Stochastic Modeling Method of Plug-in Electric Vehicle Charging Demand for Korean Transmission System Planning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A stochastic method which models the PEV charging demand as electric loads over the substations in the transmission system planning process. The method considers the uncertainty and variations in the distribution and charging profiles of the PEVs.
- The distribution of PEVs is estimated by the substation based on the number of electricity customers, the PEV expansion target, and existing statistics. An individual PEV charging profile is modeled using the statistics of existing internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles driving.
- By aggregating the PEV charging profiles per 154 kV substation, the charging demand of PEVs can be determined for consideration as a part of the total electricity demand in the planning process of transmission systems.
2. Penetration Trend and Charging Demand of EVs in Korea
3. Stochastic Modeling for PEV Charging Demand
3.1. Distribution of PEVs
3.2. Charging Demand of PEVs
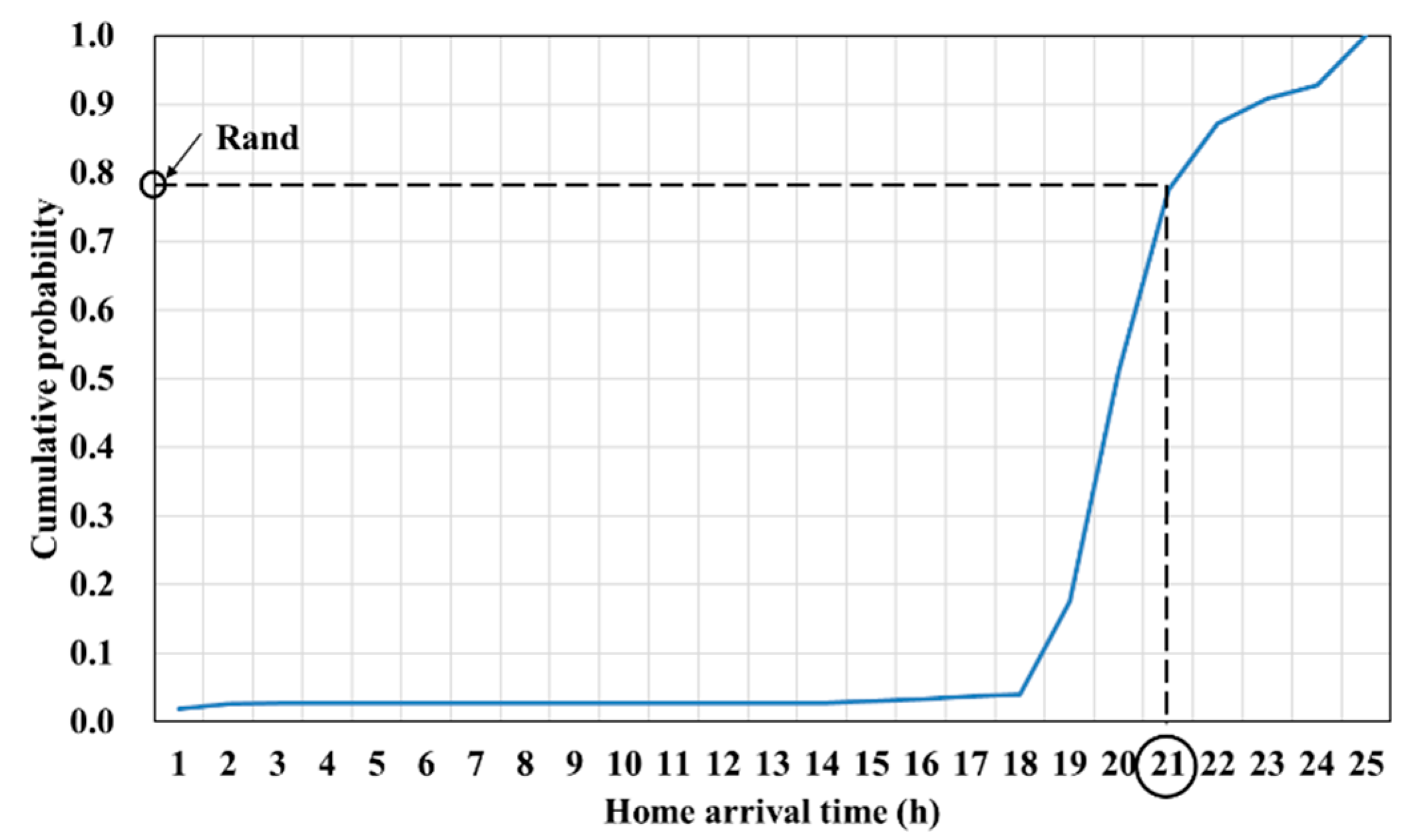
3.3. Charging Profile of PEV
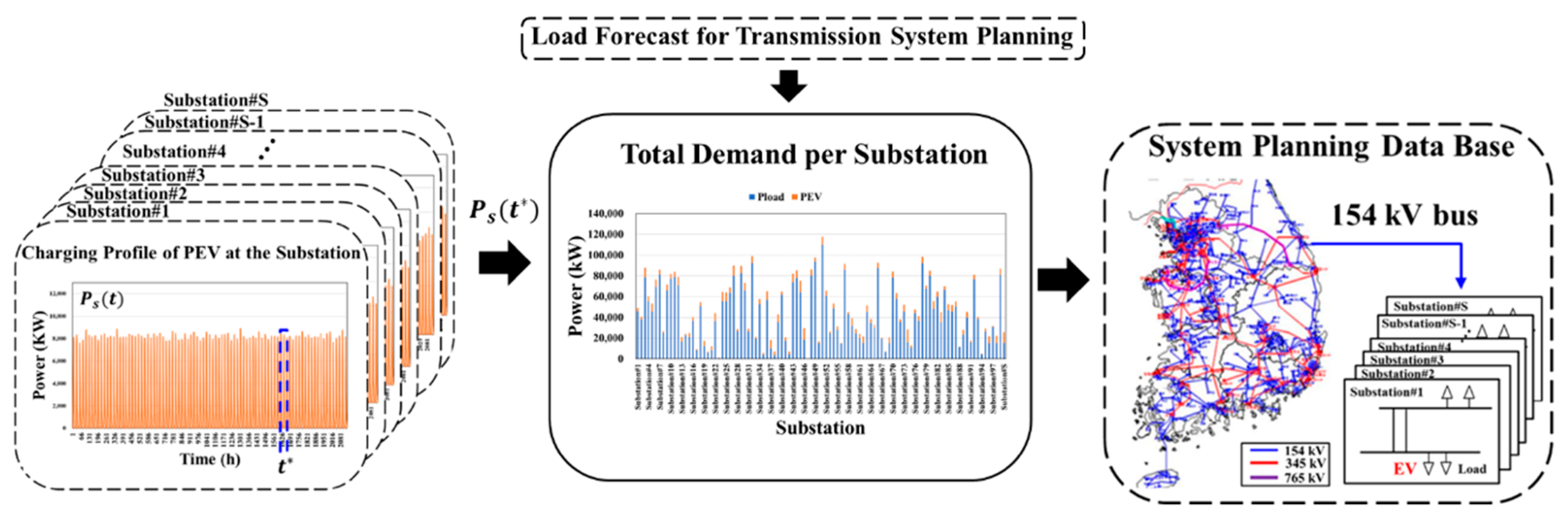
3.4. Charging Demand of PEVs per Substation
4. Case Study
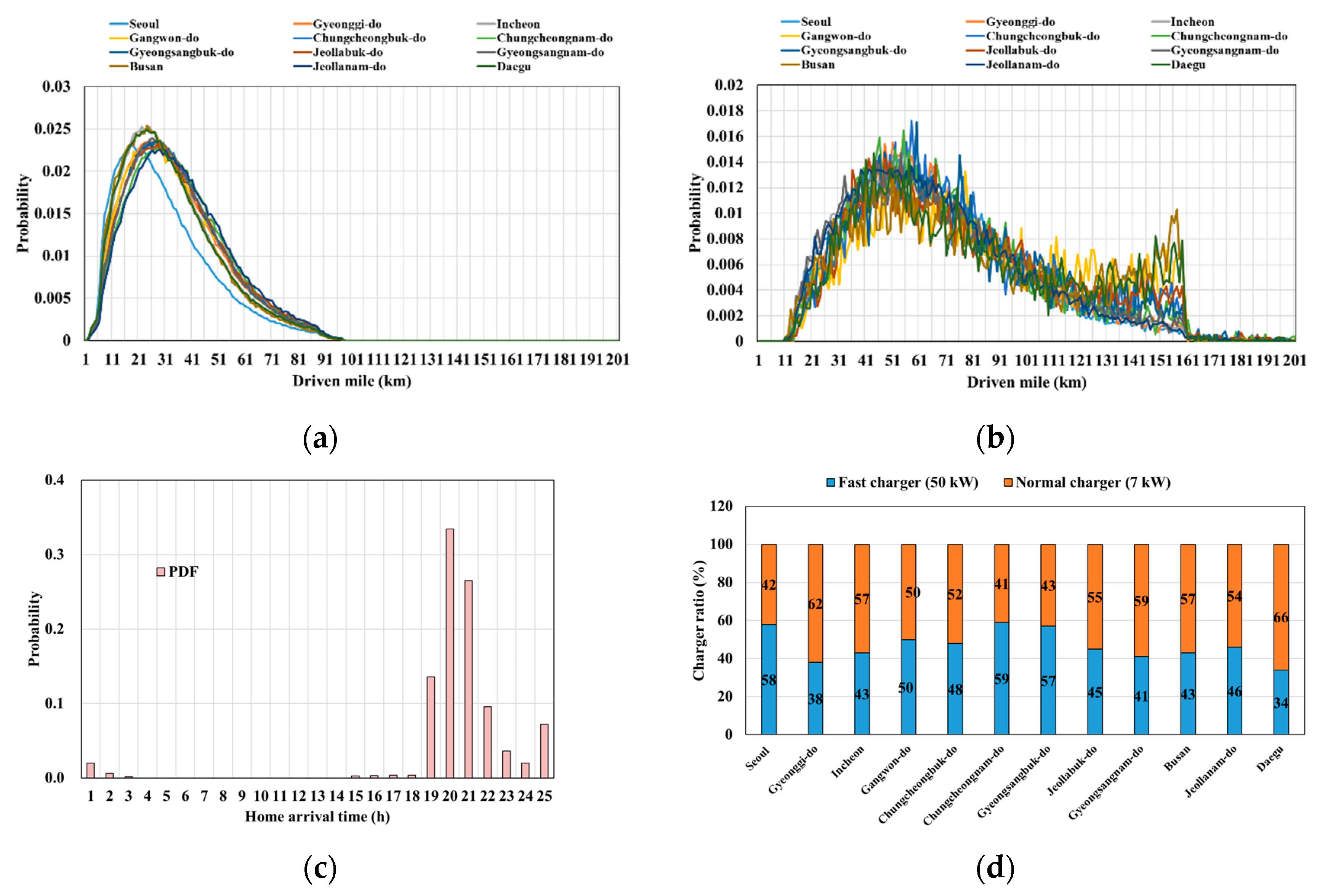
4.1. Distribution of PEVs in Korean Power System
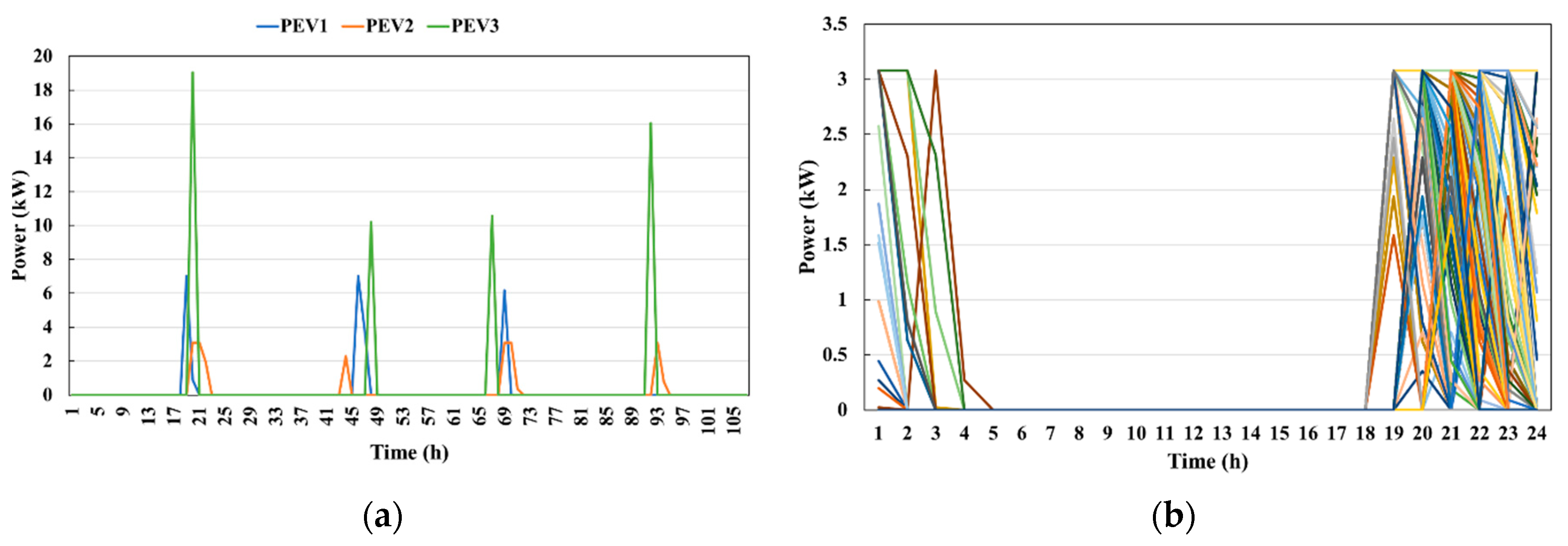
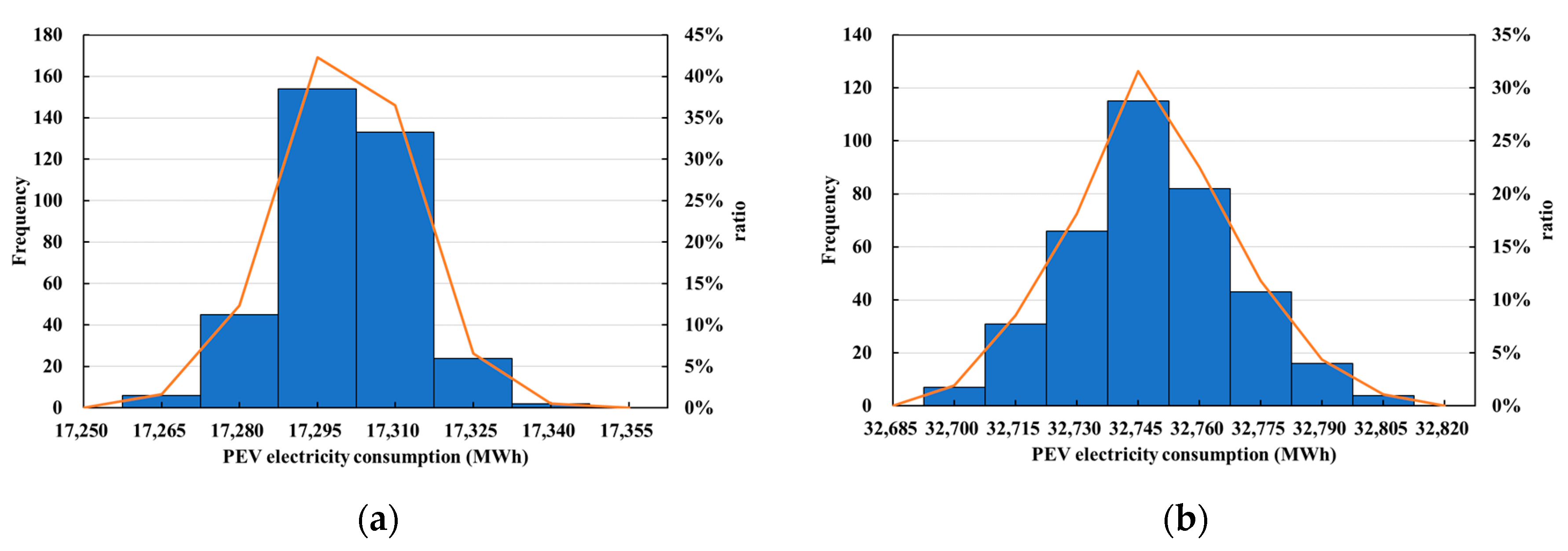
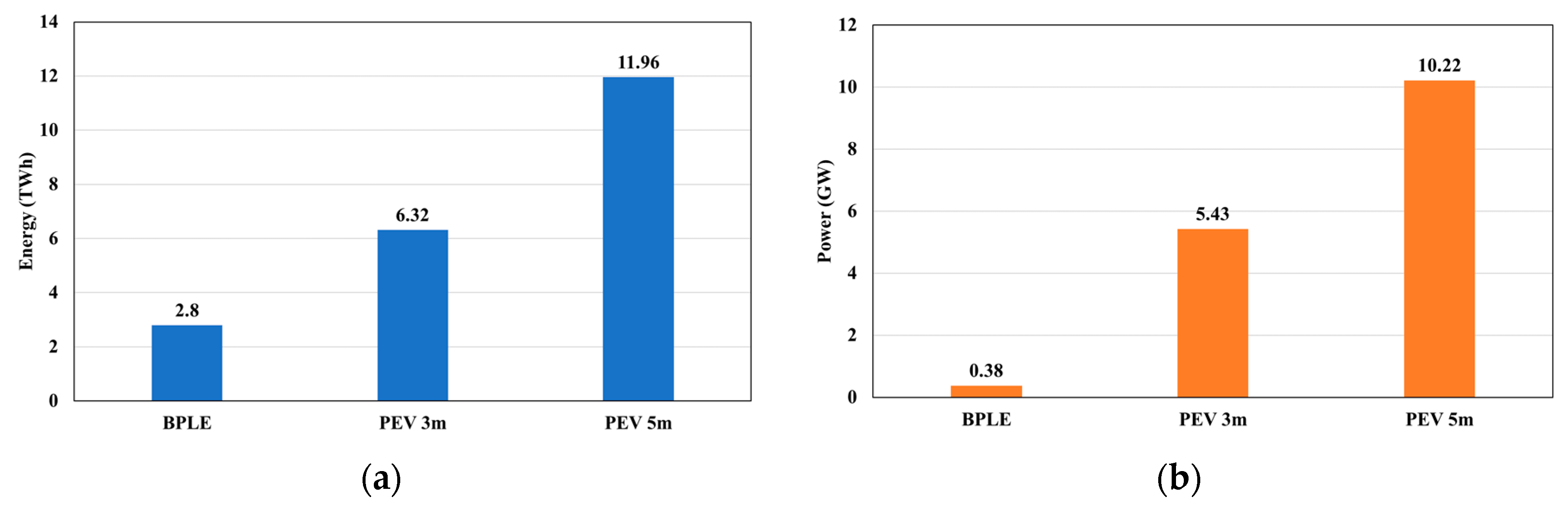
4.2. Modeling Results of PEV Charging Demand
4.3. Characteristics Analysis of PEV Charging Demand
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNFCC. Paris agreement. In Report of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change; UNFCC: New York, NY, USA, 11–30 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization of Motor Vehicles Manufacturers, Climate Change and CO2. May 2008. Available online: http://oica.net/wp-content/uploads/climate-change-and-co2-brochure.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2020).
