Searching for the Most Suitable Loss Model Set for Subsonic Centrifugal Compressors Using an Improved Method for Off-Design Performance Prediction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Empirical Loss Correlations
3.1. Internal Losses
3.1.1. Incidence Loss
3.1.2. Choke Loss
3.1.3. Entrance Diffusion Loss
3.1.4. Blade Loading Loss
3.1.5. Skin Friction Loss
3.1.6. Clearance Loss
3.1.7. Mixing Loss
3.2. External Losses
3.2.1. Recirculation Loss
3.2.2. Disk Friction Loss
3.3. Vaneless Diffuser Loss
4. Subsonic Eckardt’s Compressors
5. Algorithm Input Parameters
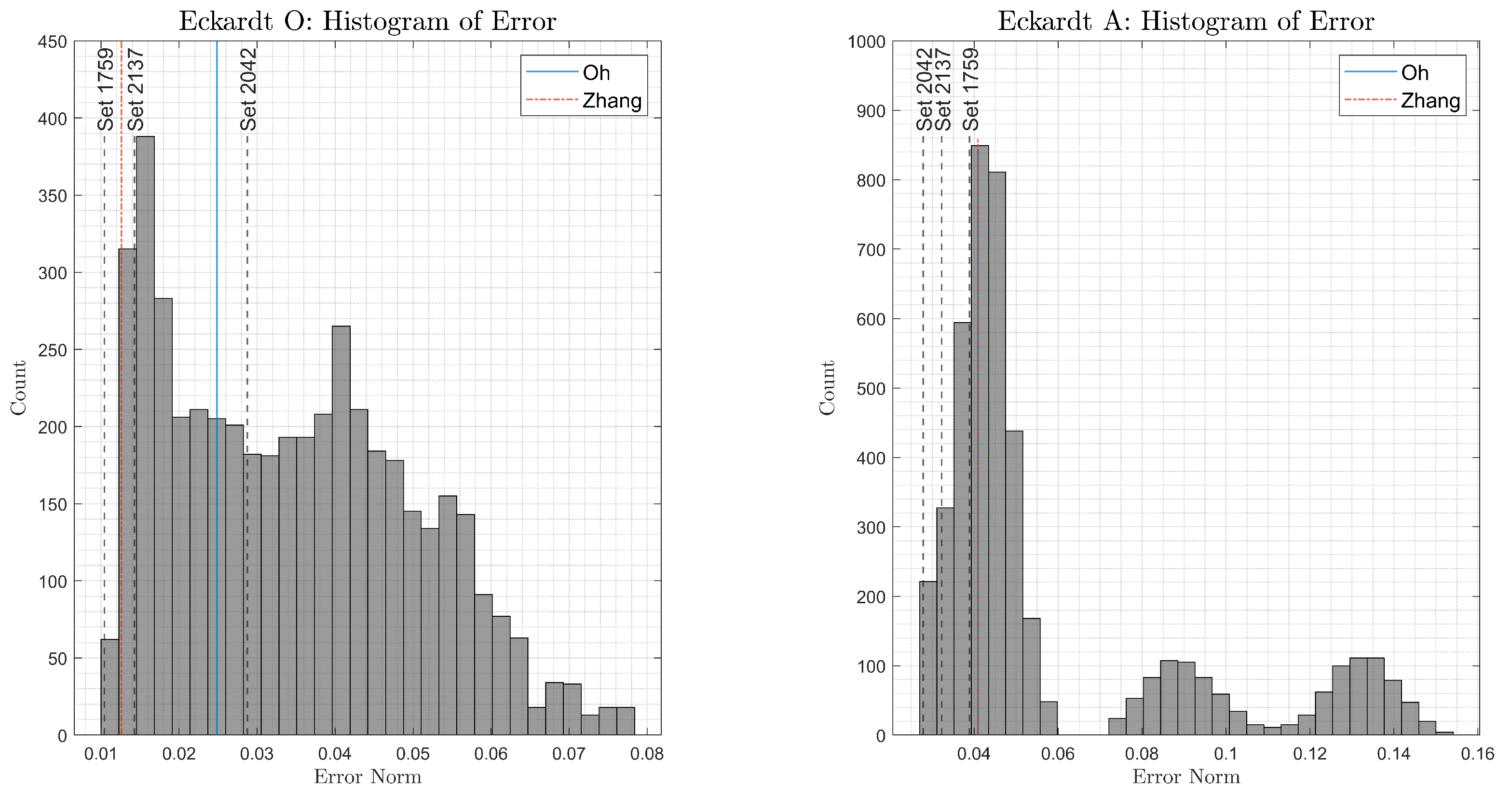
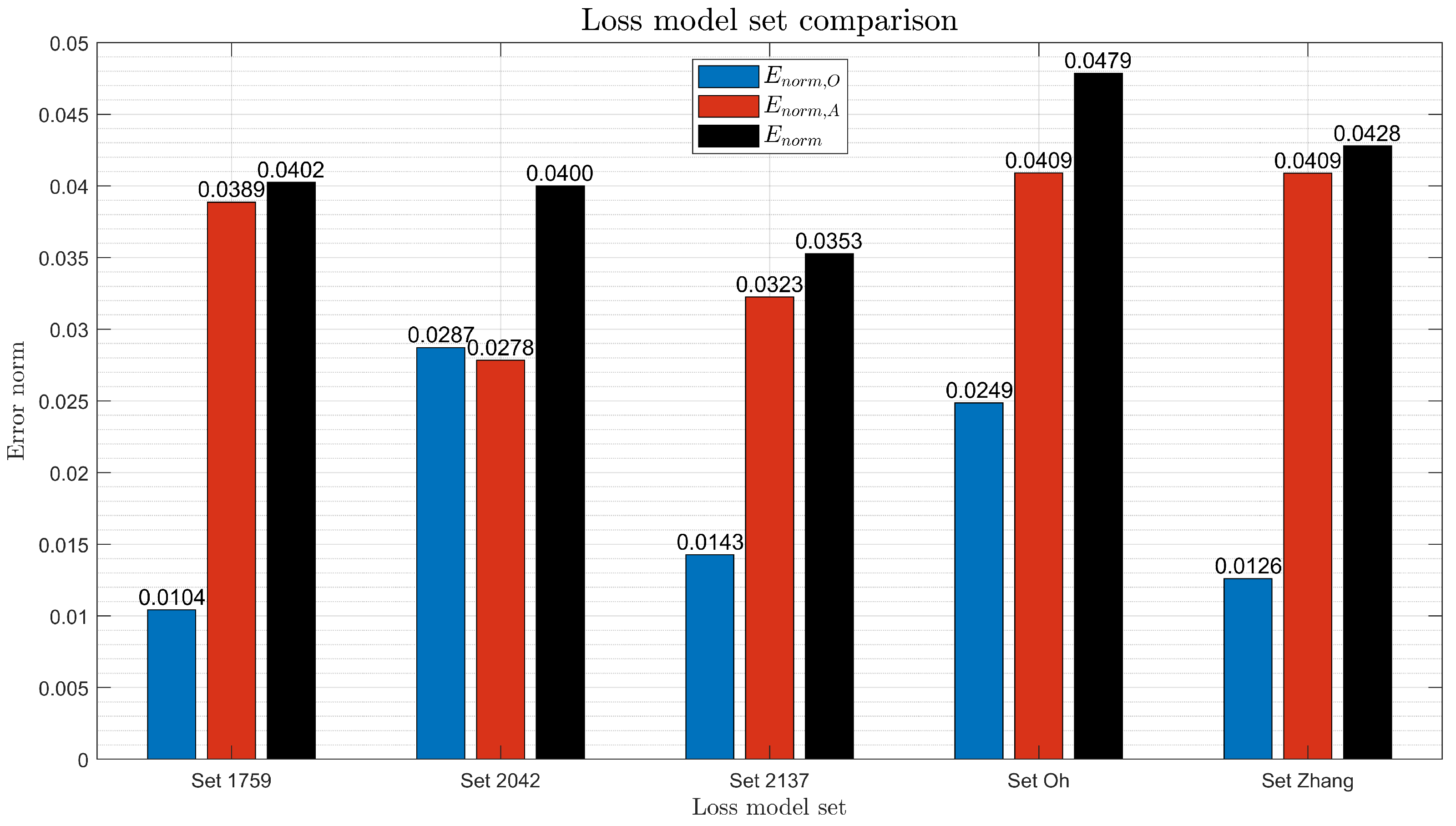
6. Loss Model Suitability Evaluation
| Loss Origin | Correlation According to |
|---|---|
| Incidence (4) | Aungier [12], Conrad [28], Gravdahl [29], Stanitz [27] |
| Choke (1) | Aungier [12] |
| Entrance diffusion (1) | Aungier [12] |
| Blade loading (2) | Aungier [12], Coppage [8] |
| Skin friction (3) | Coppage [8], Jansen [32], Aungier [12] |
| Clearance (4) | Aungier [12], Jansen [32], Krylov and Spunde [33], Rodgers [34] |
| Mixing (2) | Aungier [12], Johnston [35] |
| Recirculation (3) | Coppage [8], Coppage [8], Oh [13] |
| Disk friction (4) | Aungier [12], Boyce [41], Daily [39], Shepherd [38] |
| Vaneless diffuser (2) | Coppage [8], Stanitz [27] |
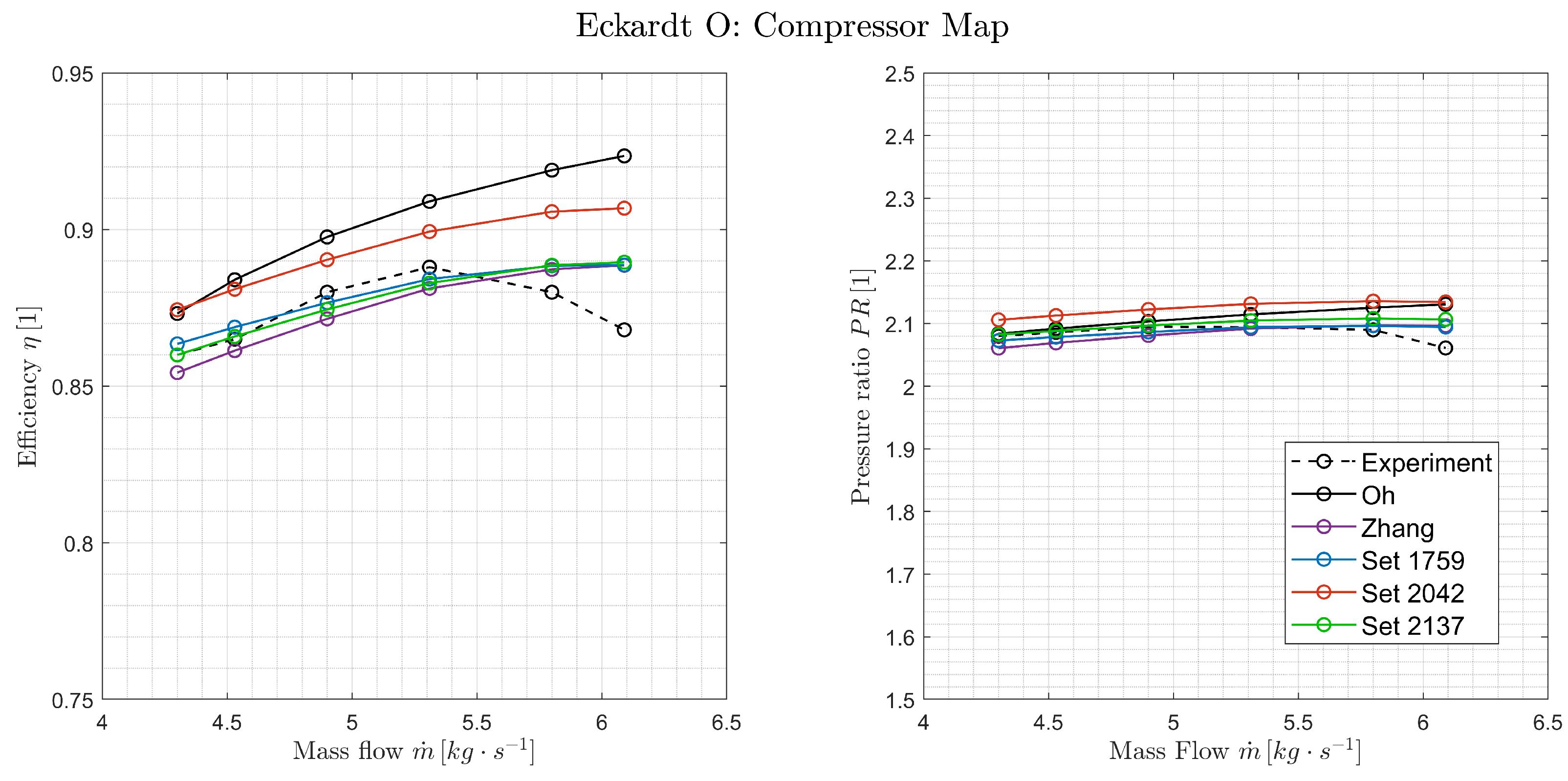
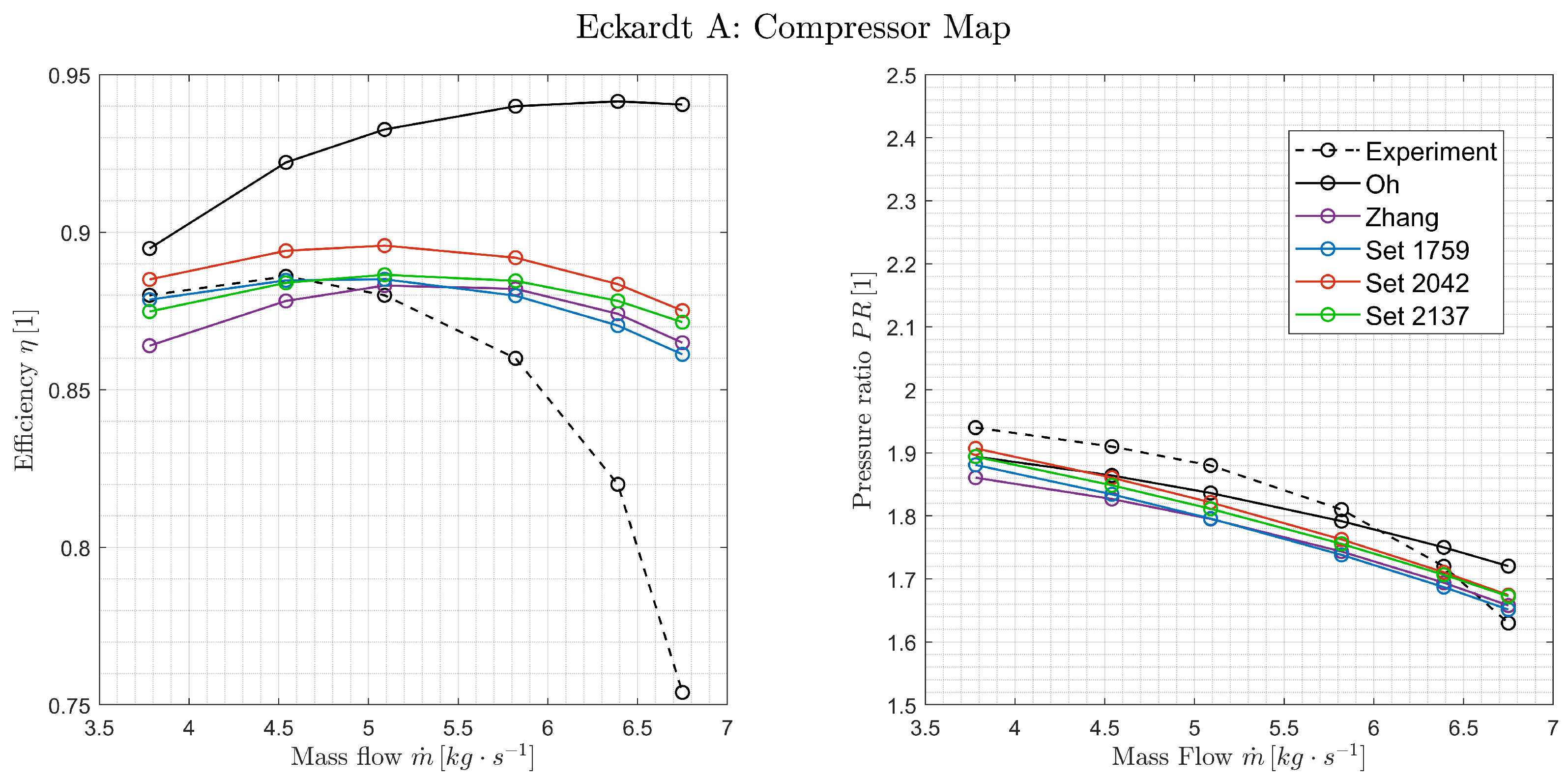
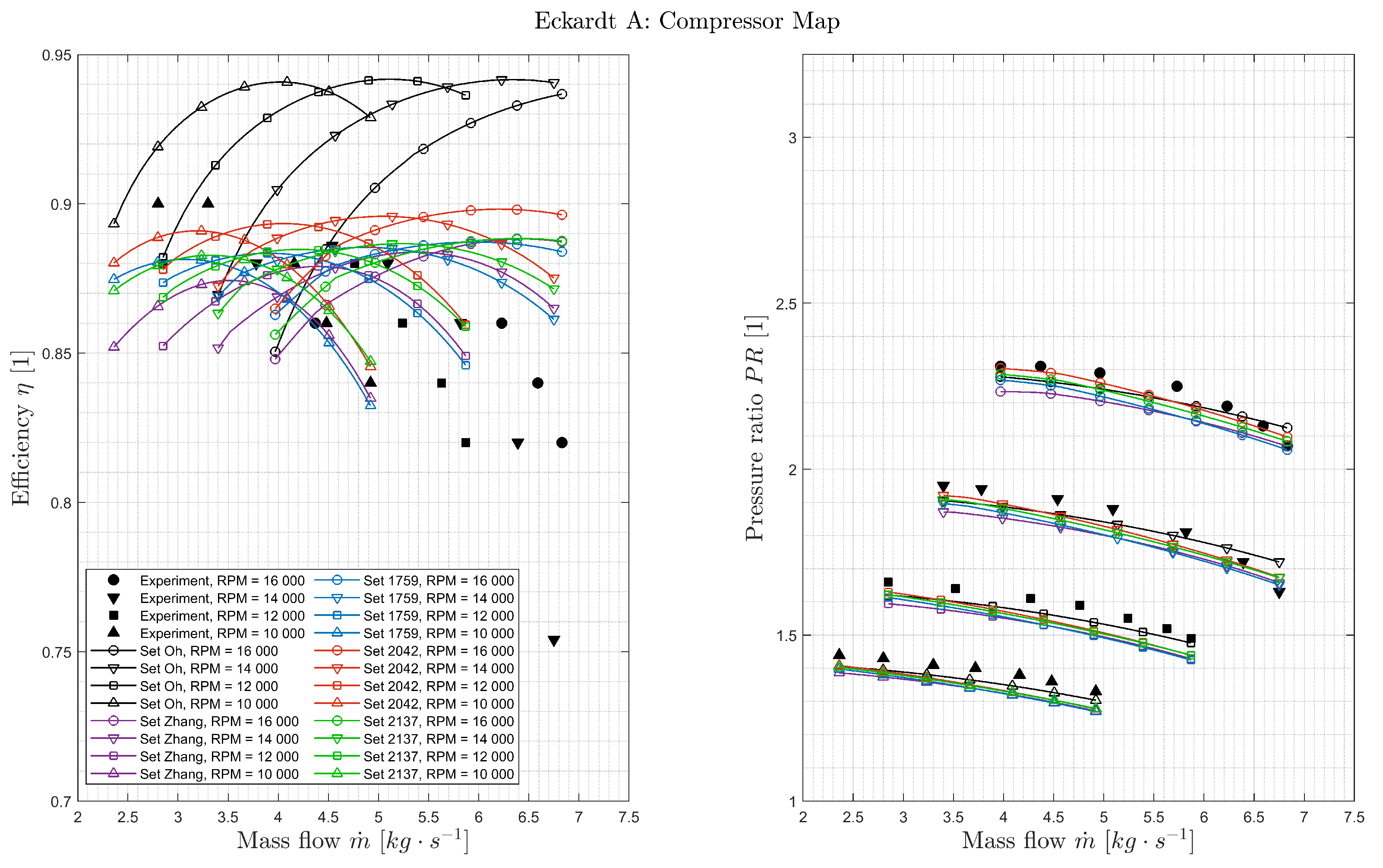
7. Results
7.1. Loss Model
7.2. Performance of Candidate Loss Model Sets
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | Area (excluding blade area) |
| C | Absolute velocity |
| Friction coefficient | |
| Slip velocity | |
| D | Diameter |
| Equivalent diffusion factor | |
| Diffusion coefficient | |
| L | Length |
| M | Mach number |
| Pressure ratio | |
| Reynold’s number | |
| Slip factor | |
| T | Thermodynamic temperature |
| U | Circumferential speed |
| W | Relative velocity |
| a | Speed of sound |
| b | Impeller channel width |
| Specific heat capacity at constant pressure | |
| Hydraulic diameter | |
| h | Enthalpy |
| Mass flow | |
| p | Pressure |
| r | Specific gas constant |
| t | Blade thickness |
| z | Number of blades |
