PMSM Torque-Speed-Efficiency Map Evaluation from Parameter Estimation Based on the Stand Still Test
Abstract
:1. Introduction
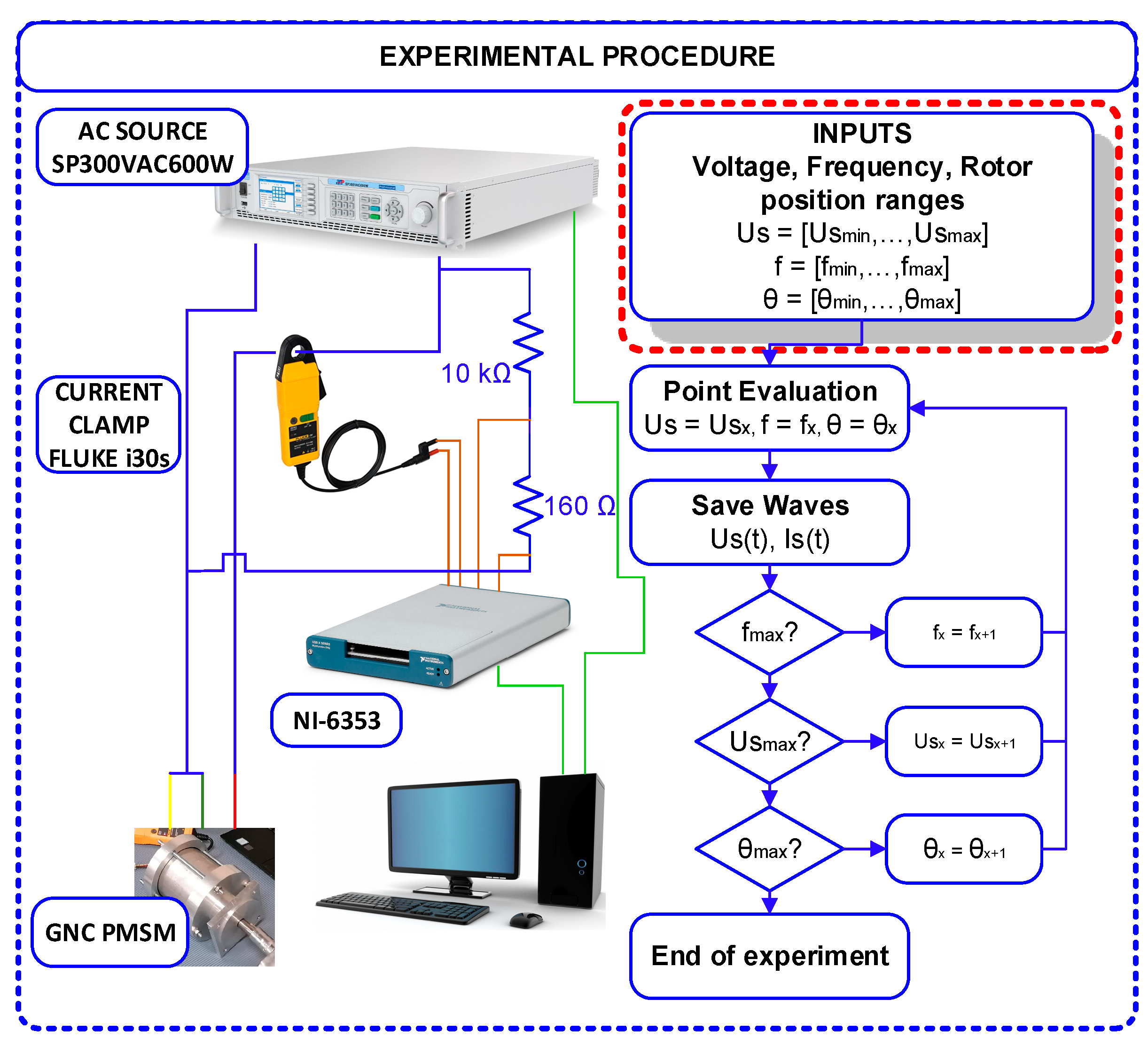
2. PMSM Blocked Rotor Test and Performance Analysis Methodology
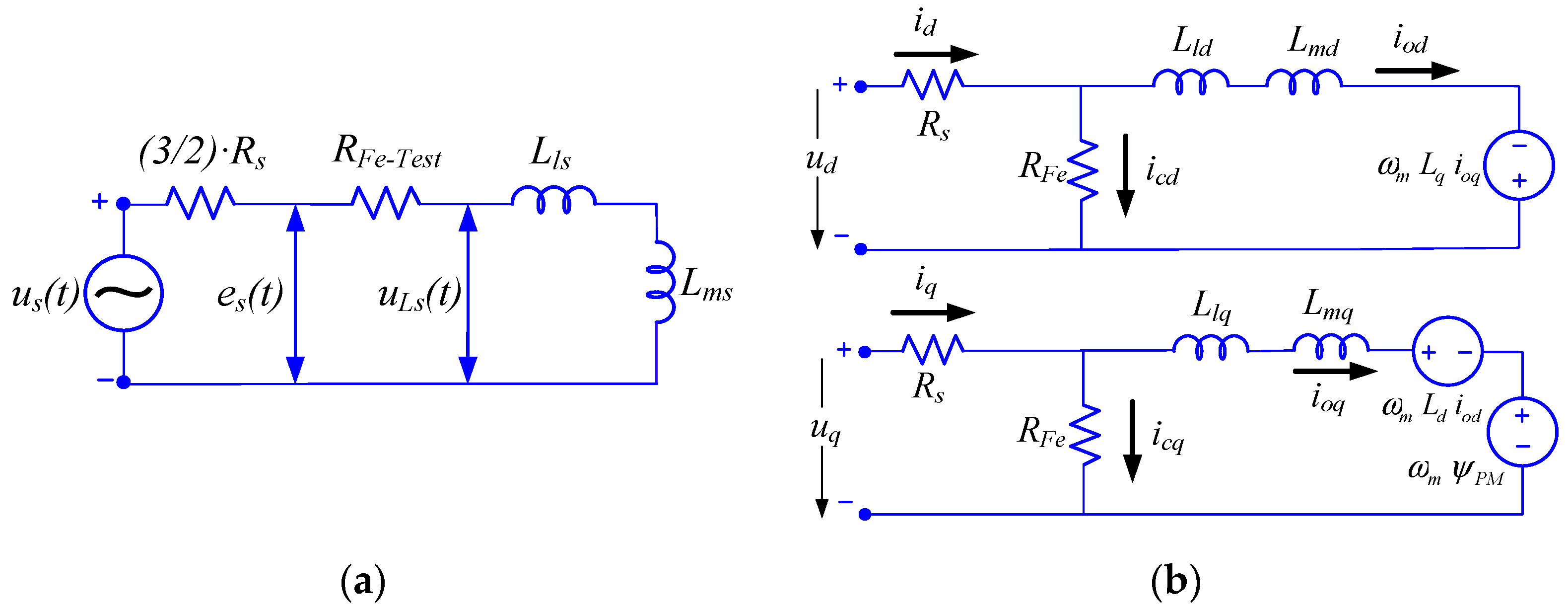
2.1. Parameter Estimation Electrical Model
| Algorithm 1. Parameter analysis extraction algorithm. |
| 1: Take and for each voltage, frequency and rotor position combination. |
| 2: Apply a digital low pass filter. |
| 3: Compute iron losses and inductance voltage drop: |
| 4: Compute instantaneous power: |
| 5: Compute mean iron losses power: |
| 6: Compute equivalent iron losses resistor: |
| 7: Compute instantaneous iron losses: |
| 8: Compute instantaneous reactive power: |
| 9: Compute linkage + leakage induction voltage: |
| 11: Linkage + leakage inductance calculation: → |
| 12: Stator inductance as a function of the d-q currents: → |
| 13: Compute the flux linkage gradient using the stator inductance : |
| 14: Determination of the d-q flux linkage: |
| 15: Selection of representative inductance for the space vector current: → |
| 16: Selection of iron losses for real operating conditions: |
2.2. d-q Electrical Model for Performance Analysis
| Algorithm 2. (d-q) electrical model computation procedure. |
| 1: od and oq current discretization. |
| 2: d-q inductances values: |
| 3: Flux linkage calculation: |
| 4: Torque computation: |
| 5: Iron losses extraction: |
| 6: Back electromotive force: |
| 7: Iron resistance loss: |
| 8: Iron resistance currents cd/cq: |
| 9: Voltage equations: |
| 10: Selection of the magnitudes from control strategy. |
3. Results
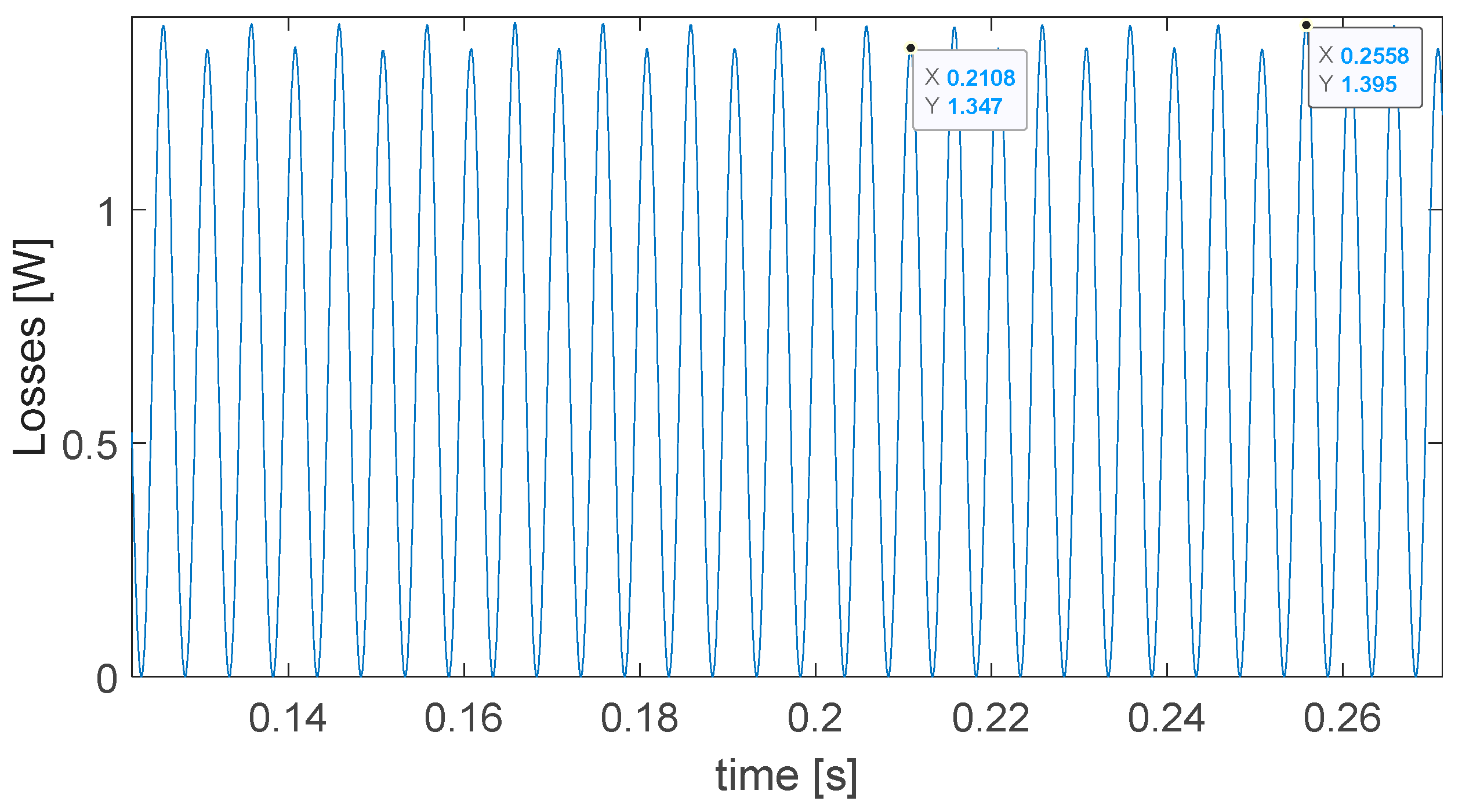
