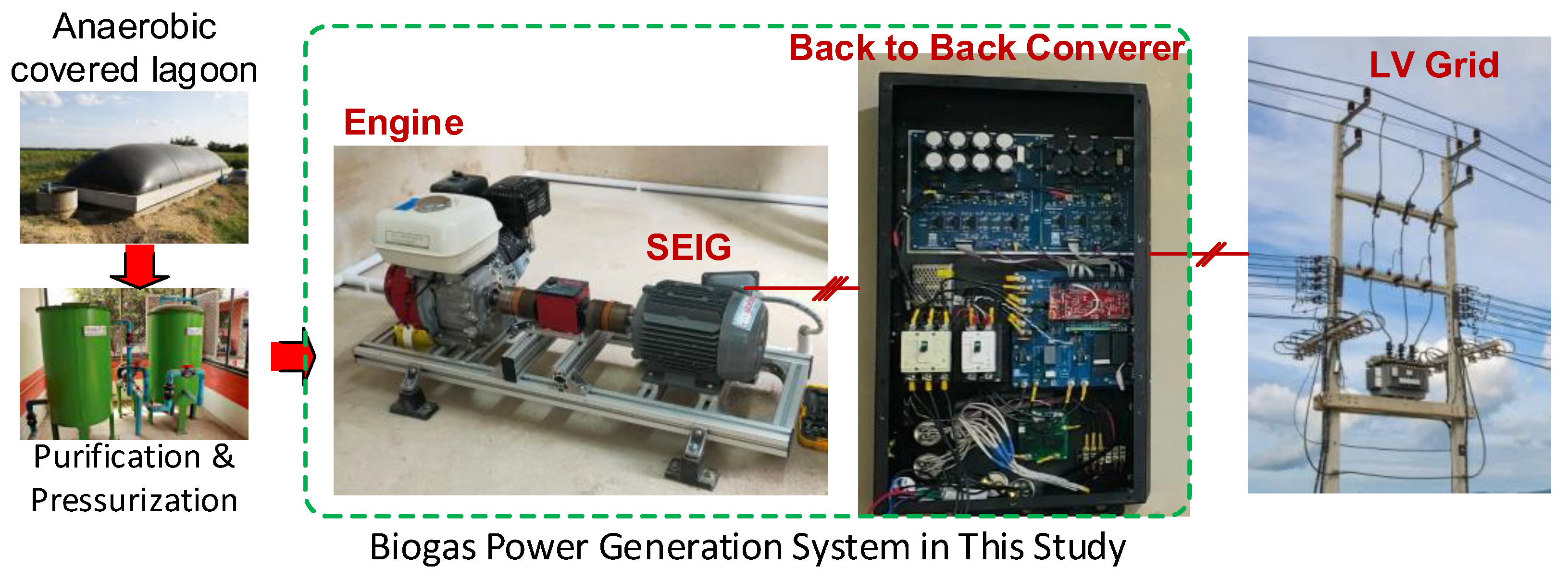
2.3. Proposed SEIG-Based Power Conversion System
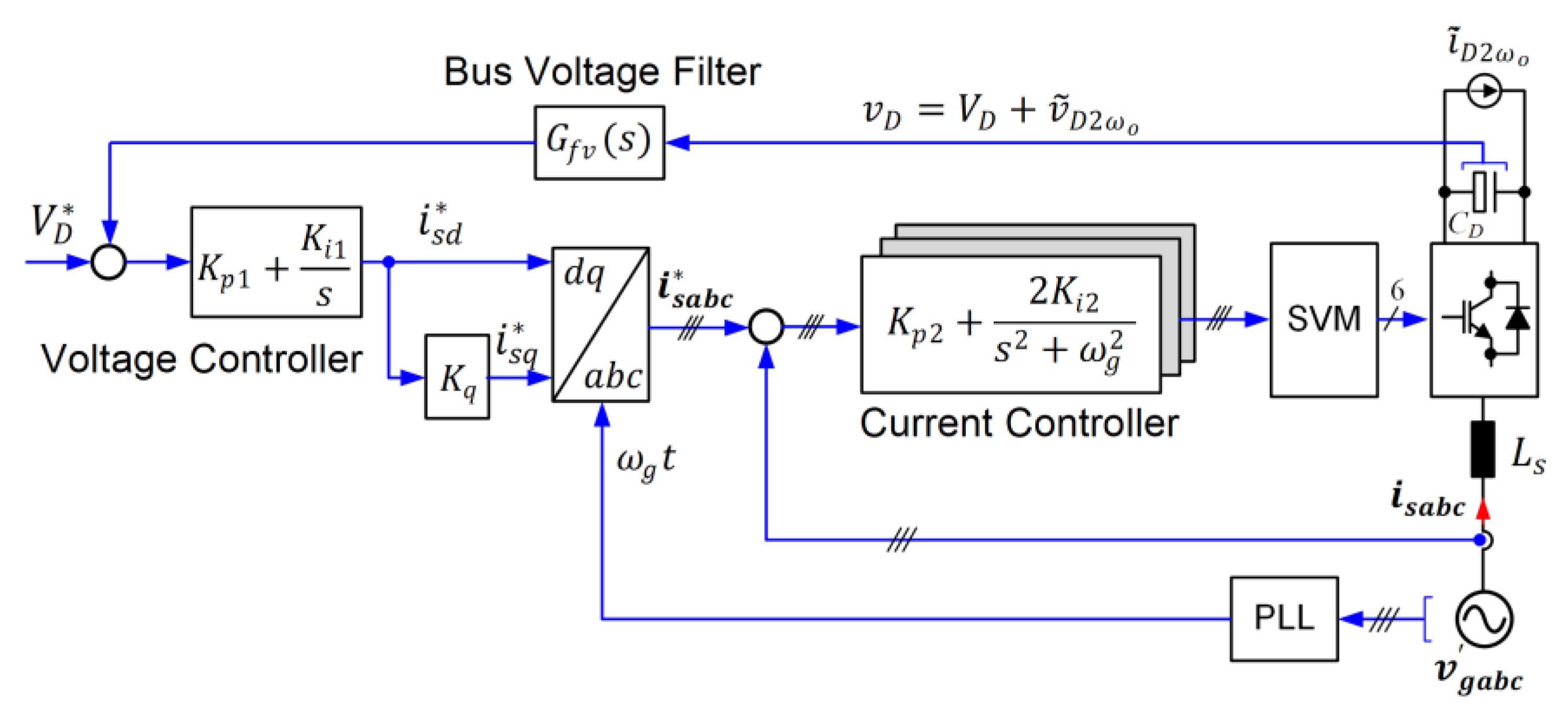
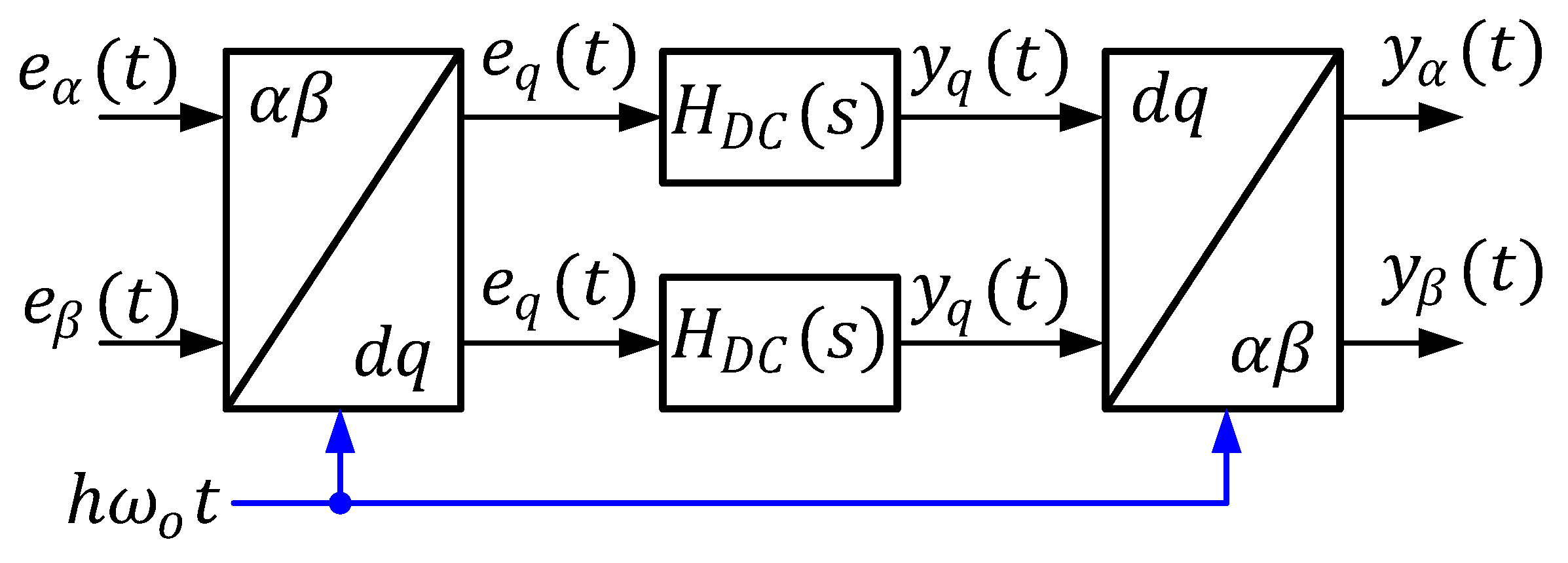
2.4. Back-to-Back Converter Design
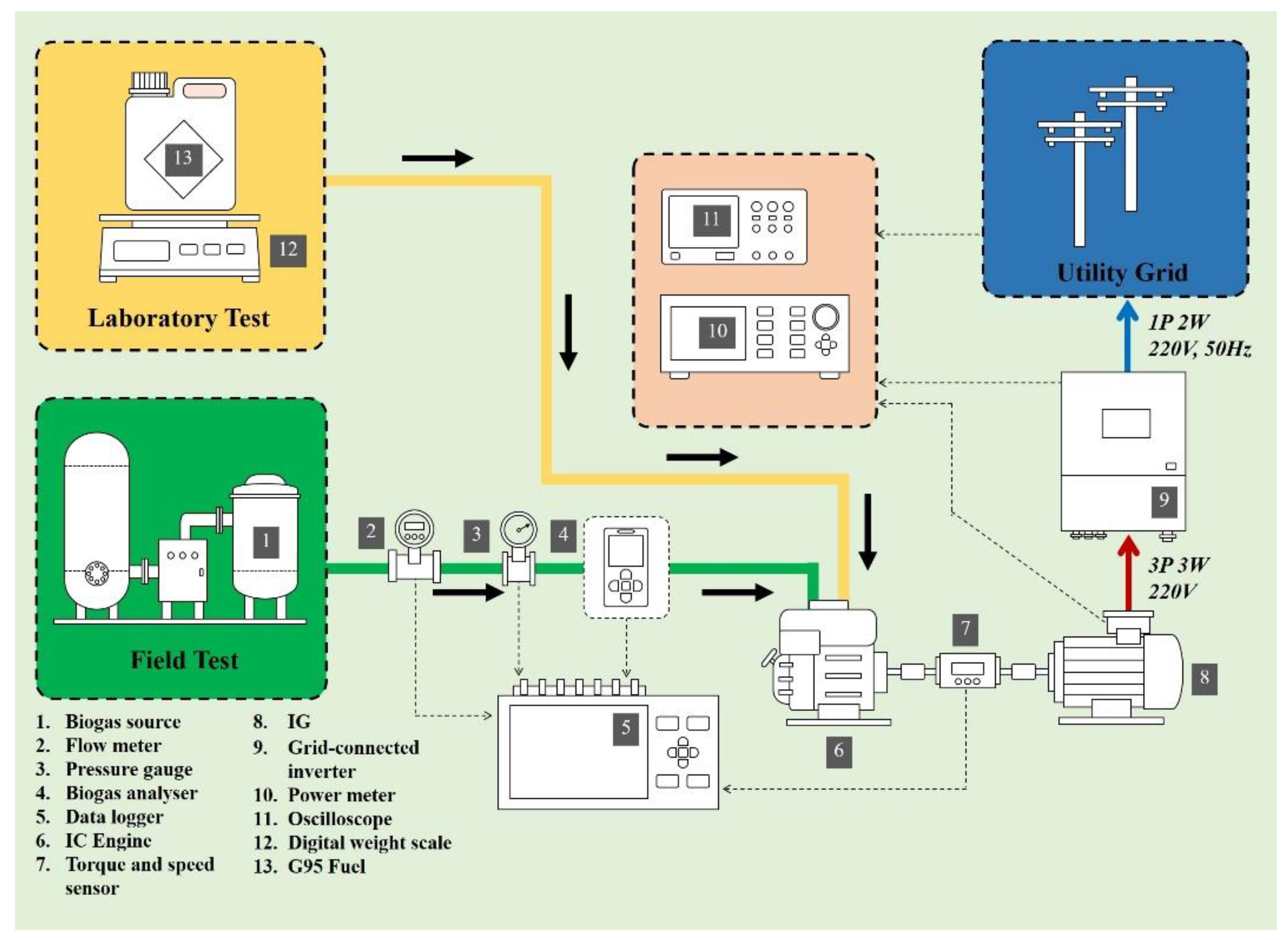
2.5. Experimental Setup
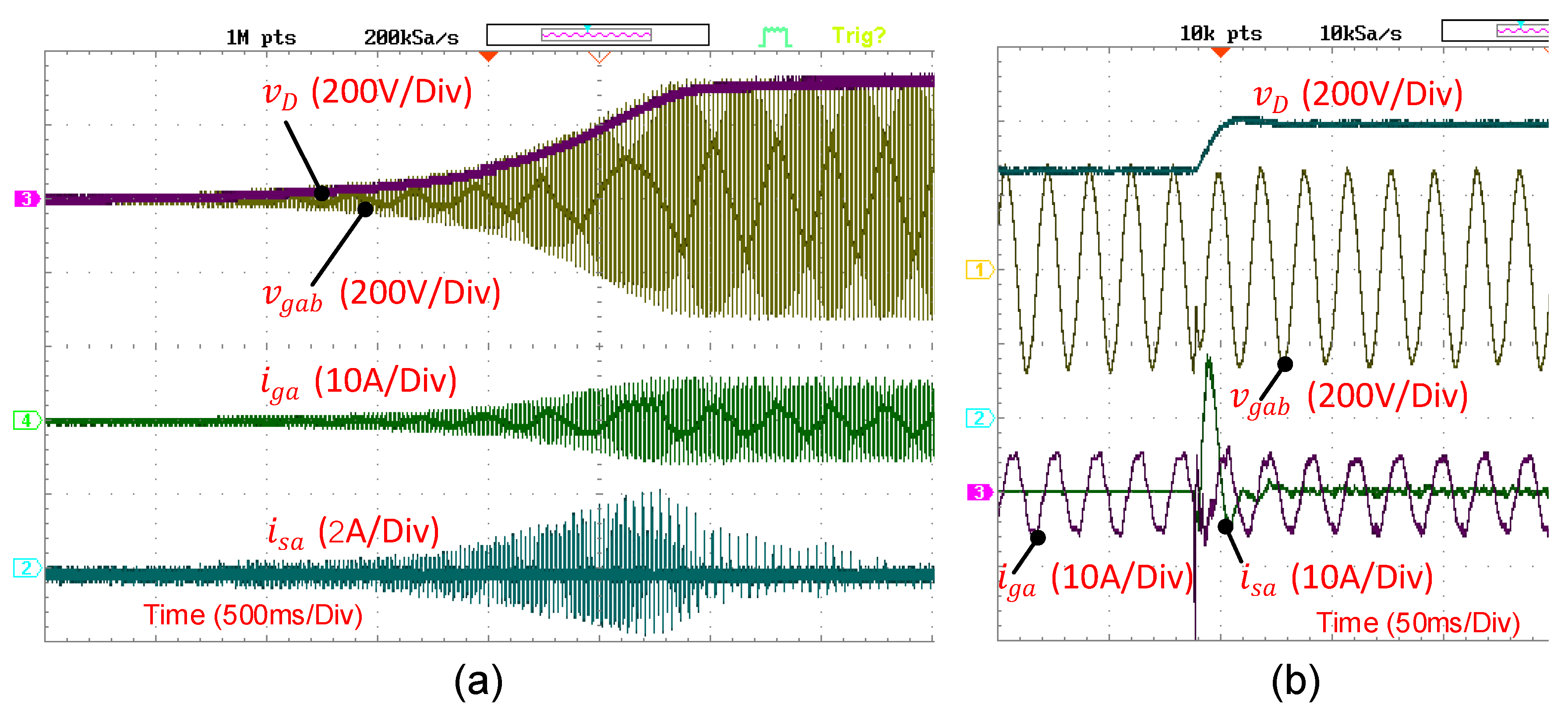
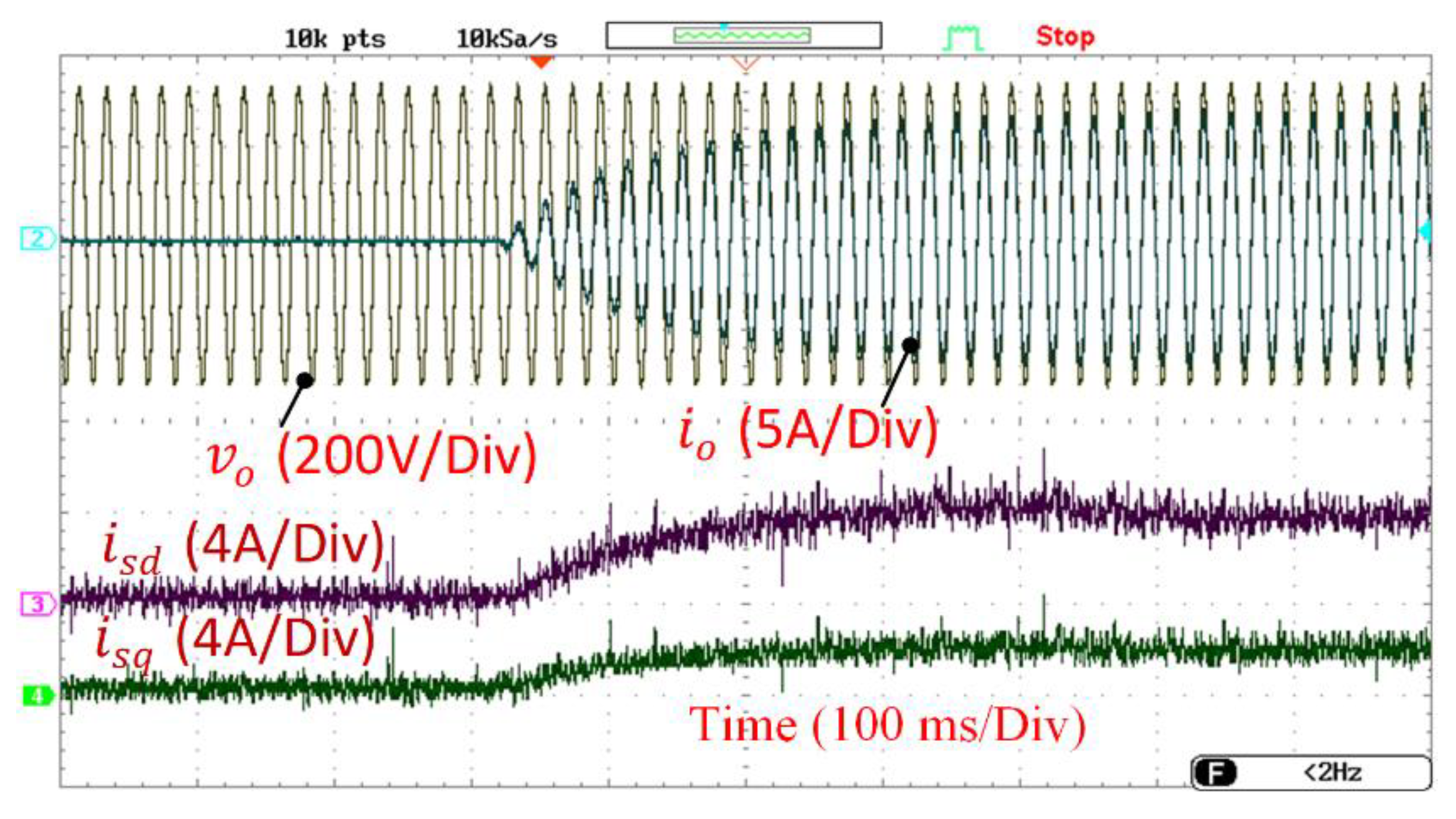
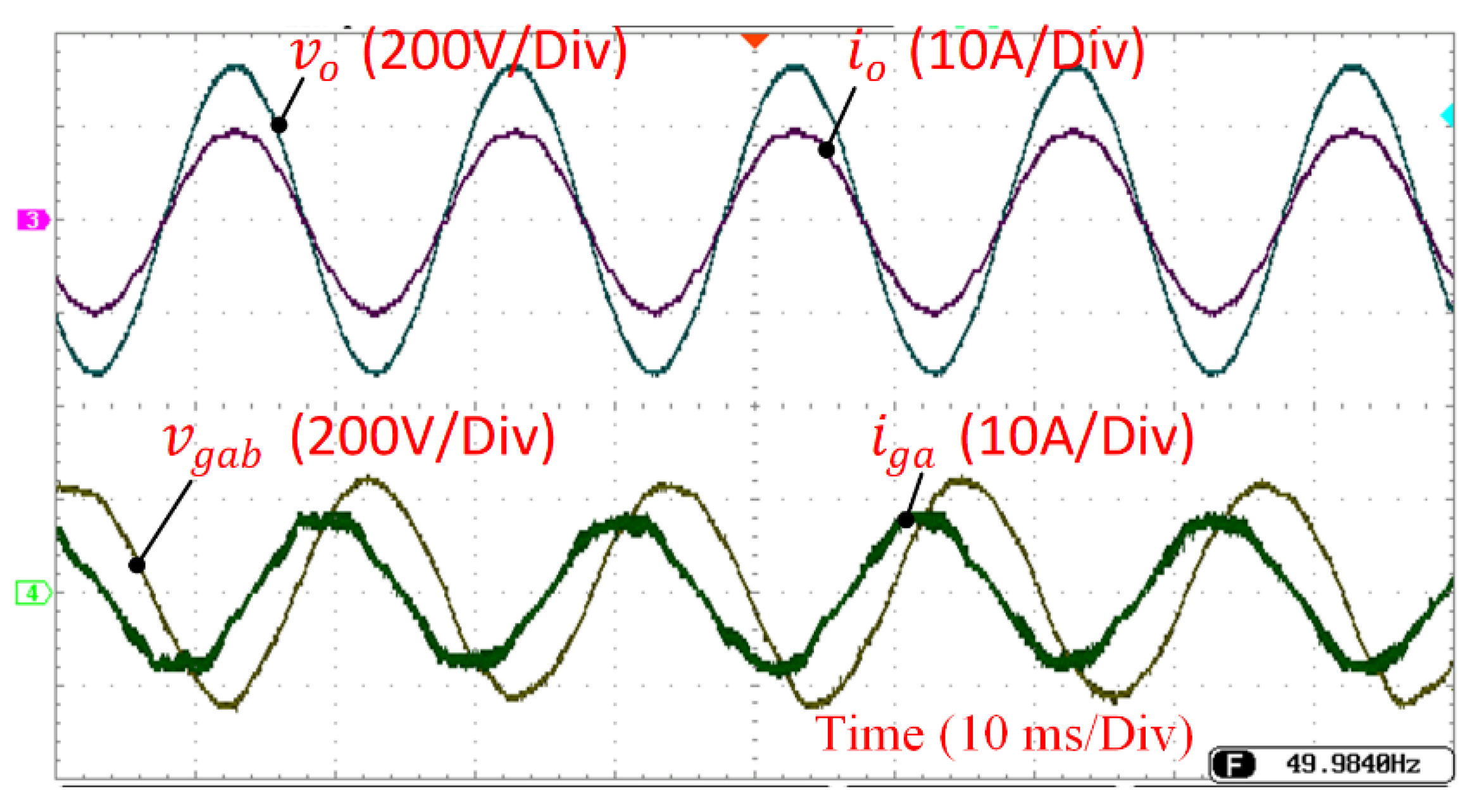
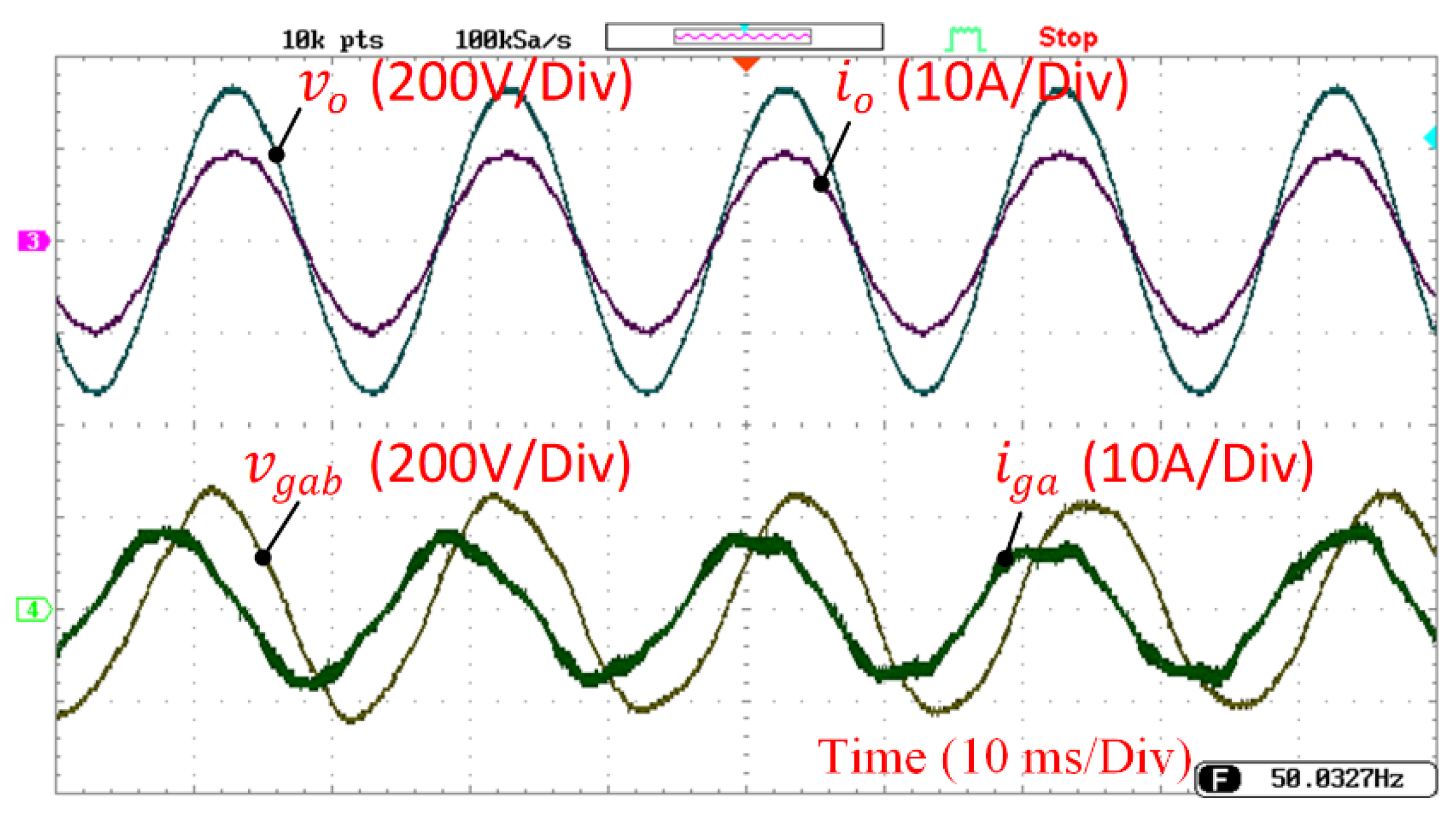
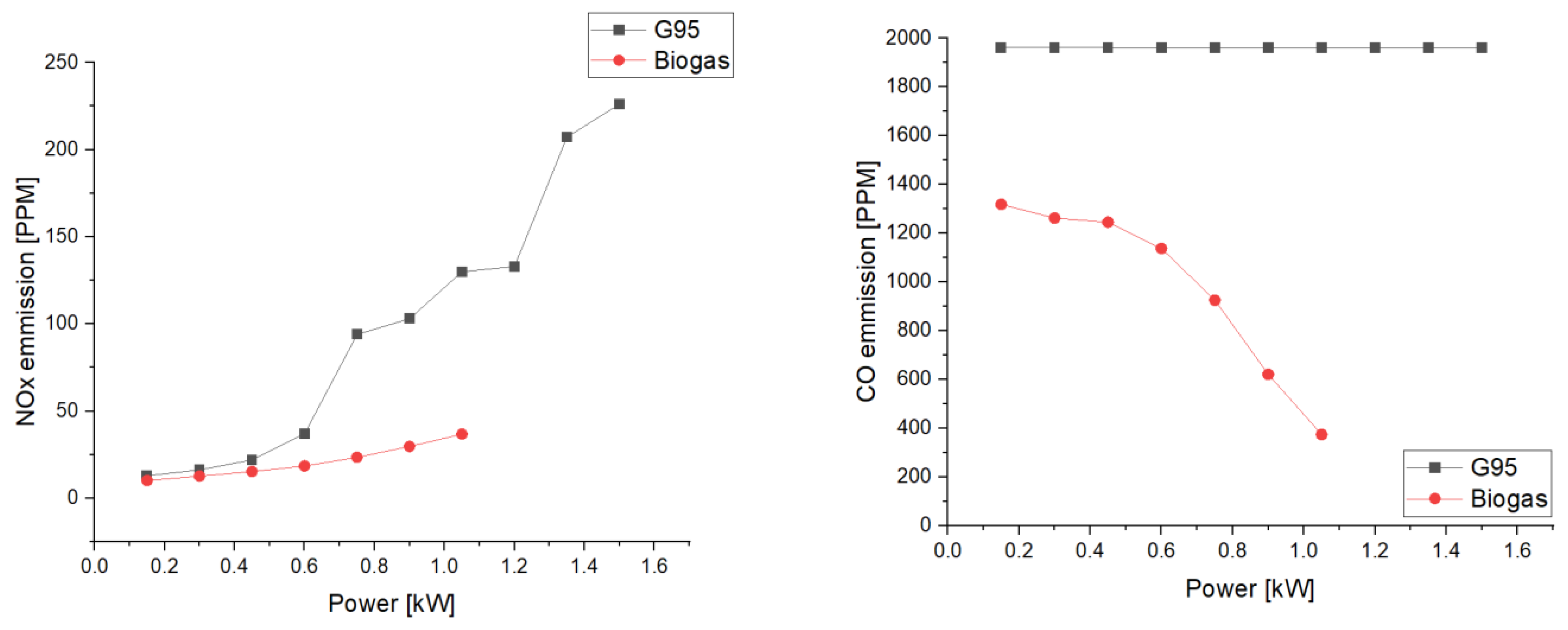
3. Results
3.1. Control Performance of the SEIG and Back-to-Back Converter
3.2. System Performance
4. Suitability and Economic Analysis
4.1. Suitability of the Proposed Biogas Power Generation System
4.2. Economic Viability
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Low investment cost;
- (2)
- Spark–ignition engines and induction machines are manufactured in Thailand and are widely available;
- (3)
- The system is easy to operate, and maintenance of the engines can be carried out in the community;
- (4)
- The system is a dispatchable renewable source that can be used for grid support;
- (5)
- Near-sinusoidal generator and output currents impose a low loss on the generator.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Obaideen, K.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Wilberforce, T.; Elsaid, K.; Sayed, E.T.; Maghrabie, H.M.; Olabi, A. Biogas role in achievement of the sustainable development goals: Evaluation, Challenges, and Guidelines. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 131, 104207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czubaszek, R.; Wysocka-Czubaszek, A.; Wichtmann, W.; Banaszuk, P. Specific Methane Yield of Wetland Biomass in Dry and Wet Fermentation Technologies. Energies 2021, 14, 8373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauber, J.; Ramsbacher, A.; Svardal, K.; Krampe, J. Energetic Potential for Biological Methanation in Anaerobic Sewage Sludge Digesters in Austria. Energies 2021, 14, 6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seruga, P.; Krzywonos, M.; Boer, E.D.; Niedźwiecki, A.; Urbanowska, A.; Pawlak-Kruczek, H. Anaerobic Digestion as a Component of Circular Bioeconomy—Case Study Approach. Energies 2023, 16, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Ingale, G.U.; Kwon, H.