Unified Strategy for Fault-Tolerant Operation of MMC with Multiple SMs Failure Based on SMs Grouping Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
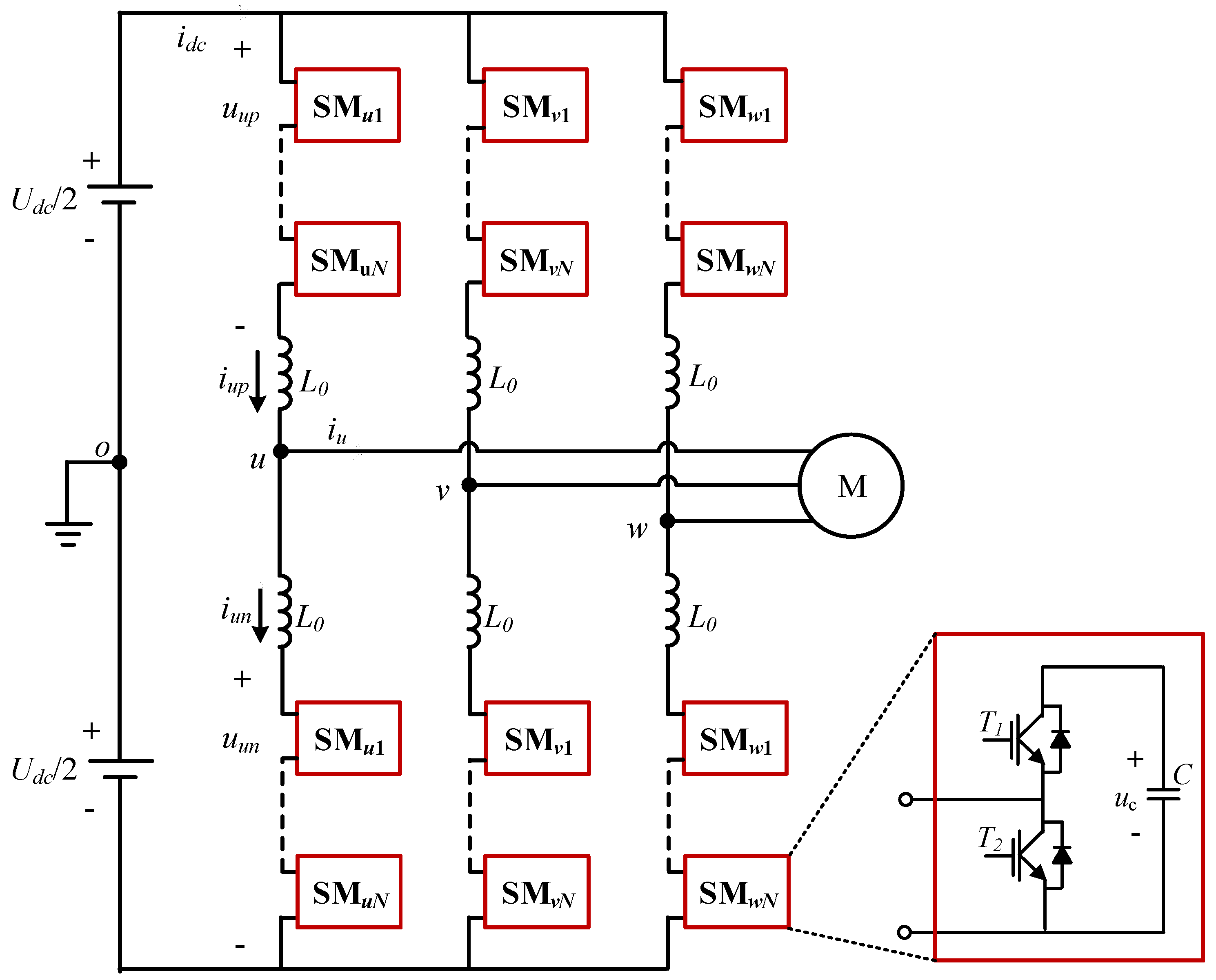
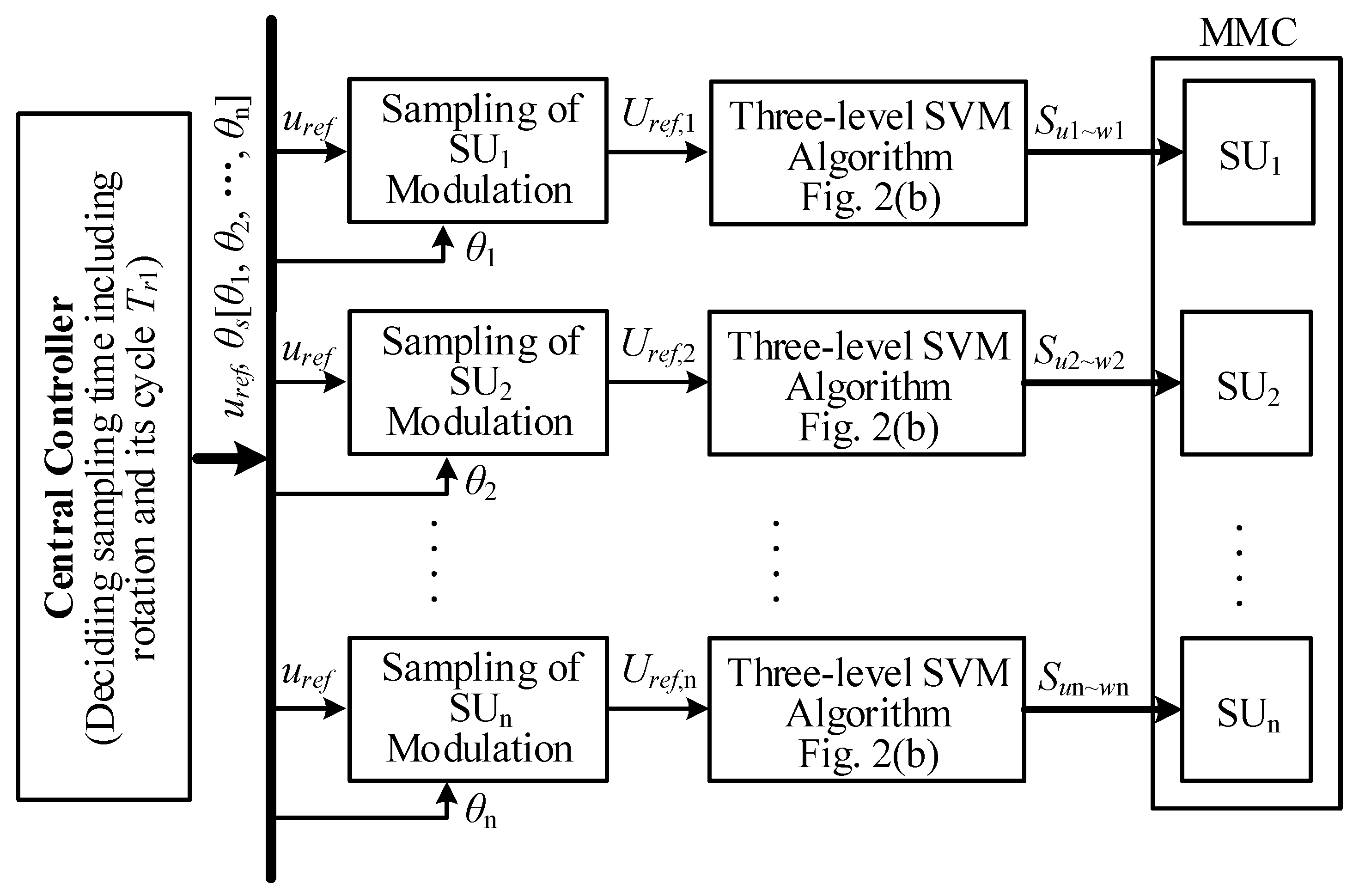
2. Proposed SMs Grouping Management and SVM Realization
2.1. Concept of the SM Grouping Management
2.2. Realization of the Simplified SVM
3. Proposed Fault-Tolerant Operation Schemes
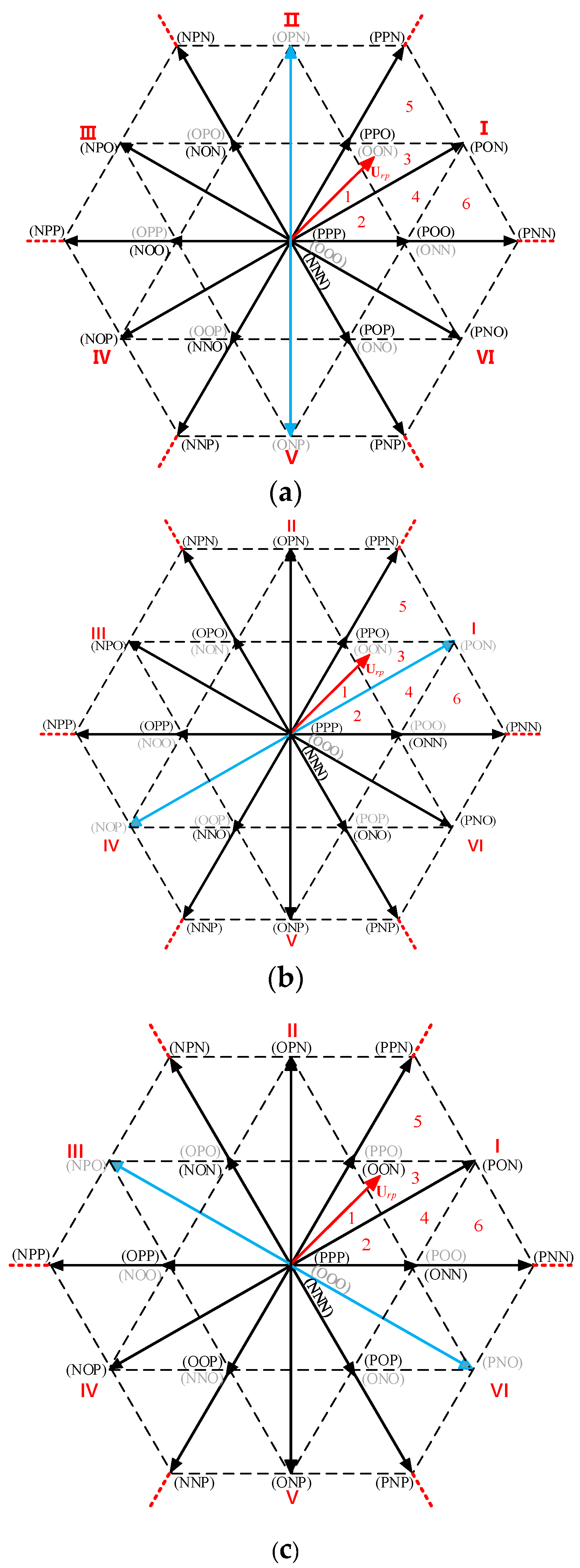
3.1. Standardization of Reference Coordinate System
3.2. Proposed Fault-Tolerant Operation Scheme
- (1)
- One SM failure
- (2)
- Multiple SMs failures
3.3. Implementation
3.4. Capacitor Voltage Balance
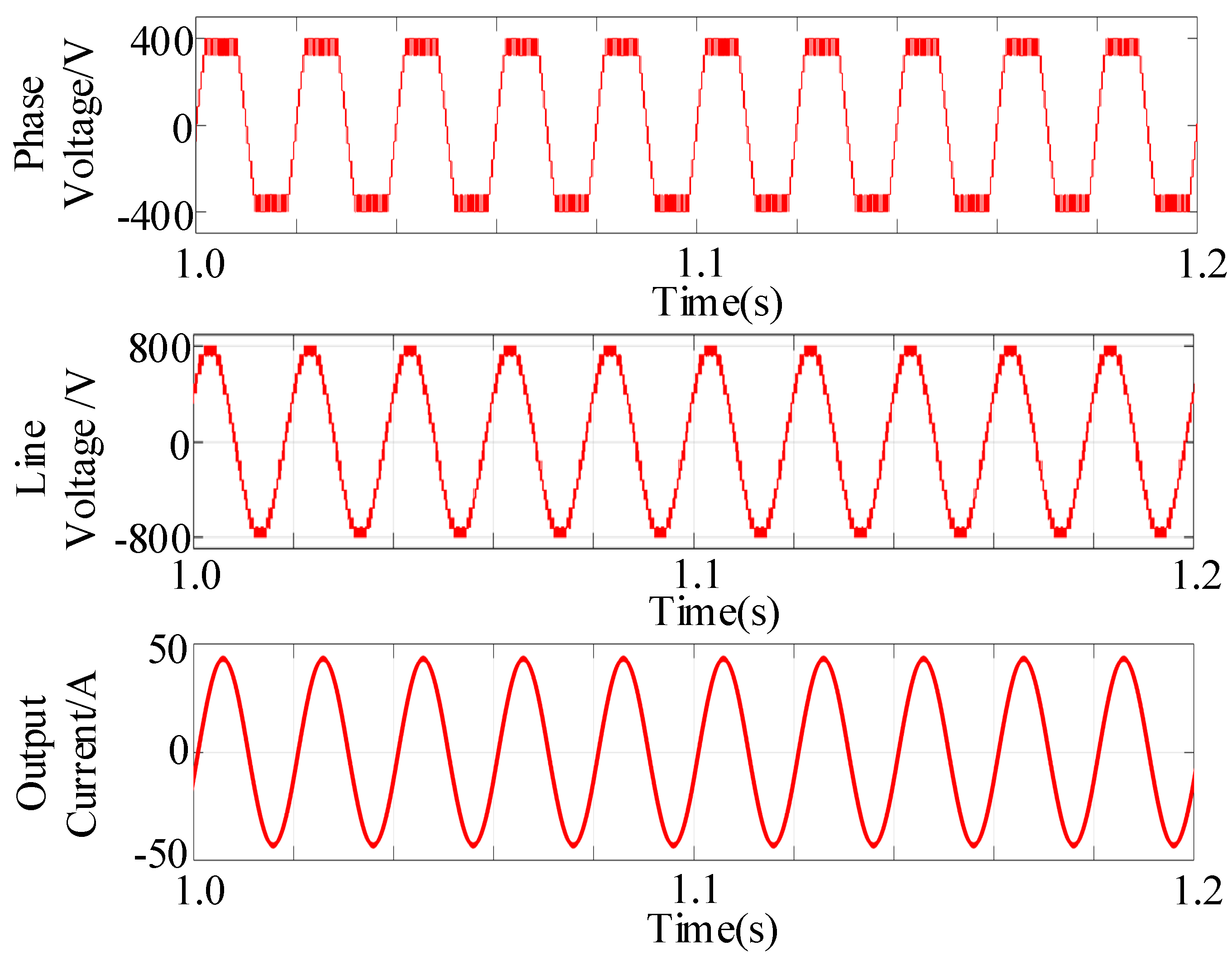
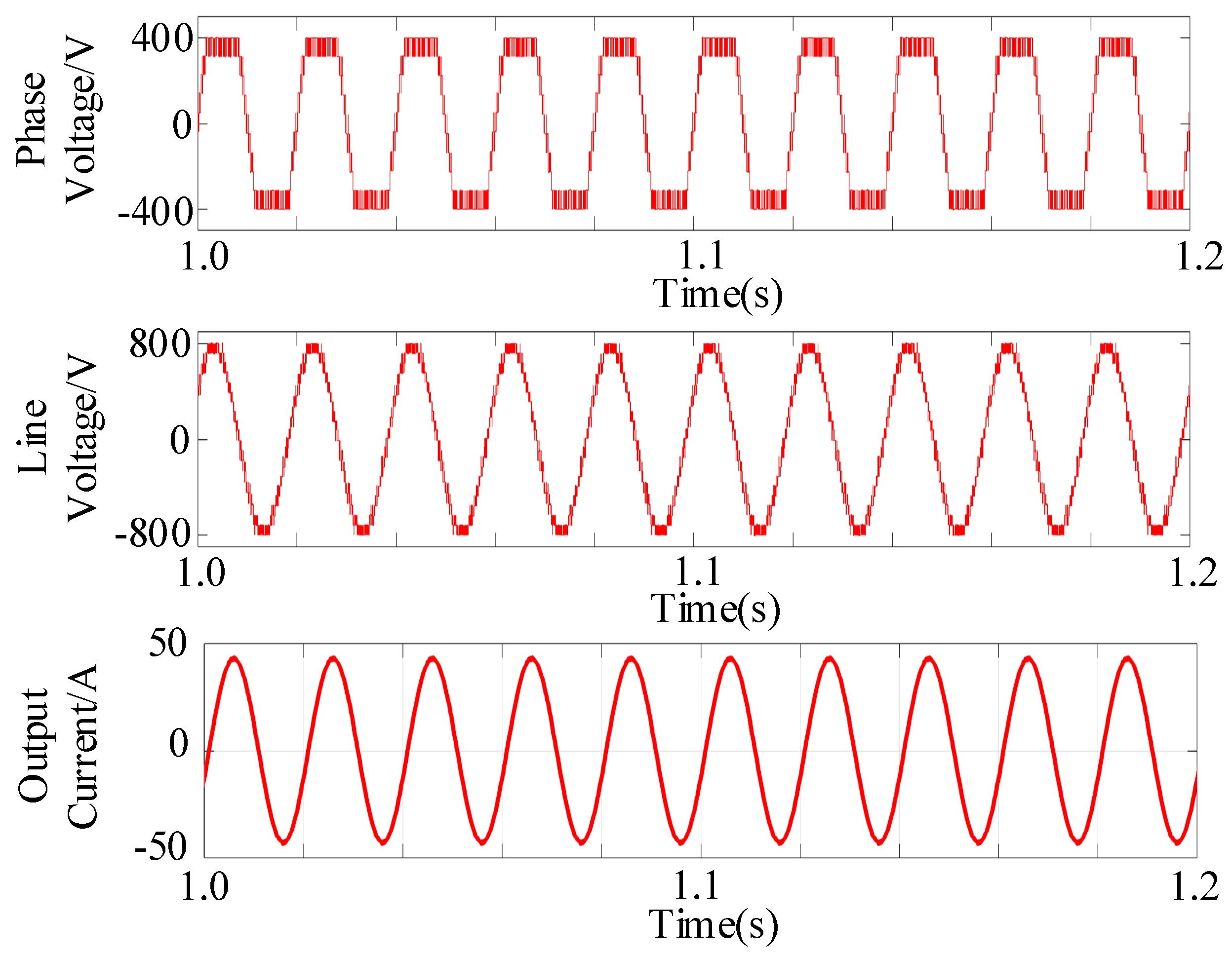
4. Simulation Results
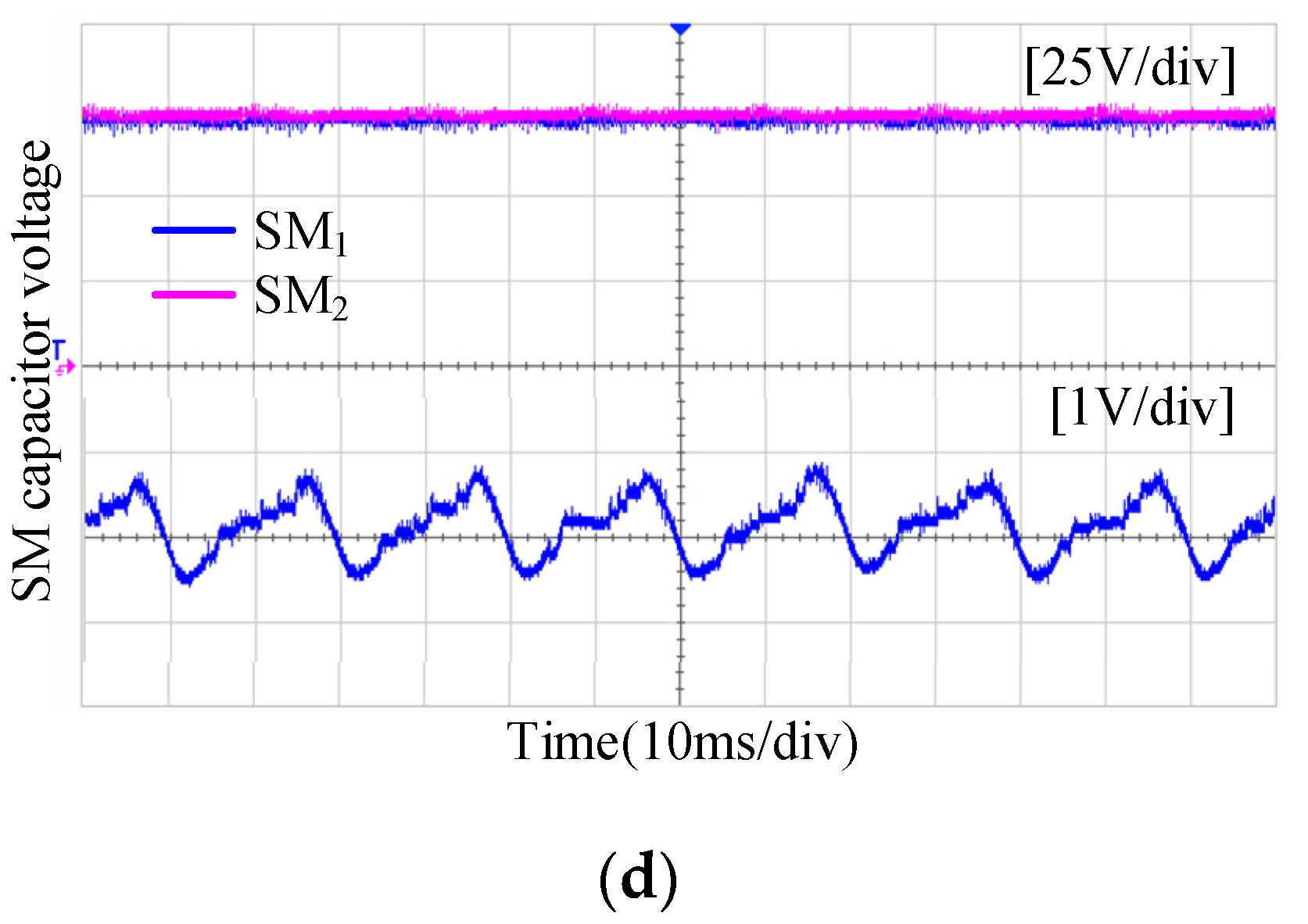
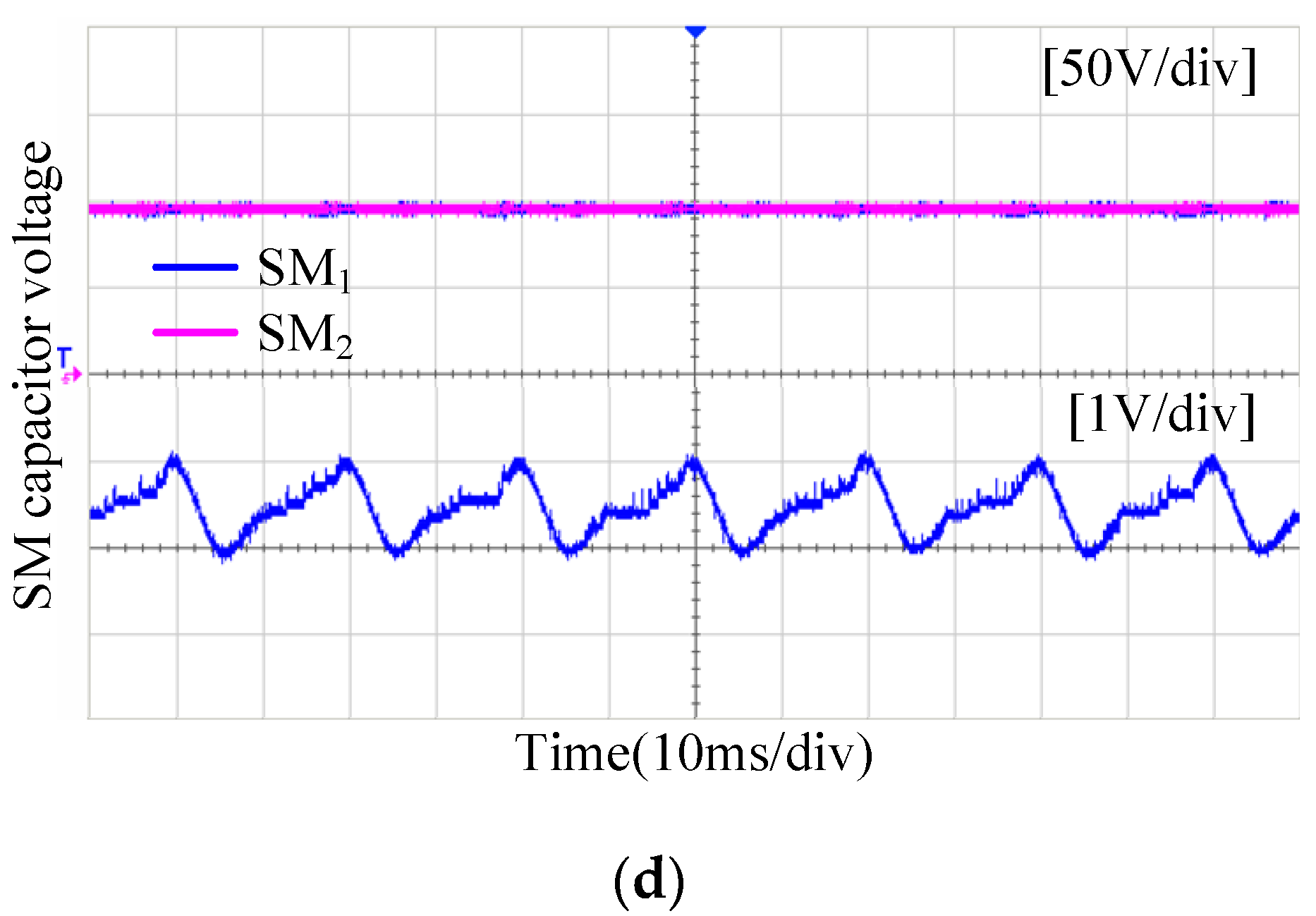
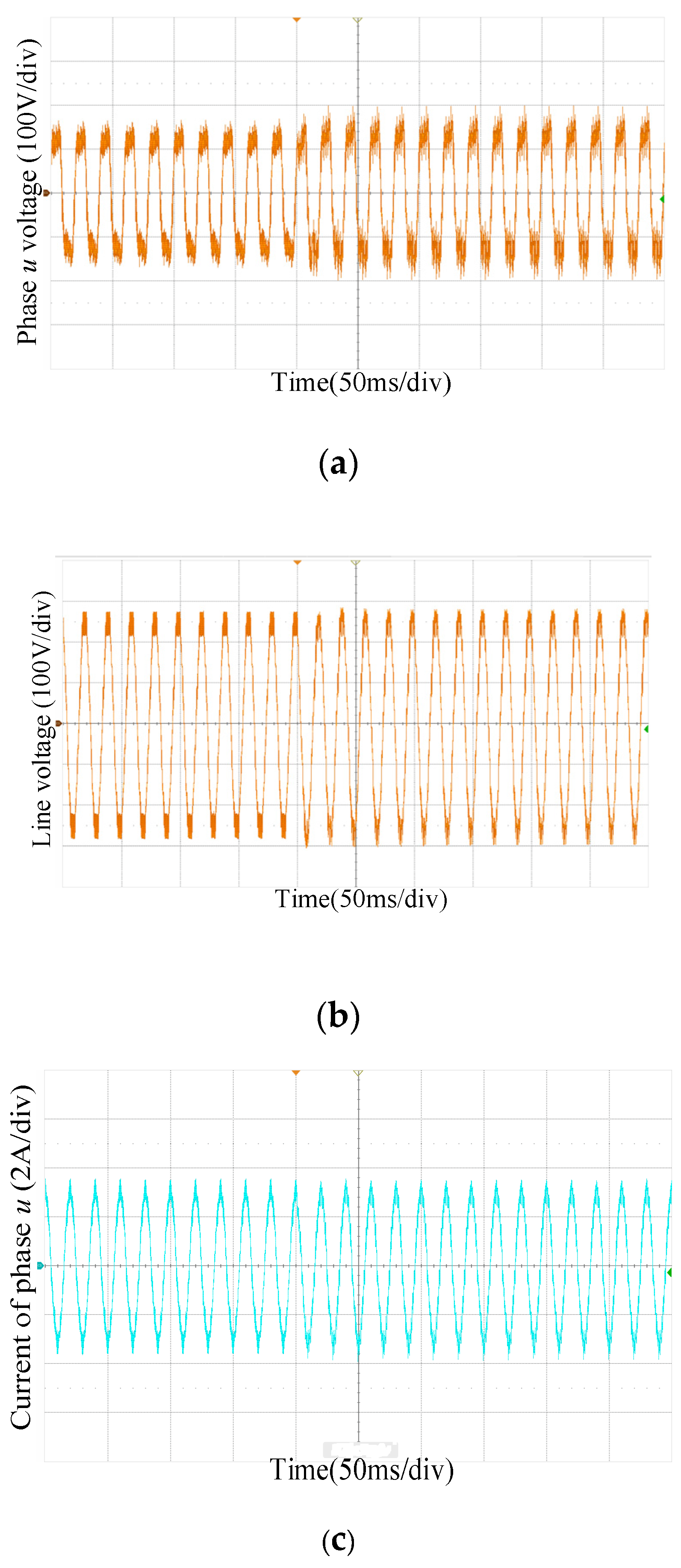
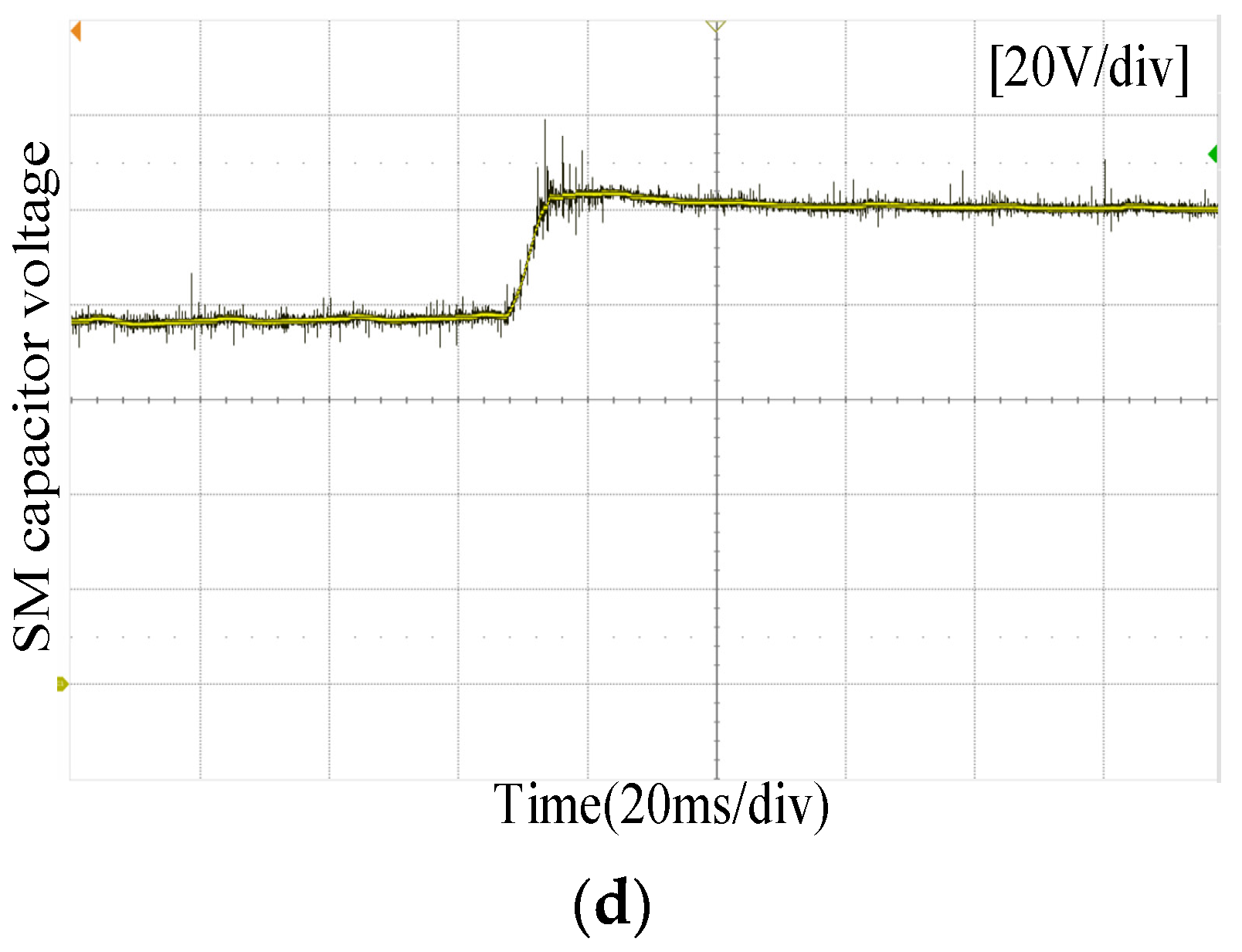
5. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, S.; Wu, B.; Tian, K.; Zargari, N.R.; Cheng, Z. An Active Cross-Connected Modular Multilevel Converter (AC-MMC) for a Medium-Voltage Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4707–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, M.; Nishimura, K.; Akagi, H. A Medium-Voltage Motor Drive with a Modular Multilevel PWM Inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 1786–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y. Impacts of three MMC-HVDC configurations on AC system stability under DC line faults. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 26–30 July 2015; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lezana, P.; Pou, J.; Meynard, T.A.; J Rodriguez, S. Ceballos and F. Richardeau, Survey on Fault Operation on Multilevel Inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelsalam, M.; Tennakoon, S.; Griffiths, A.L.; Marei, M. Investigation of sub-module fault types of modular multi-level converters in HVDC networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 50th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Stroke-on-Trent, UK, 1–4 September 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, J.; Hammond, P.W.; Pontt, J.; Musalem, R.; Lezana, P.; Escobar, M.J. Operation of a medium-voltage drive under faulty conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 52, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Bryant, A.; Mawby, P.; Xiang, D.; Ran, L.; Tavner, P. An Industry-Based Survey of Reliability in Power Electronic Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardeau, F.; Pham, T.T.L. Reliability Calculation of Multilevel Converters: Theory and Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 4225–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, R.; Xu, R.; Xu, D.; Wang, W. Seamless Transition Control for Modular Multilevel Converters When Inserting a Cold-Reserve Redundant Submodule. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 4052–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Y. Fault-Tolerant Control of MMC With Hot Reserved Submodules Based on Carrier Phase Shift Modulation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 6778–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, Y. A Fault-Tolerant Operation Method for Medium Voltage Modular Multilevel Converters with Phase-Shifted Carrier Modulation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 9459–9470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, Y.; Guo, J.; Lin, Z. Energy-balancing Control Strategy for Modular Multilevel Converters Under Submodule Fault Conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 5021–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazanfari, A.; Mohamed, Y.A.I. A Resilient Framework for Fault-Tolerant Operation of Modular Multilevel Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 2669–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, R.; Chen, Z. Fault-Tolerant Approach for Modular Multilevel Converters under Submodule Faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7253–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Bai, Z. A Submodule Fault Ride-Through Strategy for Modular Multilevel Converters with Nearest Level Modulation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Tang, Y.; Wang, P. Seamless Fault-Tolerant Operation of a Modular Multilevel Converter with Switch Open-Circuit Fault Diagnosis in a Distributed Control Architecture. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 7058–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghnazari, S.; Vahedi, H.; Zolghadri, M.R. Fault tolerant operation strategy design for modular multilevel converters. In Proceedings of the IECON 2016—42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Florence, Italy, 24–27 October 2016; pp. 2172–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Xie, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Bian, S. Model Predictive-based Fault-tolerant Control for Modular Multilevel Converters without Redundant Submodules. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Power Electronics and Application Conference and Exposition (PEAC), Shenzhen, China, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Qin, J.; Saeedifard, M. A Postfault Strategy to Control the Modular Multilevel Converter under Submodule Failure. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2016, 31, 2453–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, W.; He, X. Neutral-Point-Shift-Based Active Thermal Control for a Modular Multilevel Converter under a Single-Phase-to-Ground Fault. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 2474–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzamkia, S.; Iman-Eini, H.; Noushak, M.; Hadizadeh, A. Improved Fault-Tolerant Method for Modular Multilevel Converters by Combined DC and Neutral-Shift Strategy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 2454–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, K.; Lee, J. Fault-tolerant control scheme for modular multilevel converter based on sorting algorithm without reserved Submodules. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), San Antonio, TX, USA, 4–8 March 2018; pp. 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Shi, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Xu, D. Fault diagnosis and tolerant control of Single IGBT open-circuit failure in Modular multilevel converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 3165–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzamkia, S.; Iman-Eini, H.; Khoshkbar-Sadigh, A.; Noushak, M. A software-based fault-tolerant strategy for modular multilevel converter using DC bus voltage control. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 9, 3436–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xu, Z.; Ding, J.; Xu, D. Fault-tolerant control of medium-voltage modular multilevel converters with minimum performance degradation under submodule failures. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 11772–11781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, M.; Marei, M.I.; Tennakoon, S.B. An integrated control strategy with fault detection and tolerant control capability based on capacitor voltage estimation for modular multilevel converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 2840–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Teo, K.H.; Saeedifard, M.; Harley, R.G. Optimized Control of the Modular Multilevel Converter Based on Space Vector