Optimal Integration of Capacitor and Distributed Generation in Distribution System Considering Load Variation Using Bat Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel technique is proposed for long-term scheduling to optimally allocate DGs and capacitors.
- For the first time, consideration of load variation is given for the allocation problem of capacitors and DGs.
- A framed set of generalized equations using curve fitting techniques to help distribution network operators to choose the exact size of the DG and capacitor for any load (light load to peak load).
- The present approach is verified on three different load models to check the efficiency in all types of loads.
- Improvement of overall system efficiency is achieved by considering a multi-objective function for the enhancement of stability and reduced power loss, which are not considered previously in the literature for the allocation of capacitors simultaneously.
- For the first time, the Bat algorithm is applied for the allocation of capacitors and DGs.
2. Load Models and Formulation of the Proposed Objective Function
2.1. Formulation of Load Models
2.2. Power Loss in RDS
2.3. Reduction of Power Loss by Placement of DG/capacitor
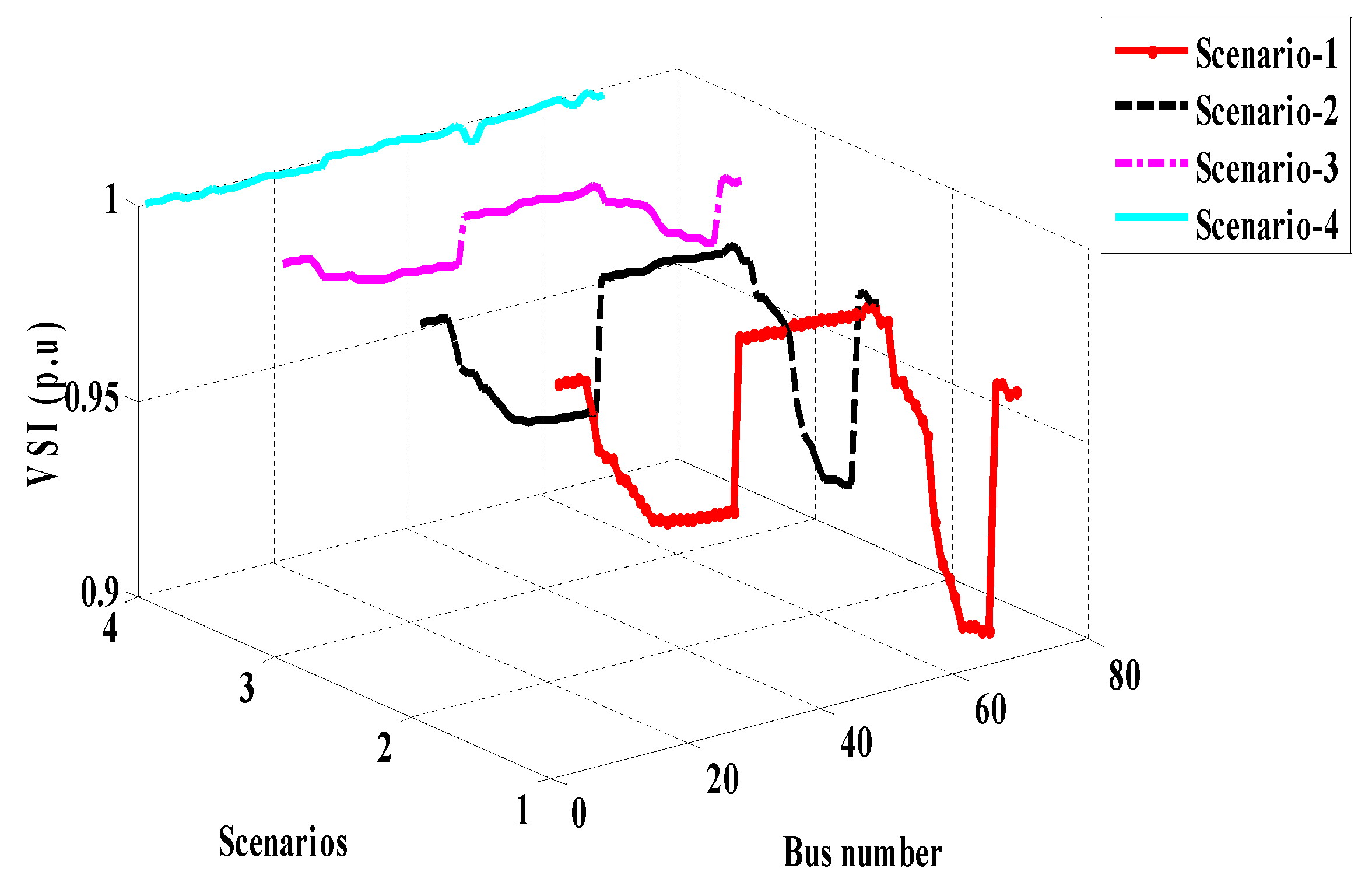
2.4. Voltage Stability Index (VSI) in RDS
2.5. VSI Maximization Using DG/capacitor Placement
2.6. Curve-Fitting Technique
- Place the suggested initial (extreme) DG/capacitor sizes one at a time at bus t. Then, run the load flow per DG capacitor size for all load factors (0.5 to 1.6 with step size of 0.01).
- Register the ΣPLoss values of these DG/capacitors individually on a scatter plot. The x and y axes are the total system power loss or DG/capacitor size and load factor, respectively.
- Plot a quadratic fitted curve of these registered results and obtain the curve function (ax2 + bx + c).
- Find the x-intersect (x = −b/2a) of the minimum point at that curve. Then, represent that intersection as the best power loss or DG/capacitor size.
- Place the designated DG/capacitor size and run the power flow. If the constraints are within the limits, that is, this is the best DG/capacitor option of this pf, then print the results. Otherwise, one of three scenarios could arise:
- and reduce the DG/capacitor size by 5% and follow step 5.
- and increase the DG/capacitor size by 5% and follow step 5.
- and increase and decrease the DG/capacitor size by 5% and follow step 5 for both DGs and capacitors one at a time. If both DGs and capacitors satisfy the constraints, retain the one that provides maximum objective function values.
2.7. Proposed Objective Function
3. Sensitivity Analysis
3.1. Voltage Stability Index
3.2. Loss Sensitivity Factor
4. Bat Algorithm
- Every bat senses the distance and sizing of the food/prey and background obstacles by echolocation, and it can also differentiate between them.
- In the process of preying, each bat flies arbitrarily with velocity of vi considered at a position xi, with a least frequency of fmin whose wavelength varies as λ and value of loudness is A0. Frequency or the wavelength is determined by target proximity and pulse emission rate r, whose value ranges between [0, 1], happening inherently.
- The value of loudness varies between a range from a large positive value A0 to a least constant value Amin.
- Population size: 20
- Number of generation: 50
- Dimension of search space: 6
- Loudness: 0.5
- Pulse rate: 0.5
- Step 1: Set the objective function.
- Step 2: Initialize the bat population (10 to 40) with variables: vi, xi, fmin, r and A0.
- Step 3: Computation of fitness value is performed for each bat and then ranking is performed.
- Step 4: Update the variables vi, xi, fmin, r and A0 by following Equations (20)–(24).
- Step 5: If (rand > ri).
- Step 6: if (rand < Ai & f(xi) < f(x*)).
- Step 7: Computation of the fitness value of each bat is performed.
- Step 8: Steps 4 to 6 are repeated until the loop ends into a criterion stopping it.
