The Potential Utilizing of Critical Element from Coal and Combustion Residues
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
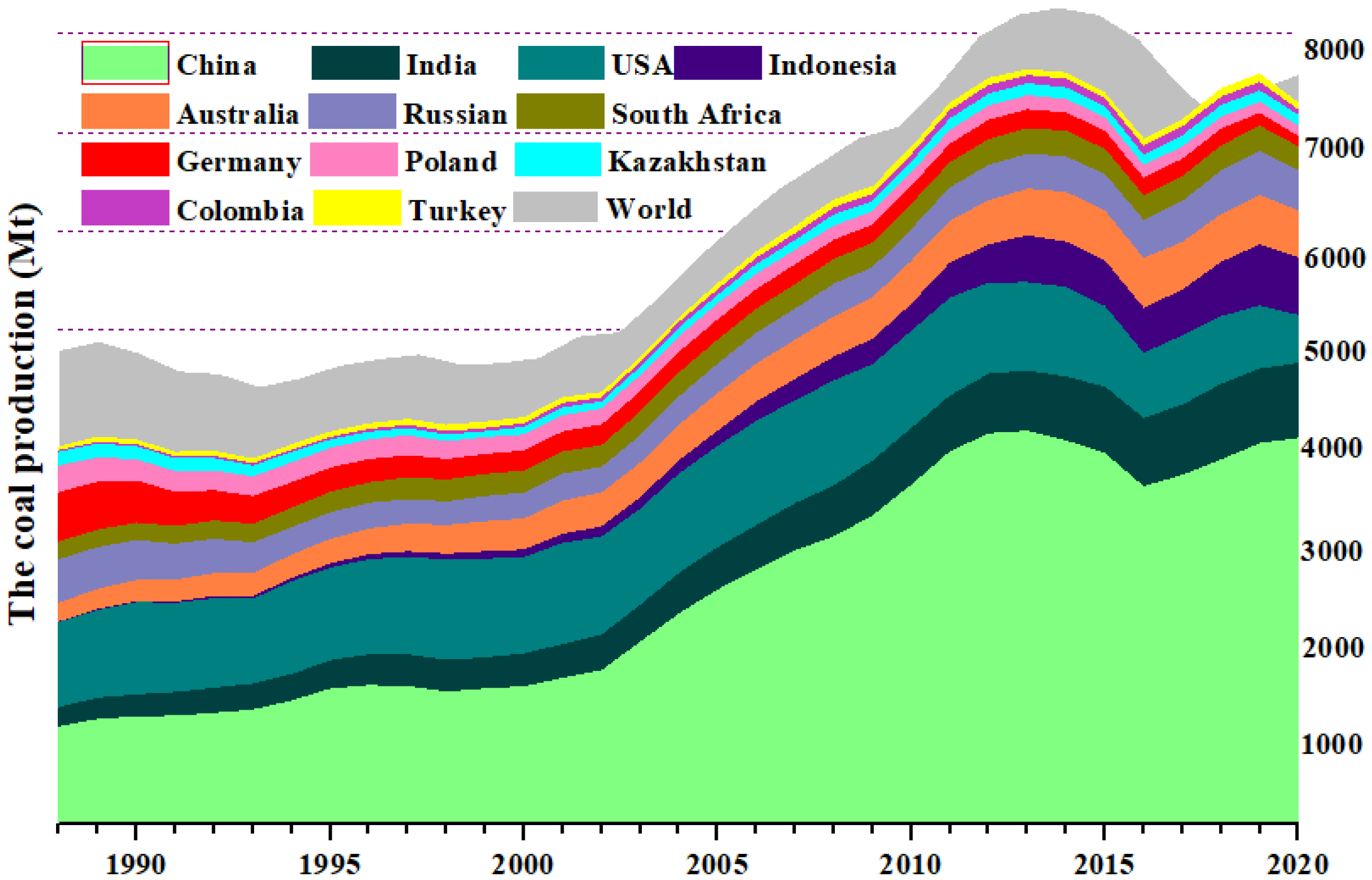
3. Coal Production and Consumption across the World
4. The Abundance of Trace Element in Coal and Coal Ash
5. The Potential Utilization of Critical Element from Coal
6. Future Prospects
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Afonso, E.L.; Carvalho, L.; Fateixa, S.; Amorim, C.O.; Amaral, V.S.; Vale, C.; Pereira, E.; Silva, C.M.; Trindade, T.; Lopes, C.B. Can contaminated waters or wastewater be alternative sources for technology-critical elements? The case of removal and recovery of lanthanides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canovas, C.R.; Chapron, S.; Arrachart, G.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Leaching of rare earth elements (REEs) and impurities from phosphogypsum: A preliminary insight for further recovery of critical raw materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, M.S.; Kotte, M.R.; Chot, M. Mining Critical Metals and Elements from Seawater: Opportunities and Challenges. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9390–9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrel, P.; Ladenberger, A.; Reimann, C.; Birke, M.; Demetriades, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Albanese, S.; Andersson, M.; Baritz, R.; Batista, M.J.; et al. GEMAS: Geochemical background and mineral potential of emerging tech-critical elements in Europe revealed from low-sampling density geochemical mapping. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 111, 104425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodius, D.; Gandha, K.; Mudring, A.V.; Nlebedim, I.C. Sustainable Urban Mining of Critical Elements from Magnet and Electronic Wastes. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.P.; Moore, K.; Kavecsanszki, D.; Finch, A.A.; Kynicky, J.; Wall, F. From mantle to critical zone: A review of large and giant sized deposits of the rare earth elements. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 315–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Etschmann, B.; Liu, W.H.; Li, K.; Dai, S.F.; Reith, F.; Falconer, D.; Kerr, G.; Paterson, D.; Howard, D.; Kappen, P.; et al. Enrichment of germanium and associated arsenic and tungsten in coal and roll-front uranium deposits. Chem. Geol. 2017, 463, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BMNT. World Mining Data 2019; Austrian Federal Ministry of Sustainability and Tourism: Vienna, Austria, 2019.
- Gutierrez-Gutierrez, S.C.; Coulon, F.; Jiang, Y.; Wagland, S.T. Rare earth elements and critical metal content of extracted landfilled material and potential recovery opportunities. Waste Manag. 2015, 42, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.X.; Fan, M.H.; Tiand, H.J. Coal and coal byproducts: A large and developable unconventional resource for critical materials—Rare earth elements. J. Rare Earths 2018, 36, 337–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinto, J.; Henriques, B.; Duarte, A.C.; Vale, C.; Pereira, E. Removal and recovery of Critical Rare Elements from contaminated waters by living Gracilariagracilis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkaczyk, A.H.; Bartl, A.; Amato, A.; Lapkovskis, V.; Petranikova, M. Sustainability evaluation of essential critical raw materials: Cobalt, niobium, tungsten and rare earth elements. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 203001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tunsu, C.; Petranikova, M. Perspectives for the recovery of critical elements from future energy-efficient refrigeration materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuss, P.; Blengini, G.A. Towards better monitoring of technology critical elements in Europe: Coupling of natural and anthropogenic cycles. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, B. BP Statistical Review of World Energy; BP Statistical Review of World Energy: London, UK, 2019; Available online: http://www.bp.com/statisticalreview (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Kolker, A.; Hower, J.C.; Karamalidis, A.K. Introduction to critical elements in coal and coal ash and their recovery, a virtual special issue. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2019, 206, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Finkelman, R.B. Coal as a promising source of critical elements: Progress and future prospects. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 186, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Ruppert, L.F.; Eble, C.F.; Clark, W.L. Geochemistry, petrology, and palynology of the Pond Creek coal bed, northern Pike and southern Martin counties, Kentucky. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2005, 62, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.C.; Honaker, R. Characterization and recovery of rare earth elements and other critical metals (Co, Cr, Li, Mn, Sr, and V) from the calcination products of a coal refuse sample. Fuel 2020, 267, 117236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Yan, X.Y.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.B.; Zhao, L.X.; Ren, D.Y.; Finkelman, R.B. Valuable elements in Chinese coals: A review. Int. Geol. Rev. 2018, 60, 590–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V. Metalliferous coals: Formation conditions and outlooks for development. Coal Resour. Russ. 2004, 6, 452–519. [Google Scholar]
- Seredin, V.V.; Dai, S.F.; Sun, Y.Z.; Chekryzhov, I.Y. Coal deposits as promising sources of rare metals for alternative power and energy-efficient technologies. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Finkelman, R.B. Metalliferous coals: A review of the main genetic and geochemical types. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 76, 253–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.C.; Liu, G.J.; Wang, X.D.; Qi, C.C.; Hu, Y.H. Combustion characteristics and arsenic retention during co-combustion of agricultural biomass and bituminous coal. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.C.; Liu, G.J.; Wu, D.; Fang, T.; Wang, R.W.; Fan, X. Mobility behavior and environmental implications of trace elements associated with coal gangue: A case study at the Huainan Coalfield in China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.C.; Liu, G.J.; Xu, Z.Y.; Sun, H.; Lam, P.K.S. Retention mechanisms of ash compositions on toxic elements (Sb, Se and Pb) during fluidized bed combustion. Fuel 2018, 213, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Ren, D.Y.; Chou, C.L.; Finkelman, R.B.; Seredin, V.V.; Zhou, Y.P. Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese coals: A review of abundances, genetic types, impacts on human health, and industrial utilization. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.H.; Soong, Y.; Granite, E.J. Evaluation of trace elements in US coals using the USGS COALQUAL database version 3.0. Part II: Non-REY critical elements. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 192, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blissett, R.S.; Rowson, N.A. A review of the multi-component utilisation of coal fly ash. Fuel 2012, 97, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.T.; Ji, X.S.; Sarker, P.K.; Tang, J.H.; Ge, L.Q.; Xia, M.S.; Xi, Y.Q. A comprehensive review on the applications of coal fly ash. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 141, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finkelman, R.B. Trace and minor elements in coal. In Organic Geochemistry; Engel, M.H., Masko, S.A., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 593–607. [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman, R.B.; Dai, S.F.; French, D. The importance of minerals in coal as the hosts of chemical elements: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2019, 212, 103251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, R.B.; Palmer, C.A.; Wang, P.P. Quantification of the modes of occurrence of 42 elements in coal. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 185, 138–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.R. Analysis, origin and significance of mineral matter in coal: An updated review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 165, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The Composition of the Continental-Crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaine, D.J. Why trace elements are important. Fuel Process. Technol. 2000, 65, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.P.; Graedel, T.E. The potential for mining trace elements from phosphate rock. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 91, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketris, M.P.; Yudovich, Y.E. Estimations of Clarkes for Carbonaceous biolithes: World averages for trace element contents in black shales and coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2009, 78, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuzov, S.I.; Ershov, V.V.; Rikhvanov, L.P.; Rikhvanov, L.P. Rare-Metal Potential of Coals in the Minusa Basin; Acad. Sci. (Siberian Division): Novosibirsk, Russia, 2003; p. 347. [Google Scholar]
