Rheology and Mechanical Properties of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Mortars with Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Addition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- (I)
- Preparation of an alkaline solution—24 h before starting the mixing. The total amount of water required in the mortar composition was added directly to the alkaline solution. Due to the exothermal character of the reaction, water evaporation was prevented during the cooling down of the alkaline solution and the container was enclosed with a lid.
- (II)
- Paste preparation. FA with an alkaline solution was mixed first for 10 min, and then GGBFS was introduced and mixed for another 3 min.
- (III)
- Incorporation of aggregate. Eventually, quartz sand sized 0/2 mm with a specific mass of 2.64 g/cm3 was added and the mortar was mixed for 2 min.
2.2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
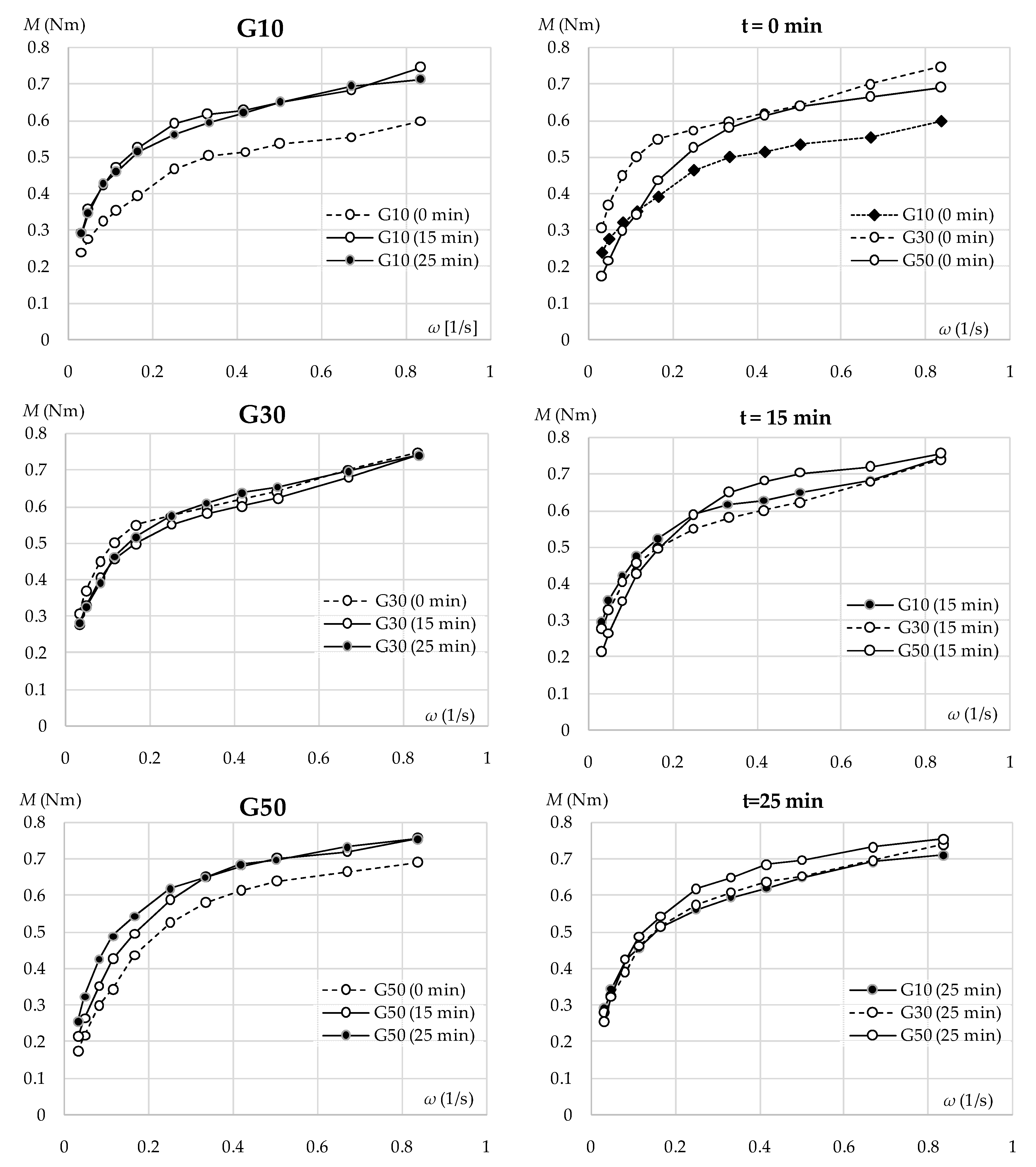
3.1. Effect of GGBFS Content on Fresh Mix Parameters
- τ—shear stress;
- τ0—yield stress;
- η—non-linear viscosity;
- —shear strain rate;
- n—exponent (non-linearity factor; for Bingham model n = 1).