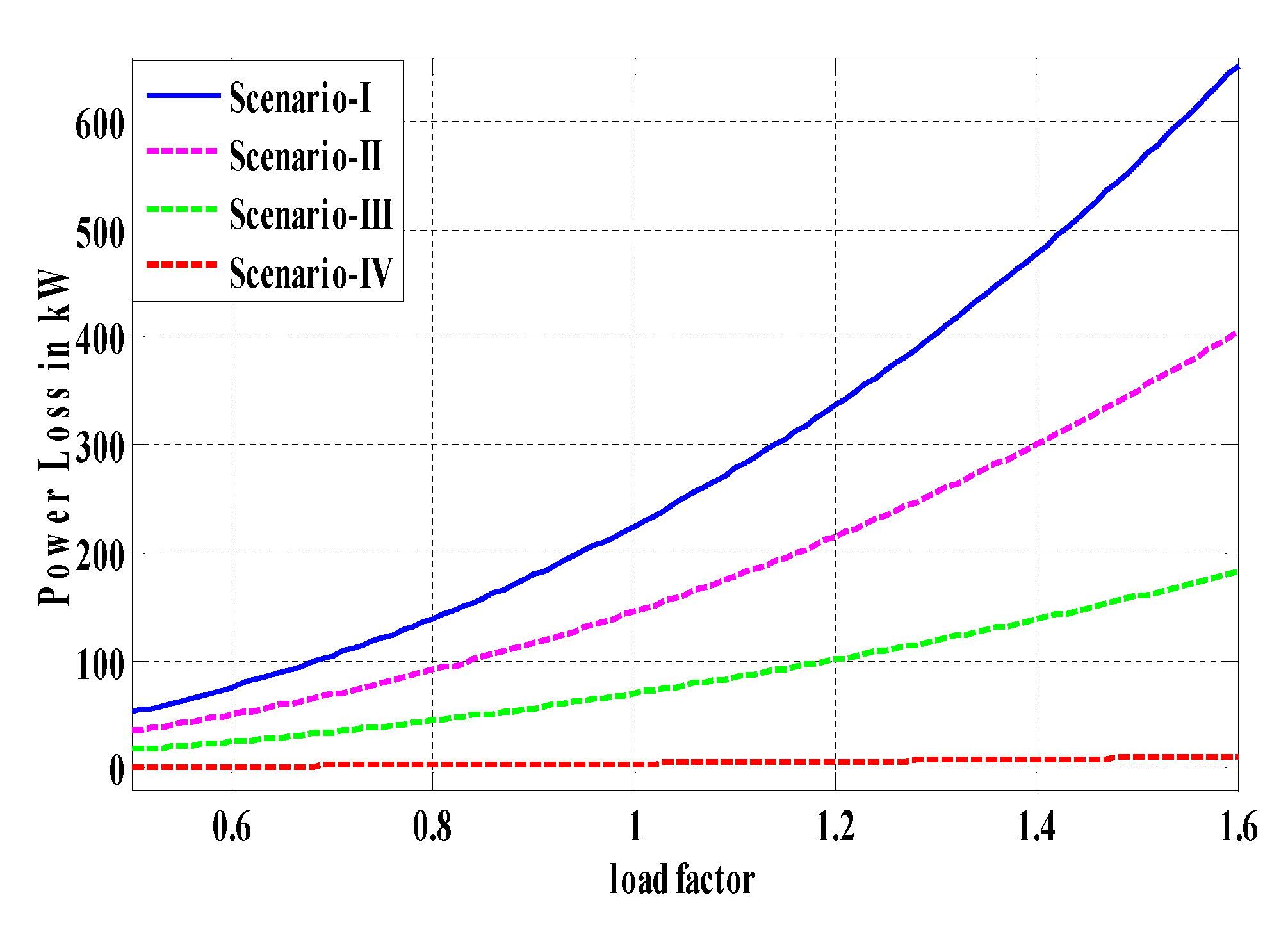
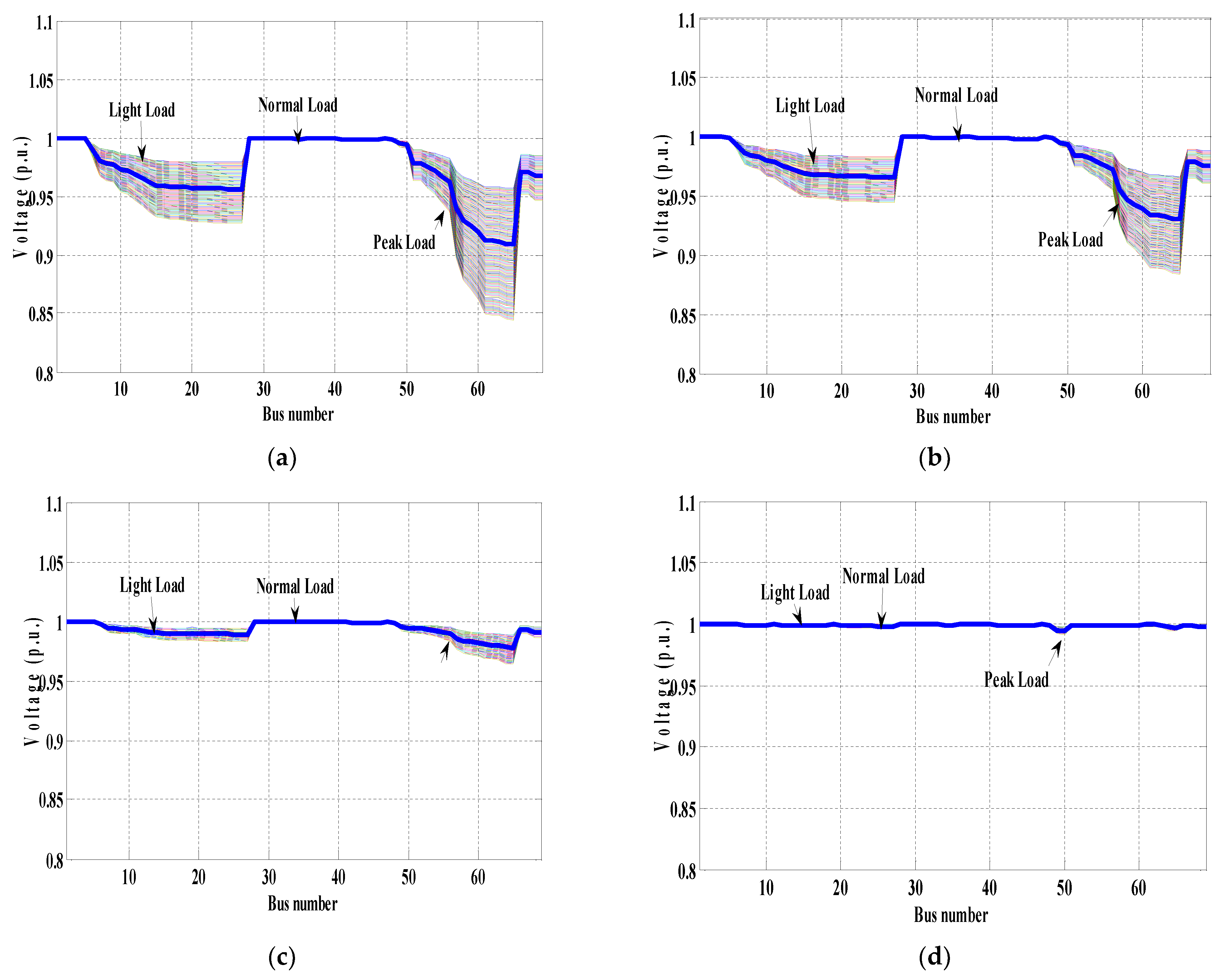
5. Simulation Results and Discussion
- System without involving compensation
- System considering capacitor
- System considering DG
- System considering both DG and capacitor
5.1. Test System Using IEEE 33-Bus
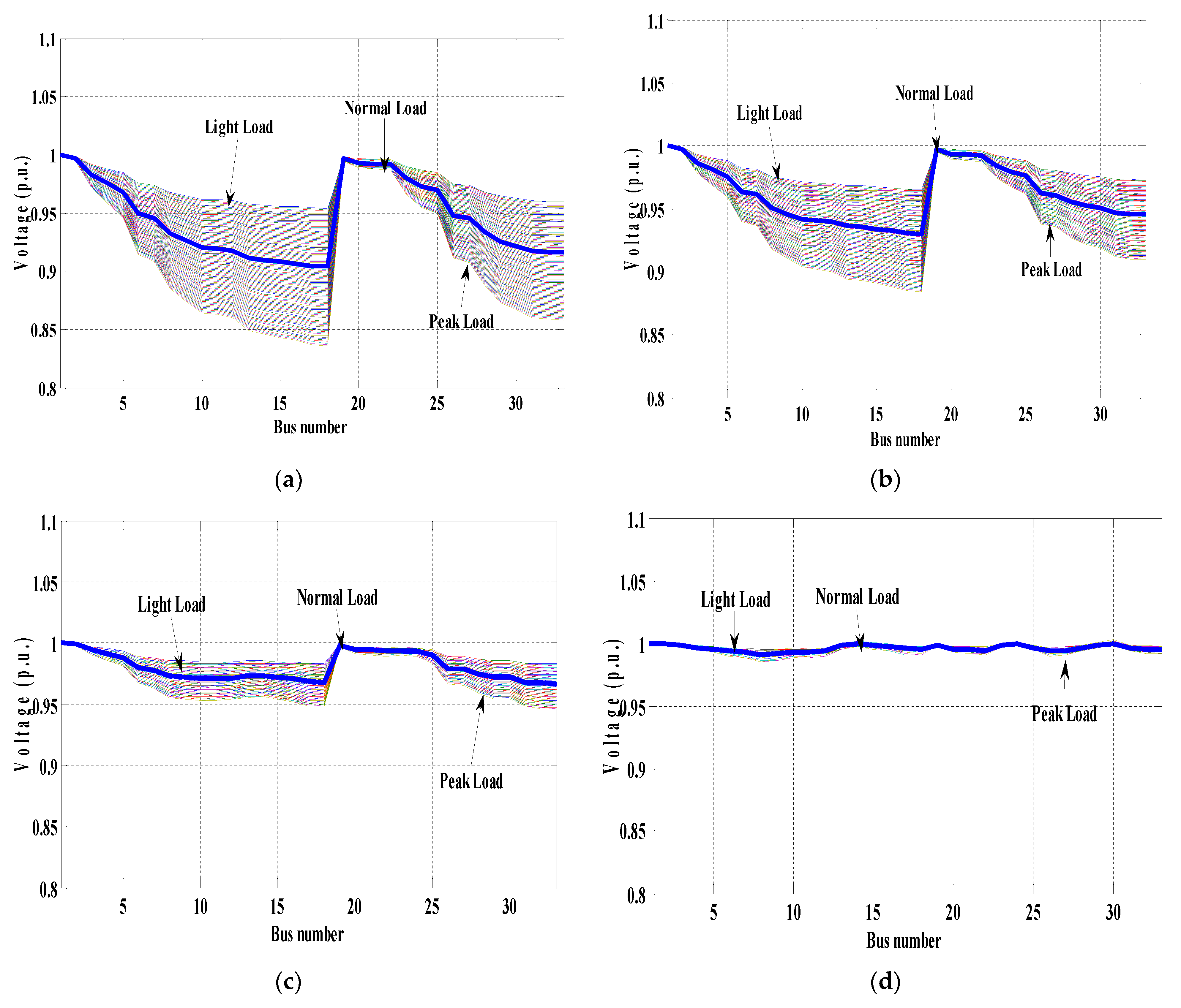
5.1.1. System without Compensation
5.1.2. System with Capacitor
5.1.3. System with DG
5.1.4. System with DG and Capacitor
5.1.5. Comparative Analysis
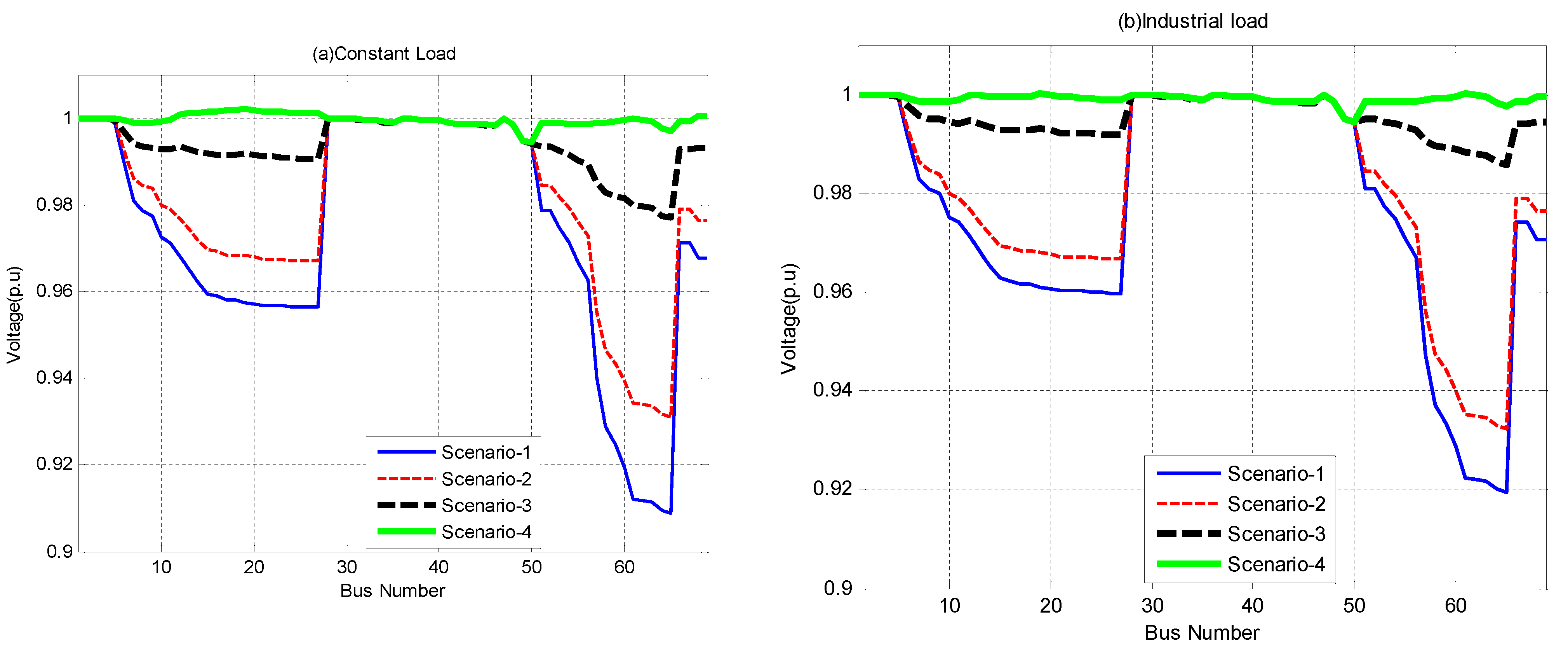
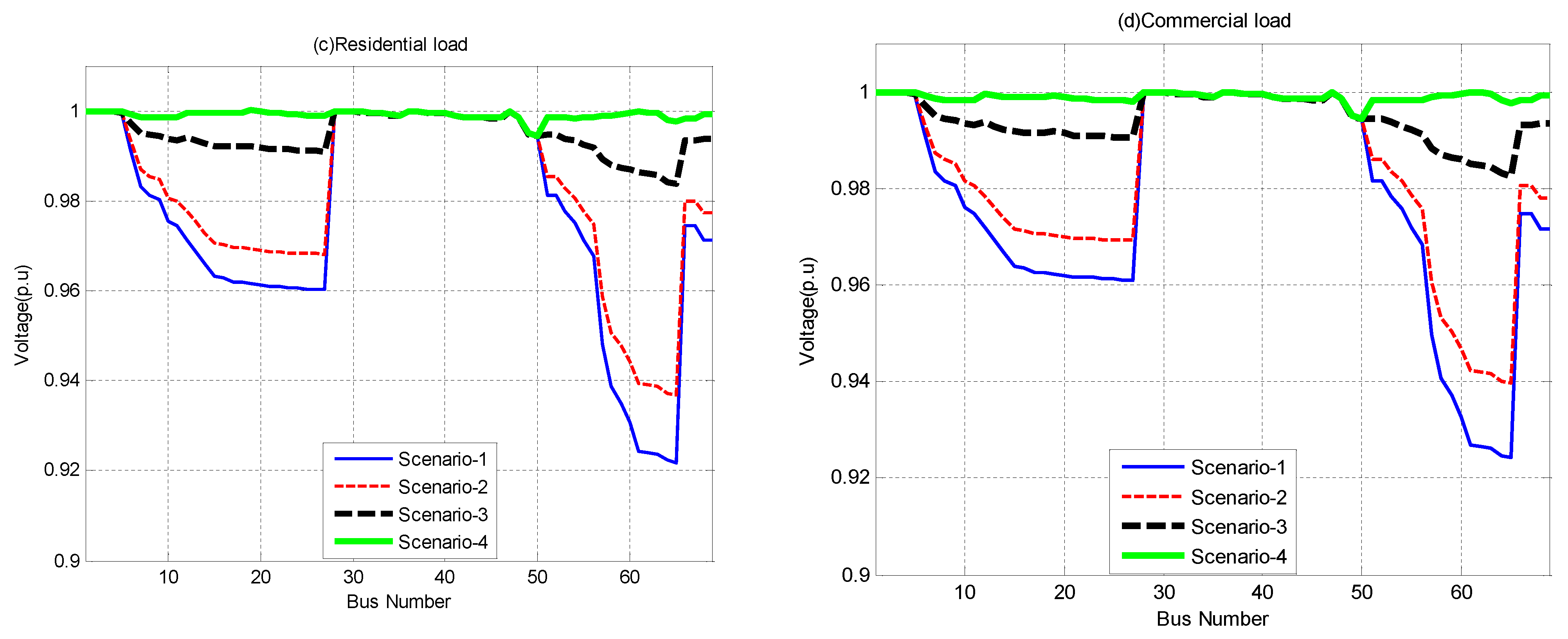
5.2. Test System Using IEEE 69-Bus
5.2.1. System without Compensation
5.2.2. System with Capacitor
5.2.3. System with DG
5.2.4. System with DG and Capacitor
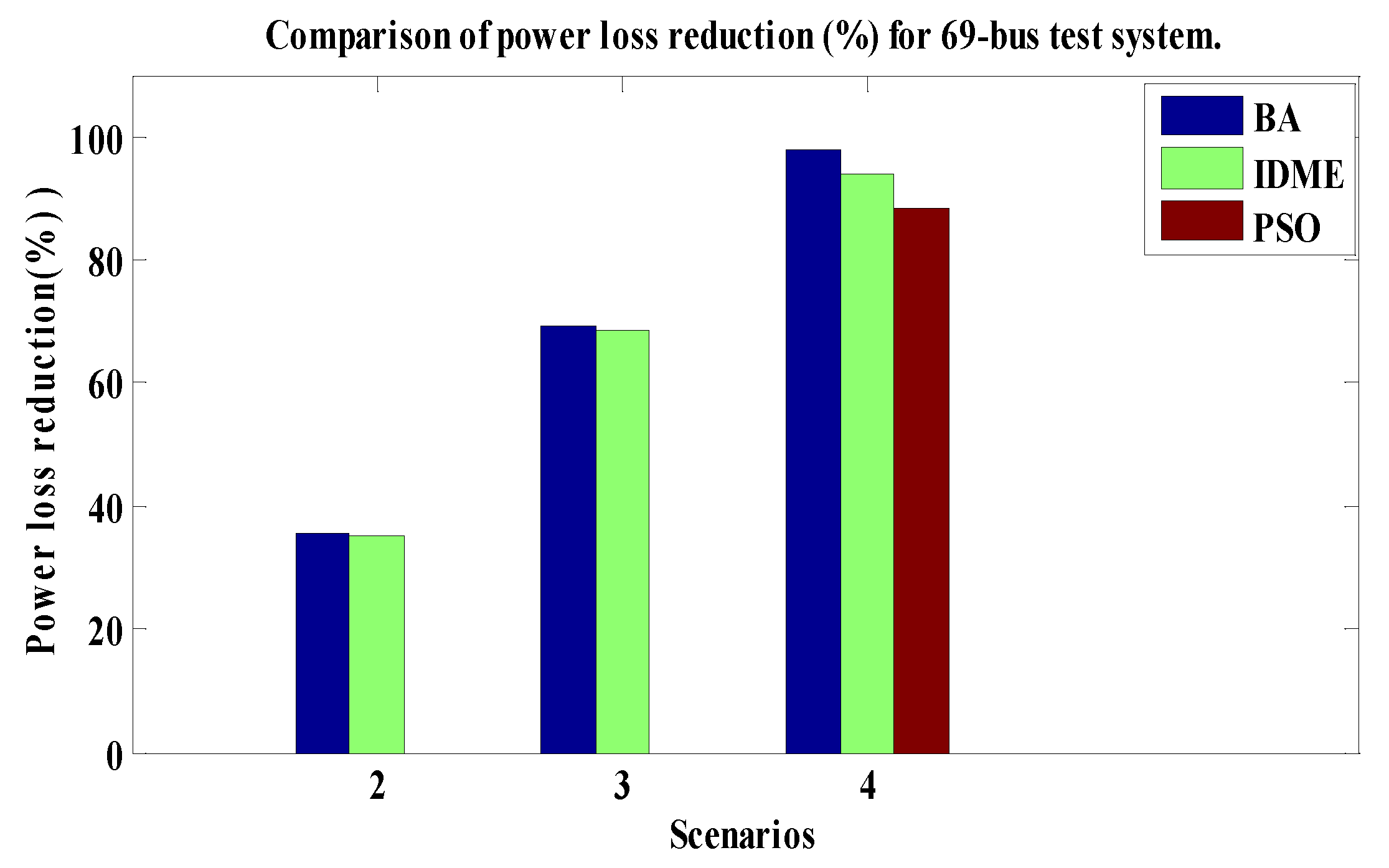
5.2.5. Comparative Analysis of 69-Bus System
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Fergany, A.A. Optimal capacitor allocations using evolutionary algorithms. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2013, 7, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fergany, A.A.; Abdelaziz, A.Y. Capacitor allocations in radial distribution networks using cuckoo search algorithm. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2013, 8, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, H.L. Distributed Power Generation: Planning and Evaluation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann, T.; Andersson, G.; Söder, L. Distributed generation: A definition. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2001, 57, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud Pesaran, H.A.; Huy, P.D.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K. A review of the optimal allocation of distributed generation: Objectives, constraints, methods, and algorithms. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 75, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, M.M.; Jasmon, G.B.; Bakar, A.H.A.; Mokhlis, H.; Karimi, M. Optimum shunt capacitor placement in distri-bution system—A review and comparative study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.G.; Khatod, D.; Sharma, M. Optimal allocation of combined DG and capacitor for real power loss minimization in distribution networks. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 53, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, M.M.; Jasmon, G.B.; Solangi, K.H.; Bakar, A.H.A.; Mokhlis, H.; Aman, M.M.; Jasmon, G.B.; Solangi, K.H.; Bakar, A.H.A.; Mokhlis, H. Optimum Simultaneous DG and Capacitor Placement on the Basis of Minimization of Power Losses. Int. J. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2013, 5, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.A.; Kowsalya, M. Optimal Distributed Generation and capacitor placement in power distribution networks for power loss minimization. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Advances in Electrical Engineering (ICAEE), Vellore, India, 9–11 January 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pradeepa, H.; Ananthapadmanabha, T.; Bandhavya, C. Optimal allocation of combined DG and capacitor units for voltage stability enhancement. Procedia Technol. 