Synergic Combination of Hardware and Software Innovations for Energy Efficiency and Process Control Improvement: A Steel Industry Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Study: Process Description and Specifications
2.2. Hardware and Software Innovations
2.2.1. Installation of an Insulated Tunnel
2.2.2. APC Design
2.2.3. Computational Framework
3. Results and Discussion
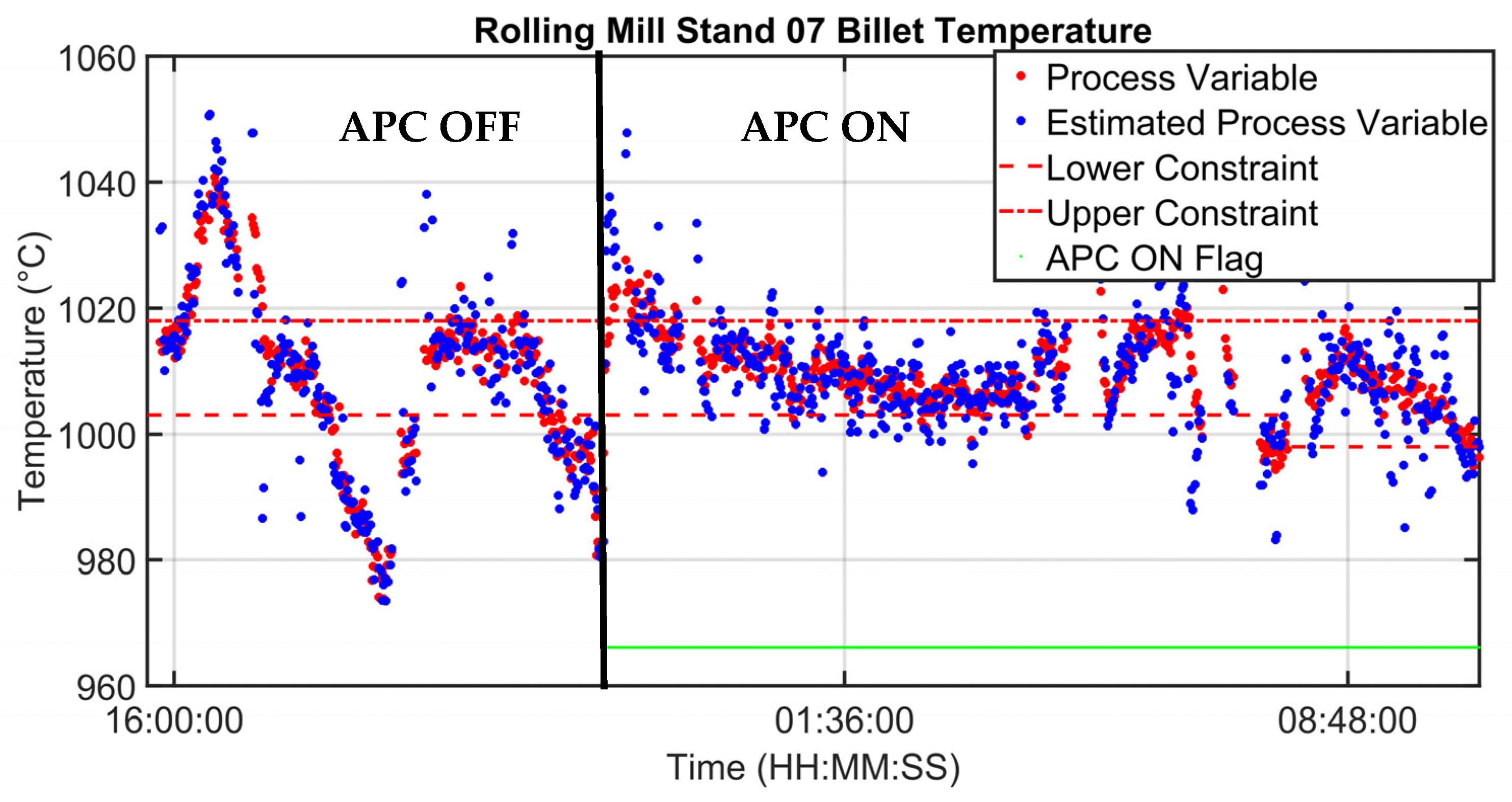
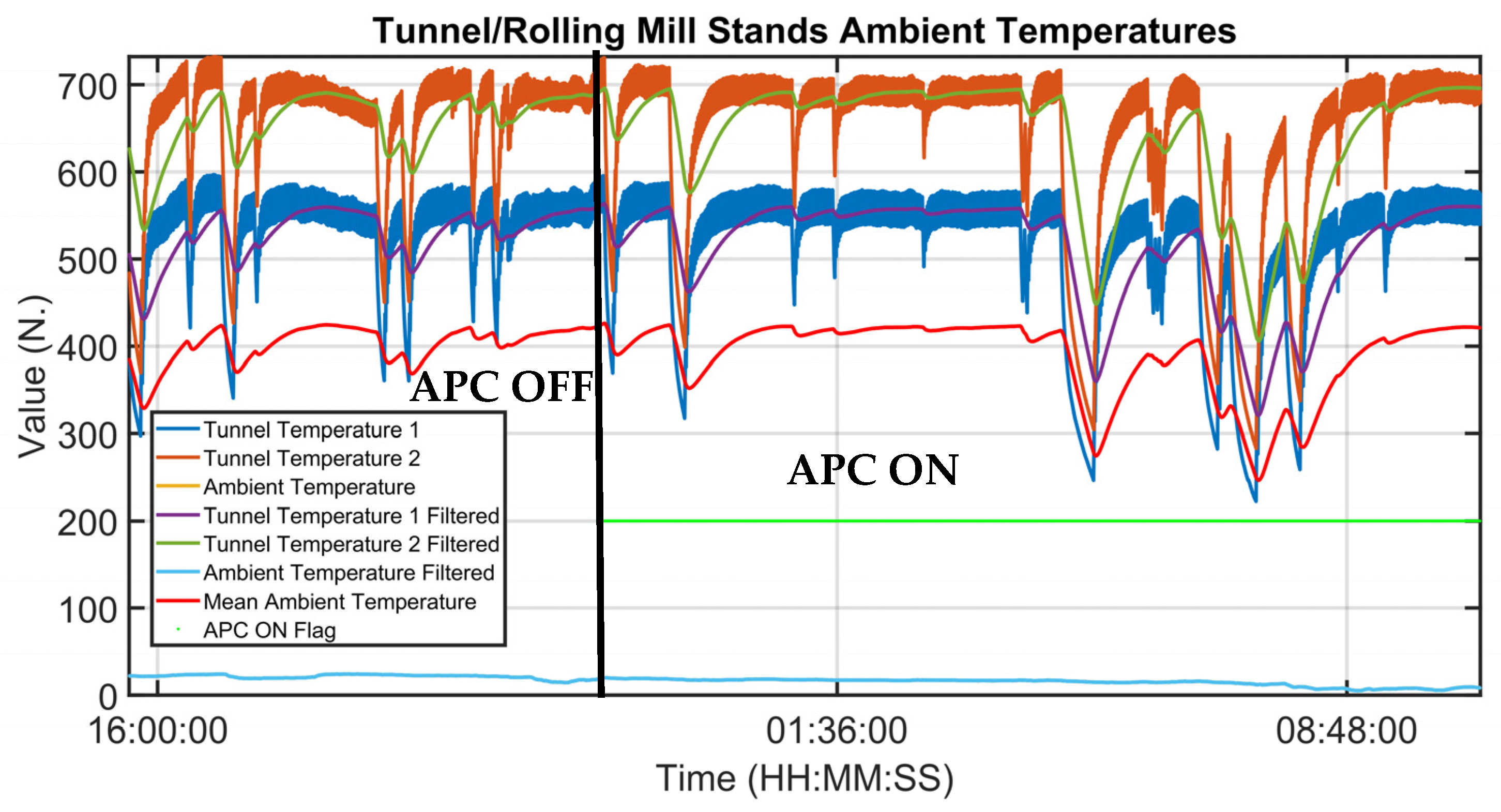
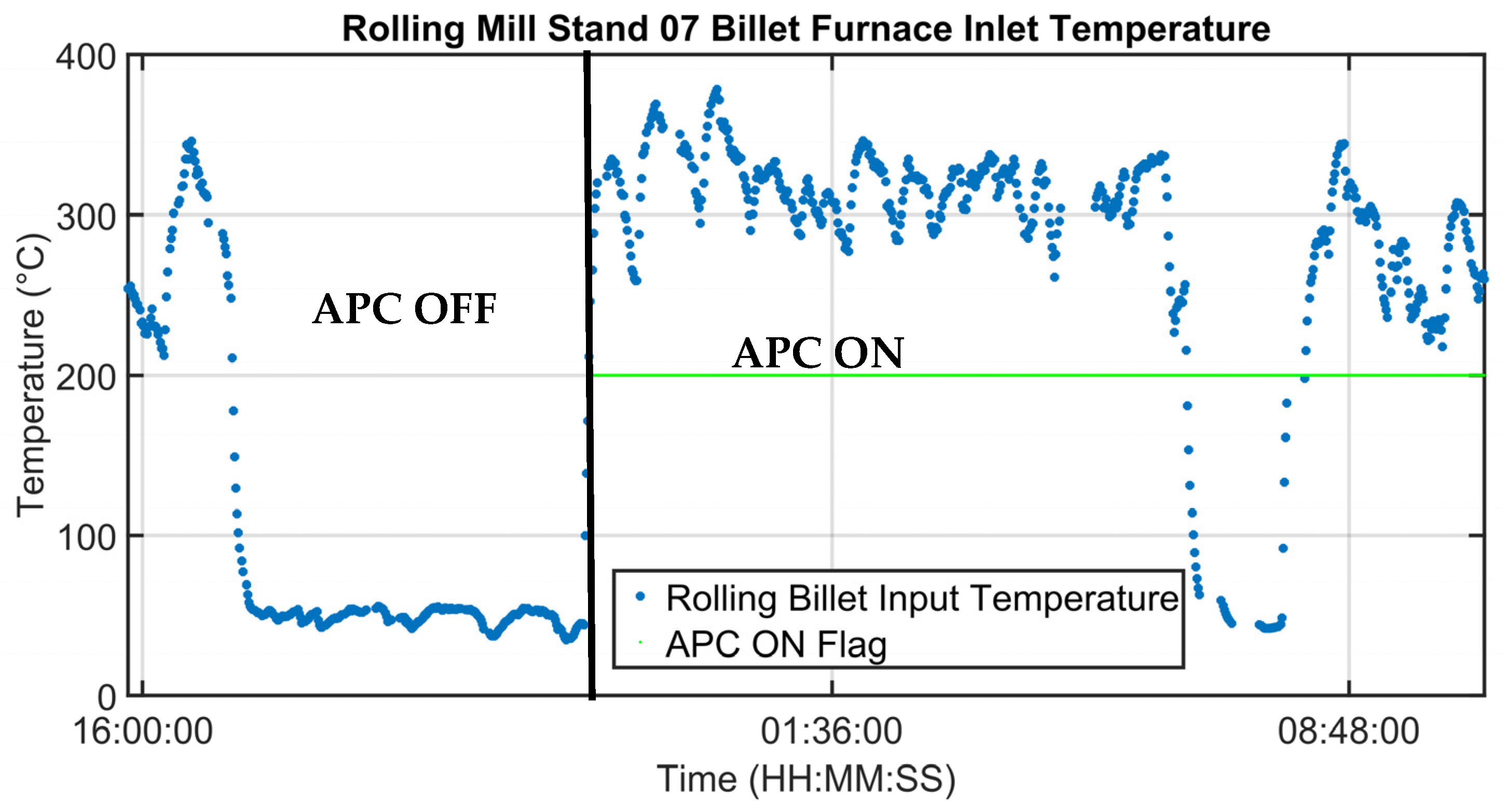
3.1. Control Results
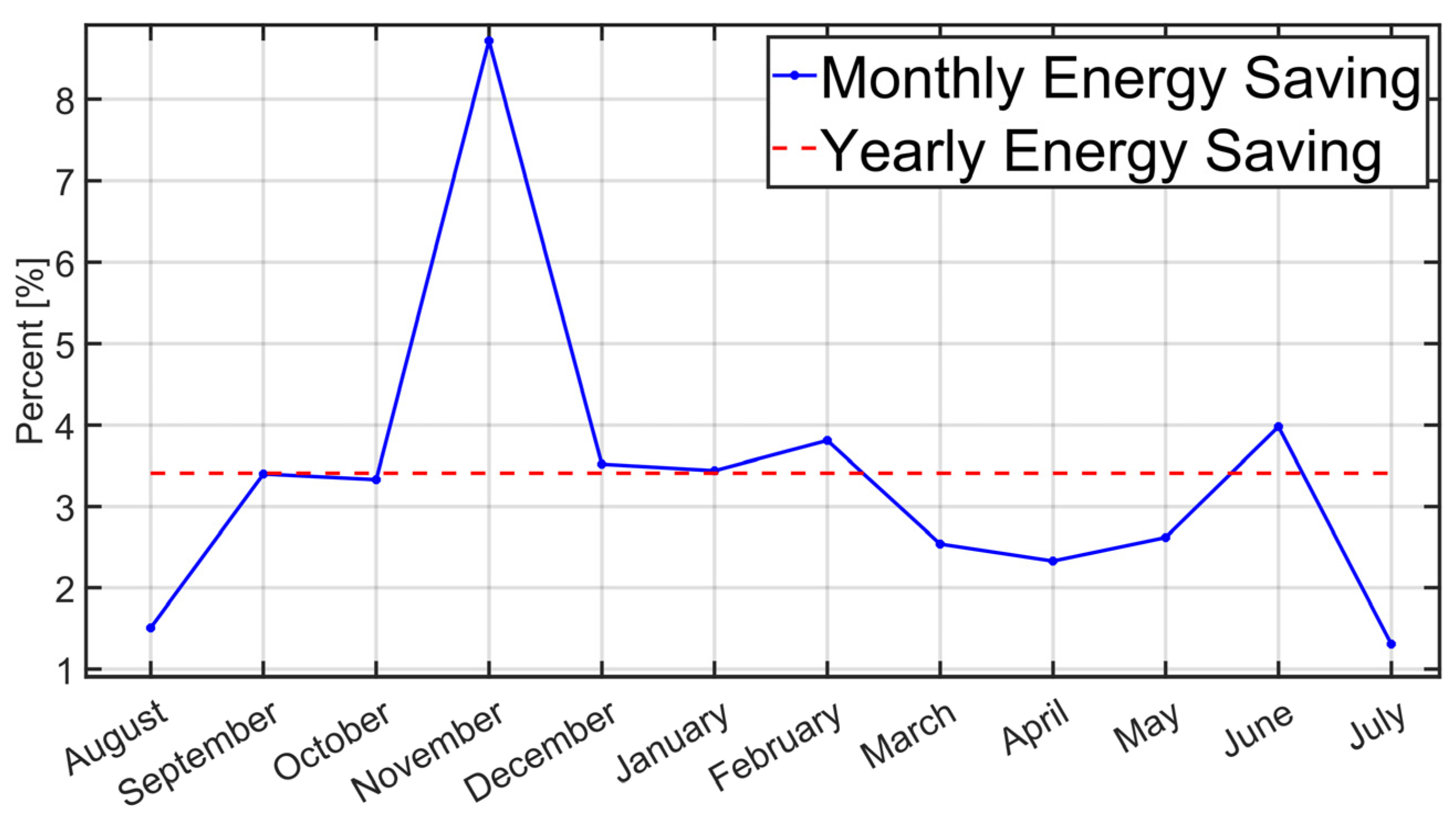
3.2. Energy Efficiency Improvement Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Directive 2009/28/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009. On the Promotion of the Use of Energy from Renewable Sources and Amending and Subsequently Repealing Directives 2001/77/EC and 2003/30/EC (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2009/28/oj (accessed on 4 July 2022).
- Agenda 2030. Available online: https://unric.org/it/agenda-2030/ (accessed on 11 August 2022).
