Mechanical Switch Based Adaptive Fault Ride-through Strategy for Power Quality Improvement Device
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- The proposed strategy uses mechanical switches as reliable bypass devices, which reduces the system cost.
- (2)
- The proposed voltage optimization method has the advantages of simplicity and self-adaptation. There is no need to change the control strategy after completing the fault ride-through process.
- (3)
- The best fault ride-through method can be selected according to the system operation and fault conditions. The proposed strategy is applicable to all voltage-controlled cascaded H-bridge topologies.
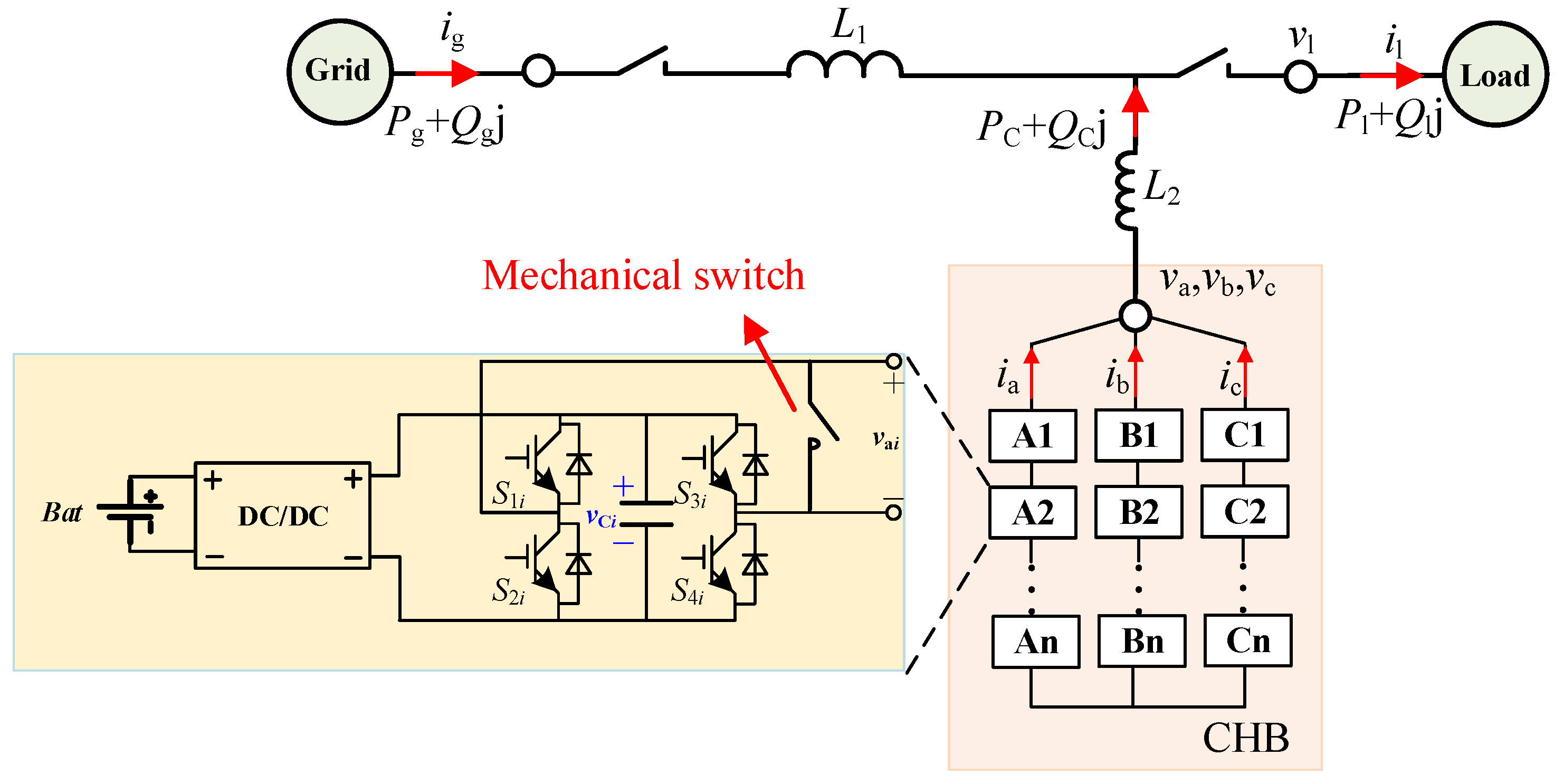
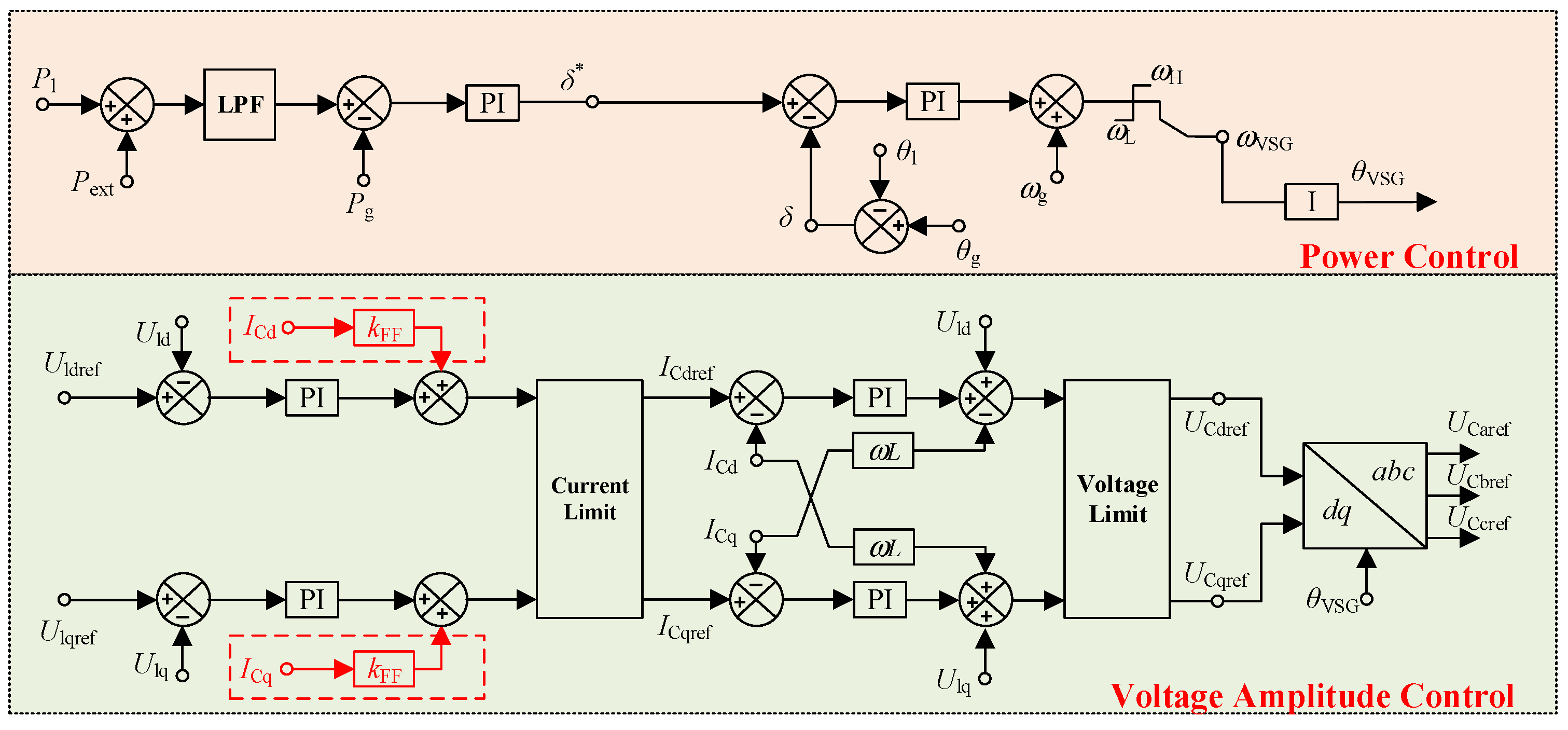
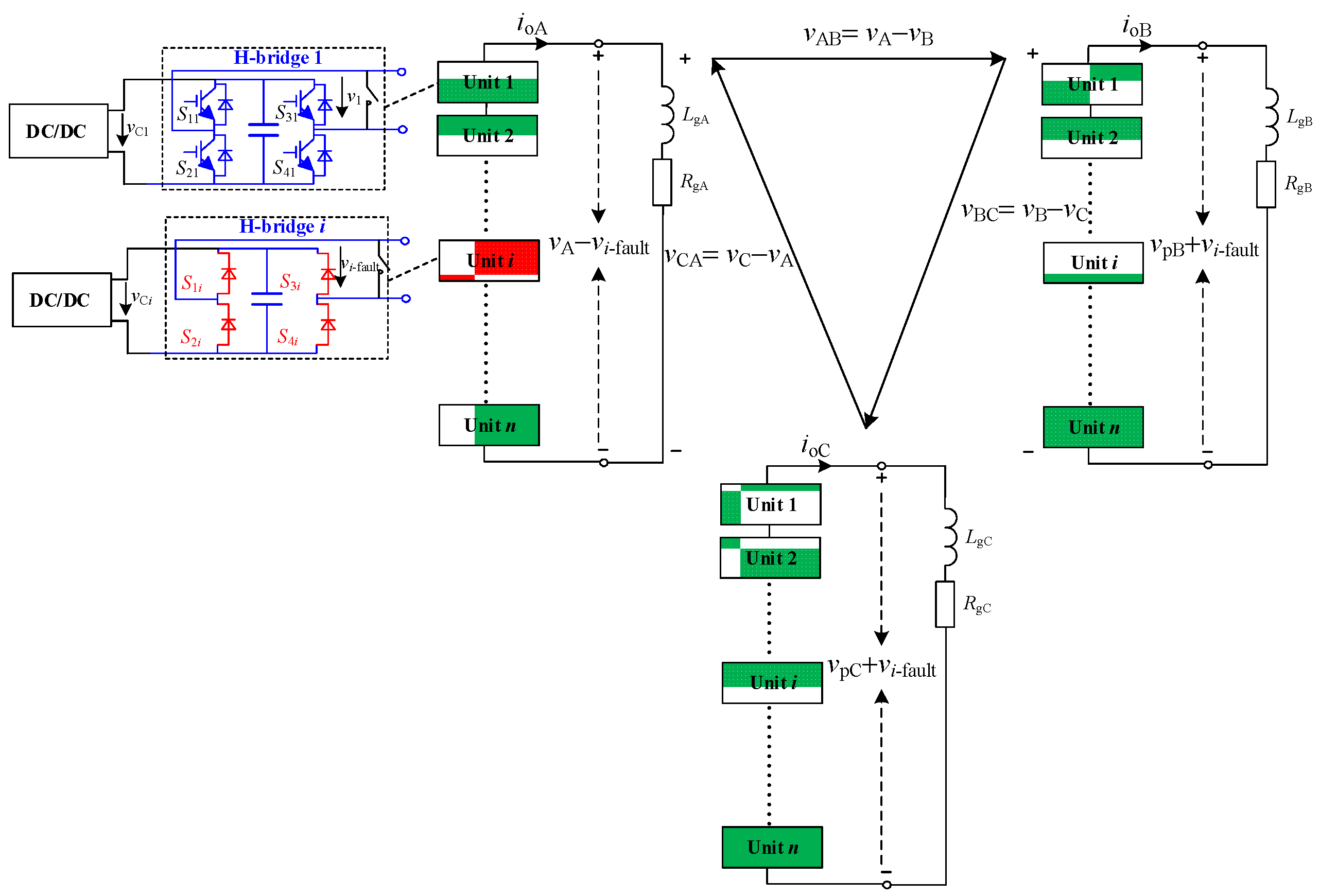
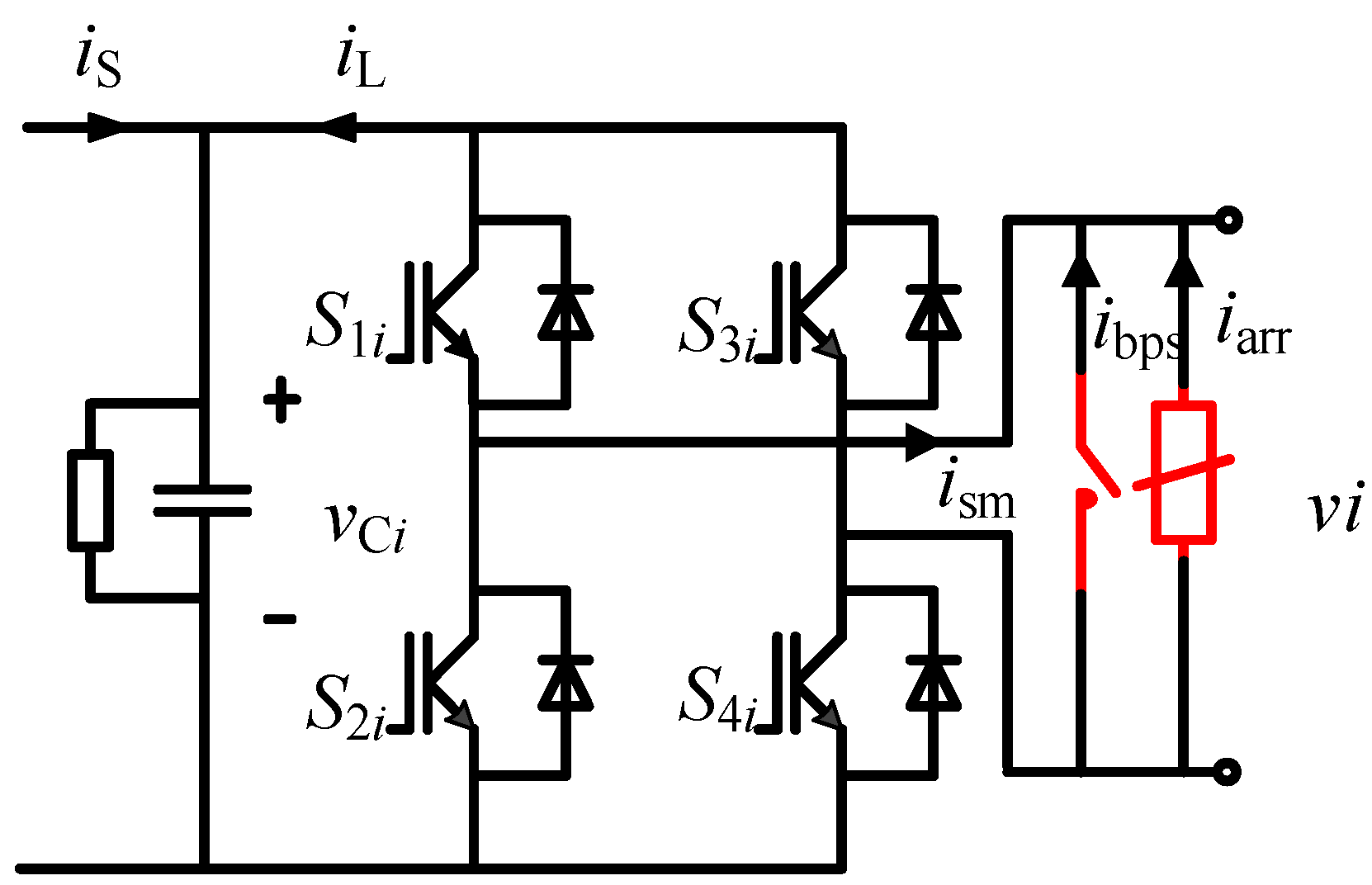
2. PQID and Its Fault Ride-through
3. Power Unit Fault Analysis
3.1. Controllable Fault
3.2. Uncontrollable Fault
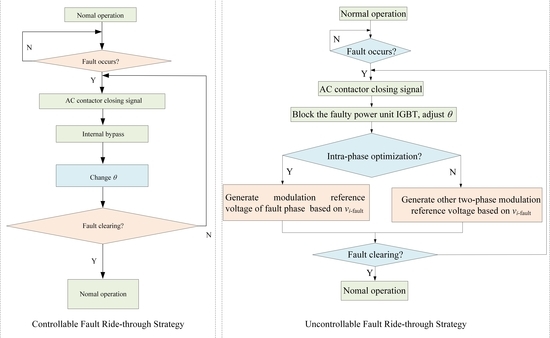
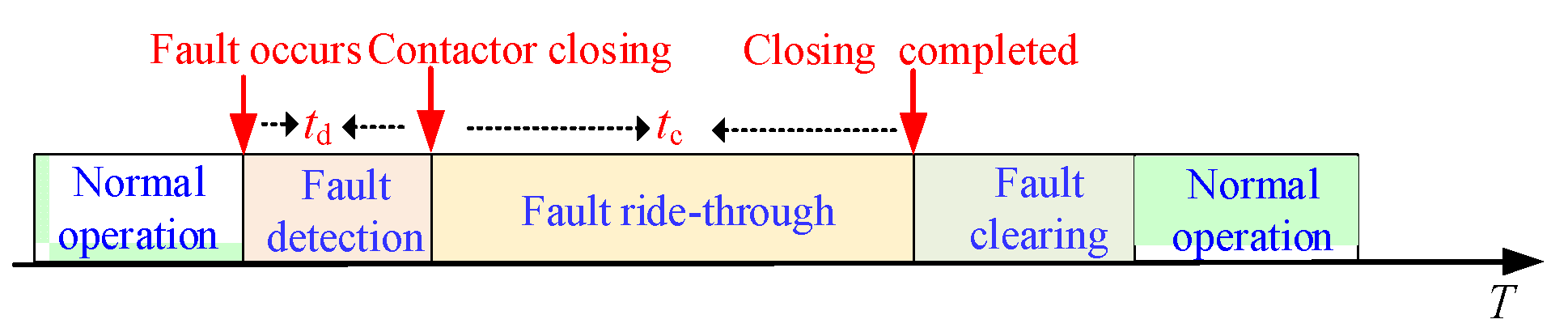
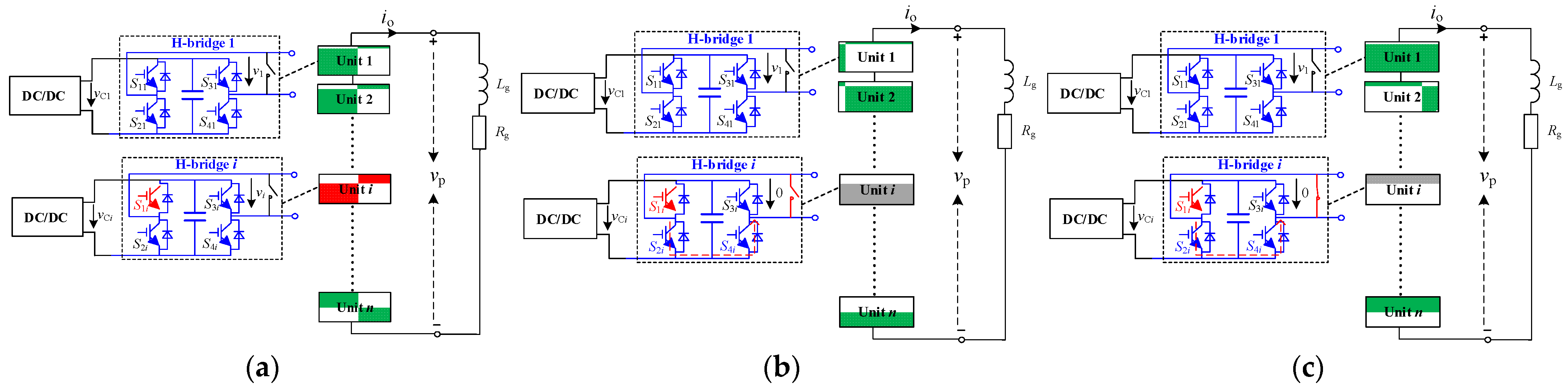
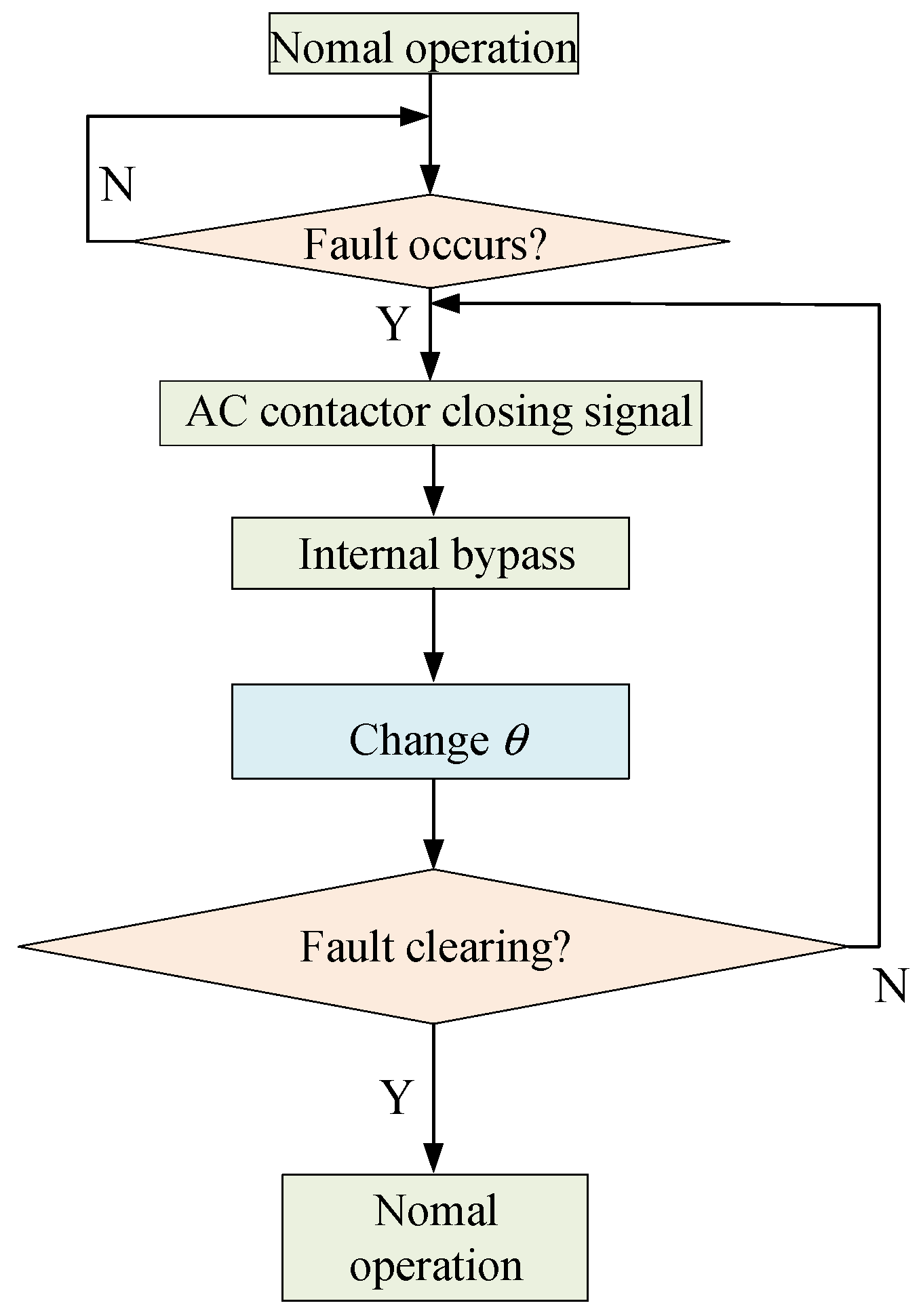
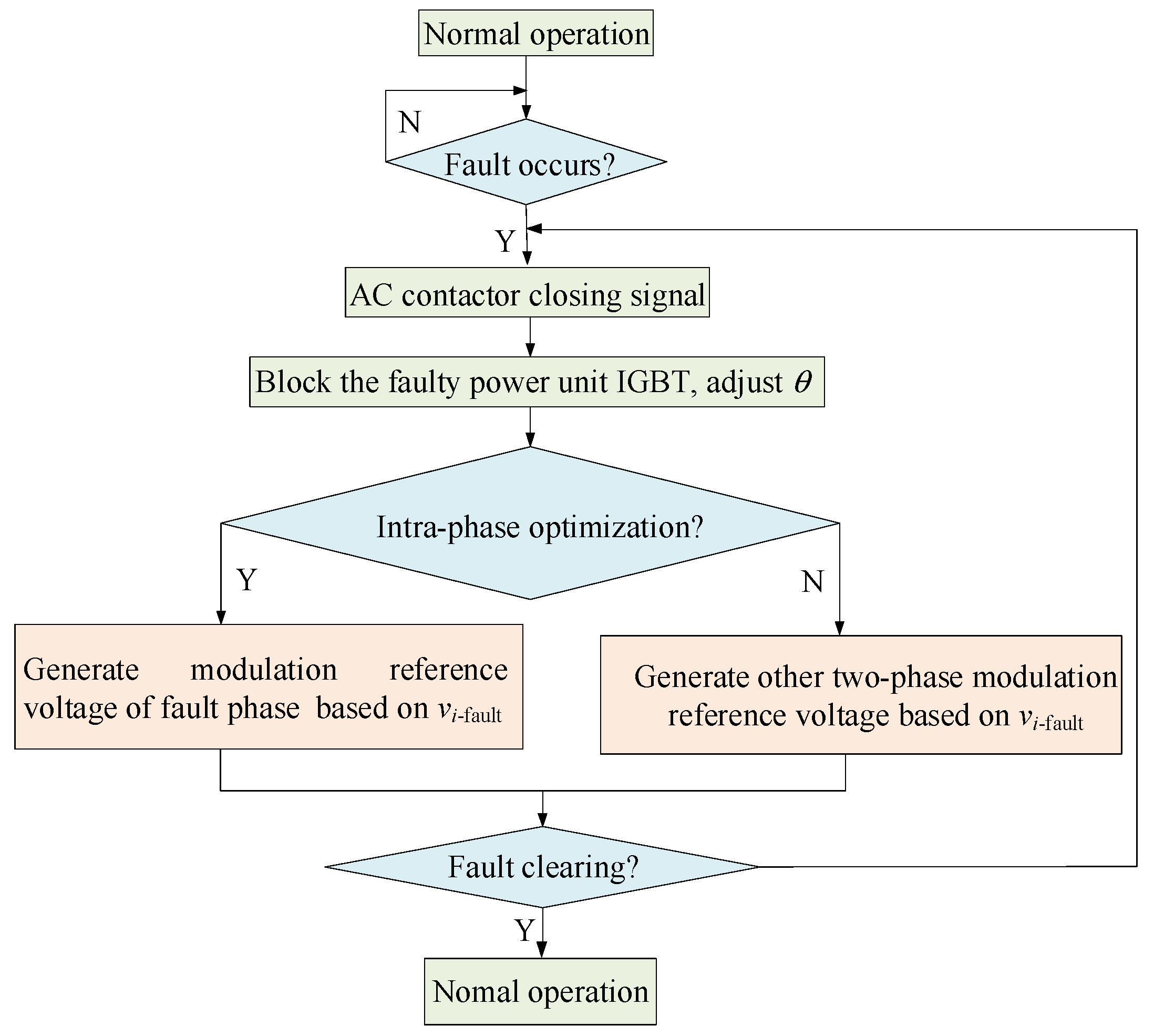
4. Fault Ride-through Strategy of PQID
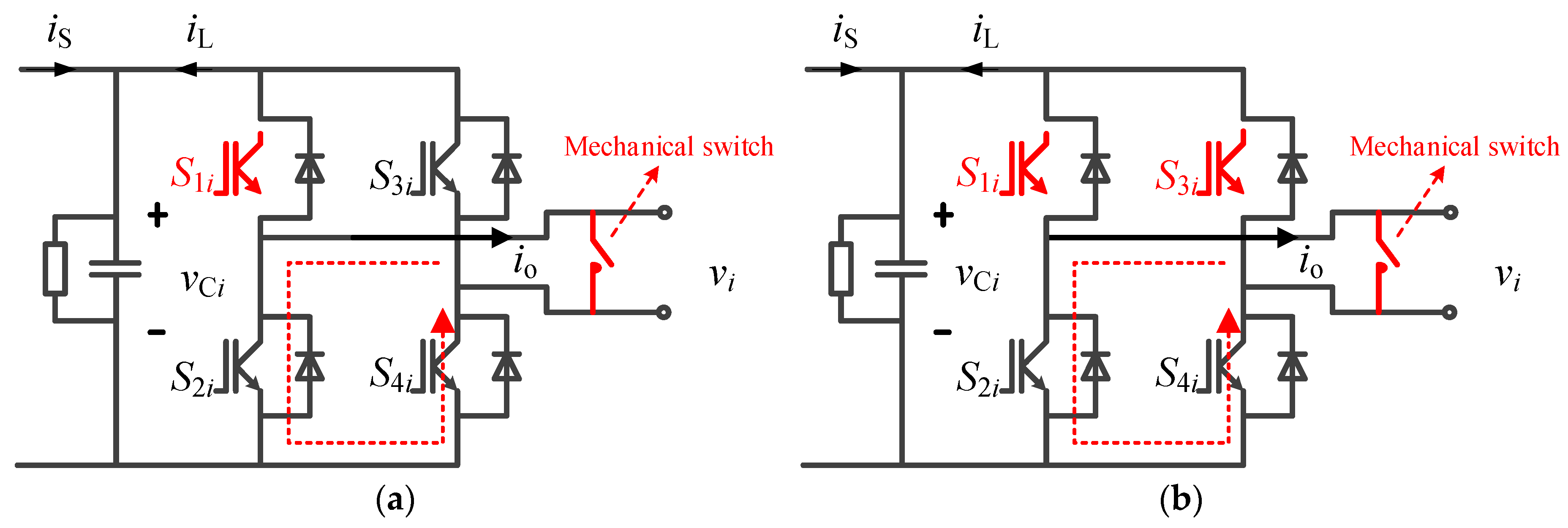
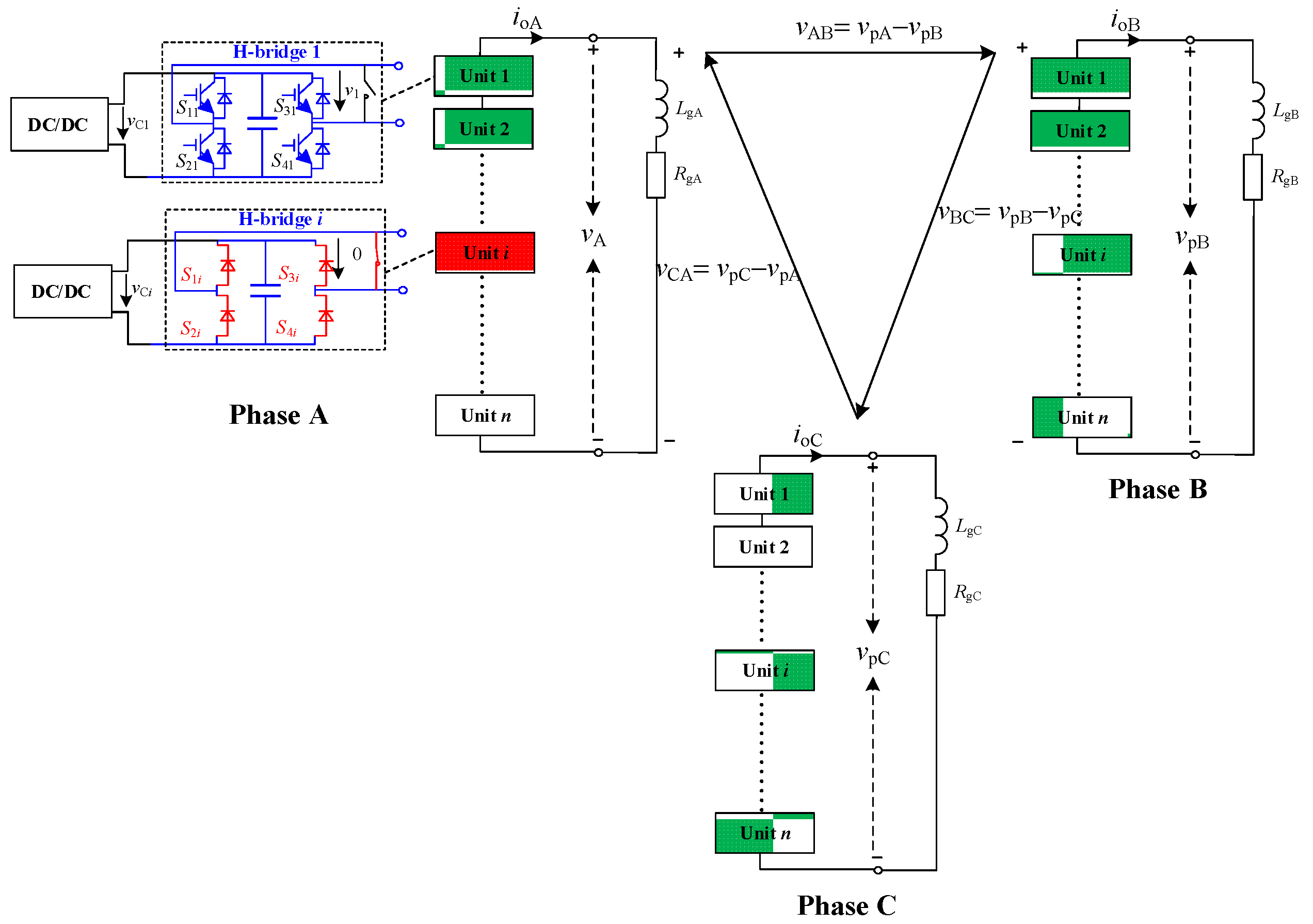
4.1. Fault Ride-through Strategy under Controllable Faults
