Discrete Terminal Super-Twisting Current Control of a Six-Phase Induction Motor
Abstract
1. Introduction
- insensitivity to a wide class of matched uncertainties and disturbances, and
- finite-time convergence of the commanded system trajectories to the selected sliding functions.
- A terminal sliding function that is a nonlinear one instead of the conventional linear sliding function in [17] is introduced. Consequently, a faster convergence is obtained during the reaching phase.
- The matched external perturbations, unmodeled dynamics due to the unmeasurable rotor currents, and electrical parameters’ variations are approximated using the TDE method. This latter is simple and easy to implement since it requires delayed determinate voltages, and actual and delayed existing measured stator currents.
- The estimated perturbations and dynamics are combined with the developed control law based on the discrete form of the super-twisting that is a second-order SM algorithm. Besides the good properties of this algorithm, the proposed combination ensures stability while choosing small super-twisting gains without a priori knowledge of the upper bound of the uncertainties. In addition, to the author’s best knowledge, few works considered this algorithm in the control part.
- The proposed Discrete-time Terminal Super-Twisting Control (DTSTC) combined with the TDE are implemented in real-time on a real asymmetrical six-phase IM to support the theoretical developments, to improve the performance, and to demonstrate that it is appropriate for multiphase IM stator current control. The proposed discrete-time technique can be extended easily to any n-phase induction motor and generator.
2. Preliminaries
- as the resistance of the stator,
- as the resistance of the rotor,
- as the magnetizing inductance,