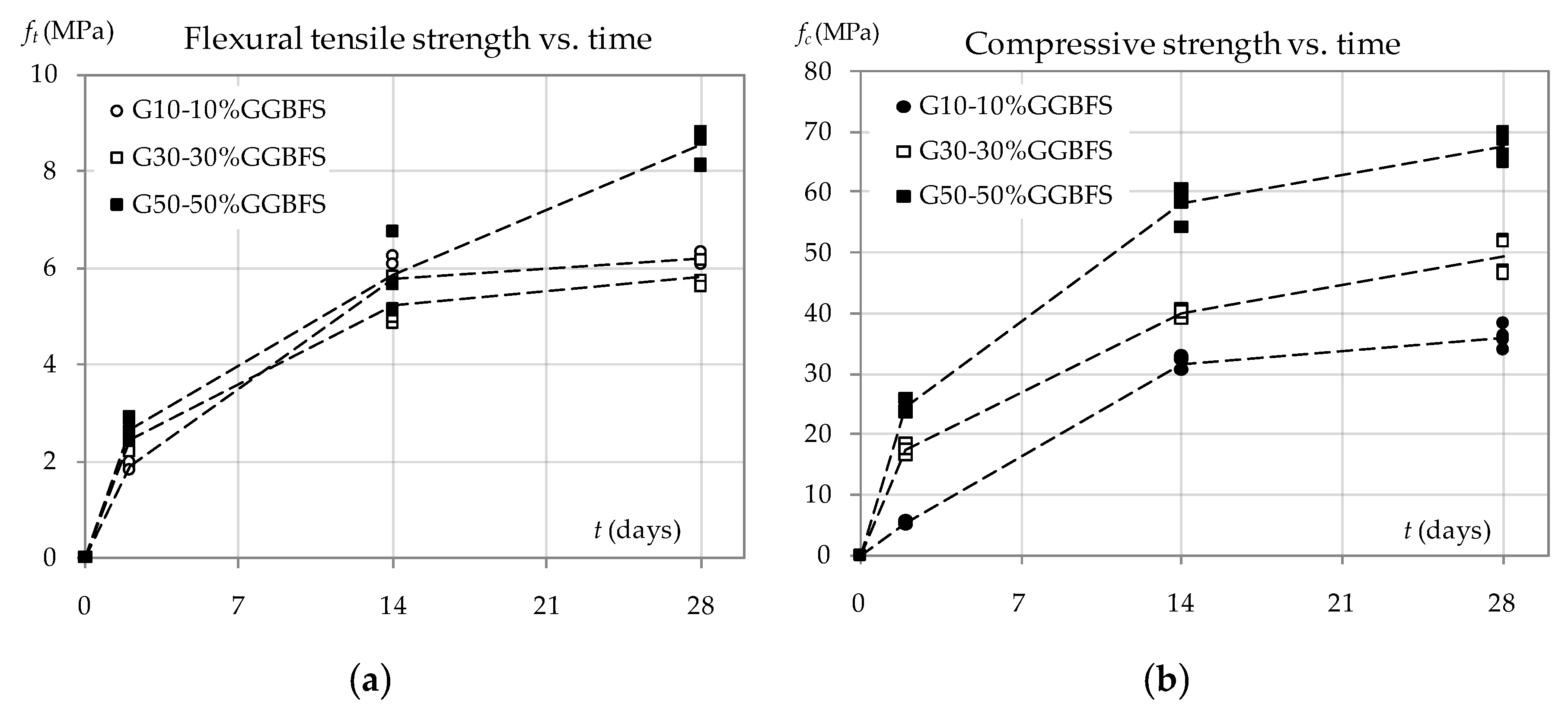
3.2. The Effect of GGBFS Content on the Density and Strength of Geopolymer Mortar
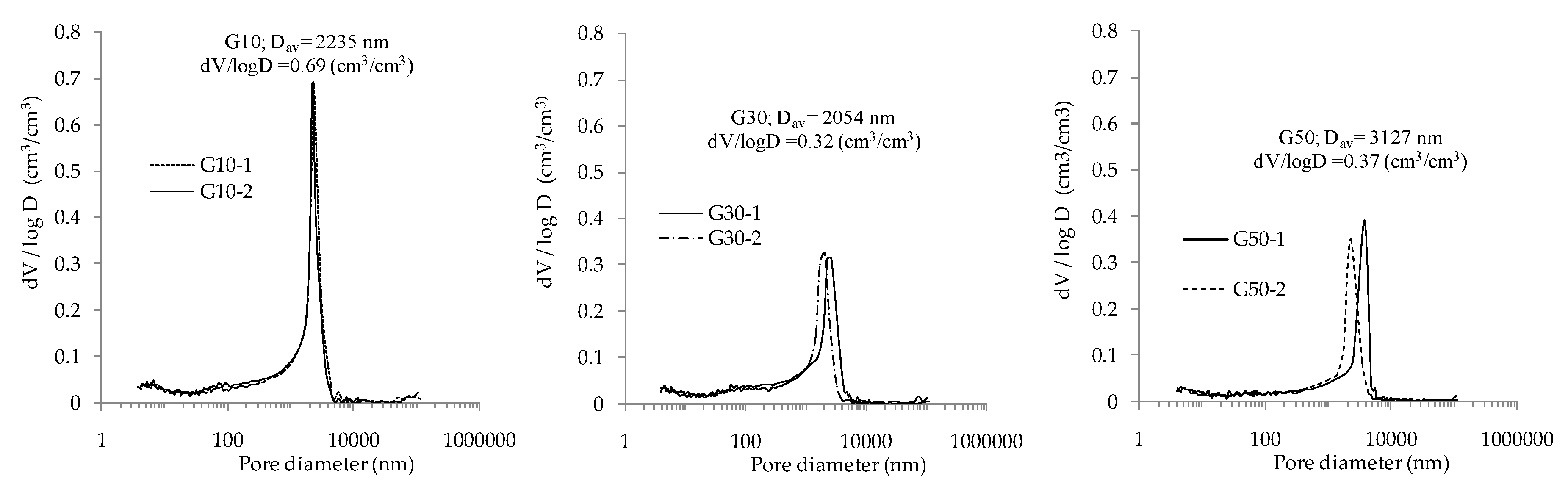
3.3. The Pore Size Distribution of Geopolymer Mortar by MIP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duxson, P.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; van Deventer, J.S.J. The role of inorganic polymer technology in the development of “green concrete”. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1590–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juenger, M.C.G.; Winnefeld, F.; Provis, J.L.; Ideker, J.H. Advances in alternative cementitious binders. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardjito, D.; Wallah, S.E.; Sumajouw, D.M.J.; Rangan, B.V. Factors Influencing The Compressive Strength of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete. Civ. Eng. Dimens. 2007, 6, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Puertas, F. Effect of activator mix on the hydration and strength behaviour of alkali-activated slag cements. Adv. Cem. Res. 2003, 15, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakharev, T.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Cheng, Y.B. Resistance of alkali-activated slag concrete to acid attack. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1607–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, V.F.F.; MacKenzie, K.J.D. Thermal behaviour of inorganic geopolymers and composites derived from sodium polysialate. Mater. Res. Bull. 2003, 38, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, A.I.; Bhattacharjee, R. Effect of Plasticizer and Superplasticizer on Rheology of Fly-Ash-Based Geopolyrner Concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2013, 110, 513–518. [Google Scholar]
- Romagnoli, M.; Leonelli, C.; Kamse, E.; Lassinantti Gualtieri, M. Rheology of geopolymer by DOE approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, M.; Sassatelli, P.; Lassinantti Gualtieri, M.; Tari, G. Rheological characterisation of fly ash-based suspensions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 65, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, H.; Li, L. A review: The comparison between alkali-activated slag (Si + Ca) and metakaolin (Si + Al) cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.E.; Monteiro, P.J.M.; Jun, S.S.; Choi, S.; Clark, S.M. The evolution of strength and crystalline phases for alkali-activated ground blast furnace slag and fly ash-based geopolymers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.L.; Sarin, P.; Driemeyer, P.E.; Haggerty, R.P.; Chupas, P.J.; Kriven, W.M. X-Ray pair distribution function analysis of a metakaolin-based, KAlSi2O6·5. 5H2O inorganic polymer (geopolymer). J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 5974–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meral, C.; Benmore, C.J.; Monteiro, P.J.M. The study of disorder and nanocrystallinity in C-S-H, supplementary cementitious materials and geopolymers using pair distribution function analysis. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 696–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Mallicoat, S.W.; Kriven, W.M.