-M.; Jeong, S.; Park, D.; Kim, W.; Bang, B.; Lim, Y.-I.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, Y.-B.; Mun, J.; et al. Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Hydrogen Production Processes: Turquoise Hydrogen vs. Steam Methane Reforming. Energies 2022, 15, 8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiou, C.; Drosakis, C.; Booto, G.K.; Elmasides, C. Economic Feasibility of Power/Heat Cogeneration by Biogas–Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) Integrated Systems. Energies 2023, 16, 404. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C.; Do, M.V.; Hsu, W.L.; Liu, B.L.; Chang, C.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Yuan, M.-H.; Lin, C.-F.; Yu, C.-P.; Chen, Y.H.; et al. A case study on the electricity generation using a micro gas turbine fuelled by biogas from a sewage treatment plant. Energies 2019, 12, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Yang, T.; Liu, H.; Ni, D.; Ferrari, M.L.; Li, M.; Luo, Z.; Cen, K.; Ni, M. Recuperators for micro gas turbines: A review. Appl. Energy 2017, 197, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanmar Holdings. Cogeneration Systems—CP Series (Bio Gas). 2023. Available online: https://www.yanmar.com/en_th/energy/cogeneration_systems/biogas/ (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Caterpillar. Gas Generator Sets G3520C. 2023. Available online: https://www.cat.com/en_US/products/new/power-systems/electric-power/gas-generator-sets/18483554.html# (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Verma, S.; Das, L.M.; Kaushik, S.C. Effects of varying composition of biogas on performance and emission characteristics of compression ignition engine using exergy analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 138, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homdoung, N.; Tippayawong, N.; Dussadee, N. Performance and emissions of a modified small engine operated on producer gas. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 94, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingjian, L.; Qi, Q.; Xiangzhu, H.; Jiezhi, L. Energy balance and efficiency analysis for power generation in internal combustion engine sets using biogas. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2014, 6, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldi, P.; Daliento, A.; Rizzo, R. An innovative 10 kW microcogenerator suitable for off grid application and fed with syngas or biogas. In Proceedings of the Universities Power Engineering Conference, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 2–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Da Costa, R.B.R.; Valle, R.M.; Hernández, J.J.; Malaquias, A.C.T.; Coronado, C.J.; Pujatti, F.J.P. Experimental investigation on the potential of biogas/ethanol dual-fuel spark-ignition engine for power generation: Combustion, performance and pollutant emission analysis. Appl. Energy 2020, 261, 114438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakitie, E.D.; Aralu, C.E.; Fadare, A.D. Performance charateristics of a conventional spark ignition petrol engine powered by biogas. Fuel Commun. 2022, 10, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bash, M.; Pekaret, S.; Sudhoff, S.; Whitmore, J.; Fratzen, M. A comparison of permanent magnet and wound rotor synchronous machines for portable power generation. In Proceedings of the 2010 Power and Energy Conference at Illinois (PECI), Urbana, IL, USA, 12–13 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Lin, P. Analysis of a Commercial Biogas Generation System Using a Gas Engine–Induction Generator Set. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2009, 24, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, A.; Franceschini, G.; Lorenzani, E.; Tassoni, C.; Tomaiuolo, M. Field Oriented Control of Self-Excited Induction Generator for Distributed Cogeneration Plants. In Proceedings of the 41st IEEE Industry Applications Conference, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Klíma, J. Stand Alone Bio-Gas Power Plants with Induction Generator and PWM Voltage Source Inverter. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1997, 30, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.K. Self-excited induction generator research—A survey. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2004, 69, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, V.M.; Sandeep, V.; Murthy, S.; Yadlapati, K. Experimental investigation on performance comparison of self excited induction generator and permanent magnet synchronous generator for small scale renewable energy applications. Renew. Energy 2022, 195, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calgan, H.; Demirtas, M. A robust LQR-FOPIλDμ controller design for output voltage regulation of stand-alone self-excited induction generator. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 196, 107175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmmiya, U.; Uma, G. Control and maximum power tracking operation of hybrid excited variable speed induction generator. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 143, 771–781. [Google Scholar]
- Capelo, B.; Pérez-Sánchez, M.; Fernandes, J.F.; Ramos, H.M.; López-Jiménez, P.A.; Branco, P.C. Electrical behaviour of the pump working as turbine in off grid operation. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilipi, R.R.; Singh, B.; Murthy, S.S. Performance of a Self-Excited Induction Generator With DSTATCOM-DTC Drive-Based Voltage and Frequency Controller. Energy Conversion. IEEE Trans. 2014, 29, 545–557. [Google Scholar]
- Marra, E.G.; Pomilio, J.A. Induction-generator-based system providing regulated voltage with constant frequency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2000, 47, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, L.G.; Tischer, C.B.; de Camargo, R.F. Power rating reduction of distribution static synchronous compensator for voltage and frequency regulation of stand-alone self-excited induction generator. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 149, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.J.; Chatterjee, J.K.; Bhere, H.; Perumal, B.V.; Sarkar, D. Synchronized Operation of DSP-Based Generalized Impedance Controller With Variable-Speed Isolated SEIG for Novel Voltage and Frequency Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayodele, T.R.; Ogunjuyigbe, A.S.O.; Adetokun, B.B. Optimal capacitance selection for a wind-driven self-excited reluctance generator under varying wind speed and load conditions. Appl. Energy 2017, 190, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, B.; Guerrero, J.M.; Thøgersen, P.B. Faroe islands wind-powered space heating microgrid using self-excited 220-kW induction generator. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, C.P.; Marinescu, C. Three-phase induction generators for single-phase power generation: An overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 22, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda. GX120/160/200. 2023. Available online: https://engines.honda.com/models/model-detail/mid-gx#Features (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Senthil Kumar, S.; Kumaresan, N.; Subbiah, M. Analysis and control of capacitor-excited induction generators connected to a micro-grid through power electronic converters. Generation, Transmission & Distribution. IET 2015, 9, 911–920. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Niwas, R. Performance of synchronous reluctance generator for DG set based standalone supply system. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2016, 133, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, A.; Rezek, A.; Silva, V.; Viana, A.; Bortoni, E.; Sanchez, W.; Ribeiro, P. Isolated induction generator in a rural Brazilian area: Field performance tests. Renew. Energy 2015, 83, 1352–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somkun, S. High performance current control of single-phase grid-connected converter with harmonic mitigation, power extraction and frequency adaptation capabilities. IET Power Electron. 