3.1. Iron Losses Estimation as a Function of the d-q Currents and Frequency
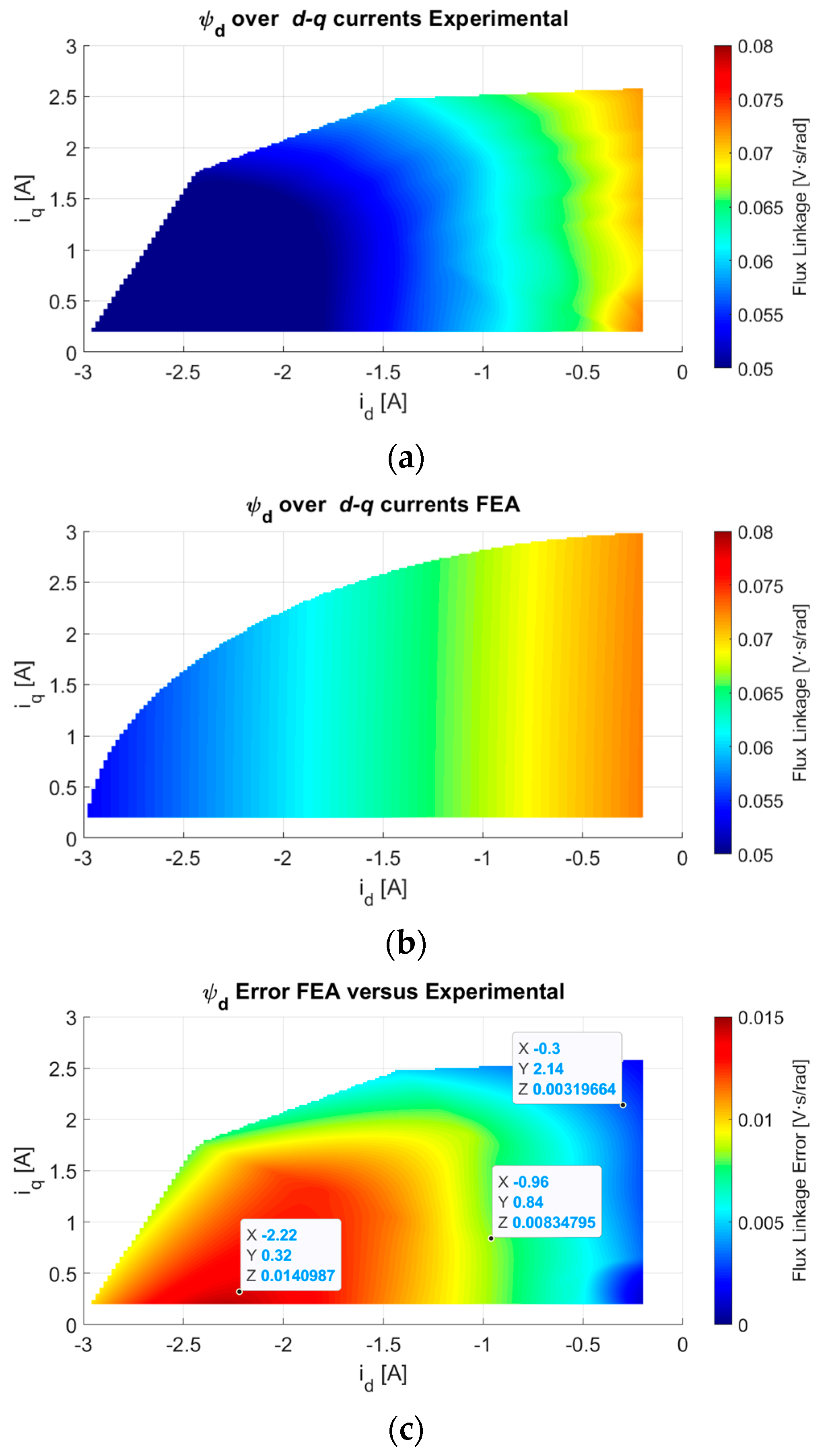
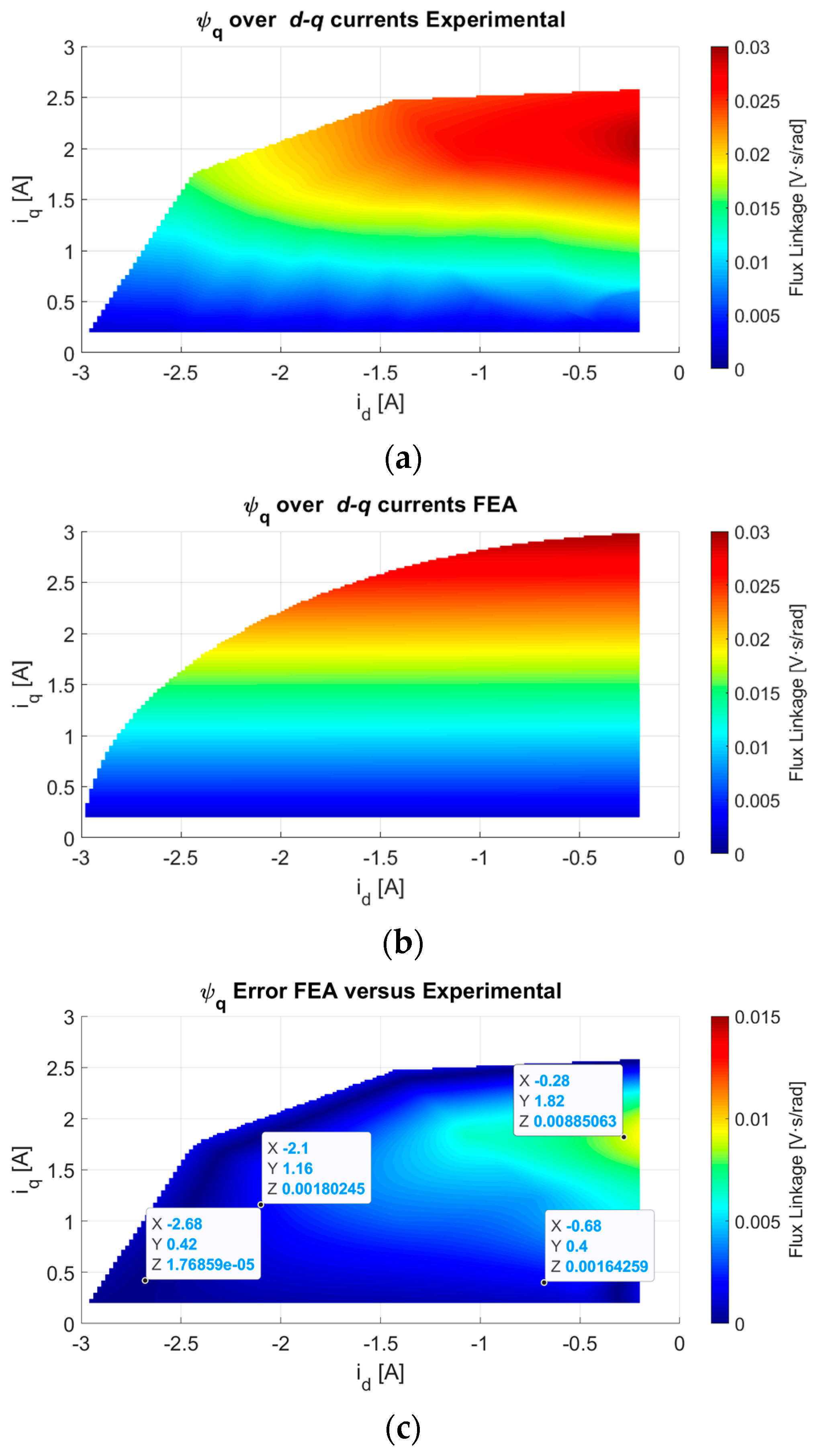
3.2. Electromagnetic Parameters Computation versus the d-q Currents
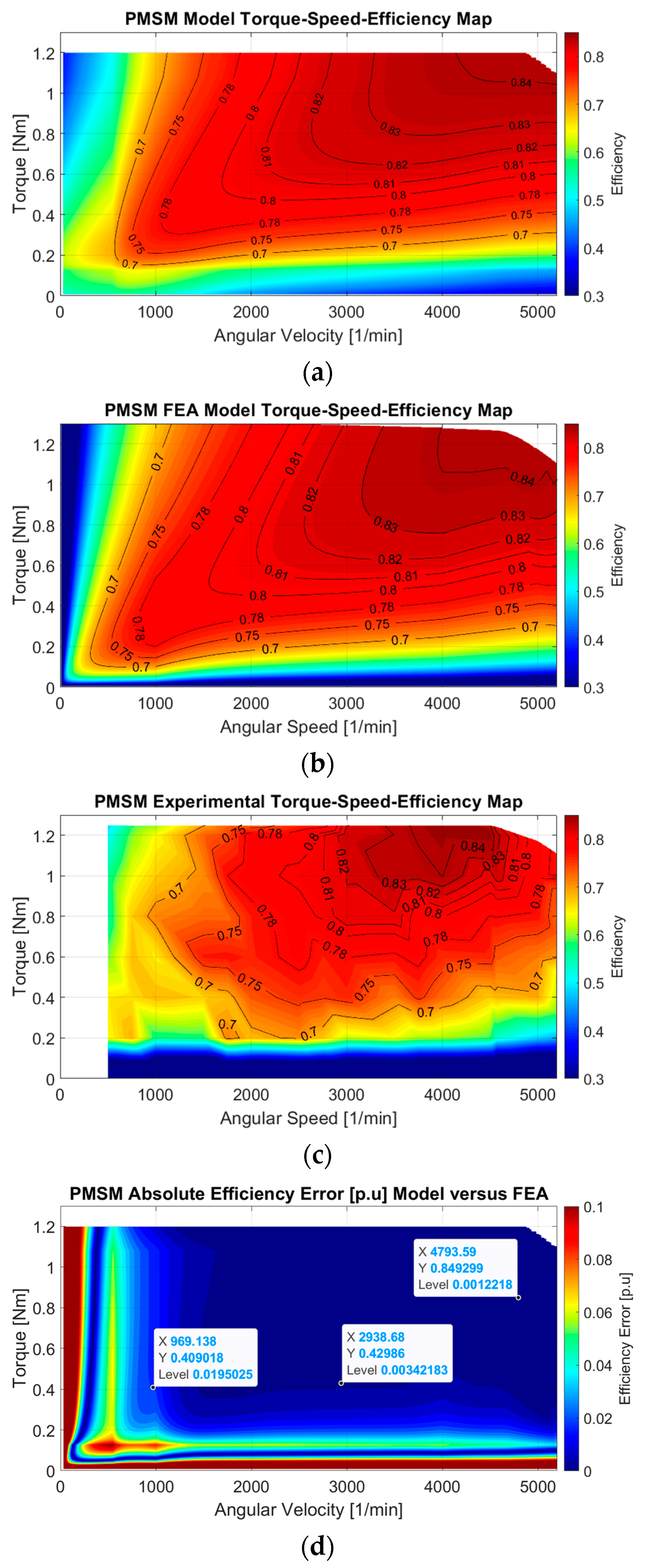
3.3. Torque-Speed-Efficiency Map Reproduction
3.4. Computational Burden
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| es | Stator back electromotive force [V] |
| id | Direct axis current [A] |
| iq | Quadrature axis current [A] |
| is | Stator phase current [A] |
| icd | Iron losses direct axis current [A] |
| icq | Iron losses quadrature axis current [A] |
| iod | Effective direct axis current [A] |
| ioq | Effective quadrature axis current [A] |
| Ls | Parameter estimation inductance [H] |
| Lls | Leakage inductance [H] |
| Lms | Magnetizing inductance [H] |
| Ld | Inductance in the direct axis [H] |
| Lld | Leakage inductance in direct axis [H] |
| Lmd | Magnetizing inductance in the direct axis [H] |
| Lq | Inductance in the quadrature axis [H] |
| Llq | Leakage inductance in quadrature axis [H] |
| Lmq | Magnetizing inductance in the quadrature axis [H] |
| m | Phases number [-] |
| n | Rotor angular speed [1/min] |
| p | Pairs of poles [-] |
| PCu | Copper losses [W] |
| PFe | Iron losses [W] |
| Pml | Mechanical losses [W] |
| RFe | d-q model resistance of the iron [Ω] |
| RFe-test | Identification model resistance of the iron [Ω] |
| Rs | Resistance of the stator windings per phase [Ω] |
| T | Output mechanical torque [N·m] |
| ud | Direct axis voltage [V] |
| uq | Quadrature axis voltage [V] |
| us | Stator phase voltage [V] |
| uLs | Parameter identification inductance voltage [V] |
| Udc | Voltage of the DC bus [V] |