- Nifantov, B.F. Valuable and toxic elements in coals. In Coal Resources of Russia; Geoinformmark: Moscow, Russia, 2003; Volume II, pp. 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Seredin, V.V. Germanium deposits. In Large and Superlarge Ore Deposits; Laverov, N.P., Rundkvist, D.V., Eds.; IGEM RAS: Moscow, Russia, 2006; Volume 3, pp. 707–736. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.F.; Li, T.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Zhou, Y.P.; Zhang, M.Q.; Song, X.L.; Song, W.J.; Zhao, C.L. Origin of minerals and elements in the Late Permian coals, tonsteins, and host rocks of the Xinde Mine, Xuanwei, eastern Yunnan, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 121, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Ruppert, L.F.; Williams, D.A. Controls on boron and germanium distribution in the low-sulfur Amos coal bed, Western Kentucky coalfield, USA. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2002, 53, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Chakravarty, S.; Shome, D.; Basariya, M.R.; Kumari, A.; Kundu, A.K.; Chatterjee, D.; Adhikari, J.; Chatterjee, D. Distribution and affinity of trace elements in Samaleswari coal, Eastern India. Fuel 2016, 181, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Zou, J.H.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ward, C.R.; Wang, X.B.; Li, T.; Xue, W.F.; Liu, S.D.; Tian, H.M.; Sun, X.H.; et al. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of the Pennsylvanian coal in the Adaohai Mine, Daqingshan Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China: Modes of occurrence and origin of diaspore, gorceixite, and ammonianillite. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 250–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Dai, S.F.; Nechaev, V.P.; Nechaeva, E.V.; Graham, I.T.; French, D.; Sun, J.H. Enrichment of critical elements (Nb-Ta-Zr-Hf-REE) within coal and host rocks from the Datanhao mine, Daqingshan Coalfield, northern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 111, 102951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Luo, Y.B.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Zhao, L.; Liu, S.D.; Zhao, C.L.; Tian, H.M.; Zou, J.H. Revisiting the late Permian coal from the Huayingshan, Sichuan, southwestern China: Enrichment and occurrence modes of minerals and trace elements. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 122, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Zhang, W.G.; Ward, C.R.; Seredin, V.V.; Hower, J.C.; Li, X.; Song, W.J.; Wang, X.B.; Kang, H.; Zheng, L.C.; et al. Mineralogical and geochemical anomalies of late Permian coals from the Fusui Coalfield, Guangxi Province, southern China: Influences of terrigenous materials and hydrothermal fluids. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2013, 105, 60–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Li, T.J.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Sun, J.H.; Liu, J.J.; Song, H.J.; Wei, J.P.; Li, Q.Q.; et al. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of the Pennsylvanian coal in the Hailiushu Mine, Daqingshan Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China: Implications of sediment-source region and acid hydrothermal solutions. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 137, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V. Anomalous concentrations of trace elements in the spetsugli germanium deposit (Pavlovka brown coal deposit, southern primorye): Communication 2. Rubidium and cesium. Lithol. Min. Resour. 