2015, 21, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabakhshian, A.; Andishgar, M.H. Simultaneous placement and sizing of DGs and shunt capacitors in distribu-tion systems by using IMDE algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 82, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinalzadeh, A.; Mohammadi, Y.; Moradi, M.H. Optimal multi objective placement and sizing of multiple DGs and shunt capacitor banks simultaneously considering load uncertainty via MOPSO approach. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 67, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghipour, R.; Hosseini, S.M. Placement of DG and capacitor for loss reduction, reliability and voltage improve-ment in distribution networks using BPSO. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2014, 4, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani-Andebili, M. Simultaneous placement of DG and capacitor in distribution network. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2016, 131, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; Tang, W. Coordinated allocation of distributed generation, capacitor banks and soft open points in active distribution networks considering dispatching results. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bompard, E.; Carpaneto, E.; Chicco, G.; Napoli, R. Convergence of the backward/forward sweep method for the load-flow analysis of radial distribution systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2000, 22, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abri, R.S.A.; El-Saadany, E.F.; Atwa, Y.M. Optimal Placement and Sizing Method to Improve the Voltage Stability Margin in a Distribution System Using Distributed Generation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 28, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizad, A.; Khazali, A.; Kalantar, M. Optimal placement of distributed generation with sensitivity factors consid-ering voltage stability and losses indices. In Proceedings of the 2010 18th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering, Isfahan, Iran, 11–13 May 2010; pp. 848–855. [Google Scholar]
- Devabalaji, K.; Ravi, K.; Kothari, D. Optimal location and sizing of capacitor placement in radial distribution system using Bacterial Foraging Optimization Algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 71, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Mouti, F.; El-Hawary, M. Heuristic curve-fitted technique for distributed generation optimisation in radial distribution feeder systems. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2011, 5, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-S. A New Metaheuristic Bat-Inspired Algorithm. In Service Orientation in Holonic and Multi Agent Manufacturing and Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Injeti, S.K.; Kumar, N.P. A novel approach to identify optimal access point and capacity of multiple DGs in a small, medium and large scale radial distribution systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 45, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, N.; Prasad, K. A fuzzy genetic approach for network reconfiguration to enhance voltage stability in radial distribution systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 3288–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, M.; Kundu, P.; Jariwala, H.R. Incorporation of distributed generation and shunt capacitor in radial distribu-tion system for techno-economic benefits. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2017, 20, 482–493. [Google Scholar]