Modulation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 5697–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleenejad, M.; Mahmoudi, H.; Jafarishiadeh, S.; Ahmadi, R. Fault-Tolerant Space Vector Modulation for Modular Multilevel Converters with Bypassed Faulty Submodules. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 2463–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Chen, H.; Ma, H. Implementation of Space Vector Modulation (SVM) for Modular Multilevel Converter Based on Submodule Regroup. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Power Electronics and Application Conference and Exposition (PEAC), Shenzhen, China, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]


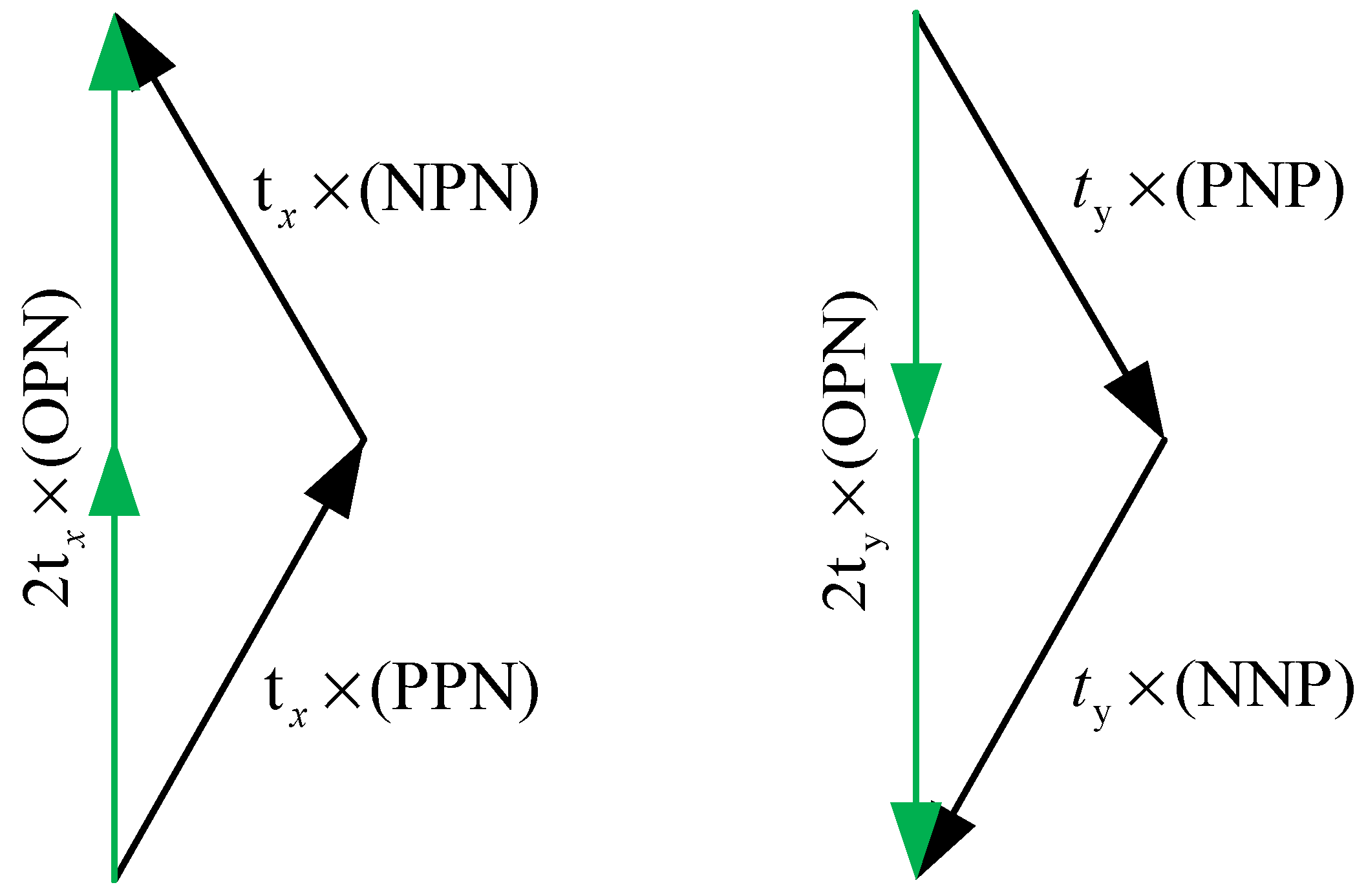



| Conditions | Action Sequence of Vectors | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | NON | NPN | OPN | OPO | OPN | NPN | NON |
| Type u fault | NON | NPN | PPN | PPN | PPN | NPN | NON |
| Sectors | Time | Switching Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| I-1 | SE7 | POO-PPO-PPP-PPP-PPP-PPO-POO |
| I-2 | SE6 | POO-PPO-PPP-PPP-PPP-PPO-POO |
| I-3 | SE8 | PON-POO-PPO-PPO-PPO-POO-PON |
| I-4 | SE7 | PON-POO-PPO-PPO-PPO-POO-PON |
| I-5 | SE8 | PON-PPN-PPO-PPO-PPO-PPN-PON |
| I-6 | SE8 | PNN-PON-POO-POO-POO-PON-PNN |
| II-1 | SE1 | NNN-NON-PPO-PPO-PPO-NON-NNN |
| II-2 | SE1 | NON-PPO-PPP-PPP-PPP-PPO-NON |
| II-3 | SE2 | NON-NPN-PPN-PPO-PPN-NPN-NON |
| II-4 | SE3 | NON-NPN-PPN-PPO-PPN-NPN-NON |
| II-5 | SE4 | NON-NPN-PPN-PPN-PPN-NPN-NON |