| θe | Electrical angular position [rad] |
| θm | Mechanical angular position [rad] |
| ωm | Electrical angular speed [rad/s] |
| Ψabc | Flux linkage in the stator [V·s] |
| ΨPM | Flux linkage of the permanent magnets [V·s] |
| Ψd | Flux linkage in the direct axis [V·s] |
| Ψq | Flux linkage in the quadrature axis [V·s] |
References
- Rafaq, M.S.; Jung, J.W. A Comprehensive Review of State-of-the-Art Parameter Estimation Techniques for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors in Wide Speed Range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 4747–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellschopp, F.S.; Arjona, M.A. Determination of synchronous machine parameters using standstill frequency response tests at different excitation levels. Proceedings of IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference, IEMDC 2007, Antalya, Turkey, 3–5 May 2007; Volume 2, pp. 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belqorchi, A.; Karaagac, U.; Mahseredjian, J.; Kamwa, I. Standstill Frequency Response Test and Validation of a Large Hydrogenerator. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoni, E.D.; Jardini, J.A. A standstill frequency response method for large salient pole synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2004, 19, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandoorn, T.L.; de Belie, F.M.; Vyncke, T.J.; Melkebeek, J.A.; Lataire, P. Generation of multisinusoidal test signals for the identification of synchronous-machine parameters by using a voltage-source inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 115-2009—IEEE Guide for Test Procedures for Synchronous Machines Part I—Acceptance and Performance Testing Part II—Test