Research on Unsteady Inverse Heat Conduction Based on Dynamic Matrix Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
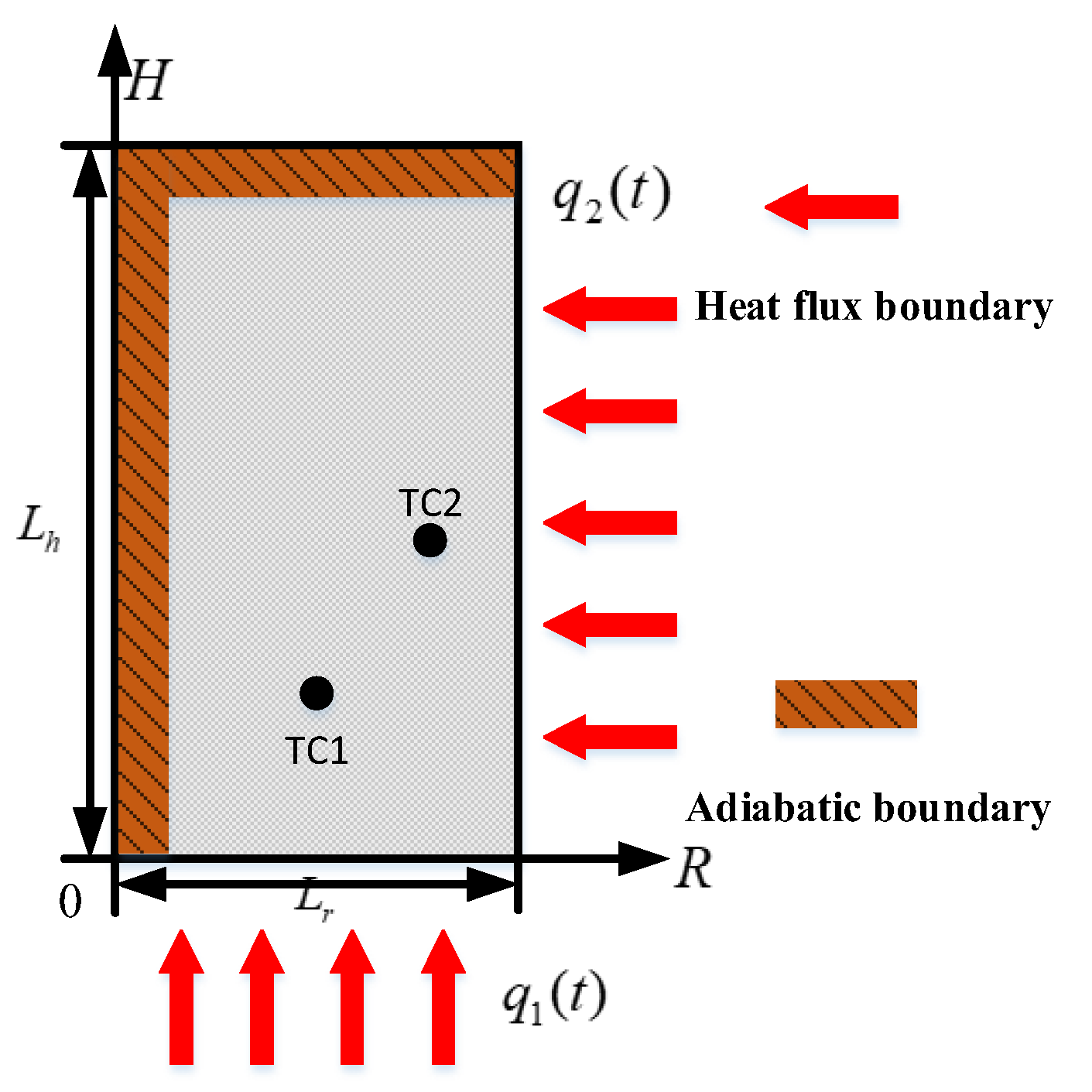
2. Two-Dimensional Heat Transfer Model and Solution
2.1. Heat Conduction Model
2.2. Finite Difference Method
3. Estimation of Boundary Heat Fluxes Based on Dynamic Matrix Control
3.1. Predictive Model of Temperature
3.2. Establishing a Rolling Optimization Objective Function
3.3. Solving for the Measurement Point Sensitivity Coefficient
3.4. Solving for Optimal Regularization Parameters by the Residual Principle
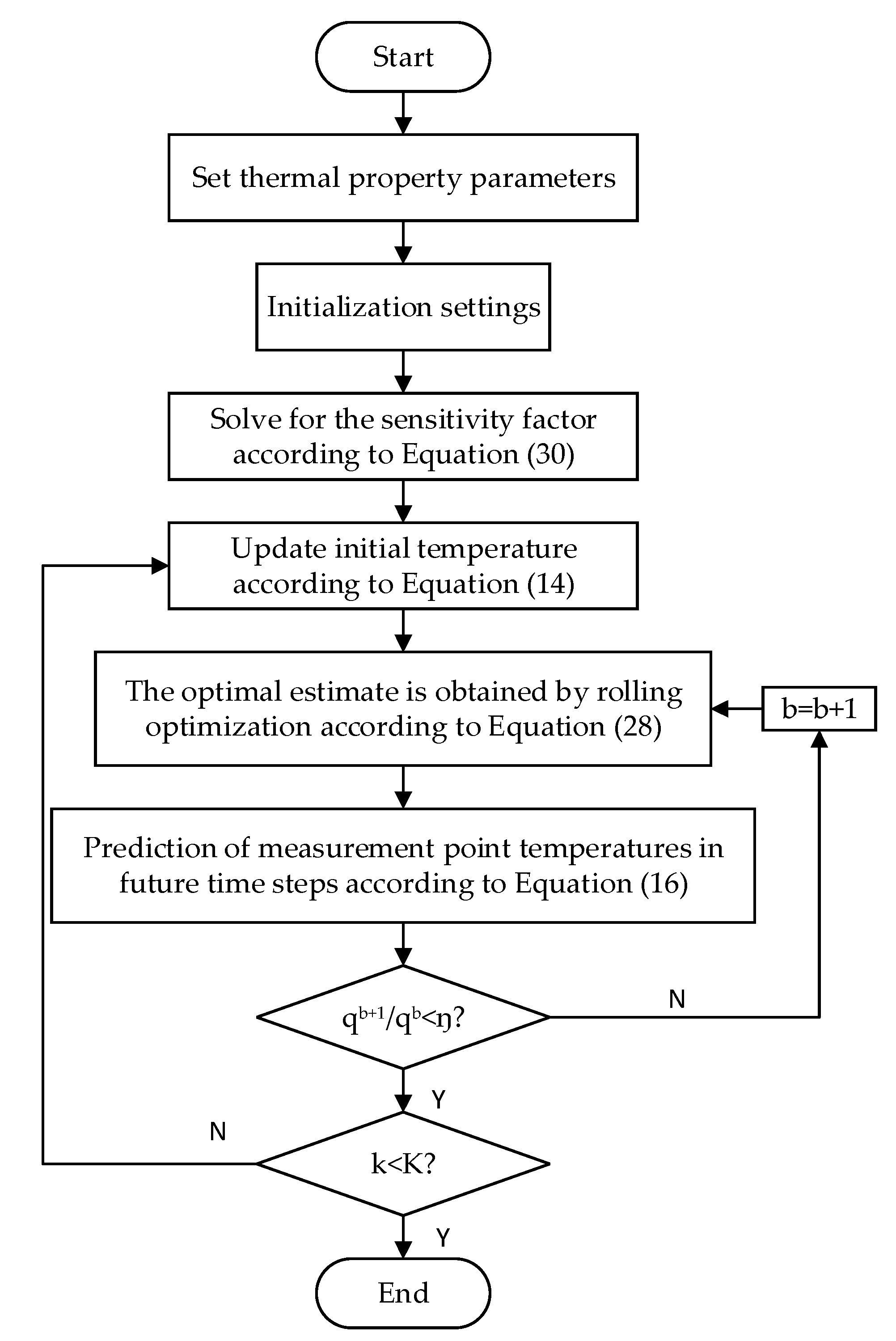
3.5. Steps of Inverse Heat Transfer Algorithm Based on Dynamic Matrix Control
4. Algorithm Verification
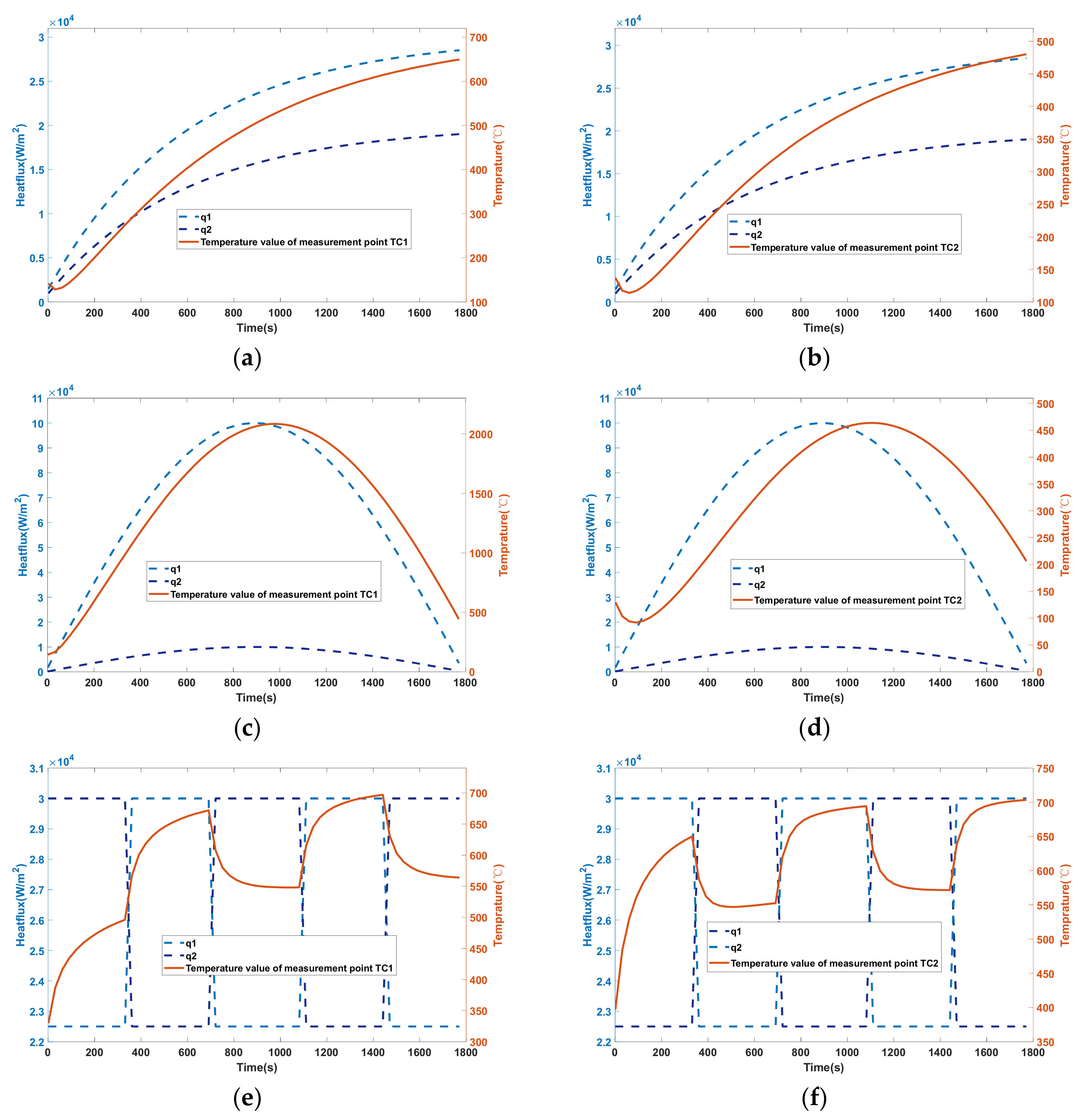
4.1. Verification of Algorithm Validity
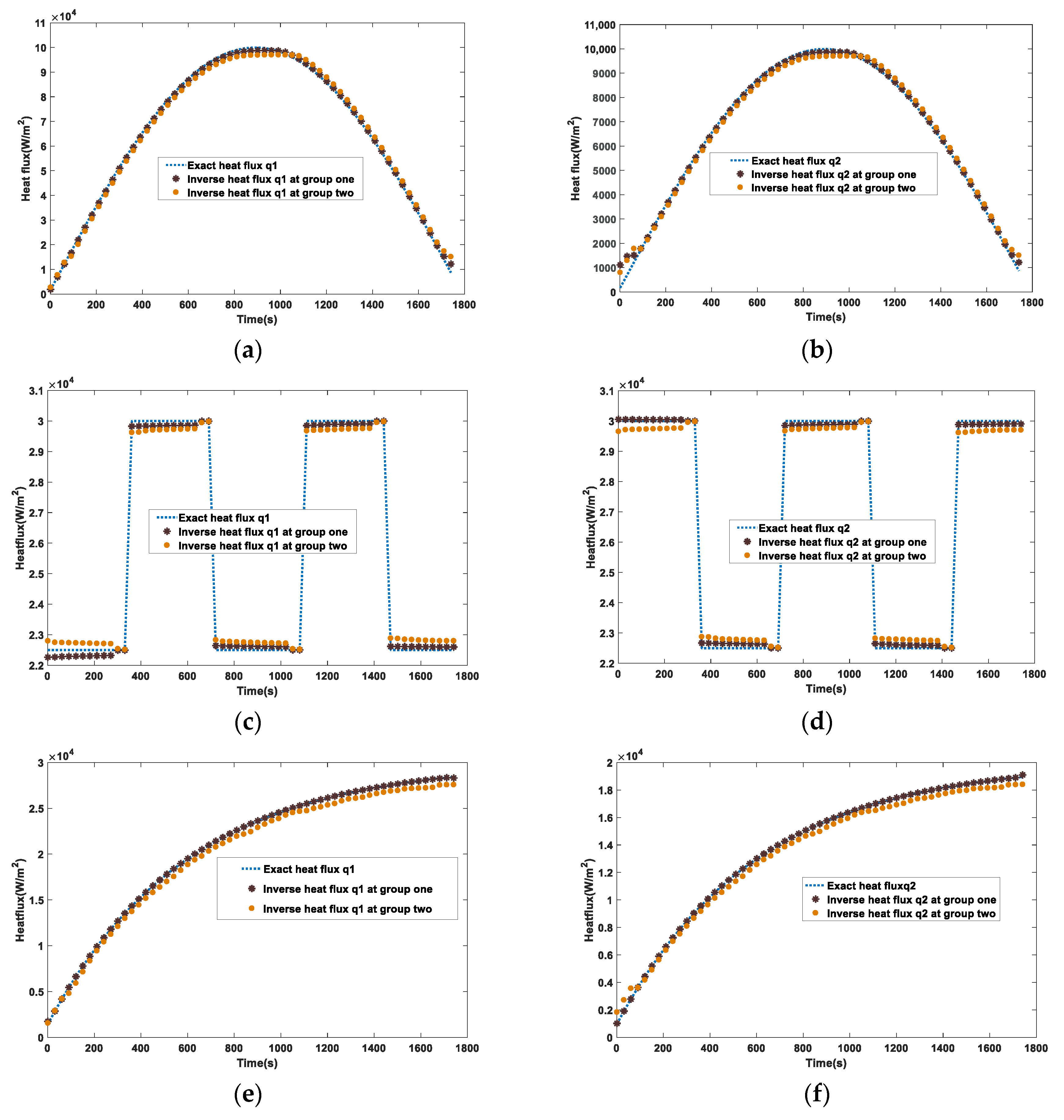
4.2. Measurement Point Location Effects on Inversion Results
4.3. Influence of the Number of Measurement Points on the Inversion Results
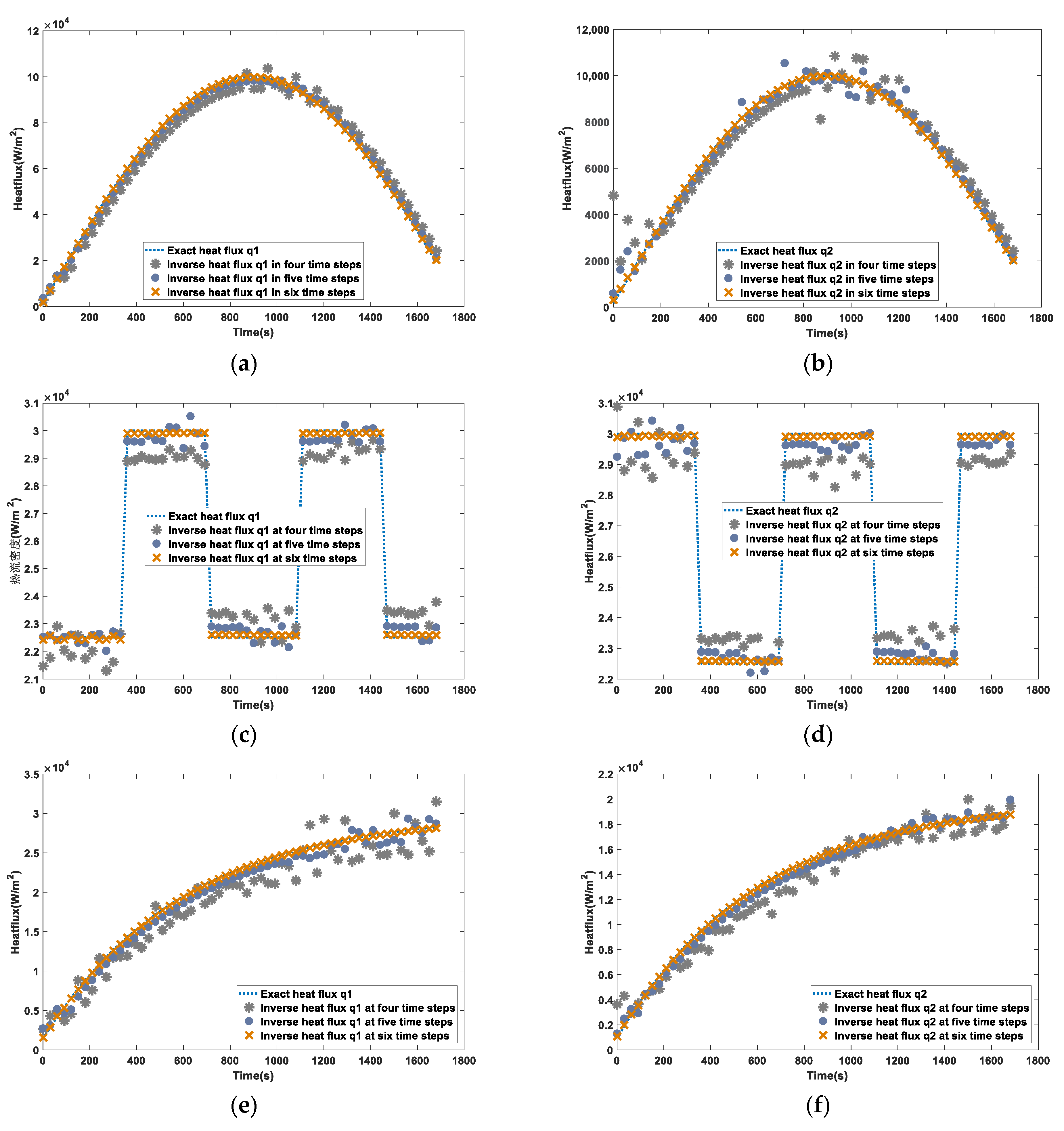