- Johansson, S.; Persson, J.; Lazarou, S.; Theocharis, A. Investigation of the Impact of Large-Scale Integration of Electric Vehicles for a Swedish Distribution Network. Energies 2019, 12, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, C.; Morstyn, T.; McCulloch, M. The opportunity for smart charging to mitigate the impact of electric vehicles on transmission and distribution systems. Appl. Energy 2020, 6, 114973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieltain Fernández, L.; Gomez San Roman, T.; Cossent, R.; Mateo Domingo, C.; Frías, P. Assessment of the Impact of Plug-in Electric Vehicles on Distribution Networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 2, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Energy Economics Institute (KEEI). Analysis of Impact of Energy Supply and Demand of Dissemination of Electric Vehicles; KEEI: Ulsan, Korea, November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Power Exchange (KPX). The Affect and Implication of the Electric Power Supply and Demand according to Dissemination Electric Vehicle; KPX: Naju, Korea, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hafez, O.; Bhattacharya, K. Queuing Analysis Based PEV load Modeling Considering Battery Charging Behavior and Their Impact on Distribution System Operation. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, Y.; Li, B.; Li, J. A Modeling Method for the Power Demand of Electric Vehicles Based on Monte Carlo Simulation. In Proceedings of the 2012 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, Shanghai, China, 27–29 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, X.; Chan, C. Optimal scheduling for vehicle-to-grid operation with stochastic connection of plug-in electric vehicles to smart grid. Appl. Energy 2015, 146, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Zhou, C.; Allan, M.; Yuan, Y. Modeling of Load Demand Due to EV Battery Charging in Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 5, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Deblecker, O.; Ioakimidis, C.S. Optimal operation of an energy management system for a grid-connected smart building considering photovoltaics’ uncertainty and stochastic electric vehicles’ driving schedule. Appl. Energy 2017, 210, 1188–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaee, S.; Mortazaci, S.S.; Niknam, T. Stochastic scheduling of local distribution systems considering high penetration of plug-in electric vehicles and renewable energy sources. Energy 2017, 121, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavousi-Fard, A.; Niknam, T.; Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M. Stochastic Reconfiguration and Optimal Coordination of V2G Plug-in Electric Vehicles Considering Correlated Wind Power Generation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 6, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nigris, M.; Gianinoni, I.; Grillo, S.; Massucco, S.; Silvestro, F. Impact evaluation of plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) on electric distribution networks. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Harmonics and Quality of Power—ICHPQ 2010, Bergamo, Italy, 26–29 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea. The 2nd Basic Plan for Climate Charge Response; MOE: Sejong, Korea, 2019.
- Ministry of the Interior and Safety, Republic of Korea. 2030 National Greenhouse Gas Reduction Basic Roadmap Amendment; MOIS: Sejong, Korea, 2018.
- Korean Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. The 8th Basic Plan for Long-Term Electricity Supply and Demand (2017–2031); Korean Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy: Sejong, Korea, 2017; pp. 70–83.
