Abstract
Nowadays, there is a renewed interest in switched reluctance machines and especially in axial-flux switched reluctance machines (AFSRM). This paper presents a comprehensive design procedure for modular AFSRM with an inner stator and two exterior rotors that have a new distribution of the stator and rotor poles, resulting in short magnetic paths with no flux reversal. After a description of the proposed machine, the output torque equation is derived from a simplified non-linear energy conversion loop and guidelines for its design are given. Once the preliminary sizing has been carried out the different modules of the AFSRM, the magnetically active parts made with SMC, are reshaped or refined using 3D printing and 3D electromagnetic finite element analysis until they reach their definitive shape and dimensions. Finally, an AFSRM has been built following the proposed design procedure and has been validated by experimental measurements.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, many applications such as fans, pumps, machine tools, and electric vehicles demand the use of axial-flux electric machines. Most usual axial-flux electric machines are DC commutator motors, brushless DC motors, or synchronous motors, all of them excited with permanent magnets. These machines can be designed in many diverse ways, such as single stage or multistage, with or without armature slots, with or without armature core, or with internal or external rotors to better adapt to the requirements of application in which they have to be used [1]. The development of these machines has gone in parallel with that of the permanent magnets. However, the abrupt increase of the raw material cost in rare earth permanent magnets happened in 2011, shifted research in the field of electrical machines towards topologies with a lower volume of permanent magnets and even without permanent magnets. This circumstance has renewed the interest for switched reluctance machines, especially in the field of electric traction [2]. Some studies carried out in axial-flux switched reluctance motors (AFSRM) demonstrate that they have higher torque density than conventional radial flux switched reluctance machines [3]. The design of AFSRM is not something new; in 1990 Krishnan et al. [4] were the first to give the basics of the design of AFSRM. Later, Arihara and Akatsu proposed the basic design methodology of a single side AFSRM [5], Labak and Kar [6] presented the design procedure and a prototype of a novel five-phase pancake-shaped AFSRM. Madhavan and Fernandes [7,8] developed a new segmented AFSRM with higher number of rotor segments and gave the basis of its design. Ebrahimi and Feyzi made some contributions to the design of AFSRM with modular stator [9]. Recently, Lin proposed a variation of the output equation for this type of machine [10] and Torkaman et al. [11] provided a review of the design of AFSRM including a comparison, considering the assessment of some performance indices among different topologies. This paper proposes a new procedure, taking into account saturation, for the sizing of a particular type of an AFSRM with an inner stator and two exterior rotors that have a new distribution of the stator and rotor poles resulting in short magnetic paths with no flux reversal that have been presented in [12,13,14,15,16]. The machine has been built modularly with stator and rotor poles made with SMC parts. The paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, a description of the proposed AFSRM is presented. Section 3 develops the output torque equation of the AFSRM. In Section 4 guidelines for sizing the AFSRM are given. Section 5 exposes a methodology of design of an AFSRM, intended for the propulsion of a light electric scooter, following the aforementioned sizing guidelines. The experimental assessment of the designed AFSRM is presented in Section 6. Finally, in Section 7, conclusions from this study are drawn.
2. Description of the Proposed Axial-Flux Switched Reluctance Machines (AFSRM) Machine
In this paper, a three phase AFSRM with an inner stator of twelve poles and two outer rotors with ten poles is designed. It is a particular case of a new type of AFSRM with a new arrangement of the stator and the rotor poles and with short flux paths without flux reversal, which has been previously reported [13]. The ten ferromagnetic poles of each rotor are joined on the opposite side of the air-gap, by means of an annular disk also of ferromagnetic material. The stator is formed by twelve poles of triangular shape of ferromagnetic material, sticking out with the same length at both ends of an aluminum structural disk attached to a hollow shaft. An exploded view of such a motor is shown in Figure 1.
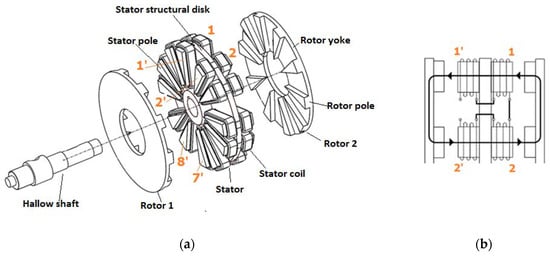
Figure 1.
(a) Exploded view of the proposed axial-flux switched reluctance machines (AFSRM) (left), (b) representation of the flux path when there is alignment between stator and rotor poles (right) [15].
As it is depicted in Figure 2, two coils are wound in both opposite ends of the stator poles and connected in series. The coils of two adjacent stator poles are also connected in series forming a double electromagnet. Having the described machine six double electromagnets, each phase is formed by connecting in parallel the two double electromagnets diametrically opposed. The terminals of the phase windings leave the machine through the hollow shaft.