| II-6 | SE5 | NPN-PPN-PPO-PPO-PPO-PPN-NPN |
| III-1 | SE8 | NNN-NON-NOO-NOO-NOO-NON-NNN |
| III-2 | SE7 | NNN-NON-NOO-NOO-NOO-NON-NNN |
| III-3 | SE7 | NON-NOO-NPO-NPO-NPO-NOO-NON |
| III-4 | SE6 | NON-NOO-NPO-NPO-NPO-NOO-NON |
| III-5 | SE6 | NOO-NPO-NPP-NPP-NPP-NPO-NOO |
| III-6 | SE6 | NON-NPN-NPO-NPO-NPO-NPN-NON |
| IV-1 | SE7 | NNN-NNO-NOO-NOO-NOO-NNO-NNN |
| IV-2 | SE8 | NNN-NNO-NOO-NOO-NOO-NNO-NNN |
| IV-3 | SE6 | NNO-NOO-NOP-NOP-NOP-NOO-NNO |
| IV-4 | SE7 | NNO-NOO-NOP-NOP-NOP-NOO-NNO |
| IV-5 | SE6 | NNO-NNP-NOP-NOP-NOP-NNP-NNO |
| IV-6 | SE6 | NOO-NOP-NPP-NPP-NPP-NOP-NOO |
| V-1 | SE1 | NNO-POP-PPP-PPP-PPP-POP-NNO |
| V-2 | SE1 | NNN-NNO-POP-POP-POP-NNO-NNN |
| V-3 | SE3 | NNO-NNP-PNP-POP-PNP-NNP-NNO |
| V-4 | SE2 | NNO-NNP-PNP-POP-PNP-NNP-NNO |
| V-5 | SE5 | NNP-PNP-POP-POP-POP-PNP-NNP |
| V-6 | SE4 | NNO-NNP-PNP-PNP-PNP-NNP-NNO |
| VI-1 | SE6 | POO-POP-PPP-PPP-PPP-POP-POO |
| VI-2 | SE7 | POO-POP-PPP-PPP-PPP-POP-POO |
| VI-3 | SE7 | PNO-POO-POP-POP-POP-POO-PNO |
| VI-4 | SE8 | PNO-POO-POP-POP-POP-POO-PNO |
| VI-5 | SE8 | PNN-PNO-POO-POO-POO-PNO-PNN |
| VI-6 | SE8 | PNO-PNP-POP-POP-POP-PNP-PNO |
| Parameters | Indexes | Values |
|---|---|---|
| No. of SMs per arm | N | 10 |
| DC-link voltage | Udc | 800 V |
| Switching frequency | fs | 1 kHz |
| Modulation index | m | 0.97 |
| Fundamental frequency | fo | 50 Hz |
| Arm inductance | Ls | 3 mH |
| Load | Lload | 3 mH |
| Rload | 10 Ω |
| Conditions | uuv | uvw | uwu | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THD (%) | Amplitude (V) | THD (%) | Amplitude (V) | THD (%) | Amplitude (V) | |