- Injeti, S.K.; Shareef, S.M.; Kumar, T.V. Optimal Allocation of DGs and Capacitor Banks in Radial Distribution Systems. Distrib. Gener. Altern. Energy J. 2018, 33, 6–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gampa, S.R.; Das, D. Simultaneous optimal allocation and sizing of distributed generations and shunt capacitors in distribution networks using fuzzy GA methodology. J. Electr. Syst. Inf. Technol. 2019, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devabalaji, K.; Imran, A.M.; Yuvaraj, T.; Ravi, K. Power loss minimization in radial distribution system. Energy Procedia 2015, 79, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakar, S.; Balci, M.E.; Aleem, S.H.A.; Zobaa, A.F. Increasing PV hosting capacity in distorted distribution systems using passive harmonic filtering. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 148, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanović, M.; Tasić, D.; Radosavljević, J.; Perović, B. Optimal Placement and Sizing of Inverter-Based Distributed Generation Units and Shunt Capacitors in Distorted Distribution Systems Using a Hybrid Phasor Particle Swarm Optimization and Gravitational Search Algorithm. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2020, 48, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaaeldin, I.; Aleem, S.A.; El-Rafei, A.; Abdelaziz, A.; Zobaa, A.F. Optimal Network Reconfiguration in Active Distribution Networks with Soft Open Points and Distributed Generation. Energies 2019, 12, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolabi, H.; Ara, A.L.; Hosseini, R. A new thief and police algorithm and its application in simultaneous reconfiguration with optimal allocation of capacitor and distributed generation units. Energy 2020, 203, 117911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderipour, A.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Hajivand, M.; Seifabad, Z.M.; Farsi, M.A.; Nowdeh, S.A.; Davoudkhani, I.F. Spotted hyena optimizer algorithm for capacitor allocation in radial distribution system with distributed generation and microgrid operation considering different load types. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouali, S.; Cherkaoui, A. Optimal Allocation of Combined Renewable Distributed Generation and Capacitor Units for Interconnection Cost Reduction. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholapandian, V.; Yuvaraj, T.; Devabalaji, K. Optimal Allocation of Capacitor Banks in Distribution Networks using Cuckoo Search Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 7th International Conference on Electrical Energy Systems (ICEES), Chennai, India, 11–13 February 2021; pp. 475–478. [Google Scholar]