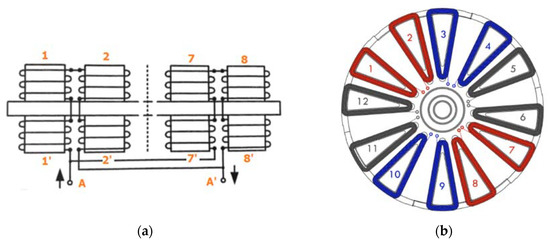
Figure 2.
(a) schematic drawing of the coil’s arrangement of the two double electromagnets diametrically opposed (stator poles 1–2 and 7–8) [15], connected in parallel to form phase A. (b) upper view of the layout of the different phases (red: Phase A; blue: Phase B and black: Phase C).
3. Output Torque Equation for AFSRM
The starting point of the design of electric rotating machines is the output torque equation, which relates the torque with the main dimensions (bore diameter and axial length in radial flux machines), magnetic loading, and electric loading [17]. In this paper, the output torque equation of the AFSRM is derived not of the expression of the average torque disregarding the saturation [4,7,9] but of the energy converted into mechanical work in each stroke, energy conversion loop, represented by the area W (OACEO) shown in Figure 3 [18], multiplied by the number of strokes per revolution, s, given by:
where m is the number of phases and NR the number of rotor poles.
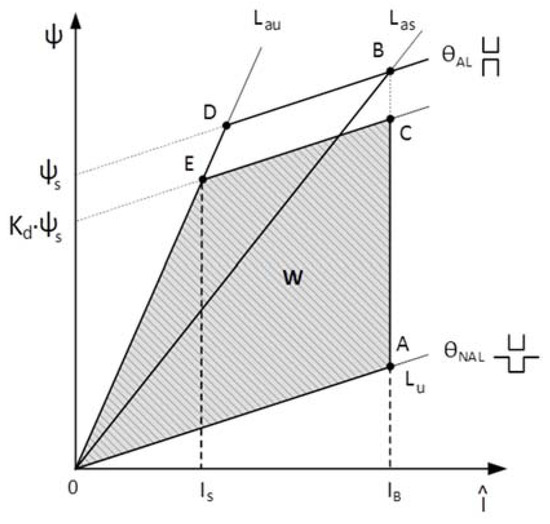
Figure 3.
Energy conversion loop.
If the phase resistance is neglected and the aligned magnetization curve is approximated by two straight lines, OD with a slope Lau, and DB parallel to the unaligned magnetization curve also a straight line, OA, with a slope Lu [15]. The current between points A and C is flat-topped and has a value of IB, being C the point where solid state switches turn-off in which flux linkage, ψs, is equal to kd Las IB, being Las the saturated inductance, slope of the straight line OB, and kd the magnetic flux linkage ratio.
Being, kL, inductance ratio given by:
The flux linkage is the product of the number of turns of the phase, Nf, by the magnetic flux density in the stator pole (magnetic loading), Bp, and by the area of the stator pole. Due to the particular geometry of the AFSRM, with Do and Di which are outer and inner stator diameters, respectively, and considering that the stator pole angle in the average stator diameter is approximately equal to a stroke, the flux linkage is given by:
Considering the linear current density (electric loading) as:
The torque, substituting (3)–(5) in (2) is:
Introducing the relationship between inner and outer diameter, diameter ratio ξ, as:
Then the torque equation can be expressed as:
An alternative expression is:
With:
Therefore, the torque per unit is given by:
The torque per unit with respect to the diameter ratio is depicted in Figure 4, where it can be seen that the maximum torque per unit is achieved when the diameter ratio is one third, nevertheless good values of ξ can be obtained in the margin between one fifth and one half.
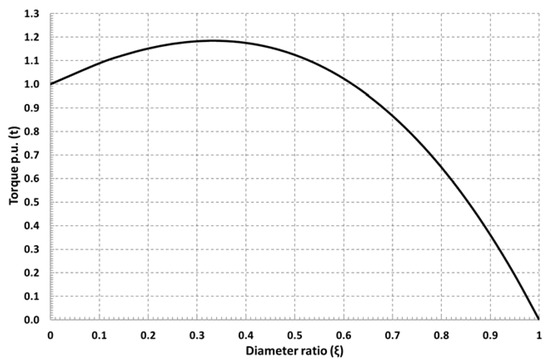
Figure 4.
Torque p.u., t, versus diameter ratio ξ.
In regards to the other terms of the Formula (10) the following considerations should be taken into account:
- Bp, magnetic loading, maximum stator pole magnetic flux density, it should be lower than magnetic flux density of saturation of the magnetic material used
- A, electric loading or linear current density, depends on cooling conditions of the machine, it should be comprised between 75,000 and 200,000 A/m.