- Son, H.J.; Kook, K.S. Stochastic Modeling of Plug-in Electric Vehicle Distribution in Power Systems. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2013, 8, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Korea. The Number of Household by the Status of the Vehicle Ownership and the Status of Transportation Uses; KOSTAT: Daejeon, Korea, 2012.
- Normal EV Charger (3 kW). Available online: https://www.ev-line.co.kr/subsidy_request/sr_one_01.asp (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Normal EV Charger (7 kW). Available online: http://www.ecarplug.com/sub/m2_product1_cpw.php (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Fast EV Charger (50 kW). Available online: http://www.ecarplug.com/sub/m2_product2_1.php (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Statistics of ICE Vehicles. Available online: https://mdis.kostat.go.kr/index.do (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Specification of HYUNDAI IONIQ EV. Available online: https://www.hundai.com/kr/ko/e/vehicles/ioniq-electric/spec (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Clairand, J.; Rodríguez-García, J.; Álvarez-Bel, C. Assessment of Technical and Economic Impacts of EV User Behavior on EV Aggregator Smart Charging. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2020, 8, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.; Josef, K. Understanding charging behavior of electric vehicle users. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2013, 21, 75–89. [Google Scholar]
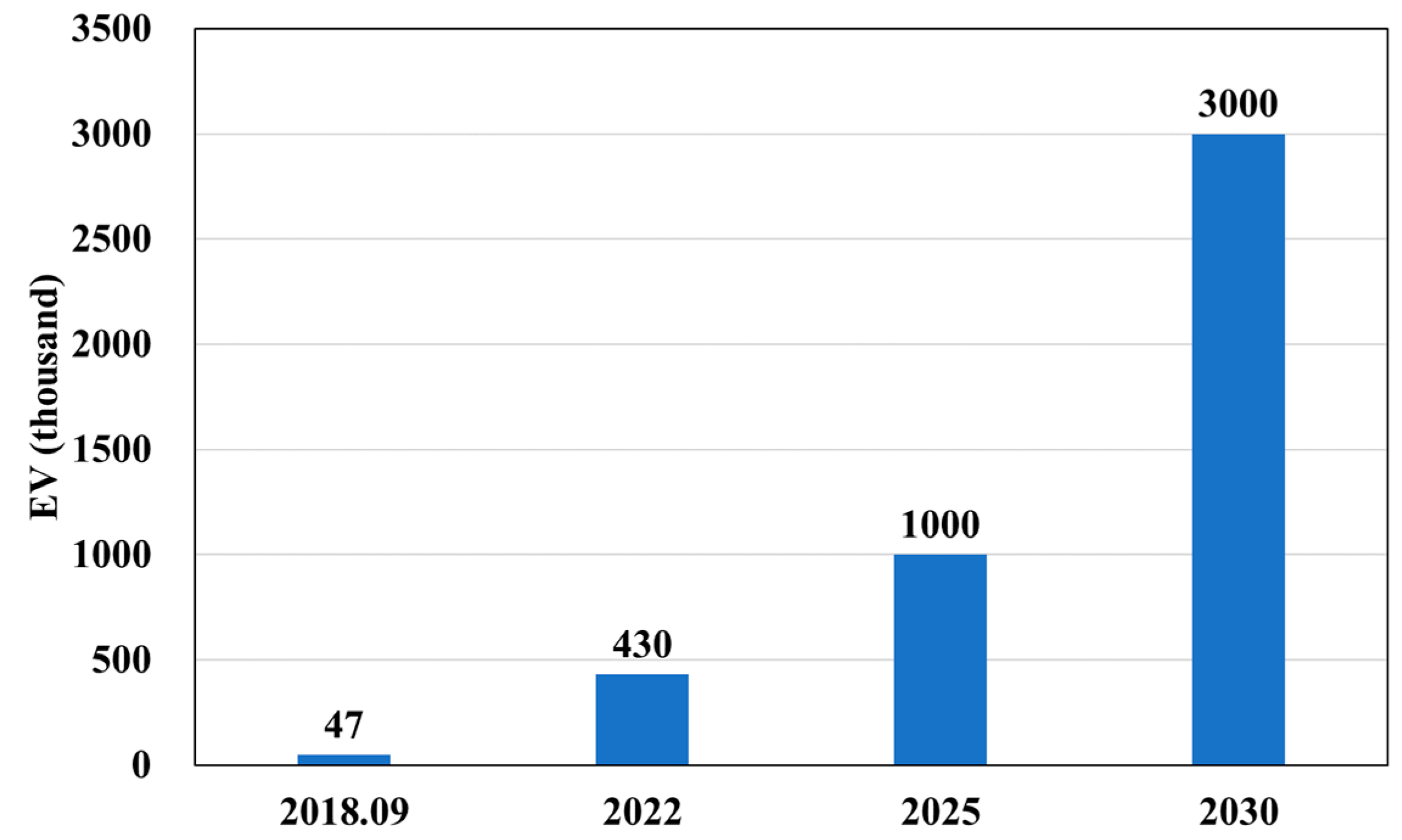
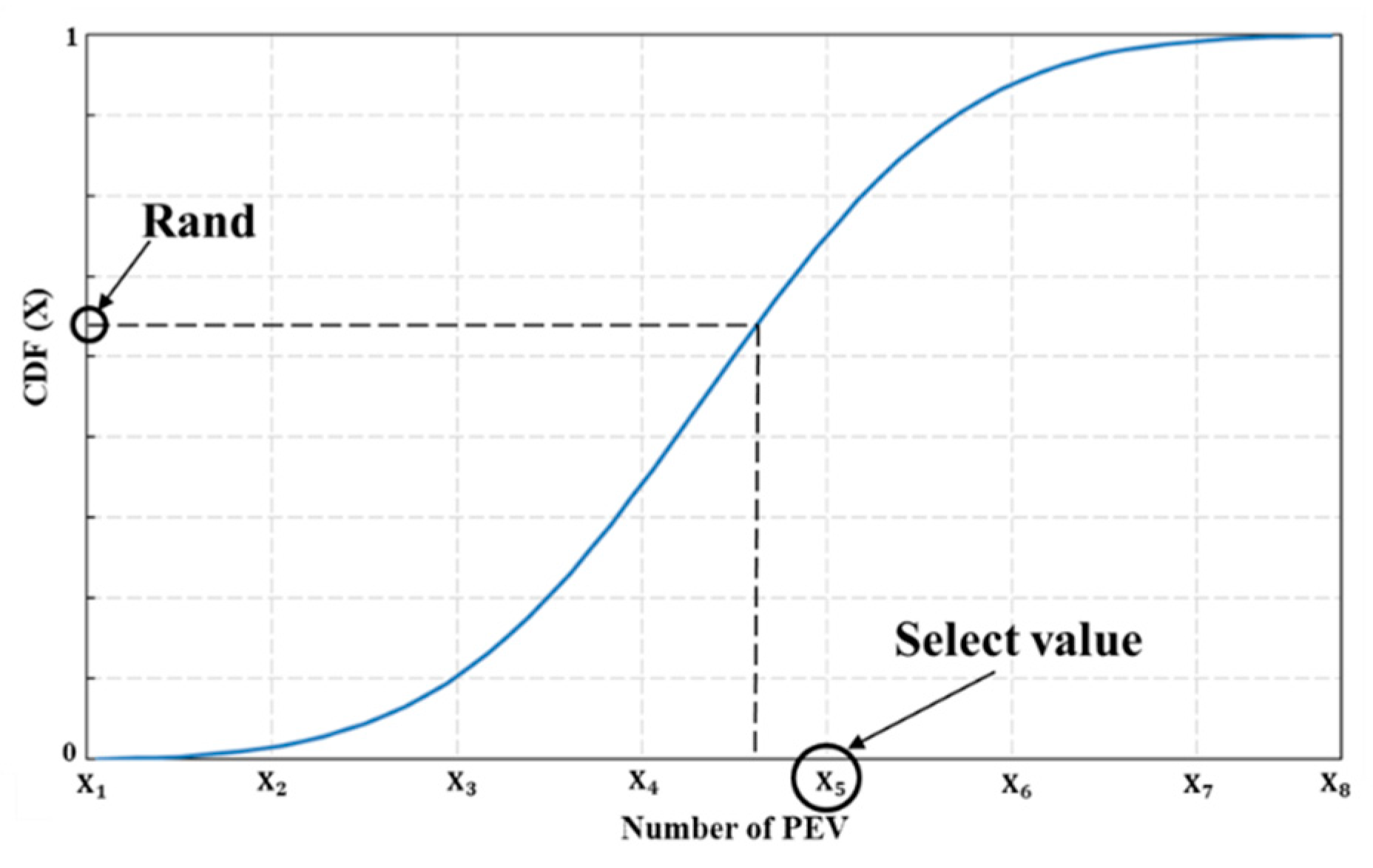
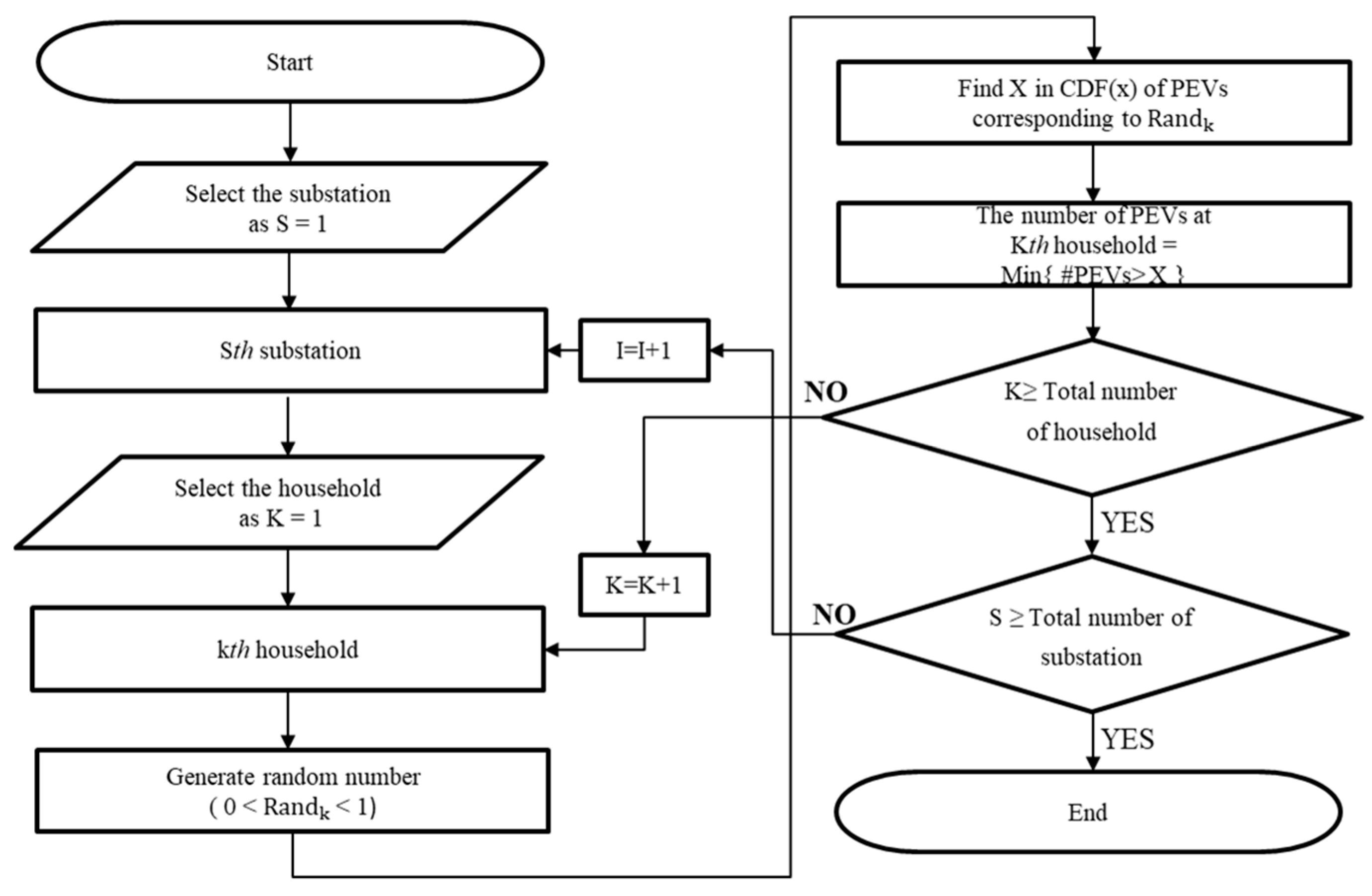
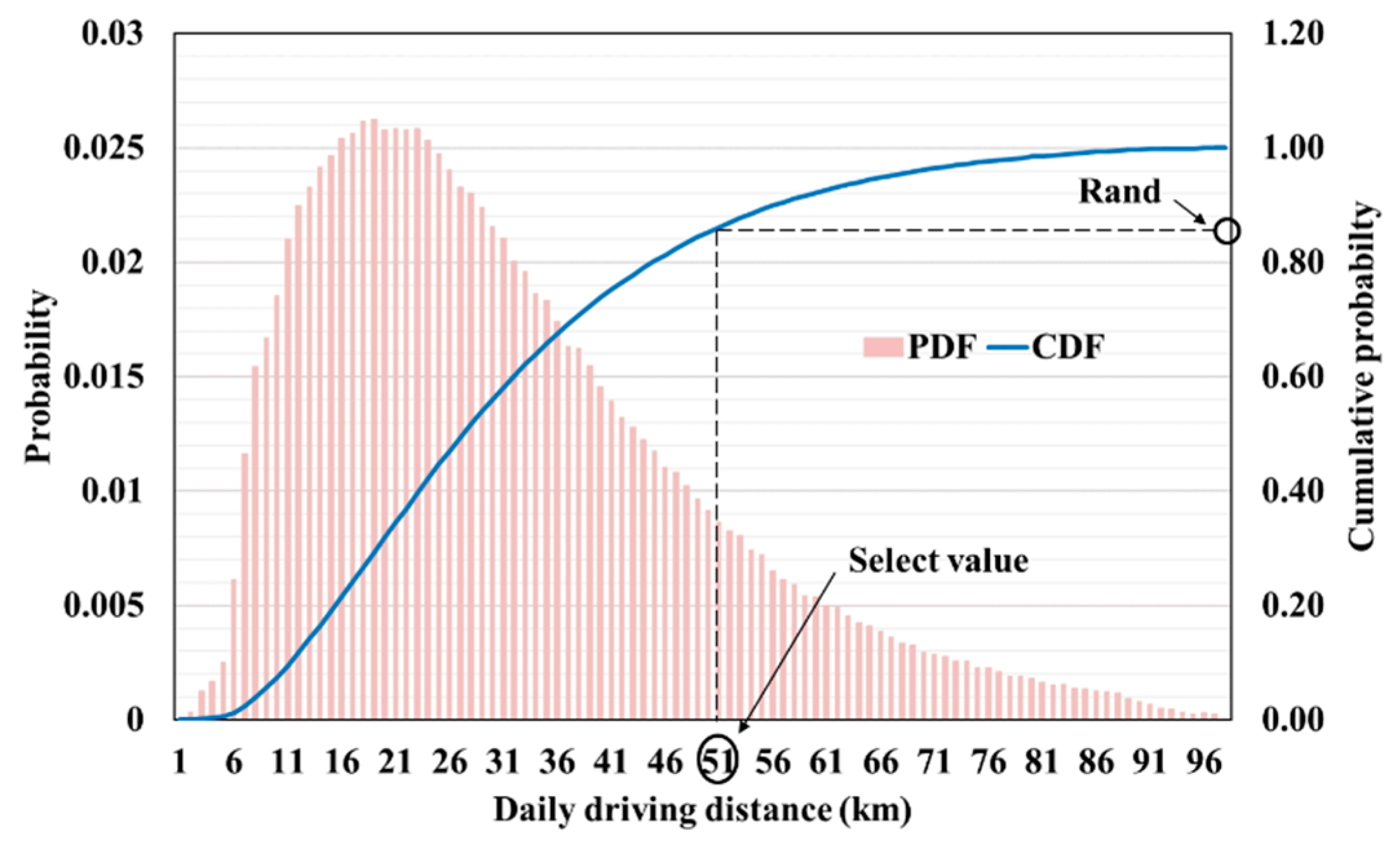




