Influence-Based Consequence Assessment of Subsea Pipeline Failure under Stochastic Degradation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Subsea Component under Stochastic Degradation
3. Consequence Assessment Approach and Application
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
- The proposed model structure is adaptive, able to explore the unstable characteristics of the corrosion propagation on the failure state of the pipeline
- The model captures the interaction among the microbial and under-deposit corrosion mechanisms that have explored the likelihood of leak failure and its influence on the consequences.
- The expected utility decision theory reliably predicted the economic costs of failure given different degrees of interactions among the influential factors.
- The result shows that at the 87% likelihood of leak failure, the expected utility gives and . This accounted for moderate oil spills with environmental consequences
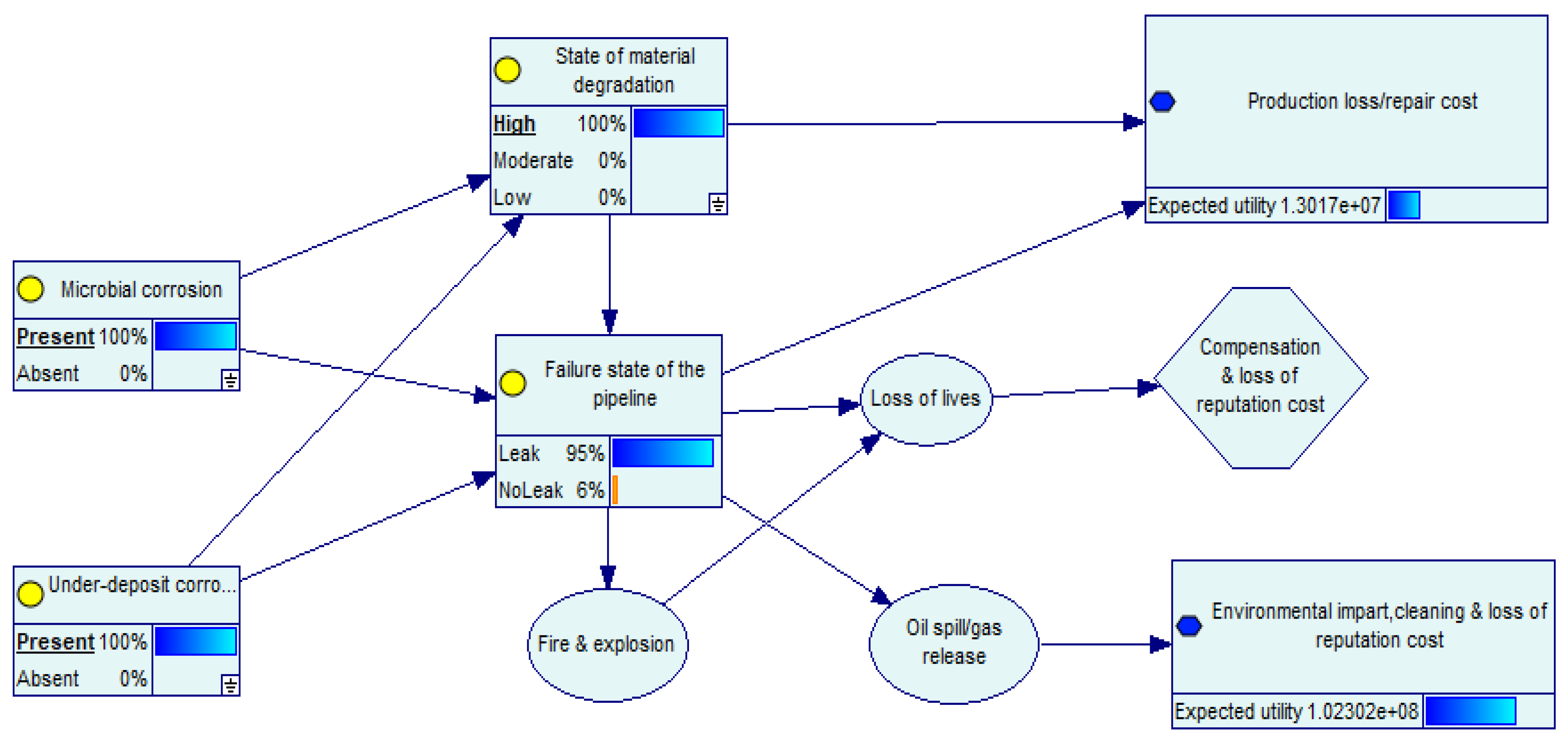
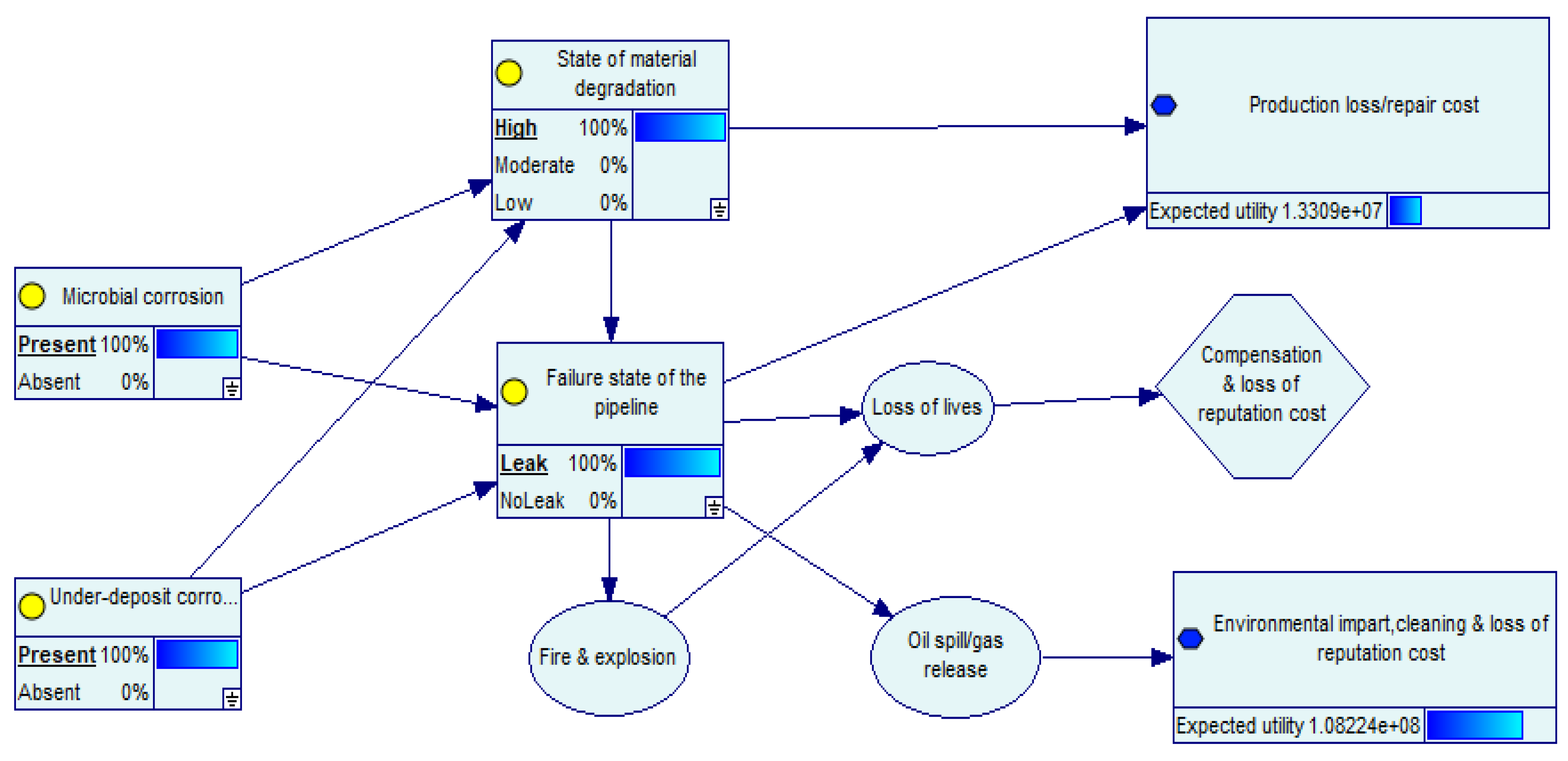
- At 100% leak failure, the economic loss due to natural resources damage and restoration, cleaning up, and loss of reputation increases by 9.1%. This represents a catastrophic oil spill with devastating impacts on the marine ecosystem and species conservation.