Procedures and Parameter Determination for Dynamic Analysis—Redline|IEEE Standard|IEEE Xplore. Available online: https://ieeexplore-ieee-org.recursos.biblioteca.upc.edu/document/5953453 (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Zou, J.; Zeng, D.; Xu, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, Q. An Indirect Testing Method for the Mechanical Characteristic of Multiunit Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines With Concentrated Windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 7402–7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Xu, Y. Analysis and Discussion of the Indirect Testing Method for the Losses of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Lai, C.; Kar, N.C. Practical Testing Solutions to Optimal Stator Harmonic Current Design for PMSM Torque Ripple Minimization Using Speed Harmonics. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 5181–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Feng, J.; Guo, S.; Xiao, L.; Zhu, Z.Q. Identification of flux linkage map of permanent magnet synchronous machines under uncertain circuit resistance and inverter nonlinearity. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Lai, C.; Mukherjee, K.; Kar, N.C. Current Injection-Based Online Parameter and VSI Nonlinearity Estimation for PMSM Drives Using Current and Voltage DC Components. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2016, 2, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaq, M.S.; Mwasilu, F.; Kim, J.; Choi, H.H.; Jung, J.W. Online Parameter Identification for Model-Based Sensorless Control of Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 4631–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivanc, O.C.; Ozturk, S.B. Sensorless