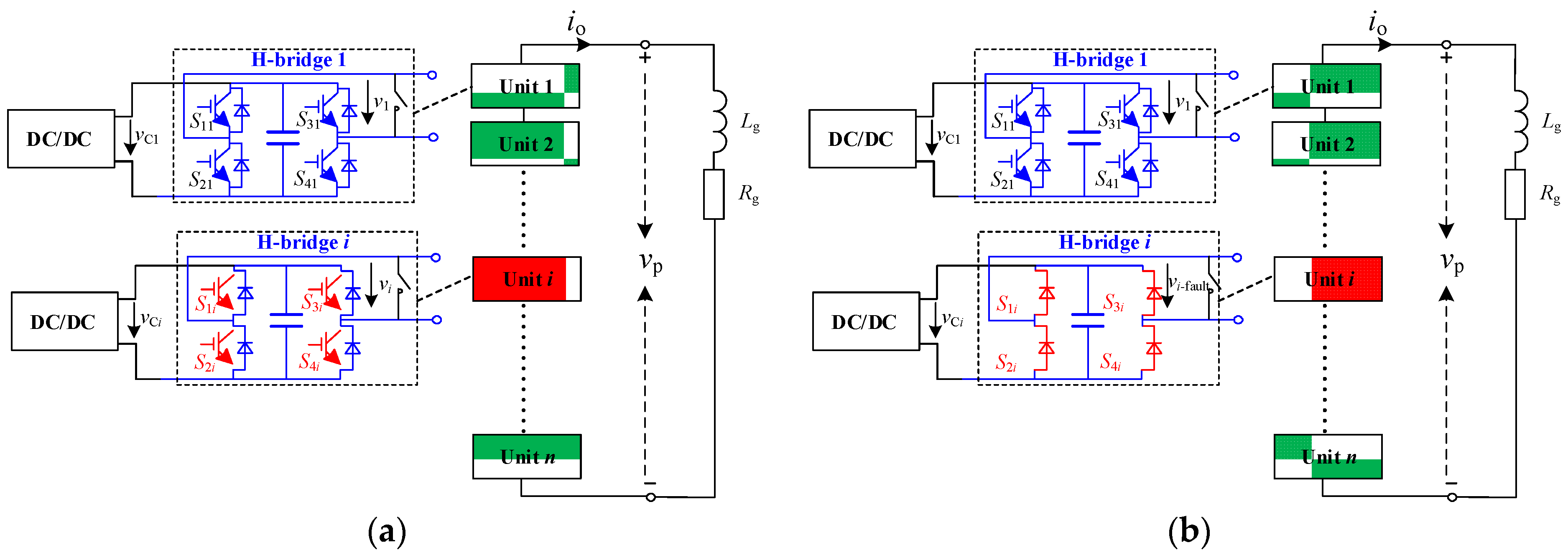
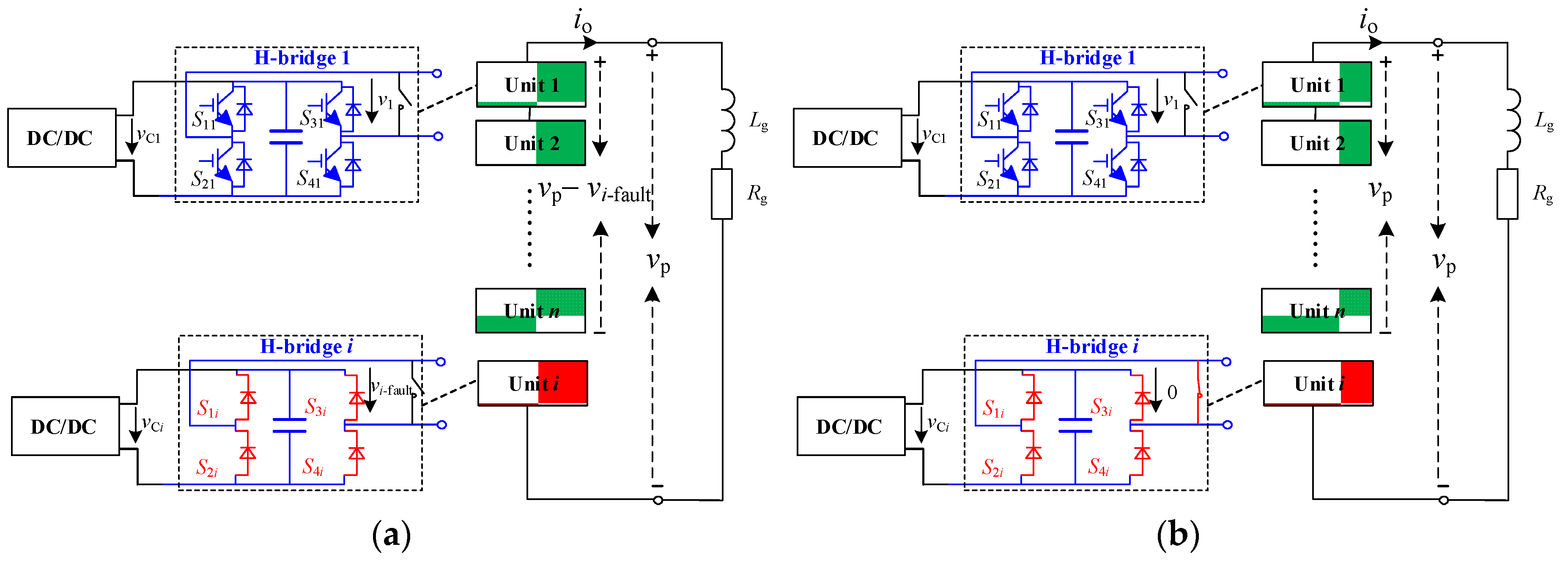
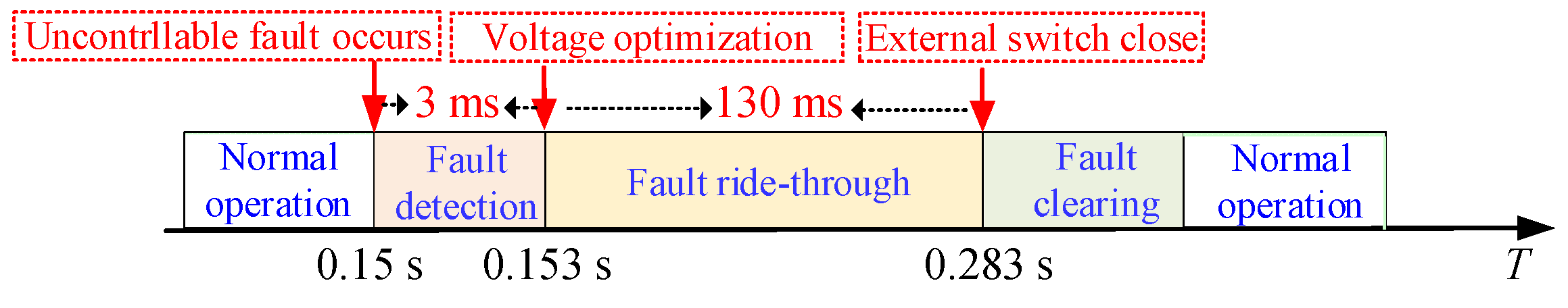
4.2. Fault Ride-through Strategy under Uncontrollable Faults
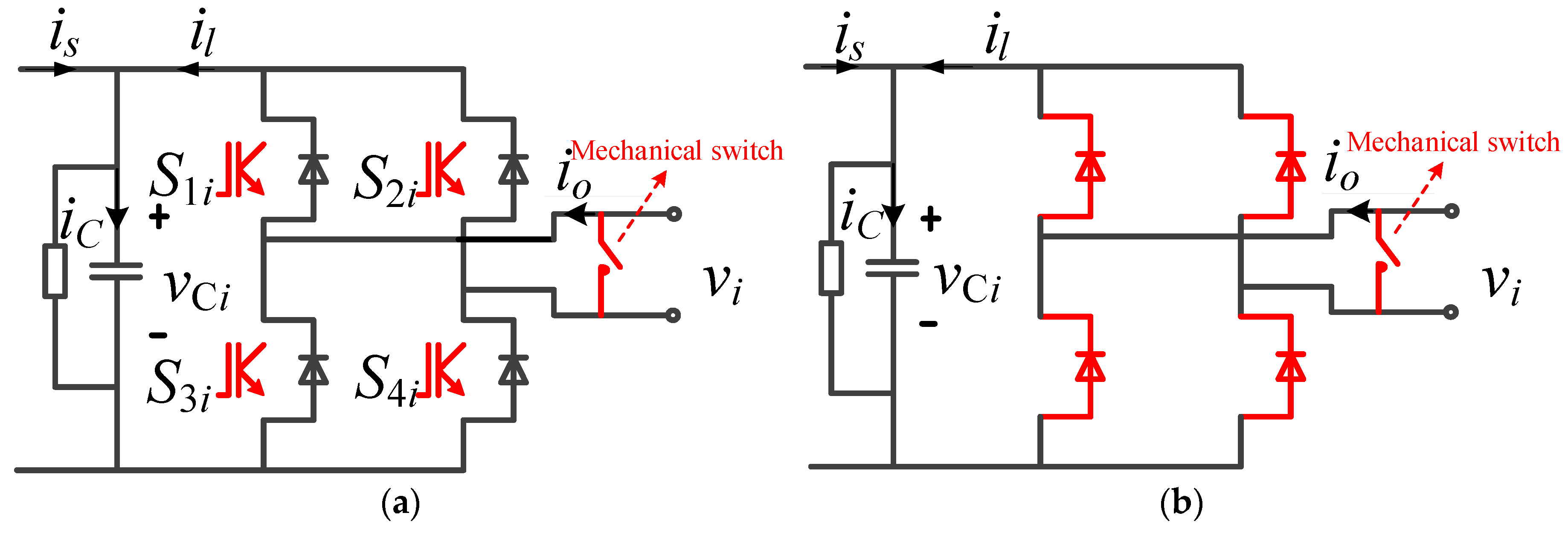
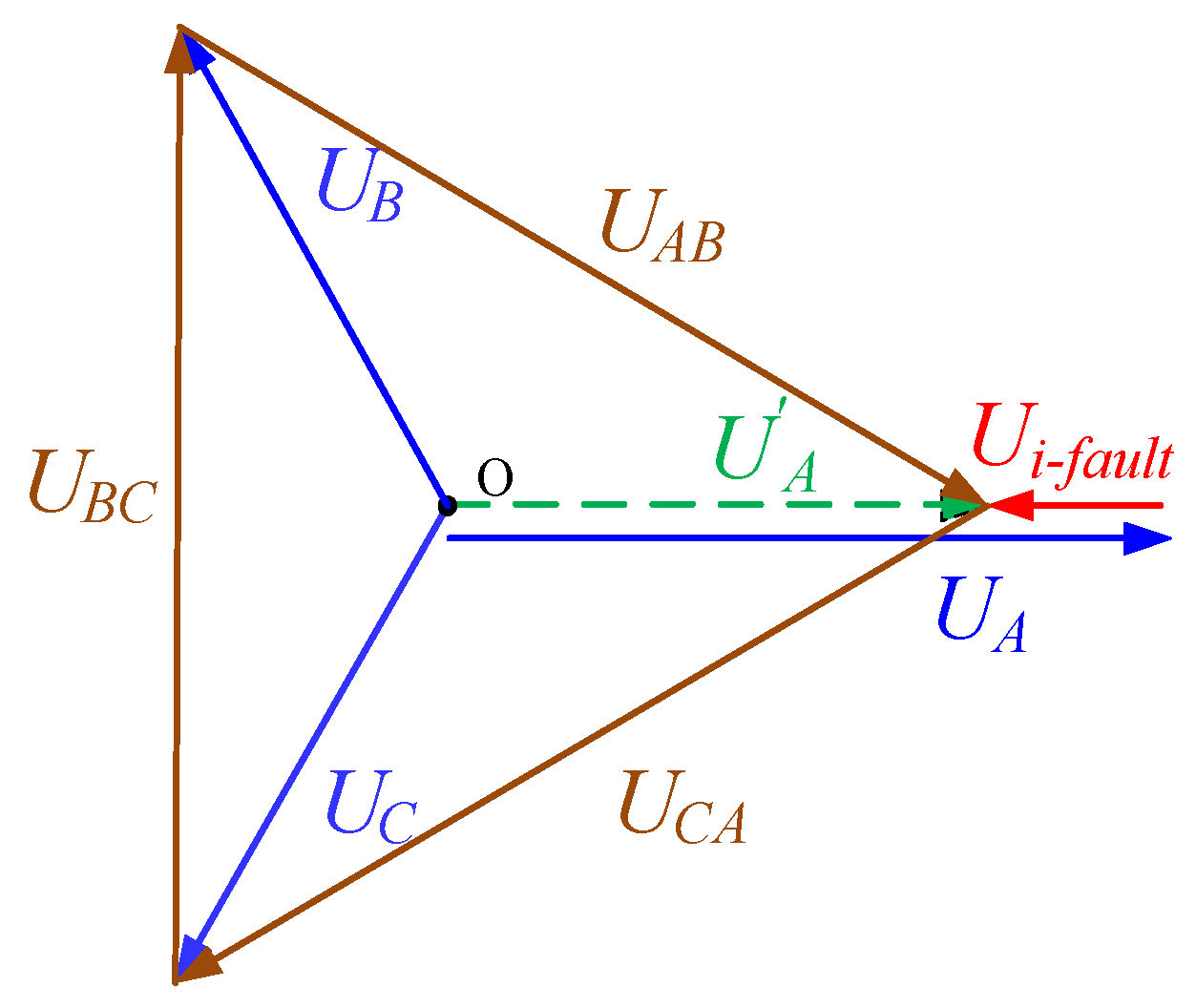
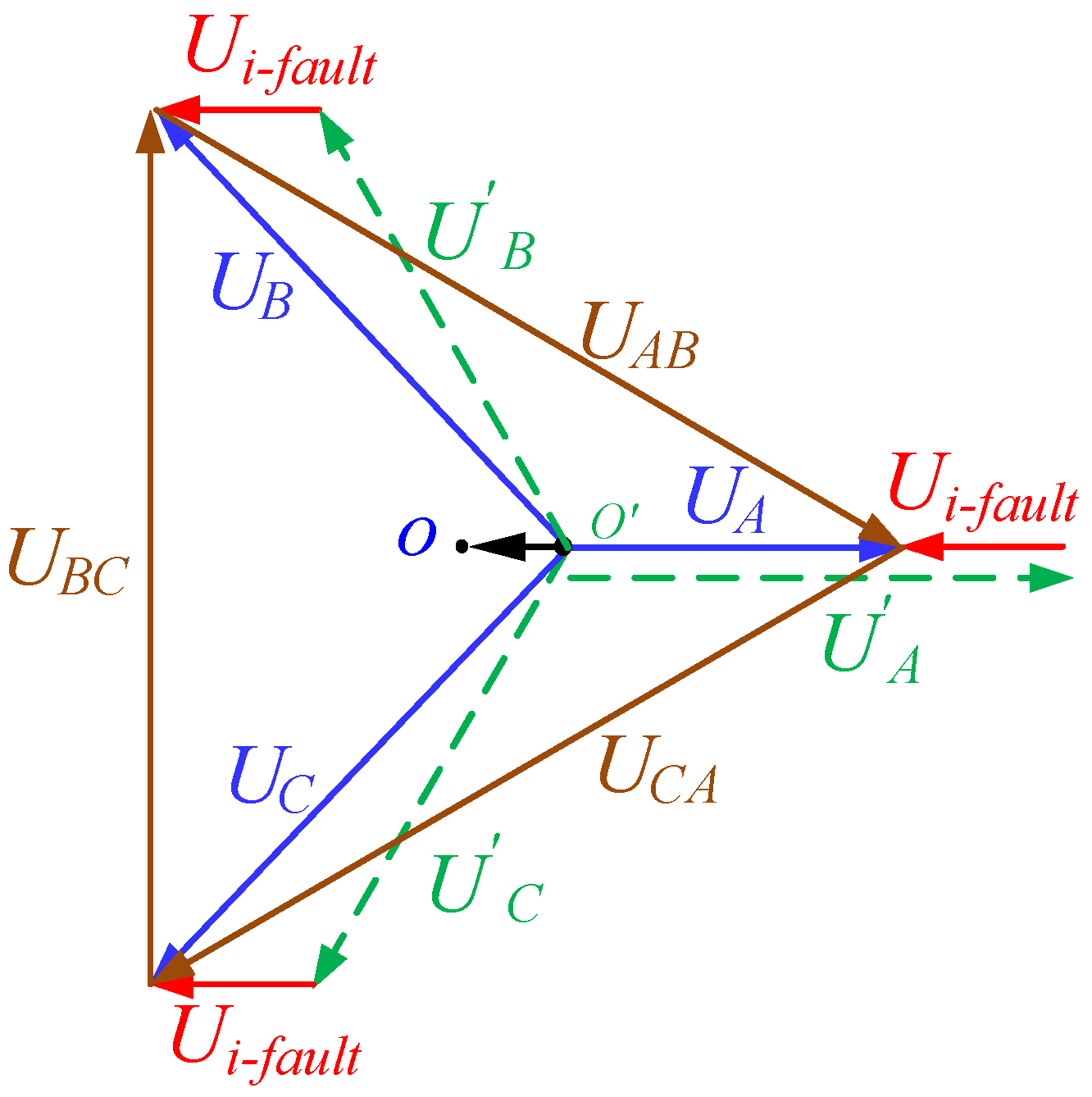
4.2.1. Intra-Phase Optimization
4.2.2. Inter-Phase Optimization
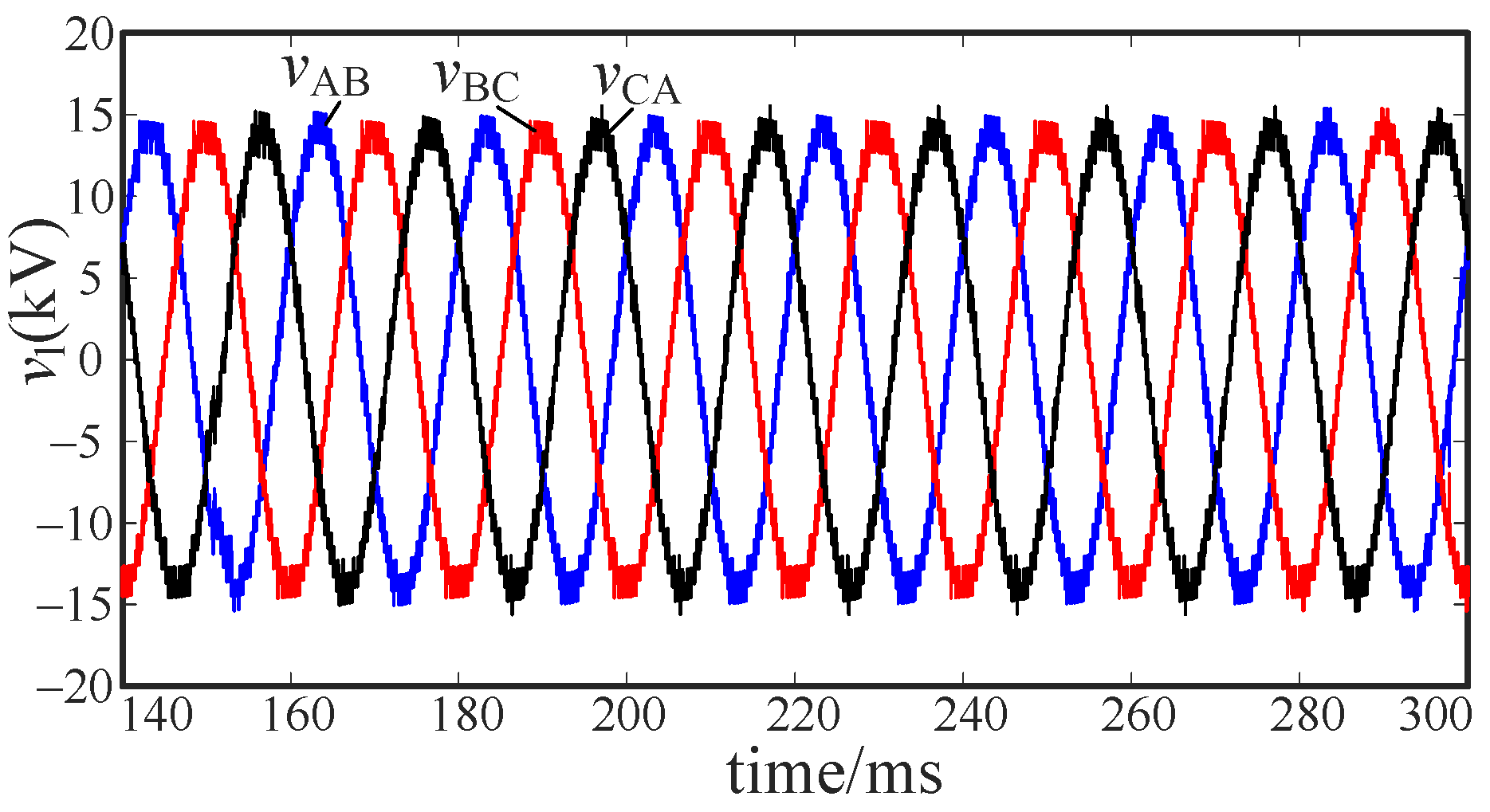
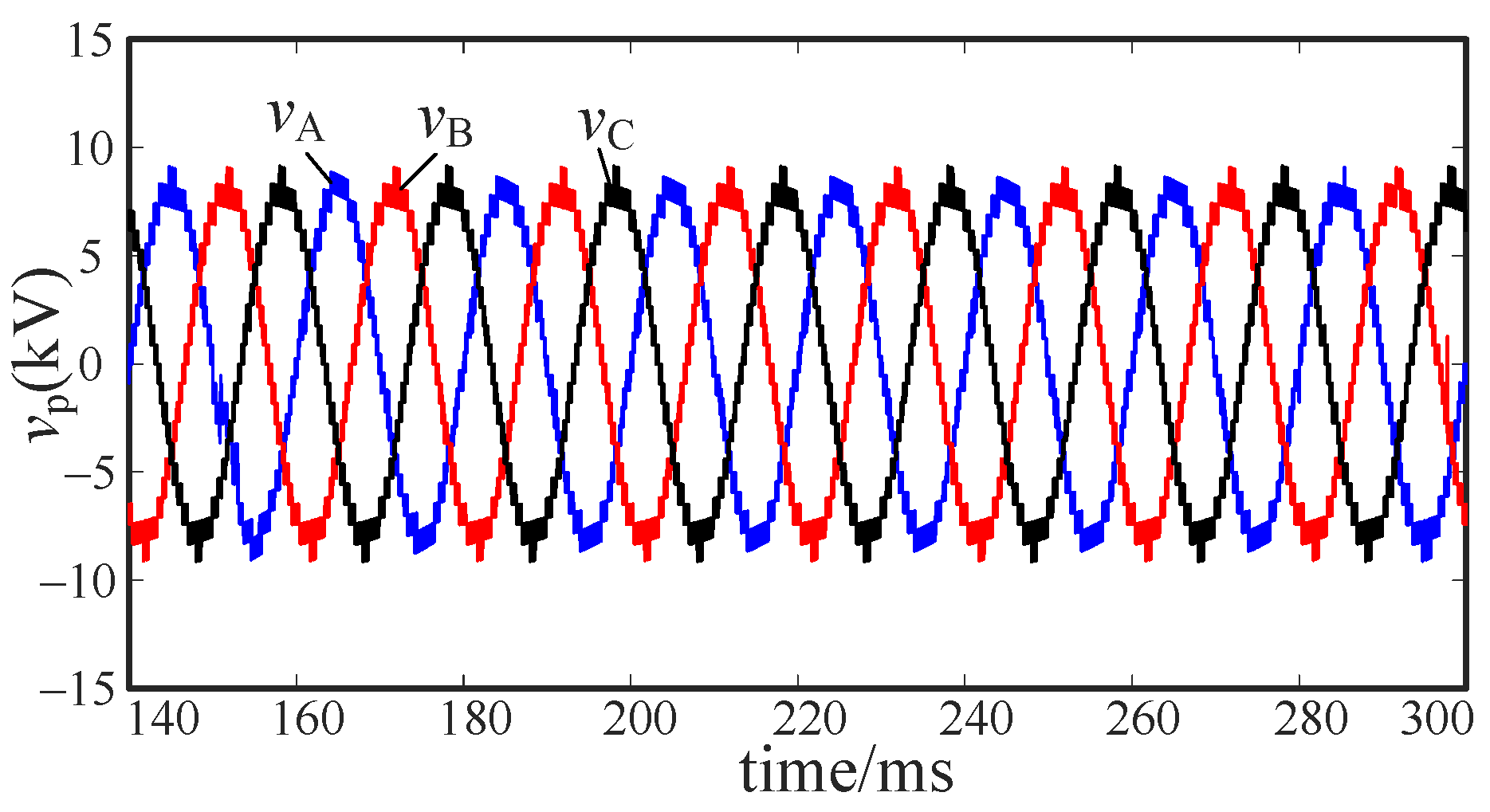
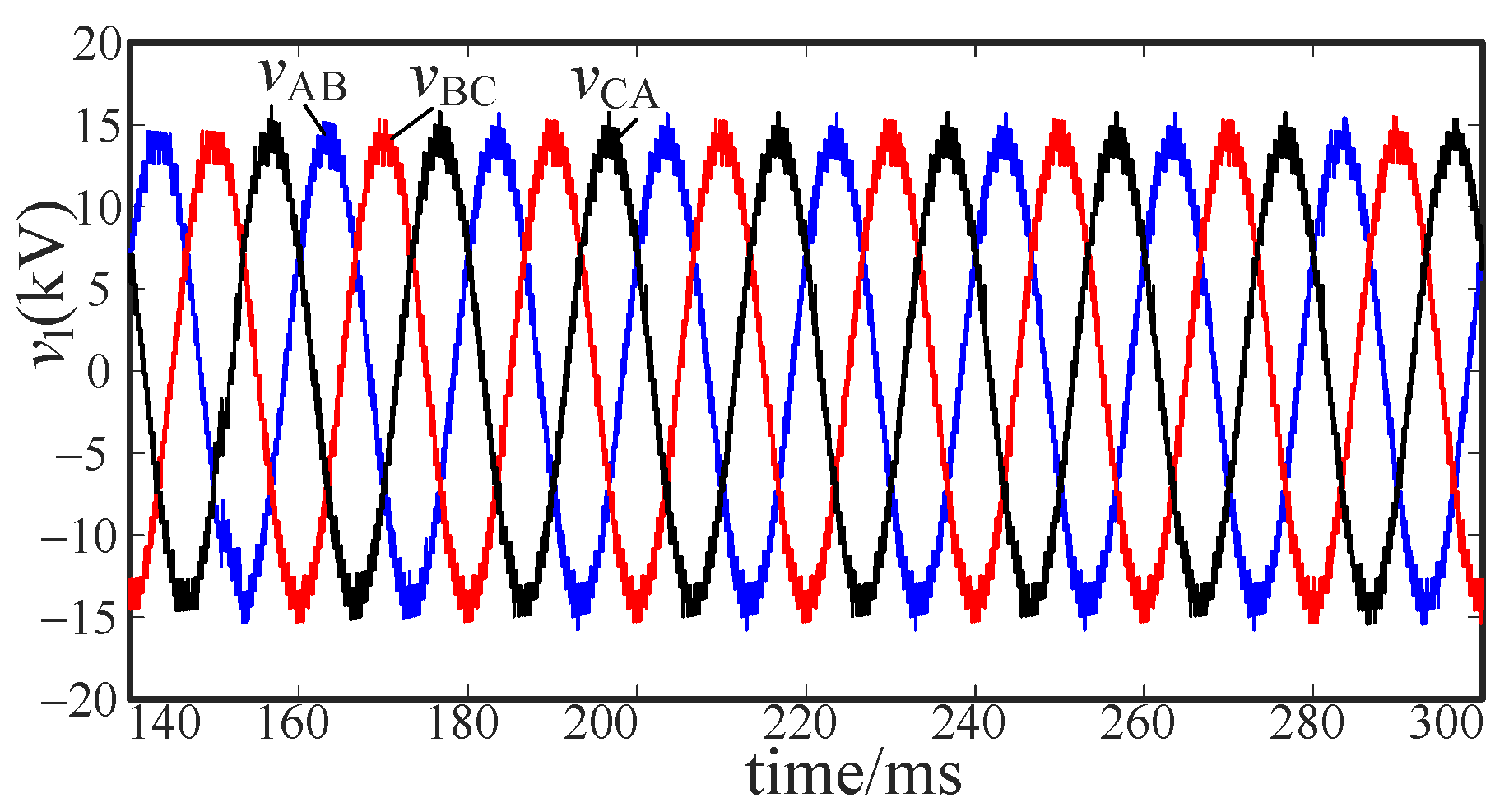
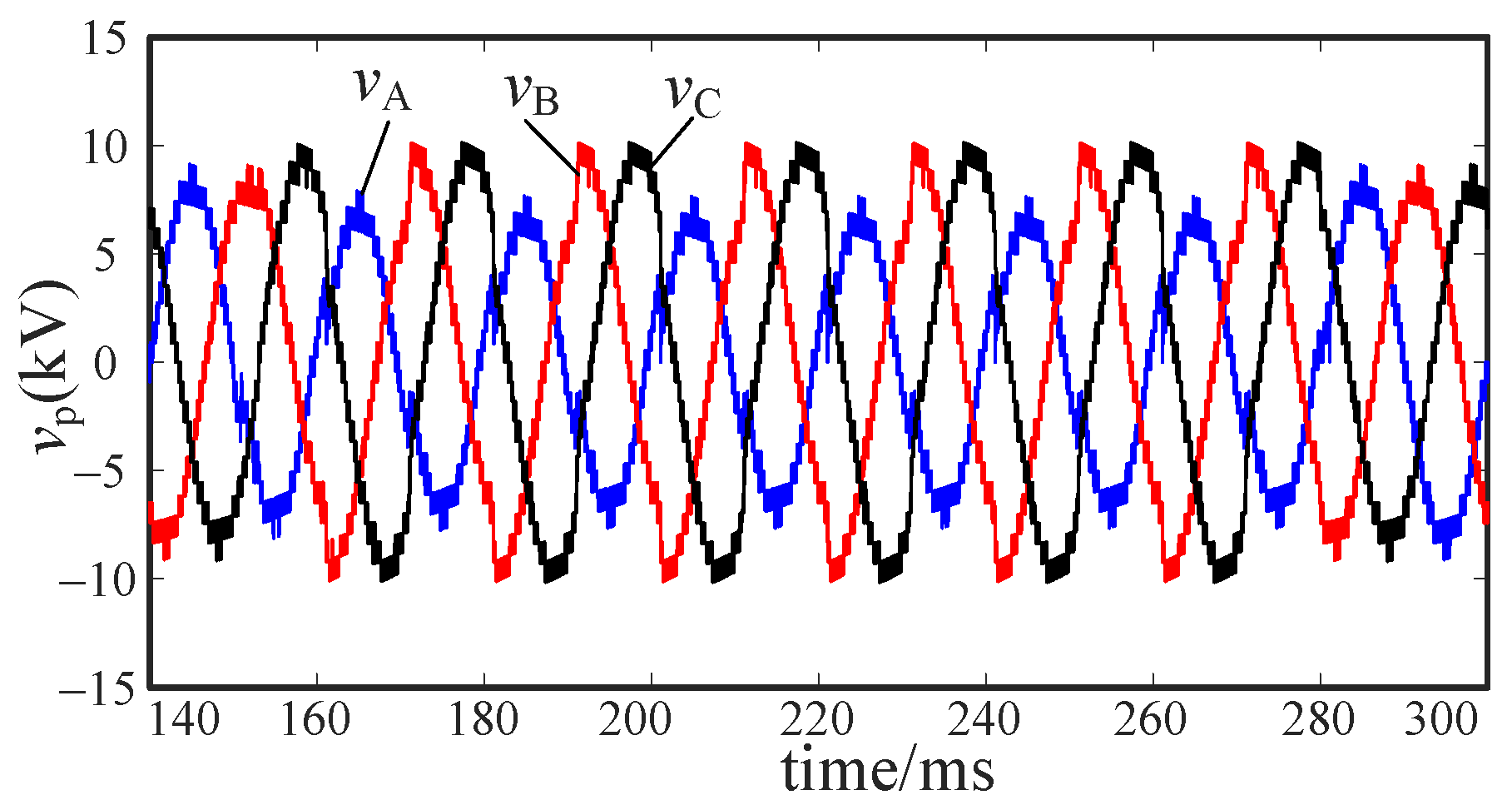
5. Simulation and Verification
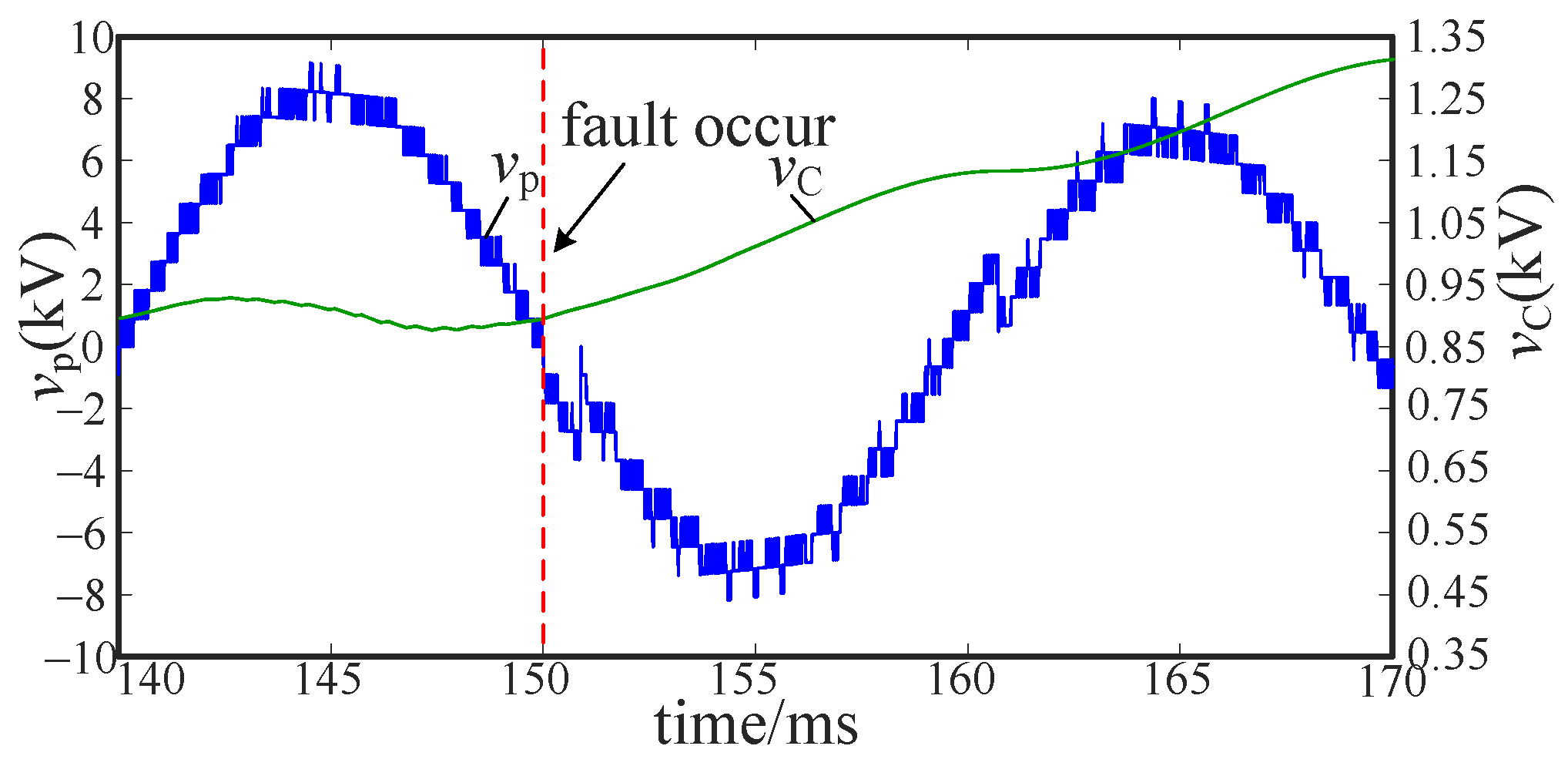
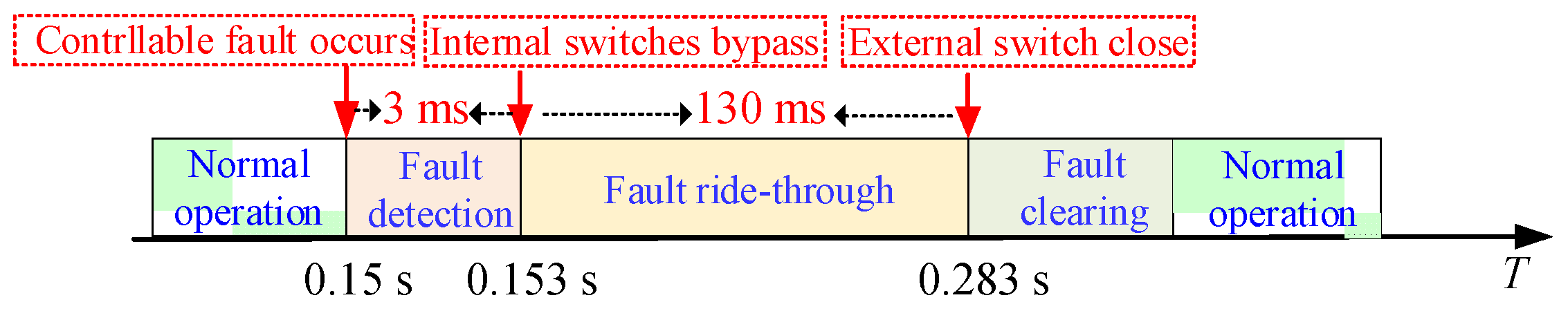
5.1. Controllable Fault Simulation
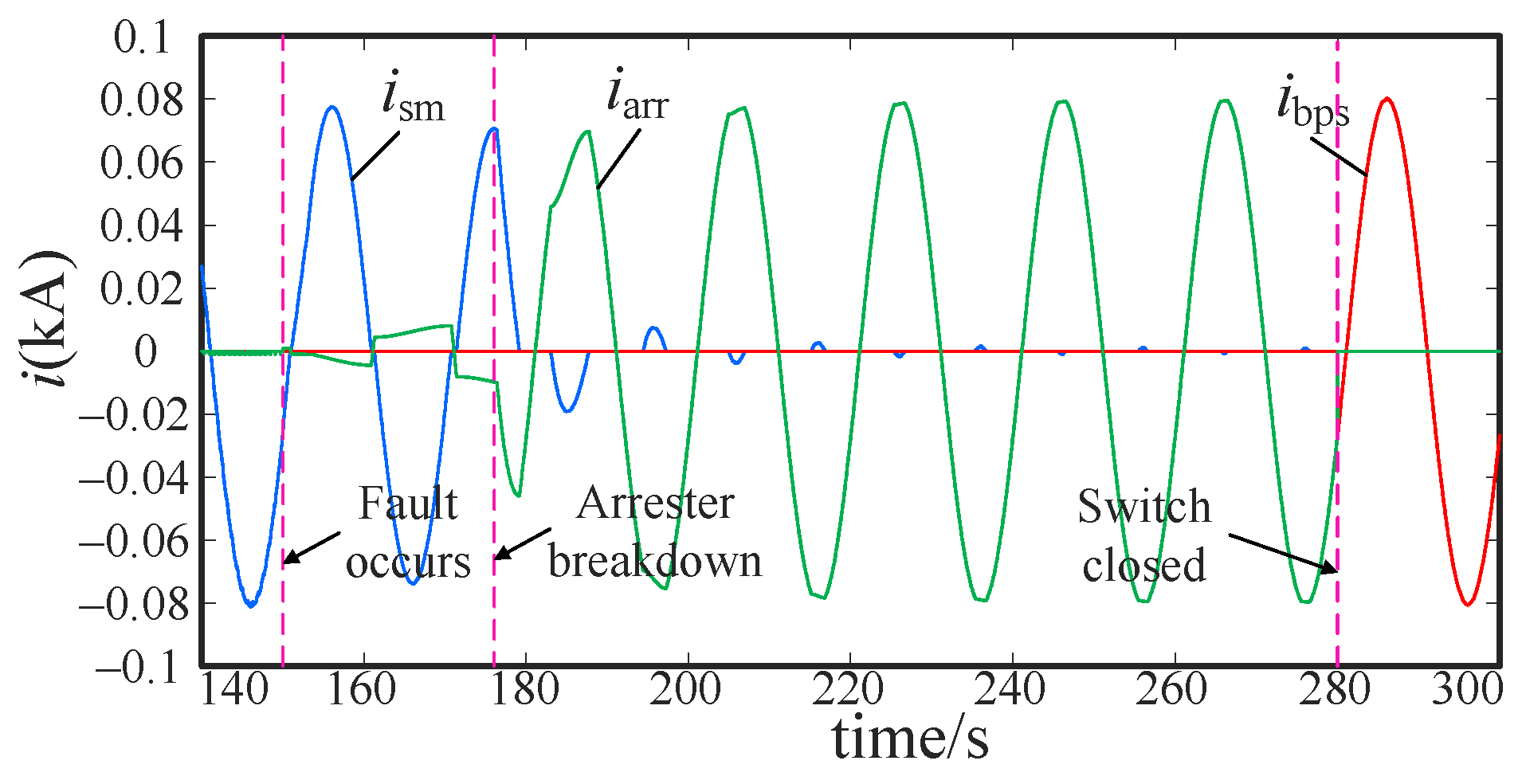
5.2. Uncontrollable Fault Simulation
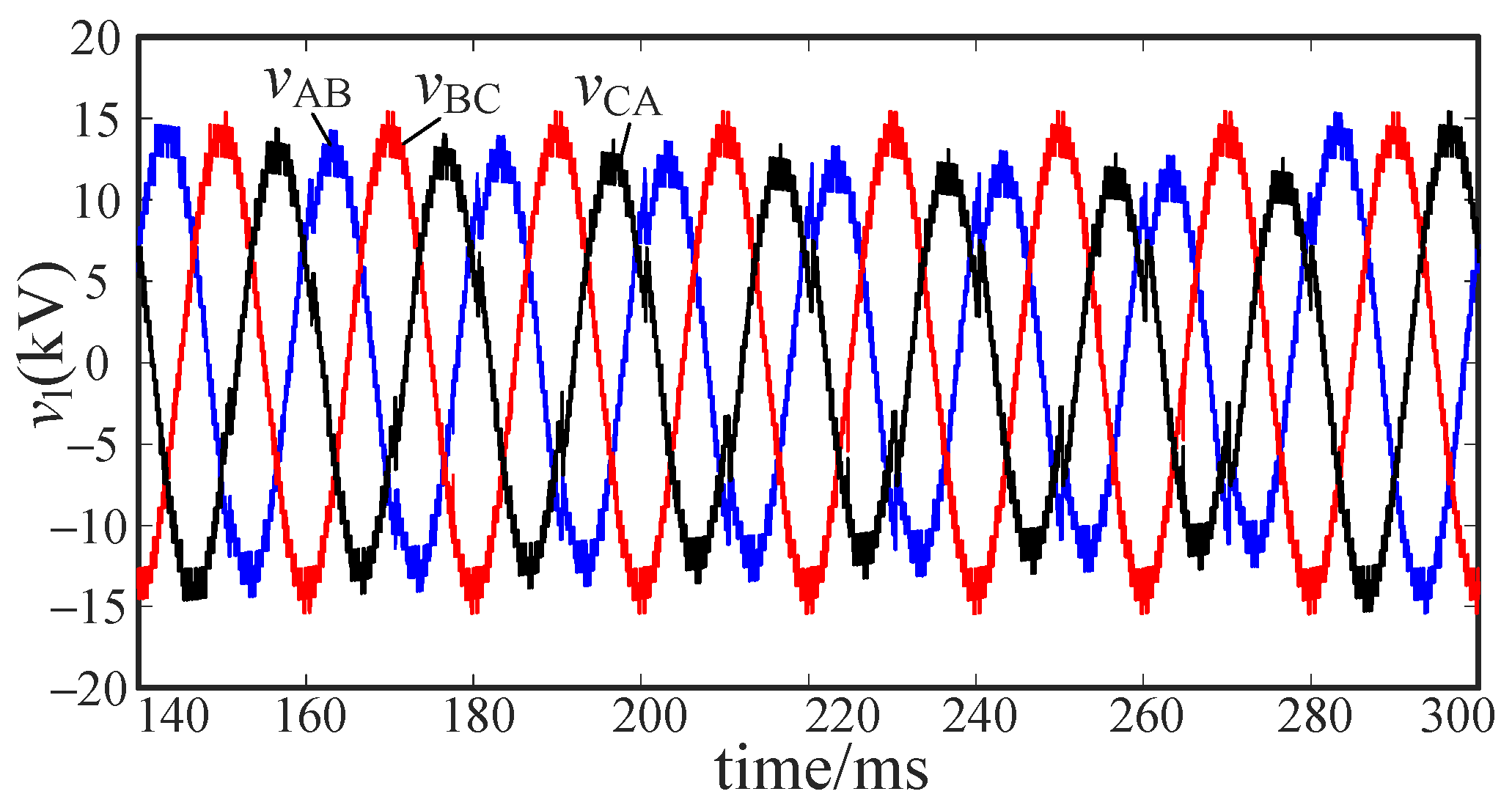
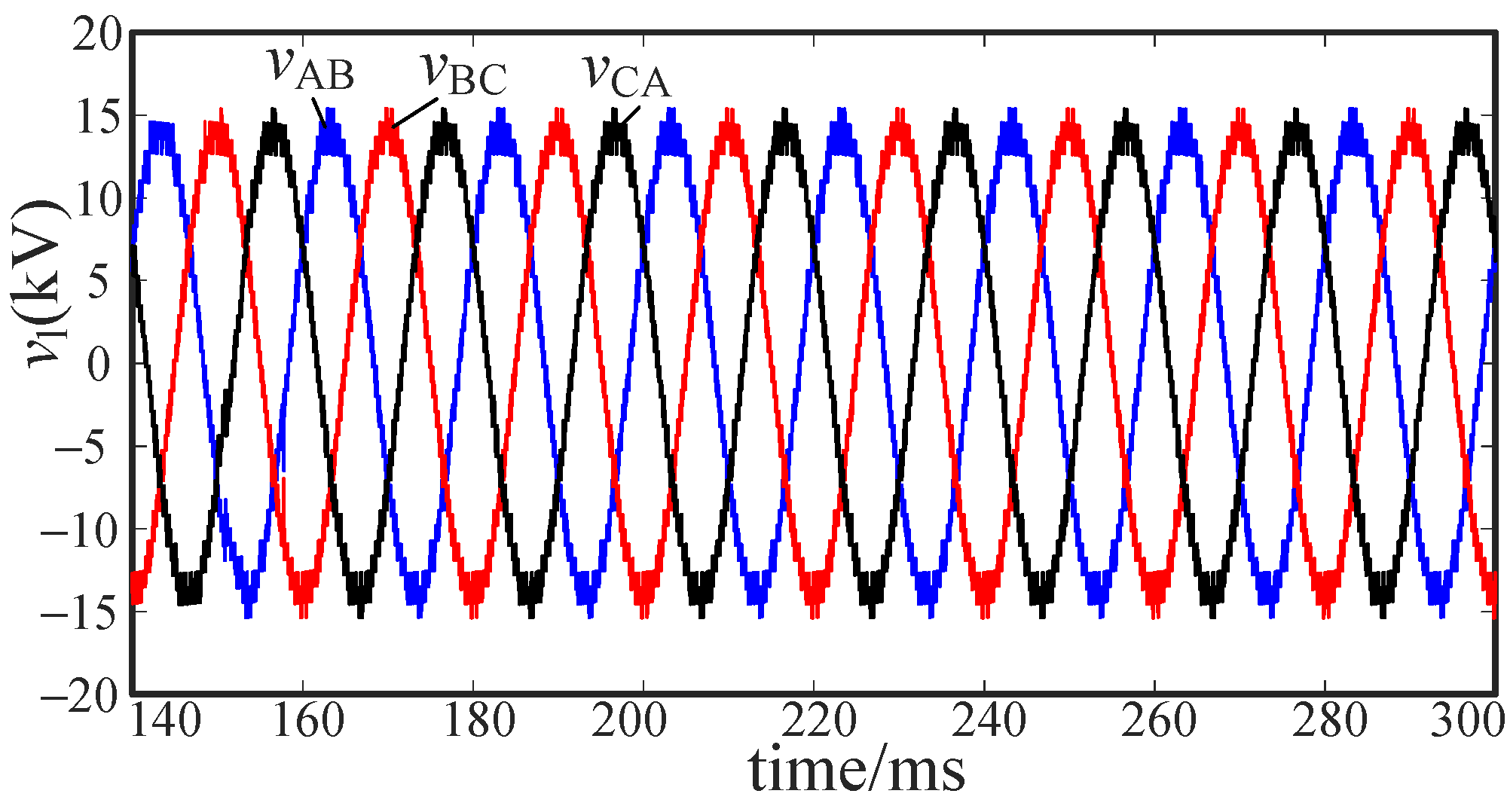
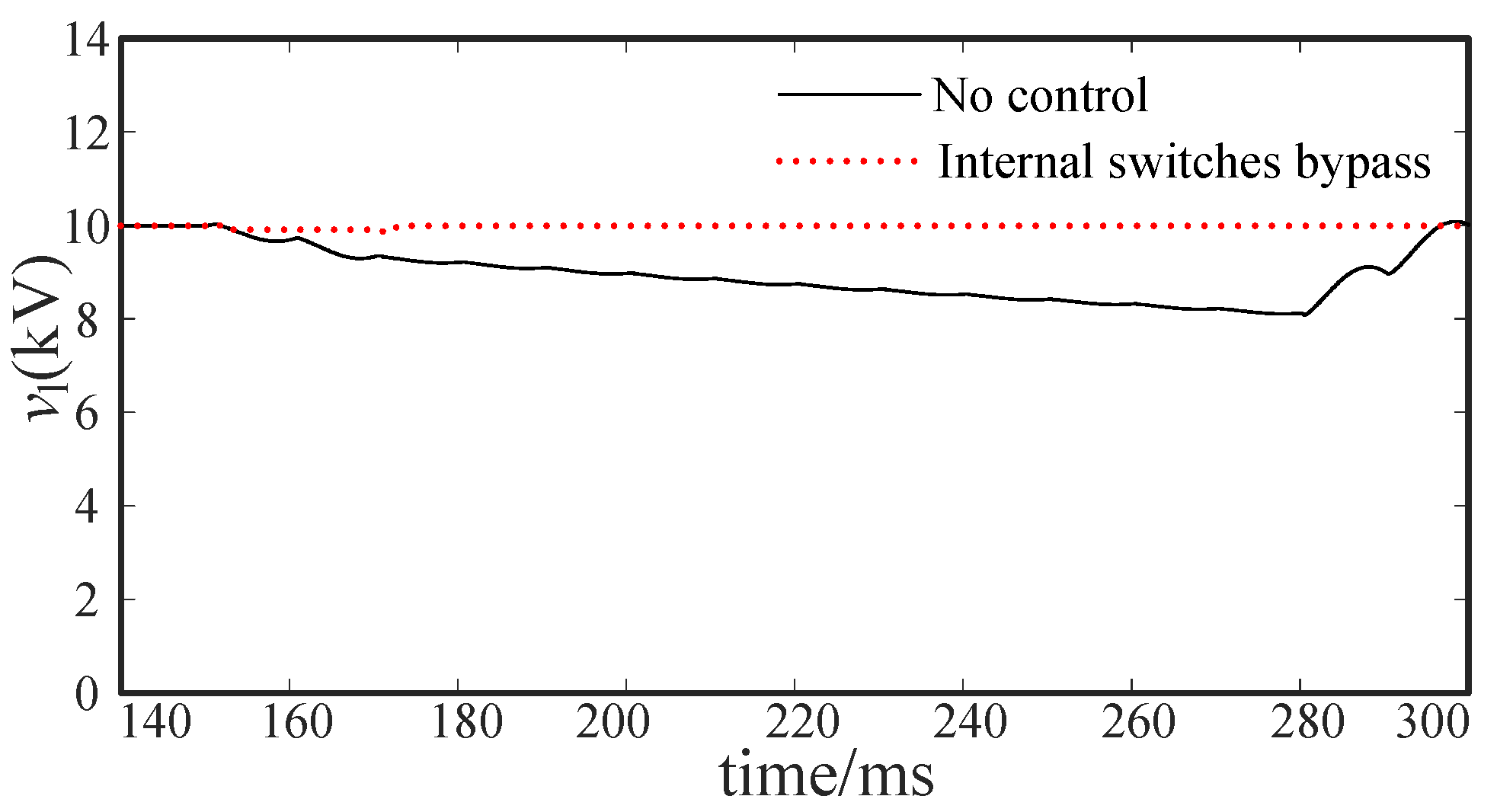
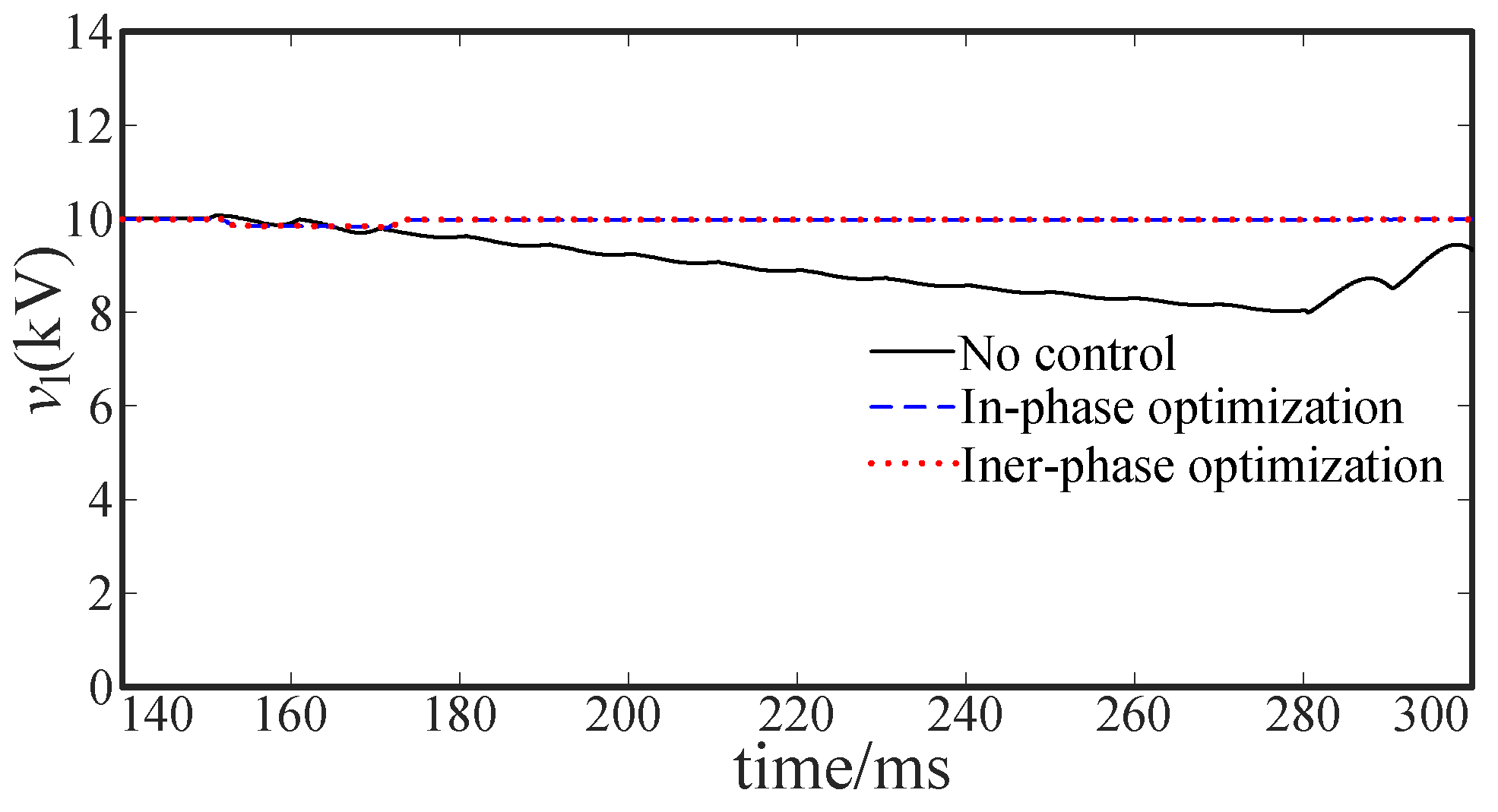
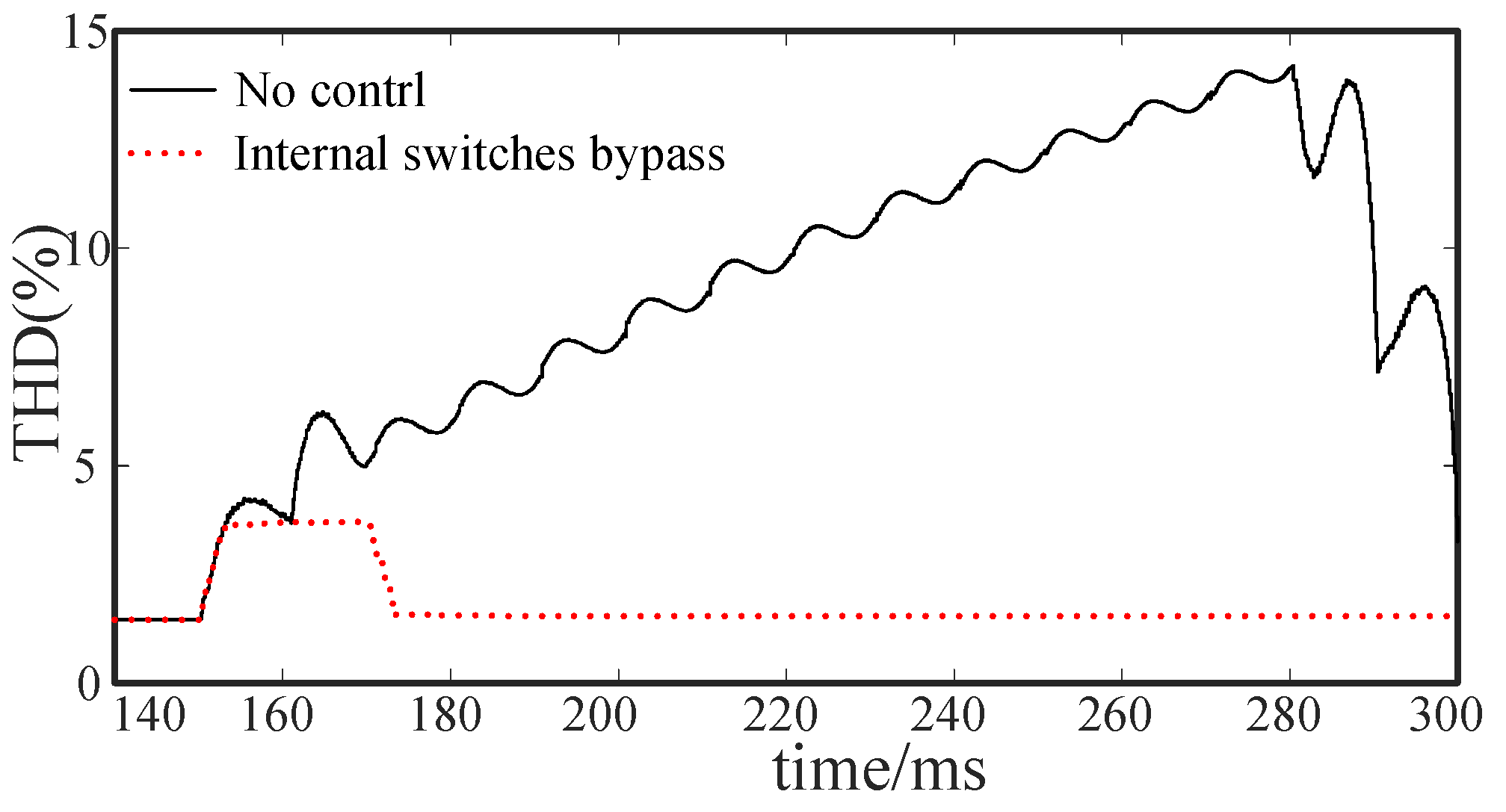
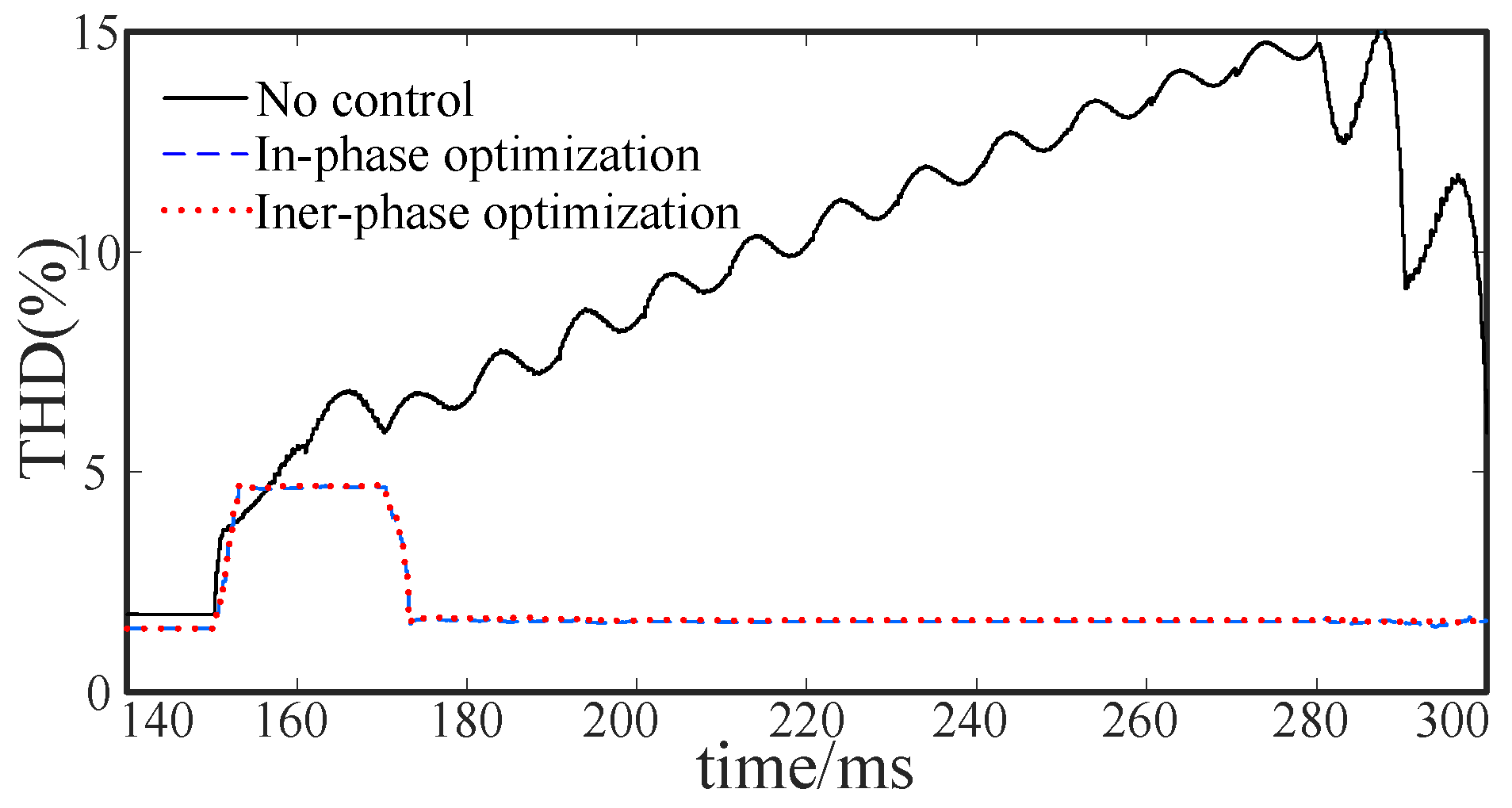
5.2.1. Intra-Phase Optimization
5.2.2. Inter-Phase Optimization
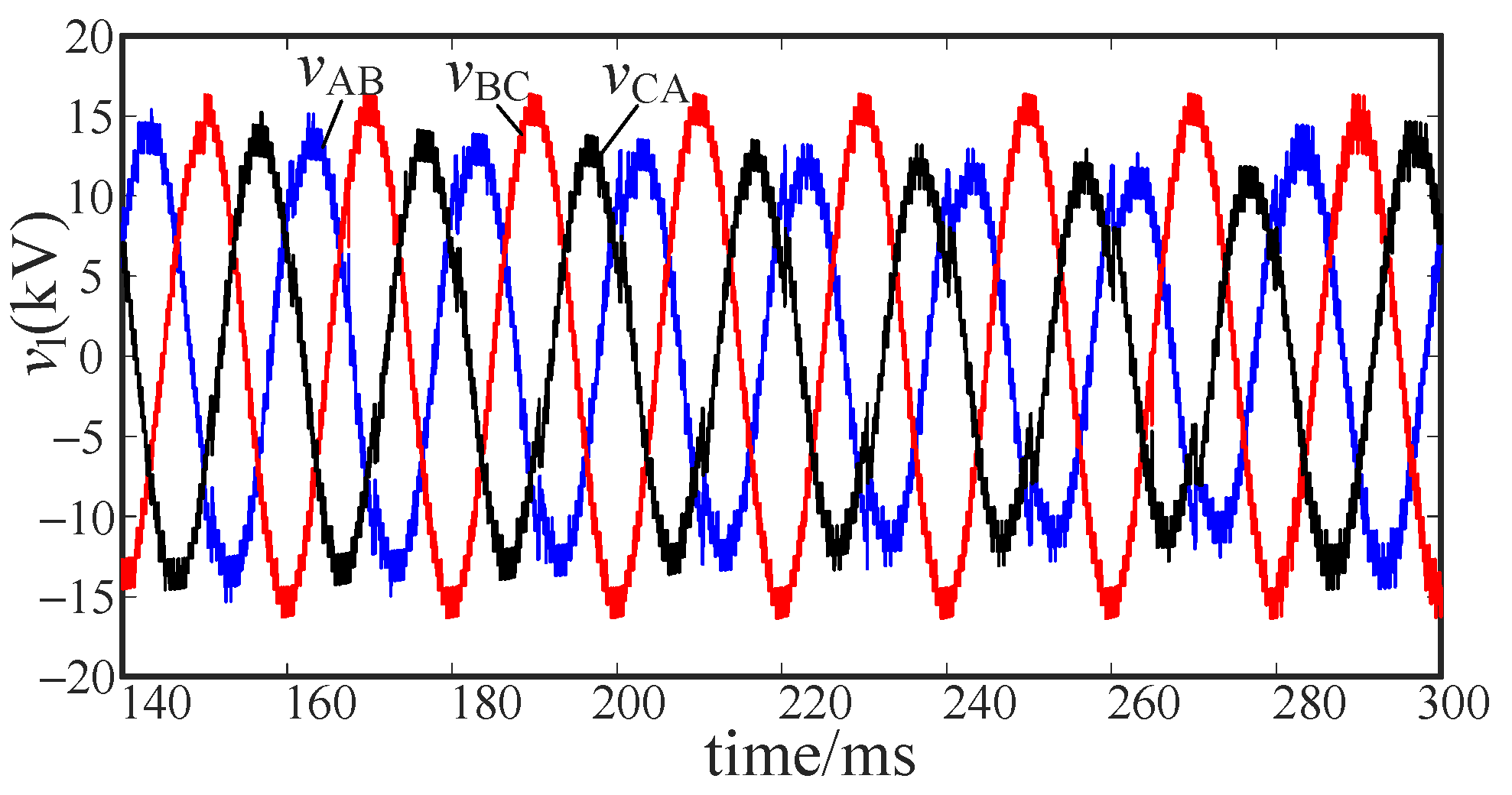
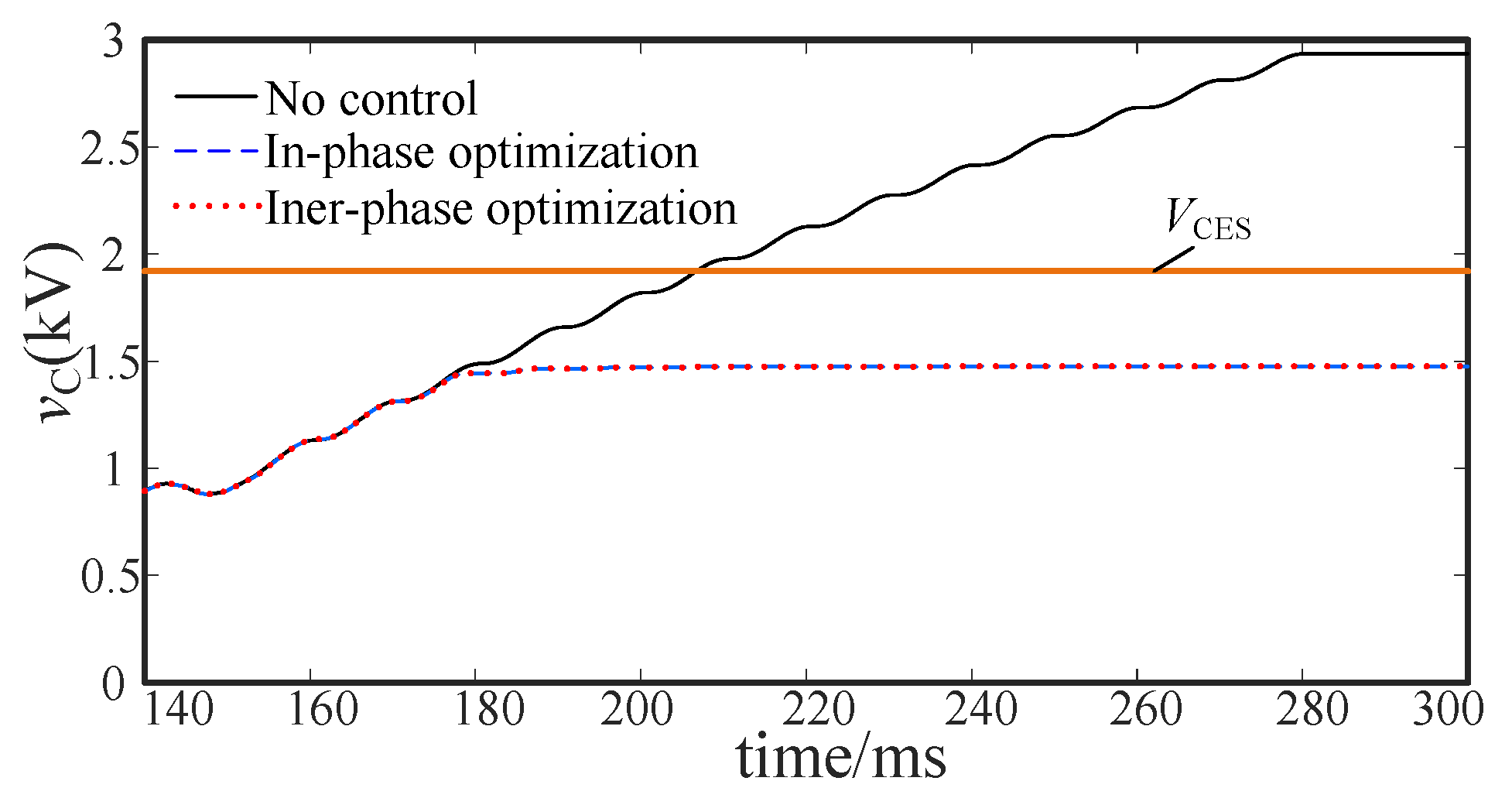
5.3. Voltage Stability Analysis
5.4. Reliability Analysis of Fault Ride-through Strategy
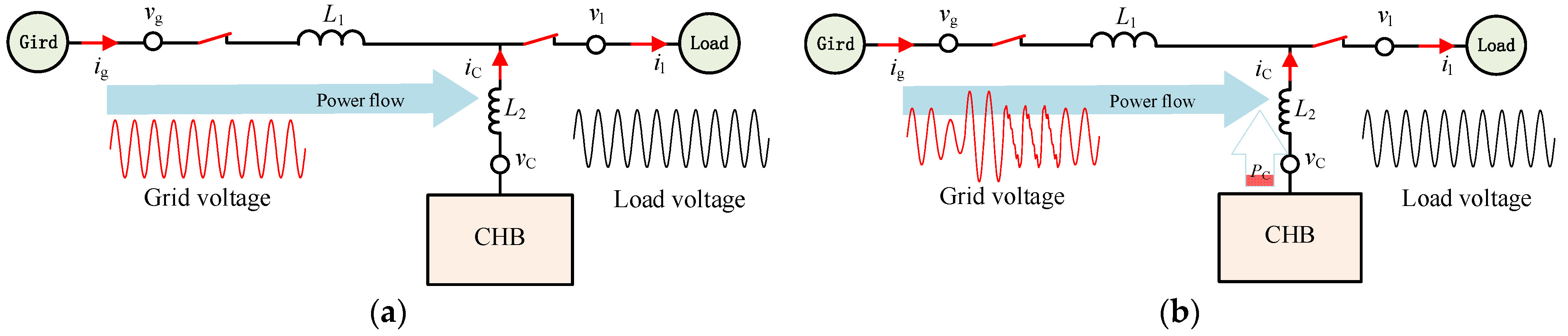
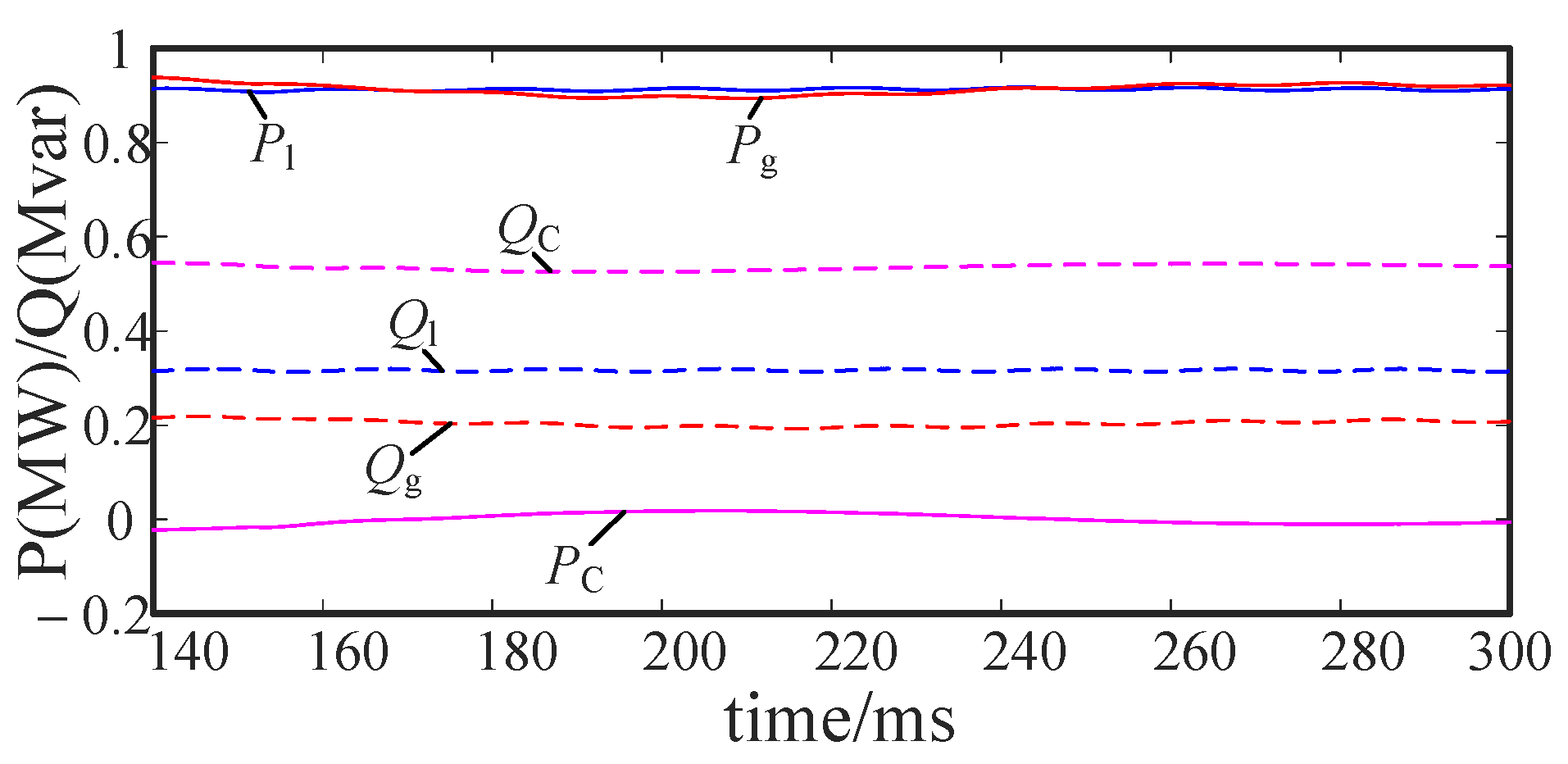
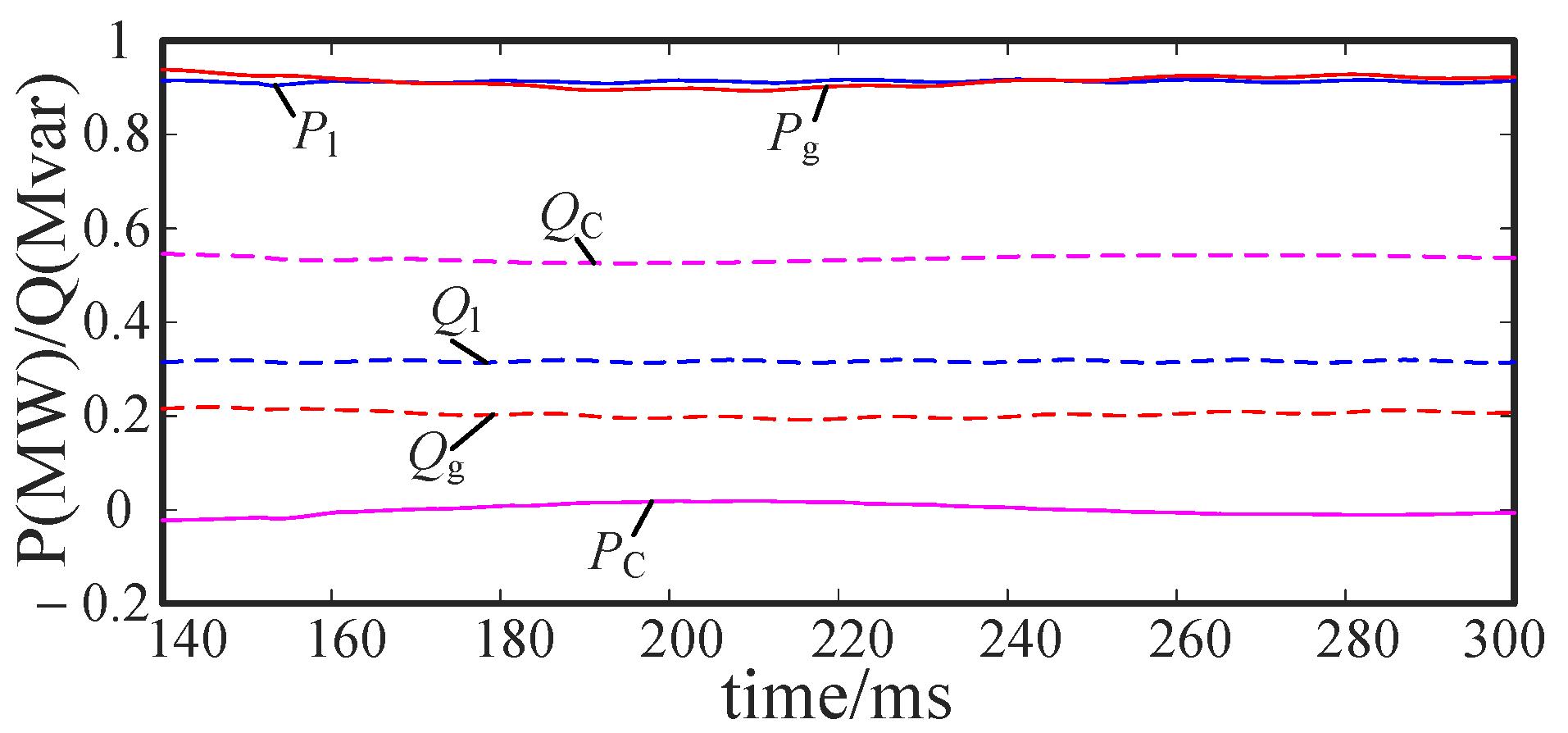