2021, 14, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfared, M.; Golestan, S.; Guerrero, J.M. Analysis, design, and experimental verification of a synchronous reference frame voltage control for single-phase inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somkun, S. Unbalanced synchronous reference frame control of singe-phase stand-alone inverter. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 107, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somkun, S.; Chunkag, V. Unified unbalanced synchronous reference frame current control for single-phase grid-connected voltage-source converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 5425–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestan, S.; Monfared, M.; Freijedo, F.D.; Guerrero, J.M. Dynamics assessment of advanced single-phase PLL structures. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, J.D.; Jiang, L.; Zou, J. Delay-dependent stability of single-loop controlled grid-connected inverters with LCL filters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.G.; Lipo, T.A.; McGrath, B.P.; Kong, W.Y. Optimized design of stationary frame three phase AC current regulators. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwongwanich, A.; Abdelhakim, A.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, K. Chapter 6—Control of Single-Phase and Three-Phase DC/AC Converters. In Control of Power Electronic Converters and Systems; Blaabjerg, F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 153–173. [Google Scholar]
- Sedpho, S. Community Biogas from Swine Farms Phase 3 at Thamanao Sub-District, Chaibadan District, Lopburi Province, Thailand; Thailand Voluntary Emission Reduction Program; Tha Manao Subdistrict Administrative Organization: Lopburi, Thailand, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pinate, W.; Dangphonthong, D.; Sirirach, S.; Sukkhon, S. Removal of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) from biogas for the community in the province of Maha Sarakham. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 901, 012049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1547-2018; IEEE Standard for Interconnection and Interoperability of Distributed Energy Resources with Associated Electric Power Systems Interfaces. Revision of IEEE Std 1547–2003; IEEE Standards Coordinating Committee: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–138.
