Abstract
The article presents experimental results of the metal-based and carbon nanotube additives influence on sorption kinetics of a silica-gel-based adsorption bed in an adsorption chiller. The purpose of the doping is to improve the efficiency of sorption processes within the bed by use of metallic and non-metallic additives characterized by higher thermal diffusivity than basic adsorption material. The higher the thermal conductivity of the bed, the faster the sorption processes take place, which directly translates into greater efficiency of the refrigerator. In this study, sorption kinetics of pure silica gel sorbent doped with a given amount of aluminum (Al) and copper (Cu) powders and carbon nanotubes (CNT) were analyzed. The tests were performed on DVS Dynamic Gravimetric Vapor Sorption System apparatus used for dynamic vapor sorption measurements. A decrease in the amount of adsorbed water was observed with an increase in the mass share of the additives in the performed studies. Experimental results show that, CNTs seems to be the most promising additive as the sorption process time was reduced with the smallest decrease in water uptake. Any significant reduction of adsorption time was noted in case of the Al addition. Whereas, in case of Cu doping, delamination of the mixture was observed.
1. Introduction
Electricity demand for cooling increases very quickly, high thermal comfort in buildings is essential for human health and well-being. However, increasing number of refrigeration devices affects the peak demand for electricity and becomes a major challenge for the energy system. Despite of the rapid development of solar energy technologies and easier access to renewable sources of energy, the highest cooling demand does not always agree with the solar energy potential during the day. Therefore, increasing demand for electricity used for cooling purposes has to be covered mostly by the power grid. Due to high energy consumption, such systems indirectly enhance environmental pollution through the consumption of fossil fuels in power plants [1,2]. There is an urgent need to move into more environmentally friendly solutions, like adsorption cooling systems [3,4]. In this technology power can by supplied by low-temperature heat extracted from the outside, like waste heat or solar energy [5,6,7]. Generation of production of heat, electricity, and useful cold (trigeneration) allows to increase the efficiency of the process and reduce the amount and cost of primary energy [1]. Sorption chillers are even a promising technology in residential applications [8].
The adsorption process is performed through the interactions of the adsorbate on the adsorbent’s specific surface area [9]. In adsorption chillers, the adsorbate is liquid and the adsorbent is a solid material with a highly developed specific surface area [10]. The sorbent saturation can be achieved through physical or chemical interactions. Physical interactions are weaker than chemical bounds; therefore, the physisorption is a reversible process of removing adsorbed adsorbate vapors and it can be achieved easily at increased temperatures [2,3].
In general, a good adsorbent should be characterized by: high thermal conductivity and low specific heat [11], it has to be non-toxic and non-corrosive [12]. High durability [13] and similar adsorption properties over time, with relatively small price and high water uptake at low temperature [14] are also crucial. In case of adsorbate, it should be characterized by a relatively low evaporation temperature, high evaporation heat and high latent heat value per unit of volume. Small molecular size, low viscosity, together with low specific heat, low specific volume in liquid state, and high thermal conductivity will additionally enhance the cooling device performance. For safety reason, the adsorbate has to be chemically and thermally stable, non-toxic, and non-flammable [4,15,16,17]. The most common working pairs in adsorption cooling devices are: activated carbon–methanol, activated carbon–ammonia, silica gel–water, and zeolite–water [16,18,19].
The most important parameter describing refrigeration systems is a coefficient of performance (COP). From the definition COP is the ratio between the heat removed in the evaporator and heat supplied for desorption and bed pre-heating process [16]. Adsorption chillers are characterized by a relatively low COP, which is usually between 0.5 and 0.6 [20,21]. Low COP directly affects dimensions and mass of the equipment, making adsorption chillers big and heavy [22]. To improve their competitiveness on the market of refrigeration systems, a huge effort is put on increasing of the COP of the adsorption chillers. Second important refrigerator performance indicator is specific cooling power (SCP), which determines the cooling capacity in relation to the mass of the adsorbent. Higher SCP increases cooling capacity from a given amount of sorbent and it allows to reduce the size of the equipment, thanks to a smaller sorbent consumption [4]. SCP strongly depends on the cooling bed water temperature [23]. There are several methods found in literature to enhance the adsorption chiller efficiency, most basic is to modify the process parameters like: bed regeneration temperature [24,25], one cycle time, number of beds [21,26,27], or reduction of the heat transfer resistance between the sorbent and metal substrate [28,29].
Low thermal conductivity of the bed is one of the most important factors affecting the low performance of adsorption chillers. The bed materials are selected based on their highly porosity and large specific surface area, both parameters determine high sorption capacity of the bed. However, in most cases highly porous materials has also low thermal conductivity coefficient [16].