- kd, flux linkage duty cycle, usually is between 0.5 and 0.8.
- kL, inductance ratio, depends on the level of saturation of the machine
4. Design Guidelines for the Sizing of the Proposed AFSRM
The AFSRM design procedure starts with the complete definition of all the specifications and restrictions that the application imposes on the machine to be designed. After the selection of the materials to be used, the main dimensions are obtained using the output torque equation. Then, by means of simple formulas, the geometrical dimensions of the stator, the number of turns of the phase windings, and the geometrical dimensions of the two rotors are determined.
4.1. Design of Stator Polar Pieces and Determination of the Number of Turns Per Pole
The stator pole pieces are arranged according to Figure 5, where γ the angle between axes of consecutive double electromagnets, with Z number of double electromagnets, is given by:
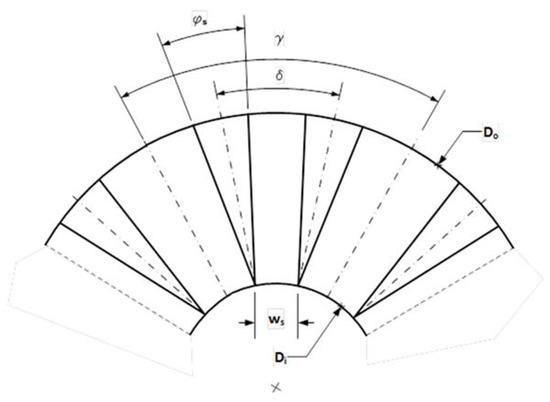
Figure 5.
Stator section showing the disposition and dimensions of stator poles.
And δ is the angle between axes of stator poles of two consecutive double electromagnets:
The polar pieces of the stator have a triangular shape and considering that in the stator pieces whose symmetry axis form an angle δ the inner sides of these pieces are parallel, that is, the distance ws is constant between Do and Di along the two stator poles, the angle φs is approximately:
In practice, it could be advisable, in order to reduce stator mass, that:
Being:
Therefore, the area of a stator pole, Asp, is:
Otherwise, the voltage equation of the AFSRM can be approximated, being ω the speed of the machine and neglecting phase resistance, by:
From Figure 3, the increment of flux linkage between points A and C can be given by:
And the variation of position between points A and C can be approximate by:
Then the number of turns per phase, Nf, is given by:
The number of turns per coil, Np, depends on the number of double electromagnets per phase, two in the AFRM considered, each consisting of four coils, and of their connection (x = 1 series connection and x = 1/2 for parallel connection), thus:
The wire section, sc, considering the connection of the double electromagnets per phase, is determined by the ratio between RMS (Root Mean Square value) phase current I and the current density, Δ, as:
The copper area, Acu, into a slot is approximately equal to:
Being kv the slot fill factor, and he the height of the protruding stator pole at one side of the structural disk:
The total height of a stator pole, het, is:
With hce thickness of stator structural disk, Figure 6.
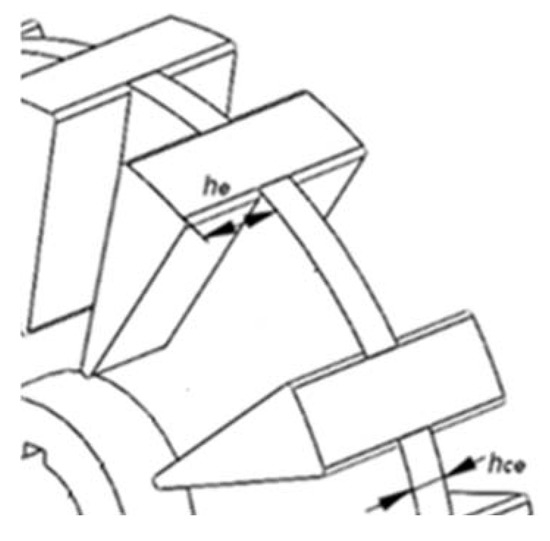
Figure 6.
Arrangement of stator poles into the structural disk.
4.2. Design of Rotor Pole and Yoke
The rotor pole pieces are equally displaced, Figure 7, by the angle α equal to:
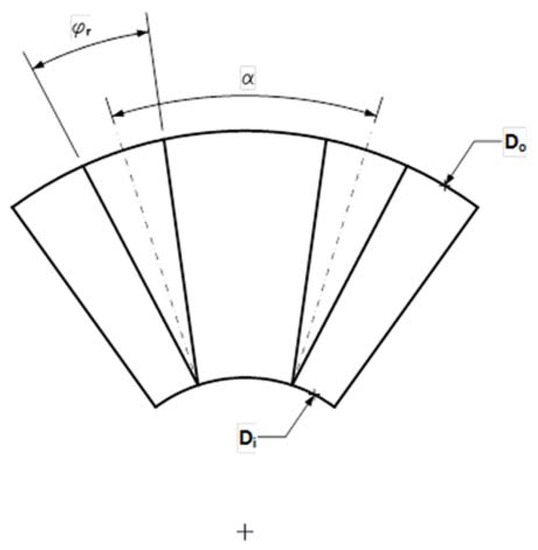
Figure 7.