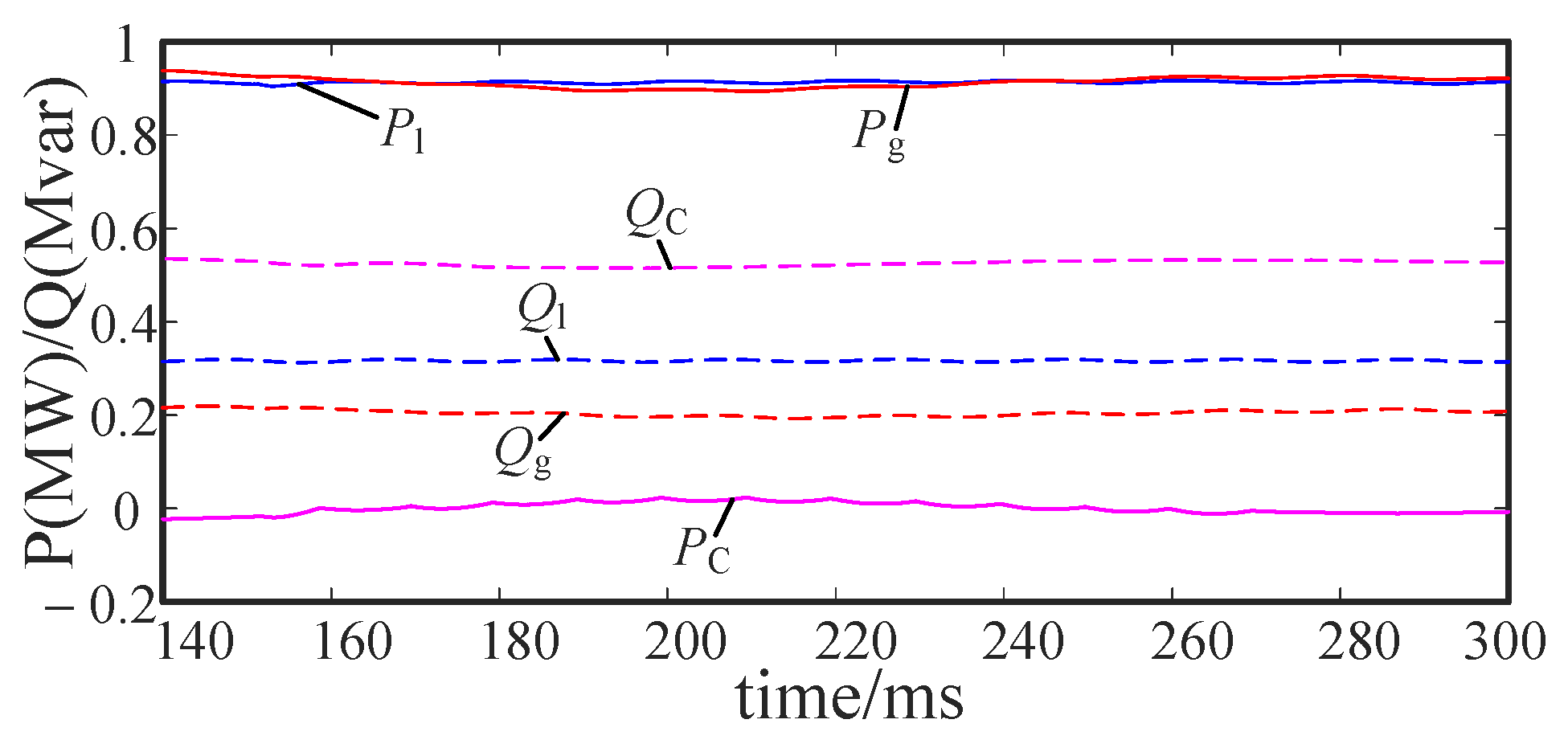
5.5. Power Transmission Analysis
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Conventional mechanical switches cannot effectively bypass the failed power unit. Its slow closing speed will cause the output voltage quality to drop and the components to be damaged.
- (2)
- When a controllable fault occurs in the power unit, the internal switch bypass fault ride-through strategy is adopted. An intra-phase optimization or an inter-phase optimization fault ride-through strategy is adopted when an uncontrollable fault occurs in the power unit.
- (3)
- Compared with the no-fault ride-through strategy, the voltage stability and reliability are significantly improved, and the proposed fault ride-through strategy has economic advantages.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, B.; Zou, J.; Chung, C.Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, N.; Voropai, N.; Xu, D. Multi-microgrid Energy Management Systems: Architecture, Communication, and Scheduling Strategies. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2021, 9, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomin, N.; Zhukov, A.; Kurbatsky, V.; Sidorov, D.; Negnevitsky, M. Development of automatic intelligent system for on-line voltage security control of power systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Manchester