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Understanding the relationship between geopolymer composition, microstructure and mechanical properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 269, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, A.; Habert, G.; D’Espinose De Lacaillerie, J.B.; Roussel, N. Mechanical properties and compositional heterogeneities of fresh geopolymer pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 48, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, A.; Hot, J.; Habert, G.; d’Espinose de Lacaillerie, J.-B.; Roussel, N. Rheology of geopolymer: Comparative study between portland cement and metakaolin based geopolymer. In Proceedings of the 1st RILEM International Conference on Rheology and Processing of Construction Materials, Paris, France, 2–4 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Flatt, R.J. Towards a prediction of superplasticized concrete rheology. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2004, 37, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paper, C.; Habert, G.; Zurich, E.T.H. Rheology of metakaolin based geopolymer: Mechanisms and improvement potentials 2. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Recent Advances in Concrete Technology and Sustainability Issues, Prague, Czech Republic, 30 October–2 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Duxson, P.; Provis, J.L. Designing precursors for geopolymer cements. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 3864–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B.; Unluer, C.; Tan, M.J. Investigation of the rheology and strength of geopolymer mixtures for extrusion-based 3D printing. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 94, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, A.; Hot, J.; Habert, G.; Roussel, N.; D’Espinose De Lacaillerie, J.B. Flow properties of MK-based geopolymer pastes. A comparative study with standard Portland cement pastes. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Rajasekaran, C. Enhancement of the properties of fly ash based geopolymer paste by incorporating ground granulated blast furnace slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N.; Lemaître, A.; Flatt, R.J.; Coussot, P. Steady state flow of cement suspensions: A micromechanical state of the art. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-W.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Xie, F. Rheology, agglomerate structure, and particle shape of fresh geopolymer pastes with different NaOH activators content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-W.; Wang, D.; Lin, X.-Q.; Zhang, T. The study of the structure rebuilding and yield stress of 3D printing geopolymer pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 184, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymer Chemistry and Applications, 4th ed.; Geopolymer Institute: Saint-Quentin, France, 2015; ISBN 9782951482050. [Google Scholar]