- Sechi, S.; Giarola, S.; Leone, P. Taxonomy for Industrial Cluster Decarbonization: An Analysis for the Italian Hard-to-Abate Industry. Energies 2022, 15, 8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, P. Clean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions Abatement; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Cao, W.; Chen, X.; She, J. Intelligent Optimization and Control of Complex Metallurgical Processes; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoli, S.M.; Barboni, L.; Cocchioni, F.; Pepe, C. Advanced process control aimed at energy efficiency improvement in process industries. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Lyon, France, 20–22 February 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoli, S.M.; Pepe, C.; Rocchi, M.; Astolfi, G. Application of Advanced Process Control techniques for a cement rotary kiln. In Proceedings of the 2015 19th International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC), Cheile Gradistei, Romania, 14–16 October 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holappa, L. Challenges and Prospects of Steelmaking towards the Year 2050. Metals 2021, 11, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Review of the Energy Consumption and Production Structure of China’s Steel Industry: Current Situation and Future Development. Metals 2020, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, N.; Sankowski, L.; Kaiser, F.; Schwotzer, C.; Echterhof, T.; Pfeifer, H. Towards CO2-neutral process heat generation for continuous reheating furnaces in steel hot rolling mills—A case study. Energy 2021, 224, 120155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ma, L.; Zayed, M.E.; Elsheikh, A.H.; Li, W.; Yan, Q.; Wang, J. Industrial reheating furnaces: A review of energy efficiency assessments, waste heat recovery potentials, heating process characteristics and perspectives for steel industry. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 147, 1209–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, G.; Barboni, L.; Cocchioni, F.; Dai Prè, M.; Manganotti, D.; Orlietti, L.; Pepe, C.; Zanoli, S.M. Optimization of Steel Industry Billets Reheating Furnaces: An EPC-Based APC Approach. In Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on Science and Technology of Steelmaking: The Challenge of Industry 4.0, Venice, Italy, 13–15 June 2018; Available online: https://www.scopus.com/record/display.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85062062626&origin=resultslist&sort=plf-f (accessed on 26 August 2022).