- Yuvaraj, T.; Devabalaji, K.R.; Thanikanti, S.B. Simultaneous Allocation of DG and DSTATCOM Using Whale Optimization Algorithm. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 2020, 44, 879–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukmani, D.K.; Thangaraj, Y.; Subramaniam, U.; Ramachandran, S.; Elavarasan, R.M.; Das, N.; Baringo, L.; Rasheed, M.I.A. A New Approach to Optimal Location and Sizing of DSTATCOM in Radial Distribution Networks using Bio-Inspired Cuckoo Search Algorithm. Energies 2020, 13, 4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devabalaji, K.; Yuvaraj, T.; Ravi, K. An efficient method for solving the optimal sitting and sizing problem of capacitor banks based on cuckoo search algorithm. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, T.; Devabalaji, K.R.; Ravi, K. Optimal Allocation of DG in the Radial Distribution Network Using Bat Optimization Algorithm. In Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; Volume 436, pp. 563–569. [Google Scholar]
- Yuvaraj, T.; Ravi, K.; Devabalaji, K. DSTATCOM allocation in distribution networks considering load variations using bat algorithm. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2017, 8, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, T.; Ravi, K.; Devabalaji, K.R. Optimal Allocation of DG and DSTATCOM in Radial Distribution System Using Cuckoo Search Optimization Algorithm. Model. Simul. Eng. 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, T.; Devabalaji, K.; Ravi, K. Optimal placement and sizing of DSTATCOM using harmony search algorithm. Energy Procedia 2015, 79, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devabalaji, K.; Ravi, K. Optimal size and siting of multiple DG and DSTATCOM in radial distribution system using Bacterial Foraging Optimization Algorithm. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2016, 7, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraj, Y. Integration of solar and wind based DGs with DSTATCOM in distribution systems using modified bat algorithm. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. 2019, 32, 895–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani-Andebili, M. Distributed Generation Placement Planning Modeling Feeder’s Failure Rate and Customer’s Load Type. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 63, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani-Andebili, M. Reliability and economic-driven switchable capacitor placement in distribution network. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2015, 9, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani-Andebili, M. Optimal power factor for optimally located and sized solar parking lots applying quantum annealing. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2016, 10, 2538–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

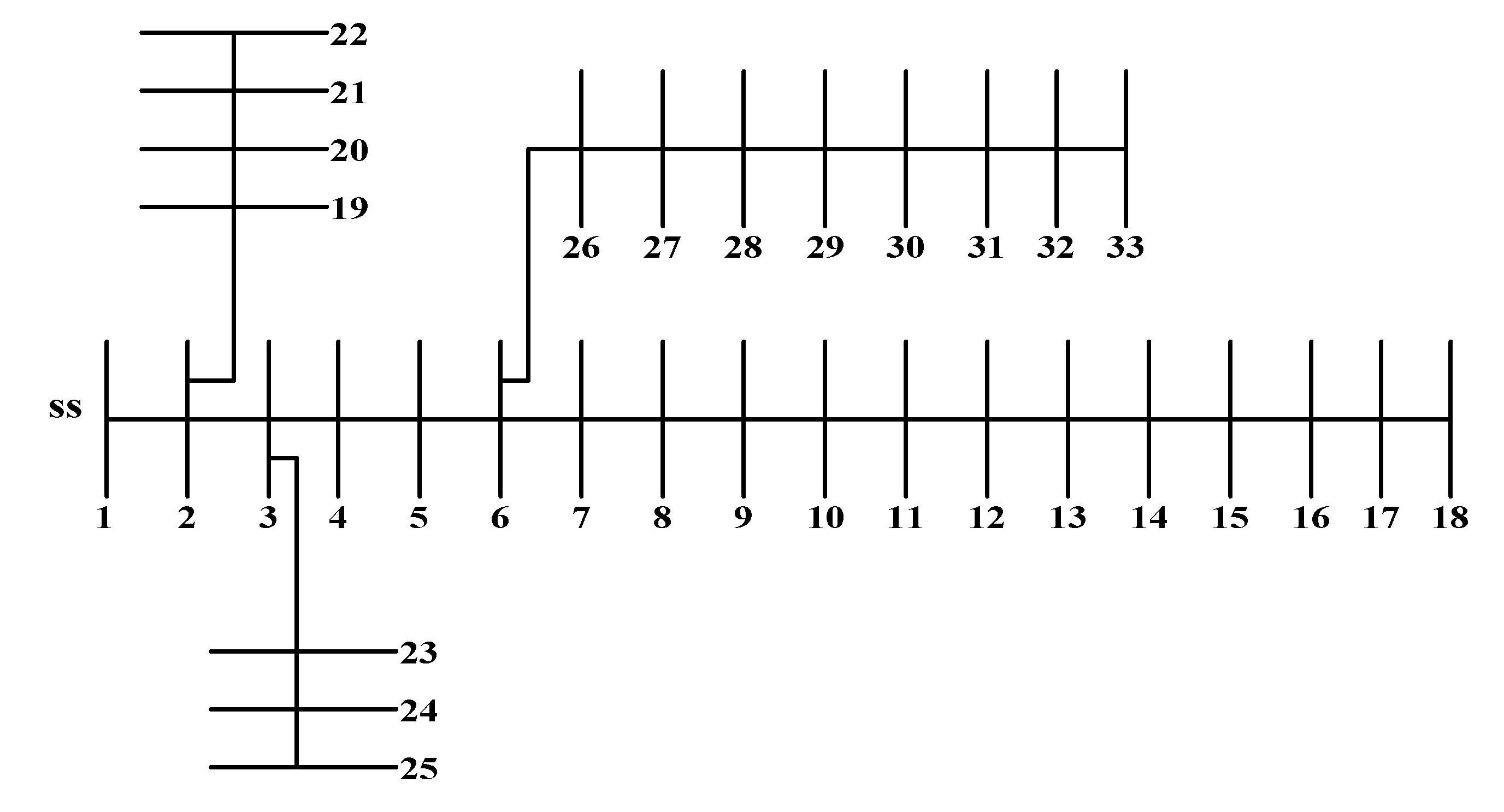
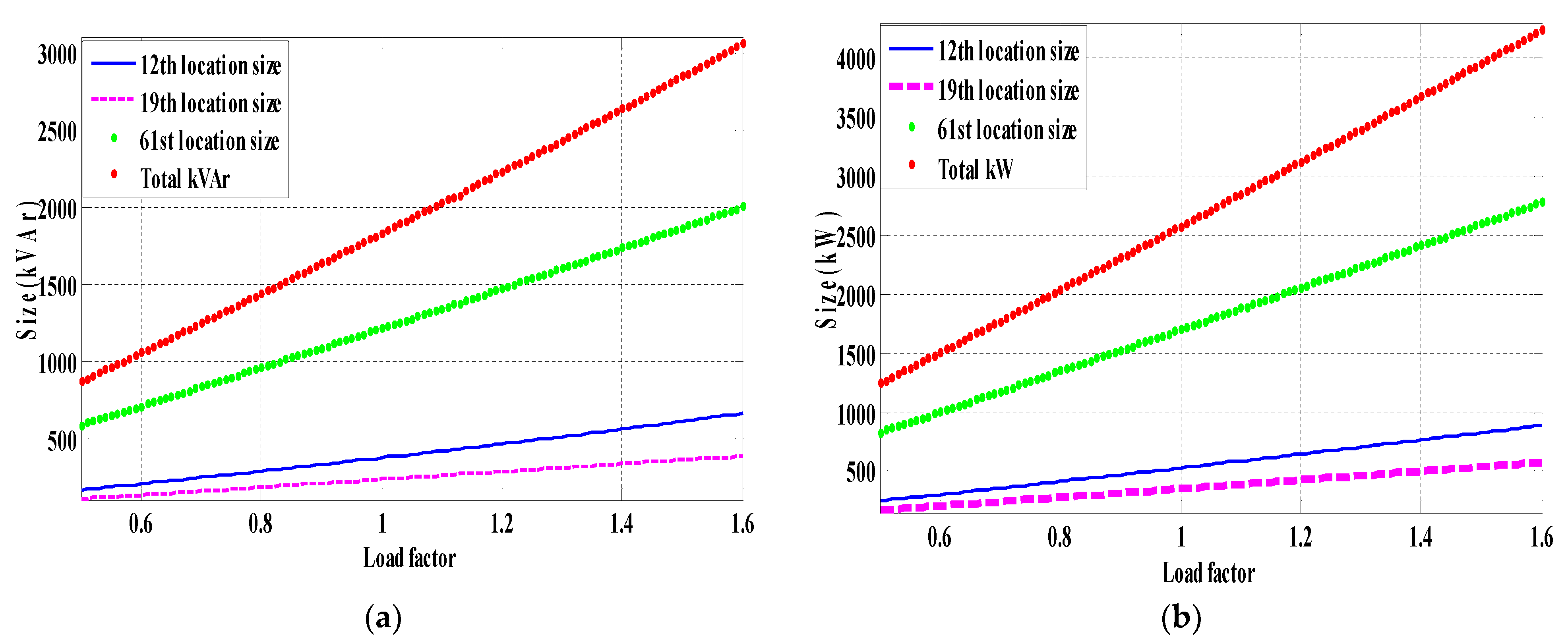
| Load Type | α | β |
|---|---|---|
| Constant | 0 | 0 |
| Industrial load | 0.18 | 6 |
| Residential load | 0.92 | 4.04 |
| Commercial load | 1.51 | 3.4 |
| Constraints | Type | Equations (t = 1, 2,……nb) |
|---|---|---|
| Power balance constraints | Equality | |
| Voltage constraint | In-equality | |
| Real power compensation | In-equality | |
| Reactive power compensation | In-equality |
| Parameters | Constant Load | Industrial Load | Residential Load | Commercial Load | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
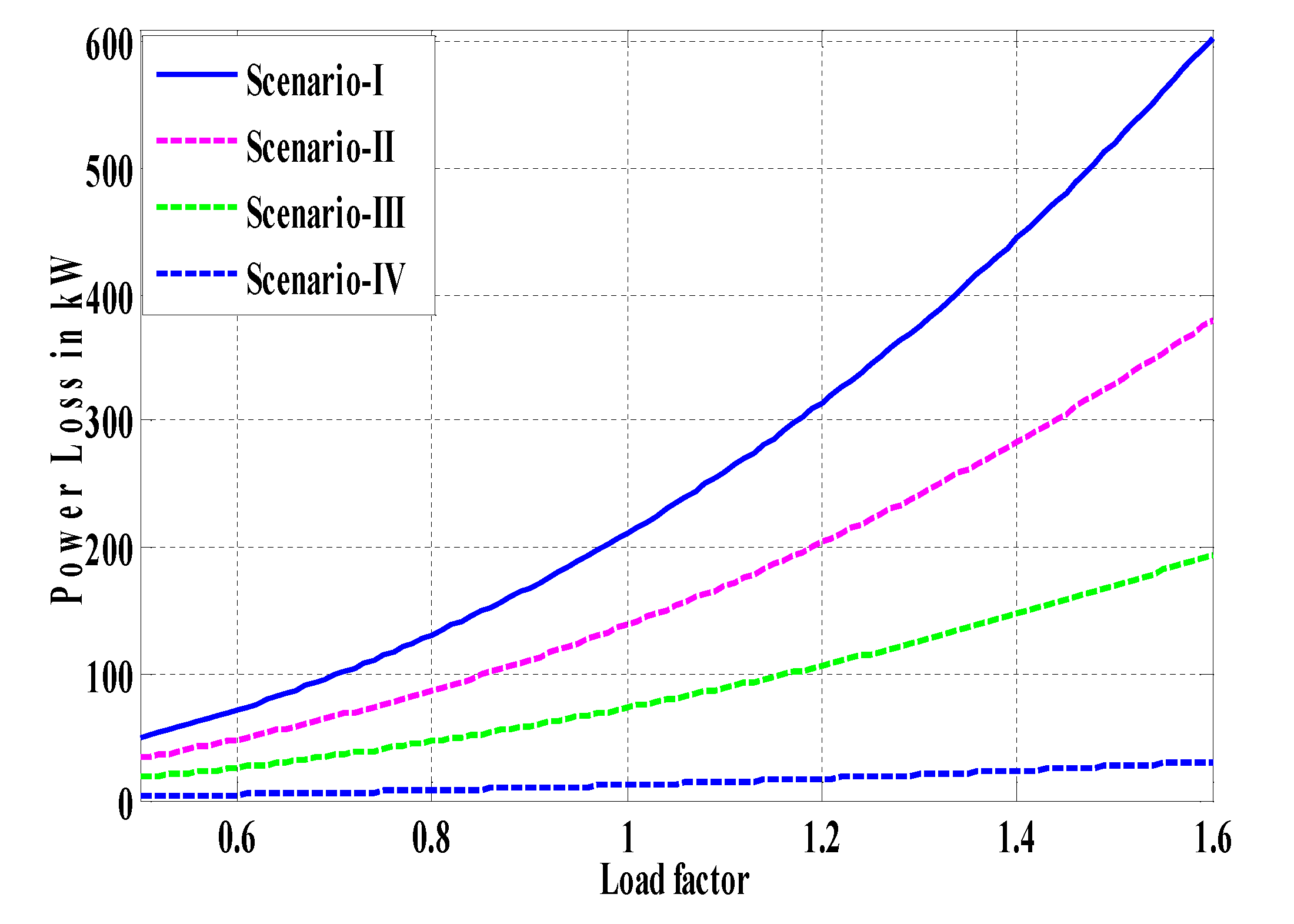
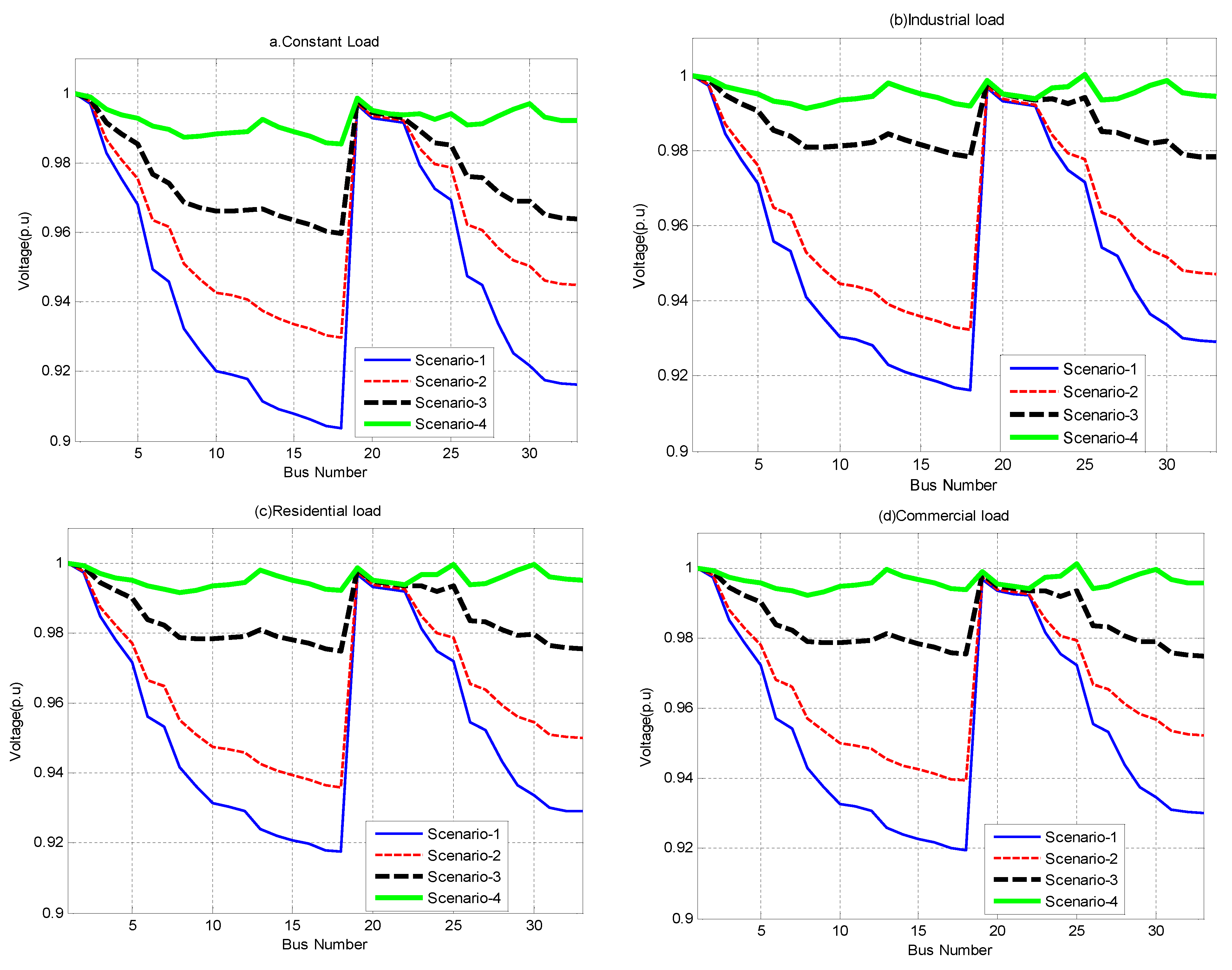
| Without Compensation (Scenario 1) | Ploss(kW) | 210.98 | 163.66 | 159.09 | 152.59 |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.6610 | 0.6987 | 0.7030 | 0.7097 | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9037 | 0.9162 | 0.9175 | 0.9195 | |