PowerTech, Manchester, UK, 18–22 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hafezi, H.; D’Antona, G.; Dedè, A.; della Giustina, D.; Faranda, R.; Massa, G. Power Quality Conditioning in LV Distribution Networks: Results by Field Demonstration. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, X.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Yong, C.; Sidorov, D.; Lv, X. Two-Stage Active and Reactive Power Coordinated Optimal Dispatch for Active Distribution Network Considering Load Flexibility. Energies 2020, 13, 5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.; Elliott, N. A new UPS topology for multi-megawatt medium voltage power protection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Electronics for Sustainable Energy Systems (IESES), Hamilton, New Zealand, 31 January–2 February 2018; pp. 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Kouro, S.; Malinowski, M.; Gopakumar, K.; Pou, J.; Franquelo, L.G.; Wu, B.; Rodriguez, J.; Pérez, M.A.; Leon, J.I. Recent Advances and Industrial Applications of Multilevel Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2553–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Lin, C.; Deng, Q.; Ge, X.; Gou, B. Fast Diagnosis Scheme for Multiple Switch Faults in Cascaded H-Bridge Multilevel Converters. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 1000–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Sharma, S.K. A Literature Review of IGBT Fault Diagnostic and Protection Methods for Power Inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 1770–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Bryant, A.; Mawby, P.; Xiang, D.; Ran, L.; Tavner, P. An Industry-Based Survey of Reliability in Power Electronic Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, U.; Blaabjerg, F.; Lee, K. Study and Handling Methods of Power IGBT Module Failures in Power Electronic Converter Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 2517–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Yu, N.; Xu, X.; Bai, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J. Tunnel Magnetoresistance-Based Short-Circuit and Over-Current Protection for IGBT Module. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 10930–10944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyshabouri, Y.; Iman-Eini, H. A New Fault-Tolerant Strategy for a Cascaded H-Bridge Based STATCOM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 6436–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, N.; Anand, A.; Jagadanand, G.; George, S. Output voltage modeling of cascaded H-bridge multilevel inverters under open-transistor fault. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Industrial Electronics and Applications Conference (IEACon), Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 20–22 November 2016; pp. 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Mao, W.; Li, F.; Wang, F.; Wang, X. Module Power Balance Control and Redundancy Design Analysis of Cascaded PV Solid-State Transformer Under Fault Conditions. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Huang, A.Q. Fault-Tolerant Design and Control Strategy for Cascaded H-Bridge Multilevel Converter-Based STATCOM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2700–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Mao, C.; Wang, D.; Nie, S.; Yang, Y. A Short-Time Transition and Cost Saving Redundancy Scheme for Medium-Voltage Three-Phase Cascaded H-Bridge Electronic Power Transformer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 9242–9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, R.; Xu, R.; Xu, D.; Wang, W. Seamless Transition Control for Modular Multilevel Converters When Inserting a Cold-Reserve Redundant Submodule. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 4052–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, P.; Yang, S.; Wang, P. Reliability- and Cost-Based Redundancy Design for Modular Multilevel Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirafzal, B. Survey of Fault-Tolerance Techniques for Three-Phase Voltage Source Inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5192–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, V.; Sadigh, A.K.; Corzine, K.A.; Enslin, J.H.; Rodriguez, J.; Blaabjerg, F. A New Control Technique for Improved Active-Neutral-Point-Clamped (I-ANPC) Multilevel Converters Using Logic-Equations Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Konstantinou, G.; Hredzak, B.; Agelidis, V.G. Operation of Cascaded H-Bridge Multilevel Converters for Large-Scale Photovoltaic Power Plants Under Bridge Failures. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 7228–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouni, S.; Narimani, M.; Cheng, Z.; Zargari, N.R. A New Postfault Control Method for CHB Inverter to Increase Maximum Output Voltage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 5499–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Symbol | Quantity | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Un | Voltage level | 10 kV |
| fn | Rated frequency | 50 Hz |
| In | Rated current | 58 A |
| cosϕ | Load power factor | 0.7 |
| fs | Switching frequency | 800 |
| n | Unit module number | 12 |
| tc | AC contactor closing delay | 130 ms |
| td | Fault detection time | 3 ms |
| E1/E2 | Rated voltage ratio | 10,000/690 |