| Flow angles (absolute, relative), respectively | |
| Specific heat ratio | |
| Variable change | |
| Blade tip clearance | |
| Wake width | |
| Efficiency | |
| Curvature | |
| The ratio of the vaneless diffuser inlet width to the impeller exit width | |
| Viscosity (dynamic, kinematic), respectively | |
| Density | |
| Streamline angle | |
| Theoretical parameter | |
| Flow parameter | |
| Losses (internal, parasitic/external), respectively | |
| Internal losses (incidence, choke, entrance diffusion, blade loading, skin friction, clearance, mixing), respectively | |
| Meridional parameter | |
| External losses (recirculation, disk friction), respectively | |
| Blade positions (shroud, hub, root mean square), respectively | |
| Total condition | |
| Throat parameter | |
| Tangential parameter | |
| Vaneless diffuser | |
| Axial direction | |
| Positions of interest (Ambient atmosphere, Impeller inlet, | |
| Impeller outlet/vaneless diffuser inlet, Vaneless diffuser outlet), respectively | |
| Blade parameter | |
| Variable in the relative system | |
| Sonic condition |
References
- Dalbert, P.; Ribi, B.; Kmeci, T.; Casey, M.V. Radial compressor design for industrial compressors. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 1999, 213, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumpsty, N. Compressor Aerodynamics; Krieger Publishing Company: Malabar, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Farokhi, S. Compressor Aerodynamics; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C. Centrifugal compressor design considerations. In Proceedings of the Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting, Miami, FL, USA, 17–20 July 2006; Volume 47519, pp. 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, J. Streamline Curvature Computational Programme for Axial Compressor Performance Prediction; Cranfield University: Cranfield, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Peyvan, A.; Benisi, A. Axial-Flow Compressor Performance Prediction in Design and Off-Design Conditions through 1D and 3D Modeling and Experimental Study. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2016, 9, 2149–2160. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Wu, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Qiang, X. Axial compressor performance prediction using improved streamline curvature approach. In Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 51012, p. V02CT42A010. [Google Scholar]