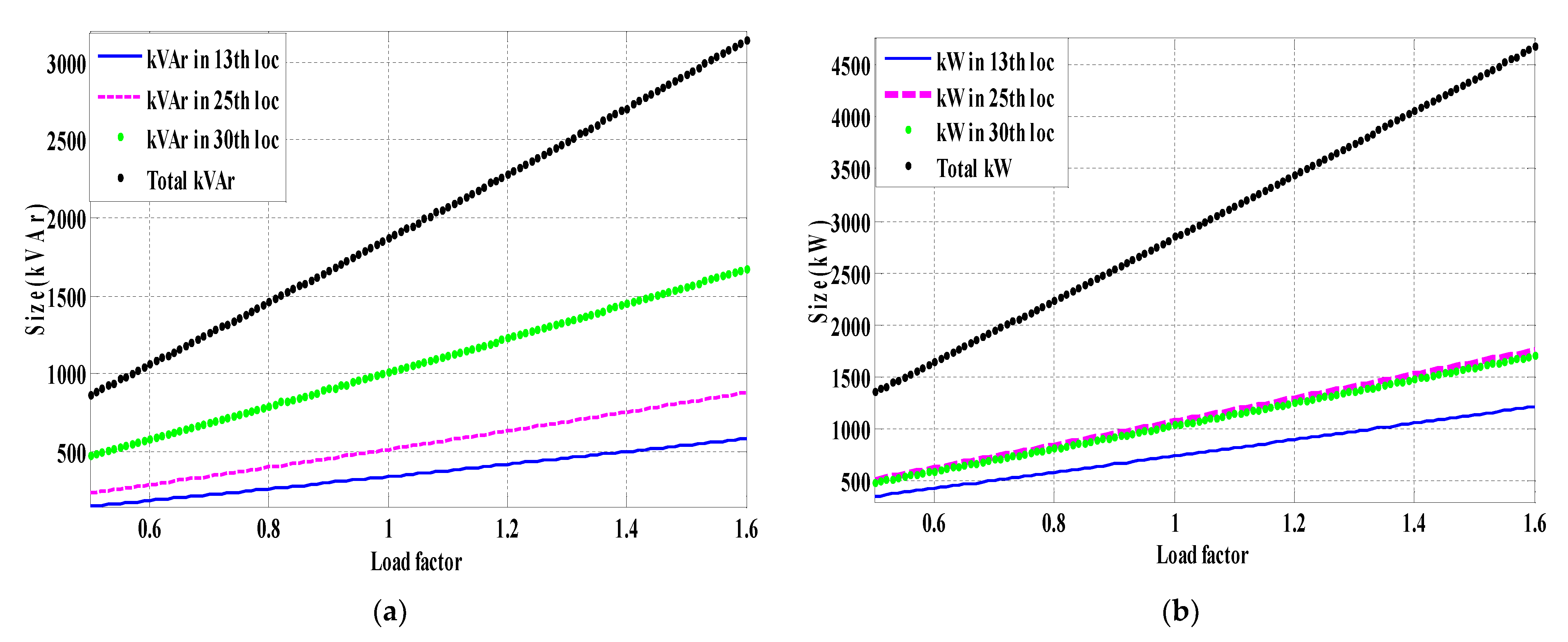
| Only Capacitor (Scenario 2) | Optimal kVAr and Sitting | 680 (13) | 240 (13) | 270 (13) | 290 (13) |
| 480 (25) | 350 (25) | 360 (25) | 380 (25) | ||
| 1050 (30) | 650 (30) | 760 (30) | 800 (30) | ||
| Ploss(kW) | 138.35 | 133.48 | 120.02 | 110.28 | |
| % Ploss Reduction | 34.4 | 18.44 | 24.55 | 27.72 | |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.7423 | 0.7499 | 0.7621 | 0.7733 | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9301 | 0.9324 | 0.9360 | 0.9393 | |
| Only DG (Scenario 3) | Optimal kW and Sitting | 380 (13) | 790 (13) | 720 (13) | 710 (13) |
| 490 (25) | 850 (25) | 830 (25) | 820 (25) | ||
| 990 (30) | 1020 (30) | 980 (30) | 940 (30) | ||
| Ploss(kW) | 72.78 | 36.01 | 43.70 | 46.42 | |
| % Ploss Reduction | 65.5 | 77.99 | 72.53 | 69.57 | |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.8652 | 0.9069 | 0.8974 | 0.8959 | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9669 | 0.9782 | 0.9749 | 0.9749 | |
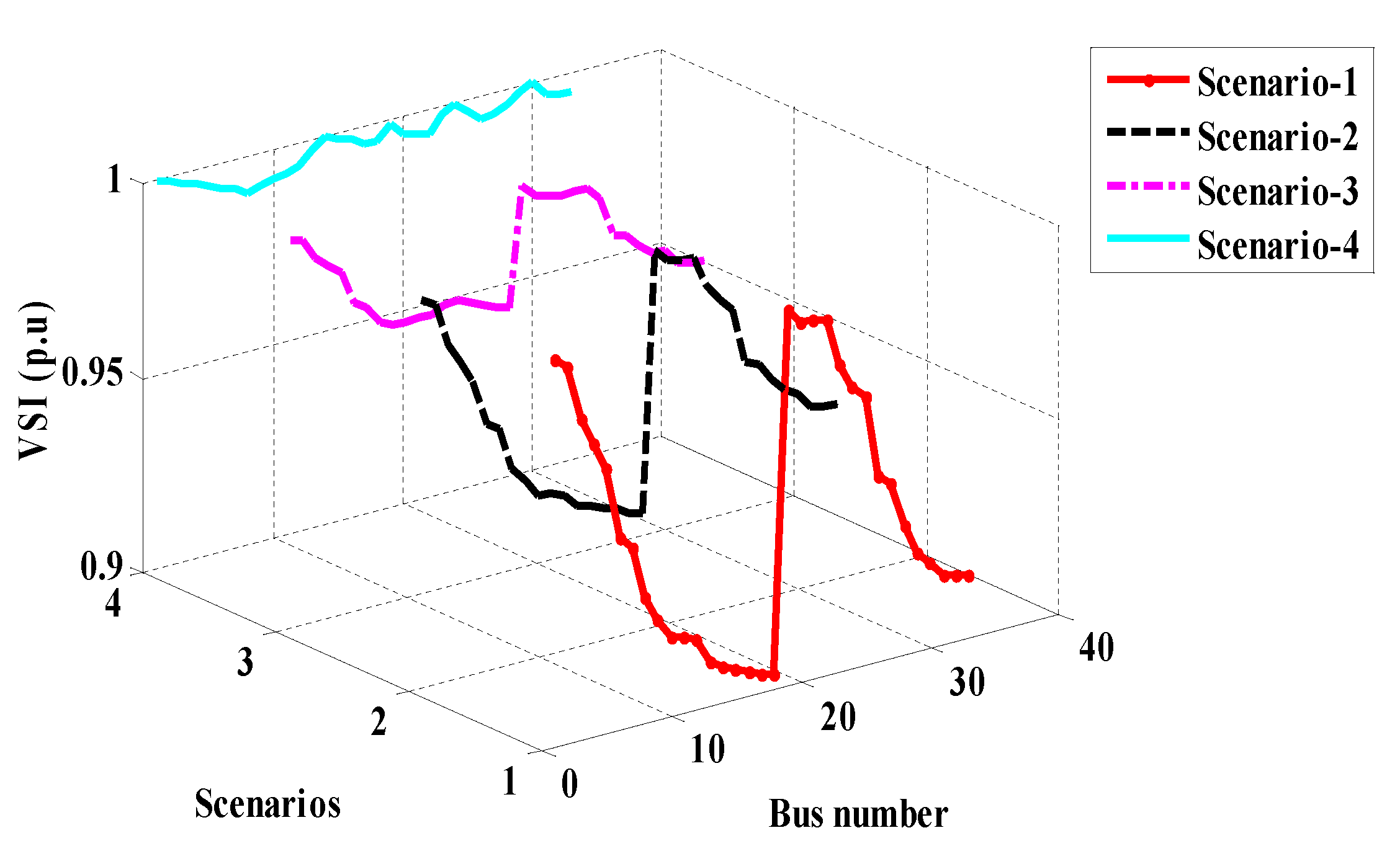
| Simultaneous DG and Capacitor (Scenario 4) | Optimal kVAr and Sitting | 380 (13) | 200 (13) | 250 (13) | 250 (13) |
| 490 (25) | 360 (25) | 360 (25) | 400 (25) | ||
| 990 (30) | 600 (30) | 750 (30) | 770 (30) | ||
| Optimal kWand Sitting | 680 (13) | 780 (13) | 720 (13) | 720 (13) | |
| 480 (25) | 850 (25) | 800 (25) | 850 (25) | ||
| 1050 (30) | 1020 (30) | 960 (30) | 920 (30) | ||
| Ploss(kW) | 11.77 | 11.37 | 10.77 | 10.30 | |
| % Ploss Reduction | 94.42 | 93.05 | 93.23 | 93.24 | |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.9601 | 0.9622 | 0.9626 | 0.9680 | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9970 | 0.9912 | 0.9914 | 0.9923 | |
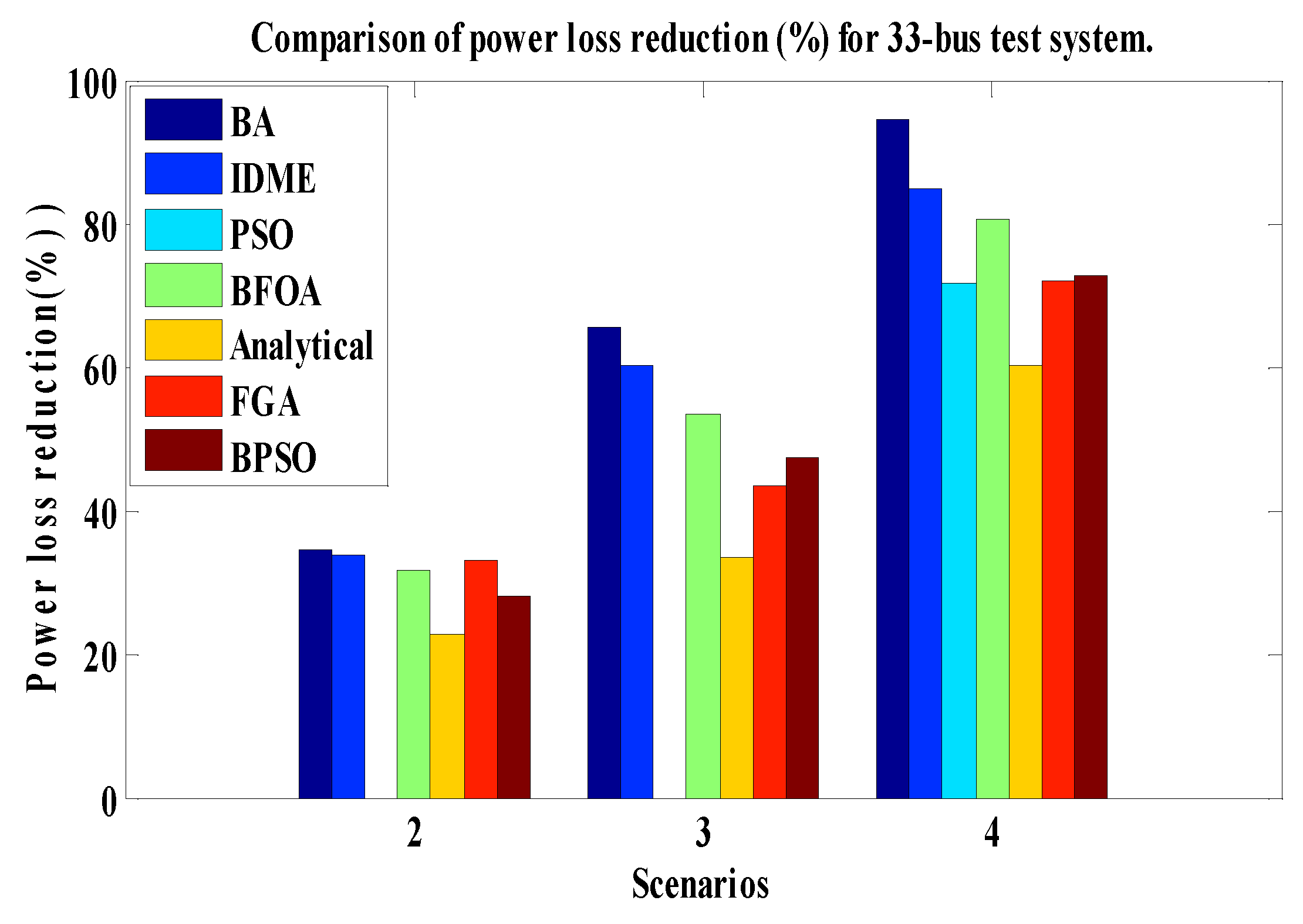
| Parameters | BA | IDME [11] | PSO [8] | BFOA [9] | Analytical [7] | FGA [12] | BPSO [13] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Compensation (Scenario-1) | Ploss(kW) | 210.98 | 210.98 | 210.98 | 210.98 | 210.98 | 210.98 | 210.98 |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.6610 | 0.6610 | 0.6610 | 0.6610 | 0.6610 | 0.6610 | 0.6610 | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9037 | 0.9037 | 0.9037 | 0.9037 | 0.9037 | 0.9037 | 0.9037 | |
| Only Capacitor (Scenario-2) | Optimal kVAr and Sitting | 380 (13) 490(25) 990(30) | 475 (14) 1037 (30) | N/A | 350 (18) 820 (30) 277 (33) | 1000 (33) | 950 (18) 700 (30) | 920 (33) 610 (14) |
| Ploss(kW) | 138.35 | 139.7 | N/A | 144.04 | 164.6 | 141.3 | 151.7 | |
| % Ploss Reduction | 34.4 | 33.79 | N/A | 31.72 | 22.83 | 33.03 | 28.1 | |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.7423 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9301 | 0.9420 | N/A | 0.9361 | 0.9160 | 0.9290 | 0.9190 | |
| Only DG (Scenario-3) | Optimal kW and Sitting | 680(13) 480(25) 1050(30) | 840 (14) 1130 (30) | N/A | 633 (7) 90 (18) 947 (33) | 1000 (18) | 600 (7) 1100 (32) | 1300 (33) 520(8) |
| Ploss(kW) | 72.78 | 84.28 | N/A | 98.3 | 142.34 | 119.7 | 111.5 | |
| % Ploss Reduction | 65.5 | 60.06 | N/A | 53.41 | 33.29 | 43.27 | 47.15 | |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.8652 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9669 | 0.9710 | N/A | 0.9645 | 0.9310 | 0.9350 | 0.9350 | |