Rotor section showing disposition and dimensions of rotor poles.
The rotor poles have the same length, half the difference between outer an inner diameter than stator poles. The angle φr should verify:
The height of the rotor pole, Figure 8, can be estimated approximately by:
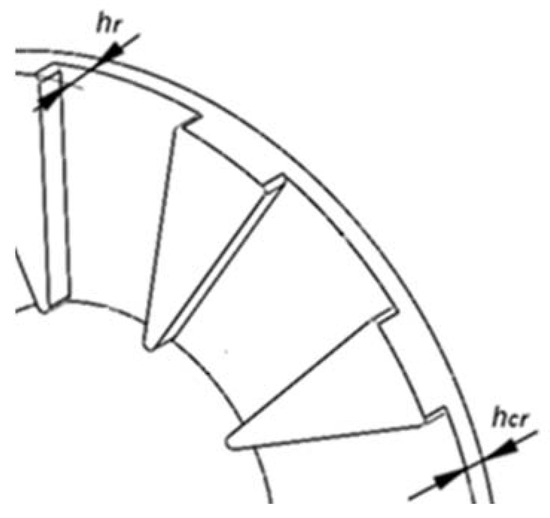
Figure 8.
Arrangement of rotor poles and rotor yoke.
The thickness of the rotor yoke, hcr, is determined considering that the yoke area is approximately half than the rotor pole area in order to reduce mass and despite this increase the flux density in the rotor yoke, therefore the yoke area can be expressed by:
The air-gap, g, should be as small as possible compatible with mechanical tolerances but it is advisable not to be less than 0.5 mm.
Active axial length of the AFSRM, LAX, excluding the thickness of the two covers is equal to:
5. Methodology of Design
In order to design an AFSRM intended for the propulsion of a light electric scooter, the following methodology is proposed. Once the materials are selected, the geometry is defined, and the number of turns per phase is determined according the sizing guidelines are exposed in Section 4, some adjustments will be made due to the modular construction of the machine using 3D printing and 3D analysis of electromagnetic fields with finite elements (3D FEA). Finally, once the definitive dimensions and parameters of the AFSRM have been specified, an electromagnetic evaluation of the AFSRM is will be carried out by means of 3D FEA. It is important to add that the design process should considerer a thermal analysis in operational conditions, but this will be an objective of a future paper.
5.1. Specifications and Restrictions
The AFSRM must develop a torque of 80 Nm at 335 rpm and provide a constant power of 2.8 kW between 335 rpm and 1215 rpm. Due to the machine has to be placed inside a wheel of 13″ the maximum external dimensions were limited to a diameter of the motor frame of 308 mm and an axial length of 116 mm. The battery voltage was 96 V and the AFSRM was controlled using the SRM controller shown in Figure 9 and described in [20].
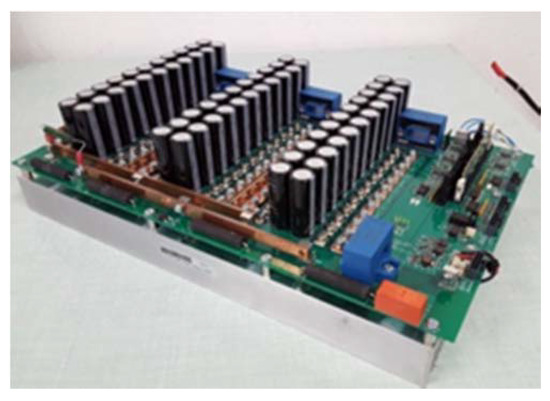
Figure 9.
View of the power electronic controller.
The construction of the magnetic circuit of the proposed AFSRM, due to the difficulties of built it with electrical steel, was made using SMC (Soft Magnetic Composites). First, commercially available Somaloy 700 3P was the selected material but finally a SMC material, with a density of 7.33 g/cm3 and with the B-H curve shown in Figure 10, was used.
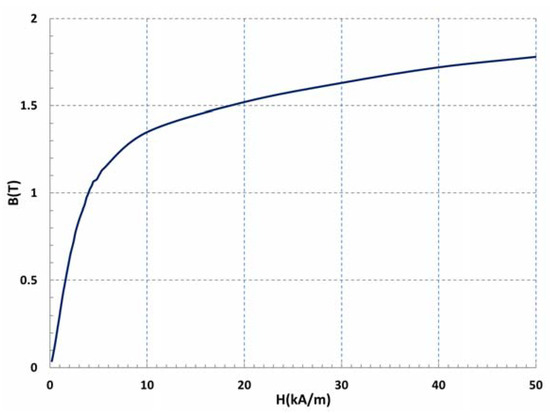
Figure 10.