4.4. Influence of Future Time Steps on Inversion Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, A.; Yuan, X.; Qian, Q. Estimation of surface heat flux for MF-1 flight test. Acta Aerodyn. Sin. 2019, 37, 938–944. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.W.; Chen, H.B.; Lu, T. Estimation of the time-dependent convective boundary condition in a horizontal pipe with thermal stratification based on inverse heat conduction problem. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 132, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, H.; Dou, B.L.; Huang, H.J.; Wu, W.D.; Wang, Z.Y. Experimental and numerical research of thermal stratification with a novel inlet in a dynamic hot water storage tank. Renew. Energy Int. J. 2017, 111, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michele, C.; Antonino, C.; Massimiliano, D.L. Solution of an inverse heat conduction problem with third-type boundary conditions. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 175, 107466. [Google Scholar]
- Frackowiak, A.; Wroblewska, A.; Cialkowski, M. Trefftz numerical functions for solving inverse heat conduction problems. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 177, 107566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, C.Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Xiao, J.E.; Hsu, S.M.; Yeih, M. A collocation method with space-time radial polynomials for inverse heat conduction problems. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2021, 122, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, C.C.; Lacerda, C.R.; Colaco, M. Automatic selection of regularization parameter in inverse heat conduction problems. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 139, 106403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Chen, W.L. A nonlinear inverse problem in estimating the heat flux of the disc in a disc brake system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2011, 31, 2439–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Li, G.; Wei, L. An improved sequential function specification coupled with Broyden combined method for determination of transient temperature field of the steel billet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 186, 122489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Wen, S.; Wang, Y.F. Real-time reconstruction of the time-dependent heat flux and temperature distribution in participating media by using the Kalman filtering technique. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 157, 113667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Wang, G.; Chen, H. Application of unscented Rauch-Tung-Striebel smoother to nonlinear inverse heat conduction problems. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 112, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; He, L. Evaluation of multi-objective inverse heat conduction problem based on particle swarm optimization algorithm, normal distribution and finite element method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 127, 1114–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Ju, H. Inverse identification of interfacial heat transfer coefficient between the casting and metal mold using neural network. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Huang, Y. Applying neural networks to the solution of forward and inverse heat conduction problems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2006, 49, 4732–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.B.; Peng, X.; Wang, K. Real-time estimation of thermal boundary of unsteady heat conduction system using PID algorithm. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2020, 153, 106395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.B.; Wang, K.; Xu, P. Numerical and experimental verification of the single neural adaptive PID real-time inverse method for solving inverse heat conduction problems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 189, 122657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S. Simultaneous reconstruction of thermal boundary condition and physical properties of participating medium. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 163, 106853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.K.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, A.P. A Survey on Ofiset-free Model Predictive Control. Acta Autom. Sin. 2020, 46, 858–877. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, W.; Liu, G.B. Overview of Intelligent Algorithms in Nonlinear Model Predictive Control. J. Syst. Simul. 2008, 20, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, C.; Park, C.; Park, D.; Kim, J. Optimal hybrid parameter selection for stable sequential solution of inverse heat conduction problem. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 183, 122076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostajeran, F.; Mokhtari, R. DeepBHCP: Deep neural network algorithm for solving backward heat conduction problems. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2022, 272, 108236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Wu, B.; Chen, Q. Numerical reconstruction of a non-smooth heat flux in the inverse radial heat conduction problem. Appl. Math. Lett. 2021, 111, 106658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.H. Contrastive Research of a New Kind of Dynamic Matrix Control and Improved PID Control. Comput. Digit. Eng. 2021, 49, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.B.; Deng, Y.Z.; Sun, X.G. Solving of Two-Dimensional Unsteady Inverse Heat Conduction Problems Based on Boundary Element Method and Sequential Function Specification Method. Complexity 2018, 2018, 6741632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
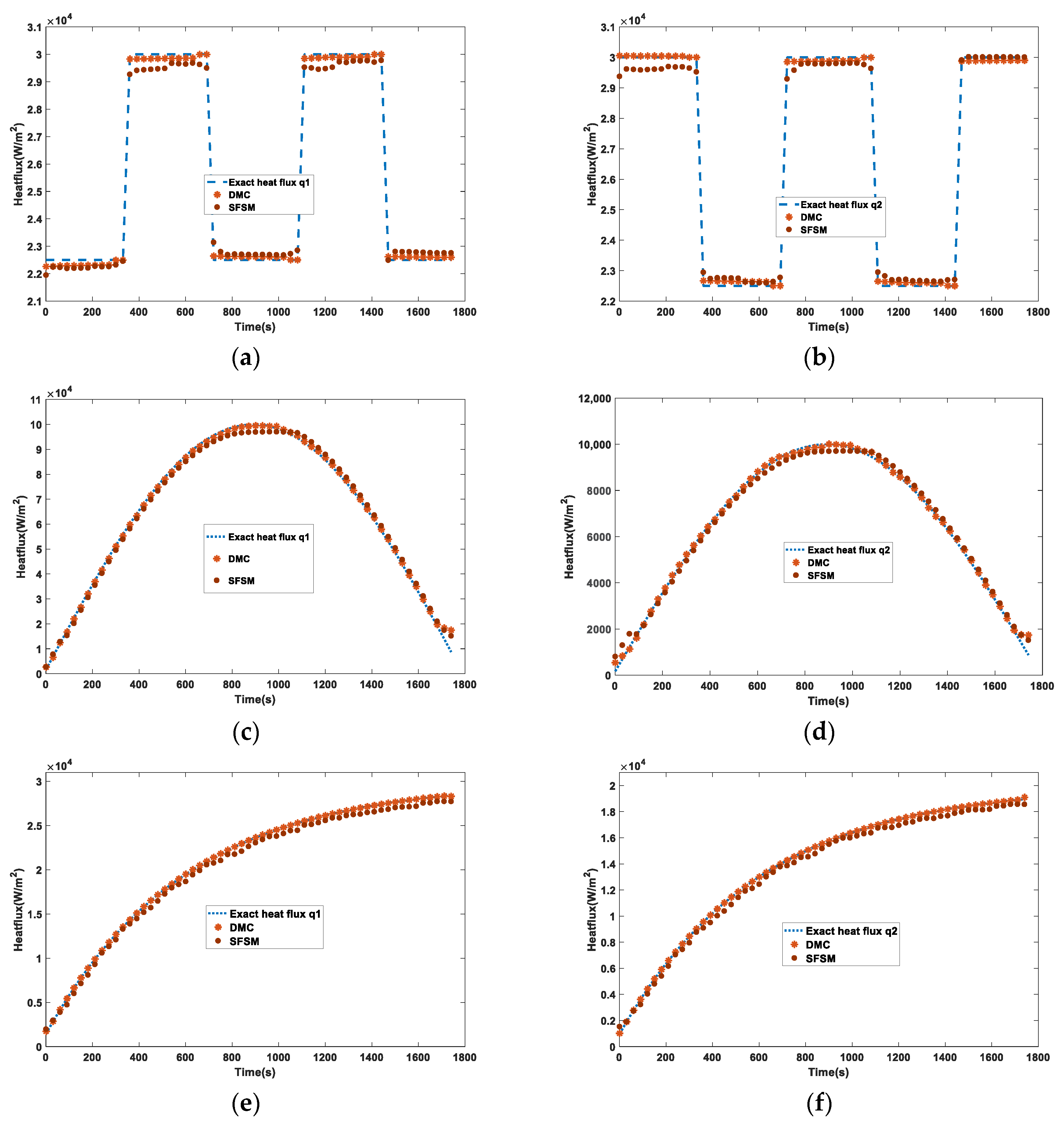

| Heat Flux Type | DMC | SFSM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sinusoidal type | 553.5310 | 0.7573 | 684.0719 | 0.9321 |
| Square type | 134.5381 | 105.6714 | 354.3405 | 280.0323 |
| Exponential type | 35.4705 | 5.224 | 634.3496 | 415.3583 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.; Li, J.; Liu, D. Research on Unsteady Inverse Heat Conduction Based on Dynamic Matrix Control. Energies 2023, 16, 4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114420
Huang W, Li J, Liu D. Research on Unsteady Inverse Heat Conduction Based on Dynamic Matrix Control. Energies. 2023; 16(11):4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114420
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Weichao, Jiahao Li, and Ding Liu. 2023. "Research on Unsteady Inverse Heat Conduction Based on Dynamic Matrix Control" Energies 16, no. 11: 4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114420
APA StyleHuang, W., Li, J., & Liu, D. (2023). Research on Unsteady Inverse Heat Conduction Based on Dynamic Matrix Control. Energies, 16(11), 4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114420