- Coppage, J.; Dallenbach, F. Study of Supersonic Radial Compressors for Refrigeration and Pressurization Systems; Technical Report; Garrett Corp Los Angeles Ca AiResearch MFG DIV: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Galvas, M.; NASA Lewis Research Center Cleveland. FORTRAN Program for Predicting Off-Design Performance of Centrifugal Compressors; NASA Technical Note; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1973.
- Thanapandi, P.; Prasad, R. Performance prediction and loss analysis of low specific speed submersible pumps. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 1990, 204, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.; Baines, N.C. Design of Radial Turbomachines; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Aungier, R.H. Mean Streamline Aerodynamic Performance Analysis of Centrifugal Compressors. J. Turbomach. 1995, 117, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.W.; Yoon, E.S.; Chung, M.K. An optimum set of loss models for performance prediction of centrifugal compressors. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 1997, 211, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravdahl, J.T.; Willems, F.; De Jager, B.; Egeland, O. Modeling of surge in free-spool centrifugal compressors: Experimental validation. J. Propuls. Power 2004, 20, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Gu, C.; Song, Y. A new optimization method for centrifugal compressors based on 1D calculations and analyses. Energies 2015, 8, 4317–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, E.I.G. Determination of a suitable set of loss models for centrifugal compressor performance prediction. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2017, 30, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, X.; Liu, X.; Sun, Z.; Wu, S.; Gao, Q.; Tan, C. A method to select loss correlations for centrifugal compressor performance prediction. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 105335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasius, H. The Boundary Layers in Fluids with Little Friction; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics: Moffett Field, CA, USA, 1950.