The heat exchange in the bed can be enhanced by increase of the heat exchange at the boundary layer of the heat exchanger wall and the adsorbent, or by an increase of adsorbent thermal conductivity [20]. In case of silica gel adsorption bad, many hollow spaces filled with still air are found, thermal conductivity coefficient of air is even lower than in case of silica gel (around 0.025 W/(mK)) [20]. Such behavior results in discontinuities in heat transport within the bed. The idea is to fill the gaps with a material characterized by higher thermal conductivity than adsorbent. The additive should not have negative influence on the adsorbent’s sorption properties [20]. The most commonly used higher thermal conductivity materials are metallic powders studied in the literature on the example of aluminum, copper, brass, and stainless steel [30,31] or fine carbon materials like carbon nanotubes [32,33]. In case of adsorbents used in sorption chillers, the goal is not only to reduce the porosity of the bed but also to improve its mechanical properties and preserve sorption capacity. In previous studies described in the literature, the main goal was to define the effect of the additives on thermal conductivity of the material. This study deals with another important issue in the subject of new sorption material development and shows the research on addition of high thermal conductivity materials to the silica gel and its influence on water sorption and desorption kinetics. The presented work is a continuation of the study published in [34] and presenting the comparative analysis of the thermal diffusivity of a silica-gel-base adsorption bed with carbon nanotubes and metals additives (Cu or Al). Thermal diffusivity was measured using the laser flash method. As a part of the article [34], the structural properties of silica gel SG and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were also investigated. The research results showed that the addition of aluminum had the greatest impact on the improvement of thermal diffusivity. The key property of the additives, apart from their thermal diffusivity, was their density, which affected the homogeneity of the mixture. The highest homogeneity was obtained for samples containing silica gel with the addition of aluminum. It has resulted in achieving the highest thermal diffusivity of these mixtures [34]. Such broad comparative investigation including both structural, thermal and sorption properties of silica gel doped with metallic and non-metallic additives was not published yet and gives a new and valuable knowledge for further development of new sorption materials dedicated for adsorption chillers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
In this study silica gel was selected as the adsorbent. It is a highly porous adsorbent, commonly used in adsorption chillers. The main aim of the study was to analyze the effect of adsorbent doping with materials of high thermal conductivity on sorption kinetics of the obtained mixture. The additives were added to the adsorbent to increase the thermal conductivity of the entire bed by reducing the discontinuity of internal heat transport and increase the mechanical strength of the bed. The reference material in this study was pure silica gel. Pure silica gel was doped with three different additives in powder form. The additives selected were: aluminum (Al), carbon nanotubes (CNT), and copper (Cu), which were used in various mass proportions: 5%, 15%, and 25%. The use of additives will result in reduction of sorption capacity of the mixture, as the additives do not show significant sorption properties. Such doping may contribute to a decrease in mass transport within the bed. Therefore, proper sample homogenization is essential and will influence the experimental results. All analyzed samples are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Use of additives Aluminum (Al), Carbon nanotubes (CNT), Copper (Cu) for Silica gel (SG).
2.2. Methods
Sorption kinetics of the tested samples were determined using Dynamic Gravimetric Vapor Sorption System DVS Vacuum. The apparatus measures the mass change of the sample during adsorption and desorption of a certain amount of adsorbent with high sensitivity, equal to 0.1 µg. Temperature stability at 25 °C is equal to ± 0.02 °C and the humidity conditions generated are typically in the range of ± 0.1% with respect to the target value [35]. Temperature range is the most fundamental experimental parameter, the device has the ability to determine the sorption kinetics from 20 °C up to 70 °C.
The DVS Vacuum offers static and dynamic sorption experiments and measures adsorption-desorption isotherms and adsorption-desorption isobars over a broad range of temperatures and various adsorbates. DVS Vacuum device automatically measures changes in the mass of the sample in a closed chamber.In the static method the volumetric sorption method is used to perform conventional vacuum sorption measurements at static mode. In this method vapor goes into a sealed chamber and the analysis is performed under static conditions (without any further gas flow). This method is recommended for higher partial pressures, measurements performed at low partial pressures result in high measurement errors. In the dynamic vacuum technique, flow rate to the chamber and from the chamber and downstream exit rate of vapor are controlled by a sensitive valve. Therefore, this method is recommended for measurements at low partial pressures. The volumetric method may not be able to give accurate results at low pressures, because system leaks may occur. In this method a pressure change is measured, and volumetric change is derived using a standard relationship:
where P = Pressure of the gas; V = Volume of the gas; T= Temperature of the gas; N = Number of particles in the gas; and k = Boltzmann constant (1.38066 × 10−23 J/K).
PV = NkT
In the volumetric method, measured vapor or gas pressure is not as precise and sensitive as weight change. Accuracy of the volumetric method is worse than in the gravimetric method. In case of volumetric method, to obtain the same accuracy like in gravimetric one, it is necessary to use large sample volume and time required to attain sorption equilibrium increases. DVS Vacuum system can work in both static and dynamic modes.