| 2017 | 2022 | 2026 | 2030 | 2031 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cumulative number of EVs (Thousand) | 46 | 334 | 629 | 1000 | 1108 |
| Annual electricity consumption (TWh) | 0.1 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 2.8 | 3.2 |
| Annual peak demand (summer, GW) | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.38 | 0.42 |
| Annual peak demand (winter, GW) | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.29 | 0.32 |
| Type of Charge | Input Voltage (V) | Output Voltage/Current (V/I) | Charging Power (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 220 ac/14 | 3 | |
| Normal | 220 ac/32 | 7 | |
| Fast | 450 dc/110 | 50 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, J.H.; Gwon, H.N.; Jo, G.R.; Choi, W.Y.; Kook, K.S. Stochastic Modeling Method of Plug-in Electric Vehicle Charging Demand for Korean Transmission System Planning. Energies 2020, 13, 4404. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13174404
Moon JH, Gwon HN, Jo GR, Choi WY, Kook KS. Stochastic Modeling Method of Plug-in Electric Vehicle Charging Demand for Korean Transmission System Planning. Energies. 2020; 13(17):4404. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13174404
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Jong Hui, Han Na Gwon, Gi Ryong Jo, Woo Yeong Choi, and Kyung Soo Kook. 2020. "Stochastic Modeling Method of Plug-in Electric Vehicle Charging Demand for Korean Transmission System Planning" Energies 13, no. 17: 4404. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13174404
APA StyleMoon, J. H., Gwon, H. N., Jo, G. R., Choi, W. Y., & Kook, K. S. (2020). Stochastic Modeling Method of Plug-in Electric Vehicle Charging Demand for Korean Transmission System Planning. Energies, 13(17), 4404. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13174404