- Prandtl, L. Bericht über Untersuchungen zur ausgebildeten Turbulenz. ZAMM-J. Appl. Math. Mech. Angew. Math. Mech. 1925, 5, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, D. Flow field analysis of radial and backswept centrifugal compressor impellers. I—Flow measurements using a laser velocimeter. In Proceedings of the ASME Twenty-Fifth Annual International Gas Turbine Conference and Twenty Second Annual Fluids Engineering Conference on Performance Prediction of Centrifugal Pumps and Compressors, New Orleans, LA, USA, 9–13 March 1979; pp. 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Eckardt, D. Instantaneous Measurements in the Jet-Wake Discharge Flow of a Centrifugal Compressor Impeller; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, W. LII. The viscosity of gases and molecular force. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1893, 36, 507–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stodola, A. Steam and Gas Turbines: With a Supplement on the Prospects of the Thermal Prime Mover; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1927; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Busemann, A. Das Förderhöhenverhältnis radialer Kreiselpumpen mit logarithmisch-spiraligen Schaufeln. ZAMM-J. Appl. Math. Mech. Angew. Math. Mech. 1928, 8, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wislicenus, G.F. Fluid Mechanics of Turbomachinery; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Wiesner, F.J. A Review of Slip Factors for Centrifugal Impellers; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Stanitz, J.D. Effect of Blade-Thickness Taper on Axial-Velocity Distribution at the Leading Edge of an Entrance Rotor-Blade Row with Axial Inlet, and the Influence of This Distribution on Alignment of the Rotor Blade for Zero Angle of Attack; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics, Lewis Flight Propulsion Lab.: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1953.