| Normal | 7.98 | 779.9 | 7.95 | 780 | 7.98 | 780 |
| Type u | 9.52 | 776.7 | 8.27 | 779.8 | 9.52 | 777.3 |
| Parameters | Indexes | Values |
|---|---|---|
| No. of SMs per arm | N | 4 |
| dc-link voltage | Udc | 300 V |
| SM capacitance | C | 2350 μF |
| Switching frequency | fs | 1 kHz |
| Modulation index | m | 0.97 |
| Fundamental frequency | fo | 50 Hz |
| Arm inductance | Ls | 7.7 mH |
| Load | Lload | 1 mH |
| Rload | 50 Ω |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Z.; Li, Y. Unified Strategy for Fault-Tolerant Operation of MMC with Multiple SMs Failure Based on SMs Grouping Management. Energies 2022, 15, 5694. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155694
Bai Z, Li Y. Unified Strategy for Fault-Tolerant Operation of MMC with Multiple SMs Failure Based on SMs Grouping Management. Energies. 2022; 15(15):5694. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155694
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Zhihong, and Yifei Li. 2022. "Unified Strategy for Fault-Tolerant Operation of MMC with Multiple SMs Failure Based on SMs Grouping Management" Energies 15, no. 15: 5694. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155694
APA StyleBai, Z., & Li, Y. (2022). Unified Strategy for Fault-Tolerant Operation of MMC with Multiple SMs Failure Based on SMs Grouping Management. Energies, 15(15), 5694. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155694