- as the inductance of the stator,
- as the leakage inductance of the stator, and
- as the inductance of the rotor;
3. Enhanced DTSTC
3.1. Outer Speed Control Loop
3.2. Inner Current Control Loop
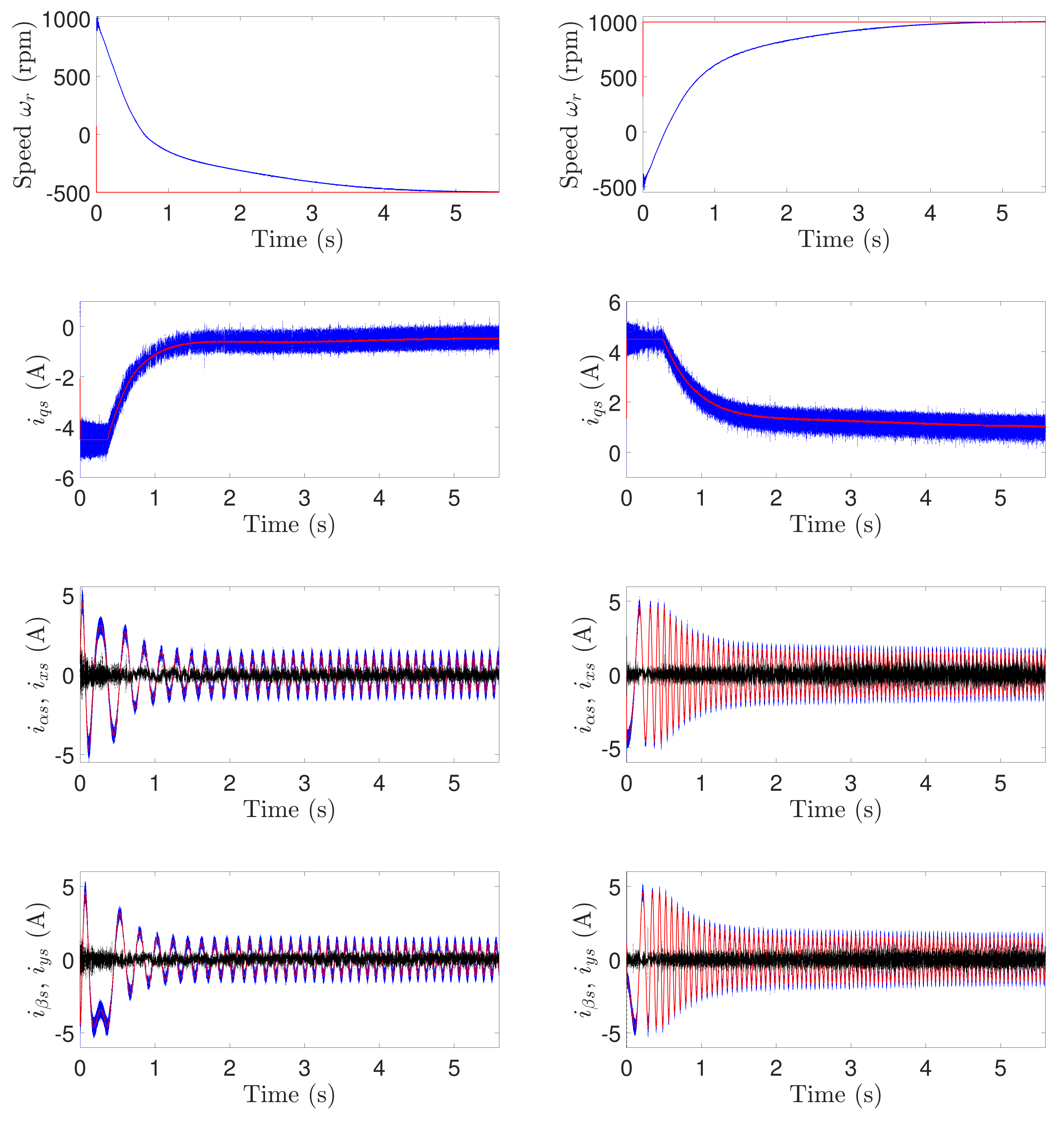
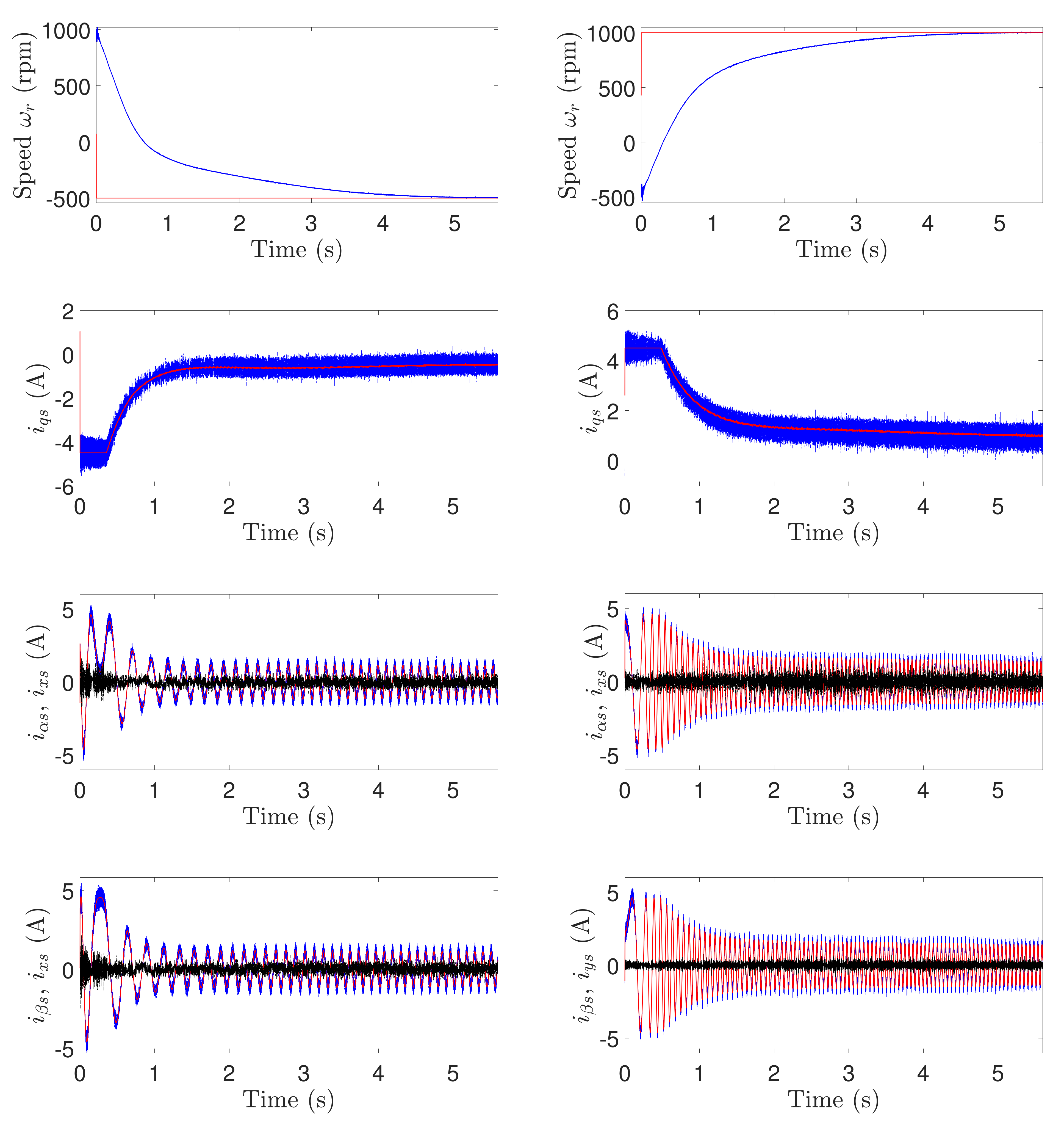
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| dc | Direct current |
| DQSM | Discrete-time quasi-sliding mode |
| DTSTC | Discrete terminal super-twisting control |
| IM | Induction motor |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
| PI | Proportional-integral |
| QSMB | Quasi sliding mode band |
| SM | Sliding mode |
| TDE | Time-delay estimation |
| VSC | Voltage source converter |
References
- Kali, Y.; Saad, M.; Rodas, J.; Mougharbel, I.; Benjelloun, K. Robust Control of a 6-Phase Induction Generator for Variable Speed Wind Energy Conversion System. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Renewable Energies for Developing Countries (REDEC), Marrakech, Morocco, 29–30 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Cheng, M.; Chau, K.; Li, F. Control and Performance Evaluation of Multiphase FSPM Motor in Low-Speed Region for Hybrid Electric Vehicles. Energies 2015, 8, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Hao, L. Coordinated and fault-tolerant control of tandem 15-phase induction motors in ship propulsion system. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.; Yoo, H.; Sul, S.; Choi, H.; Choi, Y. A Nine-Phase Permanent-Magnet Motor Drive System for an Ultrahigh-Speed Elevator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, F.; Duran, M.J. Recent Advances in the Design, Modeling, and Control of Multiphase Machines: Part I. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, M.J.; Barrero, F. Recent Advances in the Design, Modeling, and Control of Multiphase Machines: Part II. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, E. Advances in Converter Control and Innovative Exploitation of Additional Degrees of Freedom for Multiphase Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Levi, E.; Jones, M.; Rahim, N.; Hew, W.P. FCS-MPC based current control of a five-phase induction motor and its comparison with PI-PWM control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, A.; Rahmati, A.; Kaboli, S. Efficiency improvement in DTC of six-phase induction machine by adaptive gradient descent of flux. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodas, J.; Barrero, F.; Arahal, M.R.; Martín, C.; Gregor, R. Online estimation of rotor variables in predictive current controllers: a case study using five-phase induction machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 5348–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodas, J.; Martín, C.; Arahal, M.R.; Barrero, F.; Gregor, R. Influence of Covariance-Based ALS Methods in the Performance of Predictive Controllers with Rotor Current Estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 2602–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbarbary, Z.; Azeem, M.F.; Azazi, H.Z. Adaptive Fuzzy-Based IRFOC of Speed Sensorless Six-Phase Induction Motor Drive System. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2020, 29, 2050062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, D.; Ravi, G. Dynamic modeling and control of five phase SVPWM inverter fed induction motor drive with intelligent speed controller. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kali, Y.; Rodas, J.; Saad, M.; Doval-Gandoy, J.; Gregor, R. Nonlinear Backstepping with Time Delay Estimation for Six-Phase Induction Machine. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Electric Machines Drives Conference (IEMDC), San Diego, CA, USA, 12–15 May 2019; pp. 