In this study, silica gel mixtures were adsorbents and distilled water was the adsorbate. The experimental method was composed of 22 stages. First stage was dedicated to sample drying, the sample was heated up to 100 °C for 60 min. The same period of time was set for the entire system temperature stabilization. Next, 20 stages of 20 min, each were set in the experimental method. Each stage differed in the relative pressure P/P0, which was gradually increased from 10% up to 100% and then decreased again to 10%. Based on experimental results, adsorption and desorption isotherms and sorption kinetics curves were calculated. The water uptake for all samples depending on its saturation pressure was measured. The steam flow rate was constant and equal to 15 sccm (standard cubic centimeters per minute). Each sample was tested at three process temperatures: 25 °C, 40 °C, and 60 °C.
3. Results and discussion
The results of the performed experiments are presented in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10. Presented sorption kinetics graphs describe the relation of the sample reference mass change (in percent) in a function of time. The reference mass is the mass of the sample recorded at the beginning of the measurement when the relative pressure increased from 0% to 10%. Based on the results adsorption and desorption processes trends and intensity of both processes were determined. Based on the measurements, it might be concluded which stage of the process its further continuation can negatively affect the overall performance of the refrigerator. On each graph the curves for three process temperatures: 25 °C, 40 °C, and 60 °C are presented. Additional approximation calculations were made using MATLAB software and showed in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10, together with experimental results.
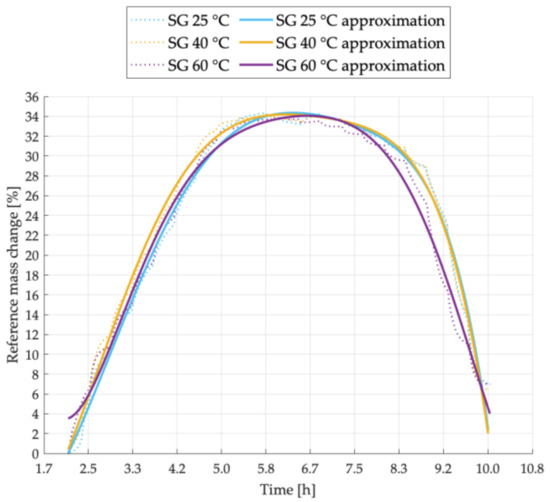
Figure 1.
Sorption kinetics graph for SG sample tested at temperatures of 25 °C, 40 °C, 60 °C.
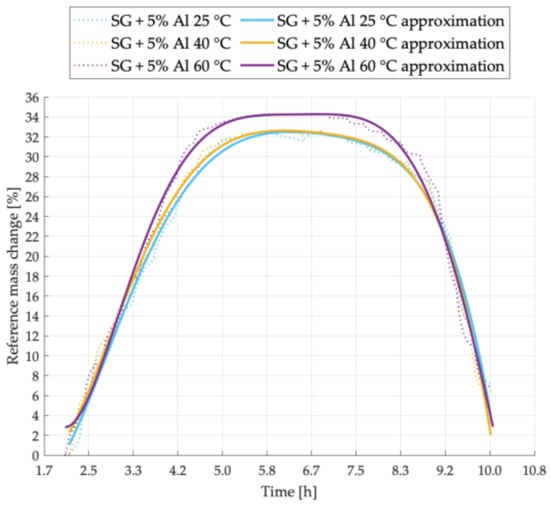
Figure 2.
Sorption kinetics graph for SG + 5% Al sample tested at temperatures of 25 °C, 40 °C, 60 °C.
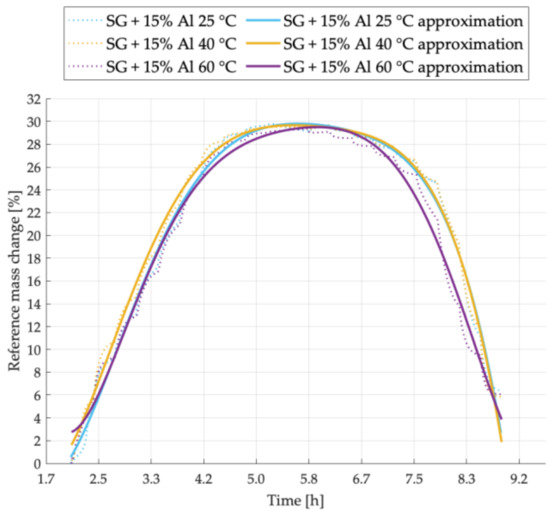
Figure 3.
Sorption kinetics graph for SG + 15% Al sample tested at temperatures of 25 °C, 40 °C, 60 °C.
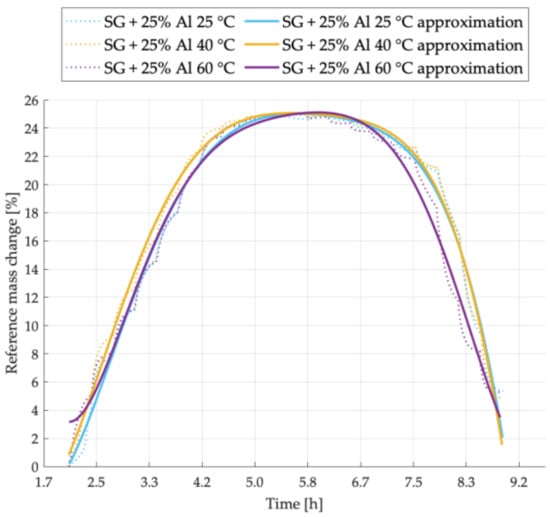
Figure 4.