- Conrad, O.; Raif, K.; Wessels, M. The calculation of performance maps for centrifugal compressors with vane-island diffusers. In Proceedings of the ASME Twenty-Fifth Annual International Gas Turbine Conference and Twenty Second Annual Fluids Engineering Conference on Performance Prediction of Centrifugal Pumps and Compressors, New Orleans, LA, USA, 9–13 March 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Gravdahl, J.T.; Egeland, O. Centrifugal compressor surge and speed control. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 1999, 7, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staff, A.R. Equations, Tables and Charts for Compressible Flow; The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics Report 1135; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics, Ames Aeronautical Lab.: Moffett Field, CA, USA, 1953.
- Kosuge, H.; Ito, T.; Nakanishi, K. A Consideration Concerning Stall and Surge Limitations Within Centrifugal Compressors. ASME J. Eng. Power 1982, 104, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Society, R. Internal Aerodynamics Turbomachinery: A Conference (on Internal Aerodynamics), Cambridge, UK, 19–21 July 1967; Institution of Mechanical Engineers: London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Krylov, E.; Spunde, E. About the Influence of the Clearance between the Working Blades and Housing of a Radial Turbine on Its Exponent; Technical Report; Air Force Systems Command Wright-Patterson AFB Oh Wright-Patterson AFB: Wright-Patterson, OH, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, C. Paper 5: A Cycle Analysis Technique for Small Gas Turbines. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Conf. Proc. 1968, 183, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.P.; Dean, R. Losses in Vaneless Diffusers of Centrifugal Compressors and Pumps: Analysis, Experiment, and Design. J. Eng. Power 1966, 88, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.W.; Yoon, E.S.; Chung, M.K. Systematic two-zone modelling for performance prediction of centrifugal compressors. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2002, 216, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieblein, S. Loss and Stall Analysis of Compressor Cascades. ASME J. Basic Eng. 1959, 81, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, D. Principles of Turbomachinery; Macmillan Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Daily, J.W.; Nece, R.E. Chamber Dimension Effects on Induced Flow and Frictional Resistance of Enclosed Rotating Disks. ASME J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aungier, R.H. Centrifugal Compressors: A Strategy for Aerodynamic Design and Analysis; ASME Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Boyce, M.P. New Developments in Compressor Aerodynamics. In Proceedings of the 1st Turbomachinery Symposium, College Station, TX, USA, 24–26 October 1972; Texas A&M University, Gas Turbine Laboratories: College Station, TX, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Watabe, K. Experiments on Fluid Friction of Rotating Disc with Blades. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. 1961, 177, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watabe, K. Effects of Clearances and Grooves on Fluid Friction of Rotating Discs. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. Bull. 1965, 8, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovář, P.; Kaňka, T.; Mačák, P.; Tater, A.; Vampola, T. Influence of input parameters in radial compressor design algorithm on the efficiency and its sensitivity analysis. Appl. Comput. Mech. 2021, 15, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, J. A Preliminary Design Tool for Radial Compressors; ISRN LUTMDN/TMHP–13/5287–SE; Lund University: Lund, Sweden, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, P.; Schmidt-Eisenlohr, U. Flow field analysis of radial and backswept centrifugal compressor impellers. II—Comparison of potential flow calculations and measurements. In Proceedings of the ASME Twenty-Fifth Annual International Gas Turbine Conference and Twenty Second Annual Fluids Engineering Conference on Performance Prediction of Centrifugal Pumps and Compressors, New Orleans, LA, USA, 9–13 March 1979; pp. 