- Govender, E.; Telukdarie, A.; Sishi, M.N. Approach for Implementing Industry 4.0 Framework in the Steel Industry. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM), Macao, China, 15–18 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niekurzak, M.; Mikulik, J. Modeling of Energy Consumption and Reduction of Pollutant Emissions in a Walking Beam Furnace Using the Expert Method—Case Study. Energies 2021, 14, 8099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Su, Z.; Li, G.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, W. Development of a double model slab tracking control system for the continuous reheating furnace. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 113, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, H.S.O.; Almeida, P.E.M.; Cardoso, R.T.N. Fuel Costs Minimization on a Steel Billet Reheating Furnace Using Genetic Algorithms. Model. Simul. Eng. 2017, 2017, 2731902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tan, C.K.; Broughton, J.; Roach, P.A.; Varga, L. Model-based multi-objective optimisation of reheating furnace operations using genetic algorithm. Energy Procedia 2017, 142, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.G.; Kong, L.P.; Guo, J.H.; Song, M.X.; Jiao, Z.J. Multi-Objective Optimization of Slab Heating Process in Walking Beam Reheating Furnace Based on Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Steel Res. Int. 2020, 92, 2000382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Wang, C.; Hu, Y.; Tan, C.K.; Roach, P.A.; Varga, L. Function Value-Based Multi-Objective Optimisation of Reheating Furnace Operations Using Hooke-Jeeves Algorithm. Energies 2018, 11, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinböck, A. Model-Based Control and Optimization of a Continuous Slab Reheating Furnace; Shaker Verlag GmbH: Aachen, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Steinboeck, A.; Wild, D.; Kugi, A. Nonlinear model predictive control of a continuous slab reheating furnace. Control Eng. Pract. 2013, 21, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, S. System of Energy-Saving Optimal Control of Metal Heating Process in Heat Treatment Furnaces of Rolling Mills. Machines 2019, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinboeck, A.; Graichen, K.; Kugi, A. Dynamic Optimization of a Slab Reheating Furnace With Consistent Approximation of Control Variables. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2011, 19, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.Y.; Huang, J.B. Optimization of a slab heating pattern for minimum energy consumption in a walking-beam type reheating furnace. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 85, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X.M.; Rodriguez-Ayerbe, P.; Lawayeb, F.; Dumur, D.; Mouchette, A. Temperature control of reheating furnace based on distributed model predictive control. In Proceedings of the 2014 18th International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC), Sinaia, Romania, 17–19 October 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carhuavilca, L.A.; Castro, E.N.; Rodriguez, A.L.; Esparta, D.B. A Comparison of GPC and Fuzzy Smith Predictor for Temperature Control of Steel Slab Reheating Furnace. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE XXVIII International Conference on Electronics, Electrical Engineering and Computing (INTERCON), Lima, Peru, 5–7 August 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenghuan, L.; Guangxiang, H.; Lizhen, W. Optimization of Furnace Combustion Control System Based on Double Cross-Limiting Strategy. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, Changsha, China, 11–12 May 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wu, M.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Cao, W.; Du, S.; Pedrycz, W. Hybrid Intelligent Control Based on Condition Identification for Combustion Process in Heating Furnace of Compact Strip Production. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 2790–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaohua, L.; Yashuai, W.; Yunhai, L. Research on the intelligent temperature control based on ANFIS for reheating furnace in rolling steel line. In Proceedings of the 27th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (2015 CCDC), Qingdao, China, 23–25 May 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, I.O.; Rivas, R.; Feliu, V.; Sanchez, L.P.; Sanchez, L.A. Fuzzy Gain Scheduled Smith Predictor for Temperature Control in an Industrial Steel Slab Reheating Furnace. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2016, 14, 4439–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinboeck, A.; Graichen, K.; Wild, D.; Kiefer, T.; Kugi, A. Model-based trajectory planning, optimization, and open-loop control of a continuous slab reheating furnace. J. Process Control 2011, 21, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, S.; Ferretti, I.; Zavanella, L.E. Energy savings in reheating furnaces through process modelling. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 42, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgür, A.; Uygun, Y.; Hütt, M.T. A review of planning and scheduling methods for hot rolling mills in steel production. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 151, 106606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Tian, H. Integrated Scheduling of Reheating Furnace and Hot Rolling Based on Improved Multiobjective Differential Evolution. Complexity 2018, 2018, 1919438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilmer, Q.; Haeussler, S.; Missbauer, H. Optimal Synchronization of the Hot Rolling Stage in Steel Production. IFAC-Pap. 2019, 52, 1615–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, K.; Kumar, S. Increase in energy efficiency of a steel billet reheating furnace by heat balance study and process improvement. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Cho, J.R.; Lee, K.H. Efficiency analysis of air-fuel and oxy-fuel combustion in a reheating furnace. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 121, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukka, A.; Heikkinen, E.-P.; Fabritius, T. The Atmosphere’s Effect on Stainless Steel Slabs’ Oxide Formation in a CH4-Fuelled Reheating Furnace. Metals 2021, 11, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillat, S. Burners in the steel industry: Utilization of by-product combustion gases in reheating furnaces and annealing lines. Energy Procedia 2017, 120, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangoli, S.; Buragino, G.; He, X.; Arsland, E.; Verderame, P.; Hendershot, R.; Slavejkov, A.; Bellis, F.; Bellis, L.; McCarthy, J.; et al. Importance of Control Strategy for Oxy-Fuel Burners in a Steel Reheat Furnace. In Proceedings of the AISTech 2013, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 6 May 2013; Available online: https://www.airproducts.de/-/media/airproducts/files/en/335/335-13-010-us-importance-of-control-strategy-for-oxy-fuel-burners.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Garcia, A.M.; Colorado, A.F.; Obando, J.E.; Arrieta, C.E.; Amell, A.A. Effect of the burner position on an austenitizing process in a walking-beam type reheating furnace. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 153, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariramani, S.K.; Yadav, V.; Bansal, R. Energy Conservation Measures in Pusher-Type Reheating Furnace through Modifications and Modernization. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Seminar On “Utilization of Non-Conventional Energy Sources for Sustainable Development of Rural Areas” (ISNCESR ‘16), Bhilai, Chhattisgarh, India, 17–18 March 2016; Available online: https://www.ijsr.net/conf/PARAS16/Mech-06.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Sung, Y.; Kim, S.; Jang, B.; Oh, C.; Jee, T.; Park, S.; Park, K.; Chang, S. Nitric Oxide Emission Reduction in Reheating Furnaces through Burner and Furnace Air-Staged Combustions. Energies 2021, 14, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinks, W.; Mawhinney, M.H.; Shannon, R.A.; Reed, R.J.; Garvey, J.R. Industrial Furnaces; Wiley Online Library: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullinger, P.; Jenkins, B. Industrial and Process Furnaces. Principles, Design and Operation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoli, S.M.; Pepe, C.; Barboni, L. Application of Advanced Process Control techniques to a pusher type reheating furnace. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 659, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoli, S.M.; Pepe, C.; Moscoloni, E.; Astolfi, G. Data Analysis and Modelling of Billets Features in Steel Industry. Sensors 2022, 22, 7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoli, S.M.; Cocchioni, F.; Pepe, C. MPC-based energy efficiency improvement in a pusher type billets reheating furnace. Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 2018, 3, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengel, Y.A. Introduction to Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer; McGraw-Hill Higher Education: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zanoli, S.M.; Cocchioni, F.; Pepe, C. Model Predictive Control with horizons online adaptation: A steel industry case study. In Proceedings of the 2018 European Control Conference (ECC), Limassol, Cyprus, 12–15 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, J.; Scherer, C.W. Control of Linear Parameter Varying Systems with Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljung, L. System Identification. Theory for the User; Prentice-Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Muske, K.R.; Badgwell, T.A. Disturbance modeling for offset-free linear model predictive control. J. Process Control 2002, 12, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannocchia, G.; Rawlings, J.B. Disturbance models for offset-free model predictive control. AIChE J. 2003, 49, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagienard, R.; Grieder, P.; Kerrigan, E.C.; Morari, M. Move blocking strategies in receding horizon control. J. Process Control 2007, 17, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejowski, J.M. Predictive Control with Constraints; Prentice-Hall, Pearson Education Limited: Harlow, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zanoli, S.M.; Pepe, C.; Rocchi, M. Control and optimization of a cement rotary kiln: A model predictive control approach. In Proceedings of the 2016 Indian Control Conference (ICC), Hyderabad, India, 4–6 January 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoli, S.M.; Pepe, C.; Rocchi, M. Cement Rotary Kiln: Constraints Handling and Optimization via Model Predictive Control Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2015 5th Australian Control Conference (AUCC), Gold Coast, QLD, Australia, 5–6 November 2015; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7361950 (accessed on 26 August 2022).
