Design and Evaluation of the Elastic and Anti-Corrosion Cement Slurry for Carbon Dioxide Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Preparation of Cement Slurry
2.3. Evaluation of Working Performance
2.4. Mechanical Properties
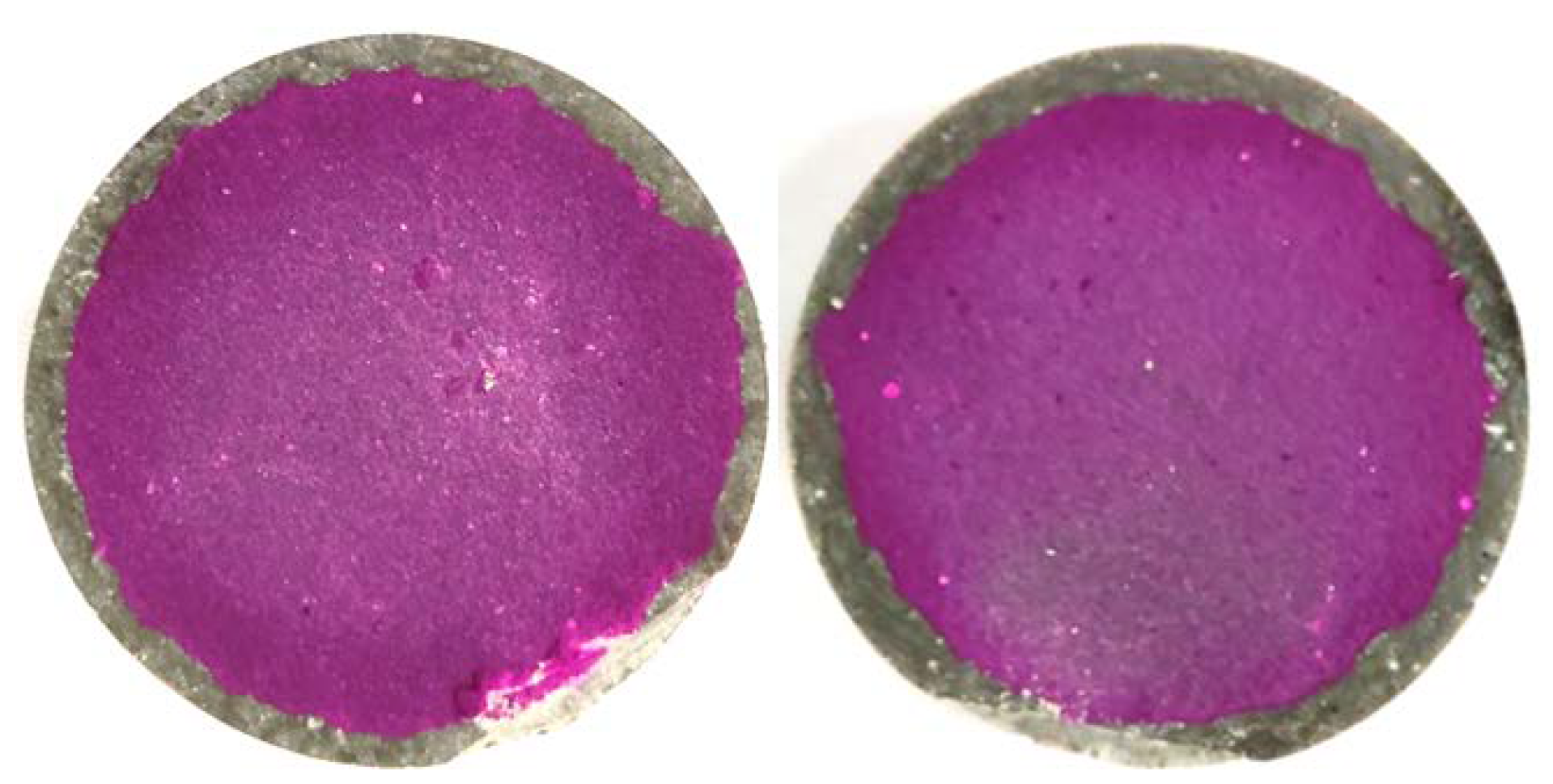
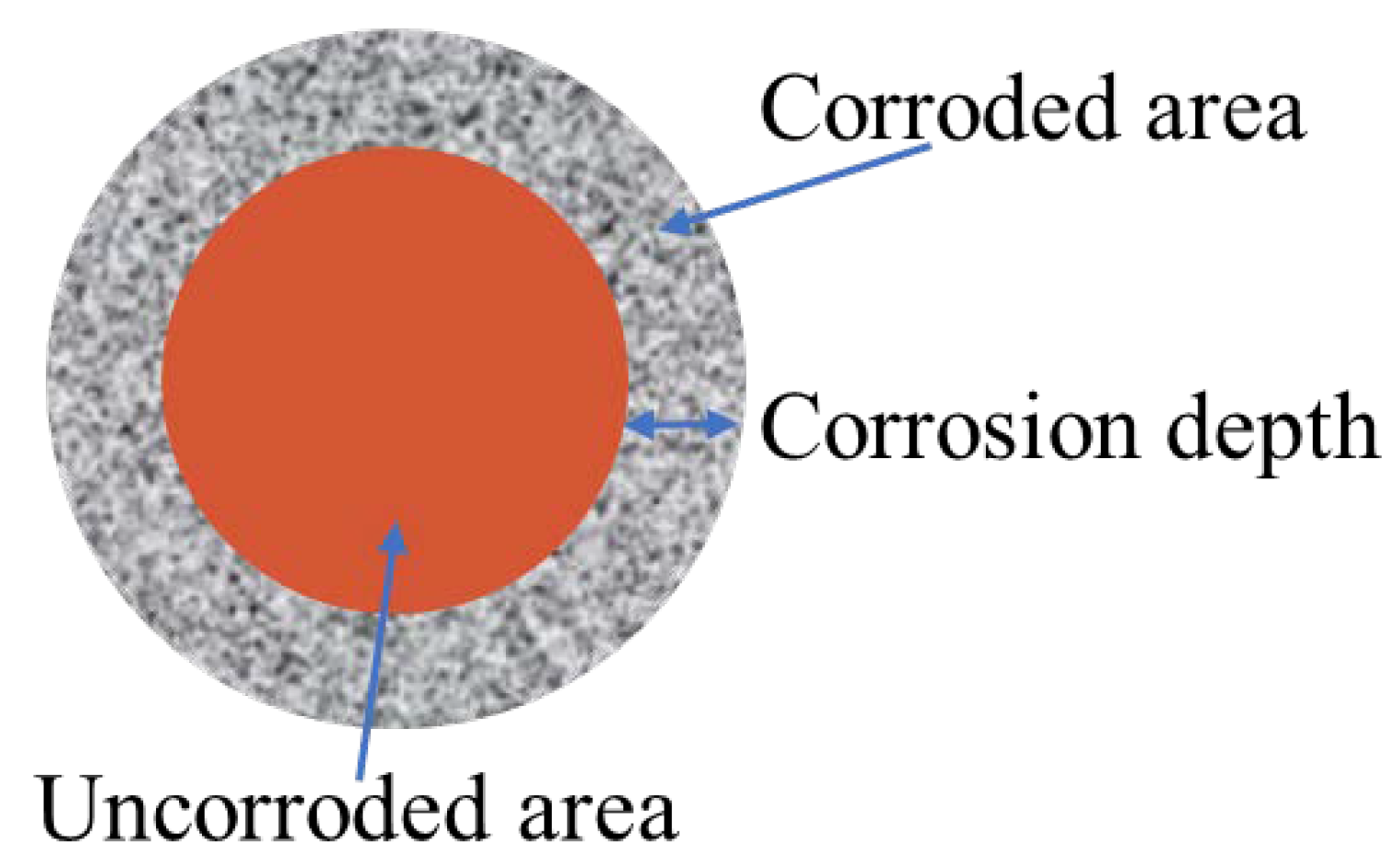
2.5. Corrosion Evaluation of Cement Samples
2.6. Analysis of Microstructure
3. Design of Cement Slurry for Carbon Dioxide Storage
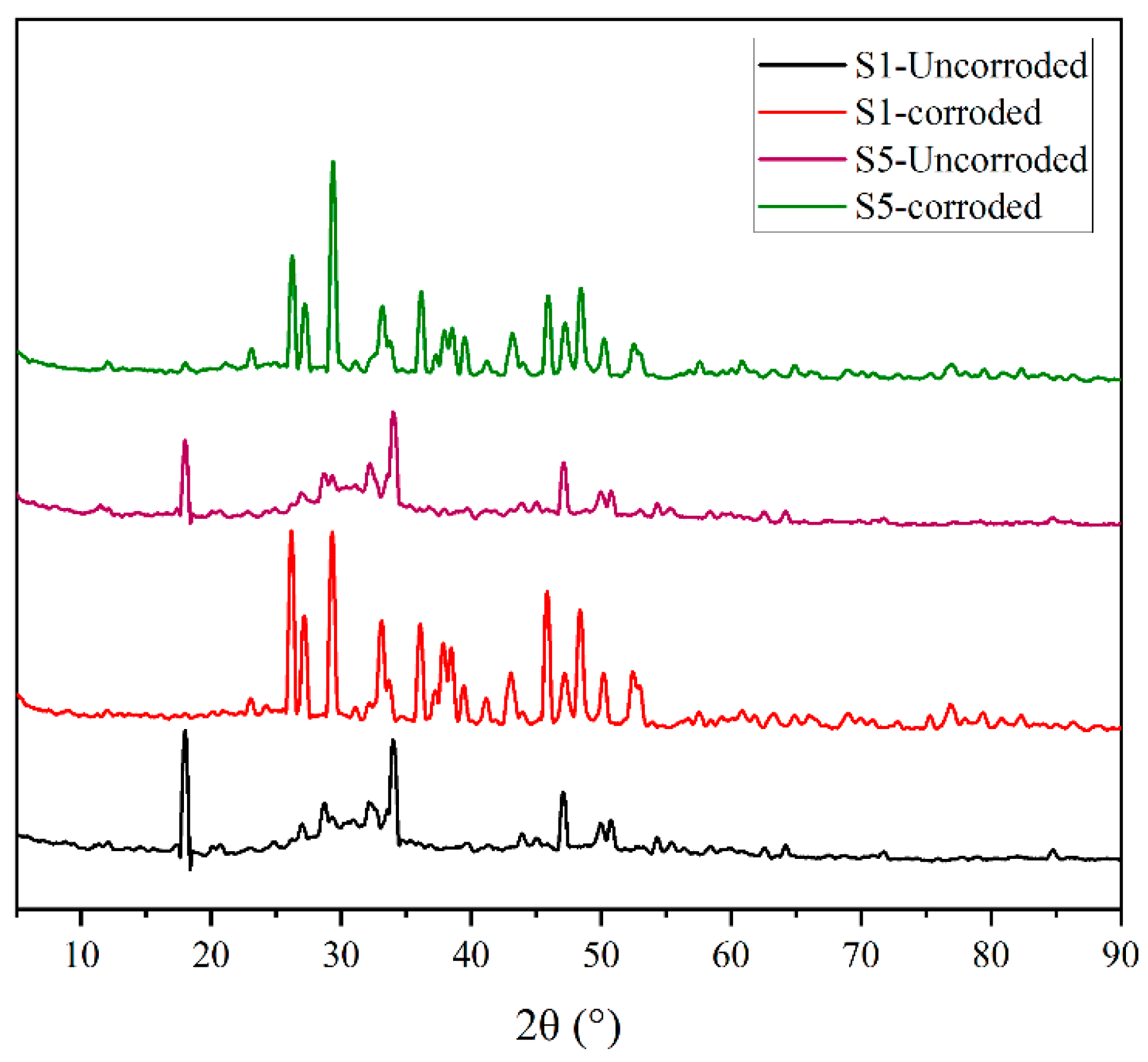
3.1. Carbonization Process of Cement Slurry
3.2. Research on Resin with Anti-Corrosion and Improved Elasticity
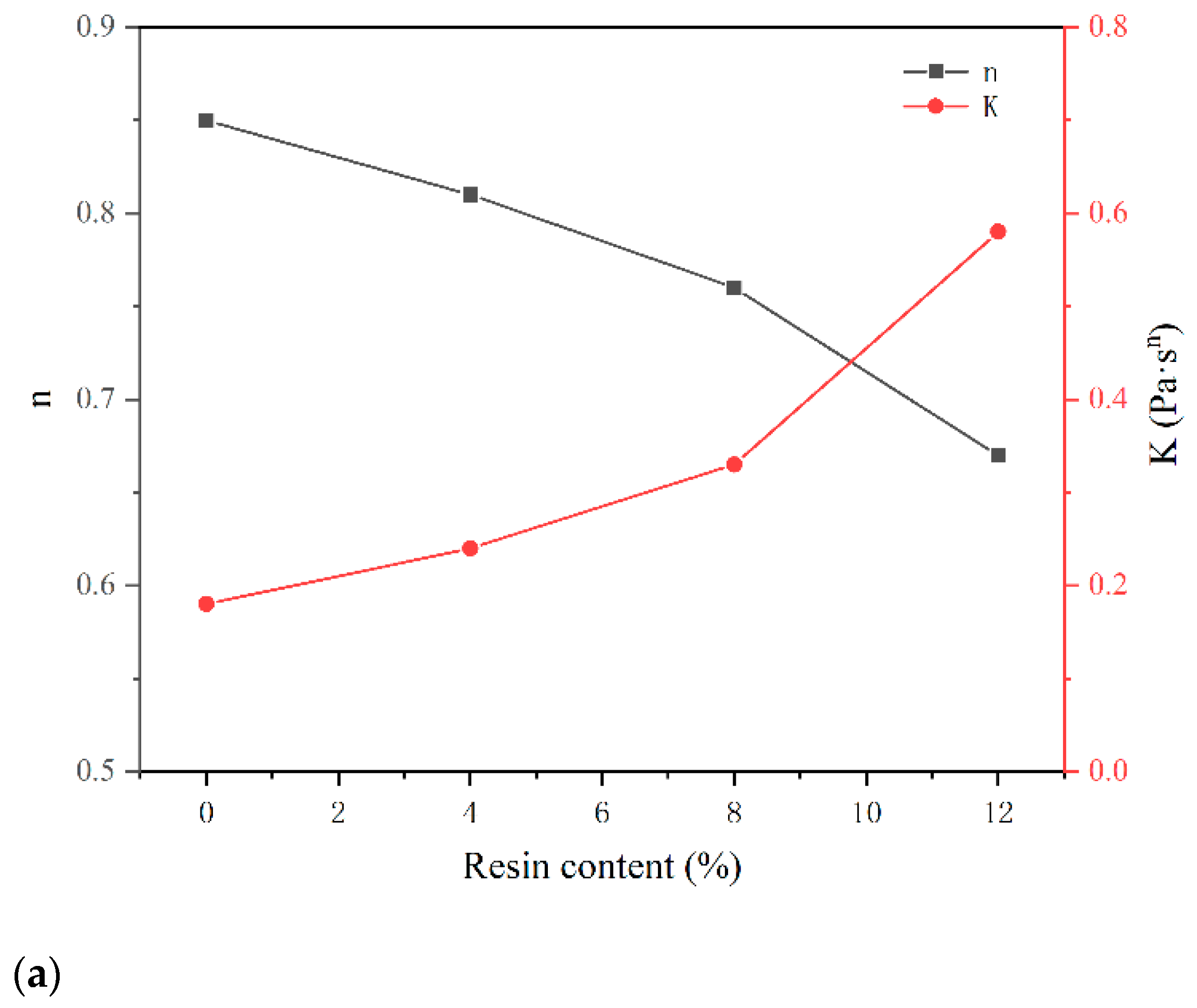
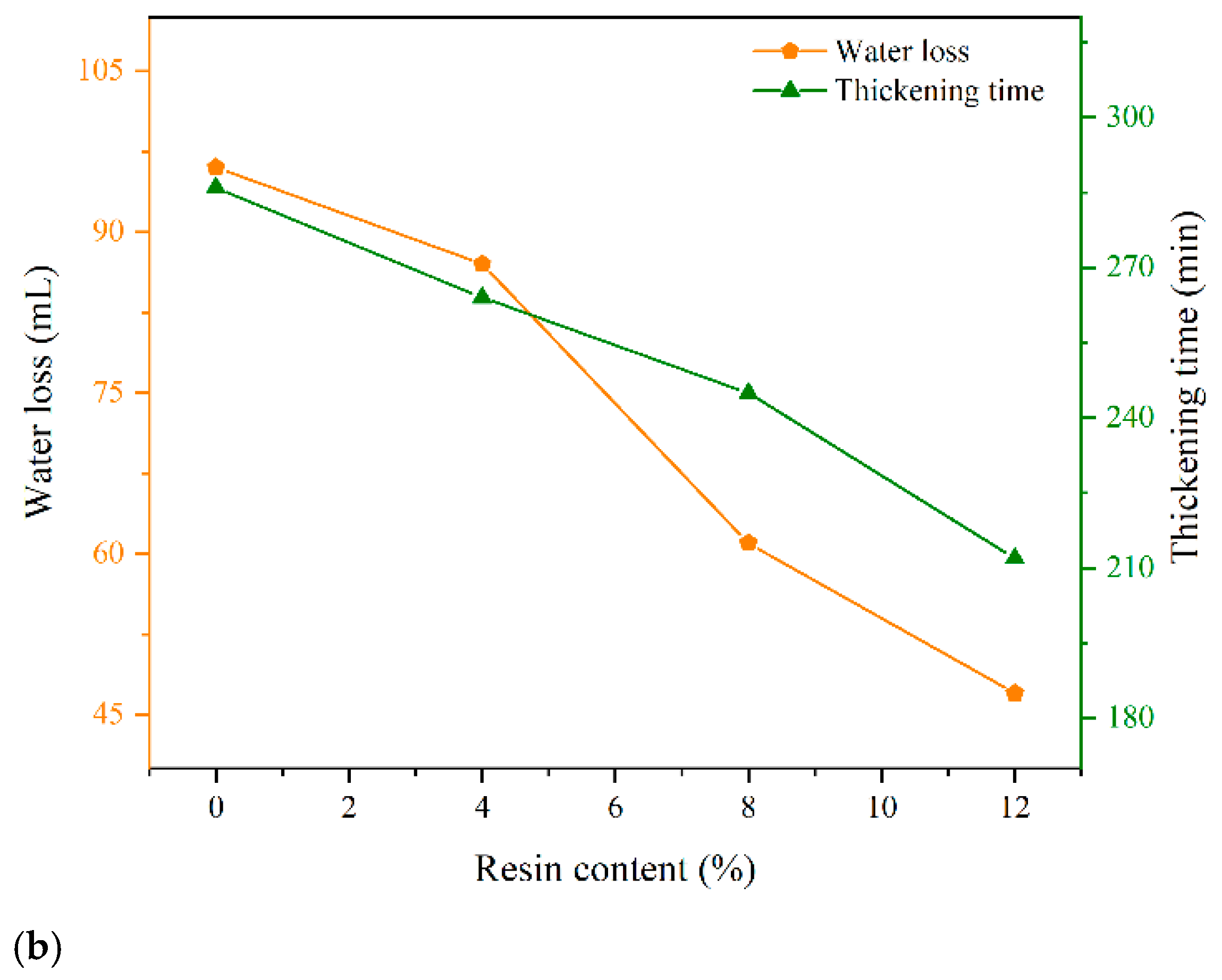
3.2.1. Influence of Resin on Working Performances of Cement Slurry
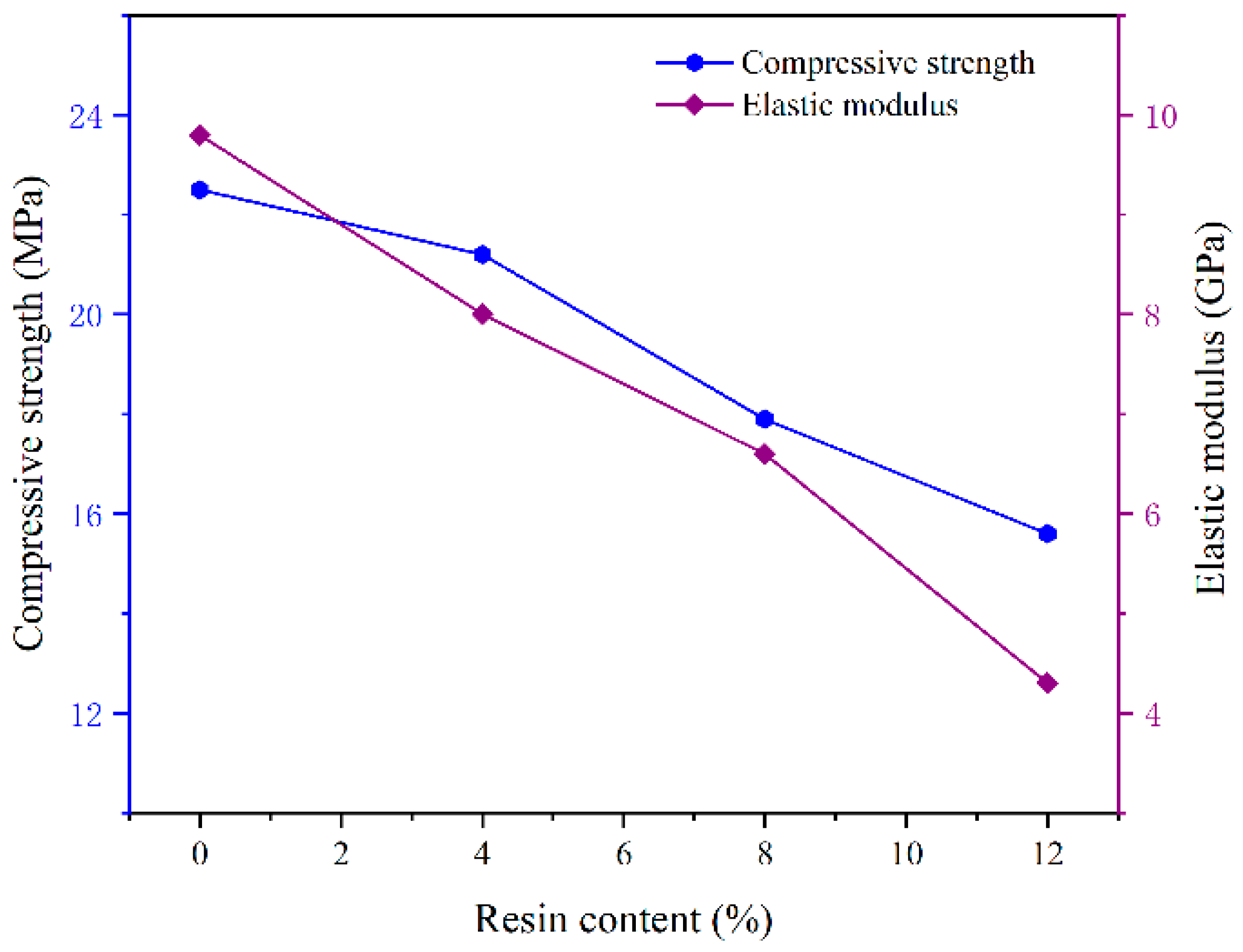
3.2.2. Effect of Resin on Mechanical Properties of Cement Slurry
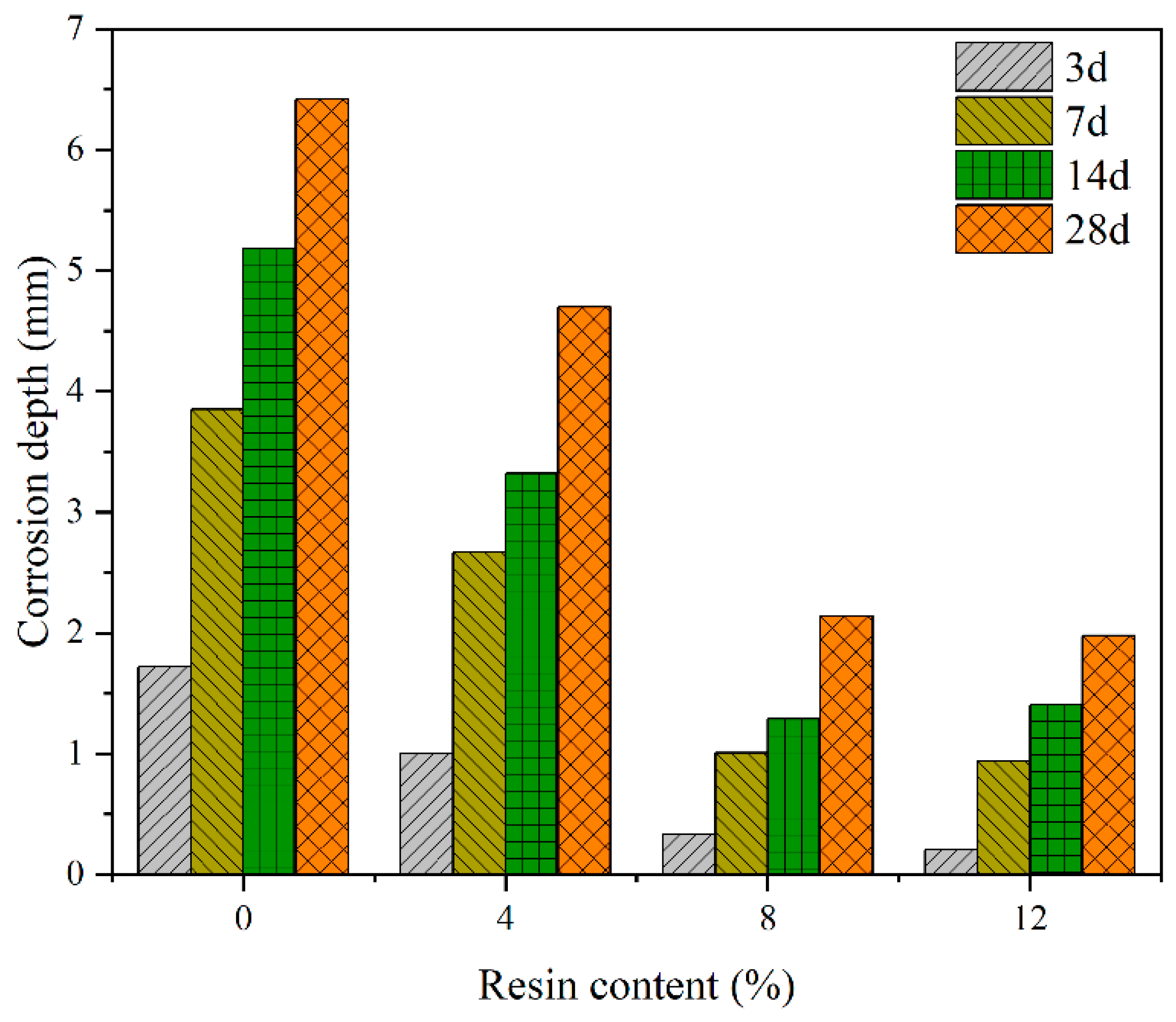
3.2.3. Influence of Resin on the Corrosion Depth of Cement Slurry
3.3. Additives for Designing the Elastic and Anti-Corrosion Cement Slurry
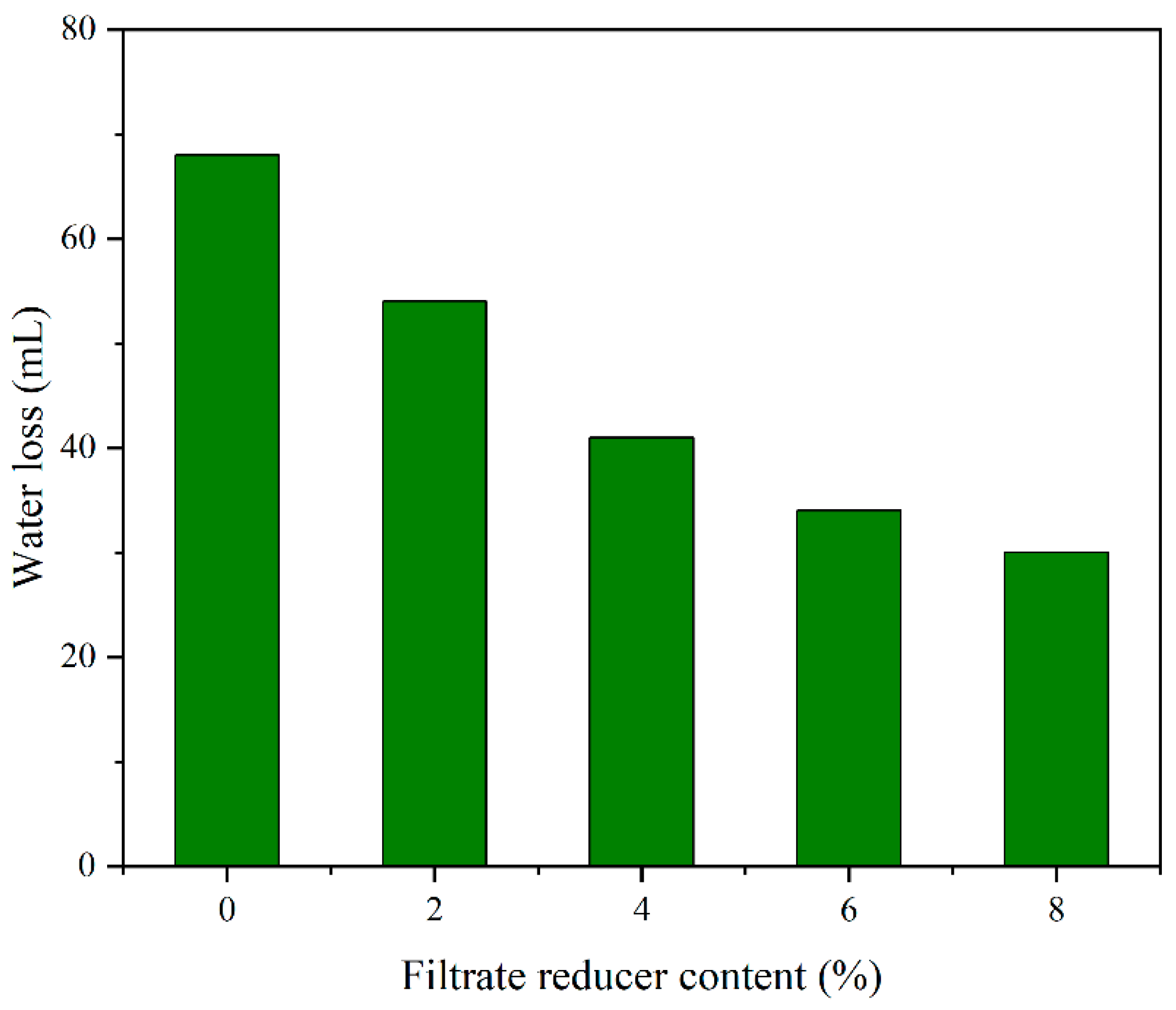
3.3.1. Filtrate Reducer
3.3.2. Dispersant
3.3.3. Retarder
4. Evaluation of the Designed Cement Slurry for Carbon Dioxide Storage
4.1. Working Performances
4.2. Corrosion Depth
4.3. Stress–Strain Behavior
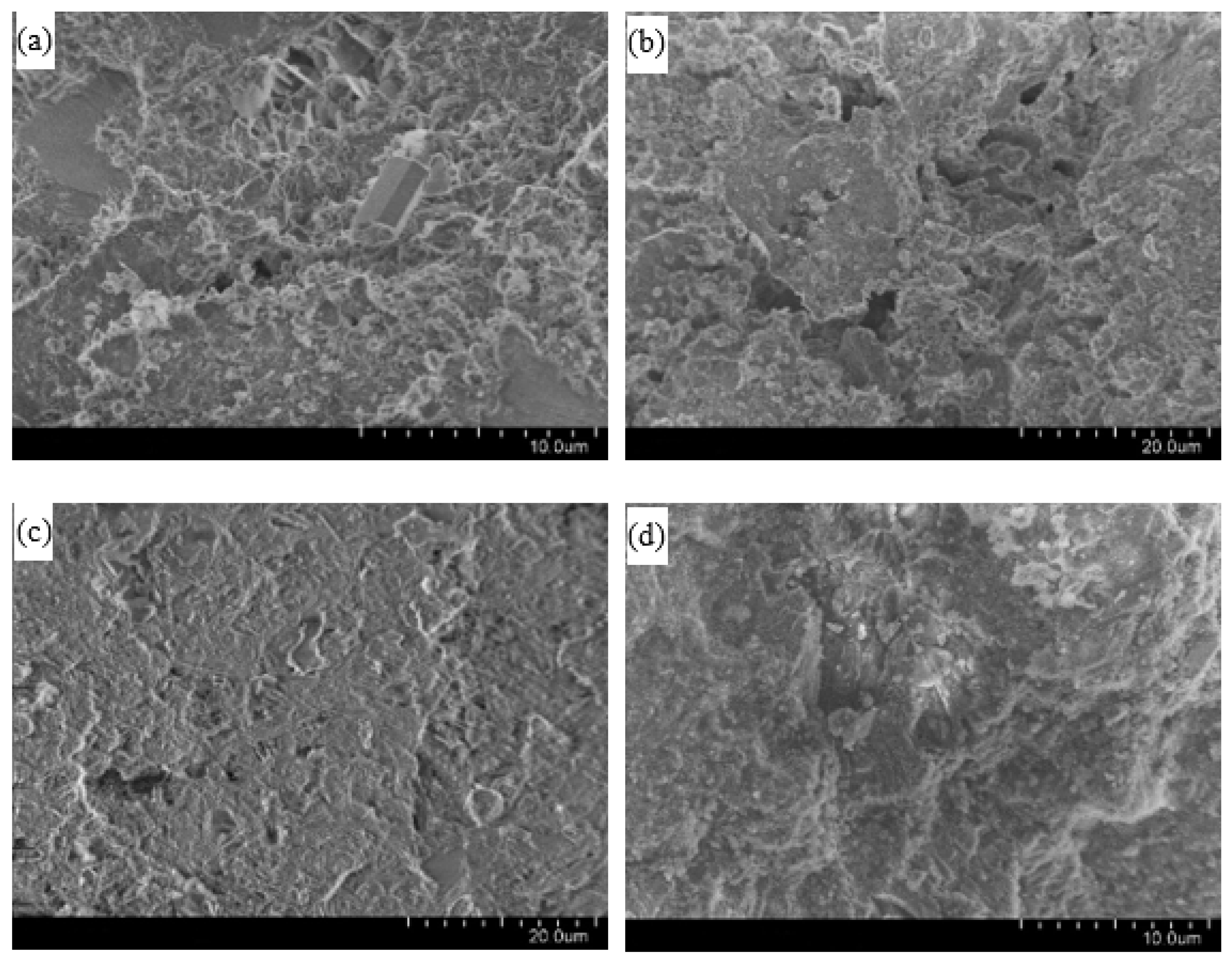