Sorption kinetics graph for SG + 25% Al sample tested at temperatures of 25 °C, 40 °C, 60 °C.
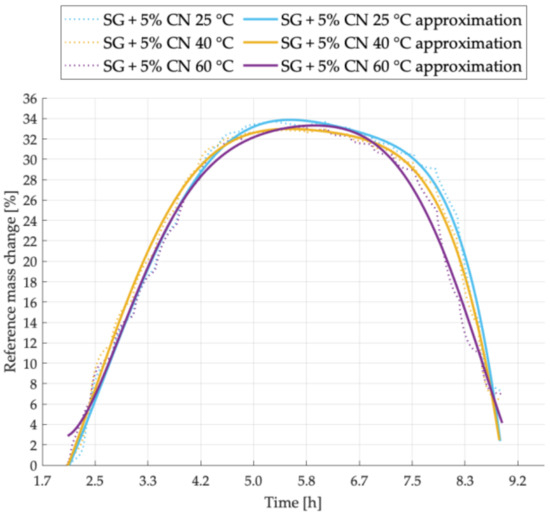
Figure 5.
Sorption kinetics graph for SG + 5% CNT sample tested at temperatures of 25 °C, 40 °C, 60 °C.
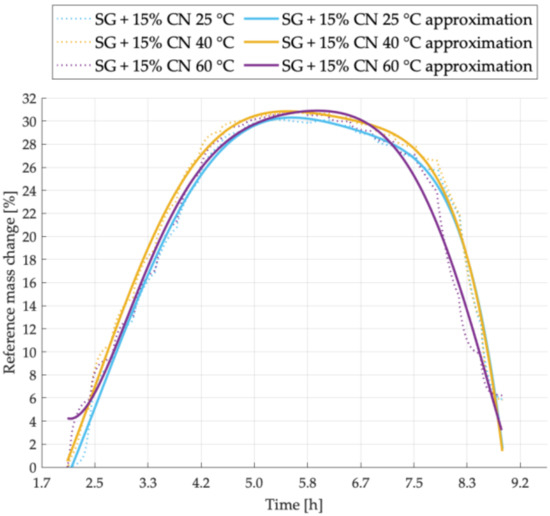
Figure 6.
Sorption kinetics graph for SG + 15% CNT sample tested at temperatures of 25 °C, 40 °C, 60 °C.
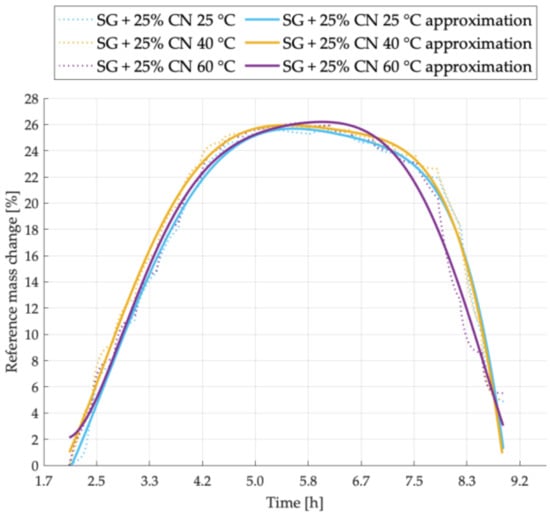
Figure 7.
Sorption kinetics graph for SG + 25% CNT sample tested at temperatures of 25 °C, 40 °C, 60 °C.
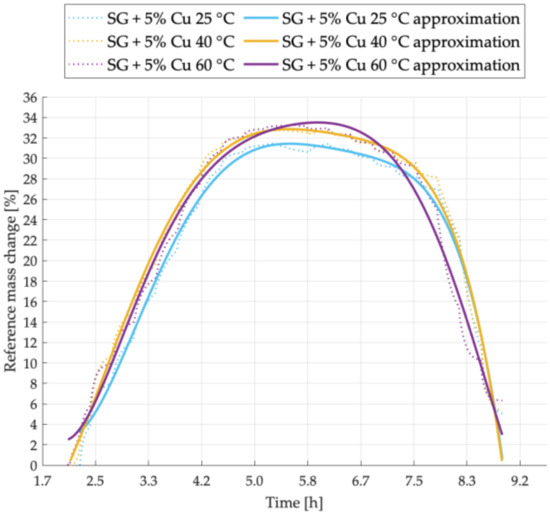
Figure 8.
Sorption kinetics graph for SG + 5% Cu sample tested at temperatures of 25 °C, 40 °C, 60 °C.