B-H curve of the SMC used.
5.2. First Approach to the Dimensions of the AFSRM
The AFSRM to be designed has to be able to provide a torque of 80 Nm at 335 rpm. Taking into account the characteristics of the SMC used, the electric loading considered, Bp, is of 1.6 T. Since the planned cooling is natural the electric loading, A, is of 121,000 A/m. With these values and taking a diameter ratio, ξ, of 0.5, a magnetic flux linkage duty cycle, kd, of 0.8 and estimating inductance ratio, kL, about 0.4 an outer diameter of 260 mm is obtained from output torque Equation (8). Value that, of course, should be lower than the external diameter of the frame. Then following the proposed sizing guidelines, the main dimensions of the stator and rotor as well as the main winding data are obtained as it is shown in the second column of Table A1 in the Appendix A. It is important to point out that the number of turns per pole is calculated according to Formula (21) considering that AFSRM has to give 2.8 kW at 1215 rpm with an RMS current of 60 A and a current density of 5 A/mm2.
5.3. Definitive Design of the SMC Parts
The modular construction of the AFSRM, the use of SMC, and the fact that its different parts, in addition to channeling the magnetic flux, must give mechanical consistency to the AFSRM, so that stator poles must fit in the structural disk and rotor poles must be glued on the covers, makes the dimensions determined by the above-mentioned procedure should be slightly modified. At this point, it is important to keep in mind that in prototyping, the pieces of SMC are made by machining blocks of SMC with dimensional limitations that condition the size of the pieces to be performed, in addition some machining operations should be avoided, circumstances that restricts the assembly possibilities of the SMC parts in the machine. In order to deal with them, two tools have been of great importance to refine and reshape the parts of SMC of the machine. The first is 3D printing that enables to easily assess the constructive modifications of the parts introduced to ease the assembly of the different parts into the machine. The second is 3D-FEA [21] that, in addition to enabling the determination of the magnetization and static torque curves that provide an assessment of the AFSRM performance, allows observing the variations in the magnetic flux density due to the modifications made in the stator or rotor poles, which facilitates the evaluation of the convenience of carrying out these modifications.
Figure 11 depicts the disposition of stator poles into the structural disk (a) made by means of 3D printing and the 3D-FEA (b) showing the map of flux magnetic density when there is full alignment with the rotor pole for a current of 100 A.
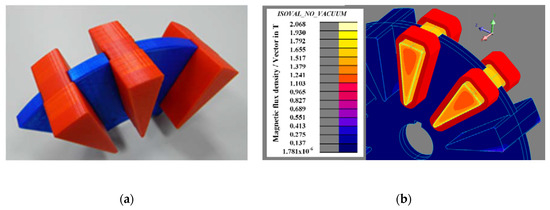
Figure 11.
(a) Stator pole arrangement into the structural disk with parts made by 3 D printing and (b) map of magnetic flux density in the stator poles obtained by 3D-FEA when there is full alignment with the rotor poles for a current of 100 A.
Figure 12 shows the evolution of the stator polar pieces from the first’s pieces obtained by 3D printing to the final of SMC. The evolution of the rotor pole pieces is also depicted in Figure 13. The final pieces of SMC both of stator and rotor are those that best respond, in shape and dimensions, to the conditioning factors of the materials, to the structural requirements, and to a minimization of its mass. Circumstances that modify some of the dimensions or parameters of the machine are indicated in the third column (final value) of Table A1 of the Appendix A.
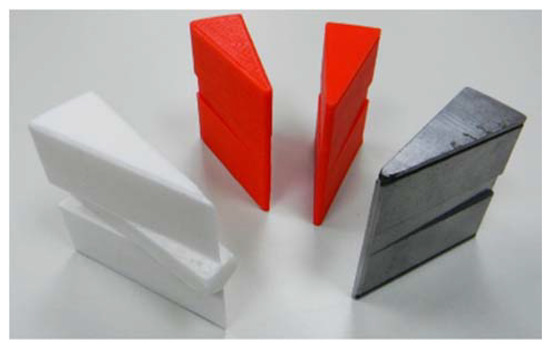
Figure 12.
Evolution of stator pole pieces.

Figure 13.
Evolution of rotor pole pieces.