- The current approach offers a hands-on consequence-based prediction tool for integrity management considering stochastic degradation in harsh offshore environments.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albu, M.; Panzirsch, B.; Schröttner, H.; Mitsche, S.; Reichmann, K.; Poletti, M.C.; Kothleitner, G. High-resolution microstructure characterization of additively manufactured x5crnicunb17-4 maraging steel during ex and in situ thermal treatment. Materials 2021, 14, 7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, J.; Opila, R.; Boyd, I.; Kaufmann, E. Materials characterization and the evolution of materials. MRS Bull. 2015, 40, 1019–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shifler, D.A. Understanding material interactions in marine environments to promote extended structural life. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 2335–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adumene, S.; Ikue-John, H. Offshore systems’ safety and operational challenges in harsh Arctic operations. J. Saf. Sci. Resil. 2022, 3, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Quraishi, M.A.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Ali, S.A.; Aljeaban, N.A.; Alharbi, B.G. Design and synthesis of a novel corrosion inhibitor embedded with quaternary ammonium, amide and amine motifs for protection of carbon steel in 1 M HCl. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 317, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handoko, W.; Pahlevani, F.; Sahajwalla, V. Enhancing corrosion resistance and hardness properties of carbon steel through modification of microstructure. Materials 2018, 11, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adumene, S.; Khan, F.; Adedigba, S.; Zendehboudi, S. Offshore system safety and reliability considering microbial influenced multiple failure modes and their interdependencies. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 215, 107862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadwa, U. A Study on Biofilm Formation in Pipelines (Issue March). Master’s Thesis, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Machuca, L.L. Microbiologically influenced corrosion: A review focused on hydrotest fluids in subsea pipelines. Corros. Prev. 2014, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Woollam, R.C.; Orazem, M. Mathematical Models for Under-Deposit Corrosion. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, C321–C329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, C.C.C.R. Marine Biofilms: A Successful Microbial Strategy With Economic Implications. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Melchers, R.E. Long-term under-deposit pitting corrosion of carbon steel pipes. Ocean Eng. 2017, 133, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ge, H.; Lin, W.; Song, Y.; Ge, F.; Huang, X.; Meng, X. Effect of different disinfection treatments on the adhesion and separation of biofilm on stainless steel surface. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzegorczyk, M.; Pogorzelski, S.J.; Pospiech, A.; Boniewicz-Szmyt, K. Monitoring of marine biofilm formation dynamics at submerged solid surfaces with multitechnique sensors. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Absolom, D.R.; Lamberti, F.V.; Policova, Z.; Zingg, W.; van Oss, C.J.; Neumann, A.W. Surface thermodynamics of bacterial adhesion. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.T.T.; Kannoorpatti, K.; Padovan, A.; Thennadil, S. A study of bacteria adhesion and microbial corrosion on different stainless steels in environment containing Desulfovibrio vulgaris. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 201577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J. Mechanistic Study of Under Deposit Corrosion of Mild Steel in Aqueous Carbon Dioxide Solution; Ohio University: Athens, OH, USA, 2013; Issue December. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adumene, S.; Khan, F.; Adedigba, S.; Zendehboudi, S.; Shiri, H. Offshore pipeline integrity assessment considering material and parametric uncertainty. J. Pipeline Sci. Eng. 2021, 1, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.T.; McFarland, B.L.; Hodgman, R.Z. Microbial Influenced Corrosion in Cargo Oil Tanks of Crude Oil Tankers. NACE Int. Corros. Conf. 1997, 535. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Cheng, Y.F. Mechanistic aspects of microbially influenced corrosion of X52 pipeline steel in a thin layer of soil solution containing sulphate-reducing bacteria under various gassing conditions. Corros. Sci. 2018, 133, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciales, A.; Peralta, Y.; Haile, T.; Crosby, T.; Wolodko, J. Mechanistic microbiologically influenced corrosion modeling—A review. Corros. Sci. 2019, 146, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adumene, S.; Adedigba, S.; Khan, F.; Zendehboudi, S. An integrated dynamic failure assessment model for offshore components under microbiologically influenced corrosion. Ocean Eng. 2020, 218, 108082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behari, N.; Sheriff, M.Z.; Rahman, M.A.; Nounou, M.; Hassan, I.; Nounou, H. Chronic leak detection for single and multiphase flow: A critical review on onshore and offshore subsea and arctic conditions. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 81, 103460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb-Berrouane, M.; Khan, F.; Hawboldt, K.; Eckert, R.; Skovhus, T.L. Model for microbiologically influenced corrosion potential assessment for the oil and gas industry. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Aldemir, T.; Denning, R. Multi-state Markov modeling of pitting corrosion in stainless steel exposed to chloride-containing environment. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2018, 172, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.; Khan, F.; Abbassi, R. Microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC) management using Bayesian inference. Ocean Eng. 2021, 226, 108852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adumene, S.; Nwaoha, T.C. Dynamic cost-based integrity assessment of oil and gas pipeline suffering microbial induced stochastic degradation. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 96, 104319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, N.; Neil, M. Risk Assessment and Decision Analysis with Bayesian Networks, 1st ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, F.V.; Nielsen, T.D. Bayesian Networks and Decision Graphs, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- de Andreis, F. A Theoretical Approach to the Effective Decision-Making Process. Open J. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robison, L.J.; Shupp, R.S.; Myers, R.J. Expected utility paradoxes. J. Socio-Econ. 2010, 39, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, C.; Ekun, O.A.; Nwume, M.I.; Lin, J. Molecular analysis of microbial community structures in Nigerian oil production and processing facilities in order to access souring corrosion and methanogenesis. Corros. Sci. 2016, 103, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Katarki, M.V.; Cherian, V. Failure analysis of a 30-in subsea oil pipeline. Mater. Perform. 2008, 47, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Heredia-Zavoni, E.; Montes-Iturrizaga, R.; Faber, M.H.; Straub, D. Risk assessment for structural design criteria of FPSO systems. Part II: Consequence models and applications to determination of target reliabilities. Mar. Struct. 2012, 28, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, M.J. Offshore pipeline construction cost in the U.S. Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Policy 2017, 82, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, R.; Brugnone, N. Oil Spill Economics: Estimates of the Economic Damages of an Oil Spill in the Straits of Mackinac in Michigan; Michigan State University: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2018; Issue May; Available online: https://flowforwater.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/FLOW_Report_Line-5_Final-release-1.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2022).

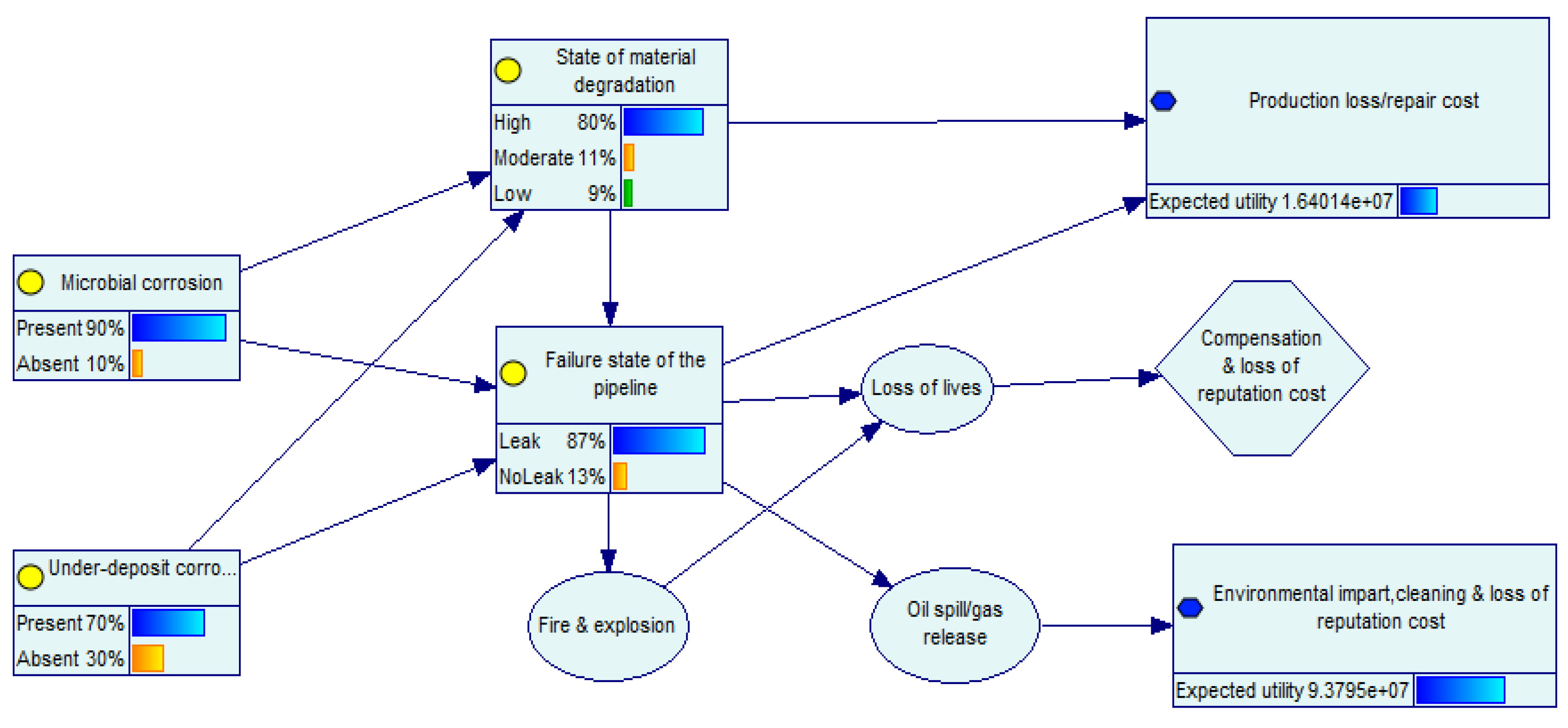

| Corrosion State | State of Degradation | Failure State Probability | Consequence States | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Probability | High | Moderate | Low | Leak | NoLeak | Production Loss/Repair Cost (USD) | Compensation and Loss of Reputation Cost (USD) | Environmental Impacts (USD) |
| Microbial | 0.899 | ||||||||
| 0.796 | 0.111 | 0.093 | 0.866 | 0.134 | 1.64 × 107 | 1.19 × 105 | 9.38 × 107 | ||
| Under-deposit | 0.701 | ||||||||
| Microbial | 1 | ||||||||
| 0.837 | 0.109 | 0.037 | 0.937 | 0.063 | 1.74 × 107 | 1.22 × 105 | 1.01 × 108 | ||
| Under-deposit | 1 | ||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adumene, S.; Islam, R.; Dick, I.F.; Zarei, E.; Inegiyemiema, M.; Yang, M. Influence-Based Consequence Assessment of Subsea Pipeline Failure under Stochastic Degradation. Energies 2022, 15, 7460. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15207460
Adumene S, Islam R, Dick IF, Zarei E, Inegiyemiema M, Yang M. Influence-Based Consequence Assessment of Subsea Pipeline Failure under Stochastic Degradation. Energies. 2022; 15(20):7460. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15207460
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdumene, Sidum, Rabiul Islam, Ibitoru Festus Dick, Esmaeil Zarei, Morrison Inegiyemiema, and Ming Yang. 2022. "Influence-Based Consequence Assessment of Subsea Pipeline Failure under Stochastic Degradation" Energies 15, no. 20: 7460. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15207460
APA StyleAdumene, S., Islam, R., Dick, I. F., Zarei, E., Inegiyemiema, M., & Yang, M. (2022). Influence-Based Consequence Assessment of Subsea Pipeline Failure under Stochastic Degradation. Energies, 15(20), 7460. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15207460









