Integrated Predictive Control of PMLSM Current and Velocity Based on ST-SMO
Abstract
:1. Introduction
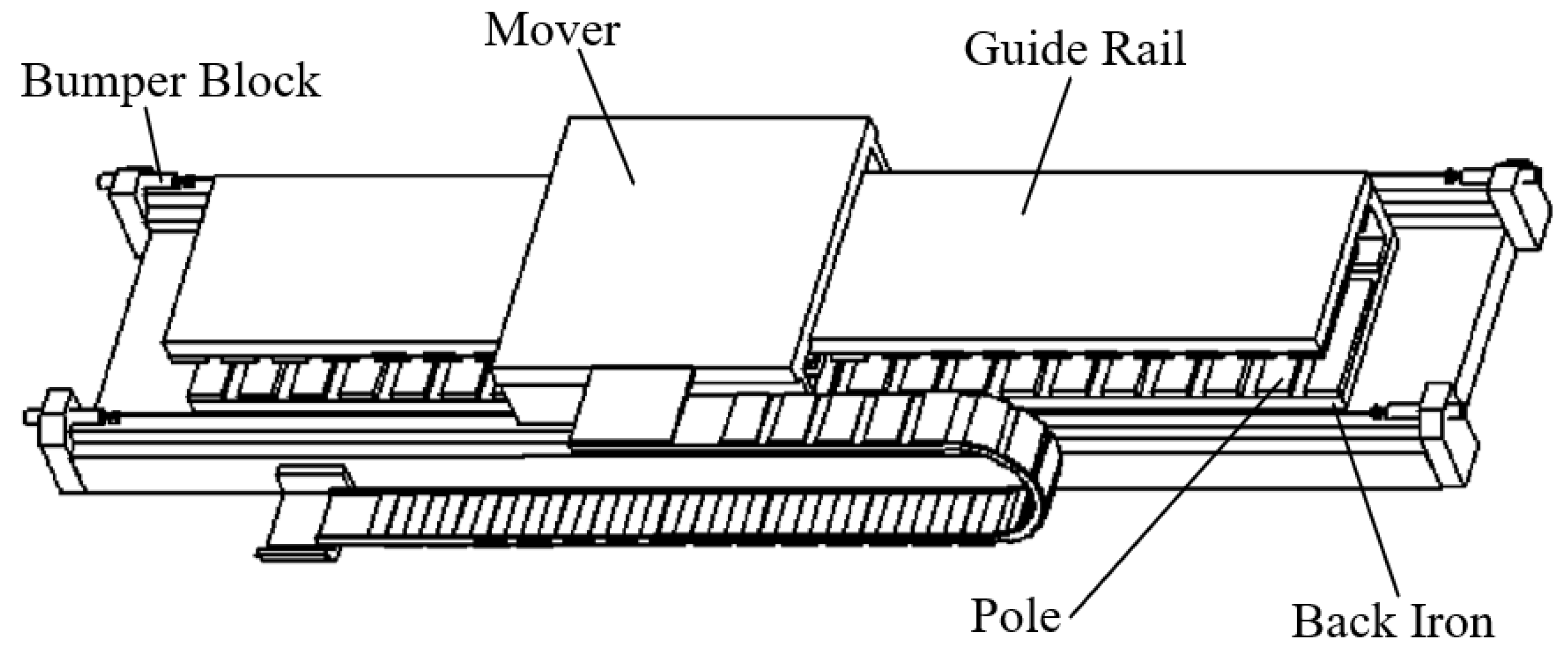
2. Mathematical Model of PMLSM
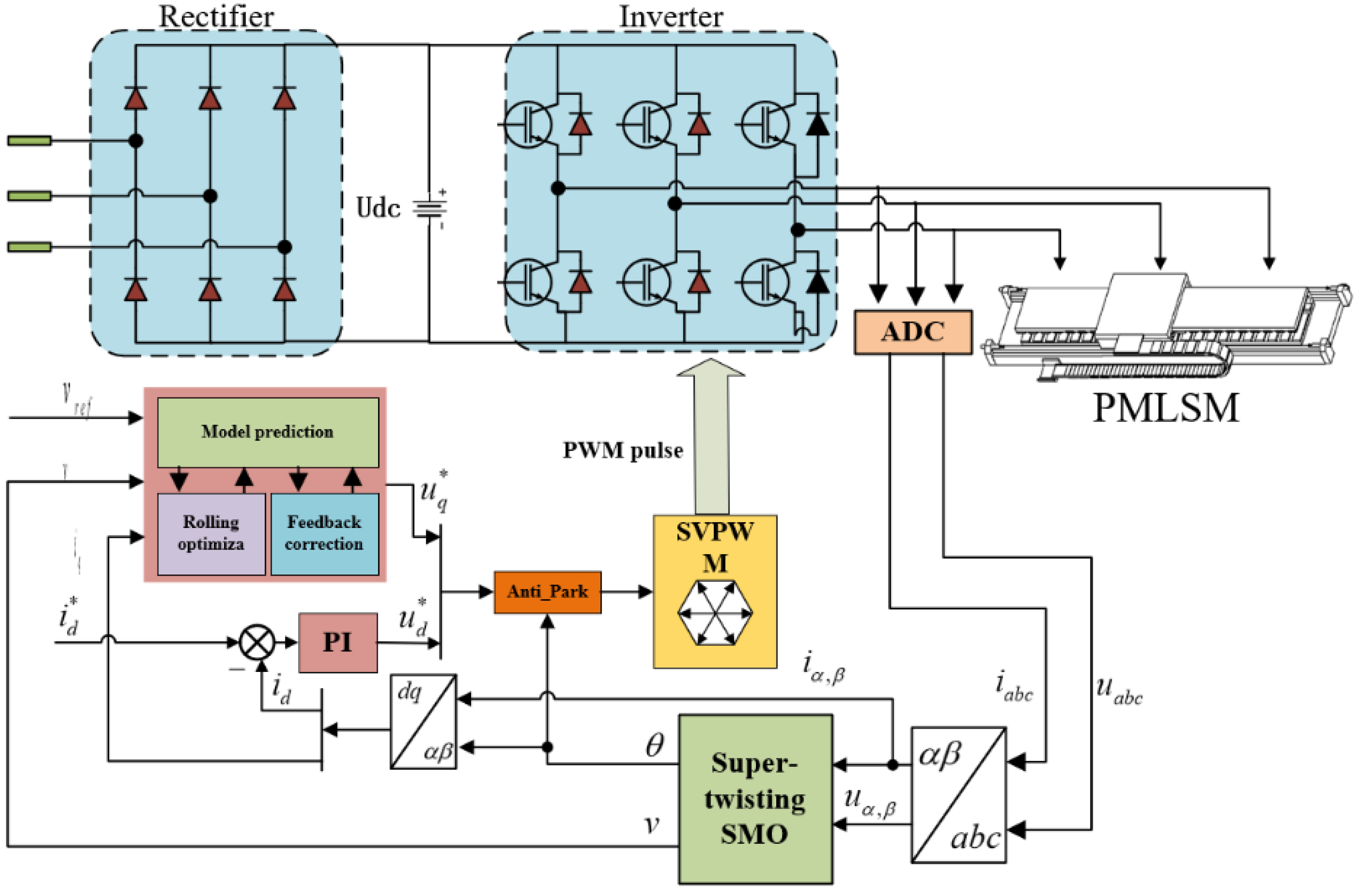
3. Speed and Current Integrated Controller
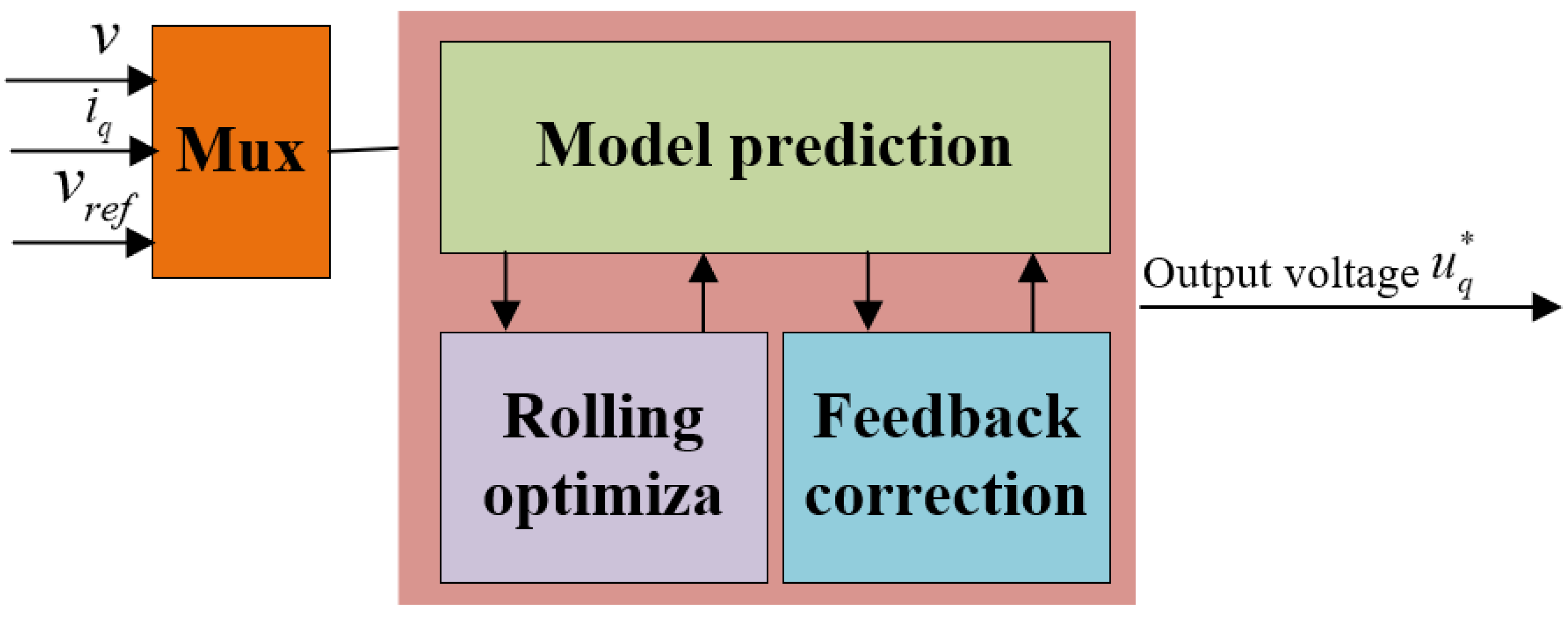
3.1. Design of the MPC Controller
3.1.1. Prediction Model
3.1.2. Closed-Loop Prediction and Reference Trajectory
3.1.3. Optimization Guidelines
3.2. Stability Analysis of the MPC
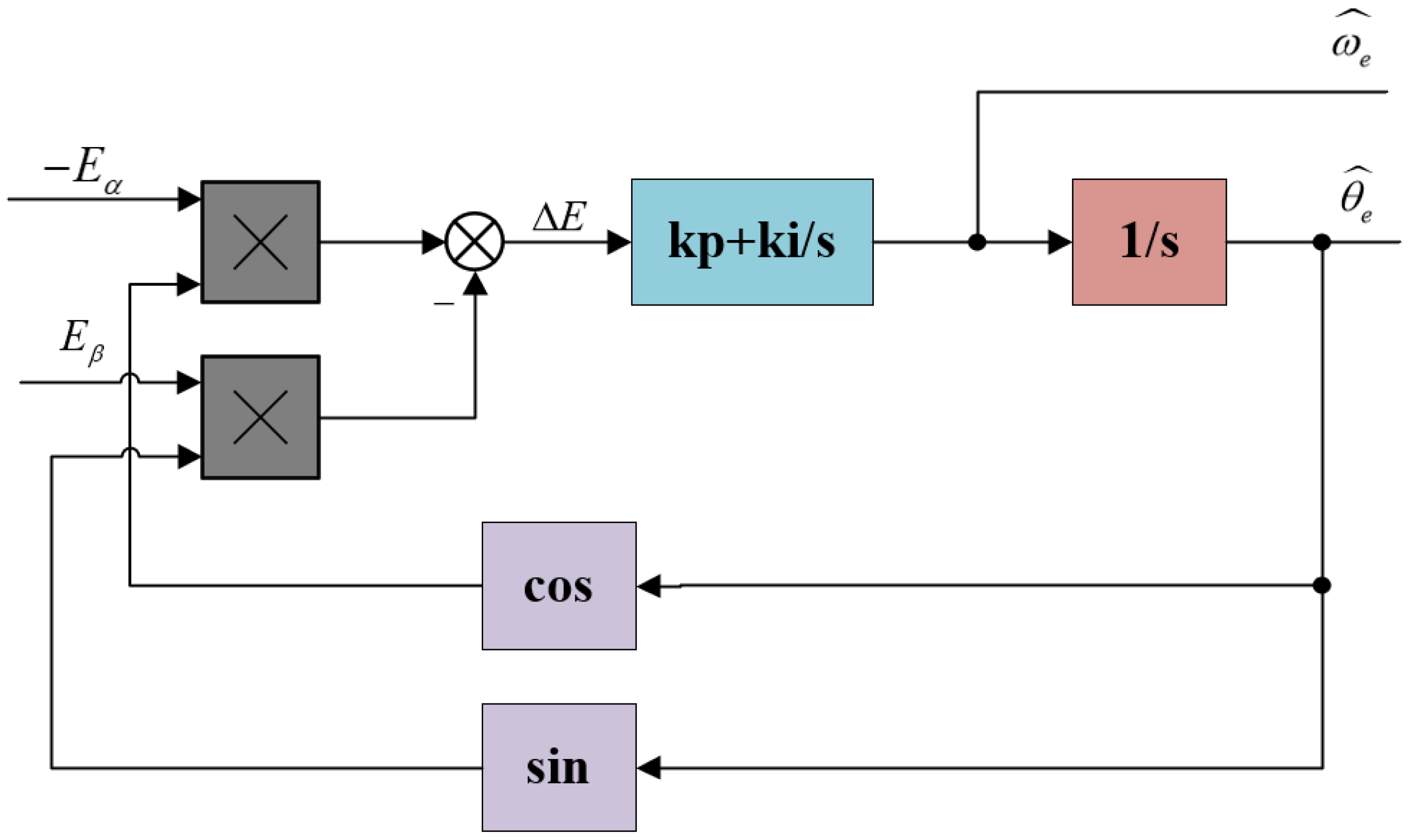
4. Super-Twisting Sliding-Mode Observer
4.1. Design of the Super-Twisting Sliding-Mode Observer
4.2. Proof of Stability
4.3. PLL Strategy Application
5. Traditional SMC Controller
5.1. Design of a Traditional SMC Controller
5.2. Stability Analysis of a Traditional SMC Controller
6. Simulation and Experimental Results
6.1. System Simulation
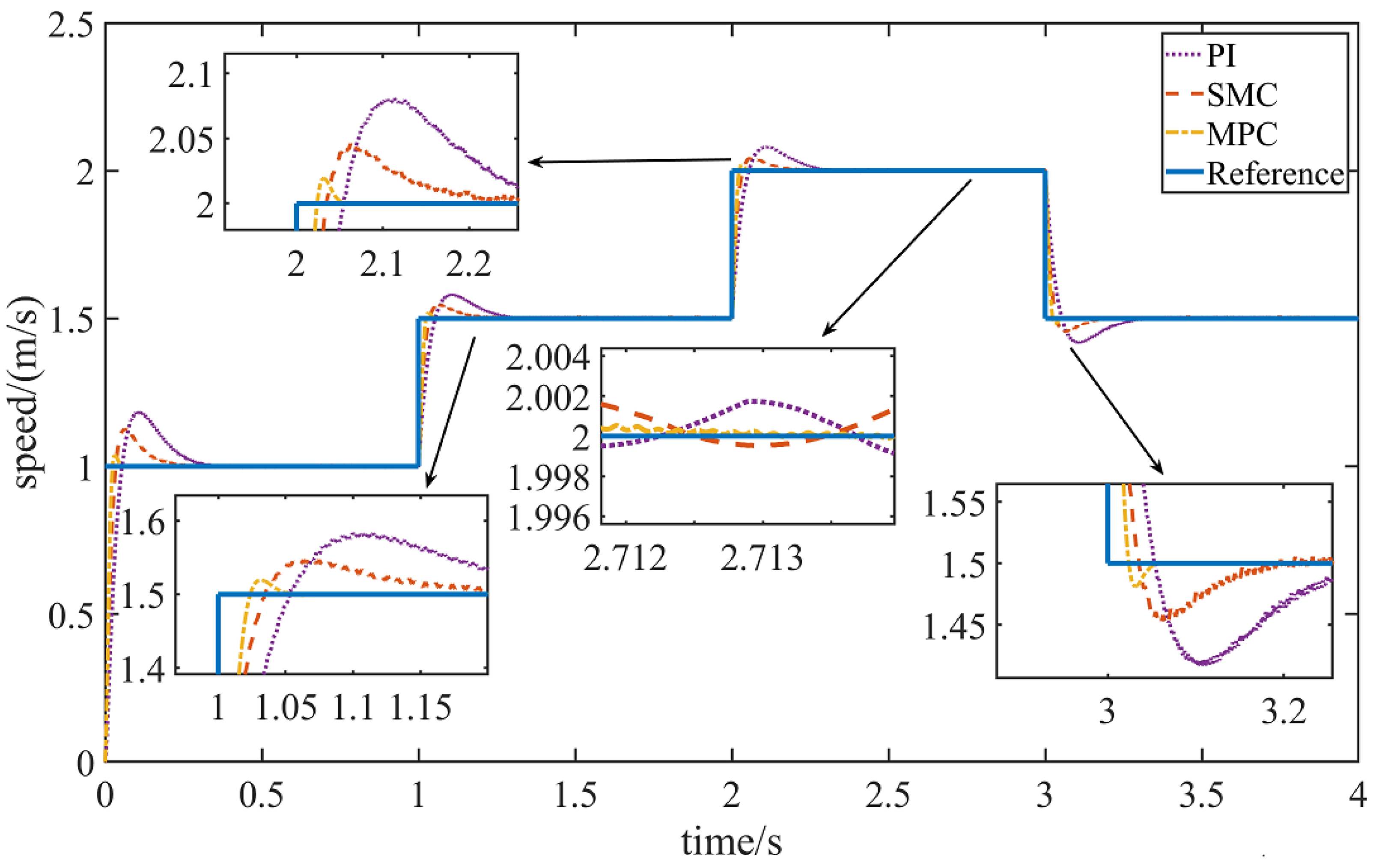
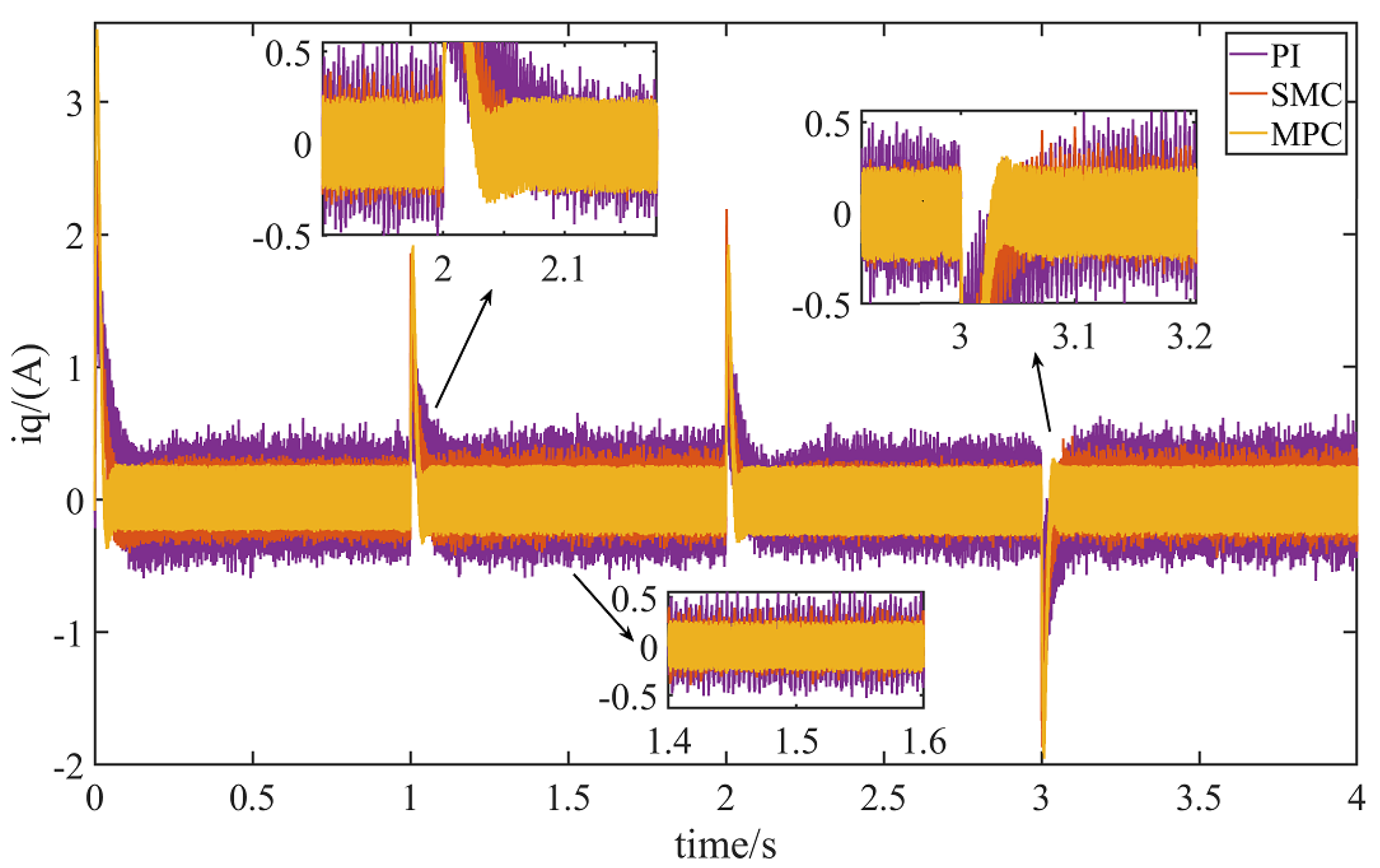
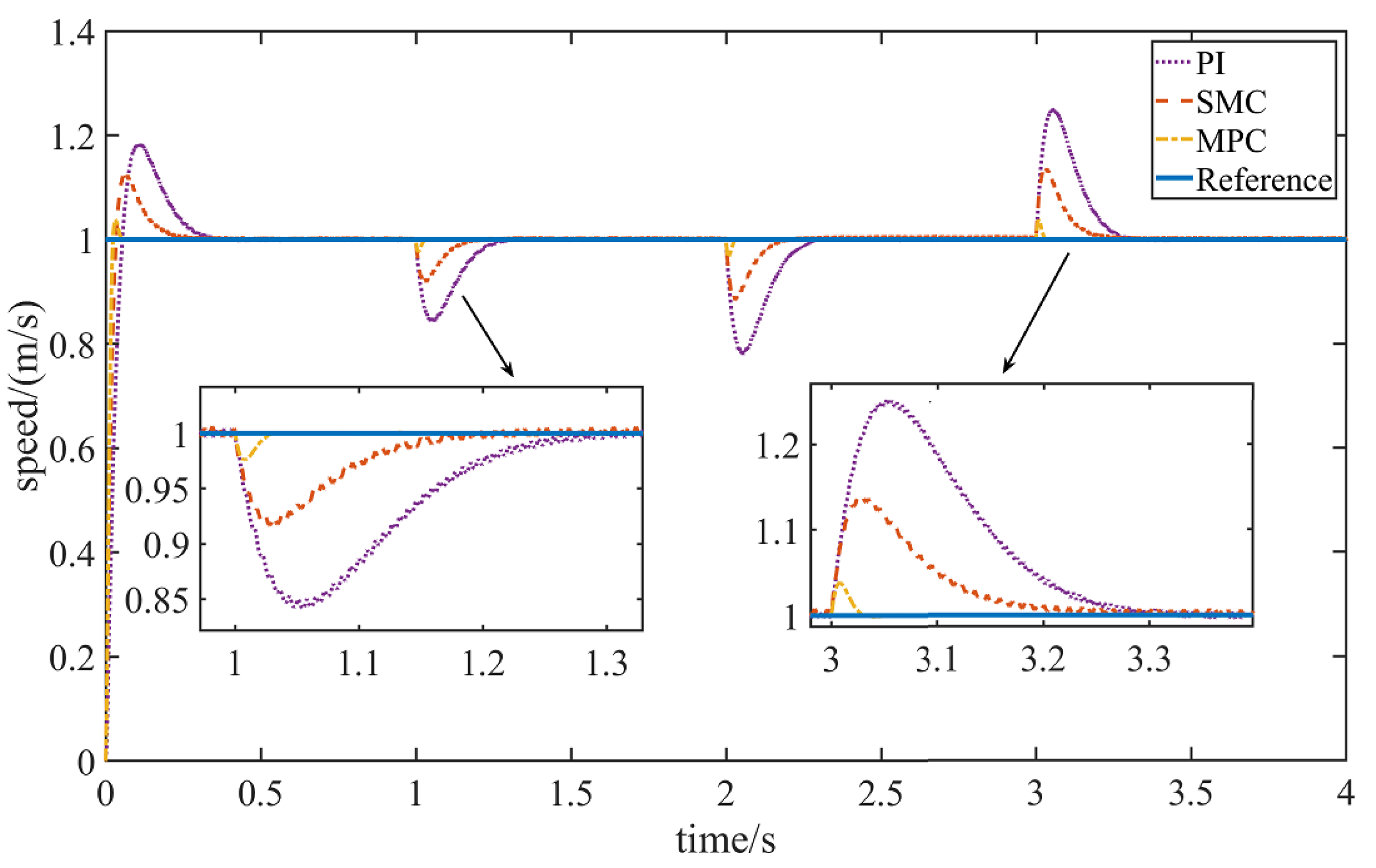
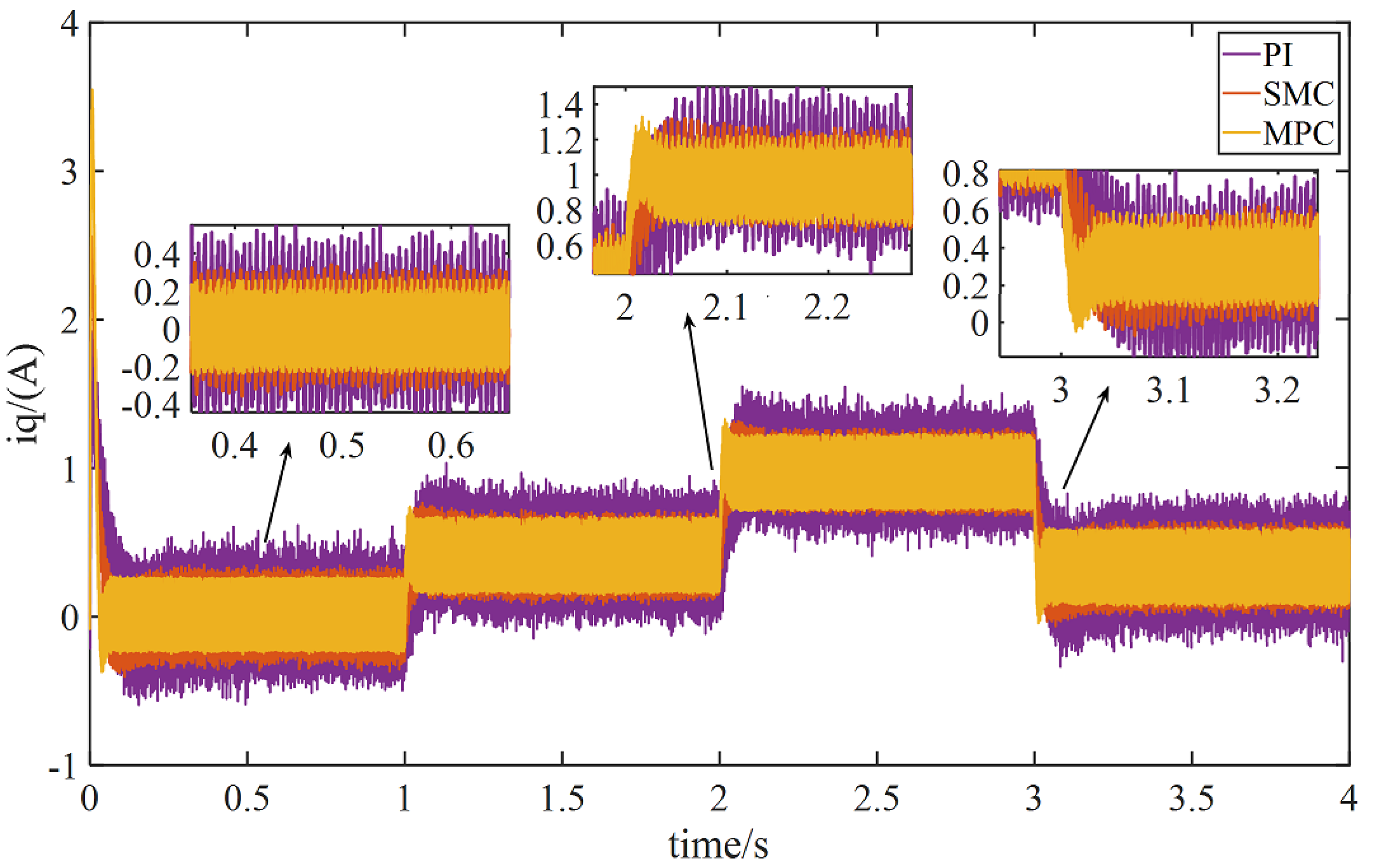
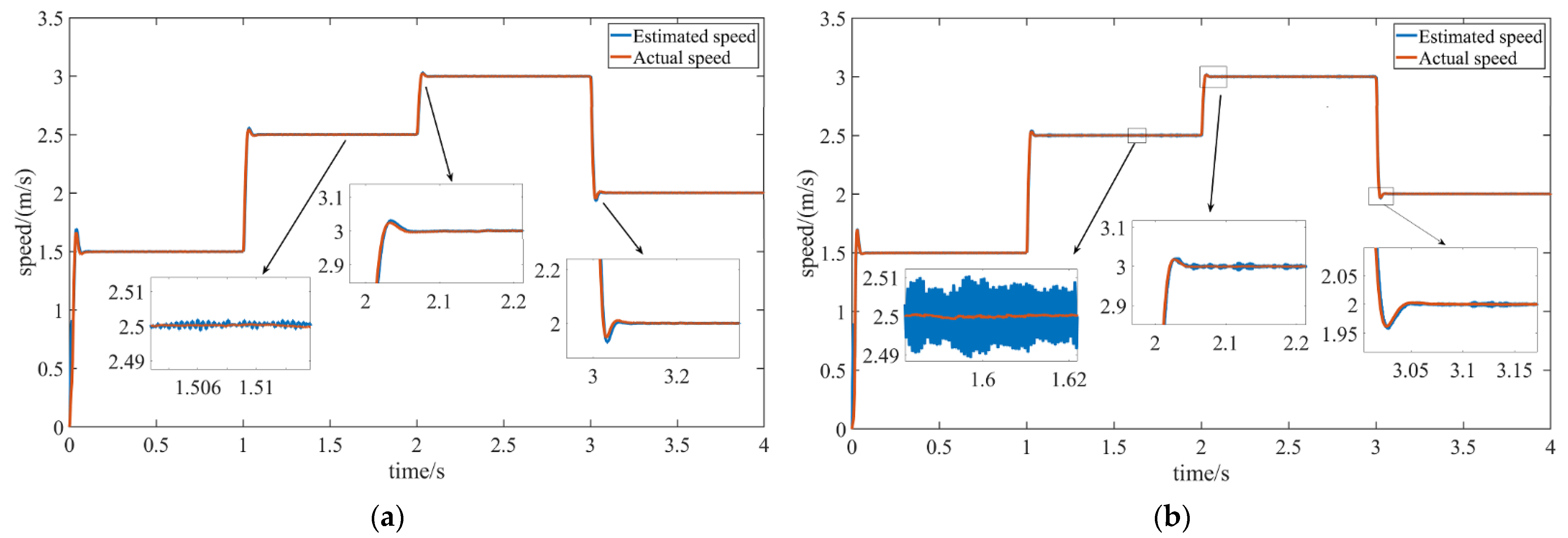