- Urban, M. Consistency measures of self compacting concrete and its rheological parameters. In Proceedings of the 16, Ibausil, Weimar, Germany, 20–23 September 2006; Volume 2, pp. 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall, G.; Banfill, P.F.G. The Rheology of Fresh Concrete; Pitman: Belfast, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Giesche, H. Mercury Porosimetry. In Handbook of Porous Solids; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 309–351. ISBN 9783527618286. [Google Scholar]
- Szwabowski, J. Influence of three-phase structure on the yield stress of fresh concrete. In Rheology of Fresh Cement and Concrete; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2010; pp. 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzentruber, A.; Catherine, C. Method of the concrete equivalent mortar (CEM)—A new tool to design concrete containing admixture. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2000, 33, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schutter, G.; Gibbs, J.; Domone, P.; Bartos, P.J.M. Self-Compacting Concrete; Whittles Publishing: Scotland, UK, 2008; ISBN 1904445306. [Google Scholar]
- Wallevik, O.; Níelsson, I. Rheological evaluation of some empirical test methods-preliminary results. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Self-compacting Concrete, Reykjavik, Iceland, 17–20 August 2003; RILEM: Reykjavik, Iceland, 2003; p. 1028. [Google Scholar]
- Khale, D.; Chaudhary, R. Mechanism of Geopolymerization and Factors Influencing Its Development: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 729–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Palomo, A.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymer technology: The current state of the art. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2917–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.; Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L.; San Nicolas, R.; Hamdan, S.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Modification of phase evolution in alkali-activated blast furnace slag by the incorporation of fly ash. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 45, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanović, N.; Komljenović, M.; Baščarević, Z.; Nikolić, V.; Petrović, R. Physical–mechanical and microstructural properties of alkali-activated fly ash–blast furnace slag blends. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 1421–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.B.; Middendorf, B. Geopolymers as an alternative to Portland cement: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 237, 117455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Dai, J.G.; Zhao, T.J.; Guo, S.Y.; Zhang, P.; Mu, B. Alternation of traditional cement mortars using fly ash-based geopolymer mortars modified by slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovnaník, P. Effect of curing temperature on the development of hard structure of metakaolin-based geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steins, P.; Poulesquen, A.; Frizon, F.; Diat, O.; Jestin, J.; Causse, J.; Lambertin, D.; Rossignol, S. Effect of aging and alkali activator on the porous structure of a geopolymer. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2014, 47, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.L.Y.