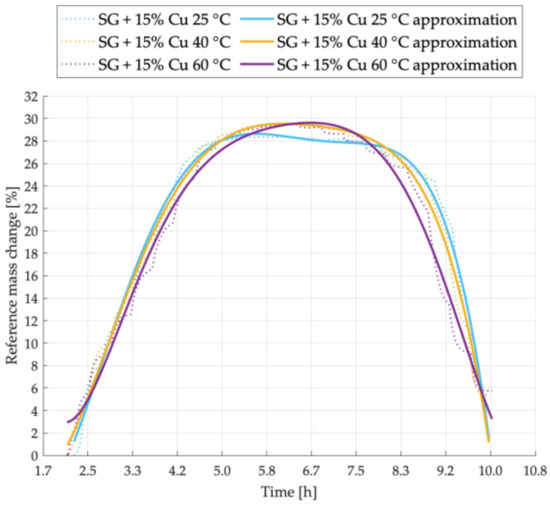
Figure 9.
Sorption kinetics graph for SG + 15% Cu sample tested at temperatures of 25 °C, 40 °C, 60 °C.
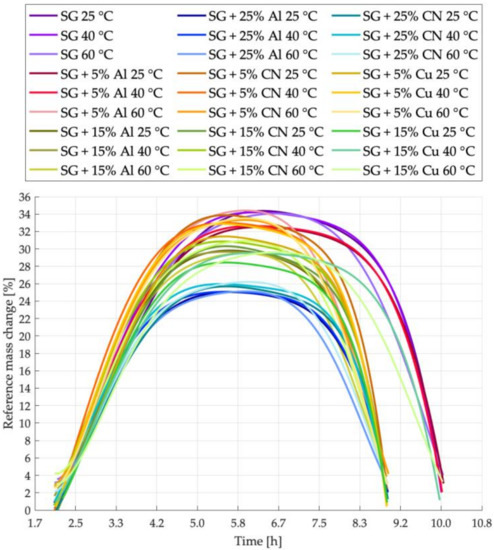
Figure 10.
Sorption kinetics graph for all tested samples.
Figure 1 shows the sorption kinetics of pure silica gel sample denoted as SG. This sample with no additives was considered as a reference sample.
In Figure 2 a comparison of the adsorption and desorption process for the SG + 5% Al sample at different temperatures is shown. At 60 °C, the sorption cycle is much shorter than in case of other process temperatures. Additionally, the sample tested at the highest process temperature - 60 °C, is characterized by the highest sorption capacity.
Experimental results of sorption kinetics for the sample SG + 15% Al are shown in Figure 3. In this case, at the highest process temperature, the lowest amount of water vapor was adsorbed by the tested sample. Additionally, the desorption process proceeds more intensively in this case. Samples tested at 25 °C and 40 °C are characterized by a similar desorption tendency and a similar water uptake. Higher intensity of the adsorption process was noted at 40 °C.
Figure 4 presents the adsorption and desorption cycles tendencies for the SG + 25% Al sample. At 40 °C, the sample was characterized by the highest adsorption intensity, while the most intense desorption process was observed at 60 °C. The maximal water uptake is similar in all analyzed cases.
Figure 5 shows the sorption kinetics for the sample with the addition of 5% carbon nanotubes to silica gel. The highest sorption capacity was observed for the sample tested at 25 °C. The temperature of 40 °C contributes to faster adsorption and the temperature of 60 °C to faster desorption.
Figure 6 shows the course of sorption kinetics for a sample designated as SG + 15% CNT. Adsorption and desorption were performed most intensively for the sample tested, respectively, at 40 °C and 60 °C. The maximum amount of adsorbed water vapor is similar in both temperatures 40 °C and 60 °C and the lowest for the sample tested at 25 °C.
Figure 7 presents the sorption kinetics for the mixture with 25% addition of carbon nanotubes. The increase in desorption intensity for the sample tested at 60 °C and the increase in adsorption intensity at 40 °C are clearly visible. The mass of adsorbed vapor is similar for each of the samples. Its highest value is achieved for the temperature of 60 °C and the lowest for 25 °C.
The sorption kinetics for the sample with 5% copper addition is shown in Figure 8. A clear decrease in the sorption capacity for the sample tested at 25 °C was noticed. Like in the graphs presented earlier, also in this case, the adsorption intensity was the highest at 40 °C and the desorption intensity increased significantly at 60 °C.
For the sample SG + 15% Cu, the sorption kinetics is shown in Figure 9. At the temperature of 25 °C, the sorption capacity of the mixture is the smallest, and the time needed to complete the entire cycle is shorter in comparison to other temperatures. At 60 °C the intensity of desorption process with a similar amount of adsorbed steam was greater than in the case of the sample tested at 40 °C. The duration of the entire cycle for this mixture was the longest in comparison to all other tested samples.