- MathWorks. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/ (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Zanoli, S.M.; Astolfi, G. Application of a Fault Detection and Isolation System on a Rotary Machine. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2013, 2013, 189359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
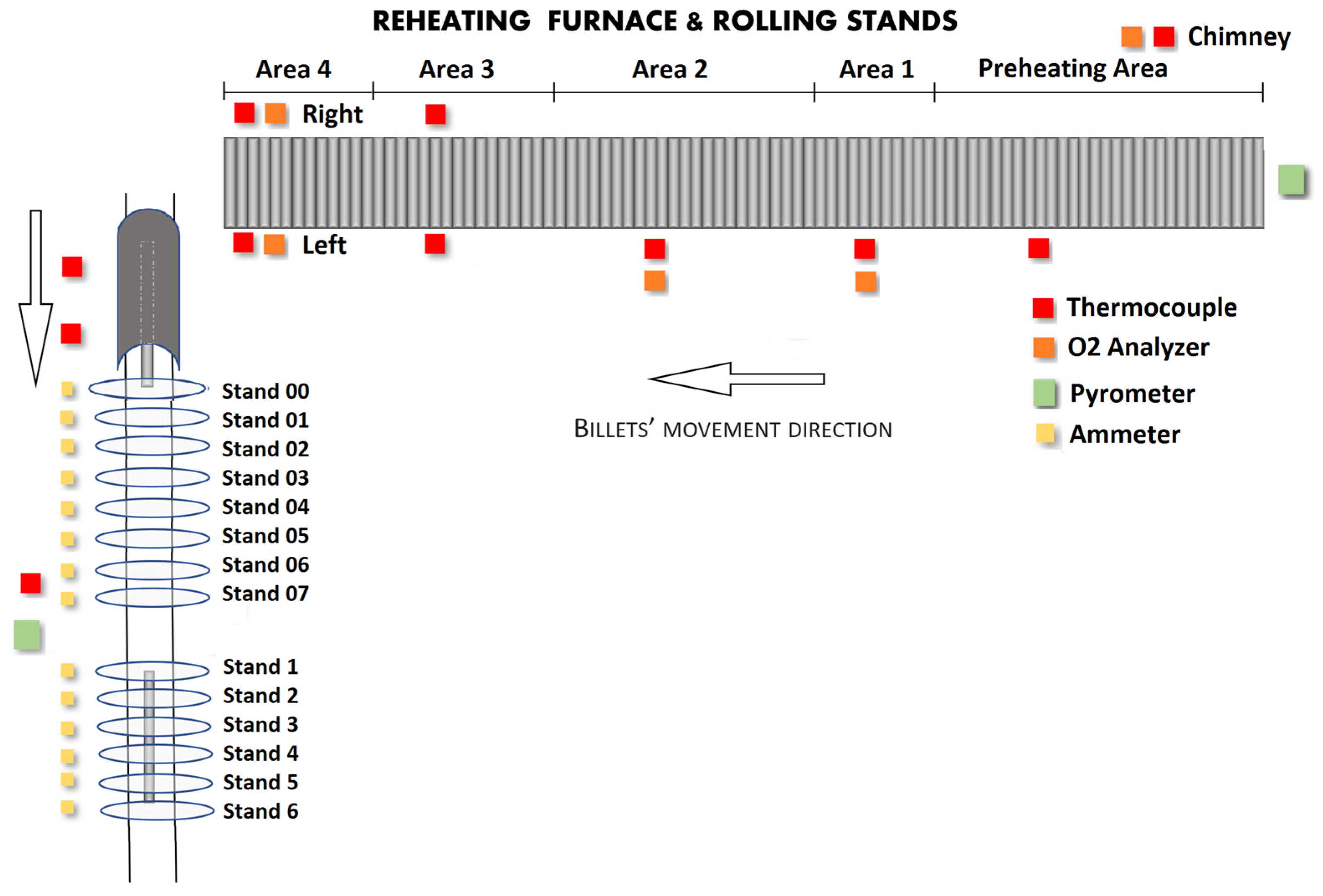




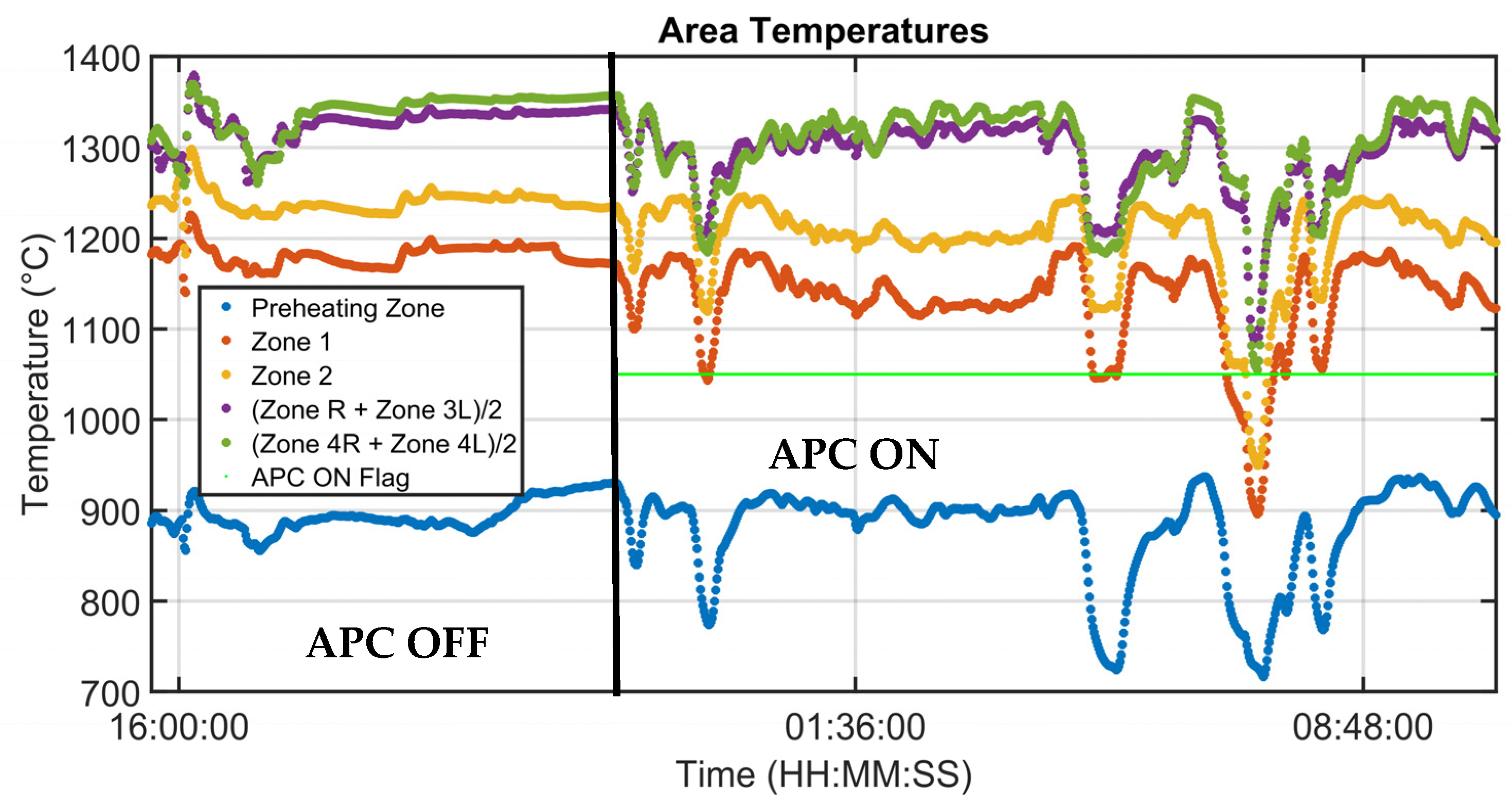

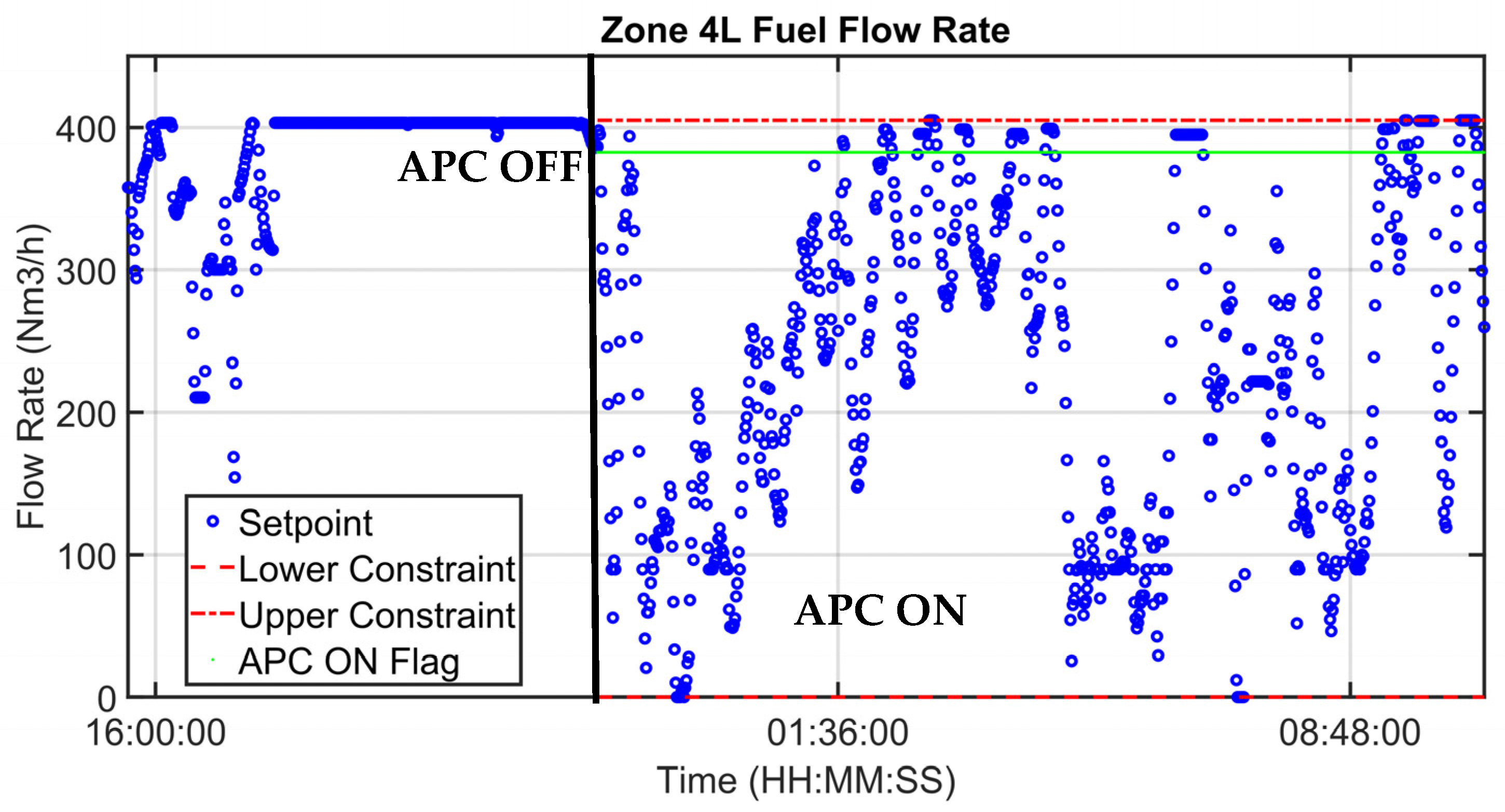
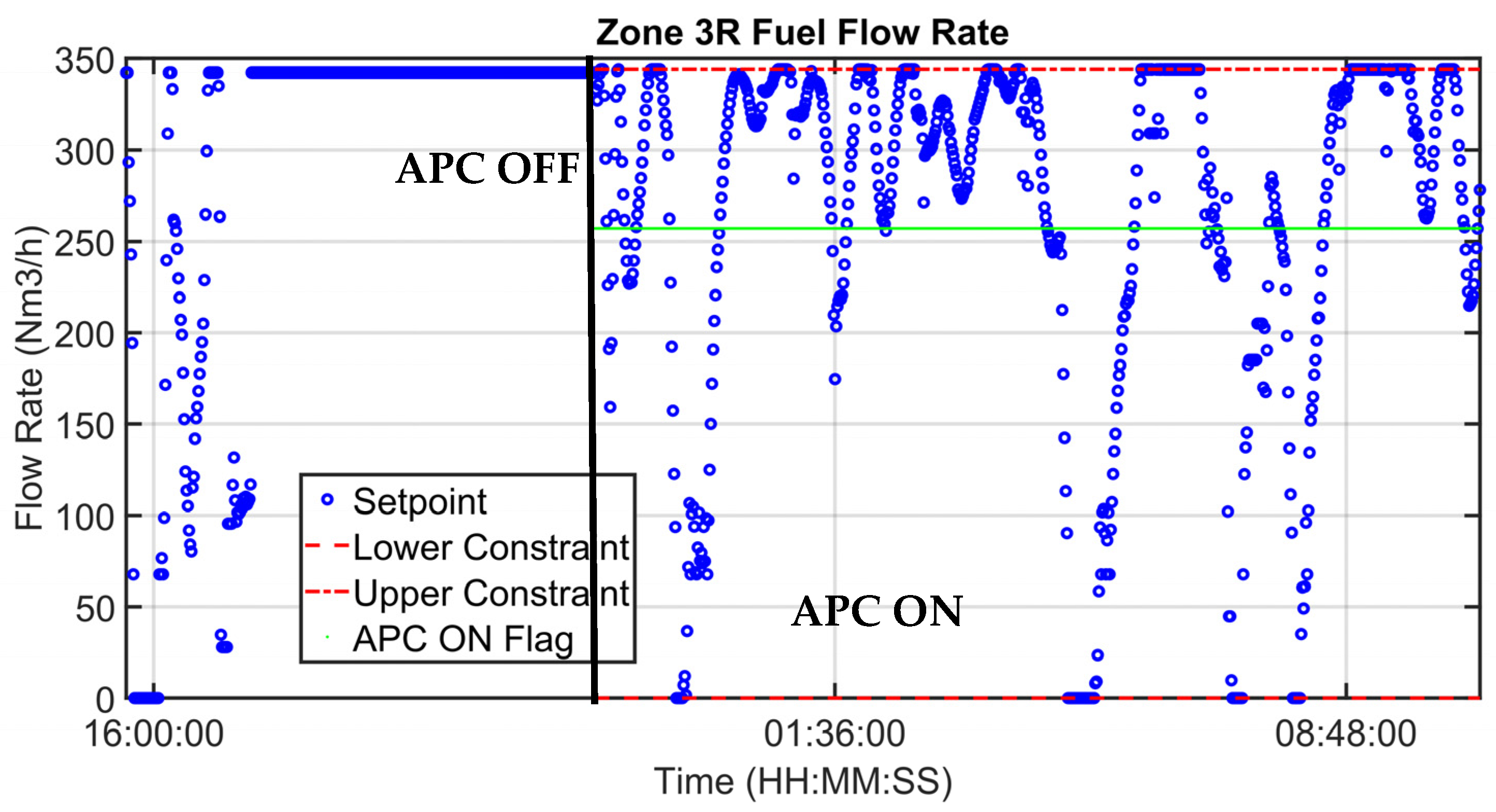

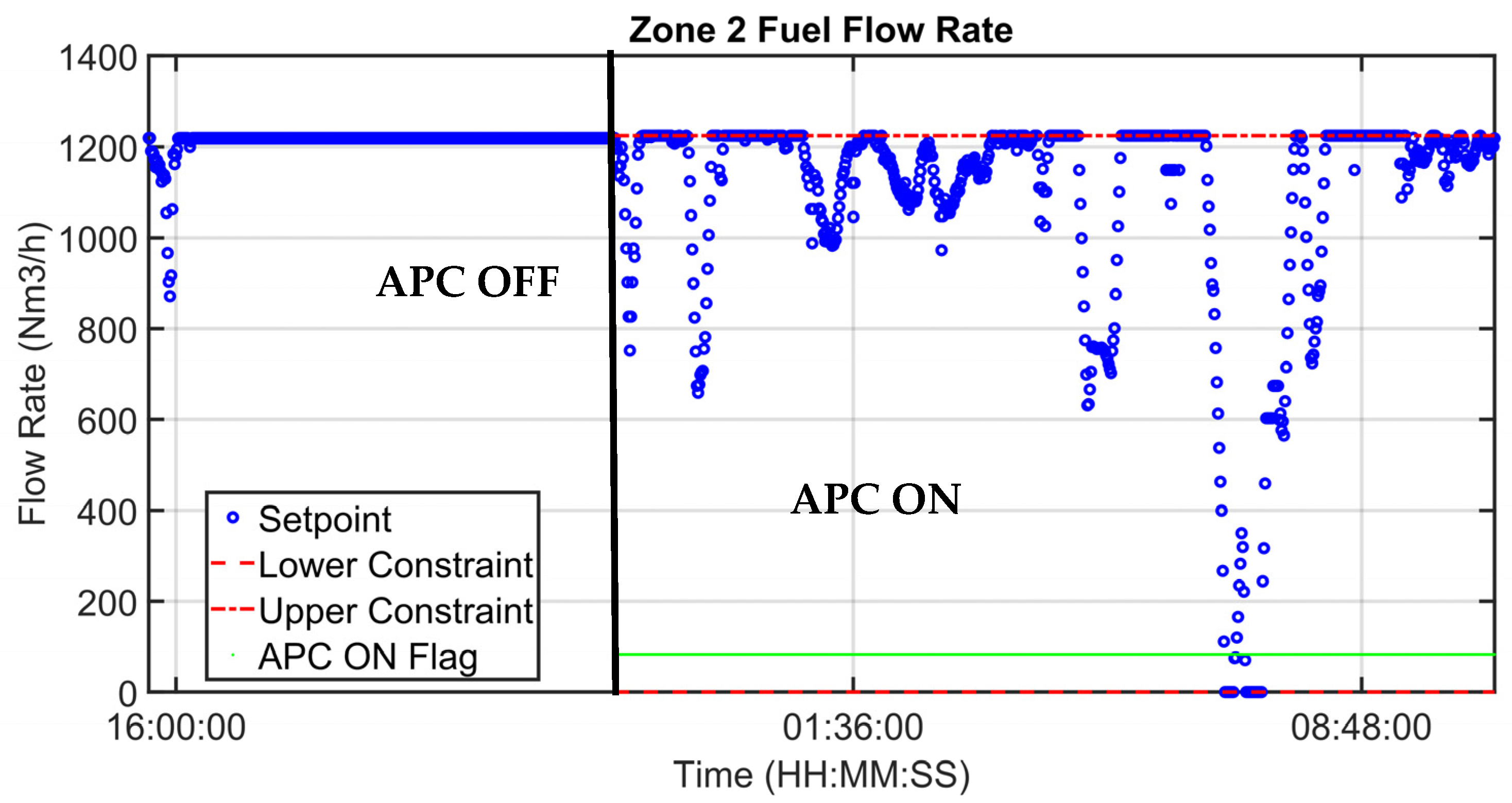

| Area | Zones | Length (mm) | Billets’ Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preheating Area | Preheating Zone | 7400 | 30 |
| Area 1 | Zone 1 | 1600 | 11 |
| Area 2 | Zone 2 | 3200 | 23 |
| Area 3 | Zone 3 Right, Zone 3 Left | 1700 | 16 |
| Area 4 | Zone 4 Right, Zone 4 Left | 2100 | 13 |
| Variable | Measurement Unit |
|---|---|
| Rolling Mill Stand 07 Billet Temperature | [°C] |
| Zone Temperature (4L, 4R, 3L, 3R, 2, 1) | [°C] |
| Zone Temperatures Difference (4R–4L, 3R–3L) | [°C] |
| Preheating Zone, Smoke Exchanger Temperature | [°C] |
| Smoke Exchanger O2 | [%] |
| O2 in Zone 4L, 4R, 2, 1 | [%] |
| Variable | Measurement Unit |
|---|---|
| Zone (4L, 4R, 3L, 3R, 2, 1) Fuel Flow Rate | [Nm3/h] |
| Zone (4L, 4R, 3L, 3R, 2, 1) Air/Fuel Ratio | [] |
| Variable | Measurement Unit |
|---|---|
| Furnace Production Rate | [ton/h] |
| Billets’ Furnace Inlet Temperature | [°C] |
| Warm Air Temperature Valve | [%] |
| Smoke Exchanger Valve | [%] |
| Rolling Mill Stands Ambient Temperature | [°C] |
| Tunnel Temperature 1,2 | [°C] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanoli, S.M.; Pepe, C.; Orlietti, L. Synergic Combination of Hardware and Software Innovations for Energy Efficiency and Process Control Improvement: A Steel Industry Application. Energies 2023, 16, 4183. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16104183
Zanoli SM, Pepe C, Orlietti L. Synergic Combination of Hardware and Software Innovations for Energy Efficiency and Process Control Improvement: A Steel Industry Application. Energies. 2023; 16(10):4183. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16104183
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanoli, Silvia Maria, Crescenzo Pepe, and Lorenzo Orlietti. 2023. "Synergic Combination of Hardware and Software Innovations for Energy Efficiency and Process Control Improvement: A Steel Industry Application" Energies 16, no. 10: 4183. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16104183
APA StyleZanoli, S. M., Pepe, C., & Orlietti, L. (2023). Synergic Combination of Hardware and Software Innovations for Energy Efficiency and Process Control Improvement: A Steel Industry Application. Energies, 16(10), 4183. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16104183