4.4. Microstructure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kazemifar, F. A review of technologies for carbon capture, sequestration, and utilization: Cost, capacity, and technology readiness. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 200–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarazar, M.; JahanianFard, D.; Sheikhnejad, Y.; Nemati, B.; Mostafaie, A.; Zandi, S.; Khalaj, M.; Kamali, M.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Underground carbon dioxide sequestration for climate change mitigation–A scientometric study. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 33, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Converti, A. Environmental and Energetic Valorization of Renewable Resources. Energies 2021, 14, 8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Borhani, T.N.; Subraveti, S.G.; Pai, K.N.; Prasad, V.; Rajendran, A.; Nkulikiyinka, P.; Asibor, J.O.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, D.; et al. Harnessing the power of machine learning for carbon capture, utilisation, and storage (CCUS)–A state-of-the-art review. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 6122–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haszeldine, R.S. Carbon Capture and Storage: How Green Can Black Be? Science 2009, 325, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guan, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Q.; Sheng, Y. A new method to protect the cementing sealing integrity of carbon dioxide geological storage well: An experiment and mechanism study. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 236, 107213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Mei, K.; Gao, Q.; Cheng, X. Study on the effect of CaCO3 whiskers on carbonized self-healing cracks of cement paste: Application in CCUS cementing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 321, 126368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkatatny, S. Improved carbonation resistance and durability of Saudi Class G oil well cement sheath in CO2 rich environments using laponite. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 196, 107812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.A.; Elkatatny, S. Improving class G cement carbonation resistance for applications of geologic carbon sequestration using synthetic polypropylene fiber. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 76, 103184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hubler, M.H.; Xi, Y. Theoretical modeling on chemical composition and mechanical properties of well cement under carbonation reactions. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Guo, X.; Li, Z.; Cheng, X.; Fan, X.; Korayem, A.; Duan, W.H. Coupled effect of CO2 attack and tensile stress on well cement under CO2 storage conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 130, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, H.; Zhou, F.; Guo, B.; Chang, X. Effect of cement sheath induced stress on well integrity assessment in carbon sequestration fields. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 46, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Xu, M.; Tan, C.; You, F.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S. Study on an Epoxy Resin System Used to Improve the Elasticity of Oil-Well Cement-Based Composites. Materials 2022, 15, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunwen, G.A.O.; Fuyuan, H.U.; Qin, H.A.N.; Binhui, L.I.U.; Chongfeng, Z.H.O.U. Effect of Mechanic Property of Cement on Seal Integrity of Borehole. Drill. Fluid Complet. Fluid 2014, 31, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; He, Y.; Zeng, D.; Shi, T. Research into sulfide resistant polymer latex cement for sour well applications. Anti Corros. Methods Mater. 2013, 60, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zou, C.; Peng, Z.; Zheng, Y. Study on the Preparation and Anti-CO2 Corrosion Performance of Soap-Free Latex for Oil Well Cement. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 23028–23038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Lv, F.; Feng, Q.; Zheng, Y. Enhancing the CO2-H2S corrosion resistance of oil well cement with a modified epoxy resin. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 326, 126854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Yuan, B.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, S.; Yang, Y. Nanosilica-latex reduction carbonation-induced degradation in cement of CO2 geological storage wells. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 65, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, M.; Hassanzadeh-Aghdam, M.K.; Mahmoodi, M.J. Elastic properties of cement-based composites reinforced by nano-tailored hybrid fiber. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2021, 29, 5232–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Xu, M.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y. Synergistic Effect of Latex Powder and Rubber on the Properties of Oil Well Cement-Based Composites. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 4843816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Xu, M.