5.4. 3D Finite Element Analysis
Once all the dimensions and parameters of the AFSRM prototype are completely defined, as it was mentioned in Section 5.3, the magnetization curves and the static torque curves of the machine can be obtained by 3D FEA. In Figure 14, magnetization curves are represented, while in Figure 15, static torque curves for different values of current are shown. The information given from these curves can be enough for a first assessment of the AFSRM or can be used in a more complete simulation considering, besides AFSRM, the power converter and control strategies performed using Matlab-Simulink as described in [12]. Anyway, once the simulation has shown that the proposed solution matches the previous expectations of the drive it is time to build a prototype with the corrected values derived of the exposed design procedure. In Figure 16a, a view of the complete stator, including winding, and the two covers with the rotor pole pieces glued to them can be seen, while Figure 16b shows a photography of the complete AFSRM prototype.
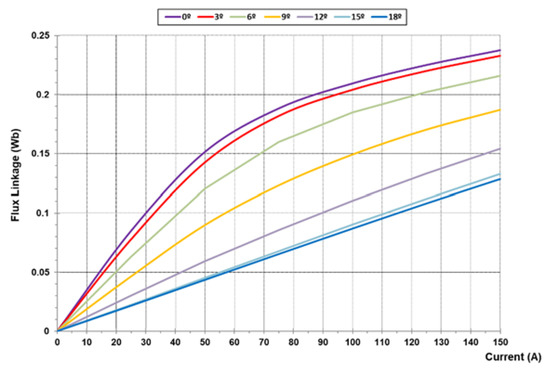
Figure 14.
Aligned and unaligned magnetization curves for AFSRM prototype.
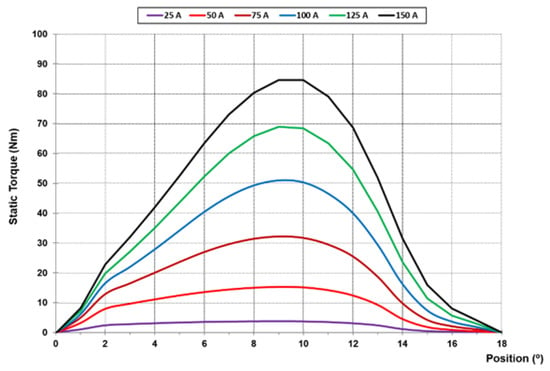
Figure 15.
Static torque curves for AFSRM prototype.

Figure 16.
(a) Stator and the two motor covers, showing in the central part the SMC rotor pieces glued on the cover and (b) view of the fully assembled AFSRM prototype.
6. Experimental Assessment of the Designed AFSRM
Once the AFSRM and the controller were built, the drive was tested in a test rig in order to assess its performance.
6.1. Test Rig Description
The AFSRM prototype was tested in the test rig shown in Figure 17. The AFSRM was coupled through a torque-meter, Kistler 4550A500S10N1KA0 500 Nm, to a DC machine acting as a brake and connected to a DC source variable in voltage and current, APS DPS 100–450, through the mentioned electronic power controller [20], controlled by a HIL platform, dSPACE ACE 1006. The measurements of torque, speed and power were monitored by means of testing power analyzer system, eDrive package GEN2tA-6ch-2Ms/s of HBM.
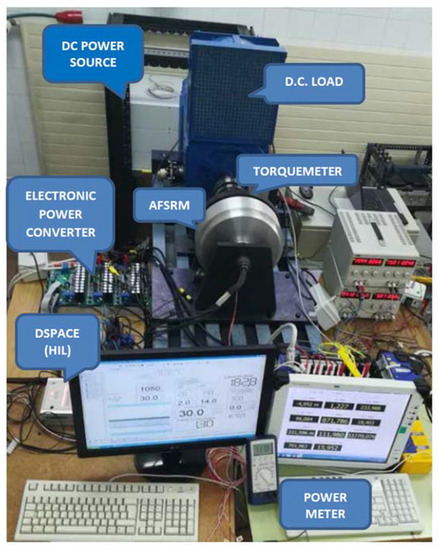
Figure 17.
AFSRM drive test rig.
6.2. AFSRM Drive Control
In order to meet the requirements of the drive, the control strategy used was hysteresis control with variable turn-on and turn-off angles in low and medium speeds and single pulse with variable turn–on and turn-off angles for high values of speed. The values of reference current and of the turn-on and turn-off angles for each point of operation were determined after many simulations performed with Matlab-Simulink, using the results of the finite element analysis of the AFSRM [12,13,14].