- Khotmanee, S.; Pinsopon, U. A Study on Biogas Production Potential in Thailand 2019. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Engineering, Applied Sciences and Technology (ICEAST), Bangkok, Thailand, 1–3 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kaparaju, P.; Rintala, J. 17–Generation of heat and power from biogas for stationary applications: Boilers, gas engines and turbines, combined heat and power (CHP) plants and fuel cells. In The Biogas Handbook; Wellinger, A., Murphy, J., Baxter, D., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 404–427. [Google Scholar]
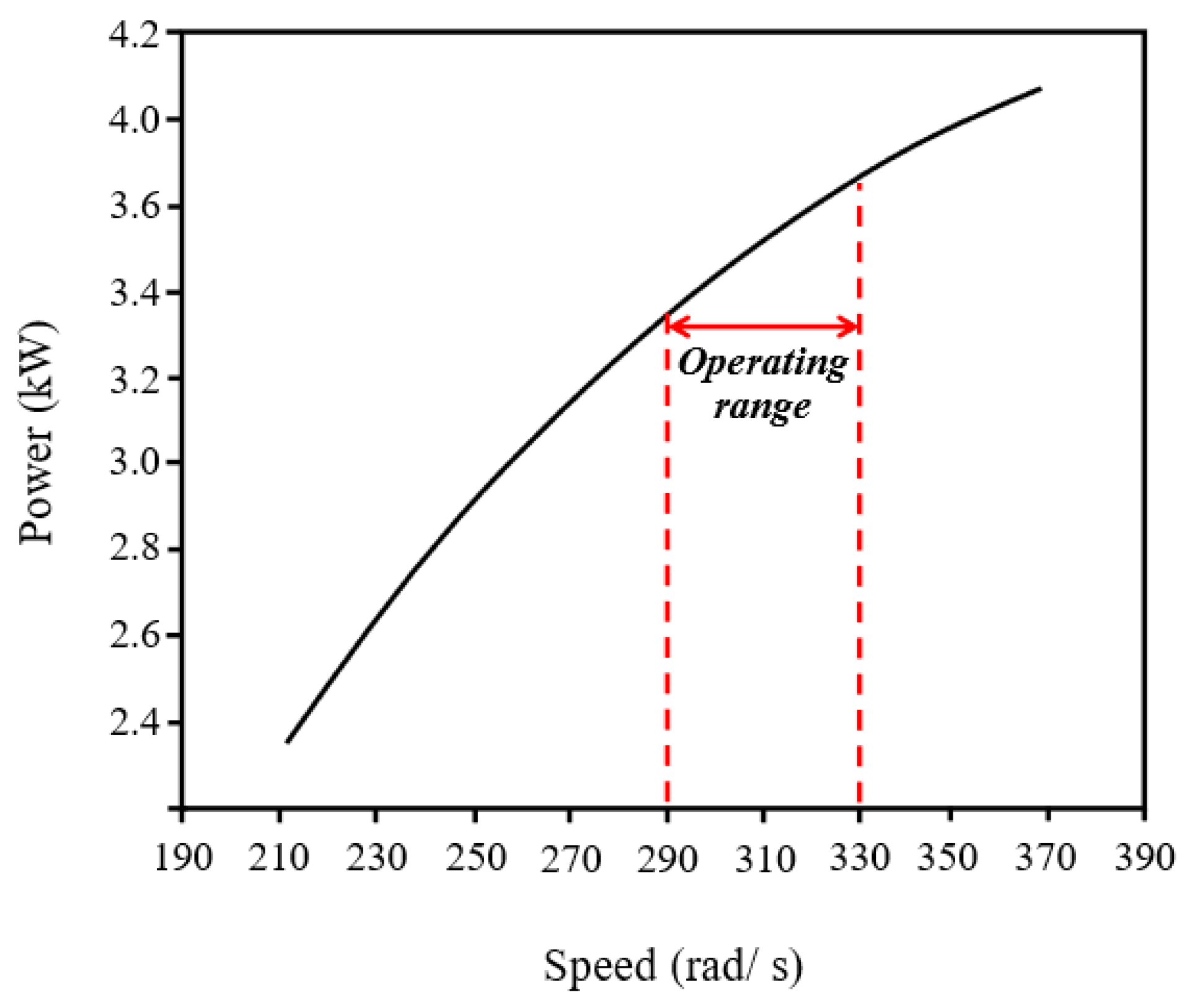
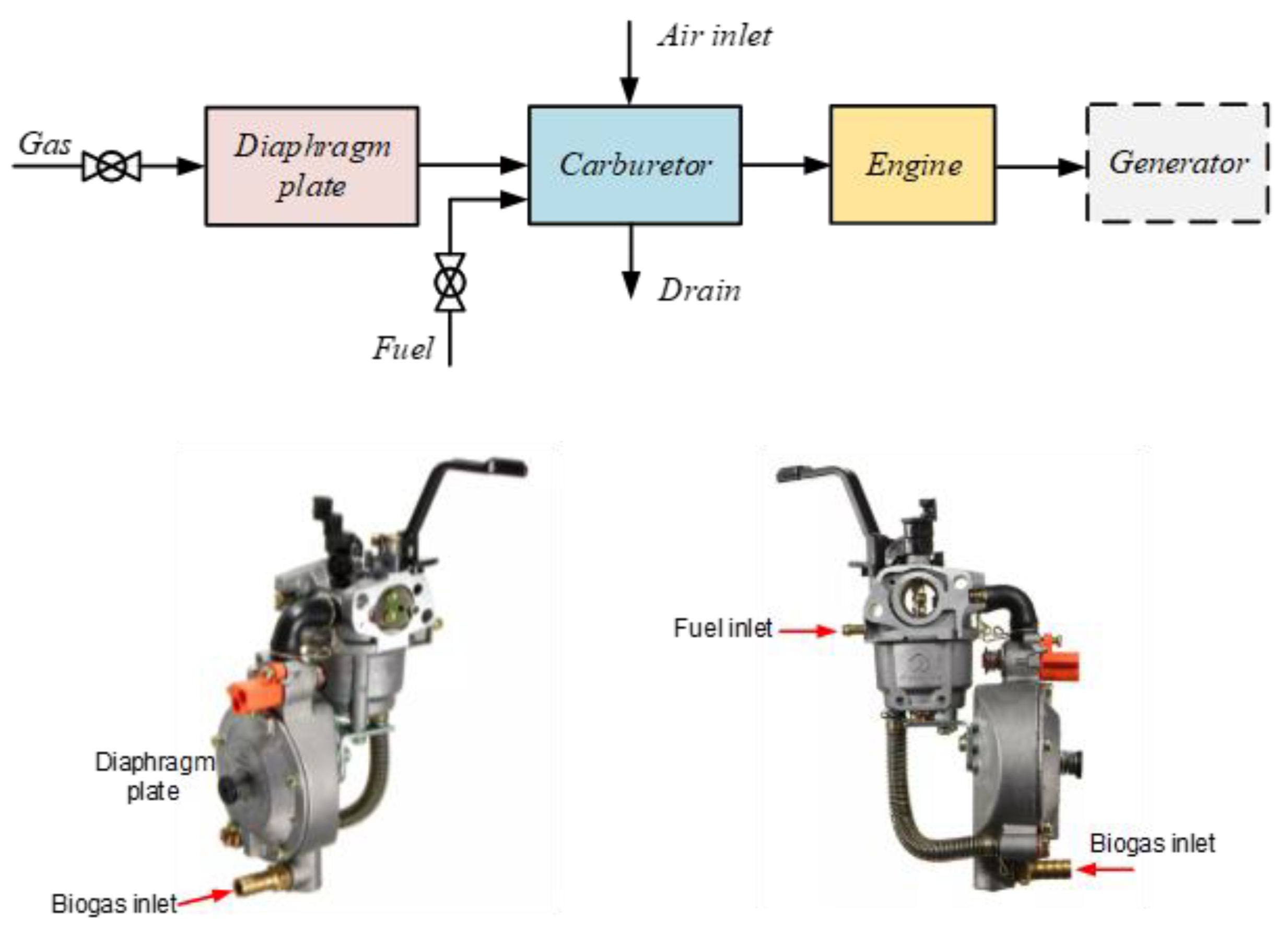

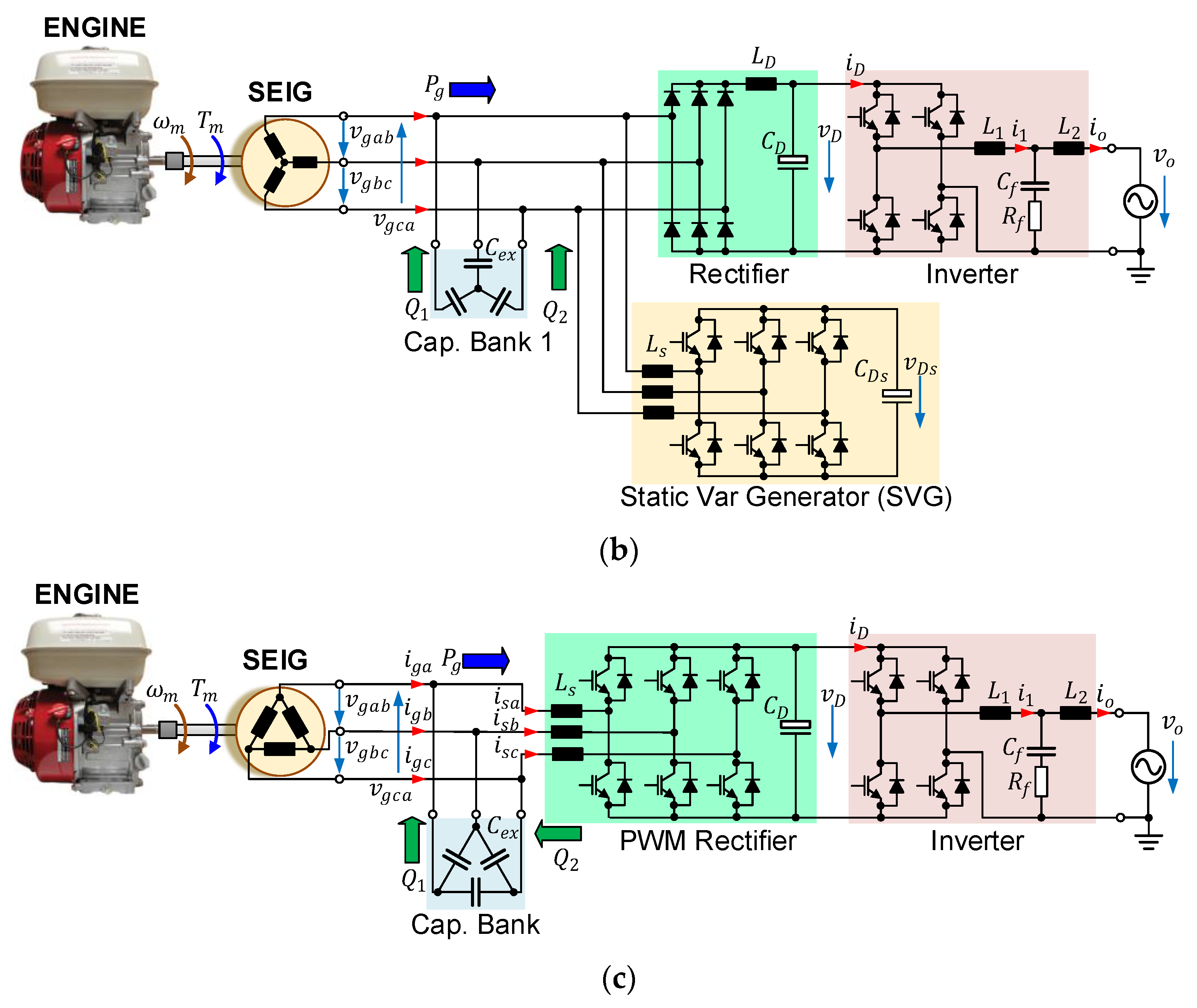

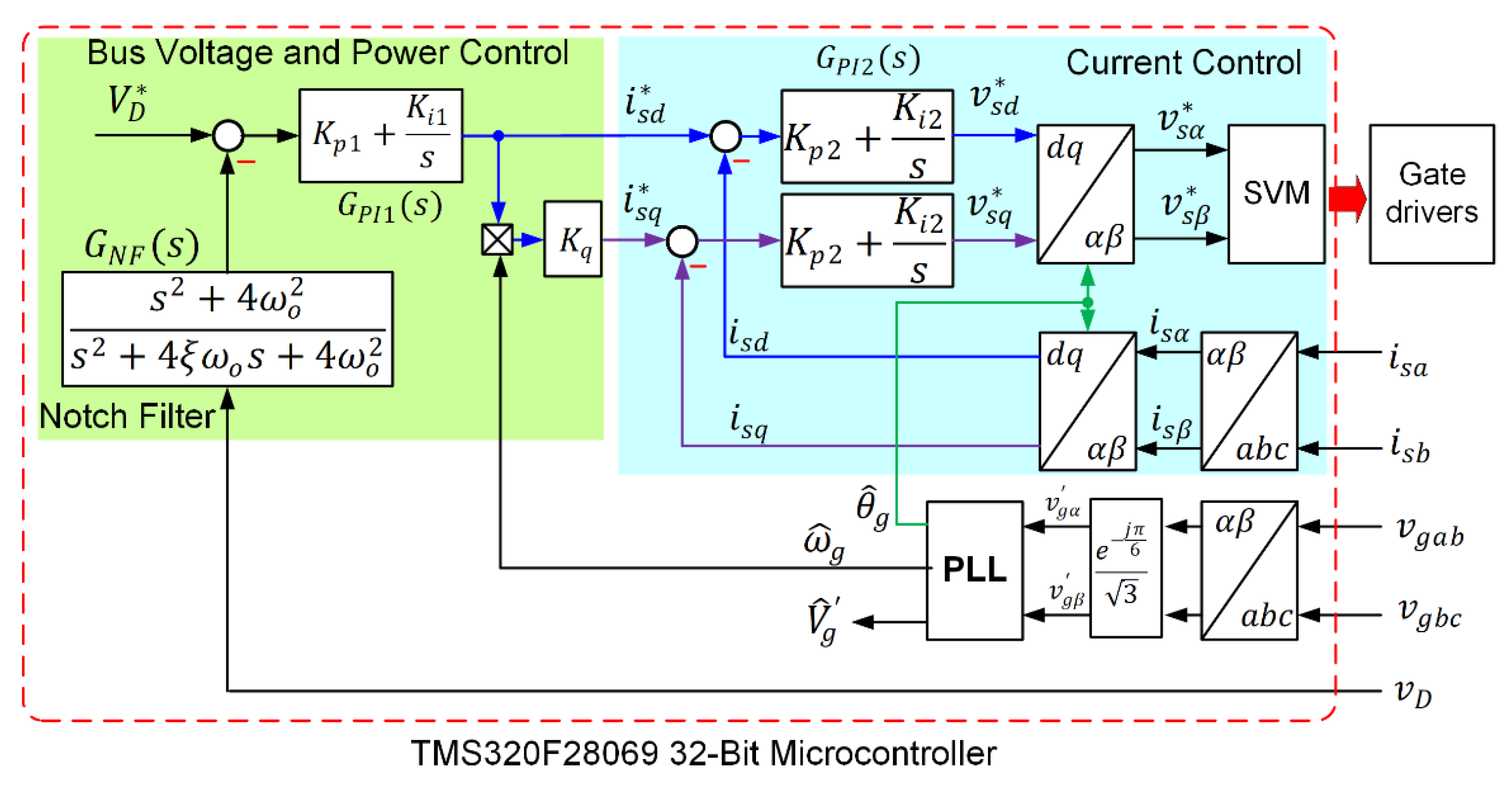


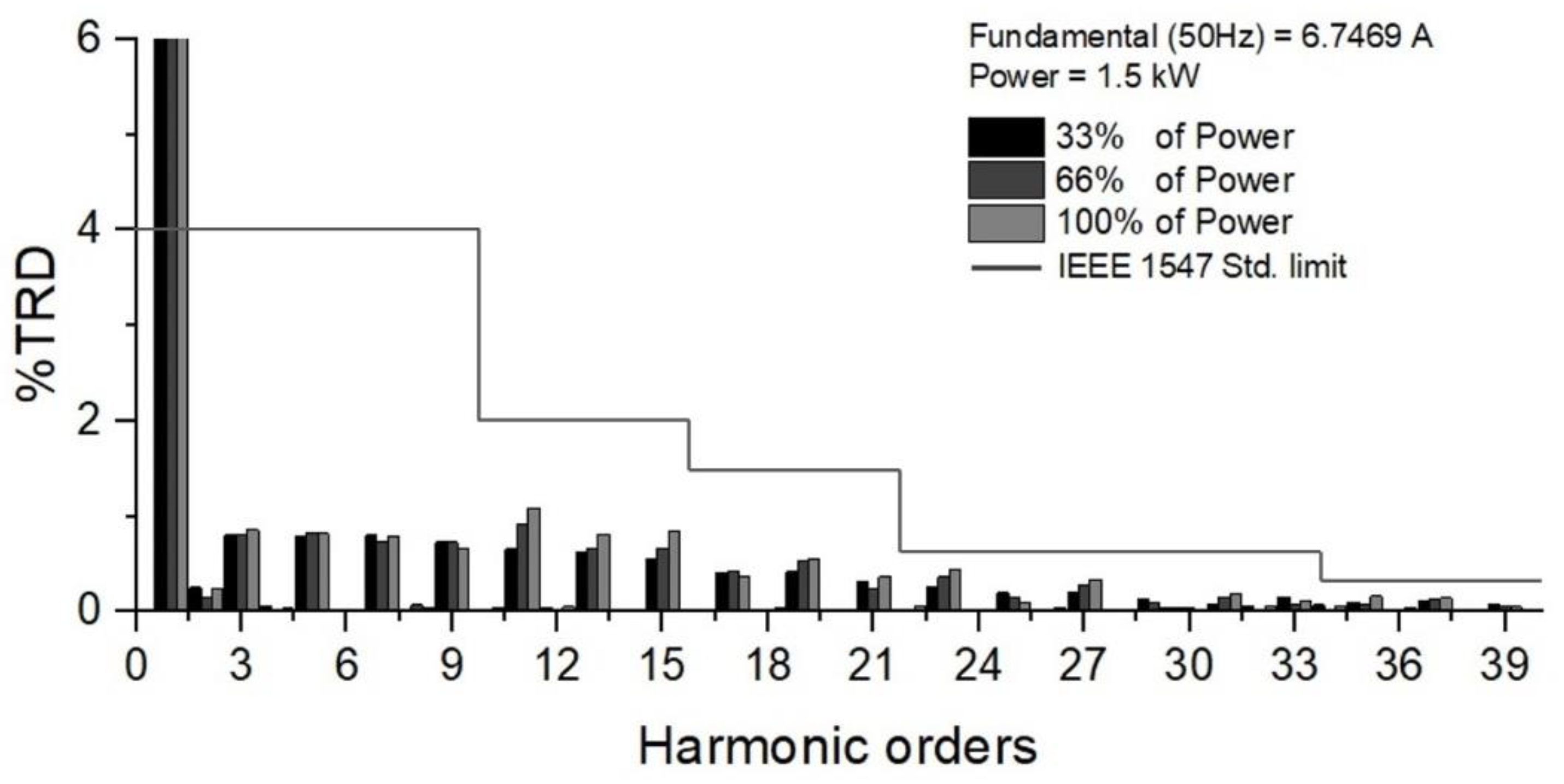
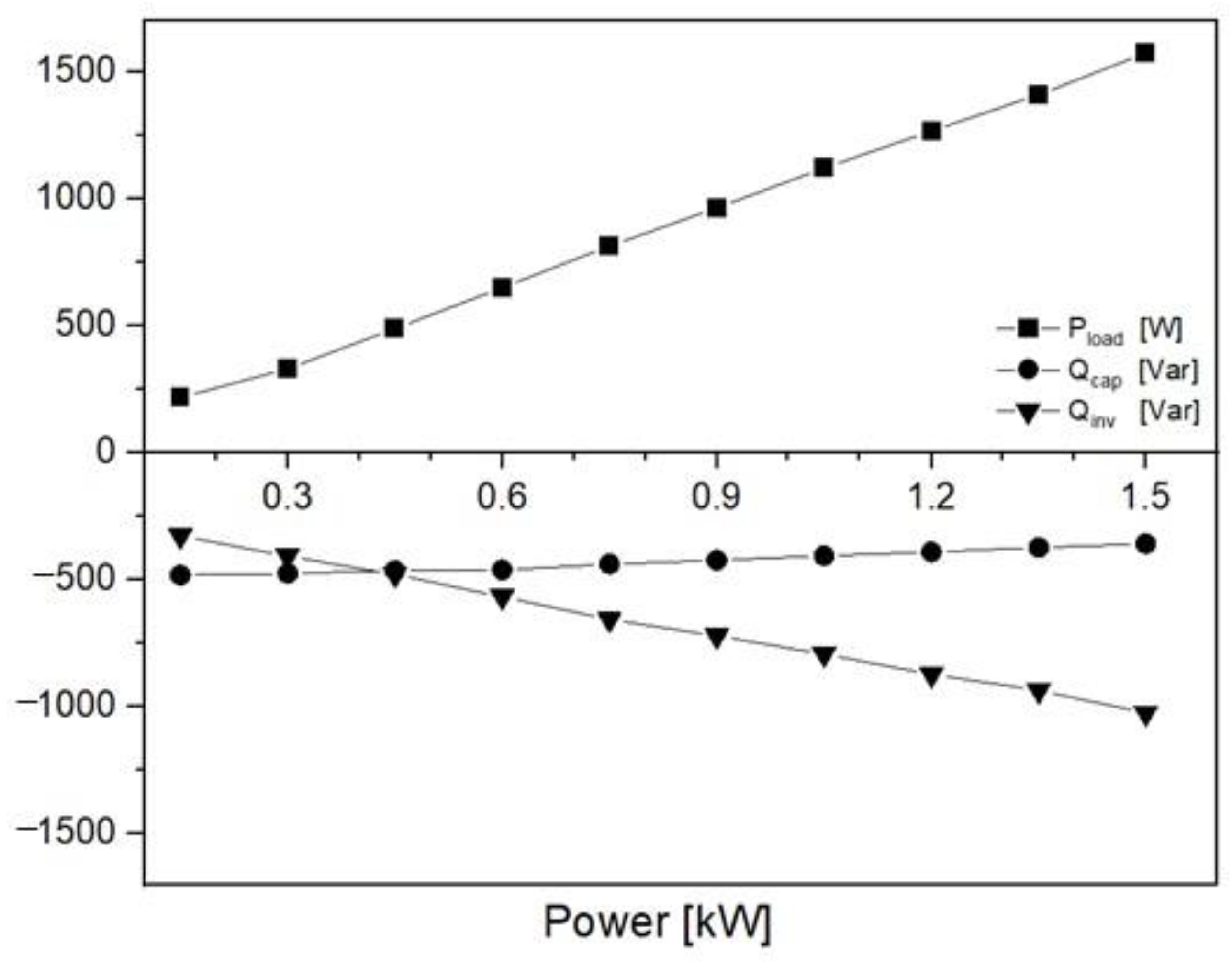
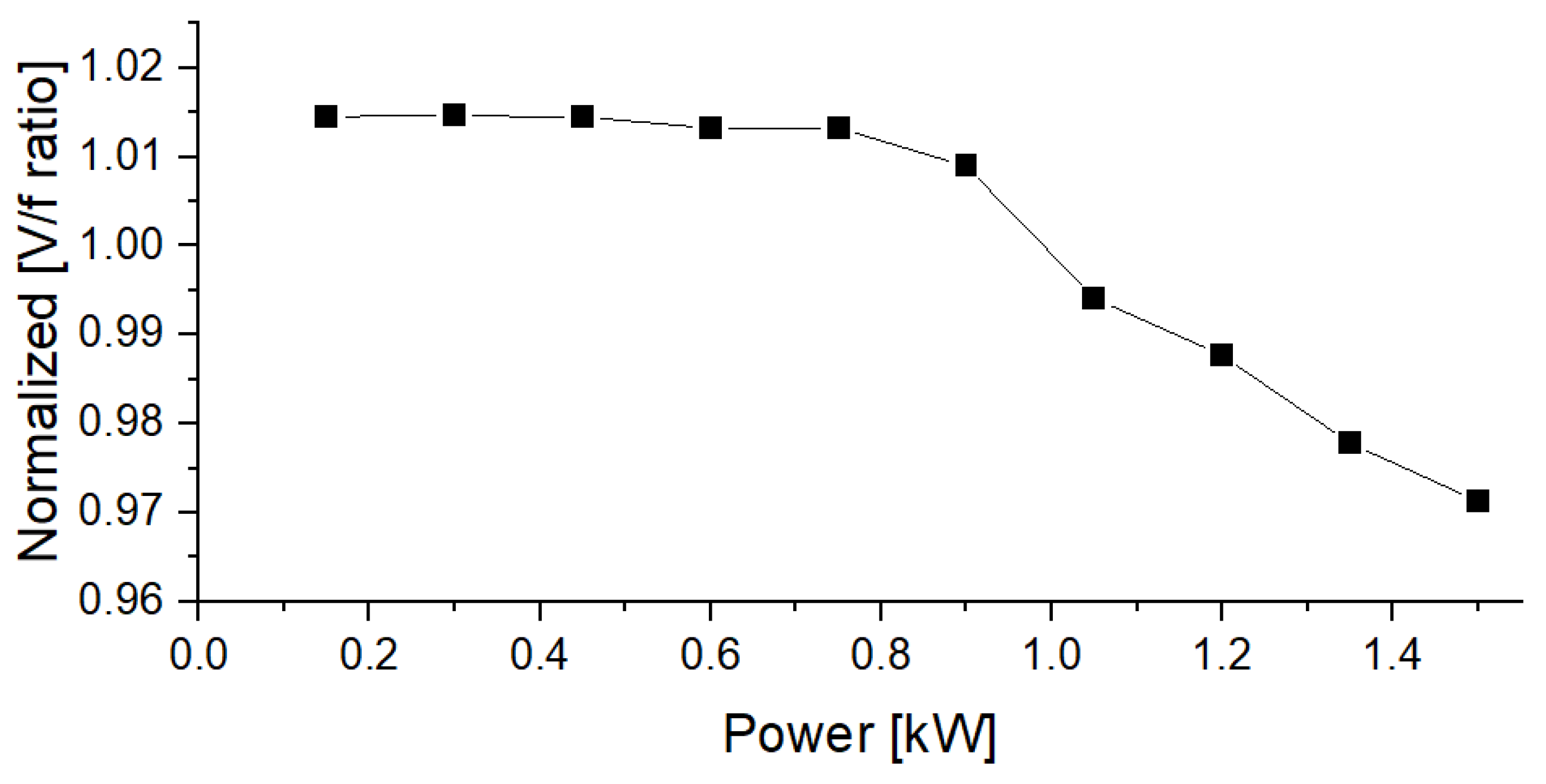
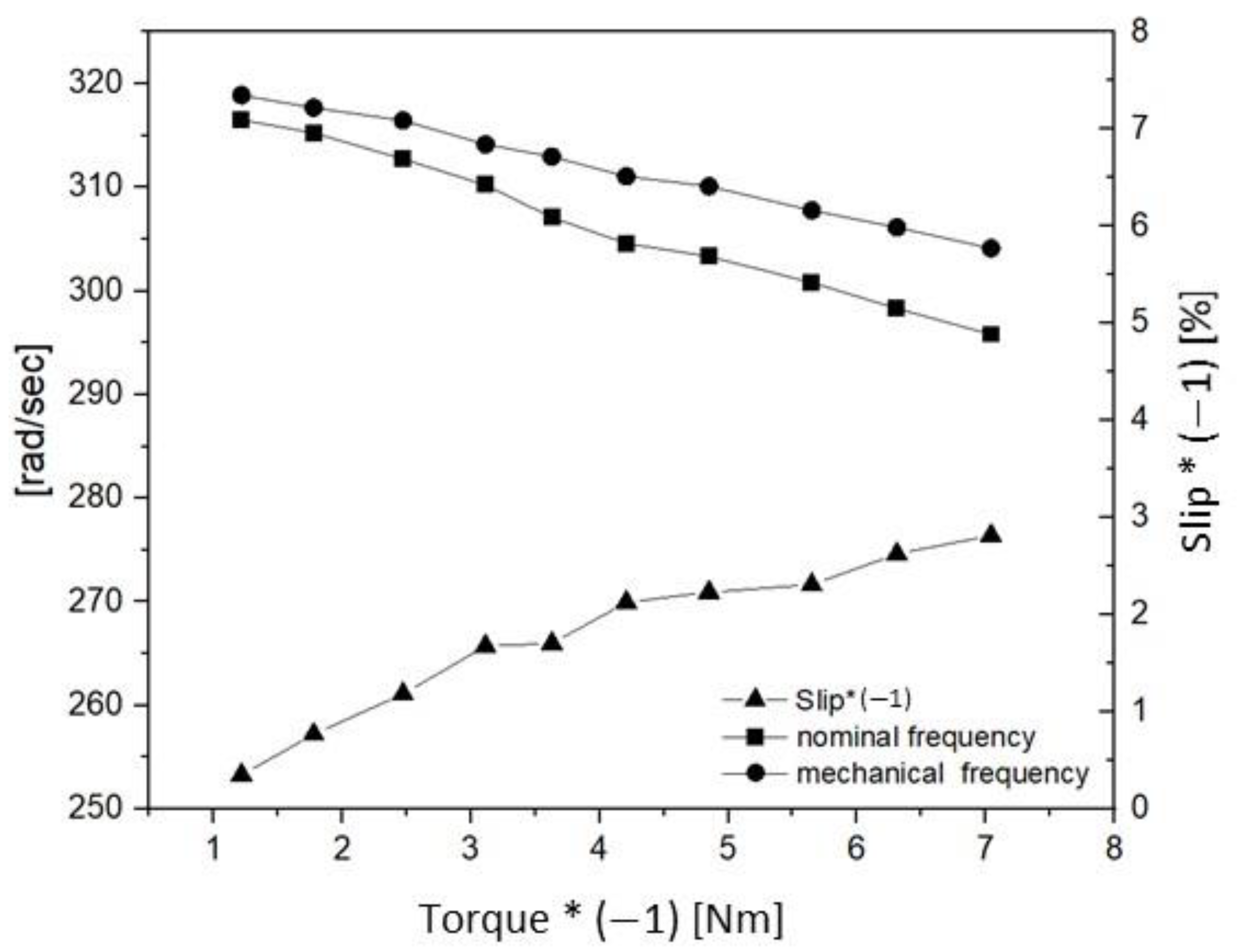
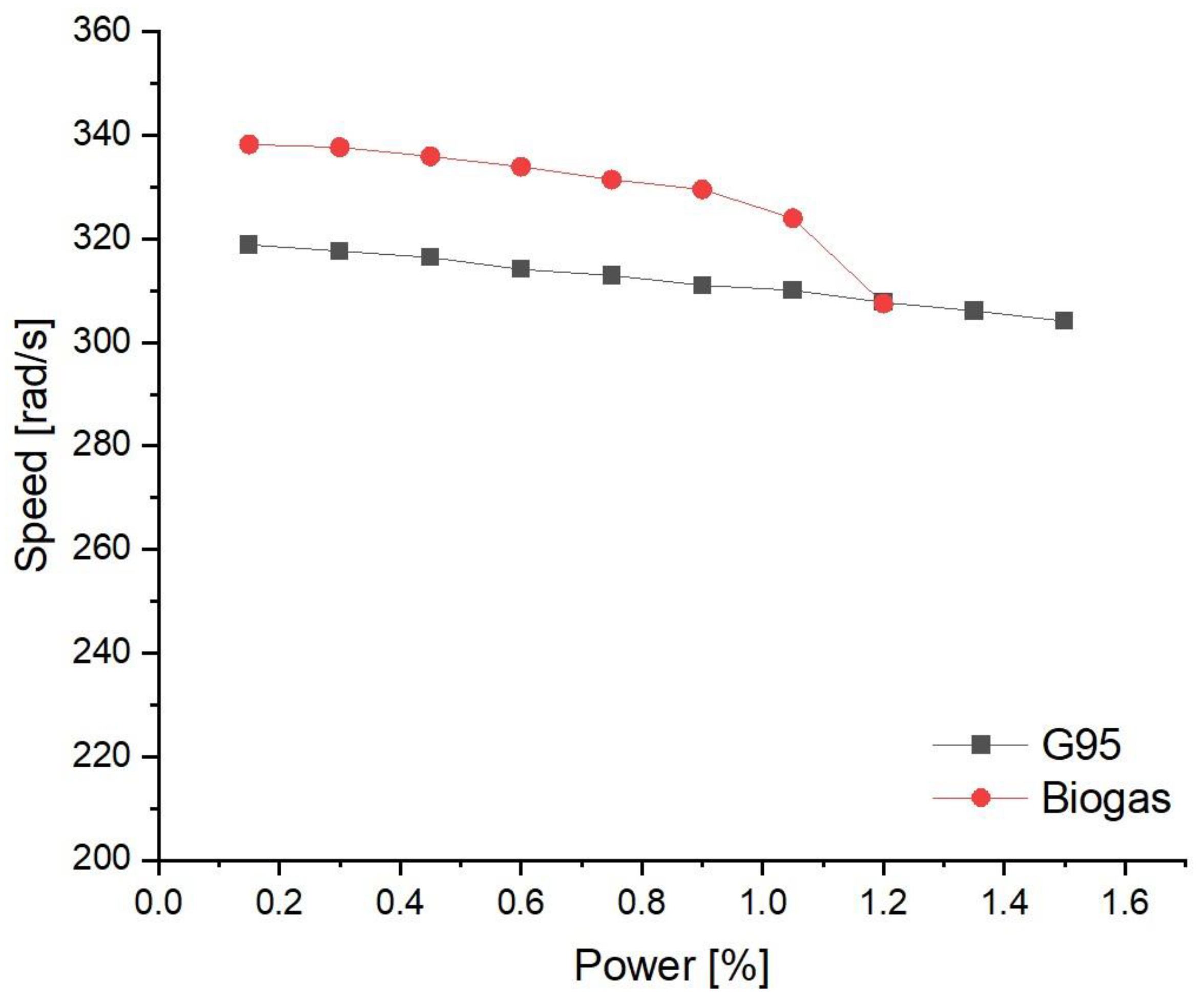
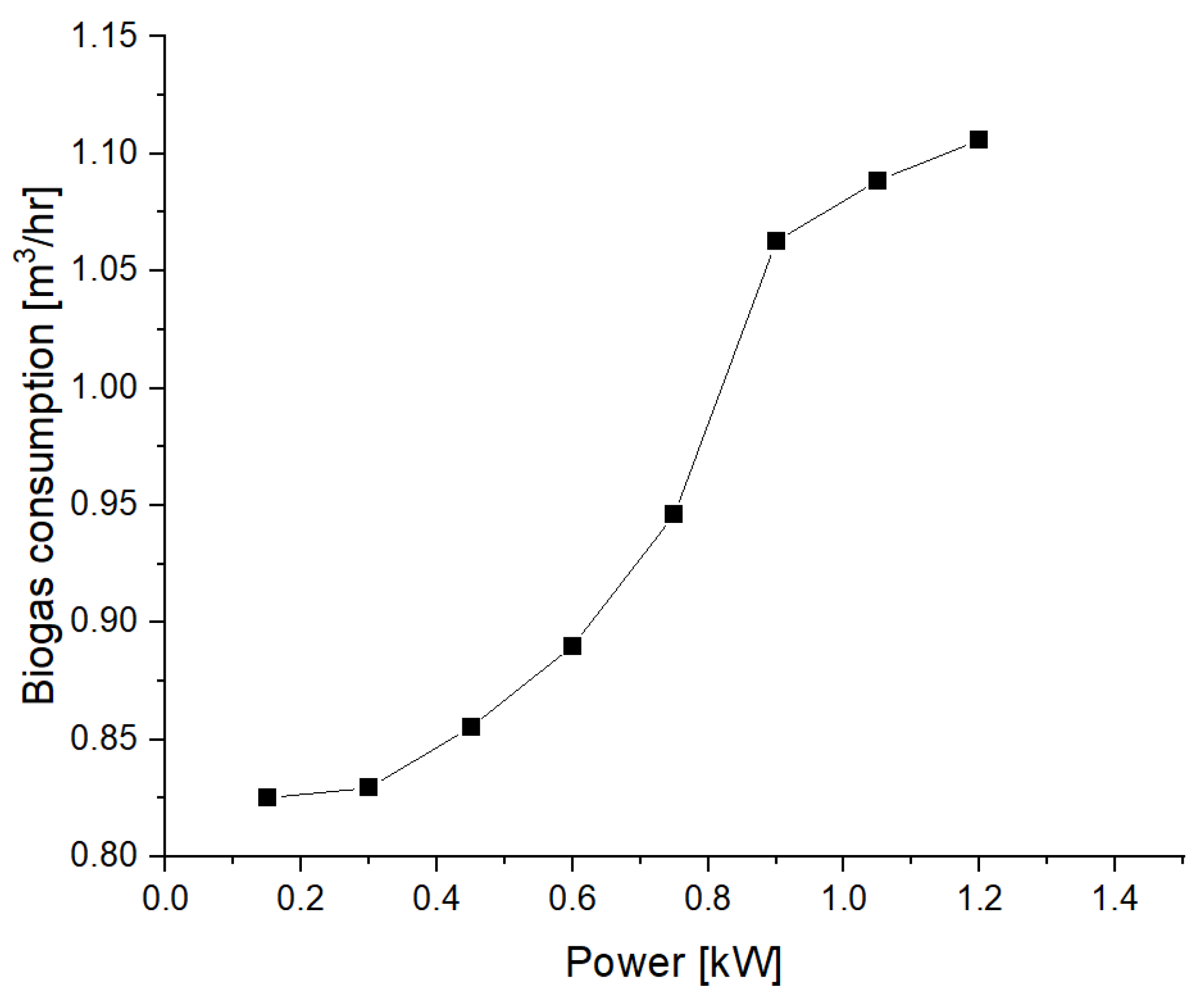
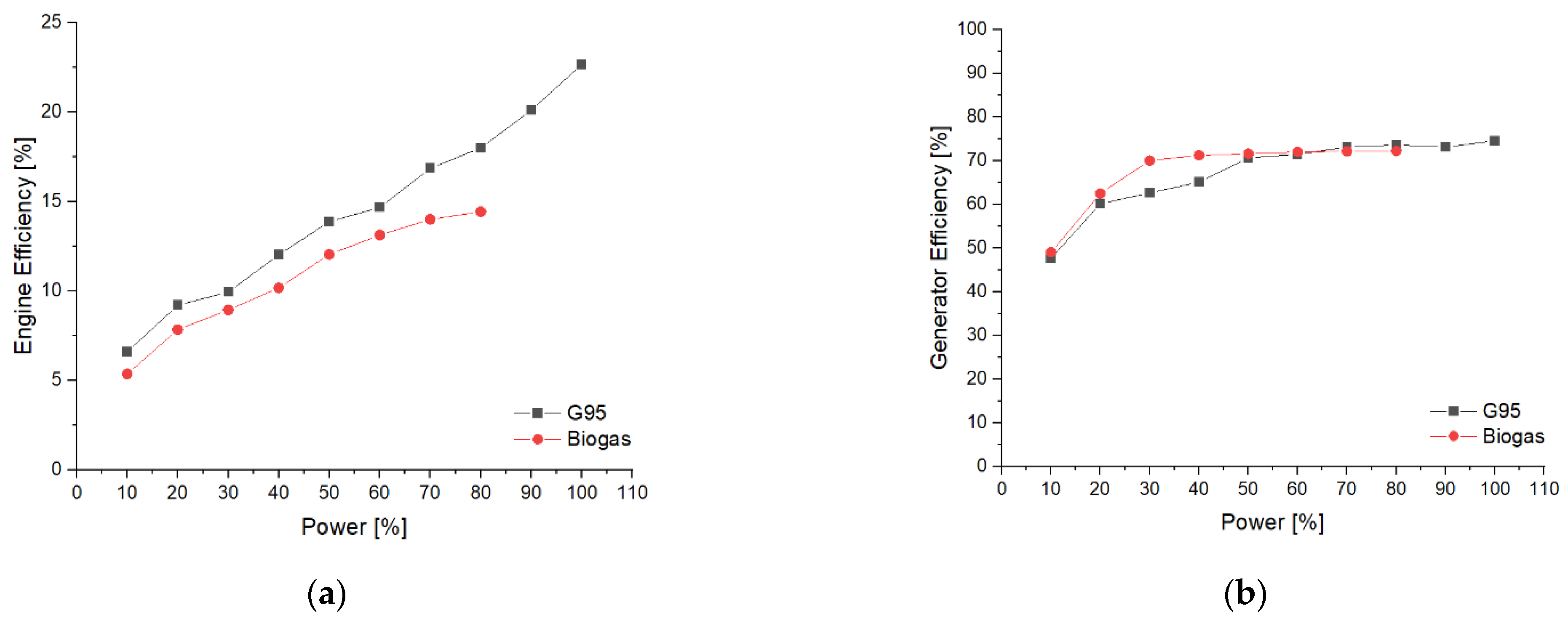
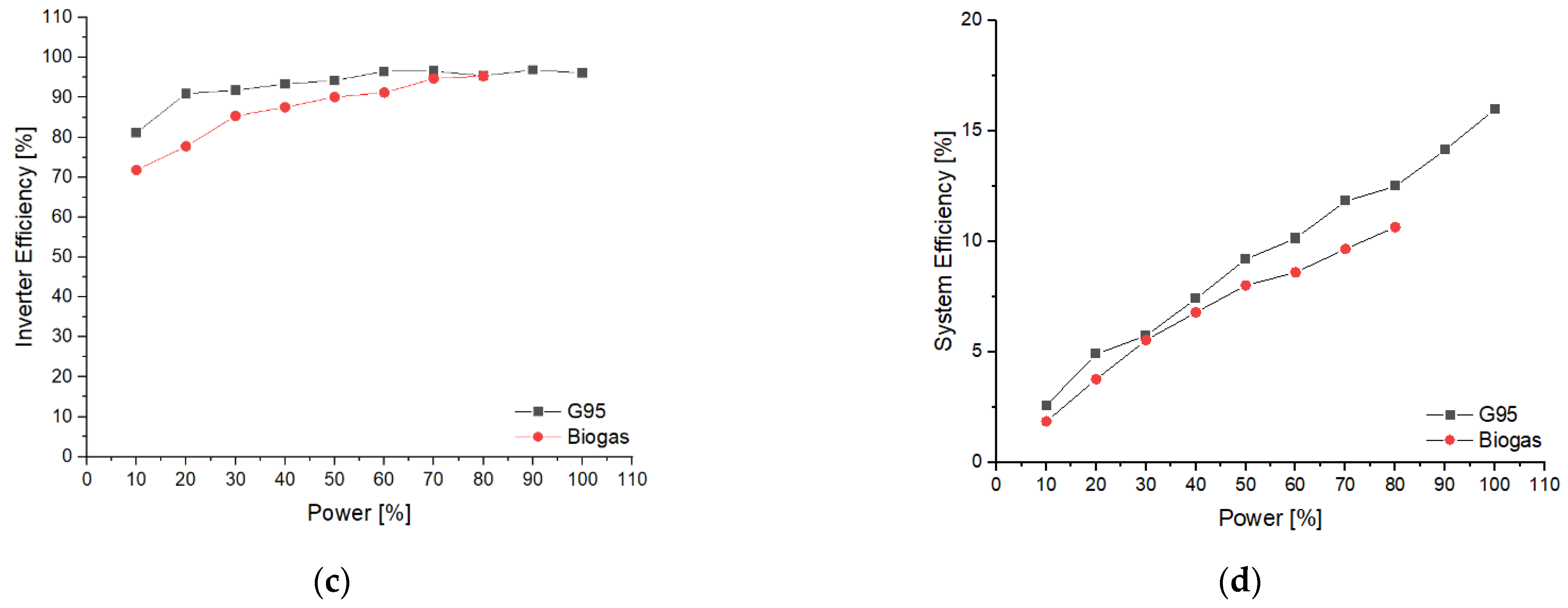
| Symbol | Quantity | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal output power | 1.5 kW | |
| Nominal SEIG line-to-line voltage | 220 V | |
| Nominal SEIG frequency | 50 Hz | |
| Excitation capacitors | 40 μF (Δ connection) | |
| Nominal DC voltage | 400 V | |
| Nominal grid voltage | 220 V | |
| Grid frequency | 50 Hz | |
| Triangular carrier frequency | 10 kHz | |
| Sampling frequency | 20 kHz | |
| SEIG-side inductor | 2 mH | |
| DC bus capacitor | 1000 μF | |
| LCL filter inductor | 1 mH | |
| Grid-side inductor | 0.5 mH | |
| LCL filter capacitor | 3 μF | |
| LCL filter damping resistor | 1 Ω |
| Composition | Content |
|---|---|
| CH4 | 68.5–70.0% |
| CO2 | 30% |