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, P.; Huang, F.; Pan, Y. Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) Modified by a Silane Coupling Agent and Its Influence on the Mechanical Properties of Oil Well Cement Pastes. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 2019, 3587081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, L.Q.; Bäßler, R.; Bettge, D.; Buggisch, E.; Schiller, B.N.; Beck, M. Corrosion Study on Wellbore Materials for the CO2 Injection Process. Processes 2021, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šavija, B.; Luković, M. Carbonation of cement paste: Understanding, challenges, and opportunities. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 117, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesti, M.; Tiemeyer, C.; Plank, J. CO2 stability of Portland cement based well cementing systems for use on carbon capture & storage (CCS) wells. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 45, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guner, D.; Ozturk, H.; Erkayaoglu, M. Investigation of the elastic material properties of Class G cement. Struct. Concr. 2016, 18, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiong, M.; Gholami, R.; Abid, K.; Rahman, M.E. Nanomodification: An efficient method to improve cement integrity in CO2 storage sites. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 84, 103612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xie, D. An effective salt-tolerant fluid loss additive-suitable for high temperature oil well cement. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 42, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bülichen, D.; Plank, J. Role of colloidal polymer associates for the effectiveness of hydroxyethyl cellulose as a fluid loss control additive in oil well cement. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, E25–E34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Component | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 63.1 | 21.6 | 3.7 | 4.9 | 1.4 | 5.3 |
| Sample | Cement | Water | Filtrate Reducer | Retarder | Dispersant | Micro Silicon | Resin | Defoamer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 100 | 44 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| S2 | 100 | 42 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 4 | 1 |
| S3 | 100 | 40 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 8 | 1 |
| S4 | 100 | 38 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 12 | 1 |
| S5 | 100 | 39 | 4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 2 | 8 | 1 |