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanets, S.; Blinov, V.; Sedunin, V.; Komarov, O.; Skorohodov, A. Validation of a CFD model of a single stage centrifugal compressor by mass-averaged parameters. In EPJ Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2019; Volume 196, p. 00026. [Google Scholar]
- Elzahaby, A.M.; Khalil, M.K.; Al Moghazy, M.E. Automated optimization of centrifugal compressors “Eckardt rotor O”. J. Eng. Res. 2018, 2, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piegl, L. On NURBS: A Survey. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 1991, 11, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyer, H.; Schodl, R. Development and Testing of Techniques for Oscillating Pressure Measurements Especially Suitable for Experimental Work in Turbomachinery. J. Basic Eng. 1971, 93, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
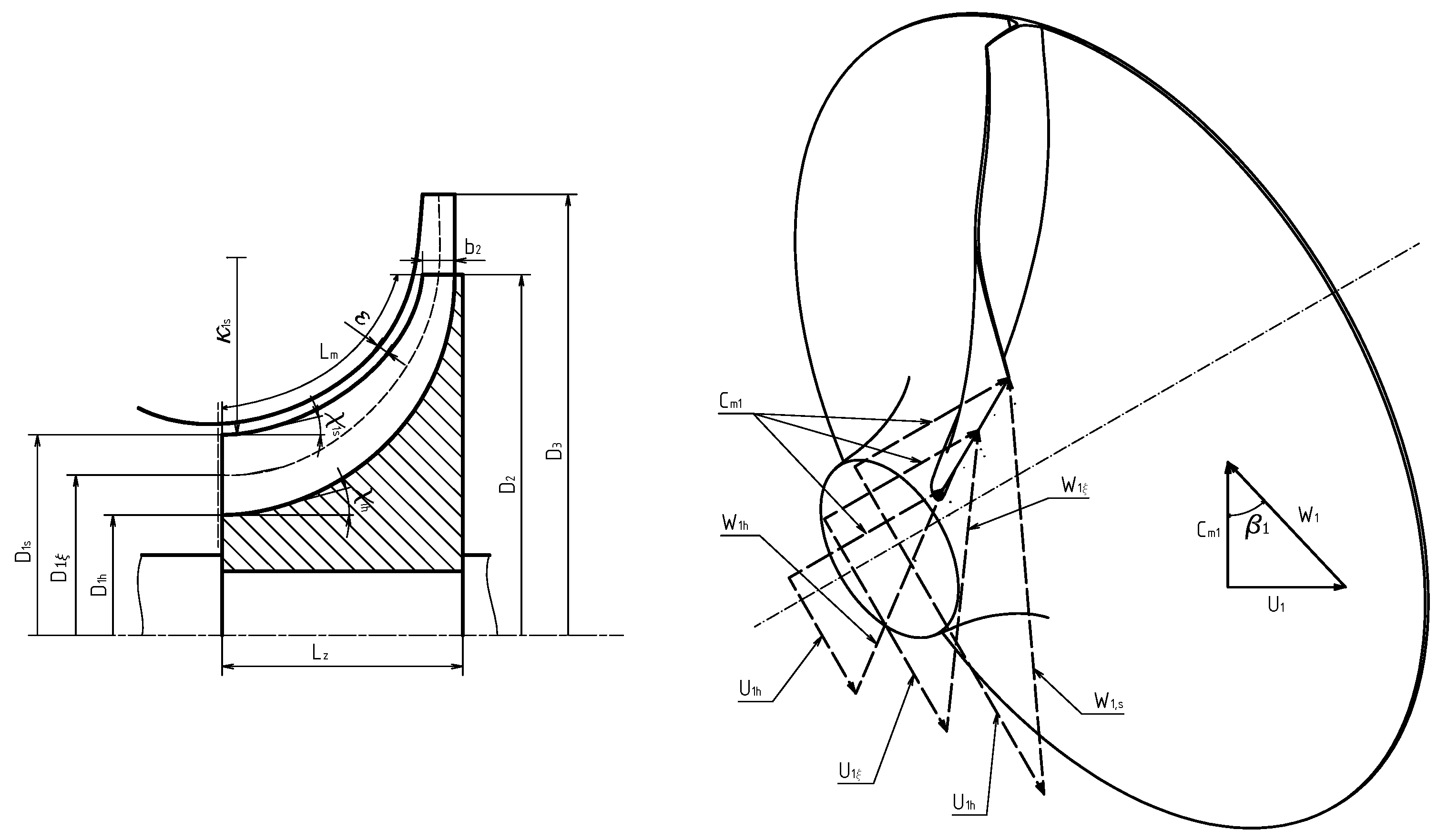
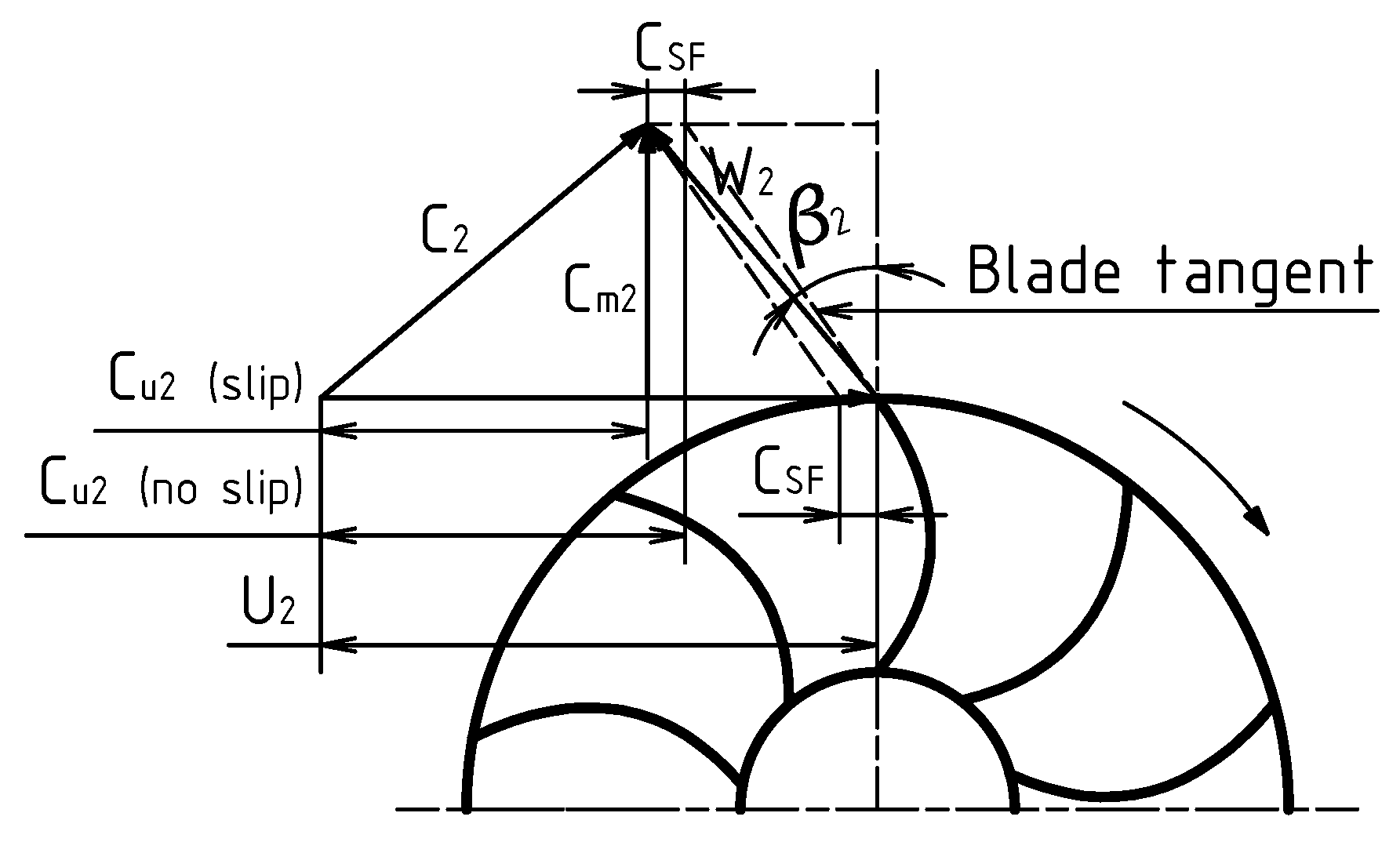
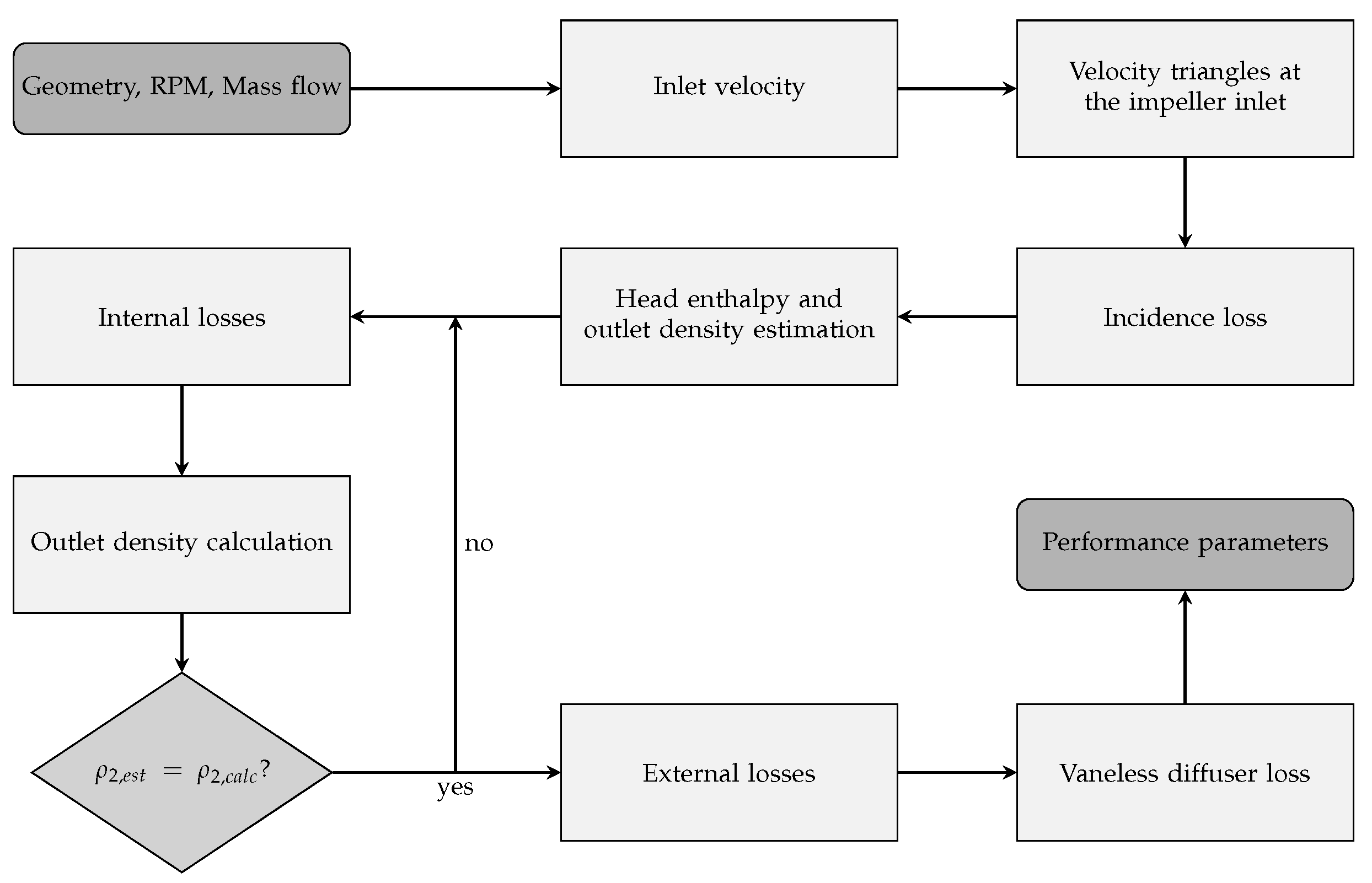
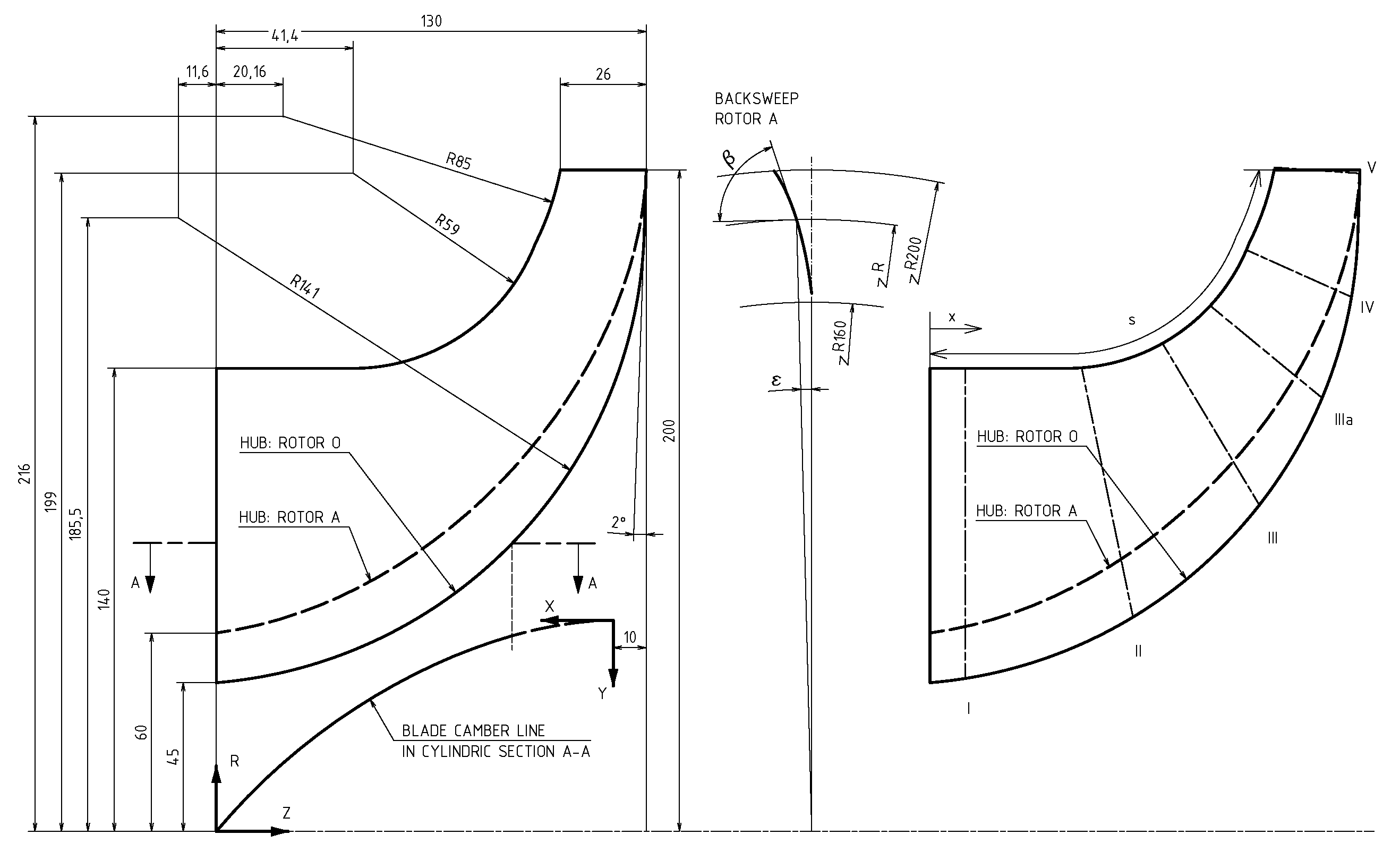
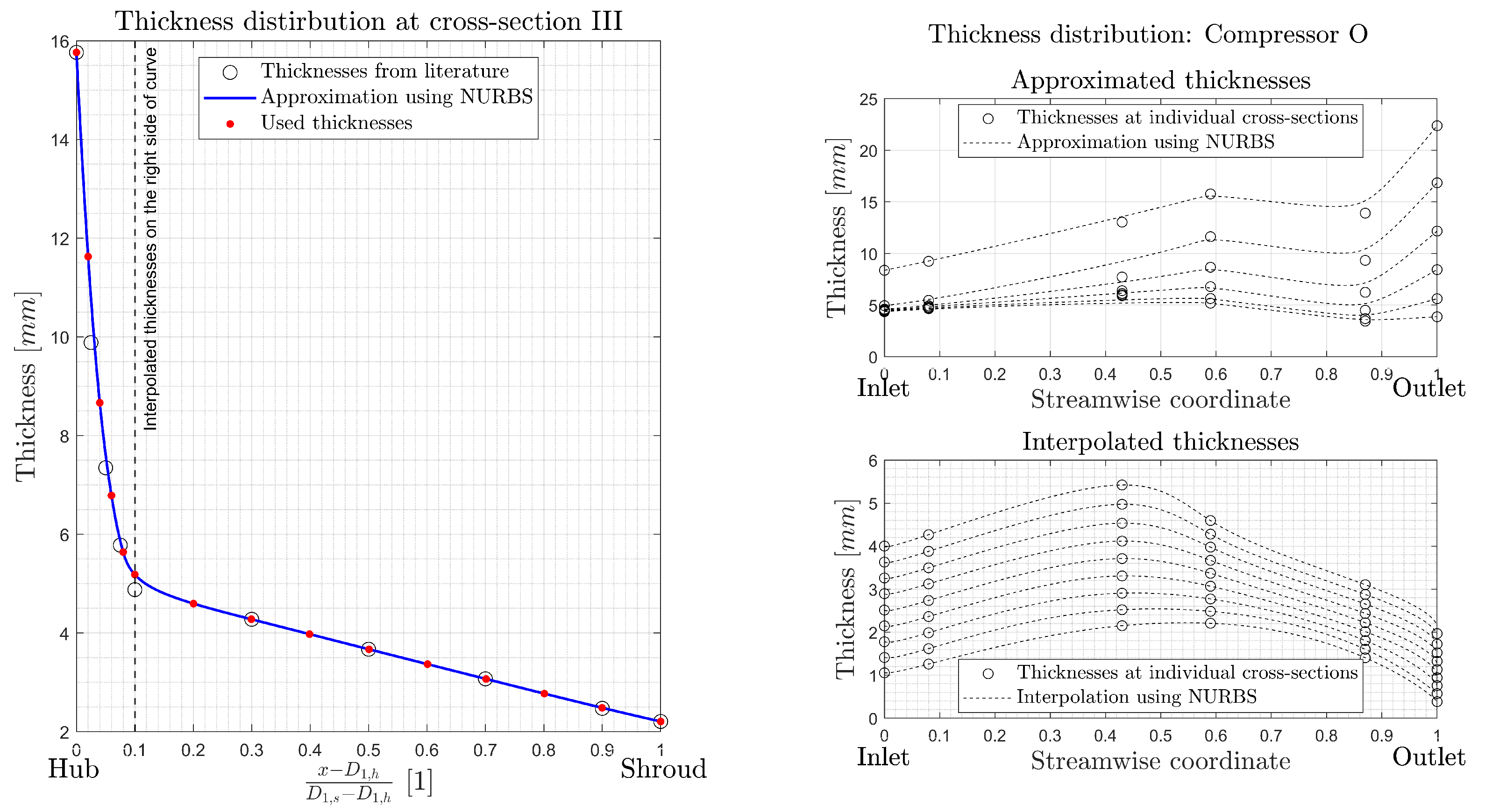

| Parameter | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | [min] | [kg·s] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [] | [] | [] |
| Type O | 14,000 | 5.31 | 90 | 208 | 280 | 5.6 | 2.1 | 0 |
| Type A | 14,000 | 4.54 | 120 | 215.4 | 280 | 12.4 | 5 | 0 |
| Parameter | ||||||||
| Unit | [m] | [m] | [m] | [] | [] | [] | [] | |
| Type O | 0.0071 | 0.0027 | 0 | 20 | 31.7 | 55 | 62.6 | 0 |
| Type A | 0.0071 | 0.0029 | 0 | 20 | 39.3 | 56 | 62.6 | 30 |
| Parameter | ||||||||
| Unit | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] |
| Type O | 2.7 | 0.5 | 400 | 26 | 130 | 173.9 | 204.8 | 676 |
| Type A | 3.4 | 0.5 | 400 | 26 | 130 | 169.3 | 204.8 | 676 |
| Loss | Set No. 1759 | Set No. 2042 | Set No. 2137 | Set Oh [13] | Set Zhang [17] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence | Conrad [28] | Conrad [28] | Conrad [28] | Conrad [28] | Aungier [12] |