| θ | Phase shift angle | 12° |
| Str | Rated power | 1.5 MVA |
| C | DC capacitor | 2520 µF |
| R | Discharge resistance | 70 kΩ |
| UC | Rated DC voltage | 900 V |
| Ues | Energy storage voltage | 690 V |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; Hu, W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Han, M.; Yang, F.; Zuo, W. Mechanical Switch Based Adaptive Fault Ride-through Strategy for Power Quality Improvement Device. Energies 2021, 14, 6623. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206623
Shen Y, Hu W, Xiao Y, Zhang G, Han M, Yang F, Zuo W. Mechanical Switch Based Adaptive Fault Ride-through Strategy for Power Quality Improvement Device. Energies. 2021; 14(20):6623. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206623
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yu, Wei Hu, Yaoyao Xiao, Ganghua Zhang, Mingyu Han, Fan Yang, and Wenping Zuo. 2021. "Mechanical Switch Based Adaptive Fault Ride-through Strategy for Power Quality Improvement Device" Energies 14, no. 20: 6623. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206623
APA StyleShen, Y., Hu, W., Xiao, Y., Zhang, G., Han, M., Yang, F., & Zuo, W. (2021). Mechanical Switch Based Adaptive Fault Ride-through Strategy for Power Quality Improvement Device. Energies, 14(20), 6623. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206623