Figure 10 shows sorption kinetics for all samples analyzed in this study to show a relationship not only between process temperatures but also to make a comparison between the materials added. Doping of SG with materials characterized by high thermal conductivity lads to cycle shortening. As expected, doping influenced also water uptake by adsorbent, as the amount of porous material decreases with increased amount of doped additive.
In this study, clear differences in sorption capacity, intensity of adsorption and desorption, and both processes times were observed in all tested mixtures. The differences result from different properties of the doped materials and different mass fractions of additives in the samples.
Table 2 shows the reference mass changes of each sample in % and the differences between the change in the reference sample mass and the mass of the sample with additive examined at the same temperature.

Table 2.
Percentage change in reference mass of all tested samples.
During samples preparation, some phenomena were observed that may significantly affect the use of porous sorbents with additives as the adsorption chiller bed material. One of the serious issues was achieving a homogeneous mixture of two different loose materials. The purpose of mixing is to obtain a relatively even dispersion of the substances in the mixture. The complexity of the process is observed after a closer analysis, especially when mixing substances with different properties such as porosity and density. Mixing can be defined as the mutual movement of two or more portions of different materials, resulting in the required level of uniformity in the final product. In the case of the silica gel sample with the addition of 5% and 15% Cu, a heterogeneous structure of the sample was observed after mixing, with a clear division between silica gel and copper fractions. The reason for not achieving homogeneity of the sample is too large difference in densities between the copper powder and silica gel, which resulted in copper sinking to the bottom of the measuring vessel. The lack of homogeneity of the material leads to decrease of effectives of the heat exchange process in the bed between the exchanger tubes and the silica gel, the copper powder layer will be deposited at the bottom of the bed and will have a much smaller impact on the heat exchange process between the bulk material and the heat exchanger tubes. As obtaining a homogeneous sample was a challenge in case of both SG + 5% Cu and SG + 15% Cu, it was decided to exclude 25% addition of copper to silica gel in the presented study.
According to the experimental results it might be concluded that the process temperature influences the sorption capacity in minor extent. In major number of cases, the sorption capacity decreases with process temperature increase. Some slight differences in the reference mass change might be explained by measurement uncertainty and sample heterogeneity, described above. As expected, samples with the addition of 5% of the mass fraction showed the closest sorption properties to the reference sample. On average, the decrease in sorption capacity with respect to a silica gel sample is about 1.0% for aluminum addition, 0.8% for carbon nanotubes and 1.6% for copper. Whereas the highest loss of sorption properties of all mixtures in relation to the reference sample was obtained for samples with a 25% mass fraction of the additives. For samples with addition of aluminum the average loss of adsorbed water for all temperatures was 9.1%, while for the addition of carbon nanotubes it was 8.2%. The maximum loss was observed for the sample with aluminum 9.3%. In case of silica gel samples with a 15% of additives, the greatest losses of sorption capacity were observed for mixtures containing copper. The average decrease in the sorption capacity of the mixtures is 4.5% for aluminum additive, 3.5% for carbon nanotubes additive and about 5.0% for copper additive.
The highest reduction of the adsorption process time was observed for the 5% addition of CNTs and Cu and 15% addition of Al to the silica gel. The 25% addition of CNTs and Al increased the adsorption process time noticeably. The shortest adsorption process time was denoted for 40 °C process temperature in all analyzed cases.
The increase of process temperature resulted in reduction of desorption process time; in most cases the shortest desorption time was noticed at 60 °C. Only samples with Cu addition, especially with 15% of Cu in the sample, did not present such a behavior, most probably due to high heterogeneity of the sample. The highest desorption time decrease was observed for samples of SG with 25% addition of Al and CNTs (26% and 20% respectively). However, the smallest addition of the CNTs resulted in very high reduction of the desorption time (12–14%) and this value did not decrease that noticeably in case of Al. When aluminum powder was added to the samples, each increase of the additive amount decreased noticeably the desorption time and the sorption capacity.
4. Conclusions
Low performance, big dimensions, and weight are main obstacles when considering adsorption cooling devices development and commercialization. Most recent research was dedicated to performance improvement by increase of thermal diffusivity of the adsorbents. The greater thermal conductivity of the bed will result in desorption process enhancement, which directly influence chiller performance factors. It also provides stabilization of temperature and chilled water production. Additionally, the reduced desorption time leads to the device energy consumption reduction. In this study the influence of additional component in the silica gel on the amount of adsorbed water vapor was analyzed.
In this study sorption properties of silica gel doped with three additives in powder form: aluminum, carbon nanotubes, and copper were analyzed. Each additive is expected to contribute in the bed sorption properties decrease but also in increase in thermal conductivity of the material (what was presented in previous works of the Authors [34]). As expected, the experimental results showed that the 5% mass fraction in the least way contributes to the loss of sorption properties in comparison to the reference sample, and the loss increases with the increasing amount of the additive in the sample. However, even 25% addition of metal powder or carbon nanotubes did not decrease sorption capacity of the mixture by more than 10%. It was also noticed that carbon nanotubes have the smallest influence on the loss of sorption capacity of the silica gel mixtures doped with a high thermal diffusivity additive. It was also observed that there is a tendency to decrease the loss of sorption properties of the samples with increasing temperature, but in a minor extent.