PMSM Drive Based on Stator Feedforward Voltage Estimation Improved with MRAS Multiparameter Estimation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 1326–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Wei, H.L.; Li, X.H.; Liu, K.; Zhong, Q.C. Global Identification of Electrical and Mechanical Parameters in PMSM Drive Based on Dynamic Self-Learning PSO. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 10858–10871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallscheid, O.; Böcker, J. Global identification of a low-order lumped-parameter thermal network for permanent magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, R.; Sebastian, T.; Wang, M. Online stator inductance estimation for permanent magnet motors using PWM excitation. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2019, 5, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Li, J.; Qu, R.; Kong, W. Adaptive second-order sliding-mode observer for PMSM sensorless control considering VSI Nonlinearity. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8994–9004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Yu, H. Robust Speed Regulation for PMSM Servo System with Multiple Sources of Disturbances via an Augmented Disturbance Observer. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Tang, B.; Ji, K.; Lu, K.; Wang, D.; Yu, Z. A New Load Adaptive Identification Method Based on an Improved Sliding Mode Observer for PMSM Position Servo System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 3211–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Xia, C.; Yan, Y.; Geng, Q.; Shi, T. Online Multiparameter Identification of Surface-Mounted PMSM Considering Inverter Disturbance Voltage. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, L.; Corradini, M.L.; Cristofaro, A.; Ippoliti, G.; Orlando, G. An Embedded Strategy for Online Identification of PMSM Parameters and Sensorless Control. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2019, 27, 2444–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, M. Enhancing Low-Speed Sensorless Control of PMSM Using Phase Voltage Measurements and Online Multiple Parameter Identification. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 10700–10710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulvirenti, M.; Scarcella, G.; Scelba, G.; Testa, A.; Harbaugh, M.M. On-line stator resistance and permanent magnet flux linkage identification on open-end winding PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, K.; Wang, D.; Blaabjerg, F. Online Identification of Intrinsic Load Current Dependent Position Estimation Error for Sensorless PMSM Drives. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 163186–163196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Wang, G.; Li, C.; Xu, D. Offline Parameter Self-Learning Method for General-Purpose PMSM Drives with Estimation Error Compensation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 11103–11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Fu, X.; Lin, M.; Jia, L. Offline Inductance Identification of IPMSM with Sequence-Pulse Injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 6127–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboeuf, N.; Boileau, T.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B.; Takorabet, N.; Meibody-Tabar, F.; Clerc, G. Estimating permanent-magnet motor parameters under inter-turn fault conditions. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armando, E.; Bojoi, R.I.; Guglielmi, P.; Pellegrino, G.; Pastorelli, M. Experimental identification of the magnetic model of synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, G.; Boazzo, B.; Jahns, T.M. Magnetic Model Self-Identification for PM Synchronous Machine Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 2246–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odhano, S.A.; Bojoi, R.; Roşu, Ş.G.; Tenconi, A. Identification of the Magnetic Model of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines Using DC-Biased Low-Frequency AC Signal Injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3208–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosfeld, A.; Hiester, F.; Konigorski, U. Analysis of DC Motor Current Waveforms Affecting the Accuracy of ‘Sensorless’ Angle Measurement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lai, J.S. Quad Sampling Incremental Inductance Measurement through Current Loop for Switched Reluctance Motor. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 4251–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Torres, C.; Colls, C.; Garcia, A.; Riba, J.-R.; Romeral, L. Development of a Behavior Maps Tool to Evaluate Drive Operational Boundaries and Optimization Assessment of PMa-SynRMs. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 6861–6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stipetic, S.; Goss, J.; Zarko, D.; Popescu, M. Calculation of Efficiency Maps Using a Scalable Saturated Model of Synchronous Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 4257–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelo-Zuluaga, C.; Riba, J.-R.; Espinosa, A.G.; Tubert, P. Customized PMSM Design and Optimization Methodology for Water Pumping Applications. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of phases | 3 |