| H2S | 0.14–0.24% |
| Parts | Capital Cost | Annual Operating Cost | Salvage Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine with biogas modification | USD 260 | USD 35 | - |
| Generator (SEIG) | USD 150 | - | USD 75 |
| Power converter | USD 450 | - | USD 200 |
| Housing and piping | USD 140 | USD 7 | - |
| Total | USD 1000 | USD 42 | USD 270 |
| Indicators | Biogas in This Study | 3 kW PV |
|---|---|---|
| Energy yield | 3153 kWh/year | 4200 kWh/year |
| Project period | 5 years | 25 years |
| LCC | USD 1046 | USD 4738 |
| Payback period | 2.8 years | 9.4 years |
| LCOE | USD 0.07/kWh | USD 0.05/kWh |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trairat, P.; Somkun, S.; Kaewchum, T.; Suriwong, T.; Maneechot, P.; Panpho, T.; Wansungnern, W.; Banthuek, S.; Prasit, B.; Kiatsiriroat, T. Grid Integration of Livestock Biogas Using Self-Excited Induction Generator and Spark-Ignition Engine. Energies 2023, 16, 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16134963
Trairat P, Somkun S, Kaewchum T, Suriwong T, Maneechot P, Panpho T, Wansungnern W, Banthuek S, Prasit B, Kiatsiriroat T. Grid Integration of Livestock Biogas Using Self-Excited Induction Generator and Spark-Ignition Engine. Energies. 2023; 16(13):4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16134963
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrairat, Panupon, Sakda Somkun, Tanakorn Kaewchum, Tawat Suriwong, Pisit Maneechot, Teerapon Panpho, Wikarn Wansungnern, Sathit Banthuek, Bongkot Prasit, and Tanongkiat Kiatsiriroat. 2023. "Grid Integration of Livestock Biogas Using Self-Excited Induction Generator and Spark-Ignition Engine" Energies 16, no. 13: 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16134963
APA StyleTrairat, P., Somkun, S., Kaewchum, T., Suriwong, T., Maneechot, P., Panpho, T., Wansungnern, W., Banthuek, S., Prasit, B., & Kiatsiriroat, T. (2023). Grid Integration of Livestock Biogas Using Self-Excited Induction Generator and Spark-Ignition Engine. Energies, 16(13), 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16134963