6.3. Experimental Results of the AFSRM Prototype
The test rig enabled the experimental determination of torque-speed curves of the AFSRM drive, keeping the speed constant while the load was increased acting on the DC machine. Figure 18 shows these curves, including power isolines for better comparison, with the drive expected requirements that are depicted by a dashed red line. The behavior of the drive at different points of operation was analyzed considering the aforementioned control strategy. Although turn-on and turn-off angles were predetermined by simulation, some adjustments had to be performed to adapt to the actual behavior of the drive. These adjustments were made to determine the angles that provided a lower absorbed current and a higher output torque, ensuring that the motor temperature was the same for all operating points. From these adjustments a new table of turn-on and turn-off angles was obtained that was better adapted to the different operating conditions of the AFSRM. Figure 19 shows the waveforms of phase current, phase voltage, and bus current for 500 rpm, 60 Nm with hysteresis control (θON = −4°, θOFF = 12°). Figure 20 depicts the waveforms of phase current, phase voltage and bus current for 900 rpm, 30 Nm with hysteresis control (θON = −7°, θOFF = 8°) and Figure 21 shows the waveforms of phase current, phase voltage, and bus current for 1400 rpm, 20 Nm with single pulse control (θON = −7°, θOFF = 8°).
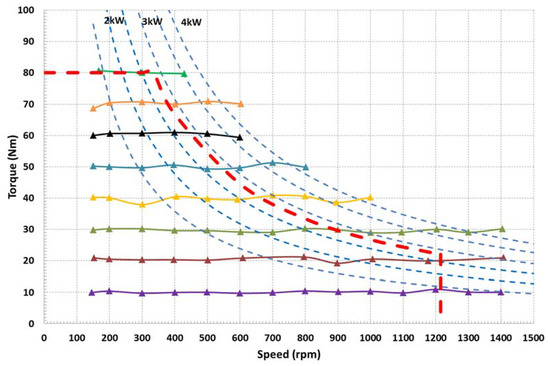
Figure 18.
Torque-speed curves experimentally obtained on the test rig. Drive requirements depicted by the red dashed line.
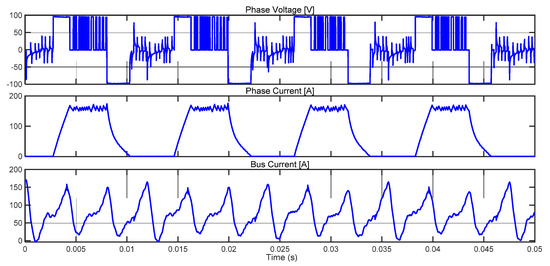
Figure 19.
Experimental waveforms of phase current, phase voltage and bus current for 500 rpm, 60 Nm with hysteresis control θON = −4°, θOFF = 12°.
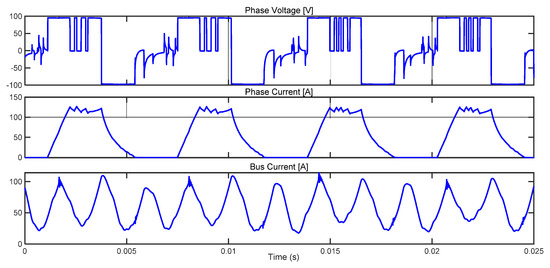
Figure 20.
Experimental waveforms of phase current, phase voltage and bus current for 900 rpm, 30 Nm with hysteresis control θON = −7°, θOFF = 8°.
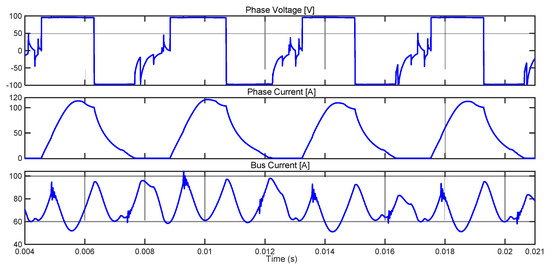
Figure 21.
Experimental waveforms of phase current, phase voltage and bus current for 1400 rpm, 20 Nm with single pulse control θON = −7°, θOFF = 8°.
7. Conclusions
This paper presents a comprehensive design procedure for an AFSRM with an inner stator and two exterior rotors that have a new distribution of the stator and rotor poles resulting in short magnetic paths with no flux reversal. In the proposed procedure, the output torque equation is derived from a simplified non-linear energy conversion loop therefore considering saturation. Then, guidelines for the sizing of the stator, rotors, and winding are given. The design is refined using 3D printing and 3D FEEA. Following the proposed design, an AFSRM prototype was built. Finally, the prototype was tested in a test rig. Experimental results proved the goodness of the proposed procedure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.A.; Methodology, P.A.; Simulation, E.M., B.B., M.T.; Mounting, B.B. and J.A.S.; Tests, B.B., J.I.P., and M.T.; Writing—original draft preparation, P.A. and M.T.; Writing—review and editing, P.A., B.B., E.M., J.I.P., J.A.S. and M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (DPI 2014-57086-R and FEDER Funds.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank AMES S.A. for providing the SMC pieces and specially Mark Dougan Chief Metallurgist, Dept. of R&D AMES S.A. and José Antonio Calero R&D Manager of AMES S.A. for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Main dimensions of the AFSRM prototype

Table A1.