| Simultaneous DG and Capacitor (Scenario-4) | Optimal kVAr and Sitting | 380(13) 490(25) 990(30) | 254.8 (16) 932.3 (30) | 1457 (30) | 163 (18) 541 (30) 338 (33) | 400 (33) 500 (32) | 800 (33) 650 (16) | 1500 (30) |
| Optimal kWand Sitting | 680(13) 480(25) 1050(30) | 1080 (10) 896.4 (31) | 2511 (6) | 542 (17) 160 (18) 895 (33) | 447 (18) 559 (17) | 600 (7) 1100 (32) | 2500 (6) | |
| Ploss(kW) | 11.77 | 32.08 | 59.7 | 41.41 | 84.28 | 59.5 | 57.3 | |
| % Ploss Reduction | 94.42 | 84.79 | 71.7 | 80.37 | 60.05 | 71.8 | 72.84 | |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.9601 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9970 | 0.9790 | 0.9550 | 0.9783 | 0.9610 | 0.9600 | 0.9590 | |
| Parameters | Constant Load | Industrial Load | Residential Load | Commercial Load | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Compensation (Scenario 1) | Ploss(kW) | 225 | 171.39 | 164.87 | 156.92 |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.6822 | 0.7136 | 0.7211 | 0.7289 | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9090 | 0.9196 | 0.9217 | 0.9242 | |
| Only Capacitor (Scenario 2) | Optimal kVAr and Sitting | 400 (12) | 290 (12) | 300 (12) | 300 (12) |
| 230 (19) | 160 (19) | 180 (19) | 190 (19) | ||
| 1237 (61) | 740 (61) | 870 (61) | 900 (61) | ||
| Ploss(kW) | 144.96 | 140.39 | 123.95 | 112.36 | |
| % Ploss Reduction | 35.57 | 18.08 | 24.81 | 28.39 | |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.7516 | 0.7490 | 0.7640 | 0.7747 | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9327 | 0.9324 | 0.9367 | 0.9398 | |
| Only DG (Scenario 3) | Optimal kW and Sitting | 535 (12) | 460 (12) | 450 (12) | 440 (12) |
| 340 (19) | 320 (19) | 310 (19) | 300 (19) | ||
| 1693 (61) | 1670 (61) | 1570 (61) | 1480 (61) | ||
| Ploss(kW) | 68.97 | 28.81 | 37.73 | 41.33 | |
| % Ploss Reduction | 69.34 | 83.19 | 77.11 | 73.66 | |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.9113 | 0.9431 | 0.9357 | 0.9314 | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9772 | 0.9857 | 0.9837 | 0.9826 | |
| Simultaneous DG and Capacitor (Scenario 4) | Optimal kVAr and Sitting | 300 (12) | 250 (12) | 240 (12) | 240 (12) |
| 269 (19) | 170 (19) | 200 (19) | 190 (19) | ||
| 1202(61) | 730 (61) | 860 (61) | 900 (61) | ||
| Optimal kWand Sitting | 479 (12) | 460 (12) | 410 (12) | 430 (12) | |
| 365 (19) | 330 (19) | 300 (19) | 300 (19) | ||
| 1680 (61) | 1660 (61) | 1550 (61) | 1480 (61) | ||
| Ploss(kW) | 5.01 | 4.08 | 4.54 | 4.02 | |
| % Ploss Reduction | 97.77 | 97.61 | 97.24 | 97.43 | |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.9607 | 0.9594 | 0.9593 | 0.9593 | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9972 | 0.9944 | 0.9944 | 0.9943 | |
| Parameters | BA | IDME [11] | PSO [8] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Compensation (Scenario 1) | Ploss(kW) | 225 | 225 | 225 |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.6822 | 0.6822 | 0.6822 | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9090 | 0.9090 | 0.9090 | |
| Only Capacitor (Scenario 2) | Optimal kVAr and Sitting | 400 (12) 230 (19) 1237 (61) | 375 (21) 12637 (61) | N/A |
| Ploss(kW) | 144.96 | 145.53 | N/A | |