| Nominal power [W] | 585 |
| Nominal voltage [VRMS] | 200 |
| Nominal current [IRMS] | 2 |
| Nominal torque [N·m] | 1.24 |
| Nominal speed [rpm] | 4501 |
| Nominal efficiency [%] | 84.2 |
| Pairs of poles | 3 |
| Slots number | 9 |
| d-axis Inductance Ld [mH] | 4.2 |
| q-axis Inductances Lq [mH] | 11.2 |
| Magnitude | Minimum Value | Maximum Value | Number of Divisions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage [V] | 1 | 20 | 7 |
| Frequency [Hz] | 100 | 800 | 8 |
| Rotor Angle [Deg] | 0 | 30 | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Candelo-Zuluaga, C.; Riba, J.-R.; Garcia, A. PMSM Torque-Speed-Efficiency Map Evaluation from Parameter Estimation Based on the Stand Still Test. Energies 2021, 14, 6804. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206804
Candelo-Zuluaga C, Riba J-R, Garcia A. PMSM Torque-Speed-Efficiency Map Evaluation from Parameter Estimation Based on the Stand Still Test. Energies. 2021; 14(20):6804. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206804
Chicago/Turabian StyleCandelo-Zuluaga, Carlos, Jordi-Roger Riba, and Antoni Garcia. 2021. "PMSM Torque-Speed-Efficiency Map Evaluation from Parameter Estimation Based on the Stand Still Test" Energies 14, no. 20: 6804. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206804
APA StyleCandelo-Zuluaga, C., Riba, J.-R., & Garcia, A. (2021). PMSM Torque-Speed-Efficiency Map Evaluation from Parameter Estimation Based on the Stand Still Test. Energies, 14(20), 6804. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206804