2003, 38, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.W.; Hu, R.Z.; Su, W.; Qi, L.; Feng, J. Continental hydrothermal sedimentary siliceous rock and genesis of superlarge germanium (Ge) deposit hosted in coal: A study from the LincangGe deposits, Yunnan, China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2004, 47, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefticariu, L.; Klitzing, K.L.; Kolker, A. Rare Earth Elements and Yttrium (REY) in coal mine drainage from the Illinois Basin, USA. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2020, 217, 103327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Calder, J.H.; Eble, C.F. Lanthanide, yttrium, and zironium anomalies in the fire clay coal bed, Eastern Kentucky. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1999, 39, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Ren, D.Y.; Chou, C.L.; Li, S.S.; Jiang, Y.F. Mineralogy and geochemistry of the No. 6 coal (Pennsylvanian) in the Junger Coalfield, Ordos Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2006, 66, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Zhou, Y.P.; Ren, D.Y.; Wang, X.B.; Li, D.; Zhao, L. Geochemistry and mineralogy of the Late Permian coals from the Songzao Coalfield, Chongqing, southwestern China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2007, 50, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Li, D.; Chou, C.L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, D.; Ma, Y.W.; Sun, Y.Y. Mineralogy and geochemistry of boehmite-rich coals: New insights from the Haerwusu Surface Mine, Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 74, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Liu, J.J.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; French, D.; Jia, S.H.; Hood, M.M.; Garrison, T.M. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of Late Permian coals and host rocks from the Guxu Coalfield, Sichuan Province, China, with emphasis on enrichment of rare metals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 166, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Xie, P.P.; Jia, S.H.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Yan, X.Y.; French, D. Enrichment of U-Re-V-Cr-Se and rare earth elements in the Late Permian coals of the Moxinpo Coalfield, Chongqing, China: Genetic implications from geochemical and mineralogical data. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ward, C.R.; Gu, L.D.; Seredin, V.V.; Liu, H.D.; Zhou, D.; Wang, X.B.; Sun, Y.Z.; Zou, J.H.; et al. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of the coal in the Guanbanwusu Mine, Inner Mongolia, China: Further evidence for the existence of an Al (Ga and REE) ore deposit in the Jungar Coalfield. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 98, 10–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Jiang, J.H.; Hower, J.C.; Song, X.L.; Jiang, Y.F.; Wang, X.B.; Gornostaeva, T.; Li, X.; et al. Composition and modes of occurrence of minerals and elements in coal combustion products derived from high-Ge coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 121, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Greb, S.F.; Cobb, J.C.; Williams, D.A. Discussion on origin of vanadium in coals: Parts of the Western Kentucky (USA) No. 9 coal rich in vanadium. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 2000, 157, 1257–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Critical Element | USA | Australia | EU | Japan | China |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum (Al) | X | X | X | ||
| Antimony (Sb) | X | X | X | X | X |
| Arsenic (As) | X | ||||
| Beryllium (Be) | X | X | X | ||
| Bismuth (Bi) | X | X | X | ||
| Cesium (Cs) | X | ||||
| Chromium (Cr) | X | X | X | X | |
| Cobalt (Co) | X | X | X | X | X |
| Copper (Cu) | X | X | |||
| Gallium (Ga) | X | X | X | X | |
| Germanium (Ge) | X | X | X | X | |
| Hafnium (Hf) | X | X | X | ||
| Nickel (Ni) | X | X | |||
| Indium (In) | X | X | X | X | |
| Iron (Fe) | X | X | |||
| Lead (Pb) | X | ||||
| Lithium (Li) | X | X | X | X | |
| Magnesium (Mg) | X | X | X | X | |
| Manganese (Mn) | X | X | X | ||
| Molybdenum (Mo) | X | X | |||
| Niobium (Nb) | X | X | X | X | |
| Potassium (K) | X | X | |||
| Rhenium (Re) | X | X | X | ||
| Rubidium (Rb) | X | ||||
| Scandium (Sc) | X | X | X | X | |
| Silicon (Si) | X | X | |||
| Strontium (Sr) | X | ||||
| Tantalum (Ta) | X | X | X | X | |
| Tellurium (Te) | X | ||||
| Tin (Sn) | X | X | X | ||
| Titanium (Ti) | X | X | X | ||
| Tungsten (W) | X | X | X | X | X |
| Uranium (U) | X | ||||
| Vanadium (V) | X | X | X | X | |
| Zinc (Zn) | X | ||||
| Zircon | X | X | X | X | |
| REE | X | X | X | X | X |
| PGE | X | X | X | X | X |
| Grade | Elements |
|---|---|
| Extremely high concern | As, Cd, Cr, Hg, Pb, Se |
| High concern | B, Cl, F, Mn, Mo, Ni, Be, Cu, P, Th, U, V, Zn |
| Moderate concern | Ba, Co, I, Ra, Sb, Sn, Tl |
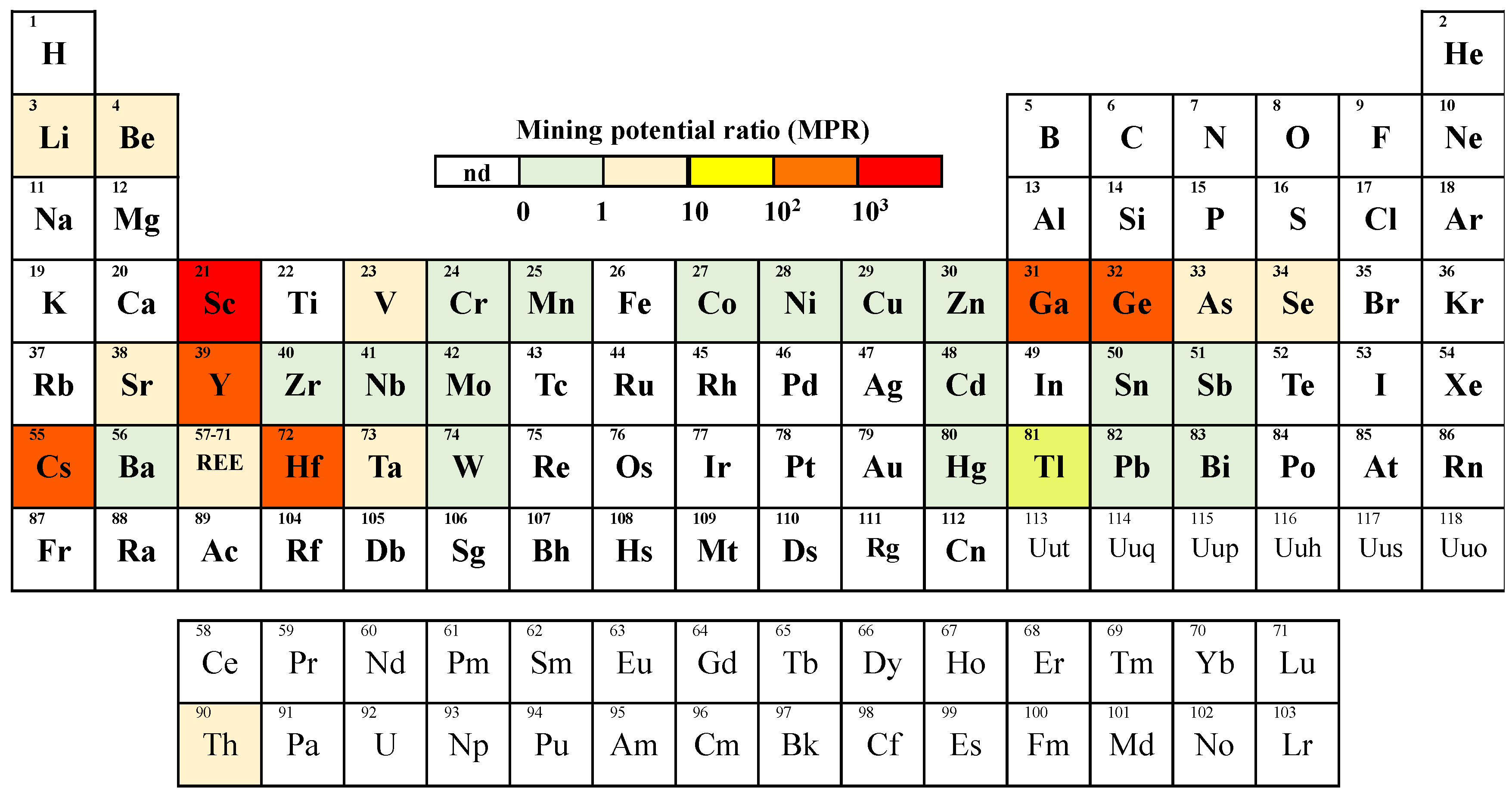
| Element | Sc | Hf | Cs | Y | Ge | Ga | Tl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPR | 0.6 | 370.6 | 351.9 | 280.6 | 234.3 | 152.7 | 93.9 |
| Element | Sr | REE | Se | V | Li | Be | |
| MPR | 6.31 | 5.06 | 4.11 | 3.06 | 2.48 | 2.33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; You, M.; Liu, G.; Dong, Z.; Jiao, F.; Meng, Y. The Potential Utilizing of Critical Element from Coal and Combustion Residues. Energies 2021, 14, 4710. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154710
Hu Y, You M, Liu G, Dong Z, Jiao F, Meng Y. The Potential Utilizing of Critical Element from Coal and Combustion Residues. Energies. 2021; 14(15):4710. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154710
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yunhu, Mu You, Guijian Liu, Zhongbing Dong, Facun Jiao, and Ying Meng. 2021. "The Potential Utilizing of Critical Element from Coal and Combustion Residues" Energies 14, no. 15: 4710. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154710
APA StyleHu, Y., You, M., Liu, G., Dong, Z., Jiao, F., & Meng, Y. (2021). The Potential Utilizing of Critical Element from Coal and Combustion Residues. Energies, 14(15), 4710. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154710