According to the Authors, the CNTs addition to silica gel seems to be the most promising mixture due to the reduction of the sorption process time with the smallest decrease in water uptake. The most advantageous amount of carbon nanotubes added to the SG is 5%, which reduces the time of adsorption and desorption at 40 °C by about 15% and 14% respectively (given for 20% difference in the reference mass of the sample in). Under these conditions, the amount of water absorbed decreased by about 1.5%. However, to obtain better desorption times a higher temperature and Al addition is required.
A similar reduction in the times of adsorption and desorption process are obtained for SG with 5% Cu addition, but due to the tendency to delamination of the mixture and deposition of copper powder at the bottom of the sample, the authors do not indicate such a mixture as applicable in real conditions. The delamination of the mixture may adversely affect the sorption processes during the operation of such an adsorption bed (lower adsorbent mass, copper accumulated at the bottom of the sample).
The addition of Al to SG did not cause a significant reduction in adsorption time in all tested temperatures. Only 5% addition of Al to SG leads to about 10% reduction of adsorption time (given for 20% difference in the reference mass of the sample) without decrease of the mixture sorption properties. It should be mentioned, however, that in the case of Al to SG, the homogeneity of the mixture can be obtained most easily due to the similar density of both materials. Furthermore, as presented in [34], the mixture containing aluminum gave the best results in terms of sample thermal diffusivity enhancement. The addition of 5% aluminum leaded to a 90% increase in thermal diffusivity in comparison to the raw silica gel.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.S. and Ł.M.; Methodology, K.S. and M.S.; Formal analysis, K.S. and Ł.M., Investigation, W.K.,K.S; Resources, W.K.; Data curation, K.S. and M.S., W.K.; Writing—original draft preparation, K.S., Ł.M., and A.M.-M.; writing—review and editing, Ł.M. and K.S., A.M; Supervision, W.N.; Project administration, K.S.; Funding acquisition, Ł.M. and W.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The paper was funded by subsidy for research Faculty of Energy and Fuels number 16.16.210.476.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| COP | Coefficient of performance |
| SCP | Specific cooling power |
| Cu | Copper |
| Al | Aluminum |
| SG | Silica gel |
| CNT | Carbon nanotubes |
References
- Sztekler, K.; Kalawa, W.; Stefanski, S.; Krzywanski, J.; Grabowska, K.; Sosnowski, M.; Nowak, W.; Makowski, M. Using adsorption chillers for utilising waste heat from power plants. Therm. Sci. 2019, 23, S1143–S1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Davarpanah, A.; Mokhtarian, N.; Farahbod, F. Integrated feasibility experimental investigation of hydrodynamic, geometrical and, operational characterization of methanol conversion to formaldehyde. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 42, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Peng, J.; Wang, R. Experimental study of an adsorption chiller for extra low temperature waste heat utilization. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 163, 114341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, M.M.; El-Sharkawy, I.I.; Kabeel, A.E.; Saha, B.B. A review on adsorbent-adsorbate pairs for cooling applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 114, 394–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.; Saha, B.B.; Chatterjee, P.K.; Sarkar, J.P. An overview of developments in adsorption refrigeration systems towards a sustainable way of cooling. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremias, F.; Fröhlich, D.; Janiak, C.; Henninger, S.K. Water and methanol adsorption on MOFs for cycling heat transformation processes. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 1846–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, S.M.; Ghazanfari, A.; Ehyaei, M.A.; Ahmadi, A.; Jamali, D.H.; Nedaei, N.; Davarpanah, A. Investigation the integration of heliostat solar receiver to gas and combined cycles by energy, exergy, and economic point of views. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandi, S.; Baloochzadeh, S.; Asayesh, M.; Ehyaei, M.A.; Ahmadi, A.; Rabanian, A.A.; Das, B.; Costa, V.A.F.; Davarpanah, A. Energy, Exergy, Economic, and Exergoenvironmental Analyses of a Novel Hybrid System to Produce Electricity, Cooling, and Syngas. Energies 2020, 13, 6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, R.; Wang, L. High-efficient thermochemical sorption refrigeration driven by low-grade thermal energy. Chinese Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 885–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir, F.; Sultan, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Saha, B.B.; Askalany, A.; Ali, I.; Zhou, Y.; Ahmad, R.; Shamshiri, R.R. Recent updates on the adsorption capacities of adsorbent-adsorbate pairs for heat transformation applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 119, 109630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y. Effect of pore size on the performance of composite adsorbent. Adsorption 2013, 19, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Huang, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Li, J. Performance of an Activated Carbon-Ammonia Adsorption Refrigeration System. Nat. Resour. 