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawiec, M.; Strankowski, P.; Lewicki, A.; Guziński, J.; Wilczyński, F. Feedback Control of Multiphase Induction Machines With Backstepping Technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 4305–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kali, Y.; Rodas, J.; Saad, M.; Gregor, R.; Doval-Gandoy, J.; Benjelloun, K. Comparative Study of Time Delay Estimation Based Optimal 1st and 2nd Order Sliding Mode for Current Regulation of Six-Phase Induction Machines. In Proceedings of the IECON 2019—45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019; Volume 1, pp. 6194–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kali, Y.; Ayala, M.; Rodas, J.; Saad, M.; Doval-Gandoy, J.; Gregor, R.; Benjelloun, K. Current Control of a Six-Phase Induction Machine Drive Based on Discrete-Time Sliding Mode with Time Delay Estimation. Energies 2019, 12, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kali, Y.; Saad, M.; Doval-Gandoy, J.; Rodas, J.; Benjelloun, K. Discrete sliding mode control based on exponential reaching law and time delay estimation for an asymmetrical six-phase induction machine drive. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2019, 13, 1660–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, V.; Guldner, J.; Shi, J. Sliding Mode Control in Electromechanical Systems; Taylor-Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Boiko, I.; Fridman, L. Analysis of Chattering in Continuous Sliding-mode Controllers. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2005, 50, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wu, J.; Xiong, Z. A Novel Exponential Reaching Law of Discrete-Time Sliding-Mode Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 3840–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Li, Y.; Xiong, Z. Discrete-Time Sliding-Mode Control With Enhanced Power Reaching Law. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 4629–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, P.; Xia, Y.; Yang, H. Discrete-Time Sliding Mode Control With Disturbance Rejection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 7967–7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wen, X.; Xue, C.; Yu, X.; Han, F. Discrete-Time Quasi-Sliding Mode Control of Induction Motors. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 8th Annual International Conference on CYBER Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems (CYBER), Tianjin, China, 19–23 July 2018; pp. 1366–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kali, Y.; Ayala, M.; Rodas, J.; Saad, M.; Doval-Gandoy, J.; Gregor, R.; Benjelloun, K. Time Delay Estimation Based Discrete-Time Super-Twisting Current Control for a Six-Phase Induction Motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 12570–12580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnefors, L.; Saarakkala, S.; Hinkkanen, M. Speed Control of Electrical Drives Using Classical Control Methods. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kali, Y.; Saad, M.; Benjelloun, K.; Fatemi, A. Discrete-time second order sliding mode with time delay control for uncertain robot manipulators. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 94, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.S. Chapter 12—Miscellaneous. In Advanced Mathematical Tools for Automatic Control Engineers: Deterministic Techniques; Poznyak, A.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, L.; Ayala, M.; Rodas, J.; Gregor, R.; Gonzalez, O.; Doval-Gandoy, J. Comparison of the Effects on Stator Currents Between Continuous Model and Discrete Model of the Three-phase Induction Motor in the Presence of Electrical Parameter Variations. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 26–28 February 2020; pp. 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
