Decision Tree for Online Voltage Stability Margin Assessment Using C4.5 and Relief-F Algorithms
Abstract
1. Introduction
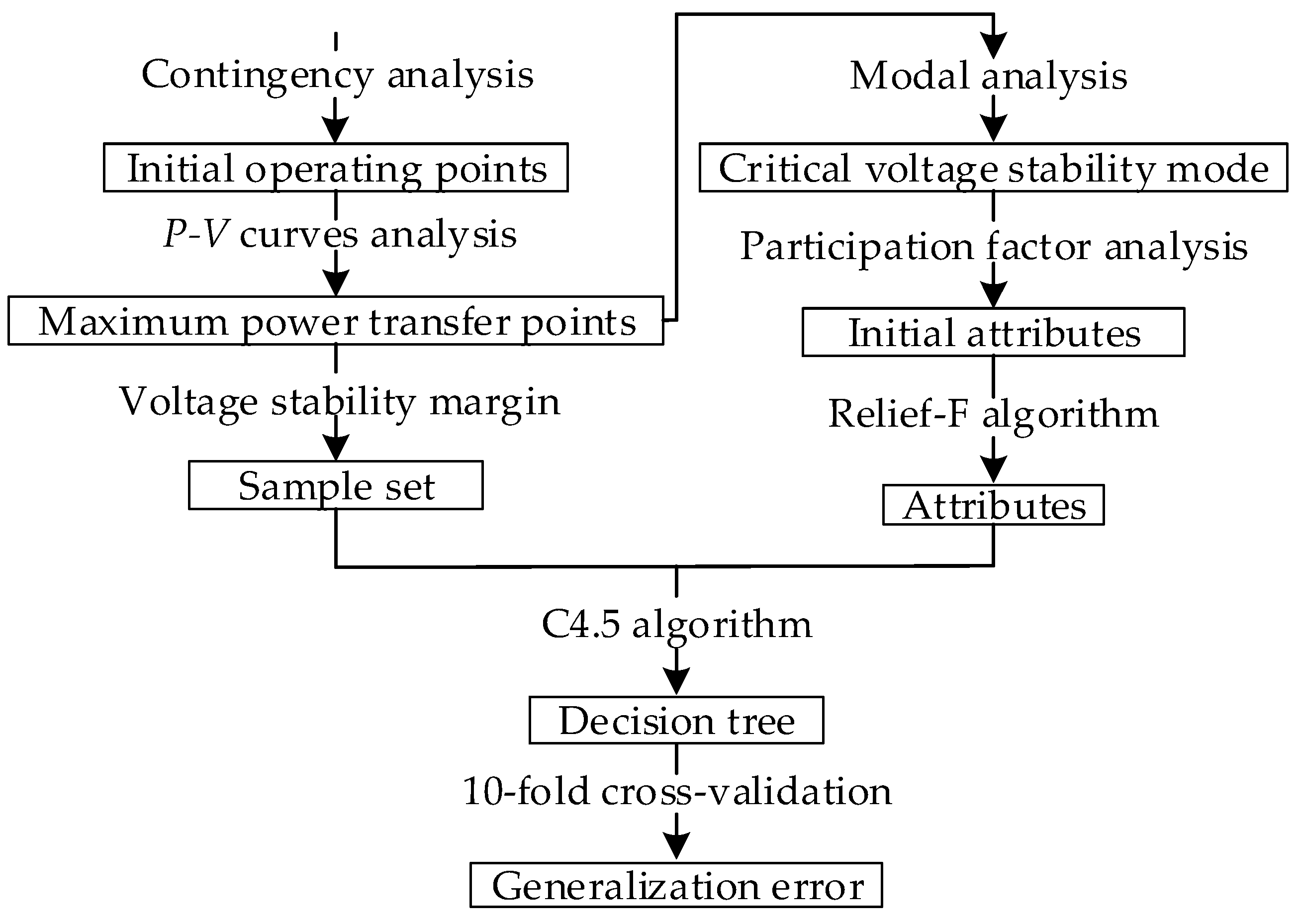
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Establish Sample Set for DT
2.2. Determine Attributes for the DT
2.3. Apply C4.5 Algorithm to Build DT
2.3.1. Calculate the Initial Information Entropy
2.3.2. Calculate the Split Entropy
2.3.3. Obtain the Information Gain
2.3.4. Calculate the Information Gain Ratio
3. Case Study
3.1. Establish the Sample Set for DT
3.2. Select Attributes for DT
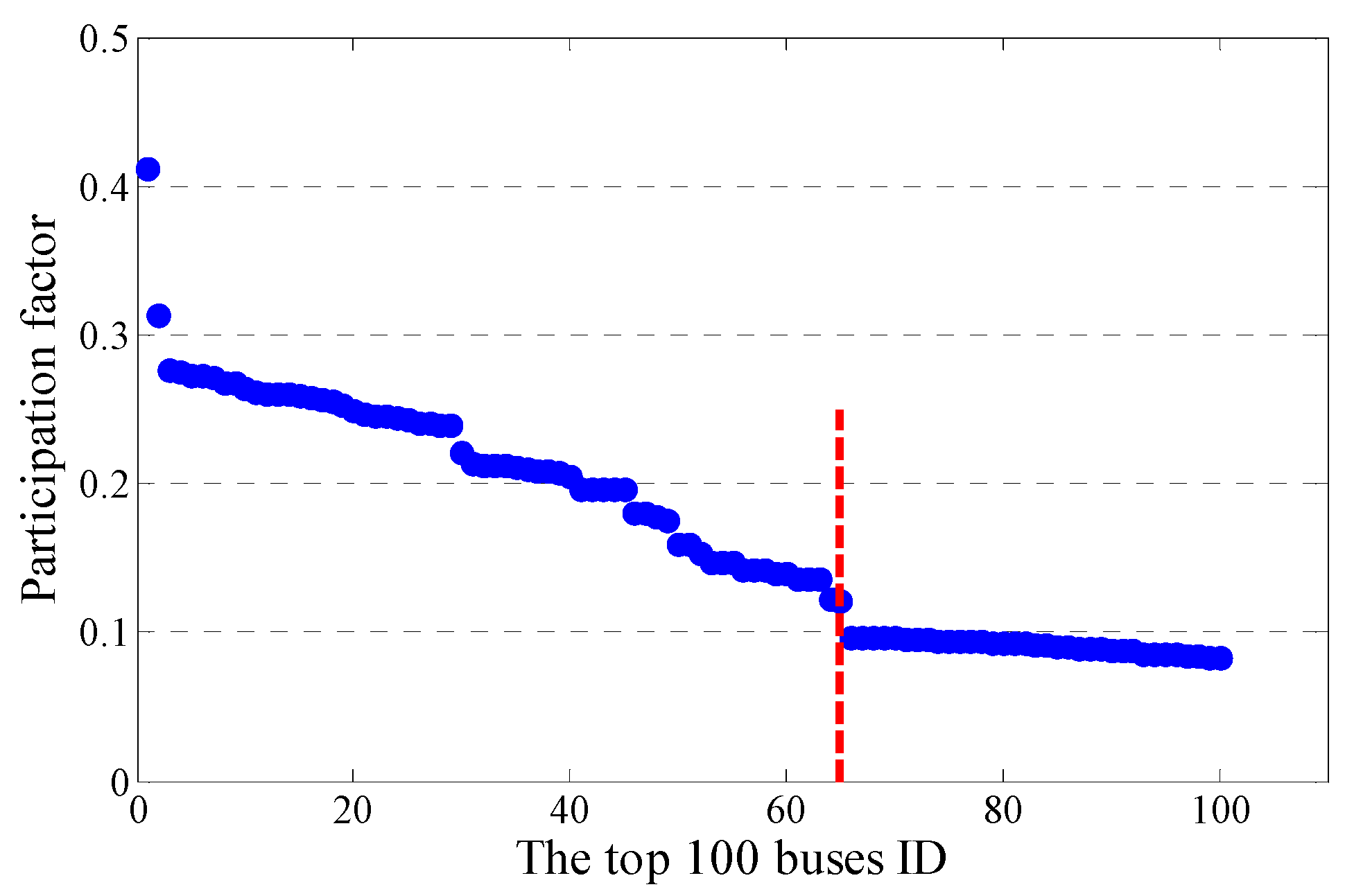
3.2.1. Initial Selection of Attributes
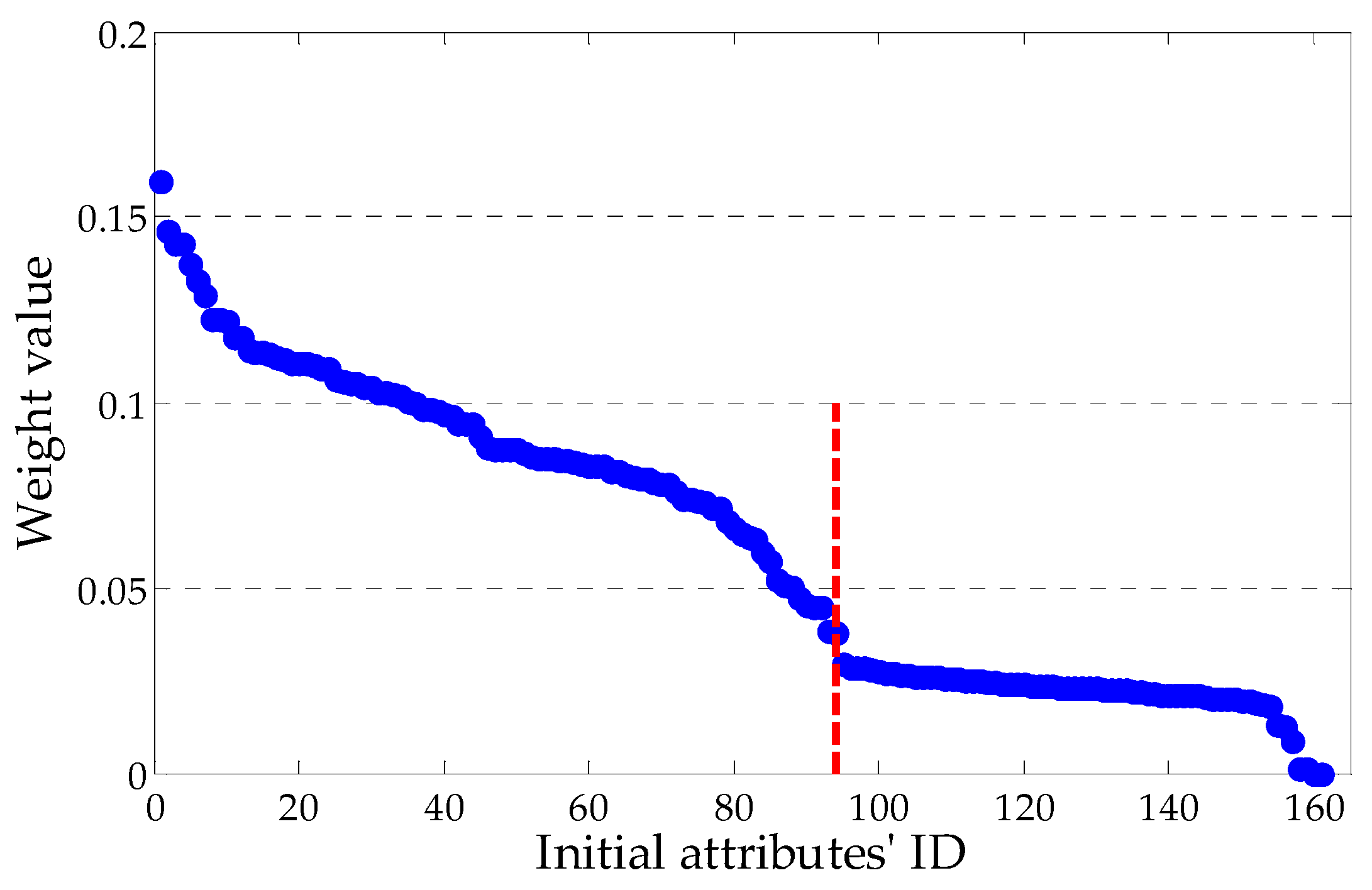
3.2.2. Determination of Attributes Set
3.3. Apply C4.5 Algorithm to Build DT
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kundur, P. Power System Stability and Control; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, C.W. Power System Voltage Stability; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kundur, P.; Paserba, J.; Ajjarapu, V.; Andersson, G.; Bose, A.; Canizares, C.; Hatziargyriou, N.D.; Hill, D.J.; Stankovic, A.M.; Taylor, C.; et al. Definition and classification of power system stability. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2004, 19, 1387–1401. [Google Scholar]
- Van Cutsem, T.; Vournas, C. Voltage Stability of Electric Power Systems; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Annakkage, U.D.; Rajapakse, A.D. Online monitoring of voltage stability margin using an artificial neural network. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyani, S.; Swarup, K.S. Classification and assessment of power system security using multiclass SVM. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. C 2010, 41, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sode-Yome, A.; Lee, K.Y. Neural network based loading margin approximation for static voltage stability in power systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES General Meeting, Providence, RI, USA, 25–29 July 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Innah, H.; Hiyama, T. A real time PMU data and neural network approach to analyze voltage stability. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Advanced Power System Automation and Protection, Beijing, China, 16–20 October 2011; pp. 1263–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, Y.; Dong, Z.Y.; Zhang, P.; Wong, K.P. Voltage stability margin prediction by ensemble based extreme learning machine. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 22–26 July 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sajan, K.S.; Tyagi, B.; Kumar, V. Genetic algorithm based artificial neural network model for voltage stability monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2014 Eighteenth National Power Systems Conference, Guwahati, India, 18–20 December 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- AbAziz, N.F.; Rahman, T.K.A.; Zakaria, Z. Voltage stability prediction by using artificial immune least square support vector machines (AILSVM). In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 8th International Power Engineering and Optimization Conference, Langkawi, Malaysia, 24–25 March 2014; pp. 613–618. [Google Scholar]
- Duraipandy, P.; Devaraj, D. On-line voltage stability assessment using least squares support vector machine with reduced input features. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Control, Instrumentation, Communication and Computational Technologies, Kanyakumari, India, 10–11 July 2014; pp. 1070–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Sajan, K.S.; Kumar, V.; Tyagi, B. ICA based Artificial Neural Network model for voltage stability monitoring. In Proceedings of the TENCON 2015-2015 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Macao, China, 1–4 November 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, H.; Wong, K.P. Assessing short-term voltage stability of electric power systems by a hierarchical intelligent system. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 27, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakili, S.; Zhao, Q.; Tong, L. Bayesian quickest short-term voltage instability detection in power systems. In Proceedings of the 2015 54th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Osaka, Japan, 15–18 December 2015; pp. 7214–7219. [Google Scholar]
- Sajan, K.S.; Kumar, V.; Tyagi, B. Genetic algorithm based support vector machine for on-line voltage stability monitoring. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 73, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, C.; Jimoh, A.A.; Kiran, S.H. Artificial neural network based voltage stability analysis in power system. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Circuit, Power and Computing Technologies, Nagercoil, India, 18–19 March 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, A.; Verma, K.; Kumar, R. Online voltage stability monitoring of distribution system using optimized support vector machine. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 6th International Conference on Power Systems, New Delhi, India, 4–6 March 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Malbasa, V.; Zheng, C.; Chen, P.C.; Popovic, T.; Kezunovic, M. Voltage stability prediction using active machine learning. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 3117–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.M.; Gupta, A.; Choudhary, D.K.; Chakrabarti, S. Voltage stability monitoring of power systems using reduced network and artificial neural network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2017, 87, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pulgar-Painemal, H.; Sun, K. Online analysis of voltage security in a microgrid using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 16–20 July 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Ajjarapu, V.; Djukanovic, M. Adaptive online monitoring of voltage stability margin via local regression. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amroune, M.; Bouktir, T.; Musirin, I. Power system voltage stability assessment using a hybrid approach combining dragonfly optimization algorithm and support vector regression. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 3023–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, L. PMU-based voltage stability prediction using least square support vector machine with online learning. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 160, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaji, S.S.; Cosma, G.; Taherkhani, A.; Alani, A.A.; McGinnity, T.M. On-line voltage stability monitoring using an Ensemble AdaBoost classifier. In Proceedings of the 2018 4th International Conference on Information Management (ICIM), Oxford, UK, 25–27 May 2018; pp. 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Shakerighadi, B.; Aminifar, F.; Afsharnia, S. Power systems wide-area voltage stability assessment considering dissimilar load variations and credible contingencies. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2019, 7, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagmar, H.; Carlsot, O.; Eriksson, R. On-Line voltage instability prediction using an artificial neural network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Milan PowerTech, Milan, Italy, 23–27 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Ma, H.; Hill, D. A data-based learning and control method for long-term voltage stability. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 1, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimi, O.A.; Ouahada, K.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. A review of machine learning approaches to power system security and stability. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 113512–113531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pei, J.; Kamber, M. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zaki, M.J.; Meira, W., Jr.; Meira, W. Data Mining and Analysis: Fundamental Concepts and Algorithms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Likhate, S.; Vittal, V.; Kolluri, S.; Mandal, S. An online dynamic security assessment scheme using phasor measurements and decision trees. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2007, 22, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, R.; Sun, K.; Vittal, V.; O’Keefe, R.; Richardson, M.; Bhatt, N.P.; Stradford, D.; Sarawgi, S.K. Decision tree-based online voltage security assessment using PMU measurements. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 24, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittal, V. Application of phasor measurements for dynamic security assessment using decision trees. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 July 2012; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Malbasa, V.; Kezunovic, M. A fast stability assessment scheme based on classification and regression tree. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Power System Technology, Auckland, New Zealand, 23–26 October 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Y.; Huo, T.; Liu, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z. Regional voltage stability prediction based on decision tree algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Intelligent Transportation, Big Data and Smart City, Halong Bay, Vietnam, 19–20 December 2015; pp. 588–591. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, P.N. Introduction to Data Mining; Pearson Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Khoshkhoo, H.; Shahrtash, S.M. On-line dynamic voltage instability prediction based on decision tree supported by a wide-area measurement system. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2012, 6, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiraghi, M.; Ranjbar, A.M. Online voltage security assessment based on wide-area measurements. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2013, 28, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprême, H.; Heniche-Oussédik, A.; Kamwa, I.; Dessaint, L.A. A novel approach for instability detection based on wide-area measurements and new predictors. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 15–18 May 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Z.; Yang, D.; Centeno, V.; Jones, K.D. A PMU-based voltage security assessment framework using Hoeffding-tree-based learning. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Intelligent System Application to Power Systems, San Antonio, TX, USA, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.Y.; Liu, T.Y. Enhanced-online-random-forest model for static voltage stability assessment using wide area measurements. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 6696–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.F.; Zhang, P.; Xu, Y.; Xie, H. Construction of decision tree based on C4.5 algorithm for online voltage stability assessment. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques; Morgan Kaufmann: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, M.; Liu, H. Feature selection for classification. Intell. Data Anal. 1997, 1, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robnik-Šikonja, M.; Kononenko, I. Theoretical and empirical analysis of ReliefF and RReliefF. Mach. Learn. 2003, 53, 23–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Iterative RELIEF for feature weighting: Algorithms, theories, and applications. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 2007, 29, 1035–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Alelyani, S.; Liu, H. Feature selection for classification: A review. Data Classif. Algorithms Appl. 2014, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.; Gong, D.; Gao, X. Feature selection and its use in big data: Challenges, methods, and trends. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 19709–19725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.R. C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]


| System State | VSM | Class Label |
|---|---|---|
| Normal State | N | |
| Alert State | A | |
| Emergency State | E |
| Bus ID | PF | Bus ID | PF | Bus ID | PF | Bus ID | PF | Bus ID | PF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 528 | 0.412 | 300 | 0.26 | 842 | 0.241 | 87 | 0.197 | 366 | 0.147 |
| 797 | 0.313 | 954 | 0.259 | 231 | 0.24 | 458 | 0.196 | 672 | 0.145 |
| 505 | 0.276 | 966 | 0.258 | 477 | 0.239 | 256 | 0.196 | 135 | 0.142 |
| 13 | 0.275 | 993 | 0.257 | 862 | 0.221 | 7 | 0.196 | 489 | 0.142 |
| 886 | 0.273 | 988 | 0.255 | 438 | 0.214 | 372 | 0.196 | 540 | 0.142 |
| 243 | 0.273 | 774 | 0.253 | 896 | 0.213 | 654 | 0.181 | 809 | 0.14 |
| 554 | 0.272 | 699 | 0.249 | 585 | 0.211 | 317 | 0.18 | 129 | 0.14 |
| 380 | 0.268 | 929 | 0.247 | 306 | 0.21 | 286 | 0.178 | 294 | 0.136 |
| 867 | 0.268 | 583 | 0.246 | 902 | 0.209 | 27 | 0.176 | 123 | 0.136 |
| 153 | 0.264 | 546 | 0.246 | 636 | 0.209 | 613 | 0.16 | 172 | 0.136 |
| 873 | 0.262 | 522 | 0.245 | 249 | 0.207 | 885 | 0.16 | 584 | 0.122 |