2017, 08, 611–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, A.; Ismail, A.B.; Thu, K.; Ng, K.C.; Loh, W.S. Performance evaluation of a zeolite—Water adsorption chiller with entropy analysis of thermodynamic insight. Appl. Energy 2014, 130, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entezari, A.; Ge, T.S.; Wang, R.Z. Water adsorption on the coated aluminum sheets by composite materials (LiCl + LiBr)/silica gel. Energy 2018, 160, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Baredar, P.; Mittal, A.; Siddiqui, A.R. Adsorption refrigeration technology—An overview of theory and its solar energy applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 1389–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.S.; Brites, G.J.V.N.; Costa, J.J.; Gaspar, A.R.; Costa, V.A.F. Review and future trends of solar adsorption refrigeration systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmroukh, A.N.; Hamza, A.; Ali, H.; Ookawara, S. Adsorption working pairs for adsorption cooling chillers: A review based on adsorption capacity and environmental impact. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, K.; Davarpanah, A. Environmental Effects Design and construction of a micro-photo bioreactor in order to dairy wastewater treatment by micro-algae: Parametric study. Energy Sources, Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 42, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarpanah, A.; Zarei, M.; Valizadeh, K.; Mirshekari, B. CFD design and simulation of ethylene dichloride (EDC) thermal cracking reactor. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2019, 41, 1573–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, K.; Krzywanski, J.; Nowak, W.; Wesolowska, M. Construction of an innovative adsorbent bed configuration in the adsorption chiller—Selection criteria for effective sorbent-glue pair. Energy 2018, 151, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztekler, K.; Kalawa, W.; Nowak, W.; Mika, L.; Gradziel, S.; Krzywanski, J.; Radomska, E. Experimental Study of Three-Bed Adsorption Chiller with Desalination Function. Energies 2020, 13, 5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askalany, A.A.; Henninger, S.K.; Ghazy, M.; Saha, B.B. Effect of improving thermal conductivity of the adsorbent on performance of adsorption cooling system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 110, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrehmand, H.; Khajehpour, M.; Bahrami, M. Finding optimal conductive additive content to enhance the performance of coated sorption beds: An experimental study. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 143, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodianitskaia, P.J.; Soares, J.J.; Melo, H.; Gurgel, J.M. Experimental chiller with silica gel: Adsorption kinetics analysis and performance evaluation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 132, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tso, C.Y.; Chan, K.C.; Chao, C.Y.H.; Wu, C.L. Experimental performance analysis on an adsorption cooling system using zeolite 13X/CaCl2 adsorbent with various operation sequences. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 85, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywanski, J.; Grabowska, K.; Herman, F.; Pyrka, P.; Sosnowski, M.; Prauzner, T.; Nowak, W. Optimization of a three-bed adsorption chiller by genetic algorithms and neural networks. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 153, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztekler, K.; Kalawa, W.; Nowak, W.; Mika, L.; Grabowska, K.; Krzywanski, J.; Sosnowski, M.; Al-Harbi, A.A. Performance evaluation of a single-stage two-bed adsorption chiller with desalination function. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.S.; Chen, M.T.; Chung, T.W. Effects of the thickness and particle size of silica gel on the heat and mass transfer performance of a silica gel-coated bed for air-conditioning adsorption systems. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2005, 25, 2330–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztekler, K.; Kalawa, W.; Medrala, A.M.; Nowak, W.; Mika, Ł.; Krzywanski, J.; Grabowska, K.; Sosnowski, M.; Debniak, M. The Effect of Adhesive Additives on Silica Gel Water Sorption Properties. Entropy 2020, 22, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, H.; Mobedi, M.; Ülkü, S. The use of metal piece additives to enhance heat transfer rate through an unconsolidated adsorbent bed. Int. J. Refrig. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, A.; Al-Dadah, R.K.; Mahmoud, S.; Elsayed, A. Effects of contact resistance and metal additives in finned-tube adsorbent beds on the performance of silica gel/water adsorption chiller. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 53, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Al-Rashed, A.A.A.A.; Barzinjy, A.A.; Shahsavar, A.; Karimi, A.; Talebizadehsardari, P. Curve-fitting on experimental thermal conductivity of motor oil under influence of hybrid nano additives containing multi-walled carbon nanotubes and zinc oxide. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmat Esfe, M.; Motahari, K.; Sanatizadeh, E.; Afrand, M.; Rostamian, H.; Reza Hassani Ahangar, M. Estimation of thermal conductivity of CNTs-water in low temperature by artificial neural network and correlation. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulakowska, A.; Pajdak, A.; Krzywanski, J.; Grabowska, K.; Zylka, A.; Sosnowski, M.; Wesolowska, M.; Sztekler, K.; Nowak, W. Effect of metal and carbon nanotube additives on the thermal diffusivity of a silica-gel-based adsorption bed. Energies 2020, 16, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surface Measurement Systems Company Materials. Operating Manual of DVS Vacuum, Book 2019.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).