| % Ploss Reduction | 35.57 | 35.2 | N/A | |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.7516 | N/A | N/A | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9327 | 0.9330 | N/A | |
| Only DG (Scenario 3) | Optimal kWand Sitting | 535 (12) 340 (19) 1693 (61) | 473 (20) 1730 (61) | N/A |
| Ploss(kW) | 68.97 | 70.92 | N/A | |
| % Ploss Reduction | 69.34 | 68.42 | N/A | |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.9113 | N/A | N/A | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9772 | 0.9808 | N/A | |
| Simultaneous DG and Capacitor (Scenario 4) | Optimal kVAr and Sitting | 300 (12) 269 (19) 1202 (61) | 1192 (61) 109 (63) | 14013 (61) |
| Optimal kW and Sitting | 479 (12) 365 (19) 1680 (61) | 479 (24) 1738 (62) | 1566 (61) | |
| Ploss(kW) | 5.01 | 13.83 | 25.9 | |
| % Ploss Reduction | 97.77 | 93.84 | 88.4 | |
| VSImin(p.u) | 0.9607 | N/A | N/A | |
| Vmin(p.u) | 0.9972 | 0.9915 | 0.9700 | |
| Investement Cost of Capacitor/DG | Size of Capacitor, kVAr | Size of DG (kW) | Maintenance Cost of Capacitor/DG | Inflation Rate, %/Year | Interest Rate, %/Year | Load Growth, %/Year | Planning Period, Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4000 | 1860 | 2210 | 400 | 10 | 15 | 1 | 20 |
| Power Loss, kW/pp | Risk Level Mwh/pp | Investment Cost | Maintenance Cost | Cost of Power Loss | Cost of Risk/pp | Total Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial status | 210.98 | 5914 | 0 | 0 | 1,678,415 | 418,874 | 2,457,841 |
| After planning | 11.77 | 3214 | 26,000 | 2400 | 1,367,845 | 251,745 | 1,744,154 |
| Power Loss, MW/pp | Risk Level Mwh/pp | Investment Cost | Maintenance Cost | Cost of Power Loss | Cost of Risk/pp | Total Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount of error/detriment | 210.98 | 11.77 | −4000 | −2400 | 9784 | 16,487 | 1147 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuvaraj, T.; Devabalaji, K.R.; Prabaharan, N.; Haes Alhelou, H.; Manju, A.; Pal, P.; Siano, P. Optimal Integration of Capacitor and Distributed Generation in Distribution System Considering Load Variation Using Bat Optimization Algorithm. Energies 2021, 14, 3548. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123548
Yuvaraj T, Devabalaji KR, Prabaharan N, Haes Alhelou H, Manju A, Pal P, Siano P. Optimal Integration of Capacitor and Distributed Generation in Distribution System Considering Load Variation Using Bat Optimization Algorithm. Energies. 2021; 14(12):3548. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123548
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuvaraj, Thangaraj, Kaliaperumal Rukmani Devabalaji, Natarajan Prabaharan, Hassan Haes Alhelou, Asokkumar Manju, Poushali Pal, and Pierluigi Siano. 2021. "Optimal Integration of Capacitor and Distributed Generation in Distribution System Considering Load Variation Using Bat Optimization Algorithm" Energies 14, no. 12: 3548. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123548
APA StyleYuvaraj, T., Devabalaji, K. R., Prabaharan, N., Haes Alhelou, H., Manju, A., Pal, P., & Siano, P. (2021). Optimal Integration of Capacitor and Distributed Generation in Distribution System Considering Load Variation Using Bat Optimization Algorithm. Energies, 14(12), 3548. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123548