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K. Comparative performance of geopolymers made with metakaolin and fly ash after exposure to elevated temperatures. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medpelli, D.; Seo, J.-M.; Seo, D.-K. Geopolymer with Hierarchically Meso-/Macroporous Structures from Reactive Emulsion Templating. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boher, C.; Martin, I.; Lorente, S.; Frizon, F. Experimental investigation of gas diffusion through monomodal materials. Application to geopolymers and Vycor® glasses. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 184, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | SO3 | K2O | Na2O | P2O5 | TiO2 | Mn3O4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 52.30 | 28.05 | 6.32 | 3.05 | 1.71 | 0.28 | 2.51 | 0.76 | 0.69 | 1.35 | 0.07 |
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | SO3 | K2O | Na2O | Cl– | Na2Oeq | Blaine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 39.31 | 7.61 | 1.49 | 43.90 | 4.15 | 0.51 | 0.356 | 0.468 | 0.038 | 0.702 | 3904 |
| Components | G 10 | G 30 | G 50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (kg/m3) | (kg/m3) | (kg/m3) | |
| Alkaline solution | 337.7 | 342.4 | 347.2 |
| Fly ash (FA) | 675.4 | 532.6 | 385.8 |
| GGBFS | 75.0 | 228.2 | 385.8 |
| Sand(0/2 mm) | 1125.6 | 1141.2 | 1157.3 |
| Sand to Binder Ratio | Alkaline Solution to Binder (FA+GGBFS) Ratio | Water to Binder Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 0.45 | 0.30 |
| Mortar | G 10 | G 30 | G 50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | (cm) | (cm) | |
| Flow | 10/12 | 10/12.5 | 14.5/16 |
| Mean Values of Apparent Density | G10 | G30 | G50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (kg/m3) | (kg/m3) | (kg/m3) | |
| 2d | 2093 | 2131 | 2223 |
| 14d | 2051 | 2082 | 2211 |
| 28d | 2048 | 2080 | 2207 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sitarz, M.; Urban, M.; Hager, I. Rheology and Mechanical Properties of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Mortars with Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Addition. Energies 2020, 13, 2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102639
Sitarz M, Urban M, Hager I. Rheology and Mechanical Properties of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Mortars with Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Addition. Energies. 2020; 13(10):2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102639
Chicago/Turabian StyleSitarz, Mateusz, Maciej Urban, and Izabela Hager. 2020. "Rheology and Mechanical Properties of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Mortars with Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Addition" Energies 13, no. 10: 2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102639
APA StyleSitarz, M., Urban, M., & Hager, I. (2020). Rheology and Mechanical Properties of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Mortars with Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Addition. Energies, 13(10), 2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102639