Main dimensions and parameters of the AFSRM prototype.
Table A1.
Main dimensions and parameters of the AFSRM prototype.
| Dimension | Value | Final Value |
|---|---|---|
| Do | 260 mm | 260 mm |
| 0.5 | 0.45 | |
| Di | 130 mm | 117.9 mm |
| D | 75 mm | 75 mm |
| α | 36° | 36° |
| γ | 60° | 60° |
| 24° | 24° | |
| 24° | 20° | |
| 26° | 24.35° | |
| ws | 27.03 mm | 20.47 mm |
| g | 0.5 mm | 0.6 mm |
| Nf | 108 turns | 108 turns |
| x | 1 | 1/2 |
| Np | 16 turns | 32 turns |
| he | 25.83 mm | 28.9 mm |
| sc | 10.91 mm2 | 4.78 mm2 |
| hce | 12 mm | 12 mm |
| kv | 0.5 | 0.57 |
| hr | 8.61 mm | 10 mm |
| hcr | 7.5 mm | 8 mm |
| Lax | 96.88 mm | 108.8 mm |
References
- Gieras, J.F.; Wang, R.; Kamper, M.J. Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Brushless Machines, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Andrada, P.; Dougan, M.J.; Egea, A.; Márquez-Fernández, M.J.; Szabó, L. Are SRM drives a real alternative for EV powertrain? In Proceedings of the Workshop on SRM An Alternative for E-Traction, Vilanova i la Geltrú, Barcelona, Spain, 2 February 2018; pp. 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; McCulloch, M.D. A review of high-power density switched reluctance machines suitable for automotive applications. In Proceedings of the ICEM 2012, Marseille, France, 2–5 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, R.; Abouzeid, M.; Mang, X. A design procedure for axial field switched reluctance motors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 7–12 October 1990; pp. 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Arihara, H.; Akatsu, K. Basic properties of an axial-type switched reluctance motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labak, A.; Kar, N.C. Designing and prototyping a novel five-phase pancake-shaped axial flux SRM for electric vehicle application through dynamic FEA incorporating flux-tube modeling. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, R.; Fernandes, B.G. Axial flux segmented SRM with a higher number of rotor segments for electrical vehicles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2013, 28, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, R.; Fernandes, B.G. A novel axial flux segmented SRM for electric vehicle application. In Proceedings of the ICEM 2010, Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, Y.; Feyzi, M.R. A high torque density axial flux SRM with modular stator. Iran. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2015, 11, 336–344. [Google Scholar]
- Birgin, B.; Jiang, J.W.; Emadi, A. Switched Reluctance Motor Drives; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Torkaman, H.; Ghaheri, A.; Keyhani, A. Axial flux switched reluctance Machines: A comprehensive review of design and topologies. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2019, 33, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrada, P.; Martinez, E.; Blanqué, B.; Torrent, M.; Perat, J.I.; Sánchez, J.A. New axial-flux switched reluctance motor for E-scooter. In Proceedings of the ESARS ITEC, Toulouse, France, 2–4 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Andrada, P.; Martinez, E.; Torrent, M.; Blanqué, B. Electromagnetic evaluation of an in-wheel double rotor axial-flux switched reluctance motor for electric traction. In Proceedings of the ICREPQ 2017, Malaga, Spain, 4–6 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Andrada, P.; Blanqué, B.; Martinez, E.; Perat, J.I.; Sánchez, J.A.; Torrent, M. In wheel-axial-flux SRM drive for light electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the Workshop on SRM An Alternative for E-Traction, Vilanova i la Geltrú, Barcelona, Spain, 2 February 2018; pp. 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Andrada, P.; Blanqué, B.; Martinez, E.; Perat, J.I.; Sánchez, J.A.; Torrent, M. Influence of manufacturing and assembly defects and the quality of materials on the performance of an axial-flux switched reluctance machine. Energies 2019, 12, 4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An Axial Flux Switched Reluctance Machine and An Electric Vehicle Comprising the Machine. WO2018077788, 5 March 2018.
- Krishnan, R.; Arumugan, R.; Lindsay, J.M. Design procedure for switched-reluctance motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1988, 24, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.J.E. Converter volt-ampere requirements of the switched reluctance motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1985, 21, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Amorós, J.; Andrada, P.; Blanqué, B. Design procedure for a longitudinal flux flat linear switched reluctance motor. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2012, 40, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrada, P.; Blanqué, B.; Capó, M.; Gross, G.; Montesinos, D. Switched Reluctance Motor Controller for Light Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the EPE’18 ECCE Europe, Riga, Latvia, 17–21 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Flux 12.1; Altair: Troy, MI, USA, 2019.
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).