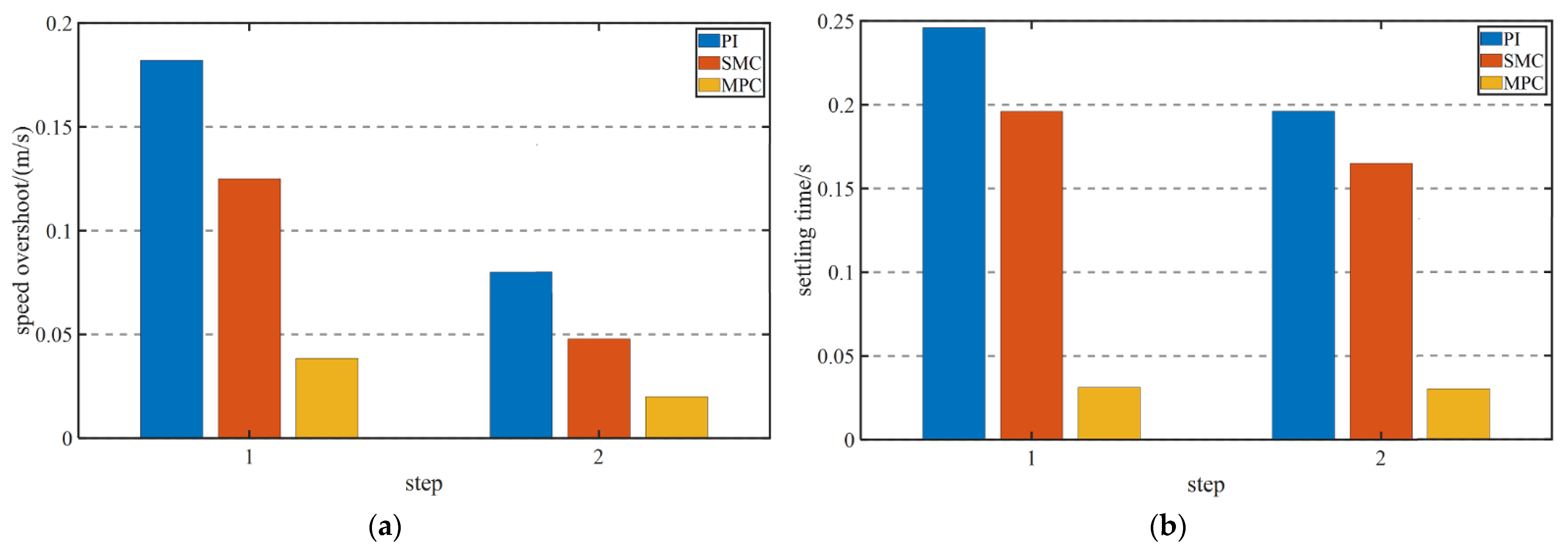
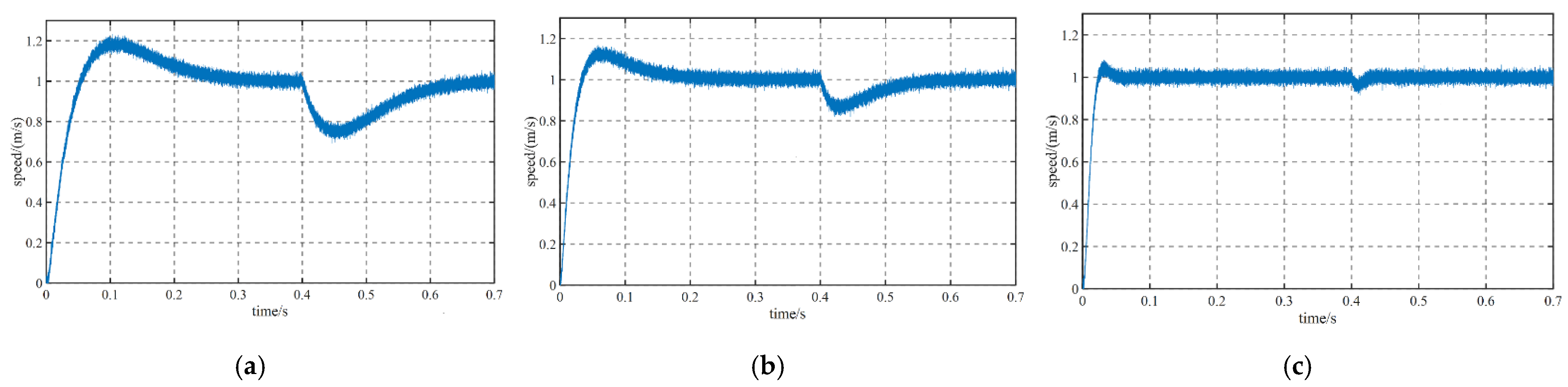
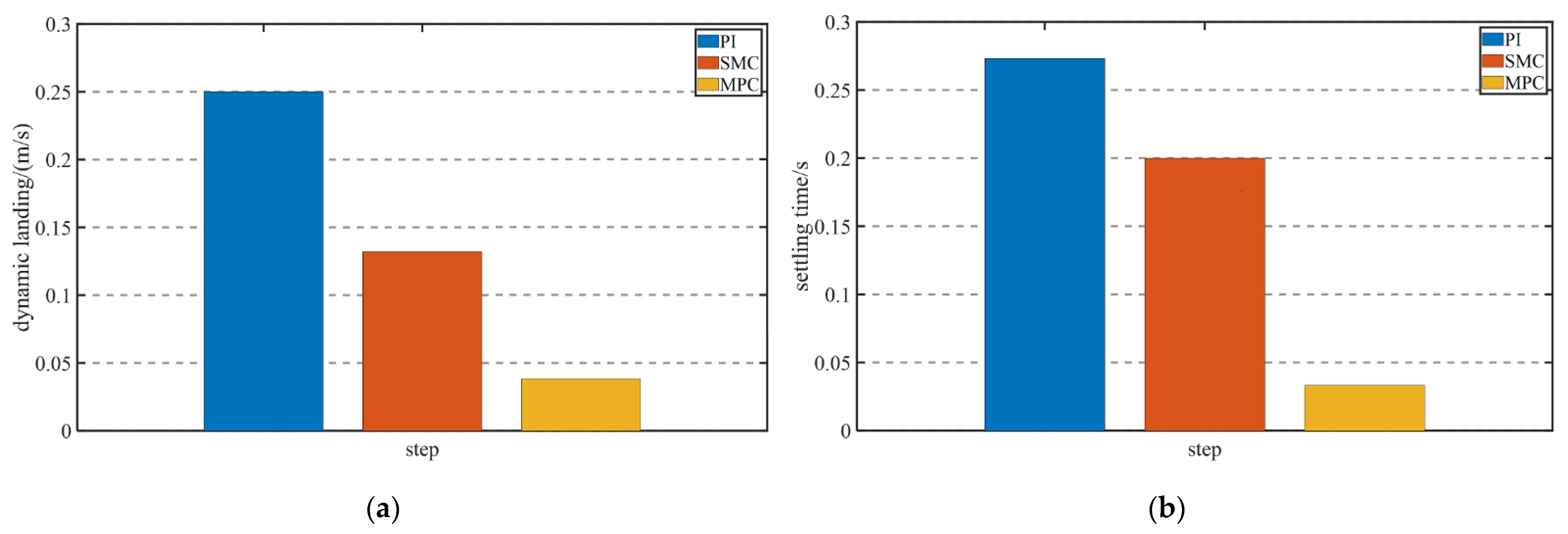
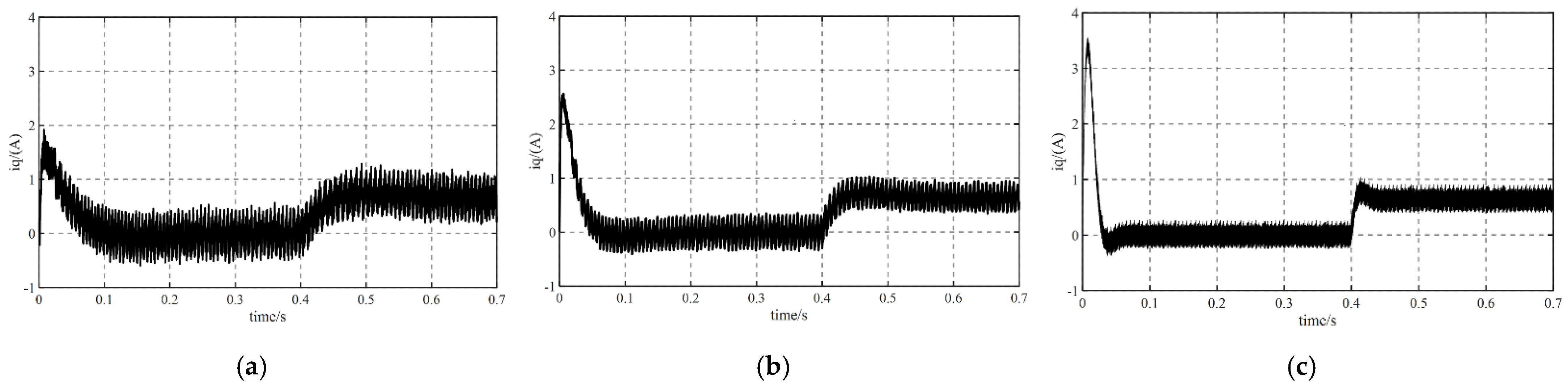
6.1.1. The Load Remains Unchanged, and the Speed Changes
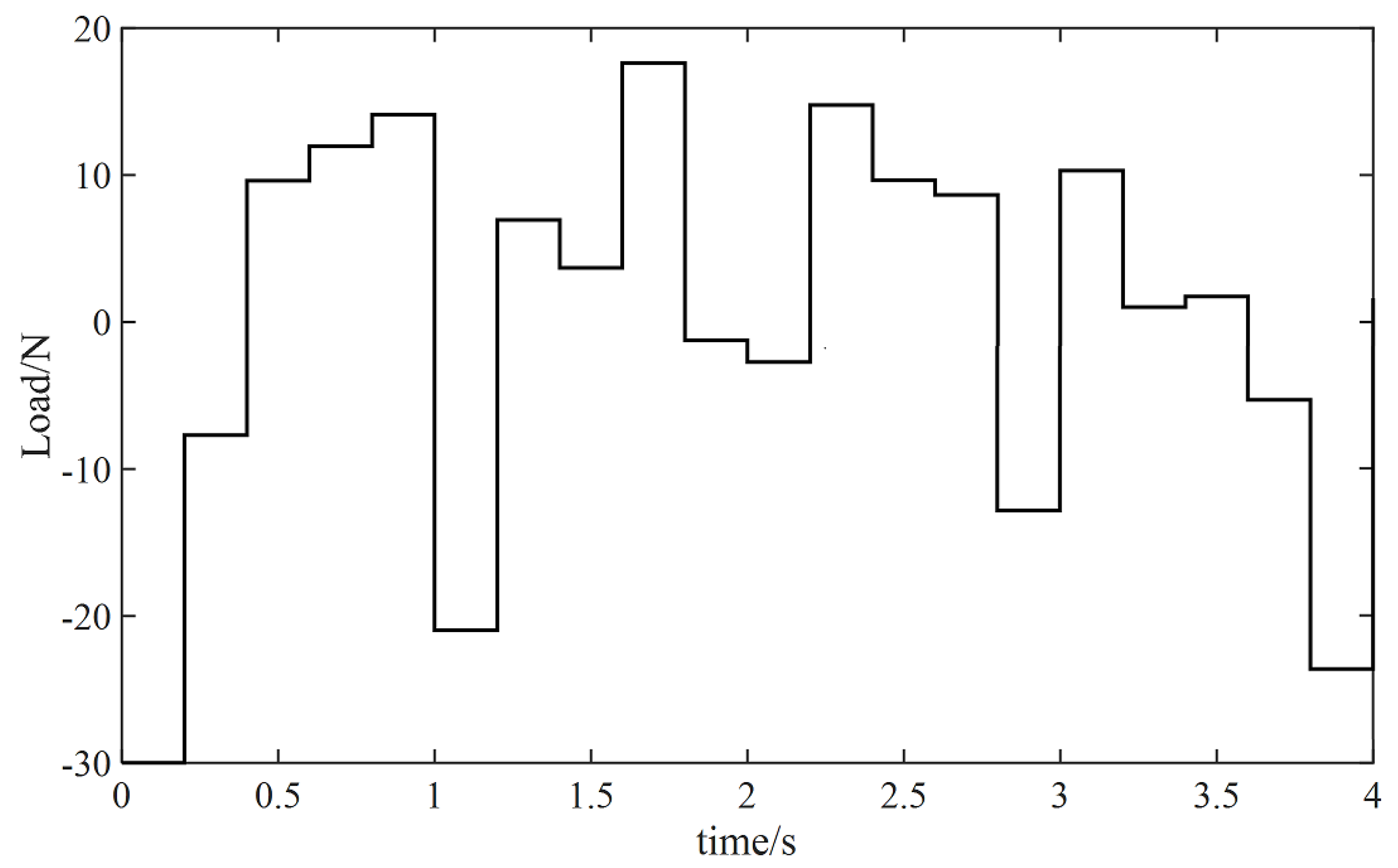
6.1.2. The Speed Remains Unchanged and the Load Changes
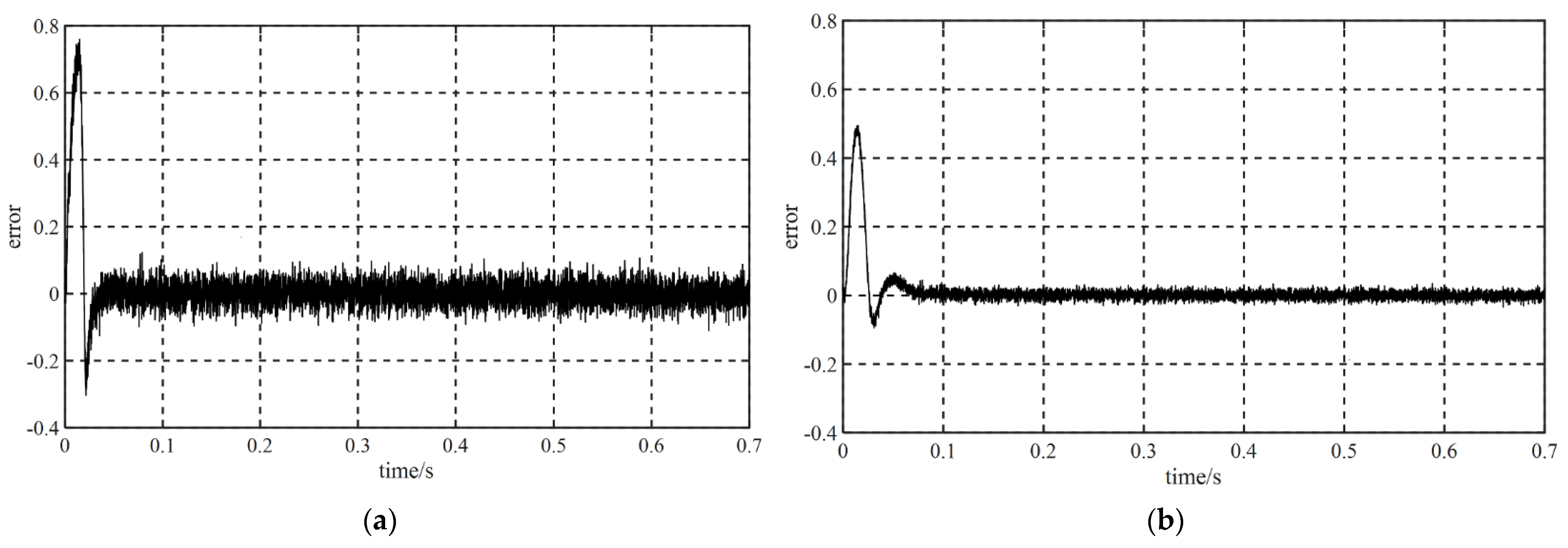
6.1.3. Comparison of Observation Effect between ST-SMO and Traditional SMO
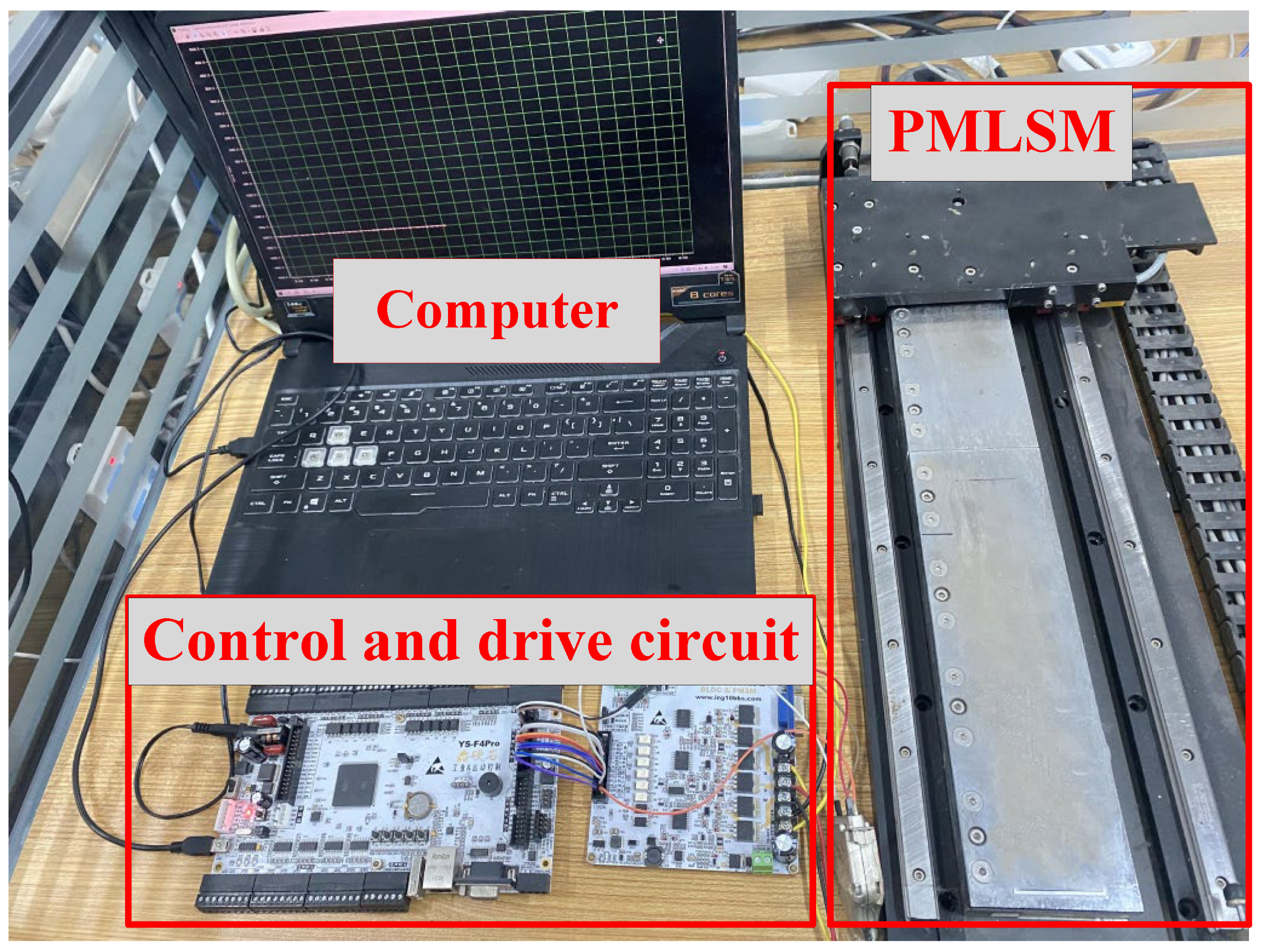
6.2. Experiment
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, H.; Sun, S.; Zhou, X.; Shao, D.; Mi, S.; Hu, Y. Sensorless DPCC of PMLSM Using SOGI-PLL-Based High-Order SMO With Cogging Force Feedforward Compensation. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.; Song, J.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Z. Robust Optimization of PMLSM Based on a New Filled Function Algorithm with a Sigma Level Stability Convergence Criterion. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 4743–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Li, L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, C. Force Ripple Compensation and Robust Predictive Current Control of PMLSM Using Augmented Generalized Proportional–Integral Observer. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Mou, Q.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, J. Study on a Double-Sided Permanent-Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor With Reversed Slots. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wang, M.; Li, L.; Wang, G.; Zhong, C. Robust Predictive Current Control of PMLSM With Extended State Modeling Based Kalman Filter: For Time-Varying Disturbance Rejection. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 2208–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongling, W.; Hong, L.; Xinda, S.; Baodong, C. Research on current harmonic suppression method of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on improved repetitive controller. Trans. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 2019, 34, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, H.; Ma, Z.; Han, Y.; Chen, G.; Liao, Z.; Lin, G. Model Predictive Control with Common-Mode Voltage Minimization for a Three-level NPC Inverter PMLSM Drive System. In Proceedings of the 2021 13th International Symposium on Linear Drives for Industry Applications (LDIA), Wuhan, China, 1–3 July 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- ZMa, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, G. Dichotomy Solution Based Model Predictive Control for Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motors. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Harbin, China, 11–14 August 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, T. Modelling and performance analysis on a bearingless fixed-pole rotor induction motor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2019, 13, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H. Fast Commutation Error Compensation Method of Sensorless Control for MSCMG BLDC Motor With Nonideal Back EMF. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 8044–8054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarsembayev, B.; Suleimenov, K.; Do, T.D. High Order Disturbance Observer Based PI-PI Control System with Tracking Anti-Windup Technique for Improvement of Transient Performance of PMSM. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 66323–66334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Rafaq, M.S.; Choi, H.H.; Jung, J.W. A Model Reference Adaptive Control Based Speed Controller for a Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 9399–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Dong, D. Dynamic Performance Enhancement Method Based on Improved Model Reference Adaptive System for SPMSM Sensorless Drives. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 135012–135023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ma, T.; Che, Z.; Zhou, L. An Adaptive-Gain Sliding Mode Observer for Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motors. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 3469–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Sliding-Mode Observer-Based Mechanical Parameter Estimation for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 5732–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Junejo, A.K.; Tang, Y.; Shahab, M.; Habib, H.U.R.; Liu, Y.; Huang, S. Composite Speed Control of PMSM Drive System Based on Finite Time Sliding Mode Observer. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 151803–151813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Laghrouche, S.; Depernet, D.; Djerdir, A.; Cirrincione, M. Disturbance-Observer-Based Complementary Sliding-Mode Speed Control for PMSM Drives: A Super-Twisting Sliding-Mode Observer-Based Approach. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 5416–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bıçak, A.; Gelen, A. Sensorless direct torque control based on seven-level torque hysteresis controller for five-phase IPMSM using a sliding-mode observer. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2021, 24, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Mohanty, S.R.; Kumar, S. Event Trigger Super Twisting Sliding Mode Control for DC Micro Grid With Matched/Unmatched Disturbance Observer. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 3837–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, S.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, L. Sensorless Vector Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Linear Motor Based on Self-Adaptive Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Controller. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 44998–45011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Tao, H.; Zheng, Z. Sensorless Control of Induction Motors Based on Fractional-Order Linear Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Observer with Flux Linkage Compensation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 172308–172317. [Google Scholar]
- Levant, A. Principles of 2-sliding mode design. Automatica 2007, 43, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| stator resistance Rs/Ω | 4.0 |
| d–q axis inductance Ldq/mH | 8.2 |
| Mover mass m/kg | 1.425 |
| Viscous friction coefficient B/N/m·s | 44 |
| Polar distance τ/m | 0.016 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z. Integrated Predictive Control of PMLSM Current and Velocity Based on ST-SMO. Energies 2022, 15, 5504. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155504
Du S, Zhang Z, Wang J, Wang K, Zhao H, Li Z. Integrated Predictive Control of PMLSM Current and Velocity Based on ST-SMO. Energies. 2022; 15(15):5504. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155504
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Shenhui, Zihao Zhang, Jinsong Wang, Kangtao Wang, Hui Zhao, and Zheng Li. 2022. "Integrated Predictive Control of PMLSM Current and Velocity Based on ST-SMO" Energies 15, no. 15: 5504. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155504
APA StyleDu, S., Zhang, Z., Wang, J., Wang, K., Zhao, H., & Li, Z. (2022). Integrated Predictive Control of PMLSM Current and Velocity Based on ST-SMO. Energies, 15(15), 5504. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155504