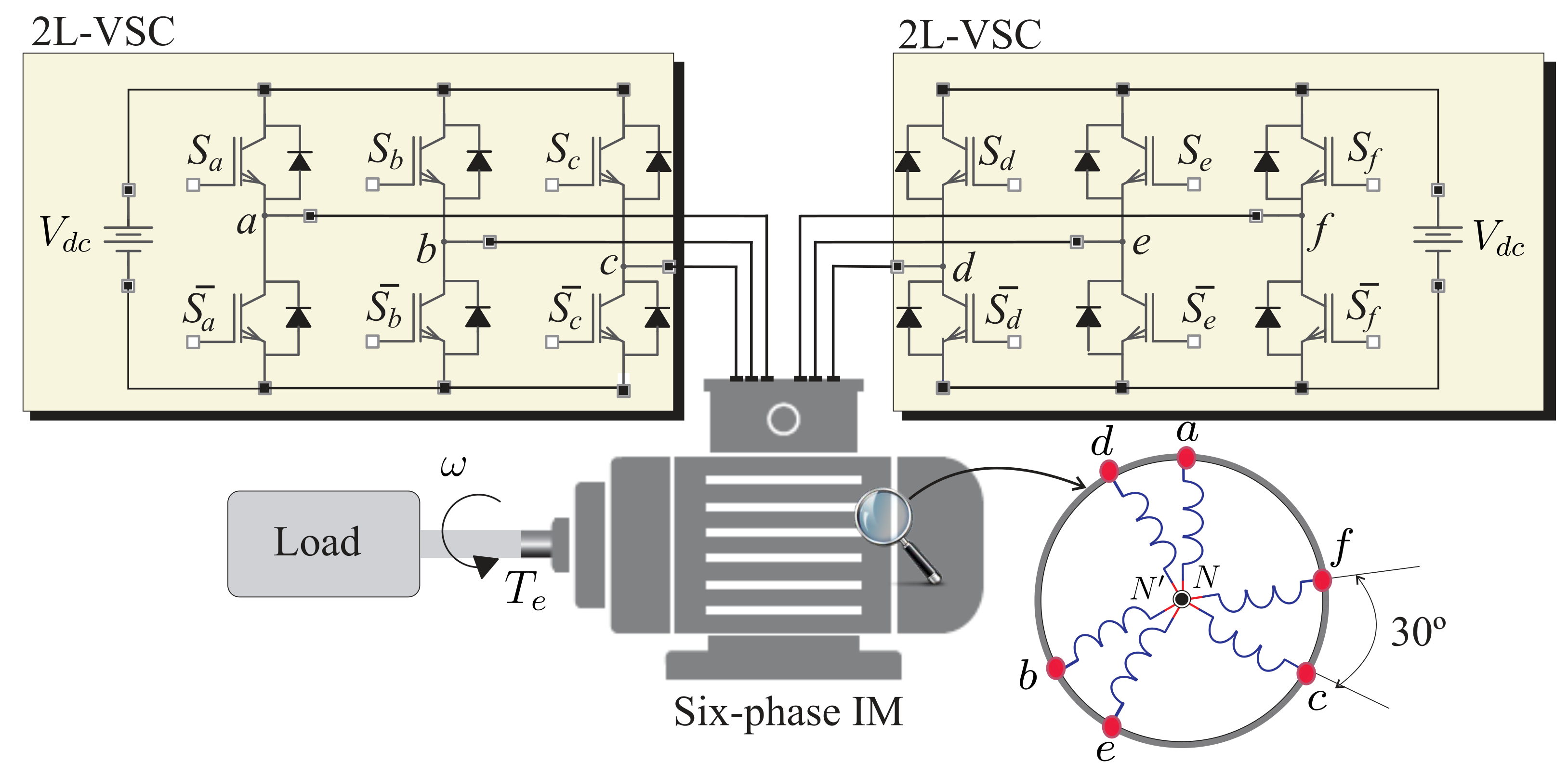

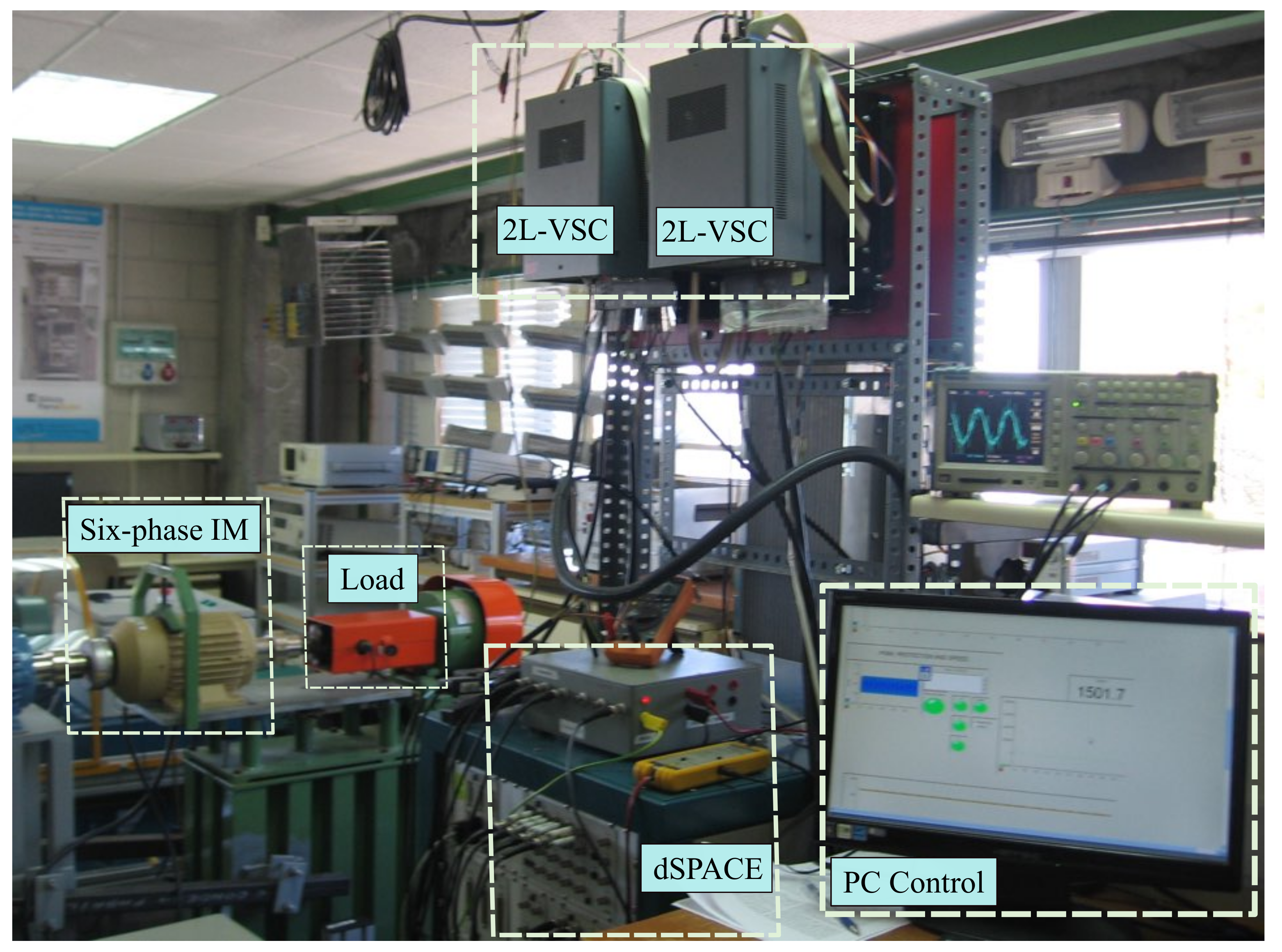

| Parameter | Value | Unit | Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.0 | 654.4 | mH | |||
| 6.7 | 0.07 | kg·m | |||
| 5.85 | mH | 0.0004 | kg·m | ||
| 708.5 | mH | 400 | V | ||
| 626.8 | mH | 1 | − |
| Poposed DTSTC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (rpm) | MSE | MSE | MSE | MSE | |
| 1000 | 0.2937 | 0.3021 | 0.2326 | 0.2280 | |
| 1500 | 0.3000 | 0.3050 | 0.2491 | 0.2456 | |
| TDE-based DSMC [17] | |||||
| (rpm) | MSE | MSE | MSE | MSE | |
| 1000 | 0.0883 | 0.0795 | 0.0401 | 0.0457 | |
| 1500 | 0.1813 | 0.1649 | 0.1107 | 0.1000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kali, Y.; Saad, M.; Doval-Gandoy, J.; Rodas, J. Discrete Terminal Super-Twisting Current Control of a Six-Phase Induction Motor. Energies 2021, 14, 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051339
Kali Y, Saad M, Doval-Gandoy J, Rodas J. Discrete Terminal Super-Twisting Current Control of a Six-Phase Induction Motor. Energies. 2021; 14(5):1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051339
Chicago/Turabian StyleKali, Yassine, Maarouf Saad, Jesus Doval-Gandoy, and Jorge Rodas. 2021. "Discrete Terminal Super-Twisting Current Control of a Six-Phase Induction Motor" Energies 14, no. 5: 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051339
APA StyleKali, Y., Saad, M., Doval-Gandoy, J., & Rodas, J. (2021). Discrete Terminal Super-Twisting Current Control of a Six-Phase Induction Motor. Energies, 14(5), 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051339