| 906 | 0.261 | 198 | 0.243 | 253 | 0.205 | 852 | 0.153 | 276 | 0.121 |
| 736 | 0.261 | 783 | 0.241 | 444 | 0.197 | 839 | 0.147 |
| Branch ID | PF | Branch ID | PF | Branch ID | PF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 366-467-I | 1.0000 | 72-634-II | 0.6484 | 896-366-I | 0.4777 |
| 366-467-II | 0.9994 | 419-105-I | 0.6415 | 896-366-II | 0.4693 |
| 274-72-I | 0.9964 | 419-105-II | 0.6415 | 378-634-I | 0.4368 |
| 274-72-II | 0.9739 | 751-467-I | 0.5676 | 378-634-II | 0.4368 |
| 839-274-I | 0.8969 | 751-467-II | 0.5676 | 452-944-I | 0.4114 |
| 839-274-II | 0.8721 | 276-314-I | 0.5480 | 452-944-II | 0.4114 |
| 72-634-I | 0.6530 | 276-314-II | 0.5443 | 105-72-I | 0.4043 |
| Generator ID | PF | Generator ID | PF | Generator ID | PF | Generator ID | PF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 254 | 0.218 | 455 | 0.216 | 316 | 0.196 | 881 | 0.139 |
| 255 | 0.217 | 988 | 0.212 | 315 | 0.190 | 520 | 0.106 |
| 456 | 0.216 | 993 | 0.212 | 883 | 0.139 | 519 | 0.104 |
| Classified Class | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | A | E | ||
| Actual Class | N | fNN = 7205 | fNA = 115 | fNE = 0 |
| A | fAN = 138 | fAA = 6994 | fAE = 188 | |
| E | fEN = 1 | fEA = 130 | fEE = 7189 | |
| The Number of Attributes | 94 | 161 |
|---|---|---|
| Modeling time (s) | 8.45 | 13.56 |
| Classification accuracy | 97.40% | 96.28% |
| C4.5 | CART | |
|---|---|---|
| Model building time (s) | 8.45 | 30.34 |
| Classification accuracy | 97.3953% | 93.1266% |
| Method | Classification Accuracy | Modeling Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| NEW | 97.40% | 8.45 |
| ANN | 94.51% | 612.31 |
| SVM | 94.32% | 13.42 |
| NB | 91.28% | 20.83 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, D. Decision Tree for Online Voltage Stability Margin Assessment Using C4.5 and Relief-F Algorithms. Energies 2020, 13, 3824. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13153824
Meng X, Zhang P, Zhang D. Decision Tree for Online Voltage Stability Margin Assessment Using C4.5 and Relief-F Algorithms. Energies. 2020; 13(15):3824. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13153824
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Xiangfei, Pei Zhang, and Dahai Zhang. 2020. "Decision Tree for Online Voltage Stability Margin Assessment Using C4.5 and Relief-F Algorithms" Energies 13, no. 15: 3824. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13153824
APA StyleMeng, X., Zhang, P., & Zhang, D. (2020). Decision Tree for Online Voltage Stability Margin Assessment Using C4.5 and Relief-F Algorithms. Energies, 13(15), 3824. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13153824