| Temperature (°C) | Water Loss (mL) | Thickening Time (min) | Fluidity Index | Consistency Index (Pa·Sn) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 33 | 248 | 0.86 | 0.28 |
| 80 | 41 | 212 | 0.86 | 0.25 |
| Temperature (°C) | 7d Corrosion Depth (mm) | 30d Corrosion Depth (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 0.78 | 1.81 |
| 80 | 0.86 | 1.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lian, J.; Yue, J.; Xing, X.; Wu, Z. Design and Evaluation of the Elastic and Anti-Corrosion Cement Slurry for Carbon Dioxide Storage. Energies 2023, 16, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010435
Lian J, Yue J, Xing X, Wu Z. Design and Evaluation of the Elastic and Anti-Corrosion Cement Slurry for Carbon Dioxide Storage. Energies. 2023; 16(1):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010435
Chicago/Turabian StyleLian, Jihong, Jiaping Yue, Xuesong Xing, and Zhiqiang Wu. 2023. "Design and Evaluation of the Elastic and Anti-Corrosion Cement Slurry for Carbon Dioxide Storage" Energies 16, no. 1: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010435
APA StyleLian, J., Yue, J., Xing, X., & Wu, Z. (2023). Design and Evaluation of the Elastic and Anti-Corrosion Cement Slurry for Carbon Dioxide Storage. Energies, 16(1), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010435