| Choke | Aungier [12] | Aungier [12] | Aungier [12] | × | Aungier [12] |
| Entrance diffusion | Aungier [12] | Aungier [12] | Aungier [12] | × | Aungier [12] |
| Blade loading | Aungier [12] | Aungier [12] | Aungier [12] | Coppage [8] | Aungier [12] |
| Skin friction | Coppage [8] | Jansen [32] | Aungier [12] | Jansen [32] | Jansen [32] |
| Clearance | Jansen [32] | Rodgers [34] | Jansen [32] | Jansen [32] | Jansen [32] |
| Mixing | Aungier [12] | Aungier [12] | Aungier [12] | Johnston [35] | Aungier [12] |
| Recirculation | Coppage [8] | Coppage [8] | Coppage [8] | Oh [13] | Coppage [8] |
| Disk friction | Boyce [41] | Shepherd [38] | Shepherd [38] | Daily [39] | Daily [39] |
| Vaneless diffuser | Stanitz [27] | Coppage [8] | Stanitz [27] | Stanitz [27] | Stanitz [27] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovář, P.; Tater, A.; Mačák, P.; Vampola, T. Searching for the Most Suitable Loss Model Set for Subsonic Centrifugal Compressors Using an Improved Method for Off-Design Performance Prediction. Energies 2021, 14, 8545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14248545
Kovář P, Tater A, Mačák P, Vampola T. Searching for the Most Suitable Loss Model Set for Subsonic Centrifugal Compressors Using an Improved Method for Off-Design Performance Prediction. Energies. 2021; 14(24):8545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14248545
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovář, Patrik, Adam Tater, Pavel Mačák, and Tomáš Vampola. 2021. "Searching for the Most Suitable Loss Model Set for Subsonic Centrifugal Compressors Using an Improved Method for Off-Design Performance Prediction" Energies 14, no. 24: 8545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14248545
APA StyleKovář, P., Tater, A., Mačák, P., & Vampola, T. (2021). Searching for the Most Suitable Loss Model Set for Subsonic Centrifugal Compressors Using an Improved Method for Off-Design Performance Prediction. Energies, 14(24), 8545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14248545






